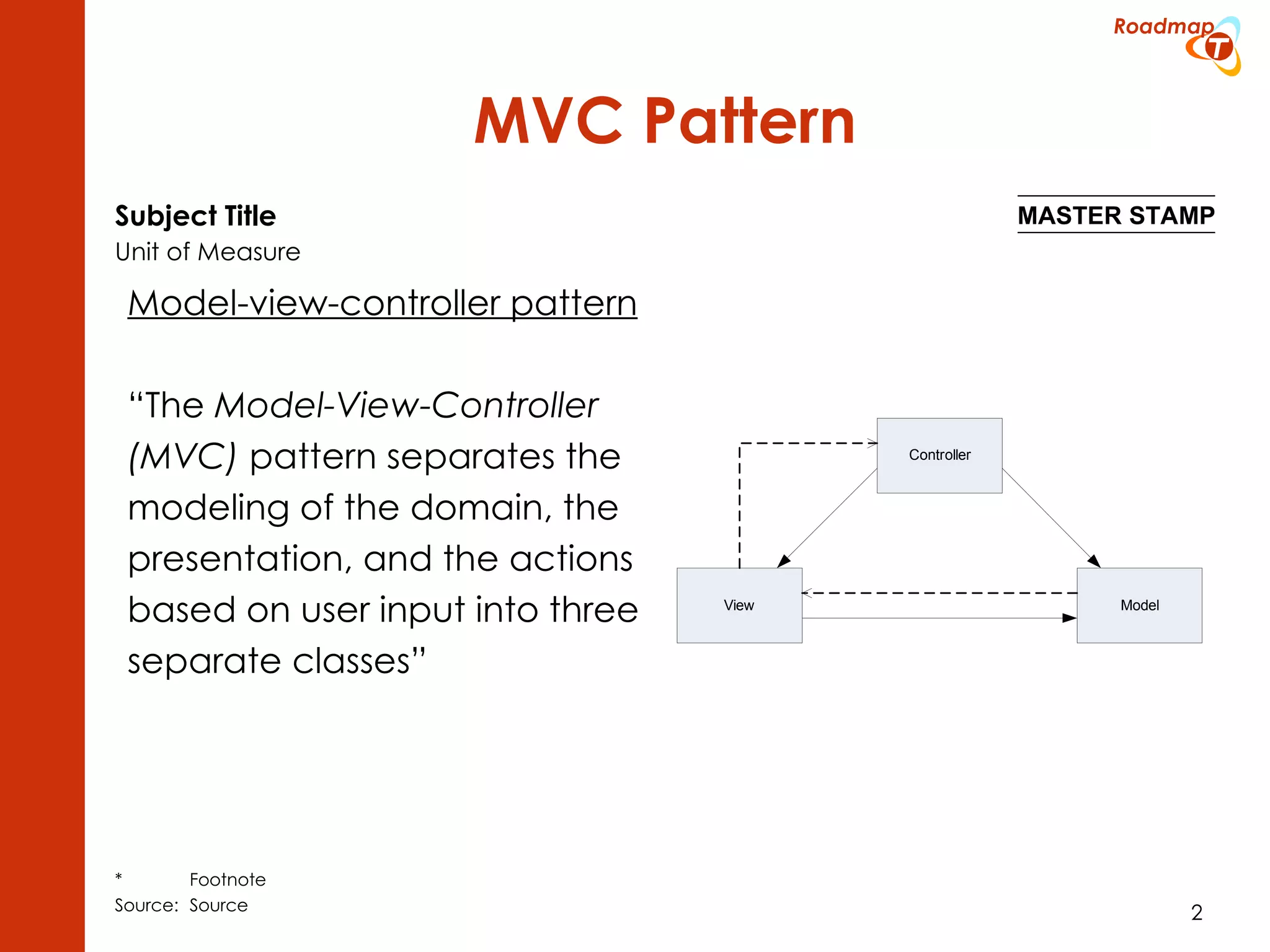
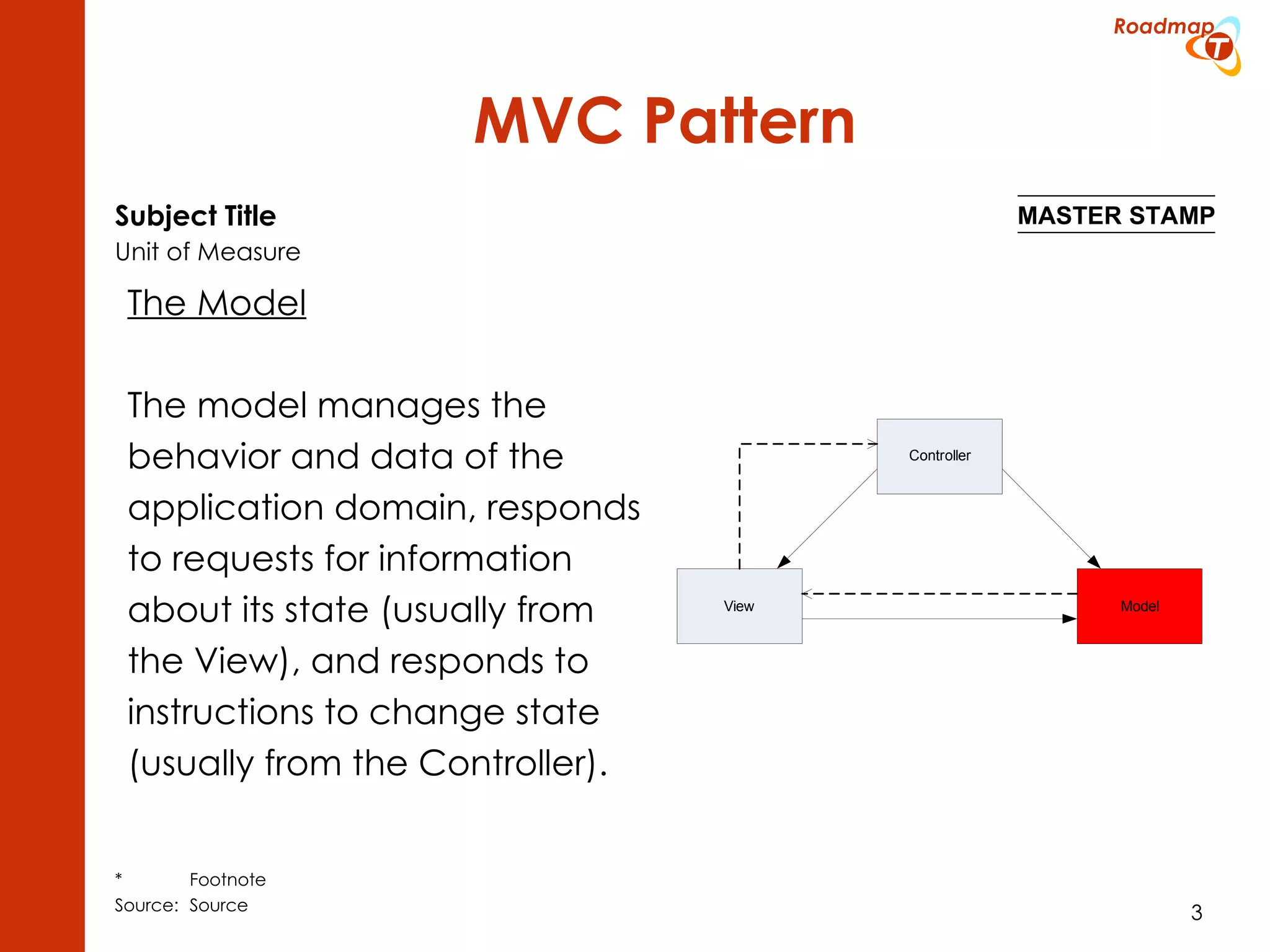
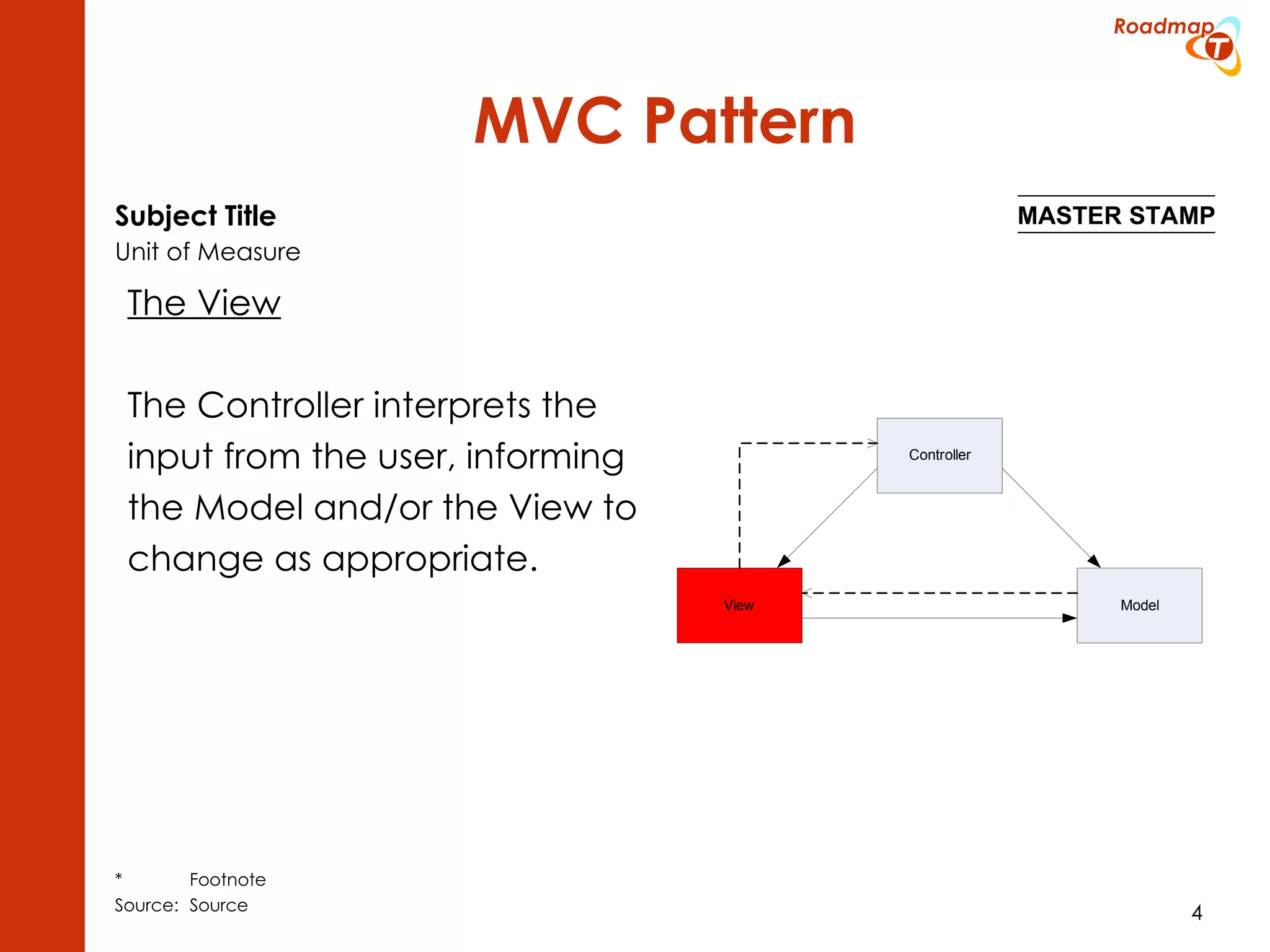
