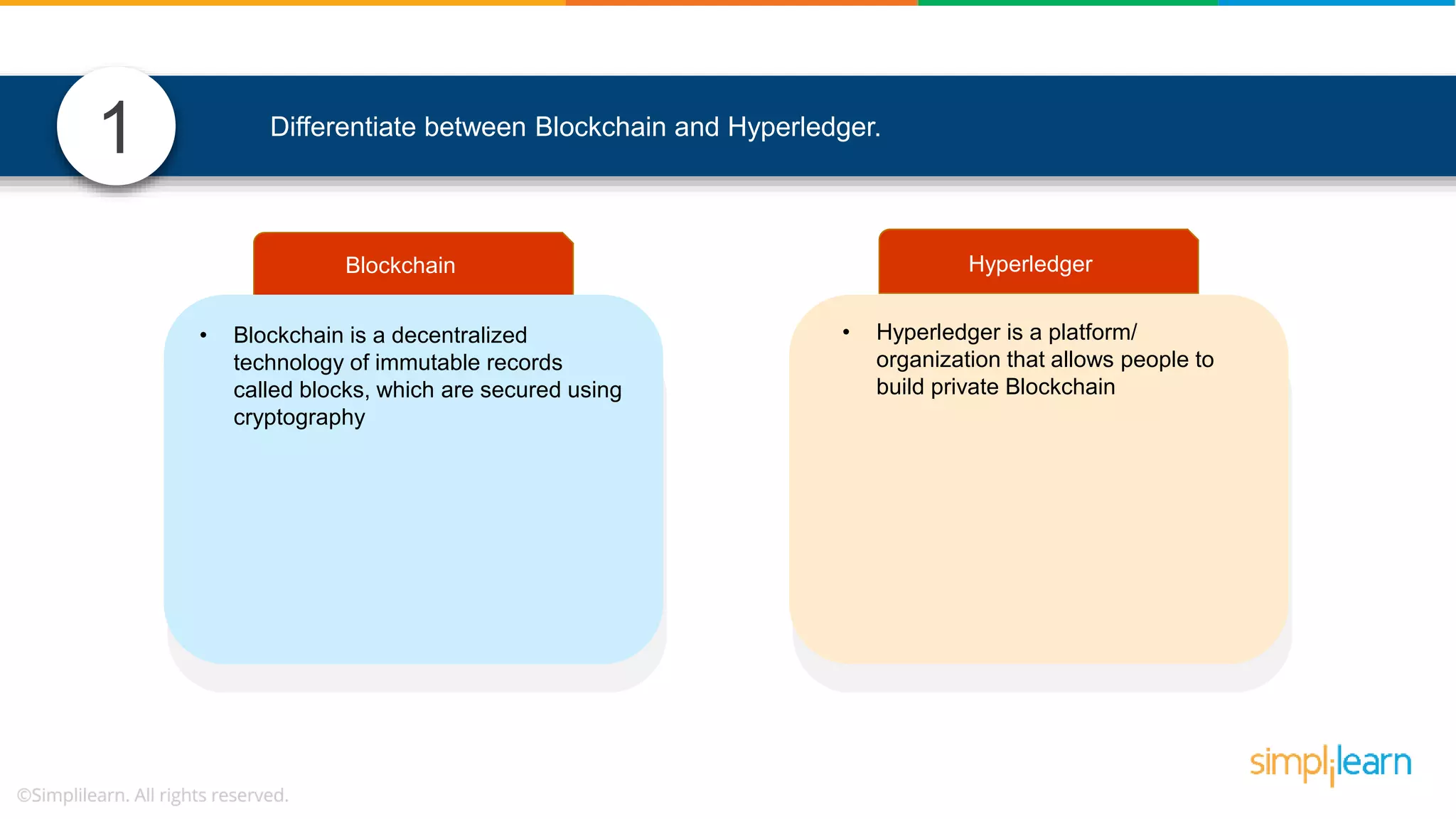
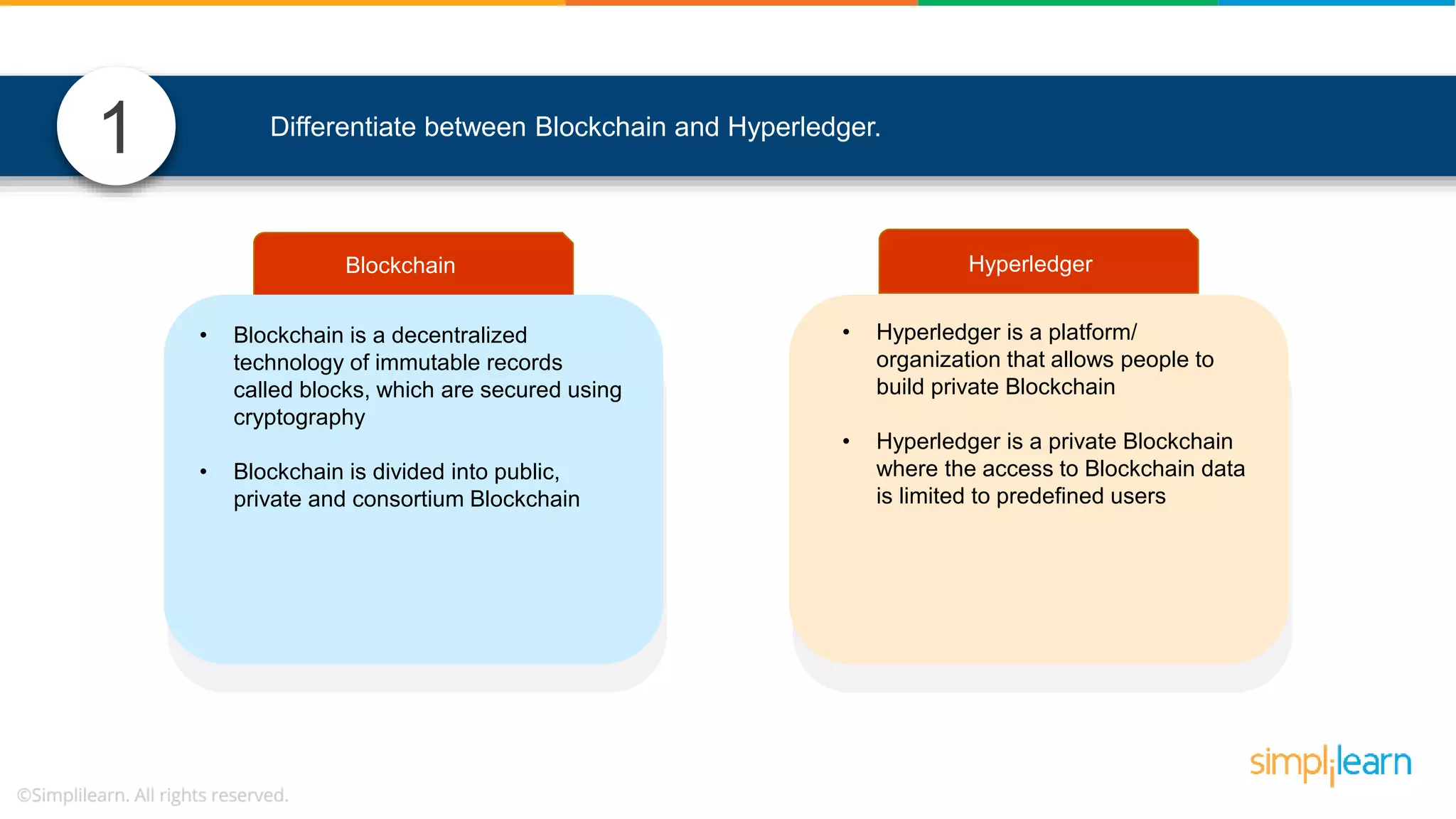
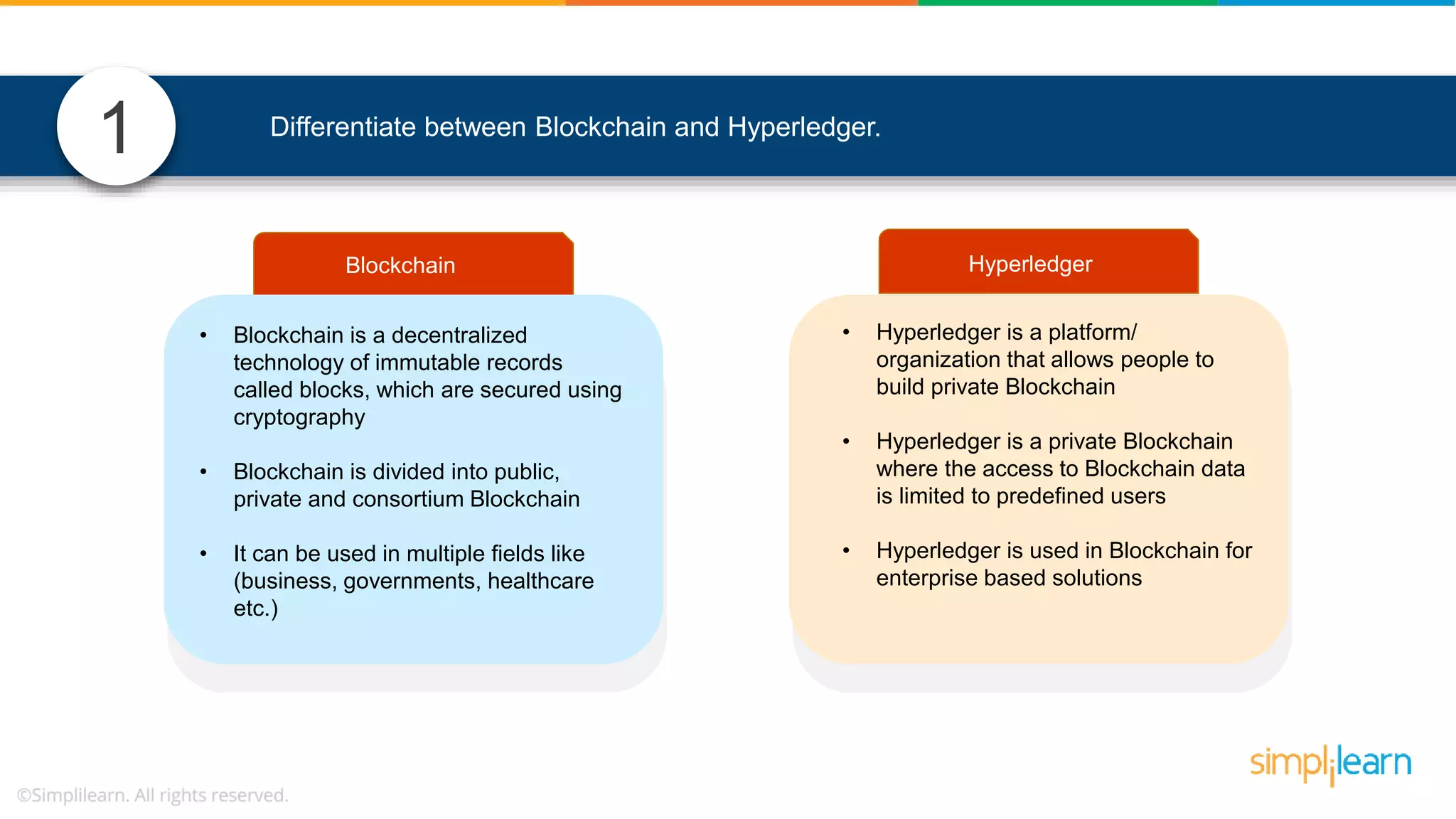
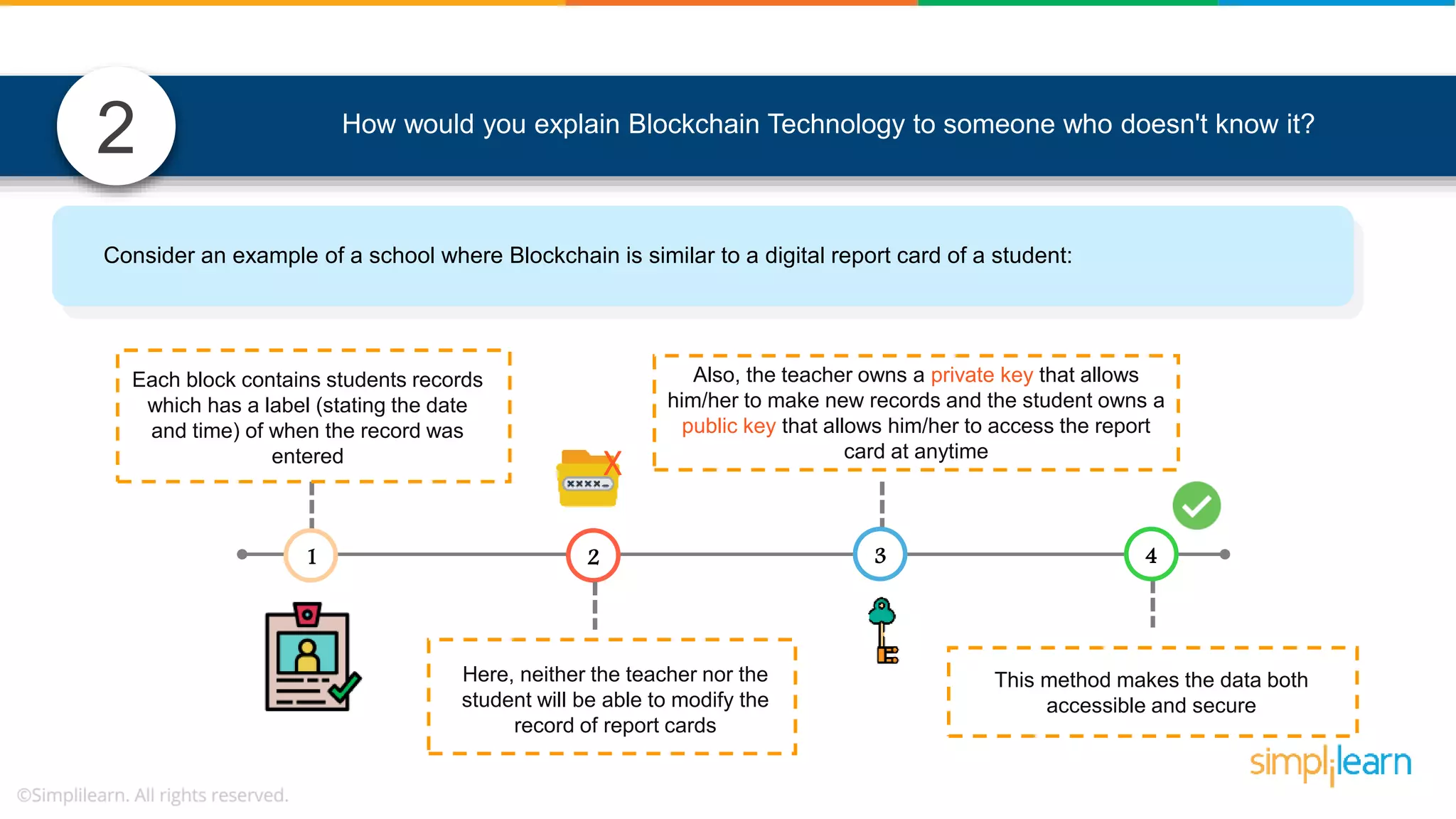
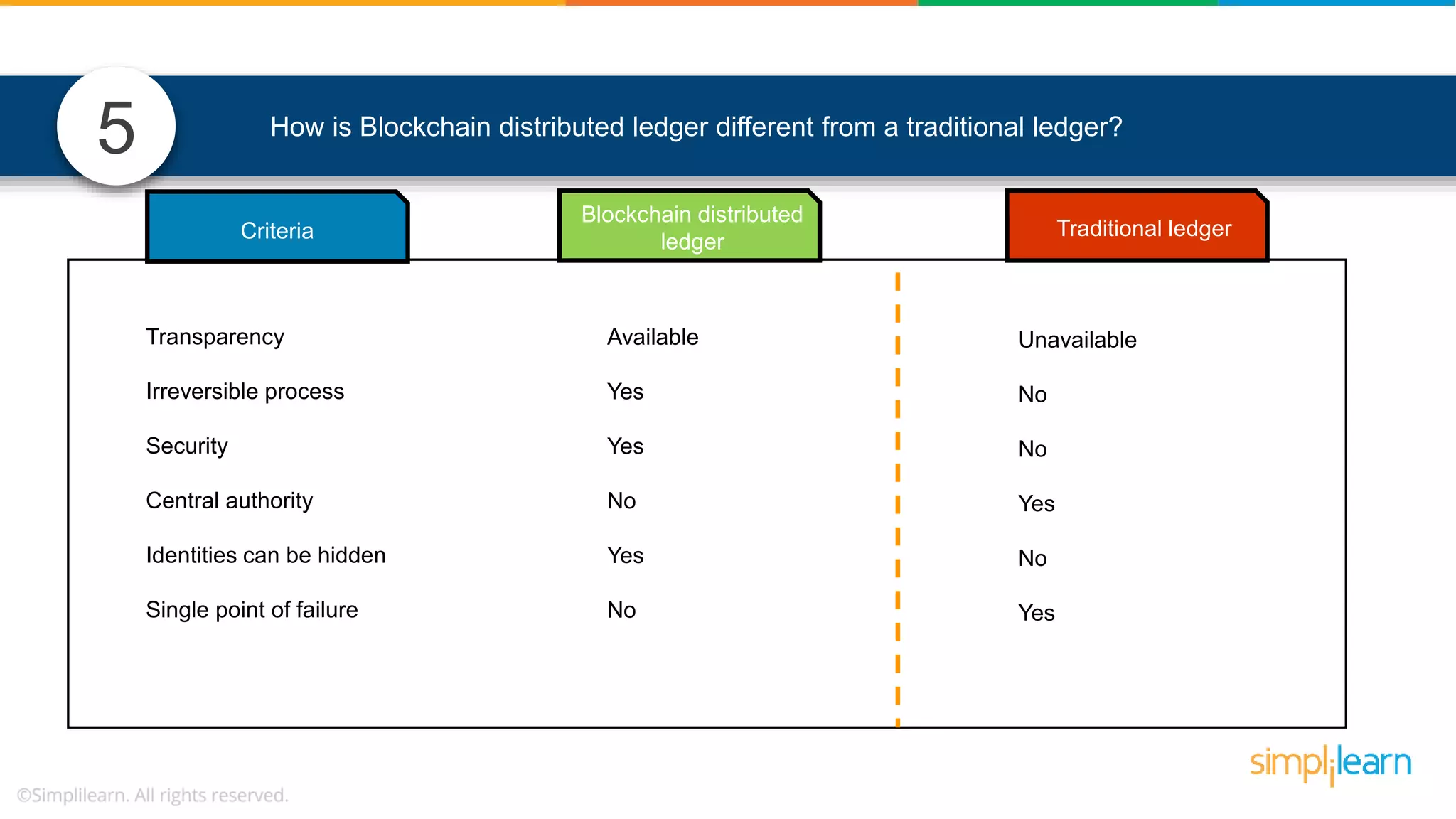
