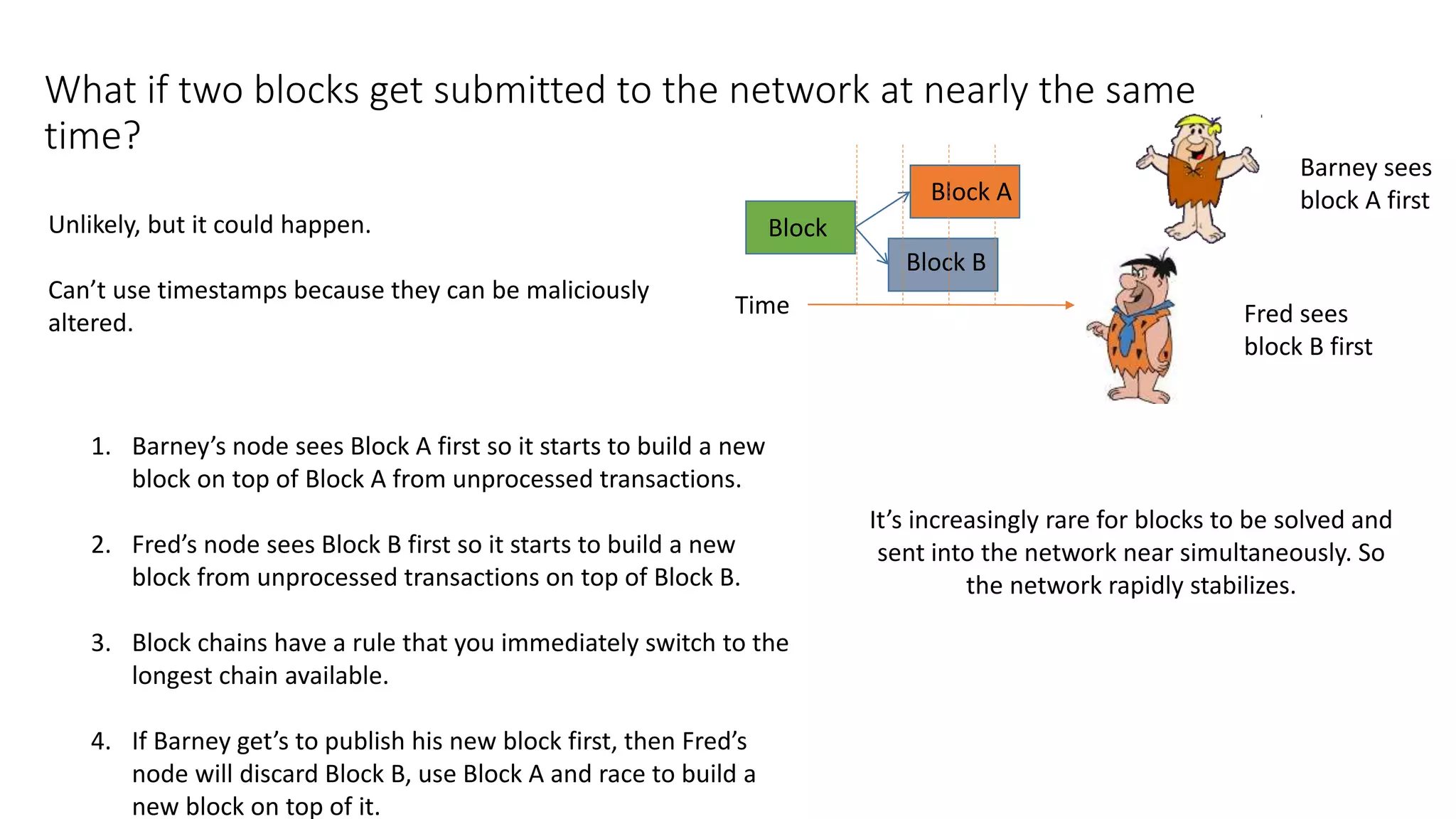
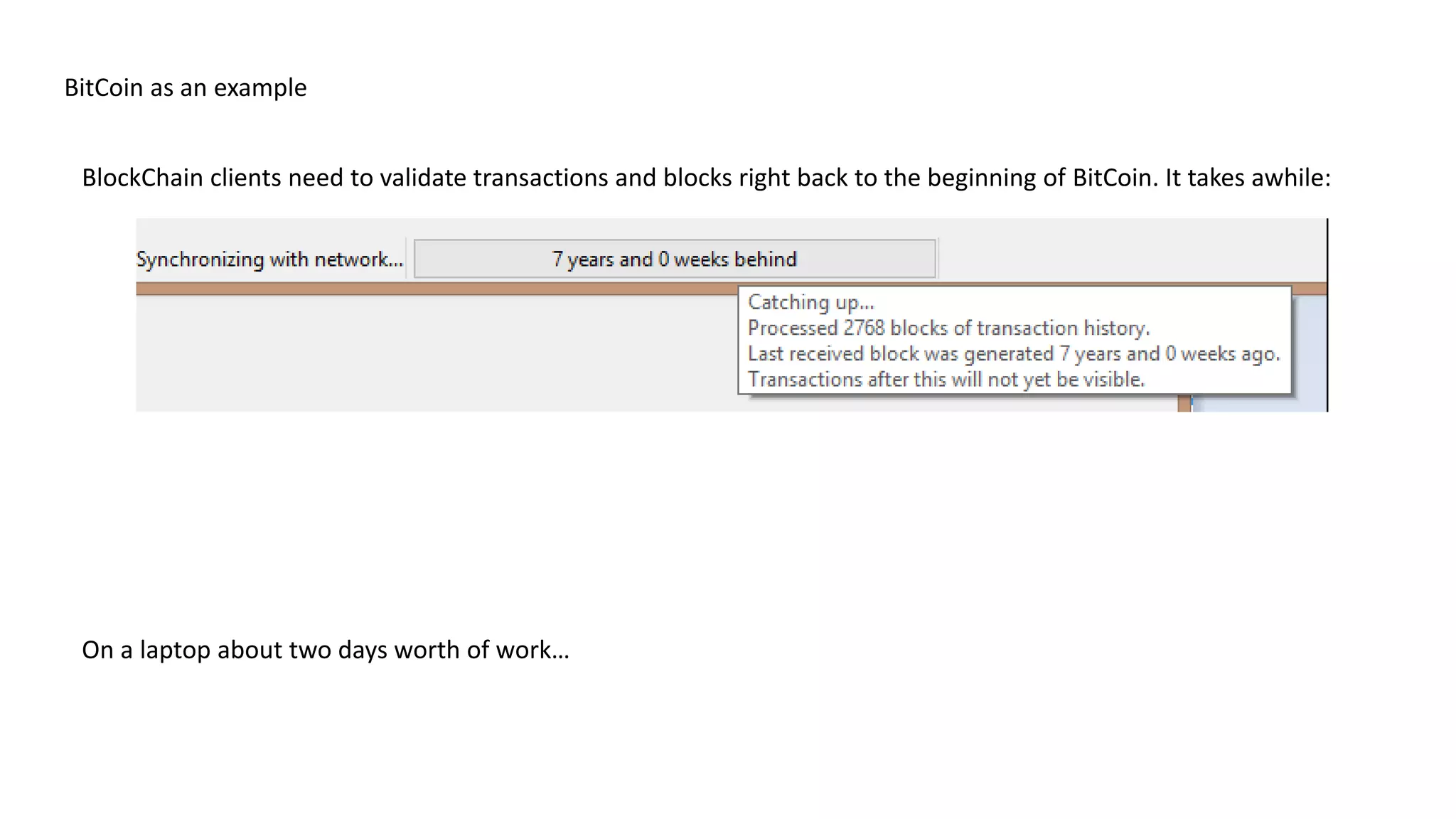
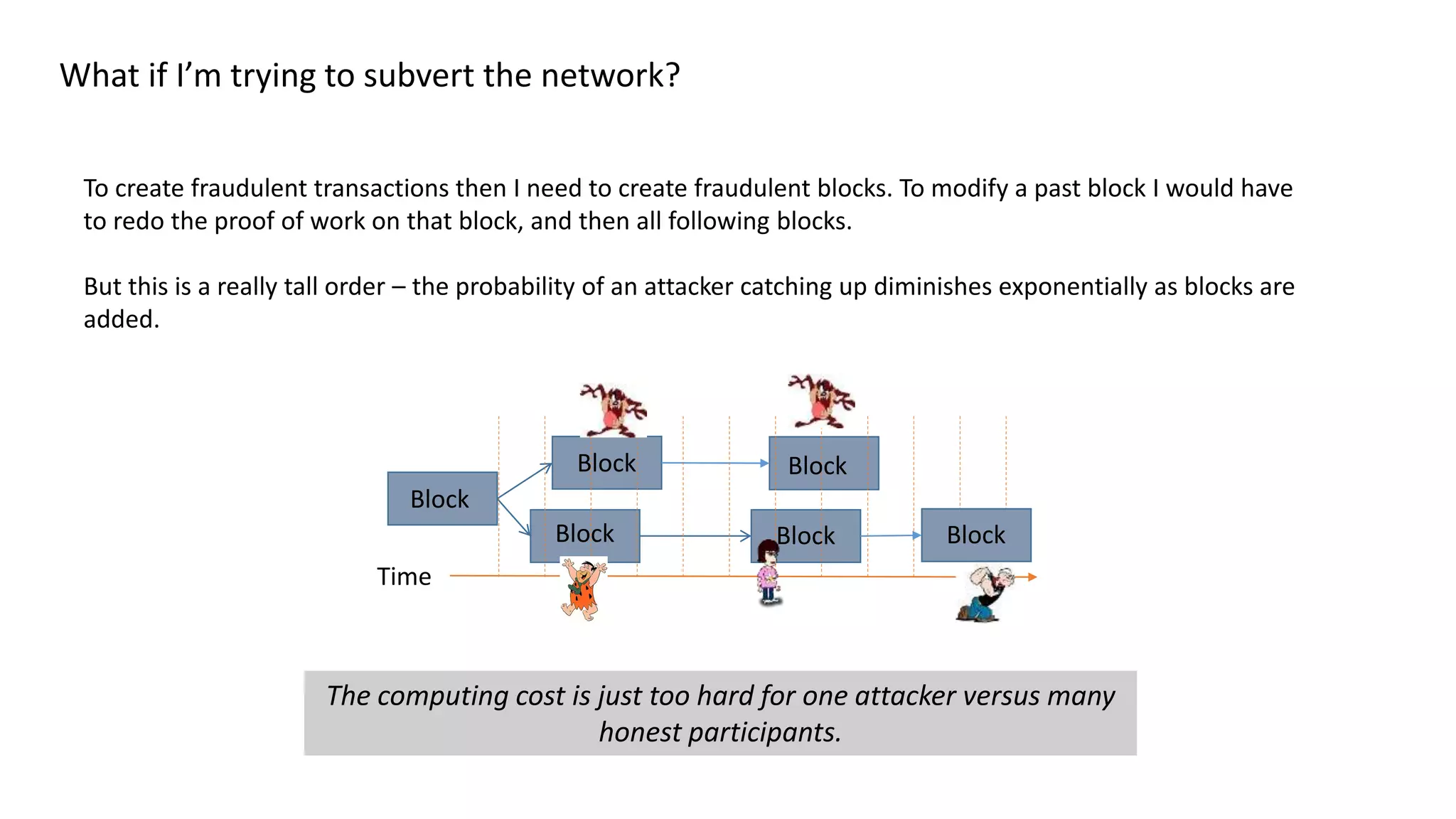
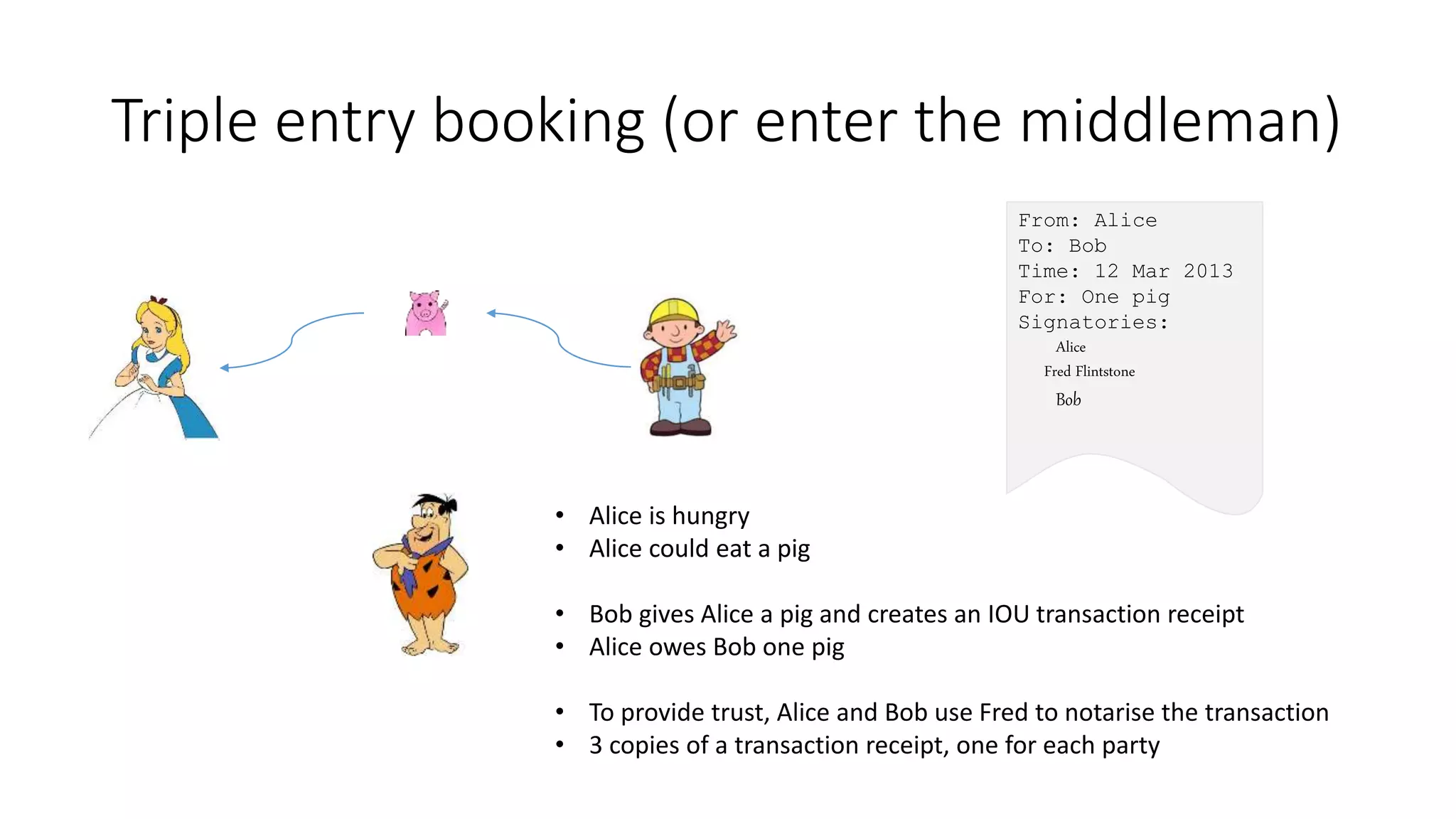
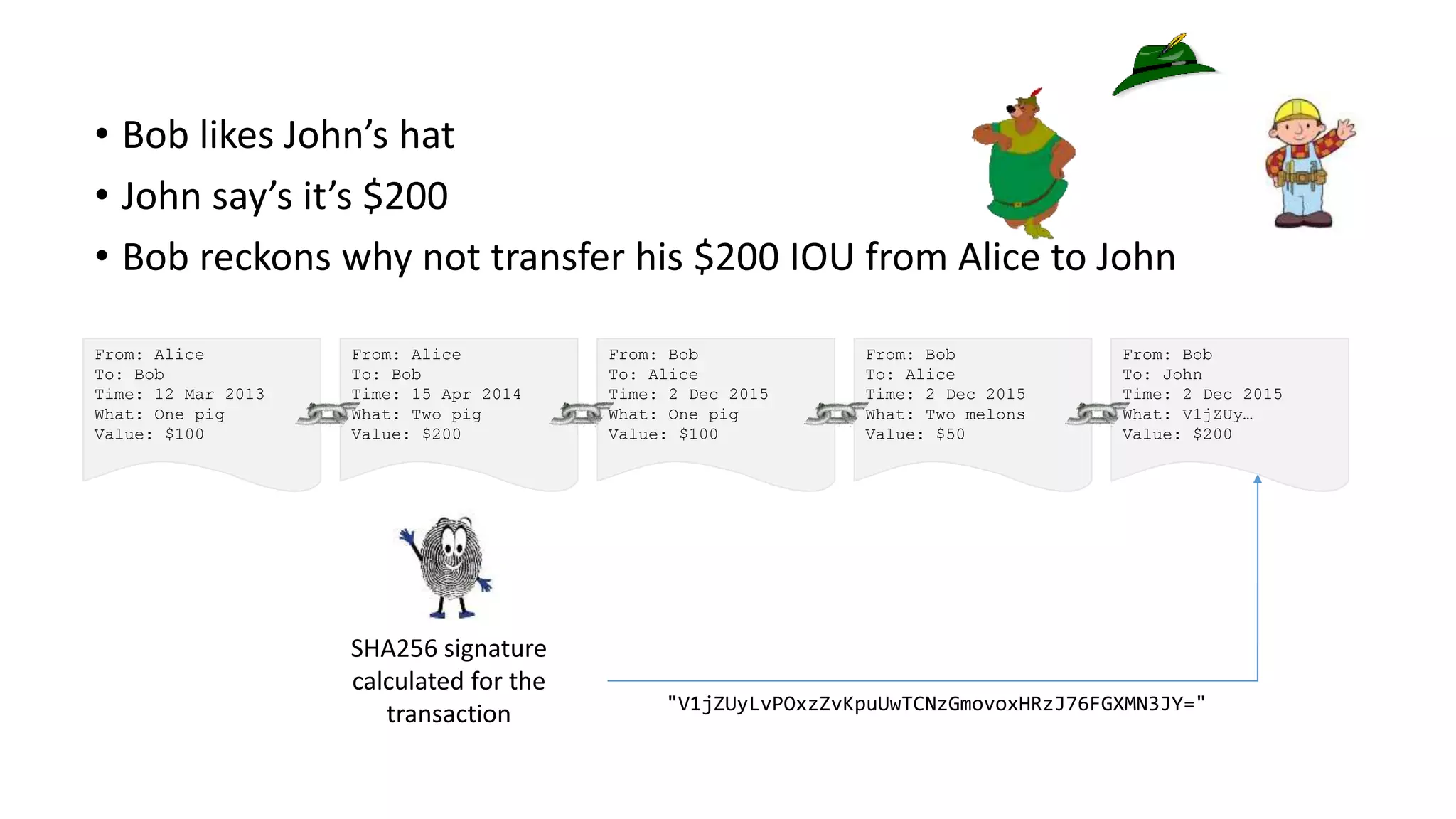
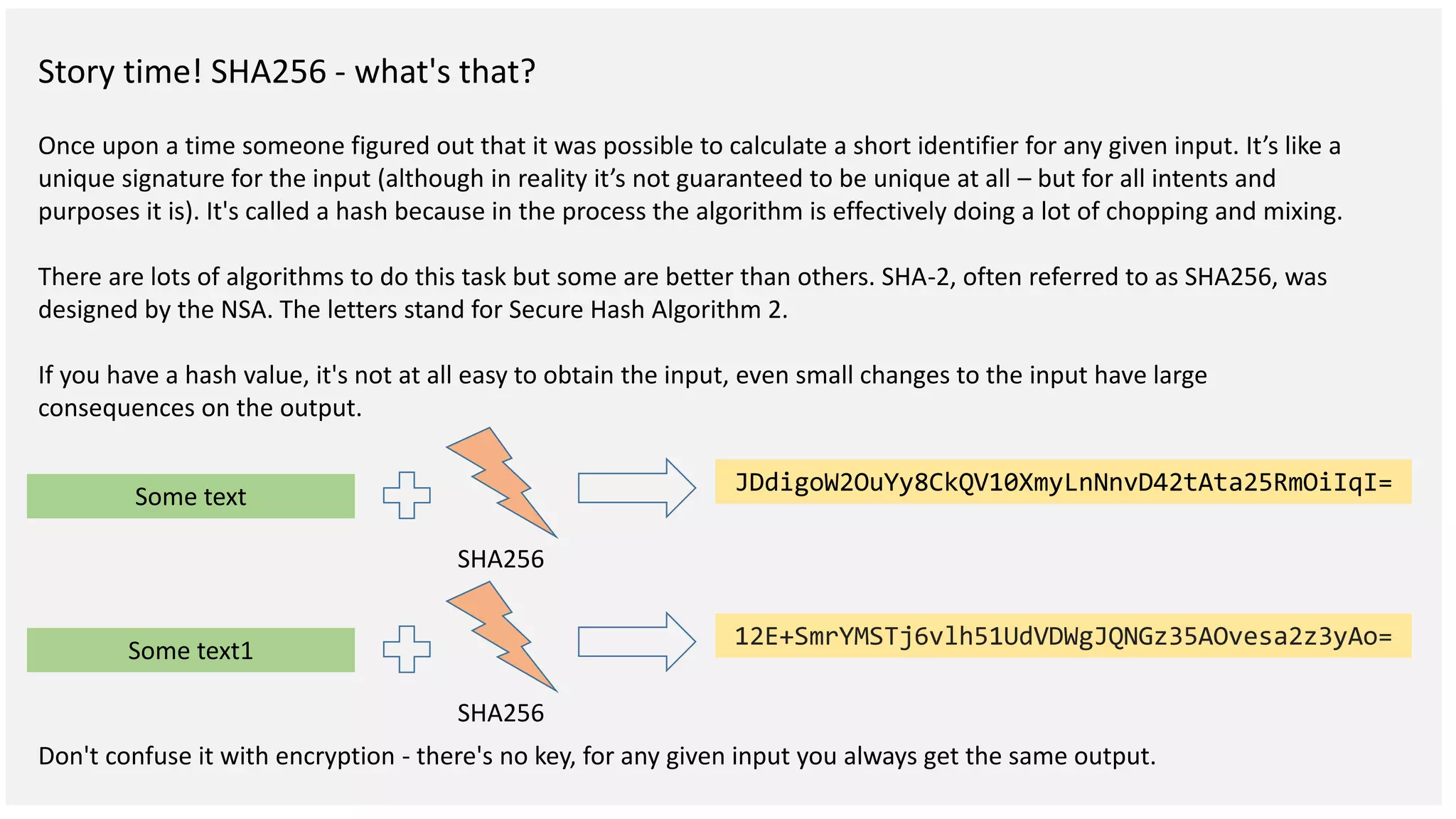
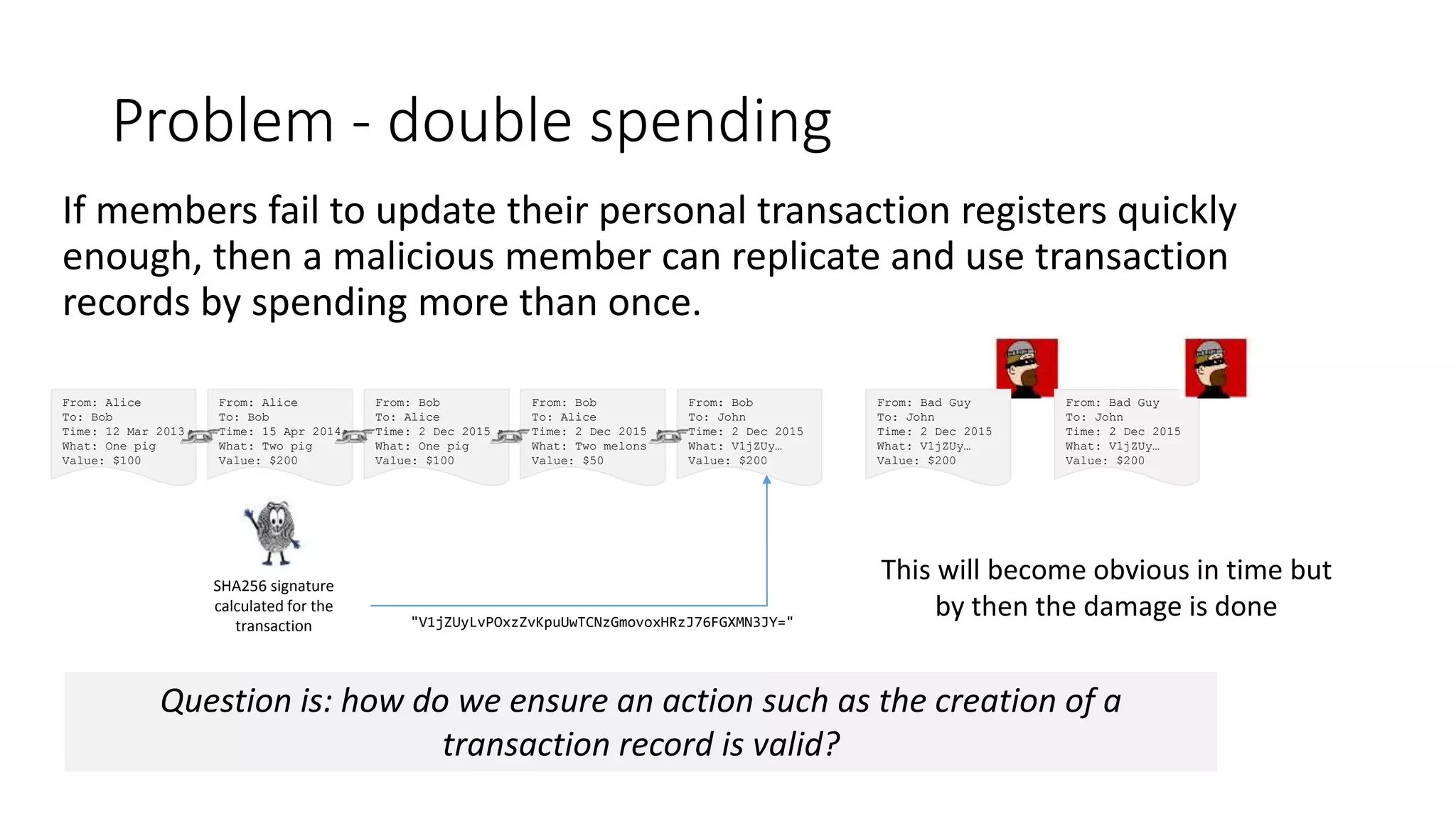