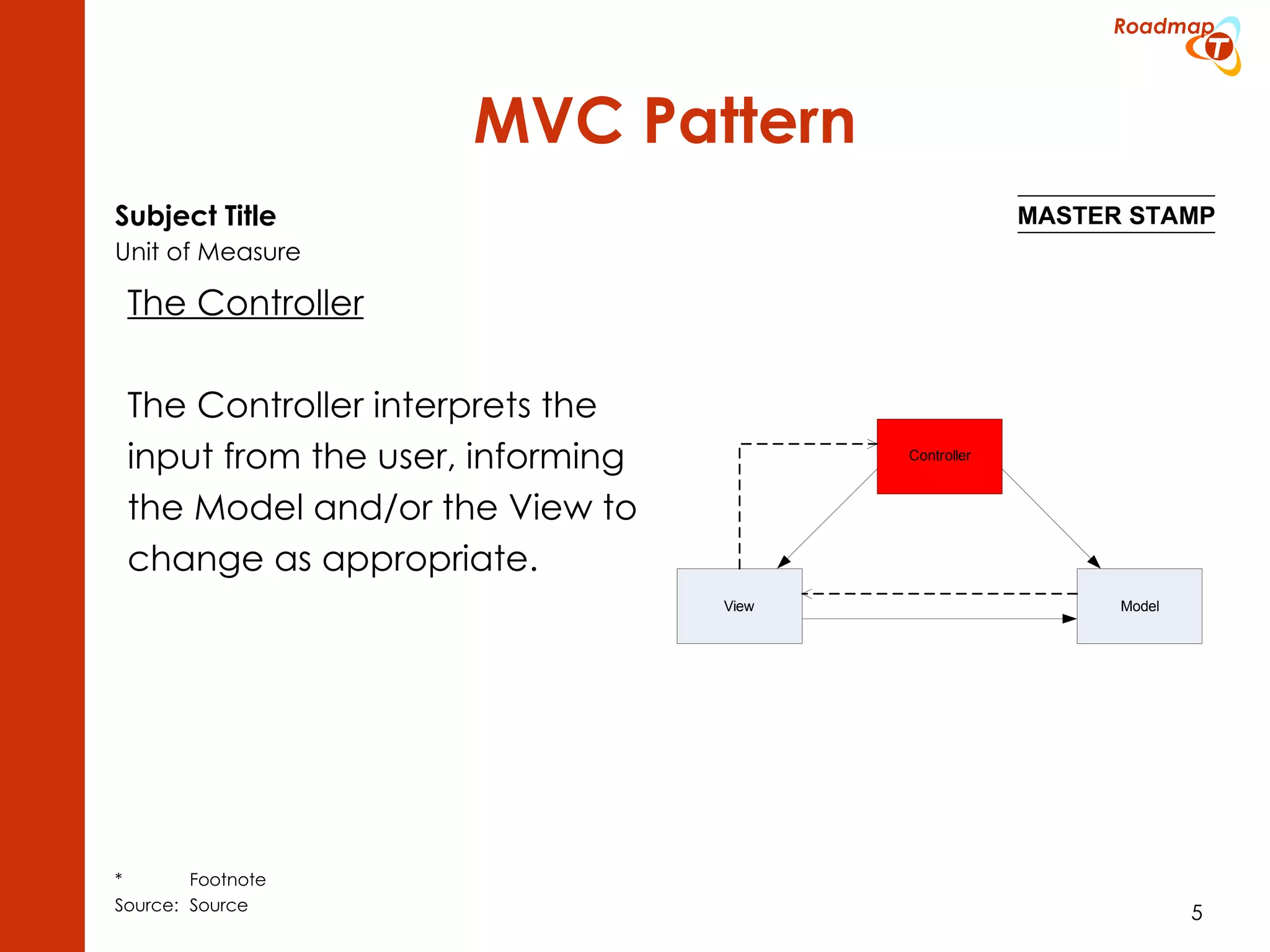
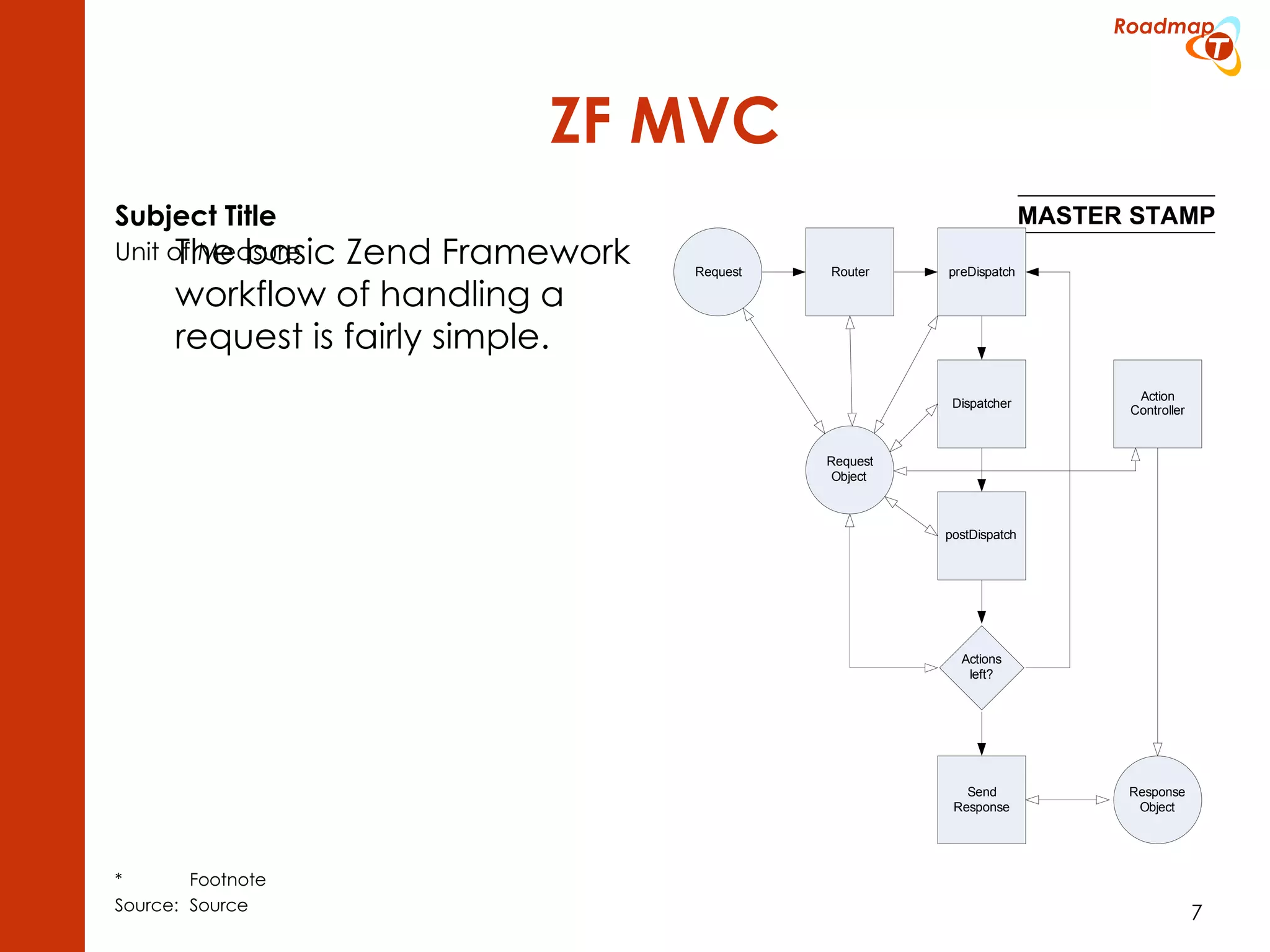
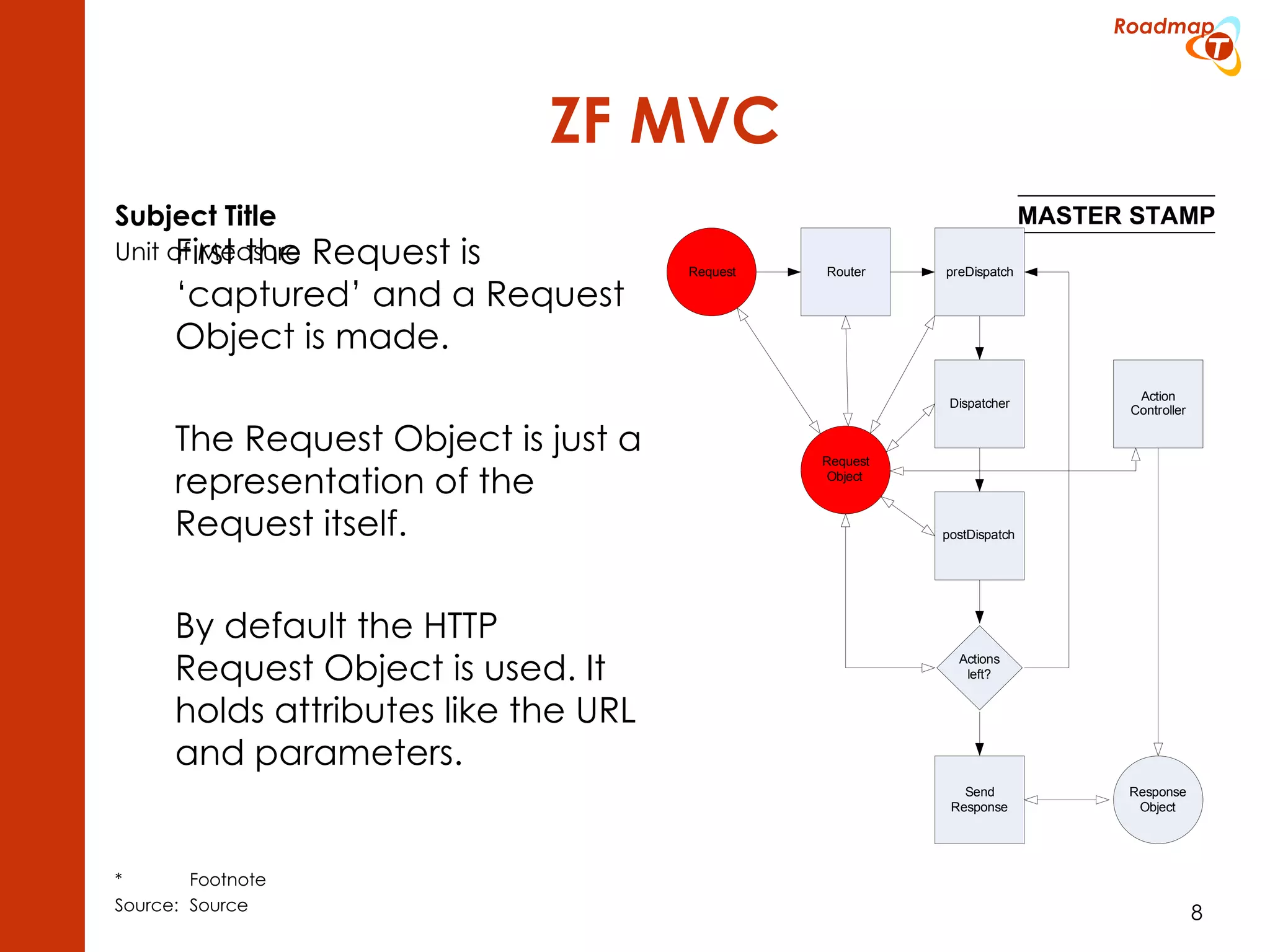