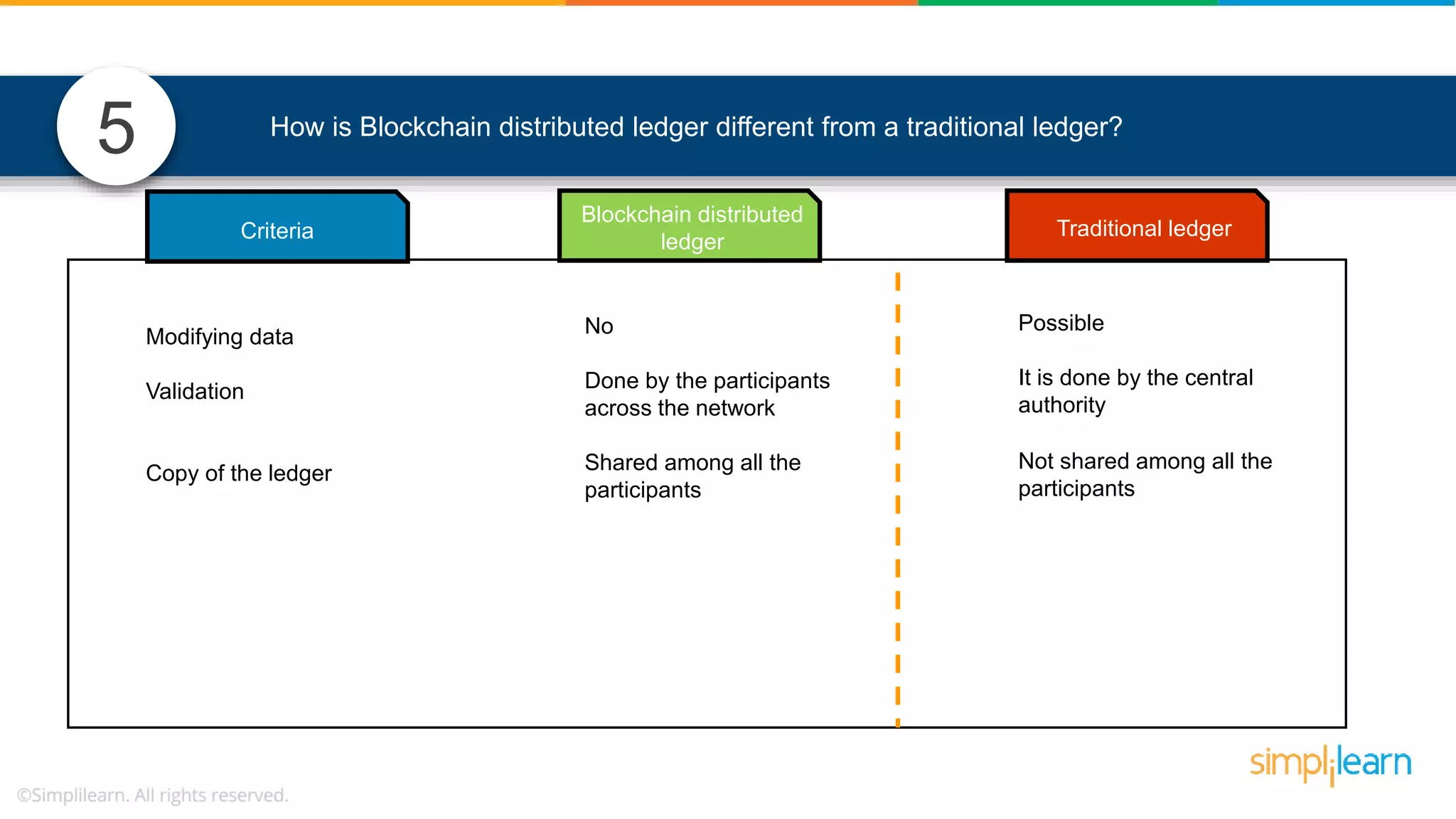
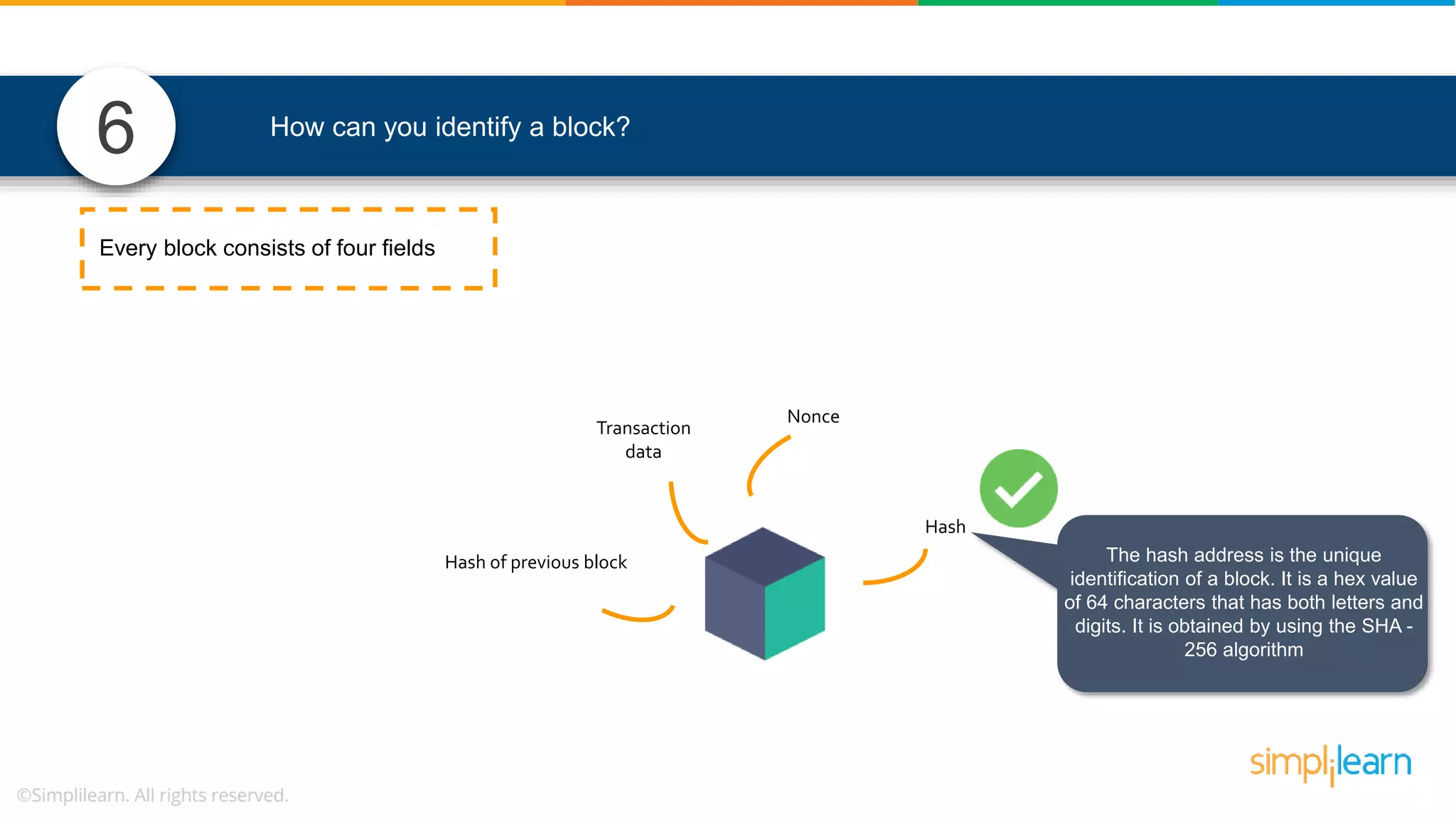
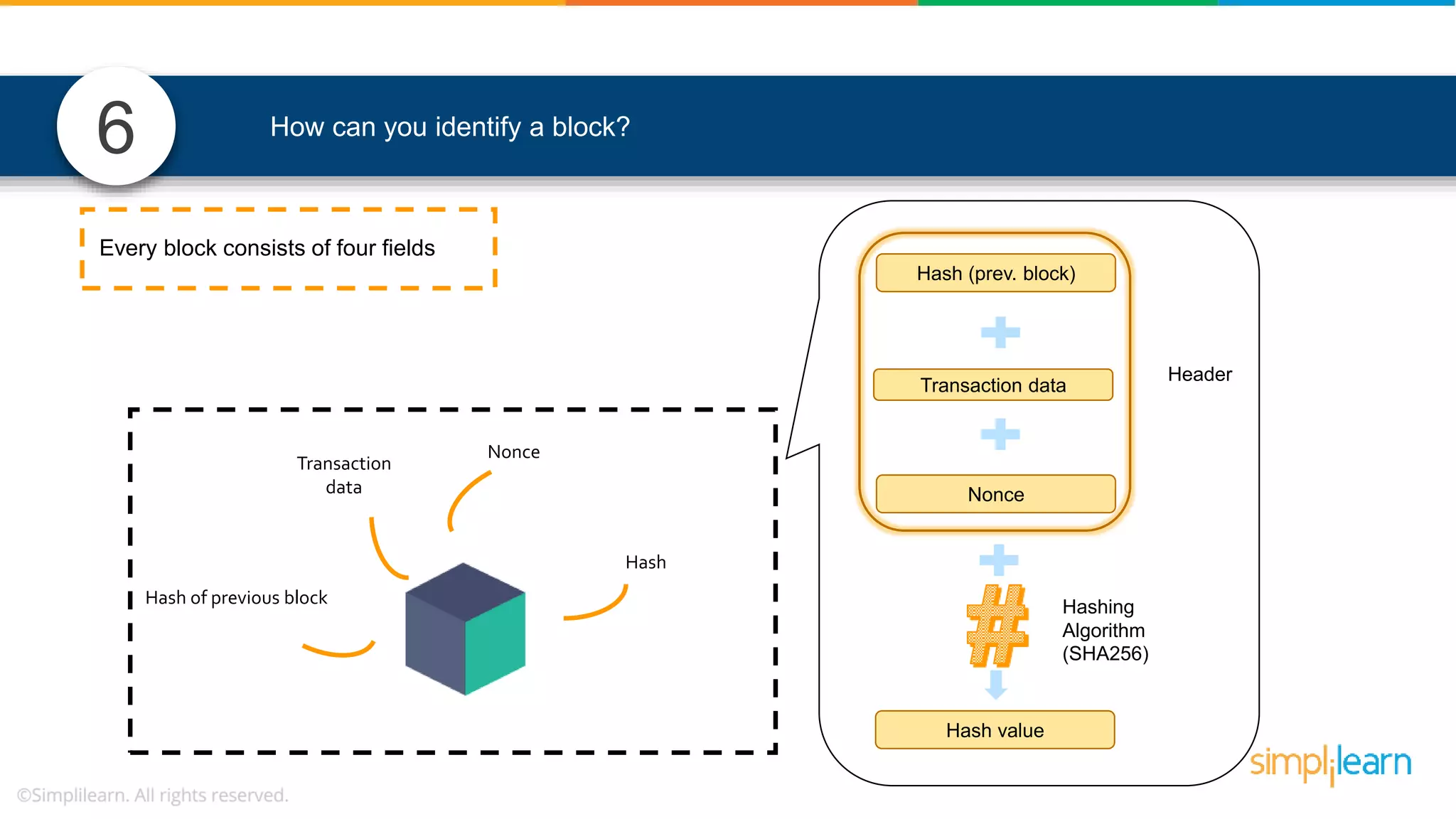
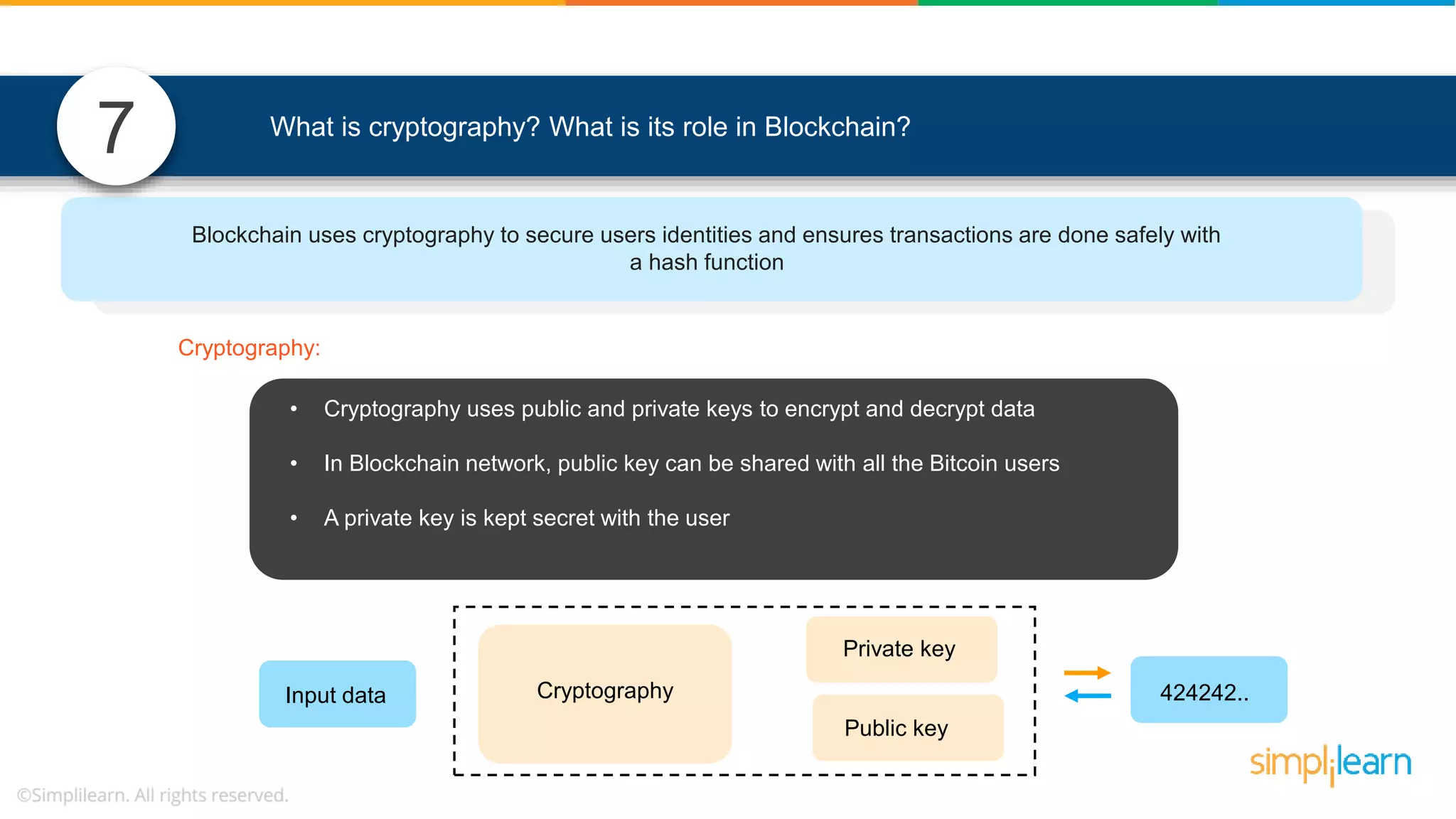
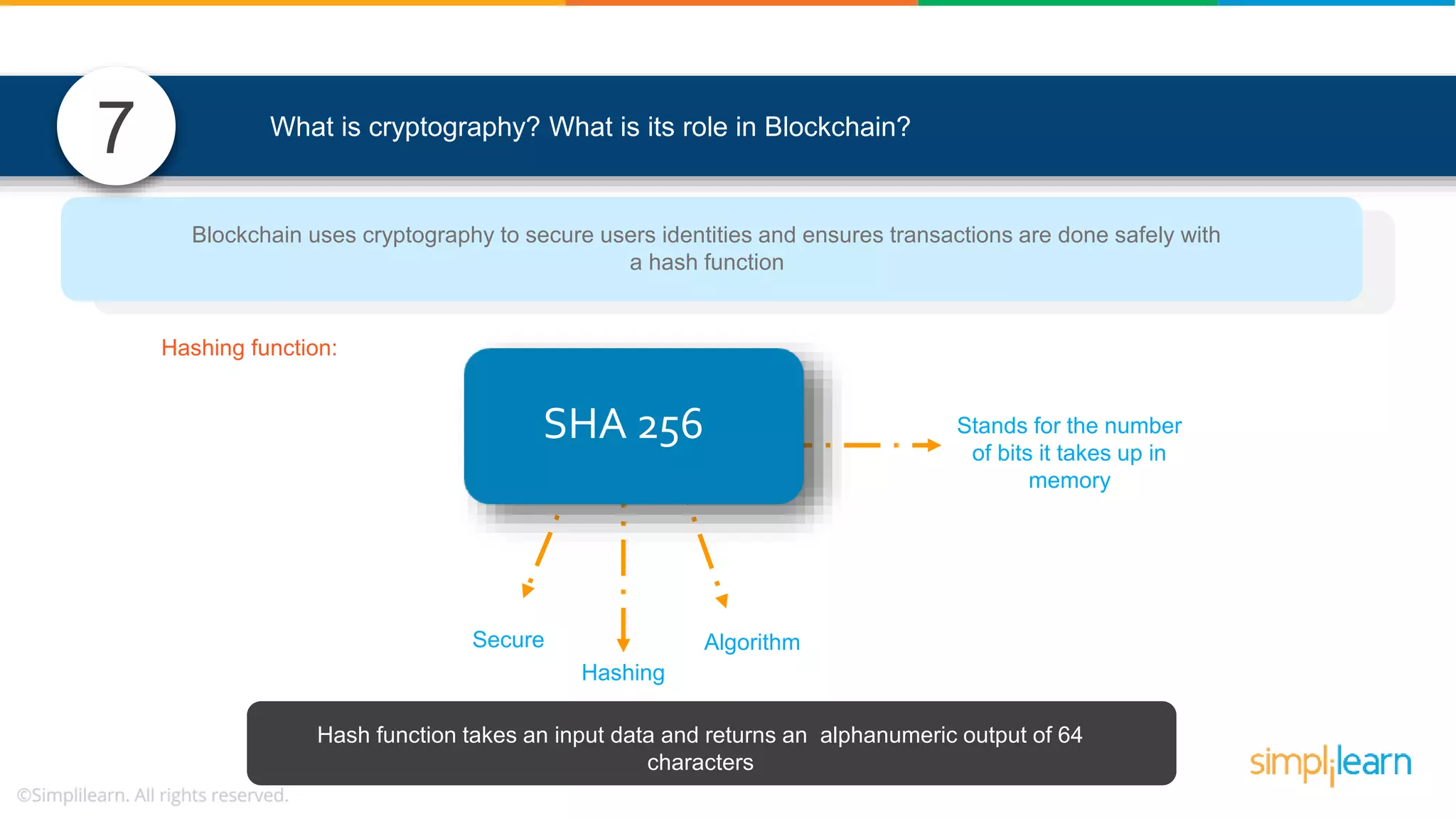
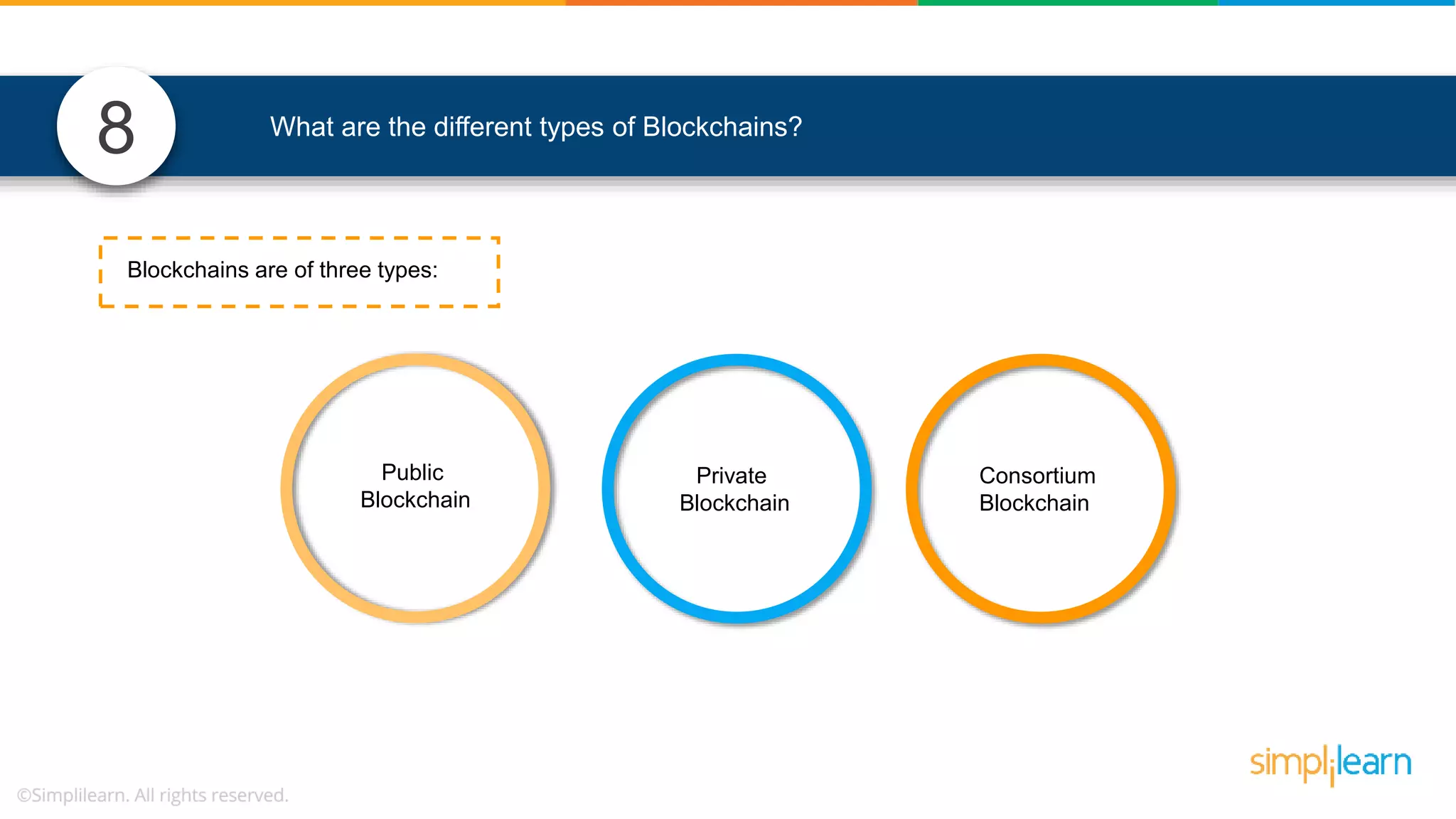
