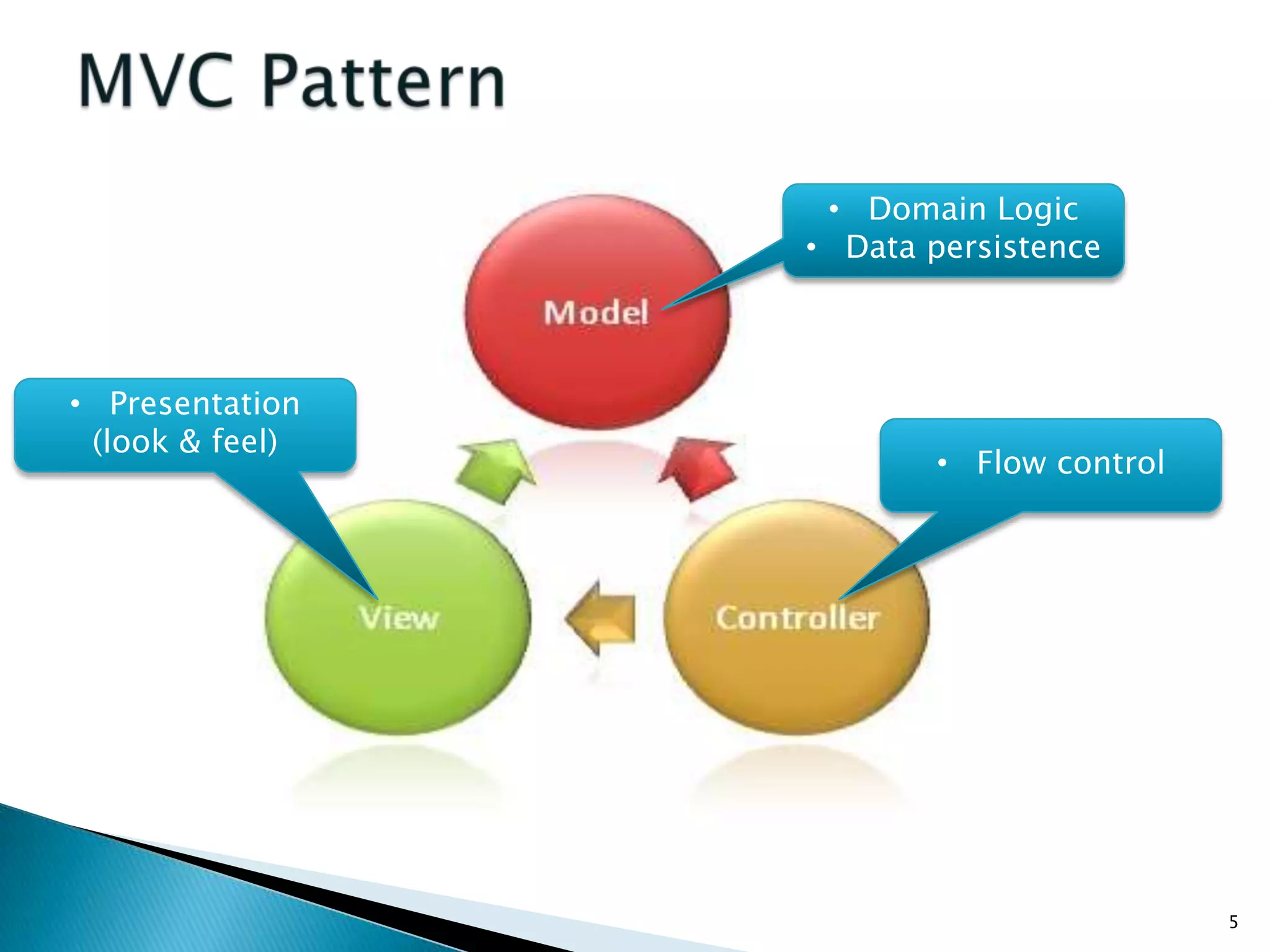
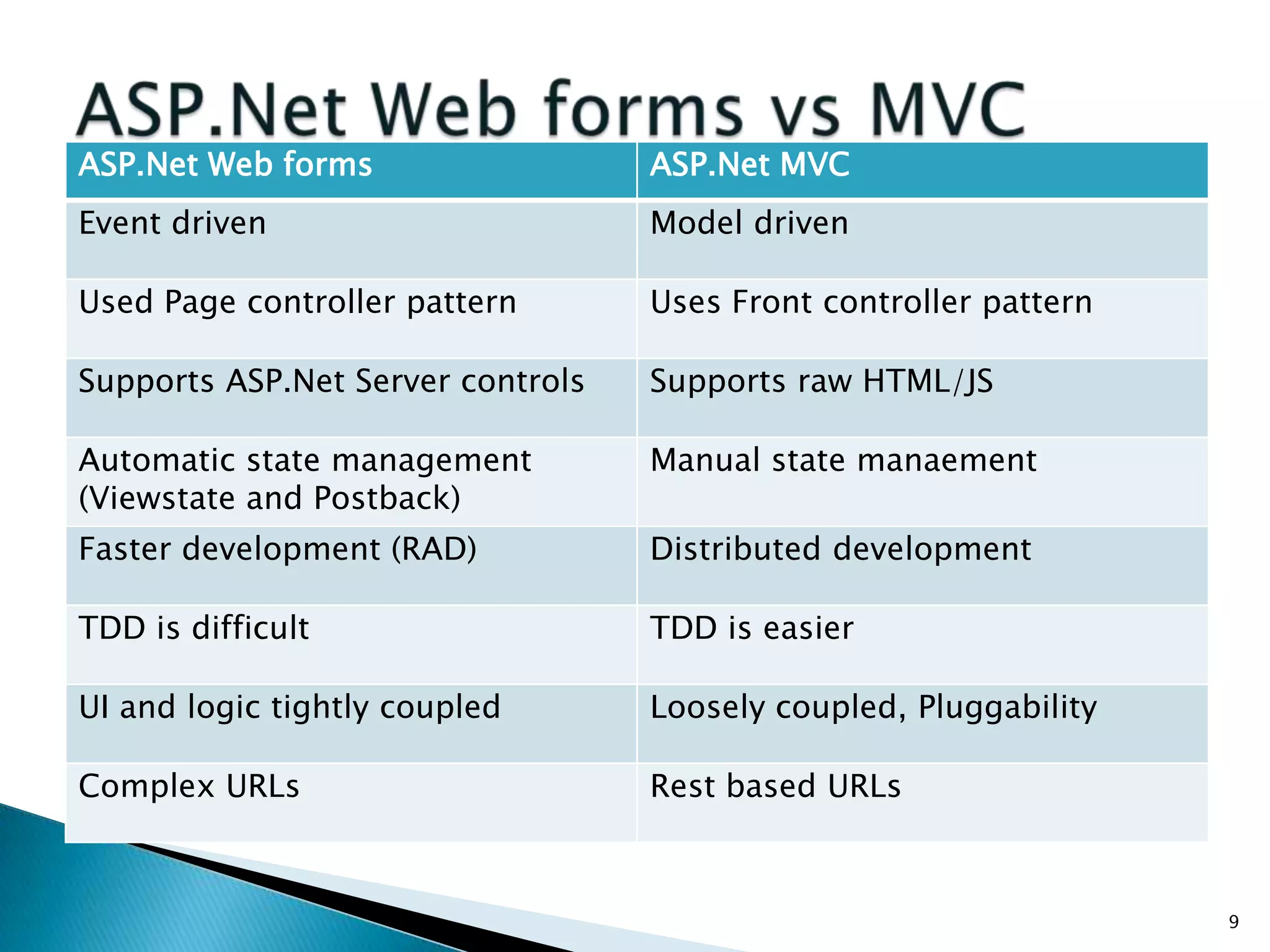
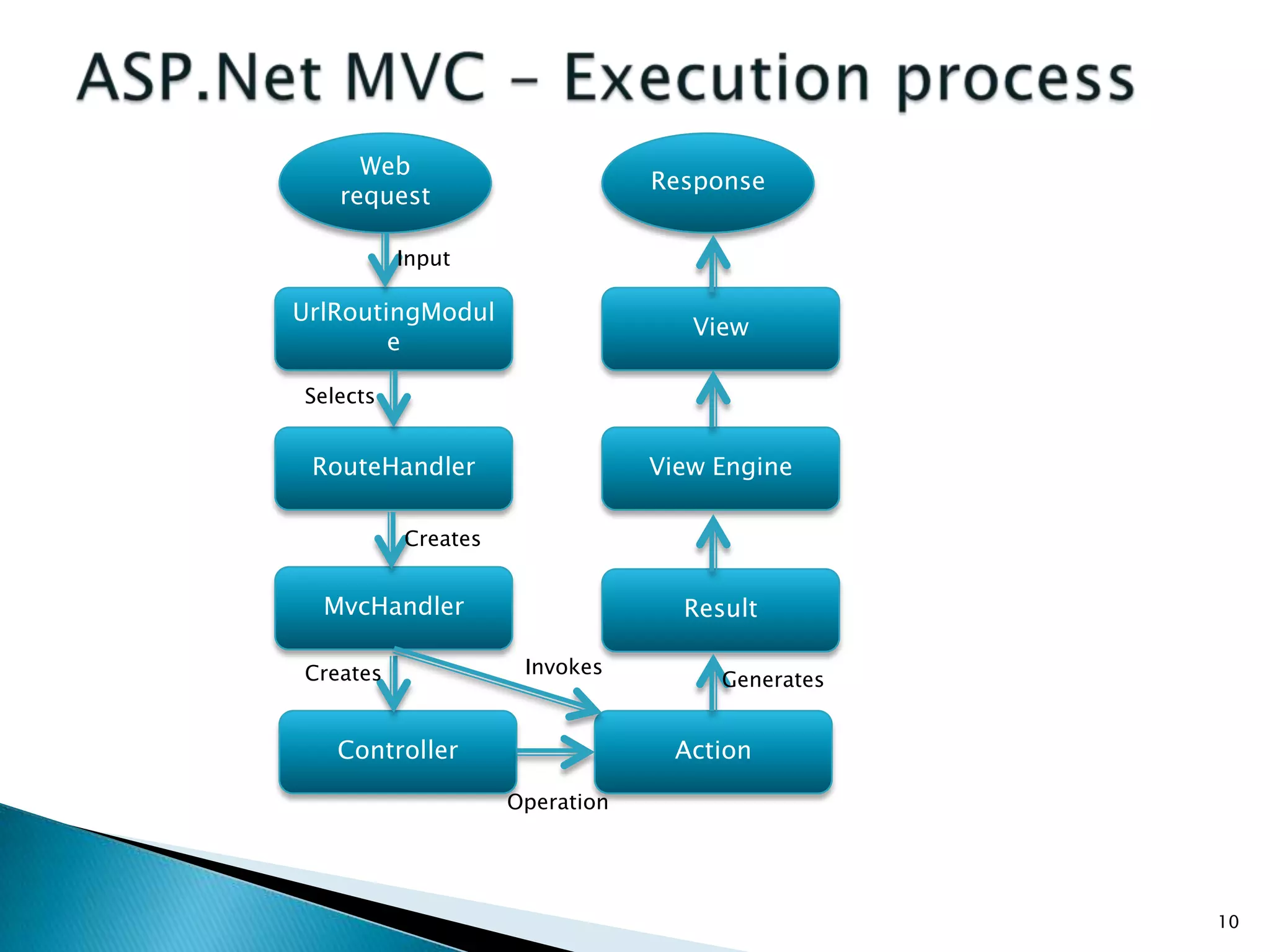