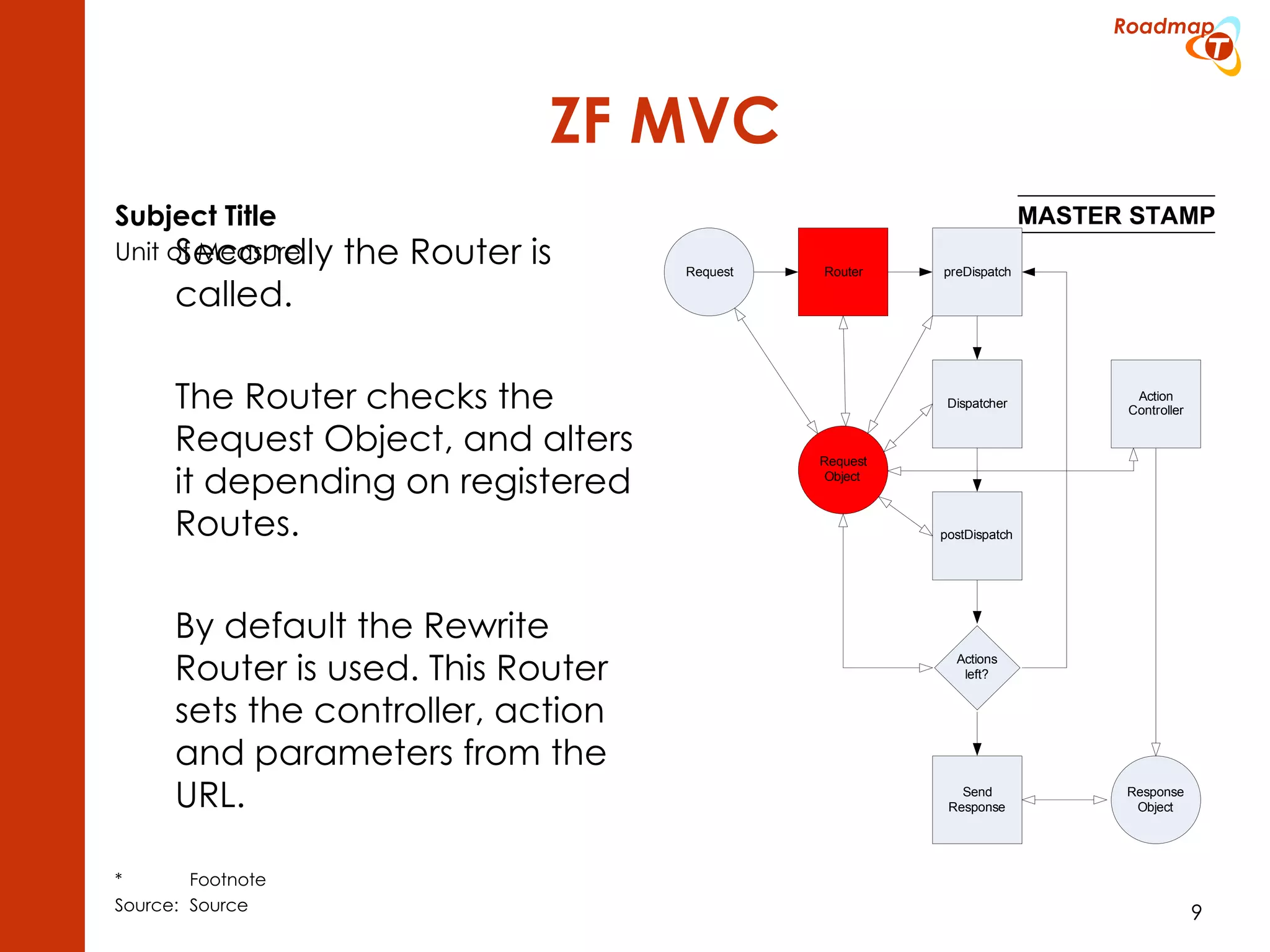
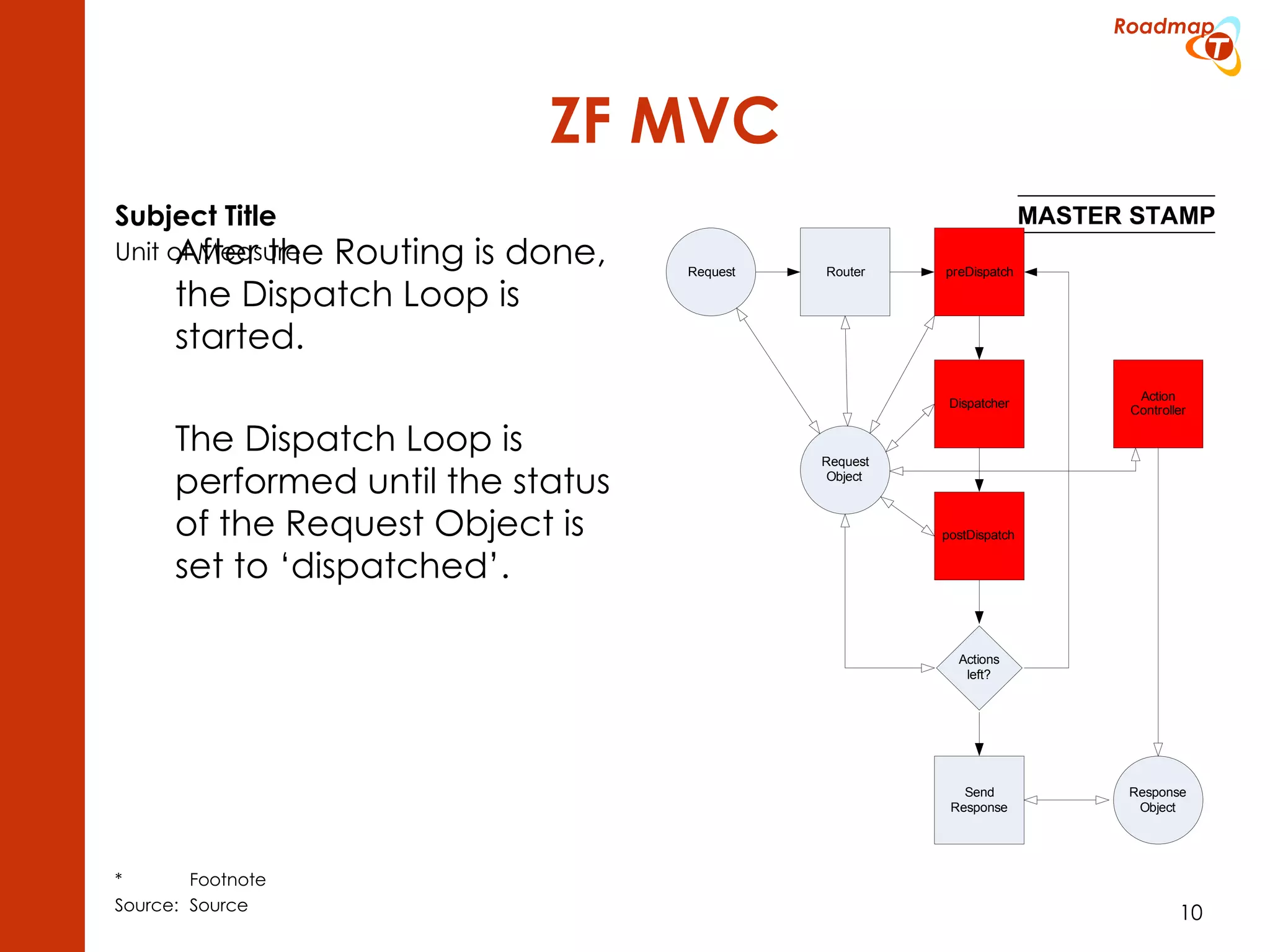
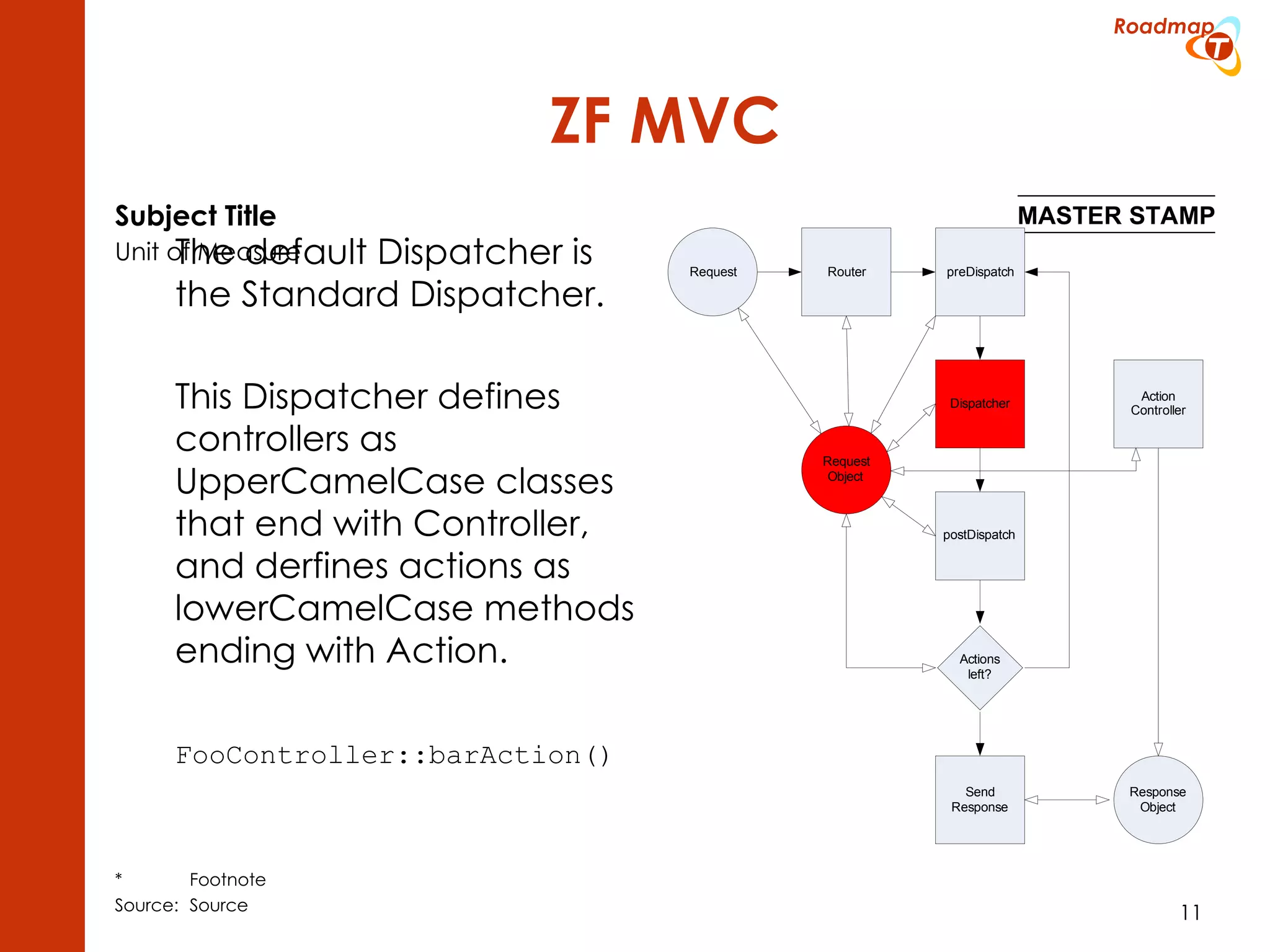