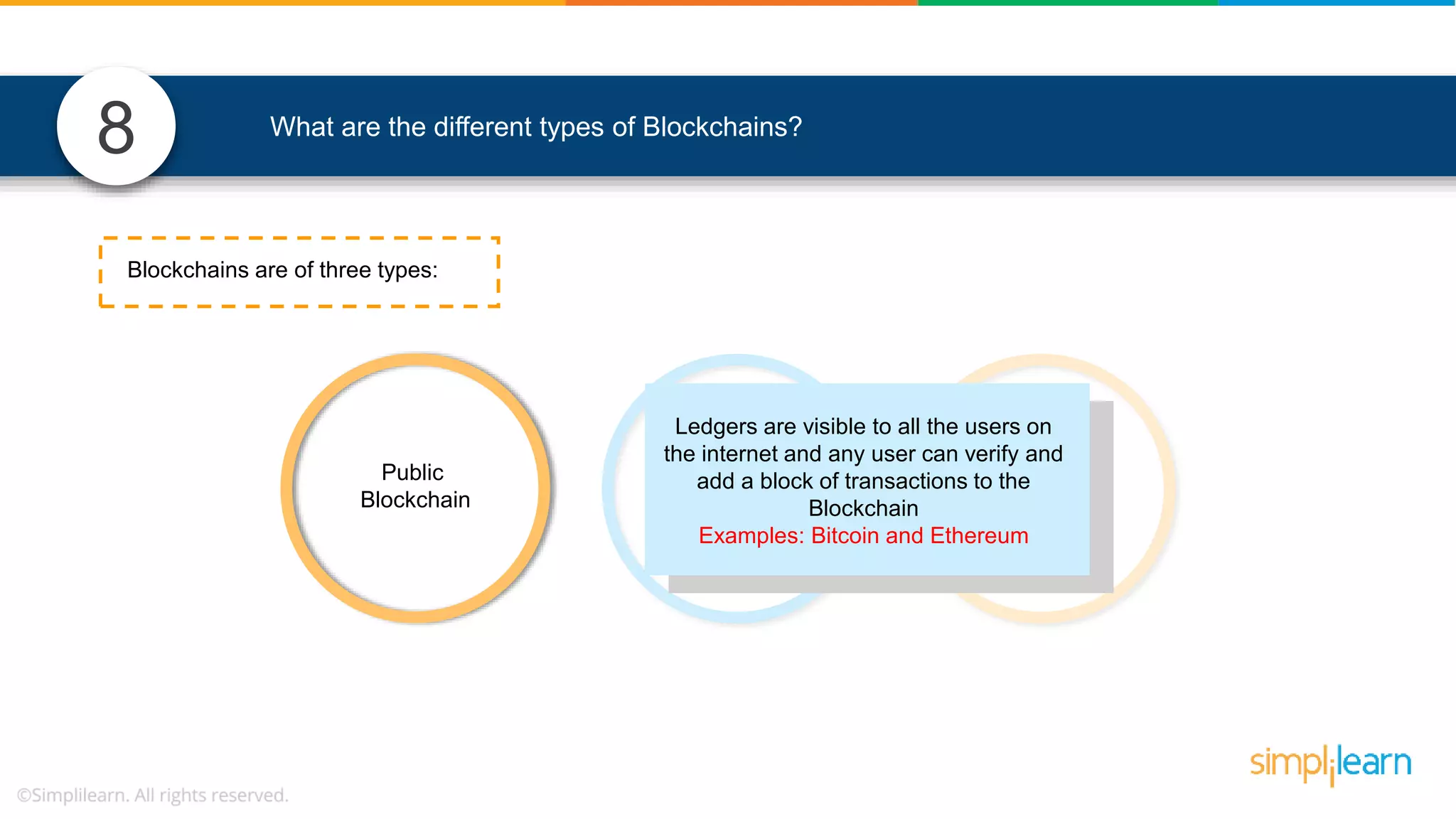
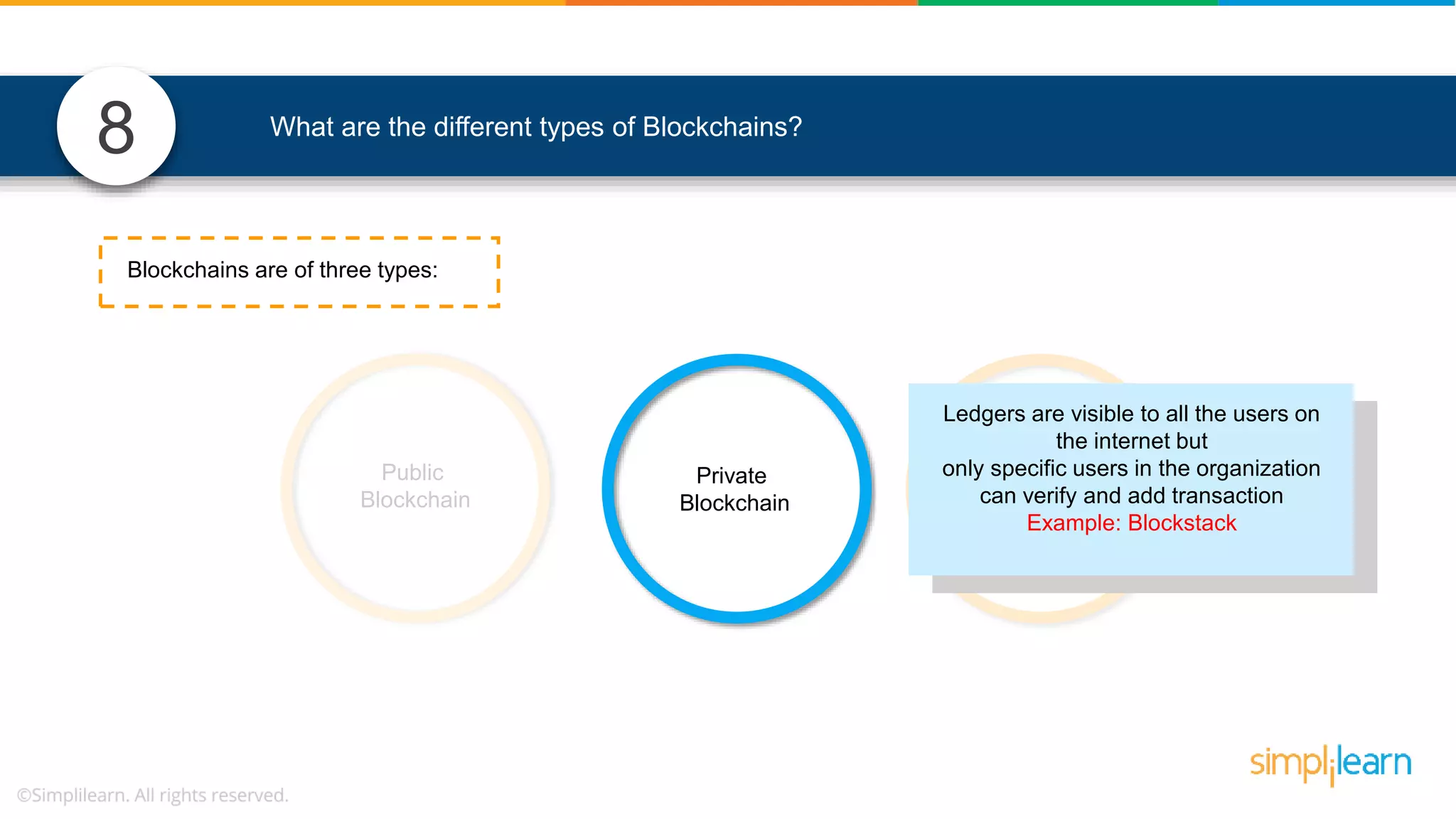
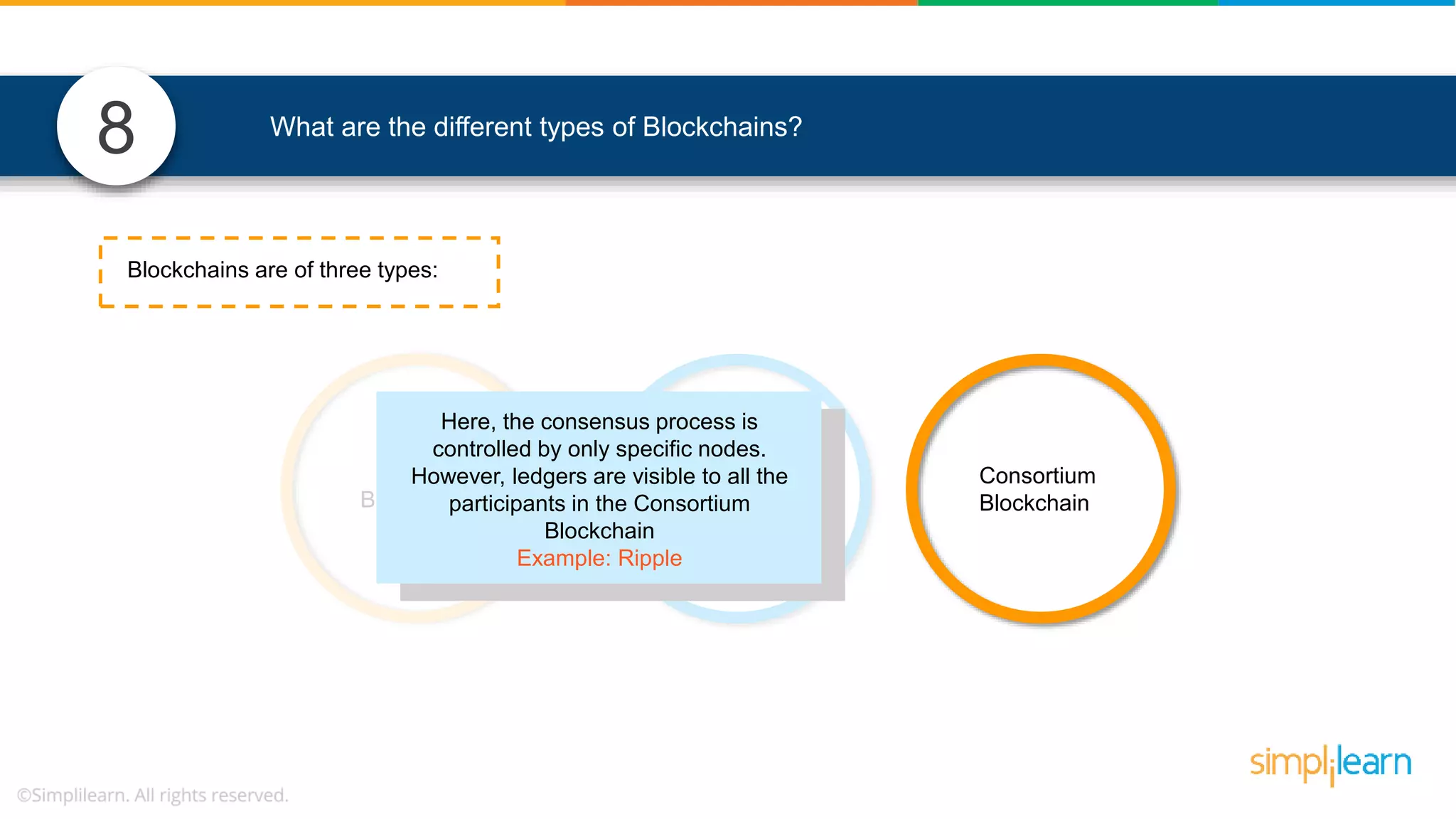
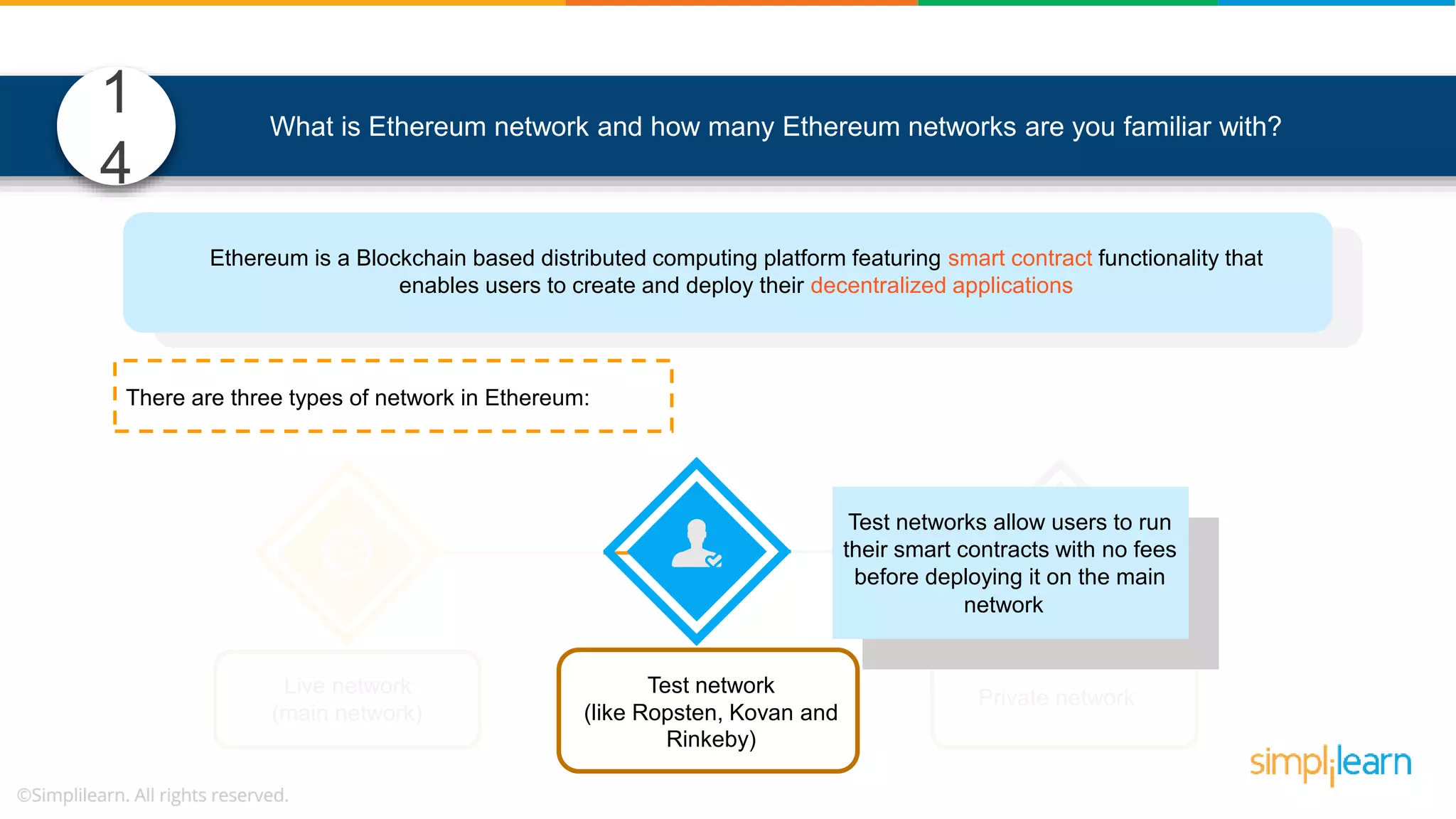
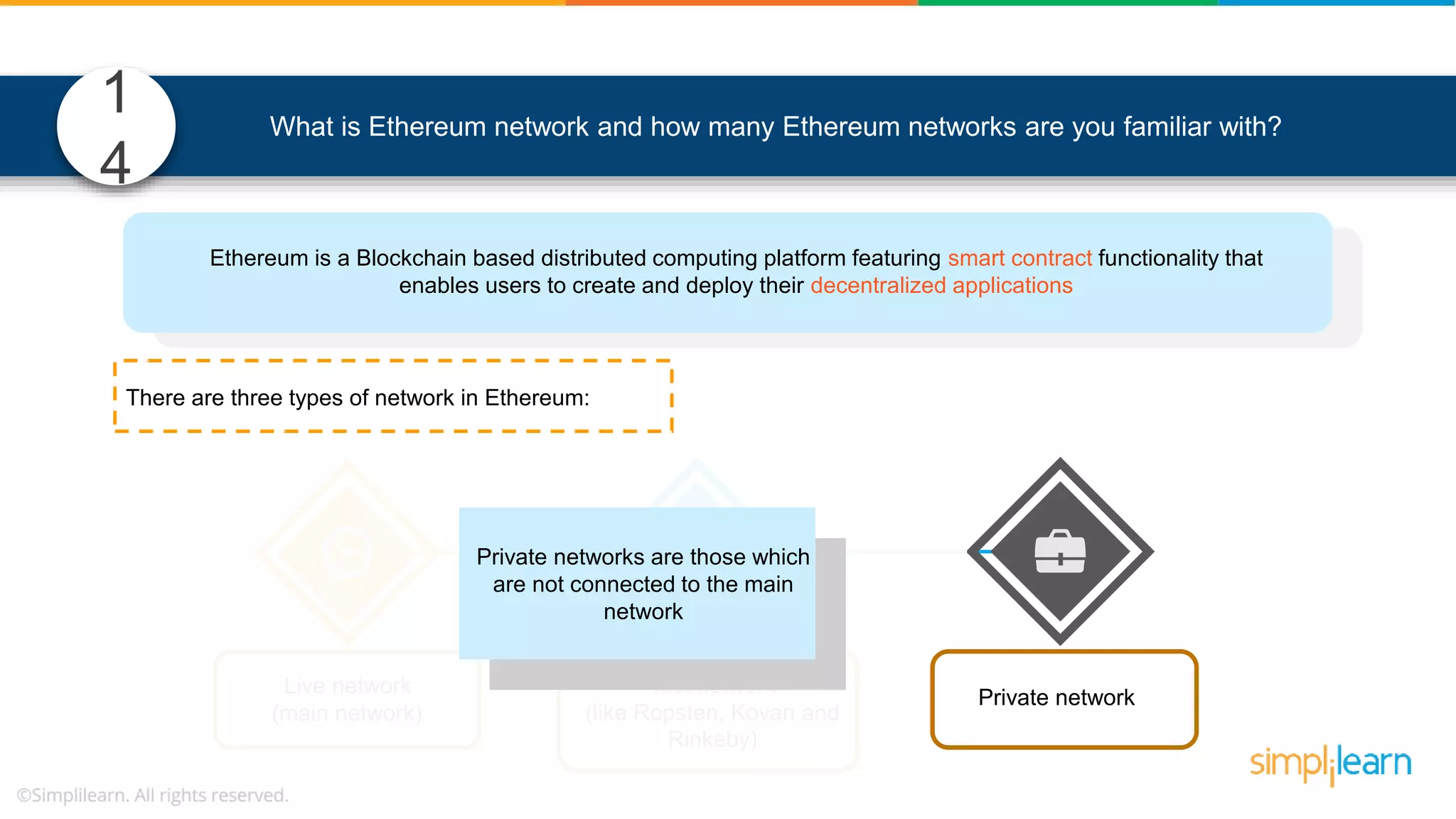