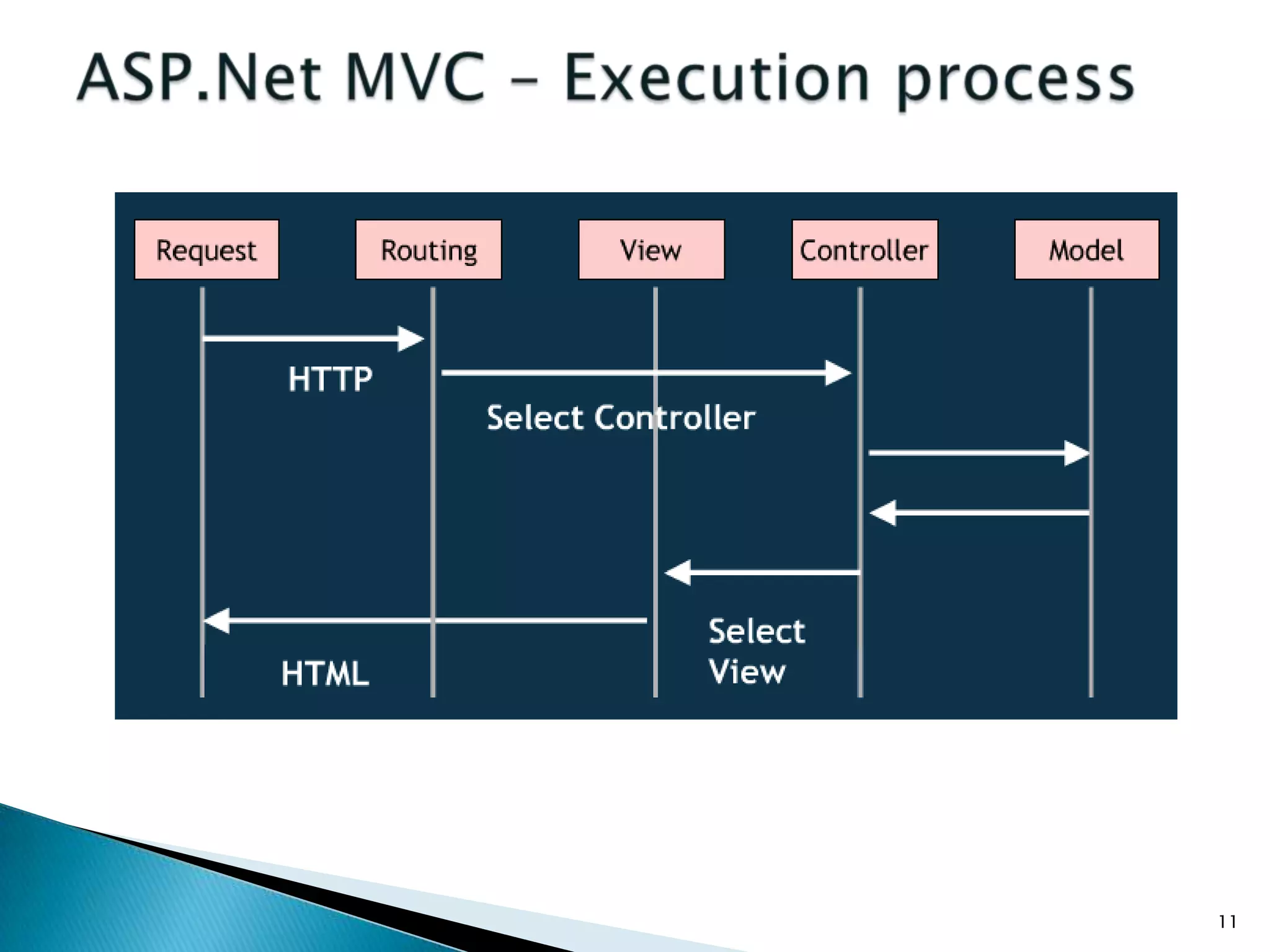
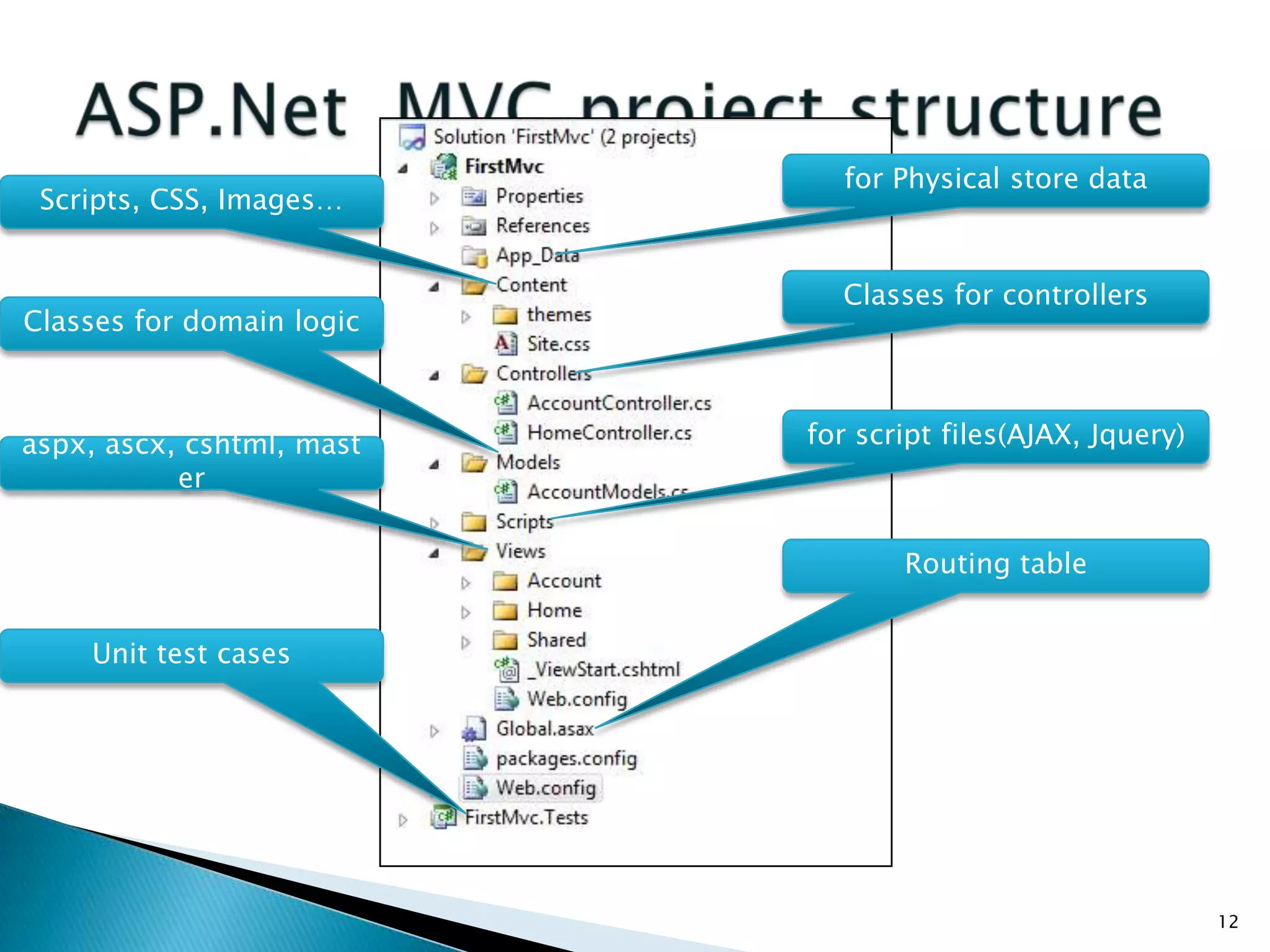