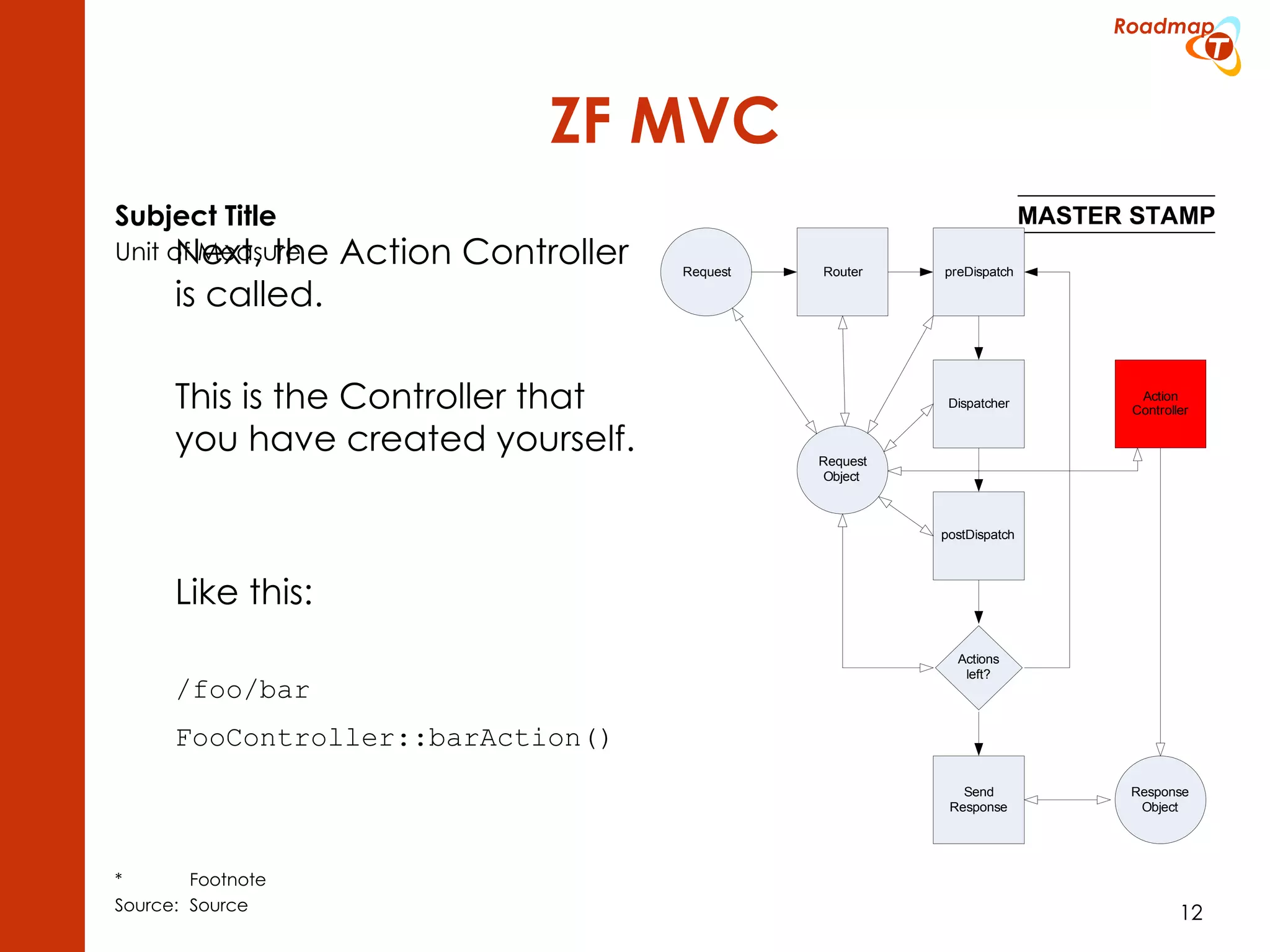
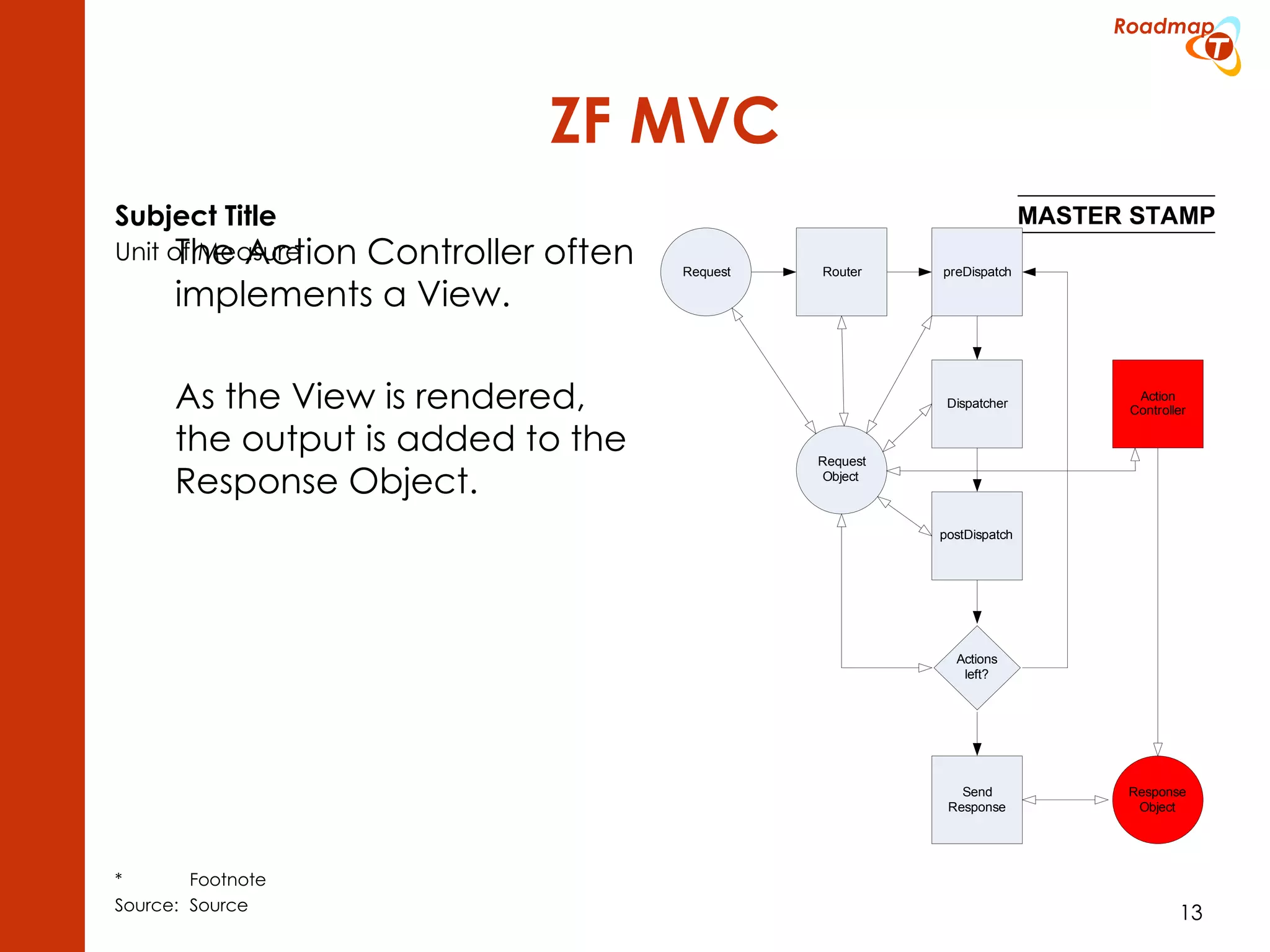
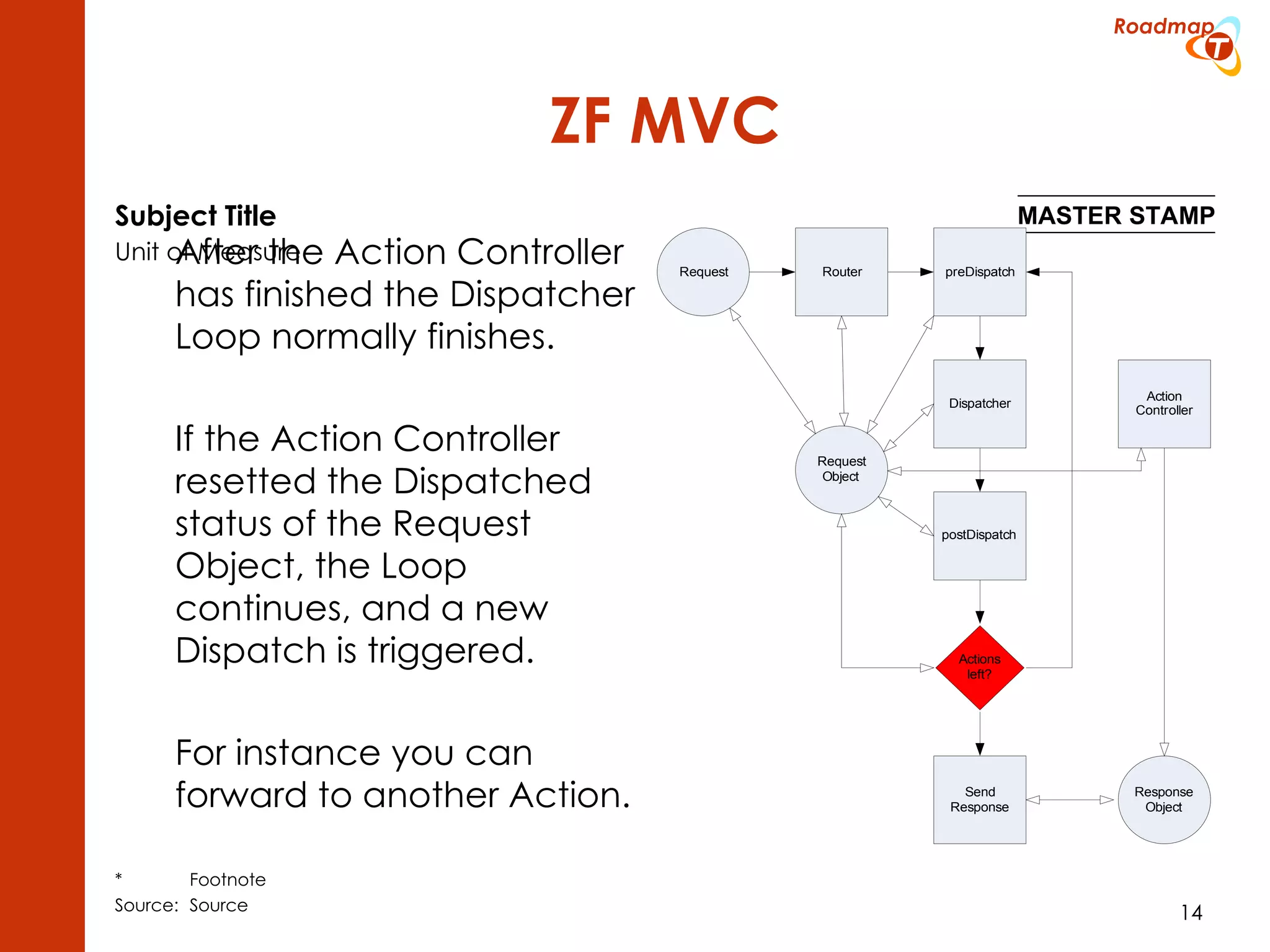