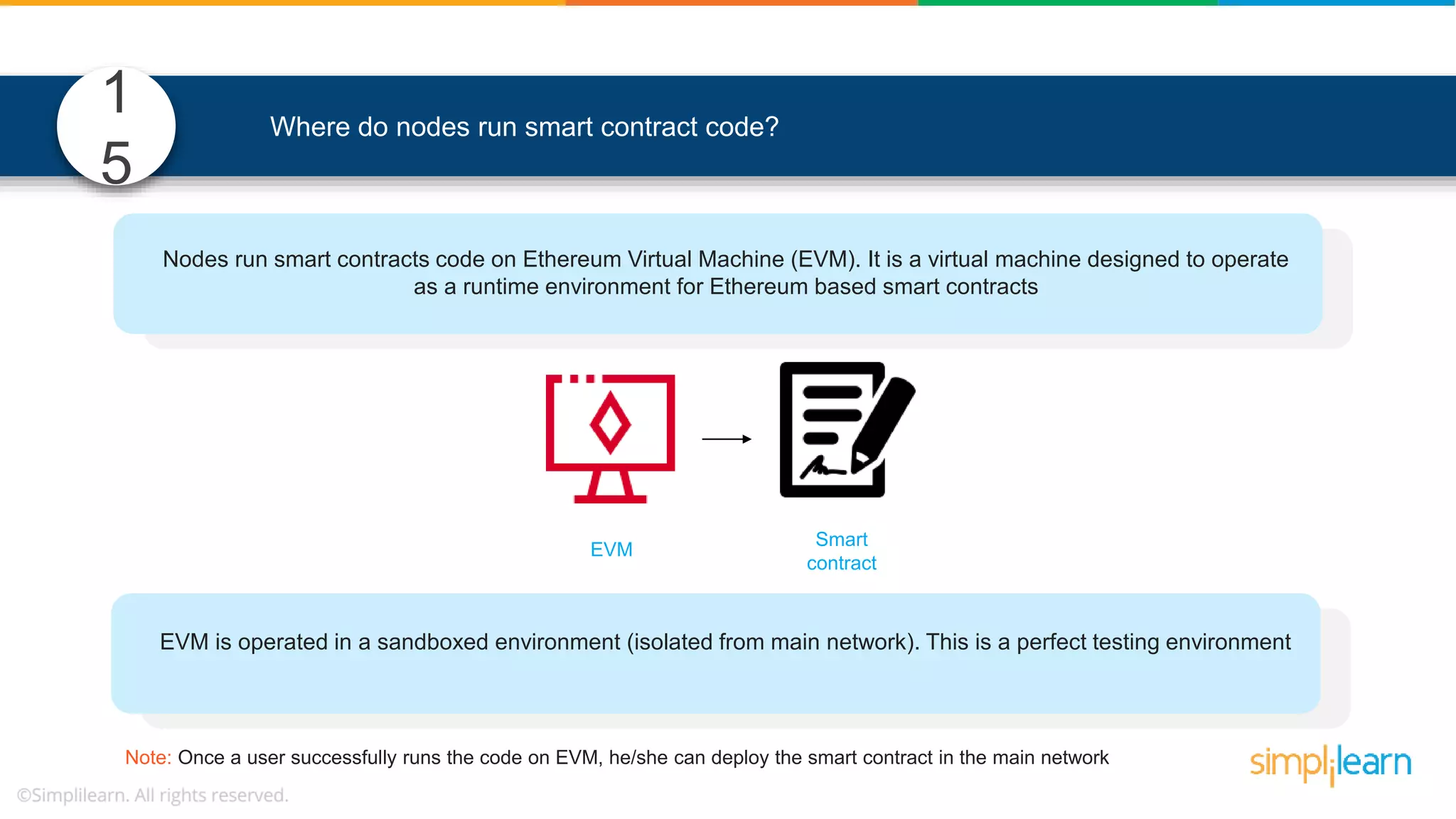
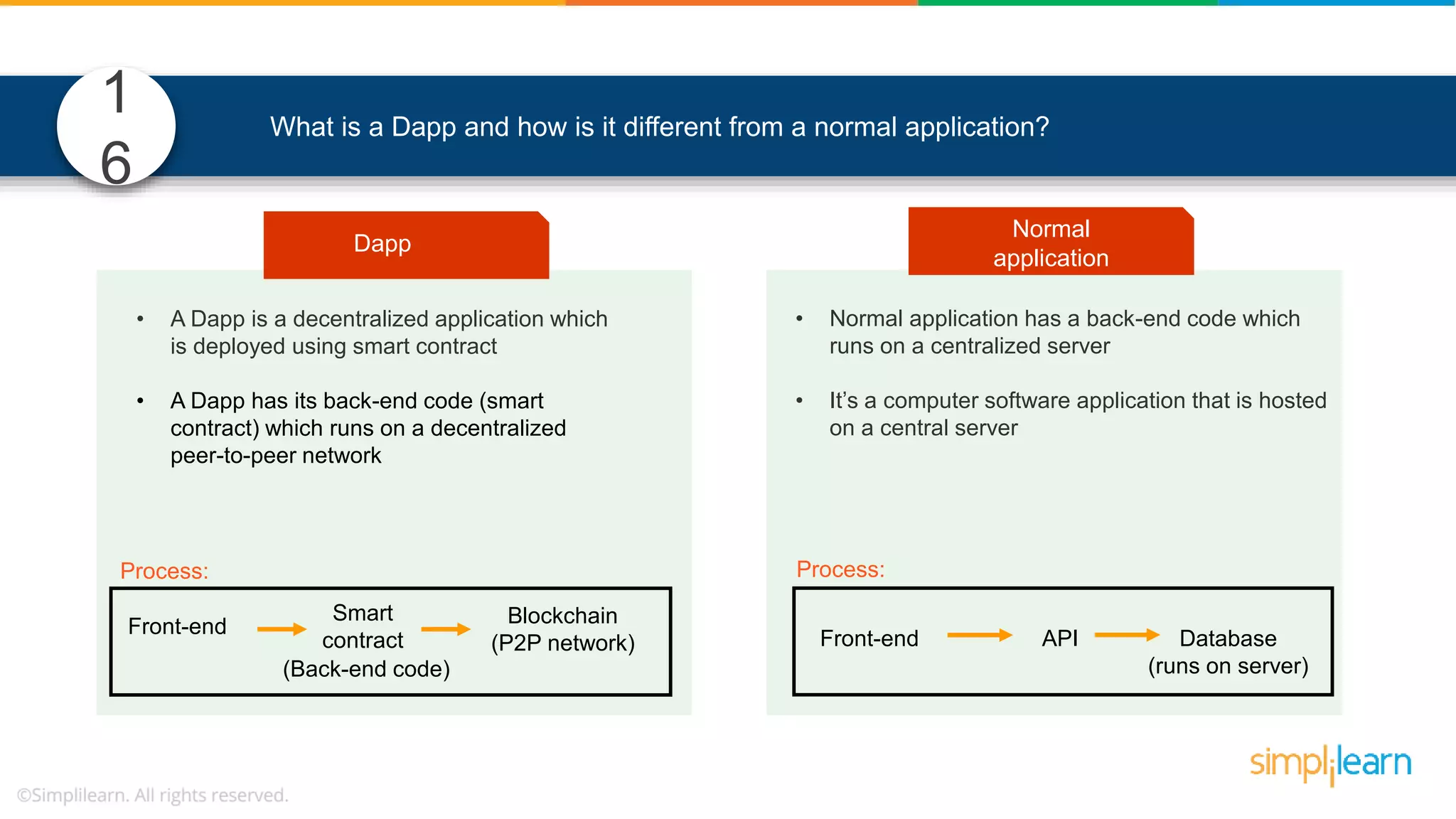
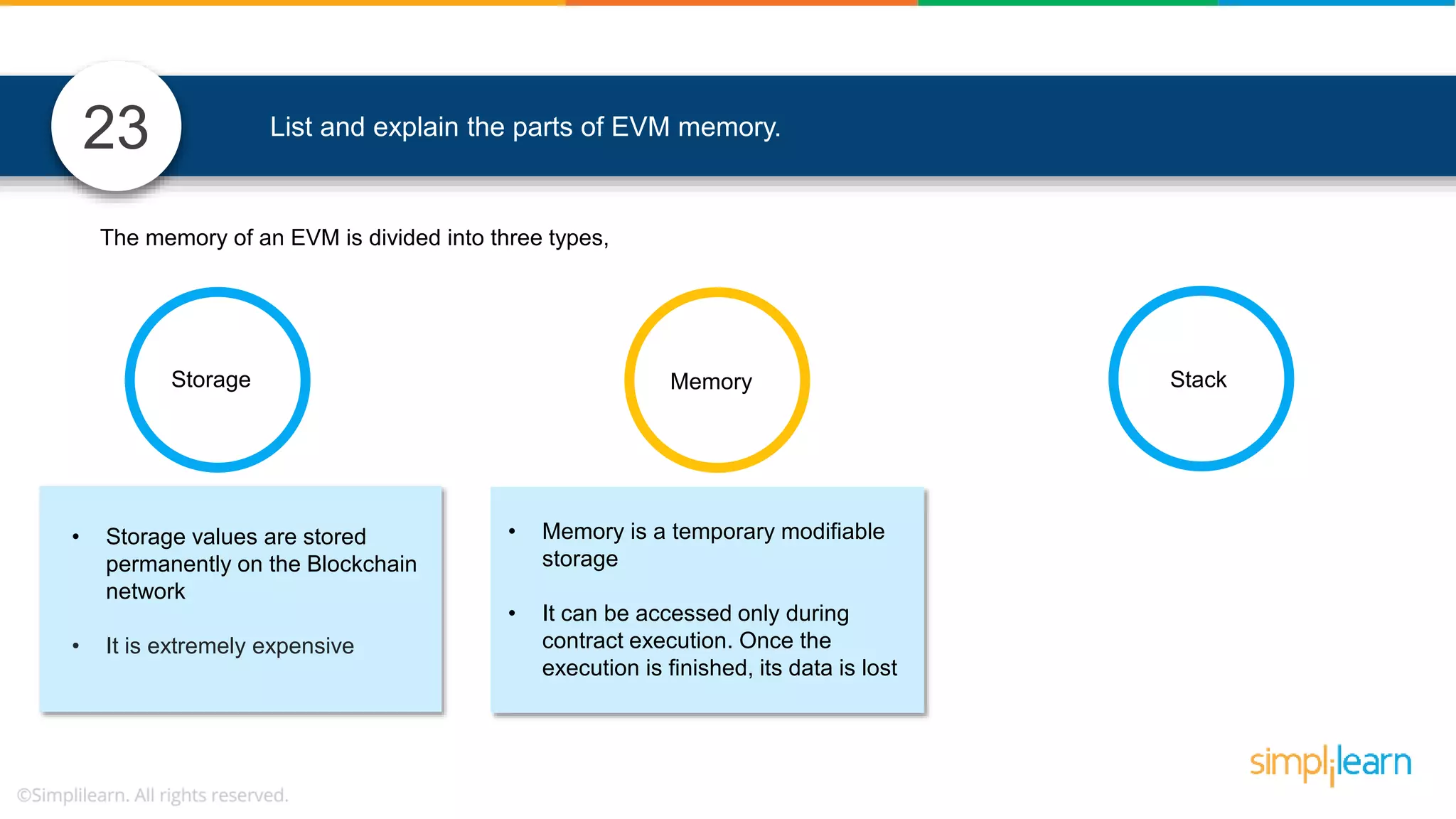
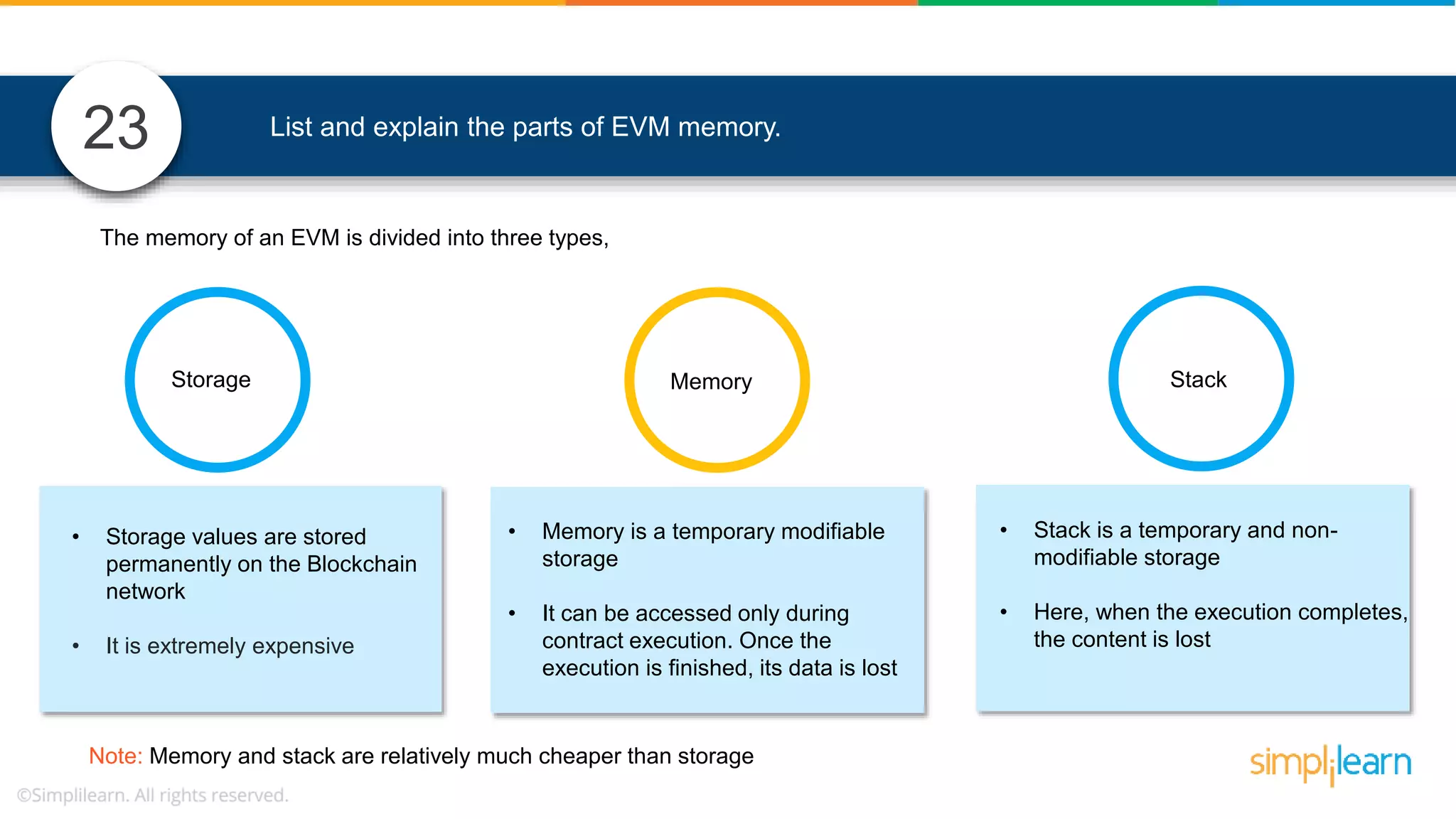
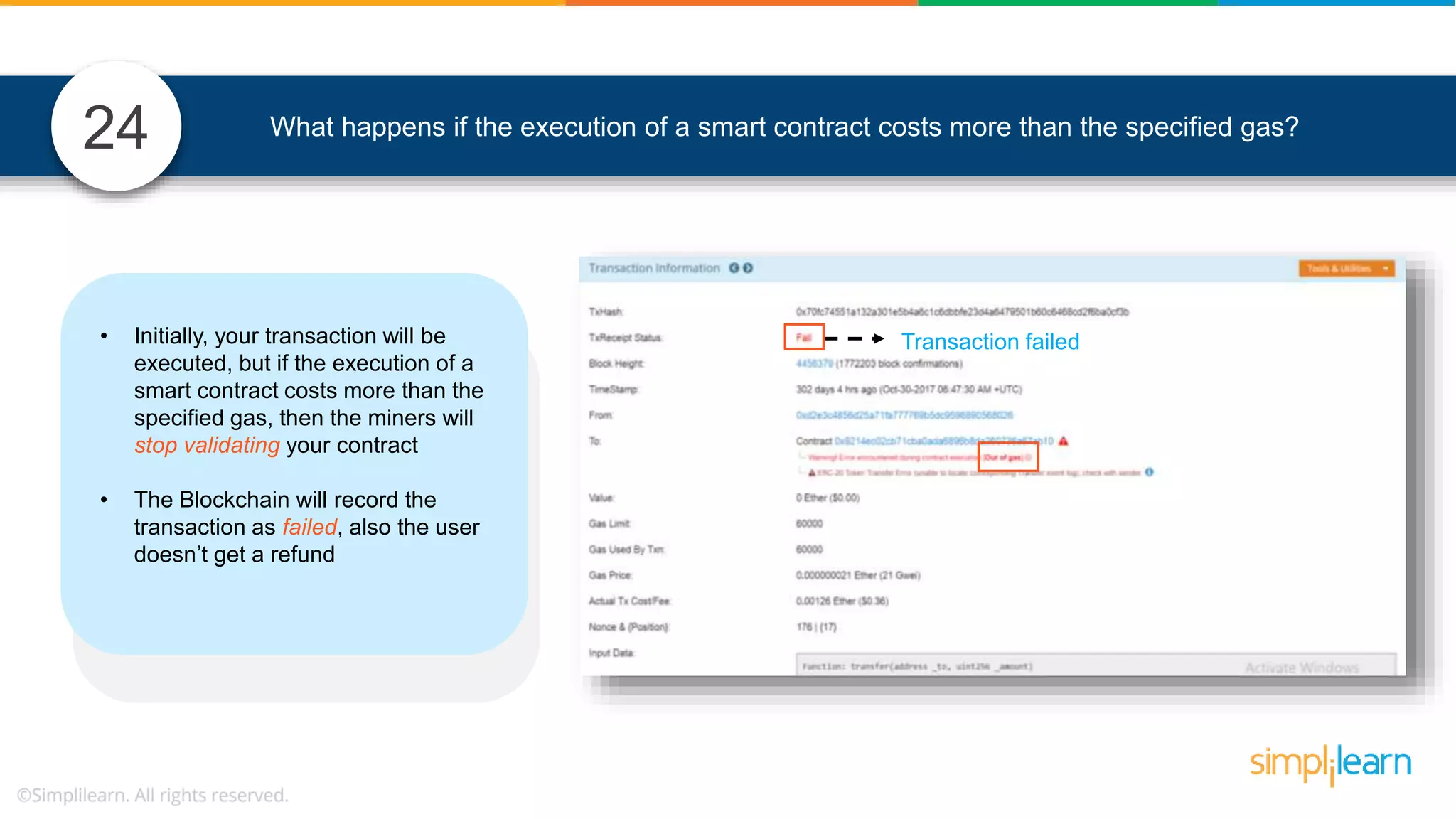