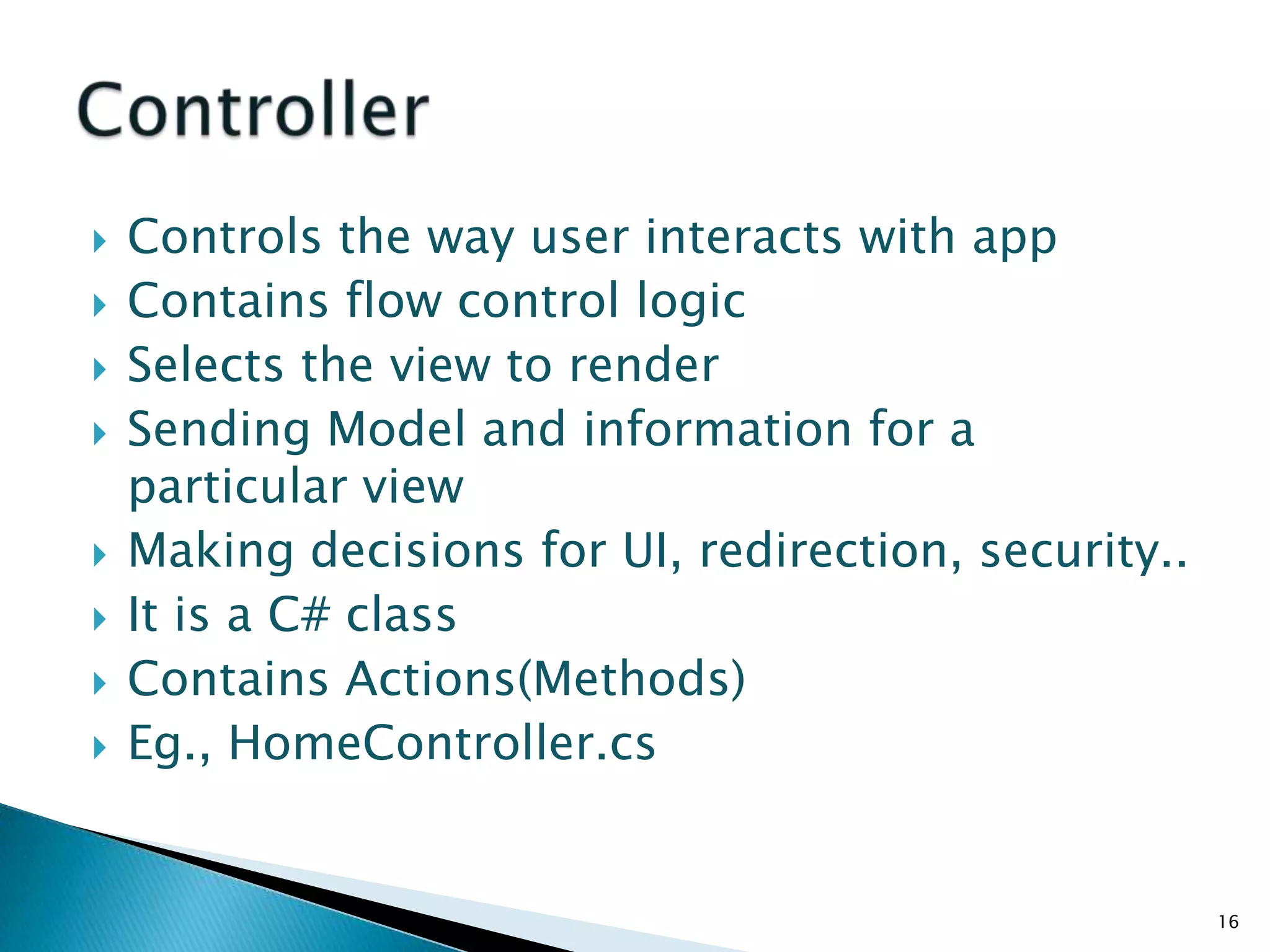
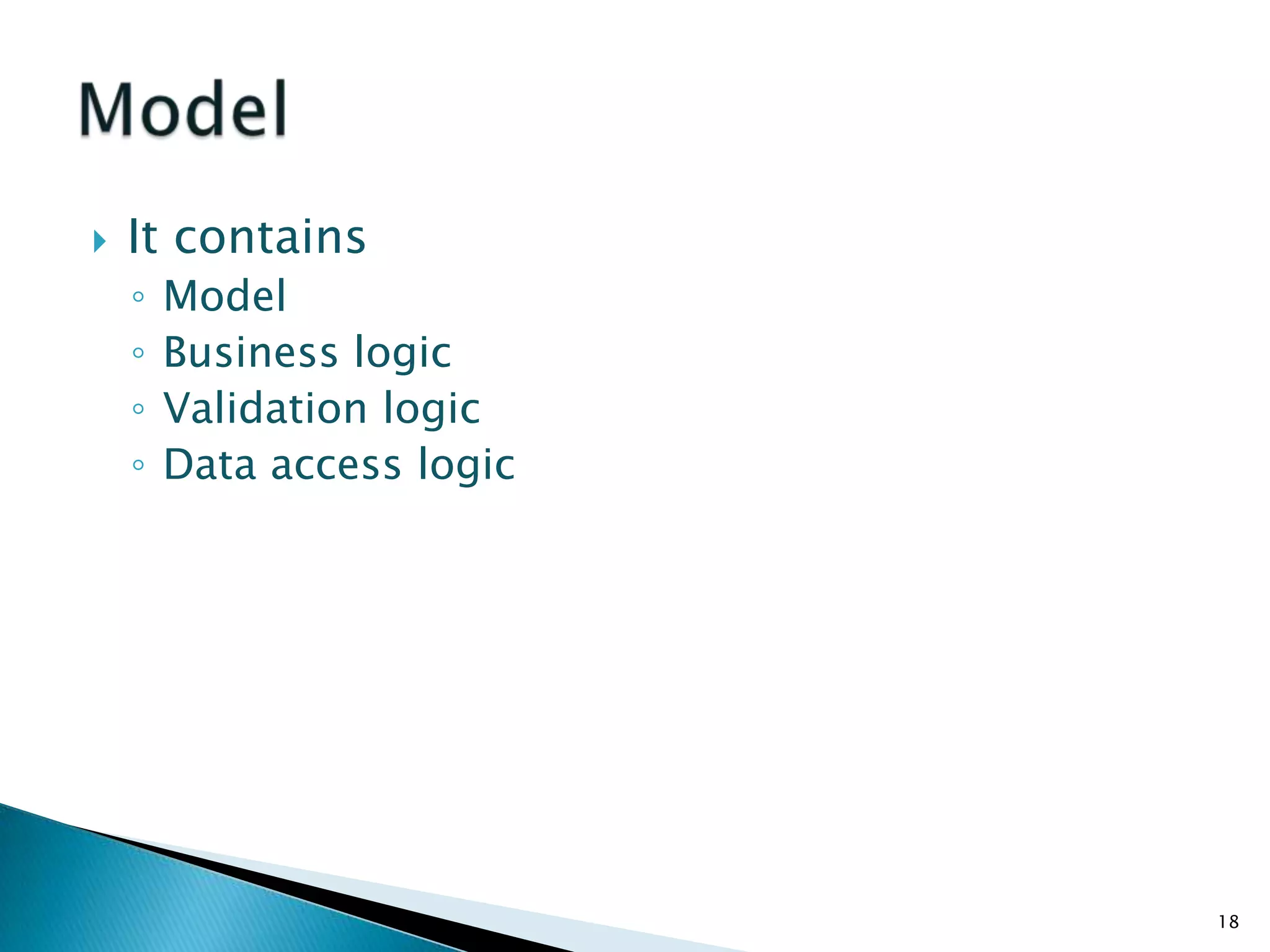
The document discusses the basics of ASP.Net MVC, including: - The MVC pattern separates application logic into three components: Model, View, Controller - ASP.Net MVC aims to follow the MVC pattern and improve on ASP.Net Web Forms by allowing for more testable code and cleaner URLs - The core components in ASP.Net MVC are controllers which handle requests and select views, views which generate the UI, and models which contain app data and logic