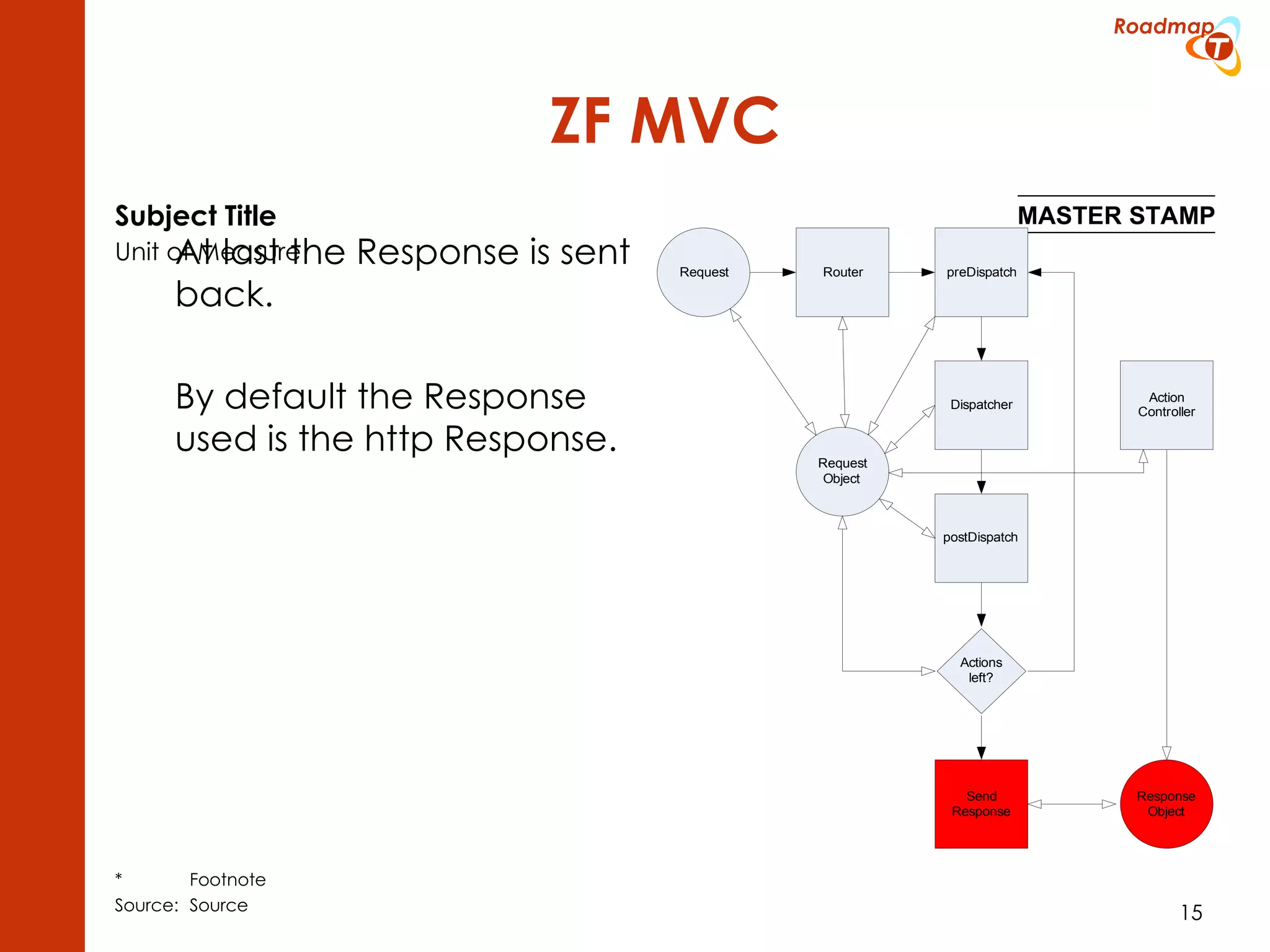
The document discusses the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern, focusing on its roles within the Zend Framework 2, which separates application behavior and data from user input processing. It outlines the basic workflow of handling a request, including capturing the request, routing, dispatching actions, and rendering views. Key advantages of MVC mentioned include high cohesion, ease of extension, and simplified automated testing.