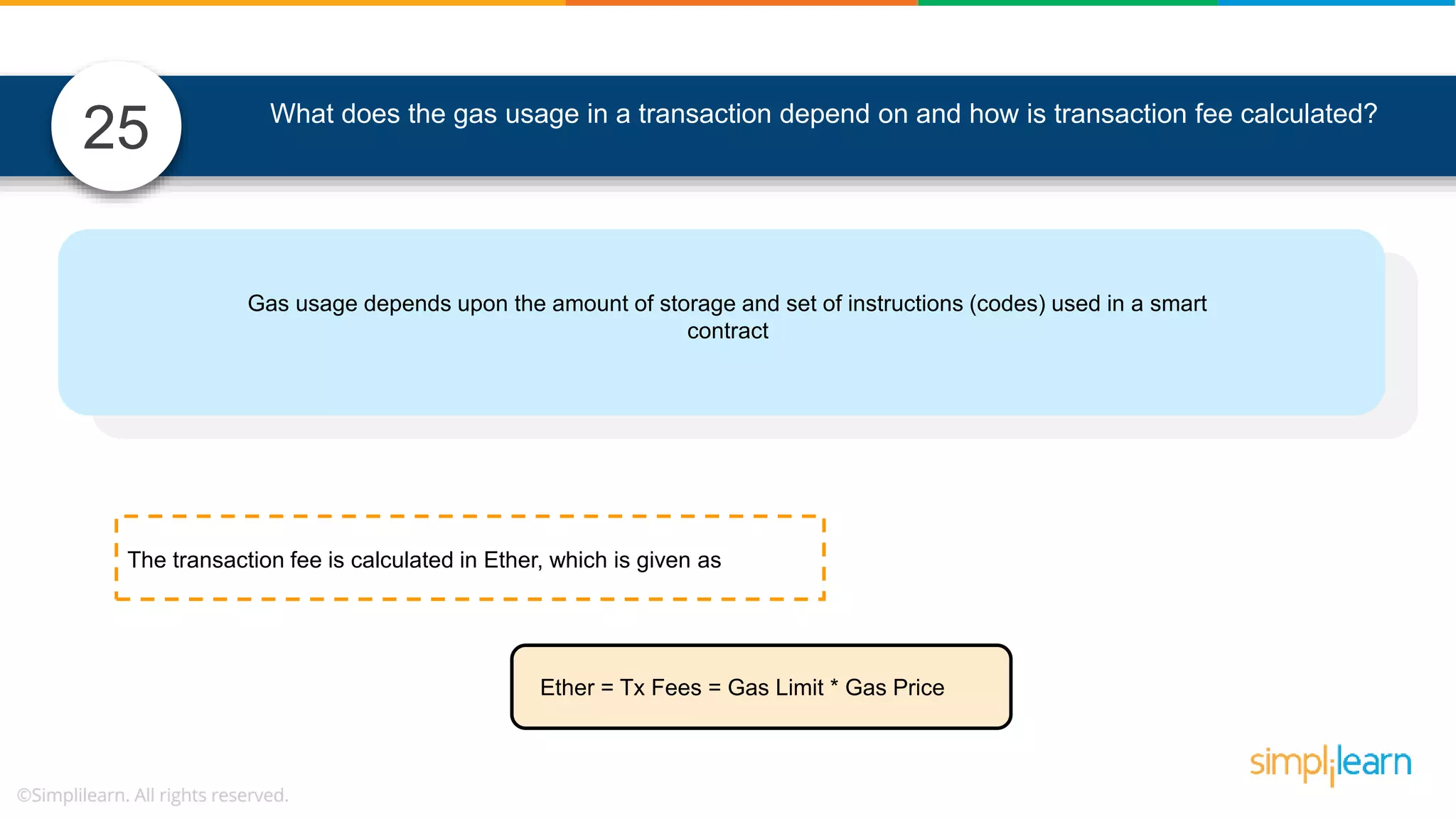
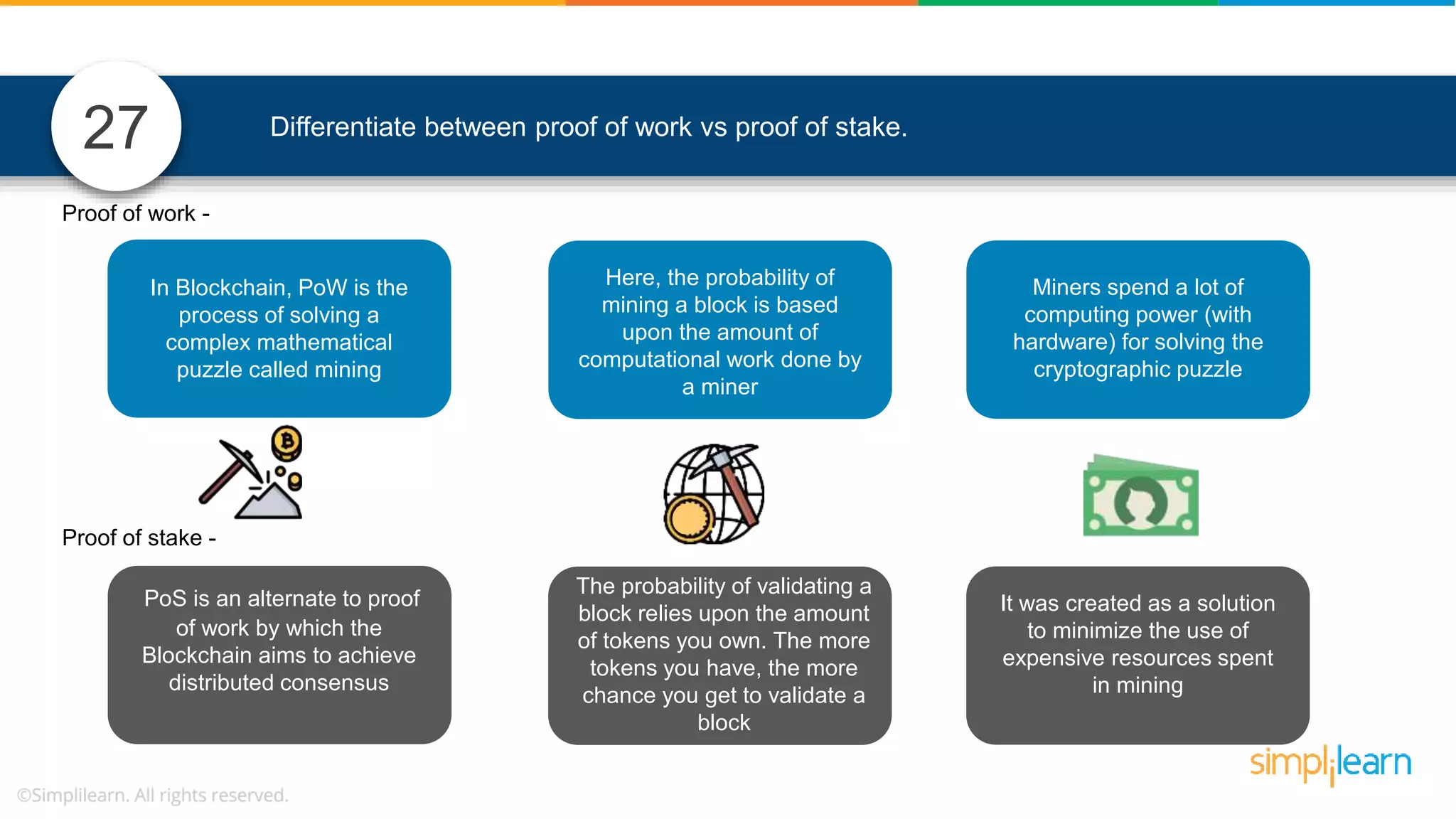
The document provides information to differentiate between Blockchain and Hyperledger: - Blockchain is a decentralized technology that records