This document discusses building a blockchain network without a central authority by using cryptographic techniques like public-private key pairs, digital signatures, and proof-of-work. It explains how transactions between parties can be recorded in a distributed ledger through digitally signing transaction receipts with private keys. It then discusses how proof-of-work can be used to establish consensus on the valid transaction history and prevent double spending by making it computationally costly to vote or generate transactions on the network.













![We can make this much harder though… Look for a hash outcome that has some arbitrary substring eg 00 at the beginning. SHA256(“I vote for Bob”) "wn8iR1xcp4JLpHC1WLkXSDS+wtNeF5TYCthCycGw1+c=“ Fail, so let’s modify the input in some way.. SHA256(“I vote for Bob - 2”) -> "O1ODEfjRTAgsbMuRSUnMPD84nAExphQ0zqQTpD3Omr8=“ Fail again, keep going… open System.Security.Cryptography open System.Text let hasher = new SHA256Managed() let bytesHash' (s:string) = hasher.ComputeHash((new UnicodeEncoding()).GetBytes(s)) let r = System.Random() let rs = [0..10000] |> List.map (fun i -> i* r.Next(0,1000)) let hashes = rs |> List.map (fun i -> System.Convert.ToBase64String(bytesHash' (i.ToString()) )) hashes |> List.filter (fun h -> h.StartsWith("00")) … I typically get 2 to 4 hashes that work in 10,001 random choices The more 0’s at the beginning, the harder work it is. The idea is to make this expensive for the member generating the vote.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildyourownblockchain-160209233120/75/Build-your-own-block-chain-25-2048.jpg)