immutable transaction records in blocks secured by cryptography. It can be public, private, or consortium. Hyperledger is a platform that allows building private blockchains where access is limited.


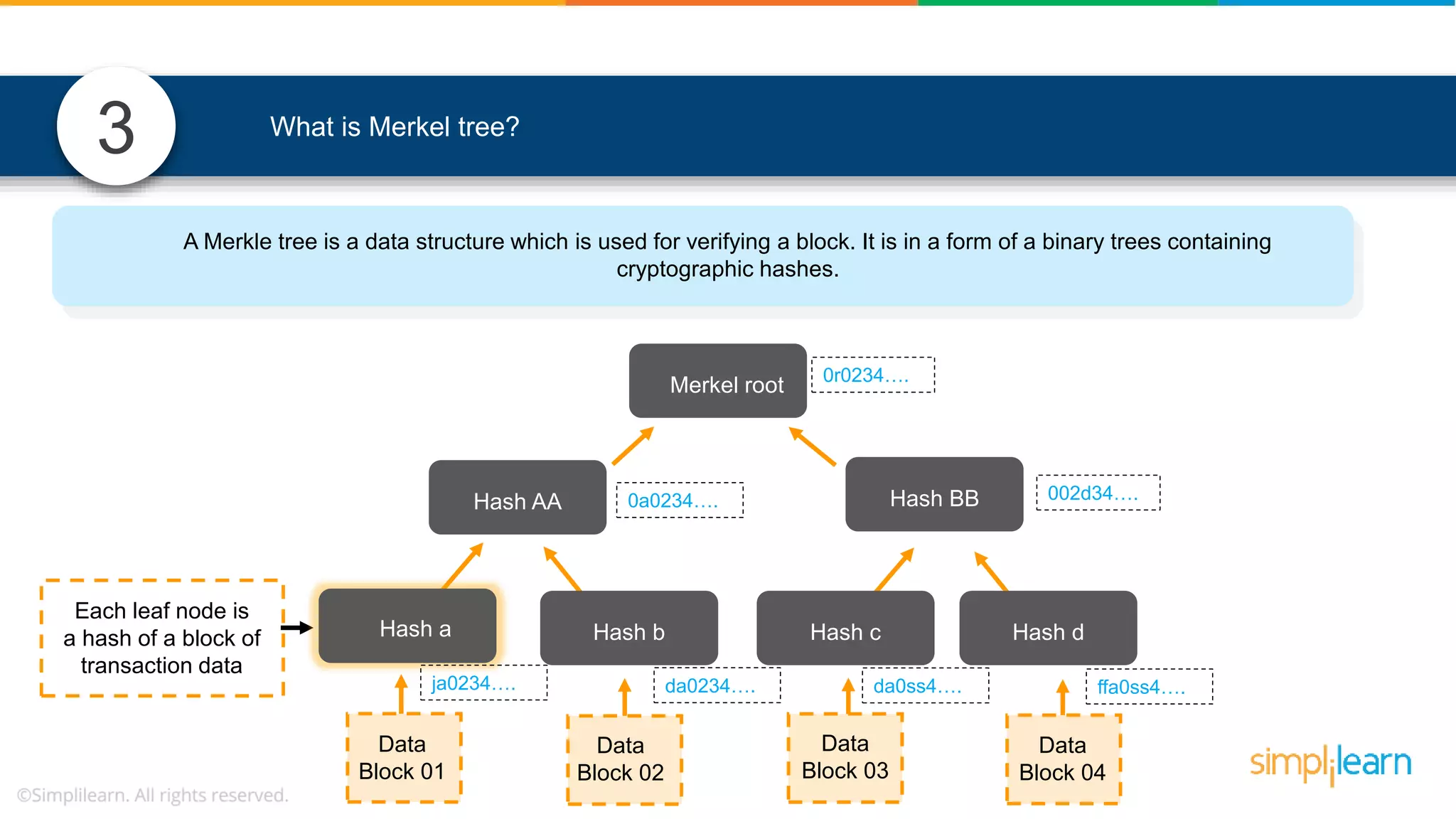
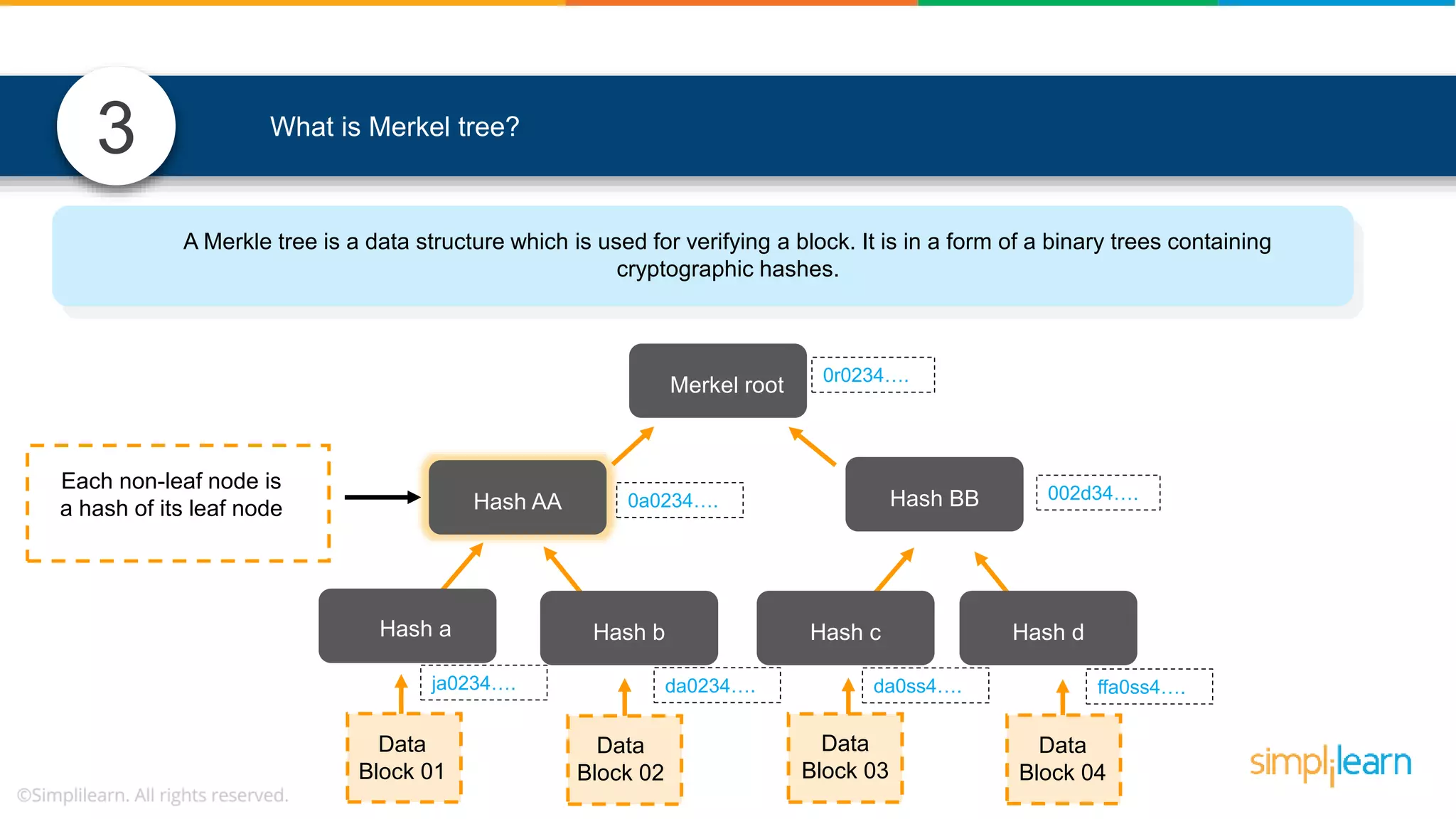
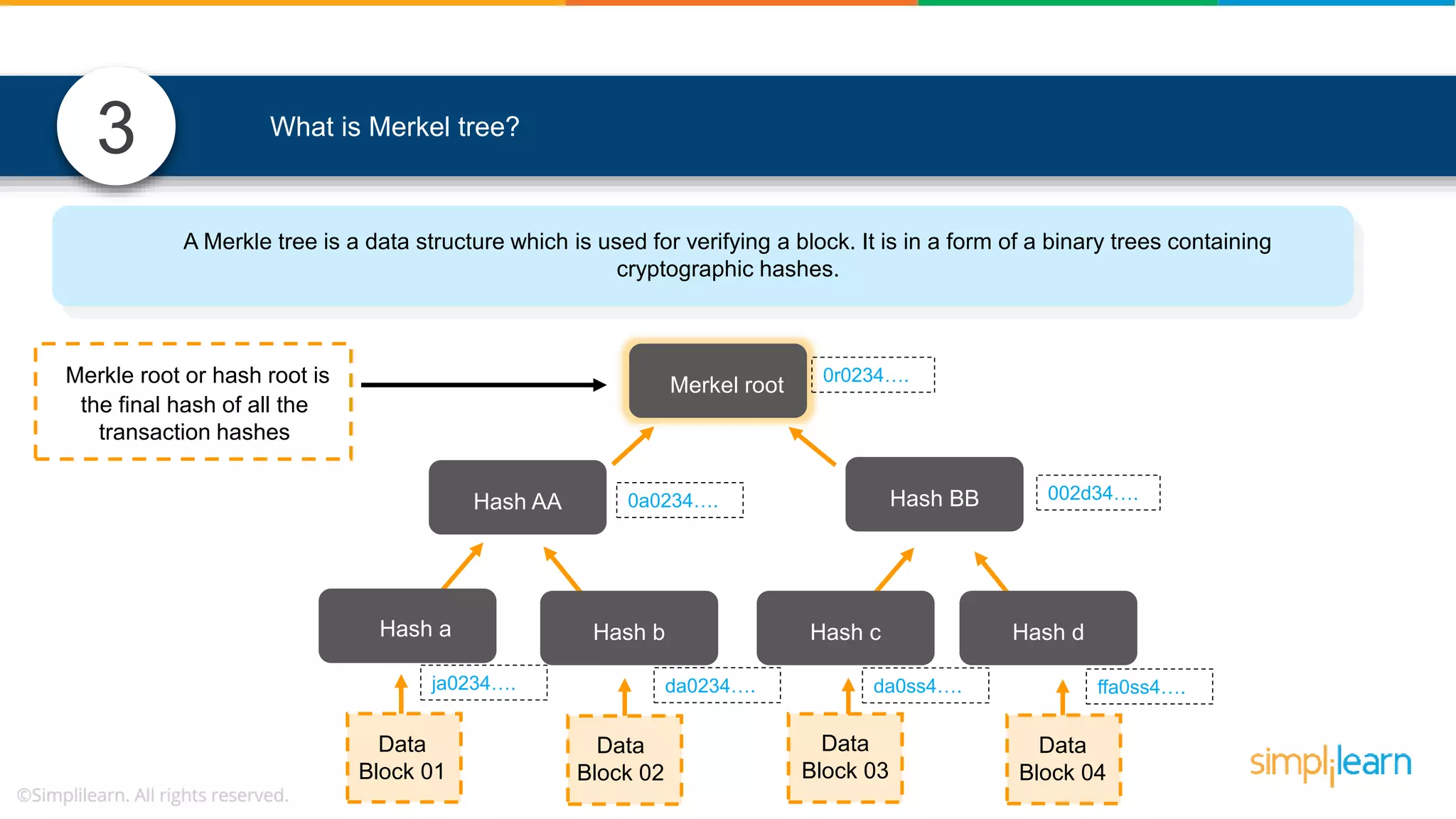
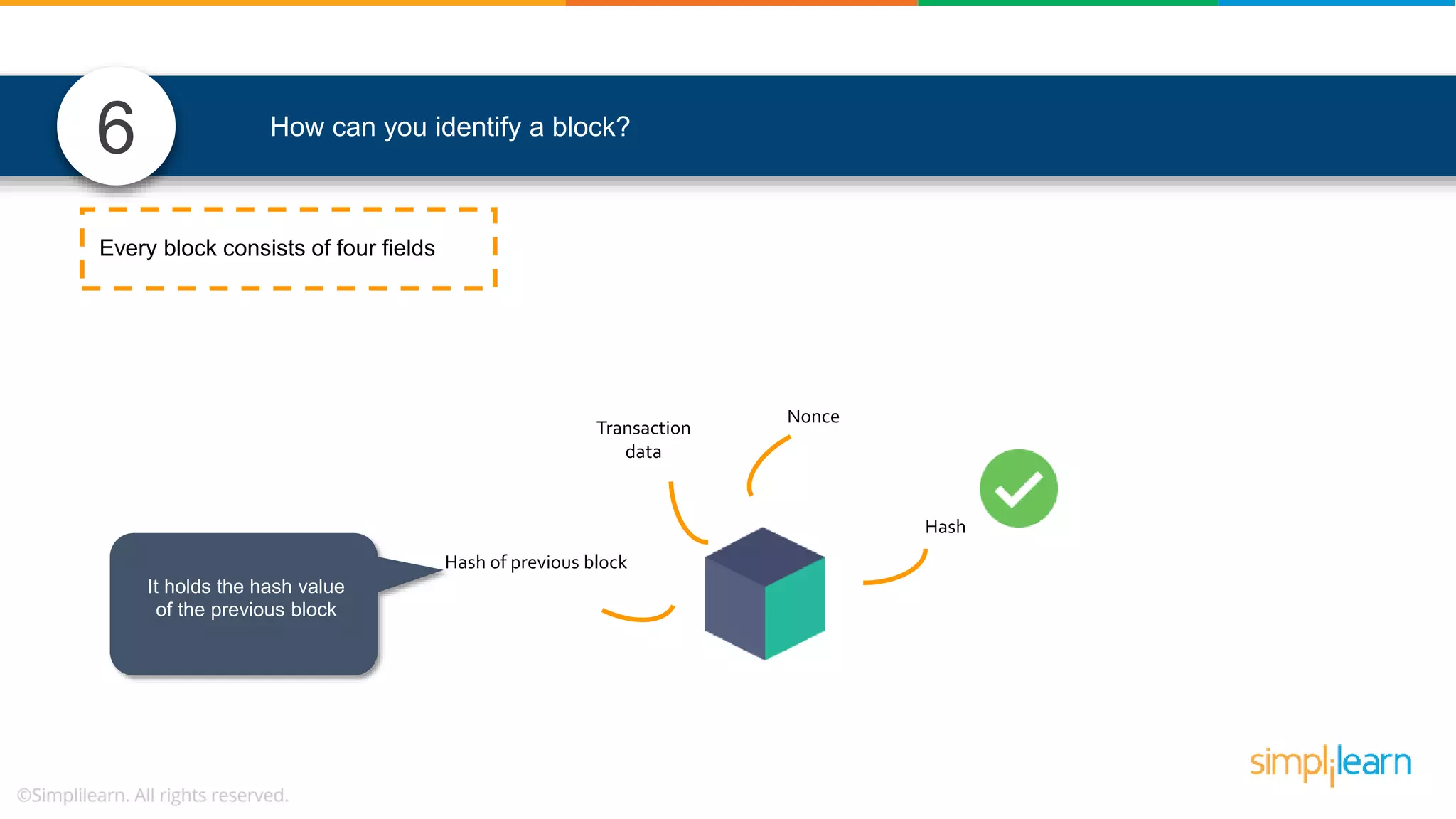
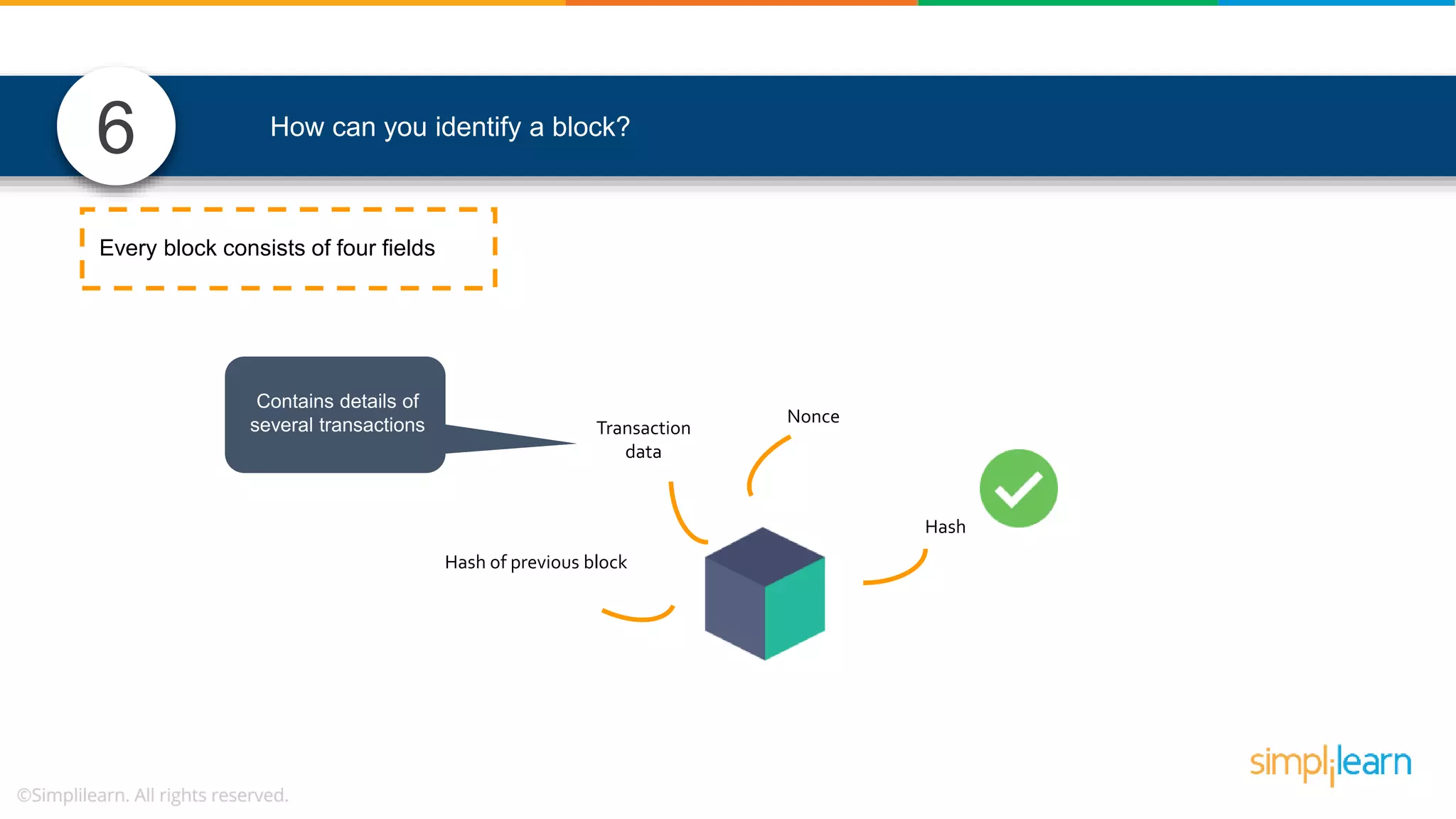
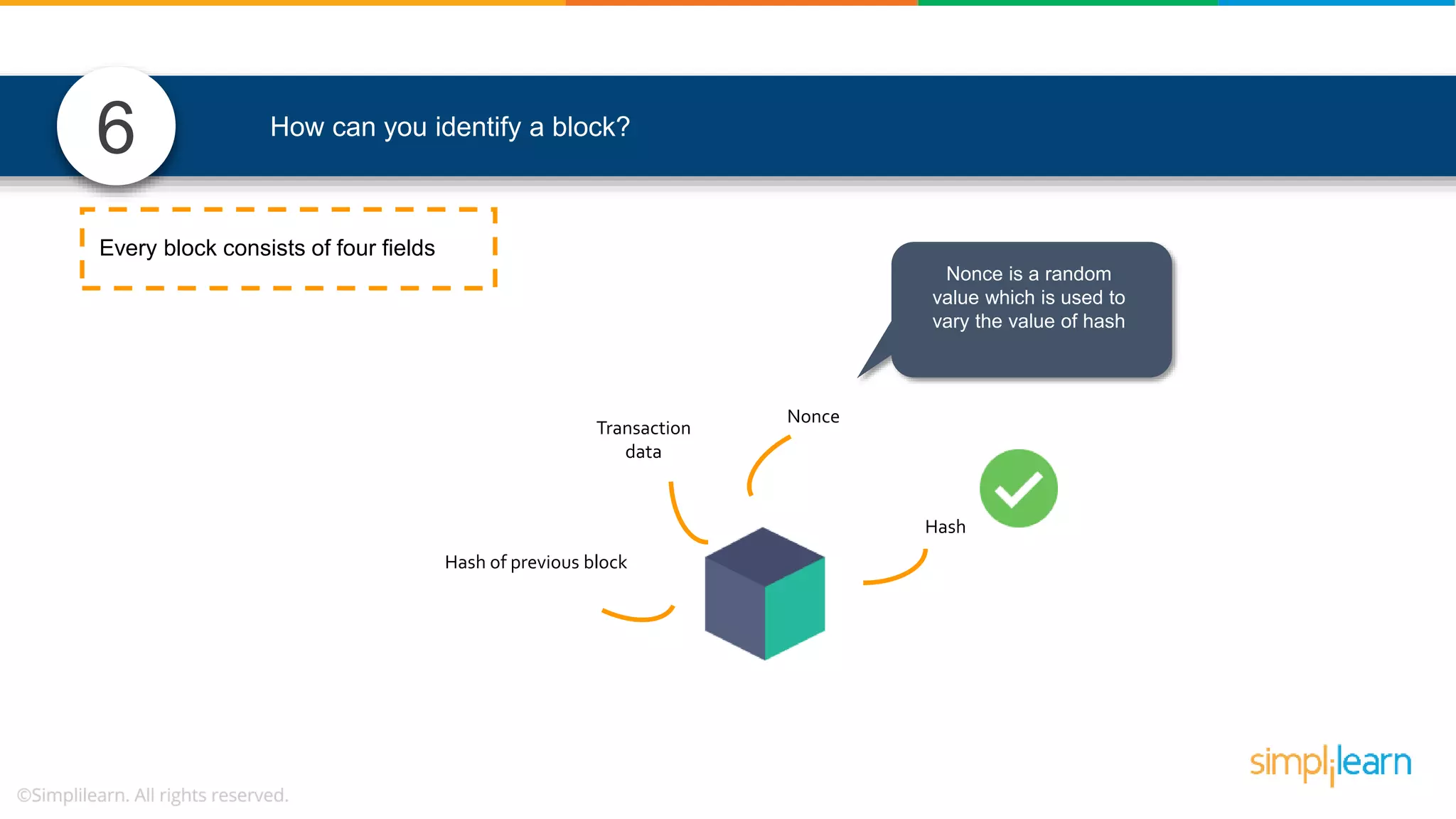
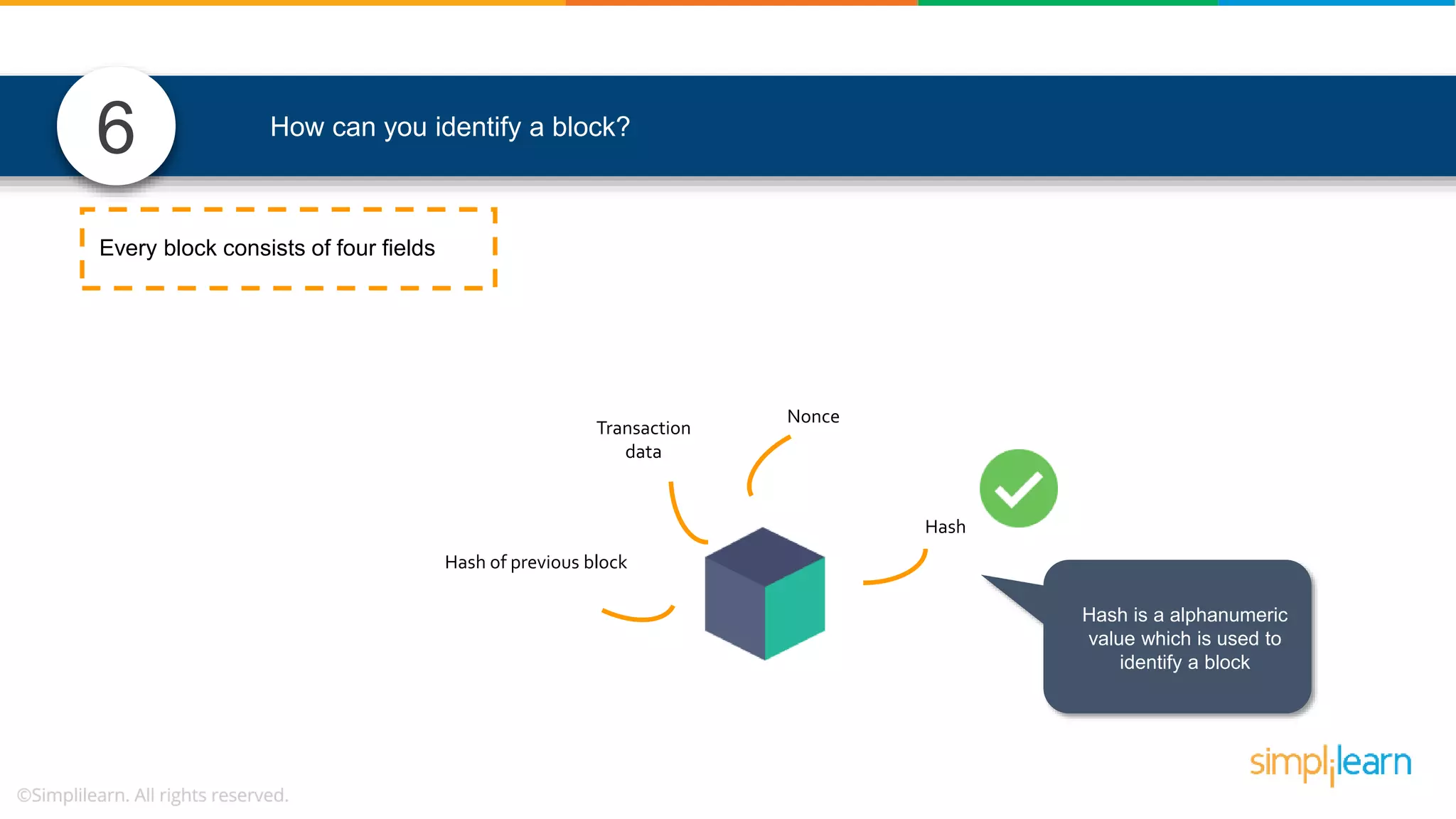


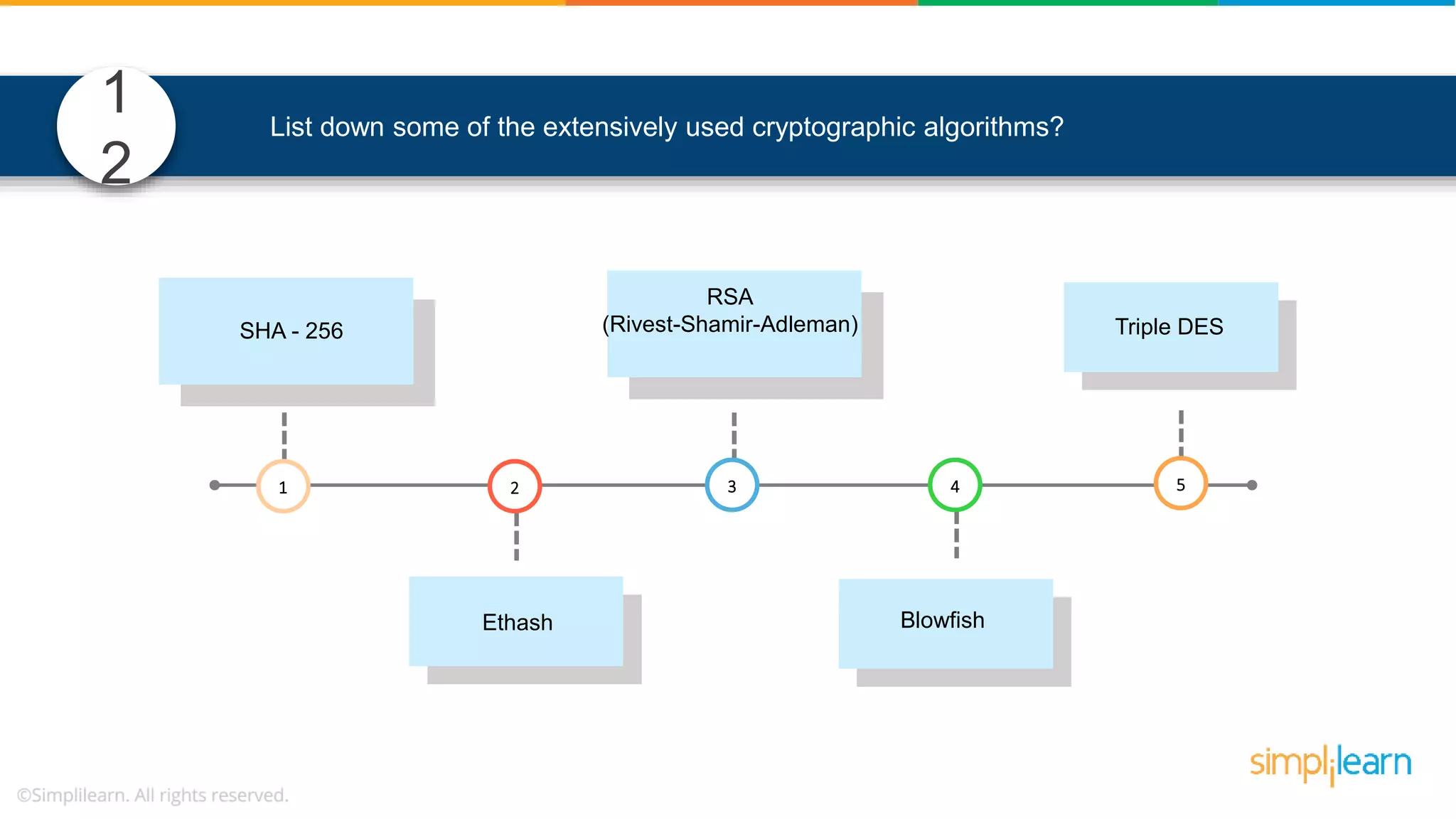
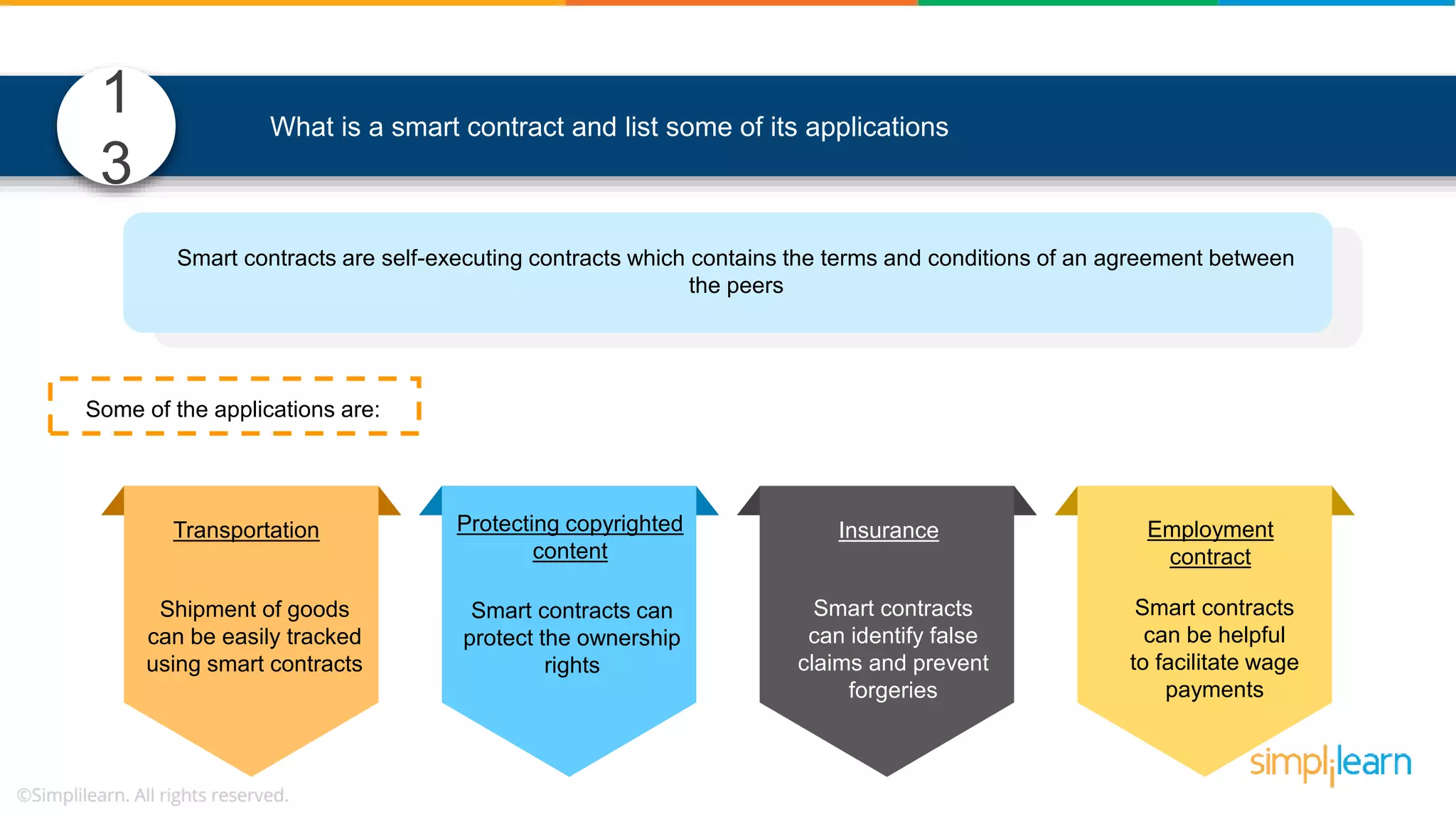
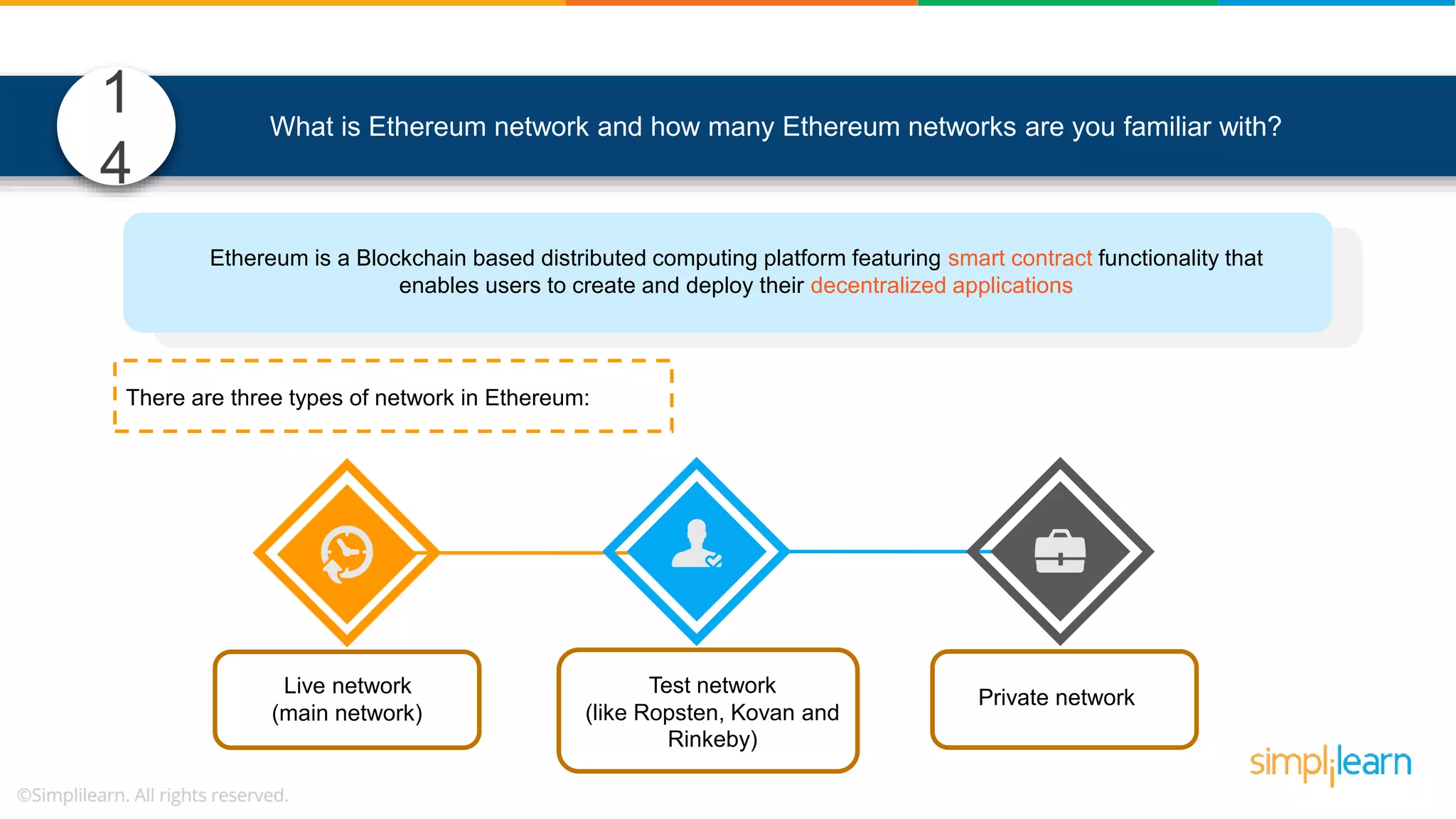
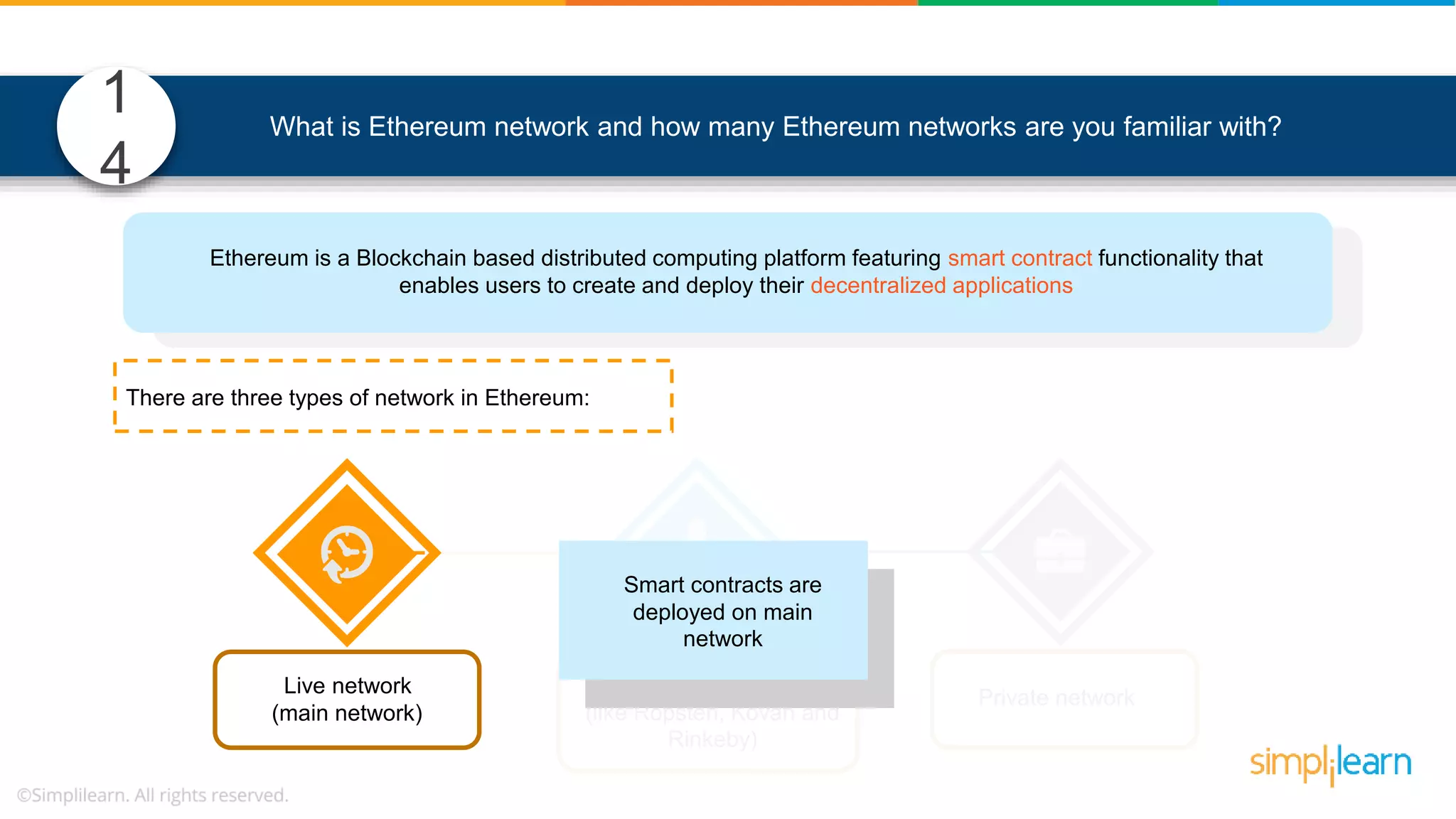


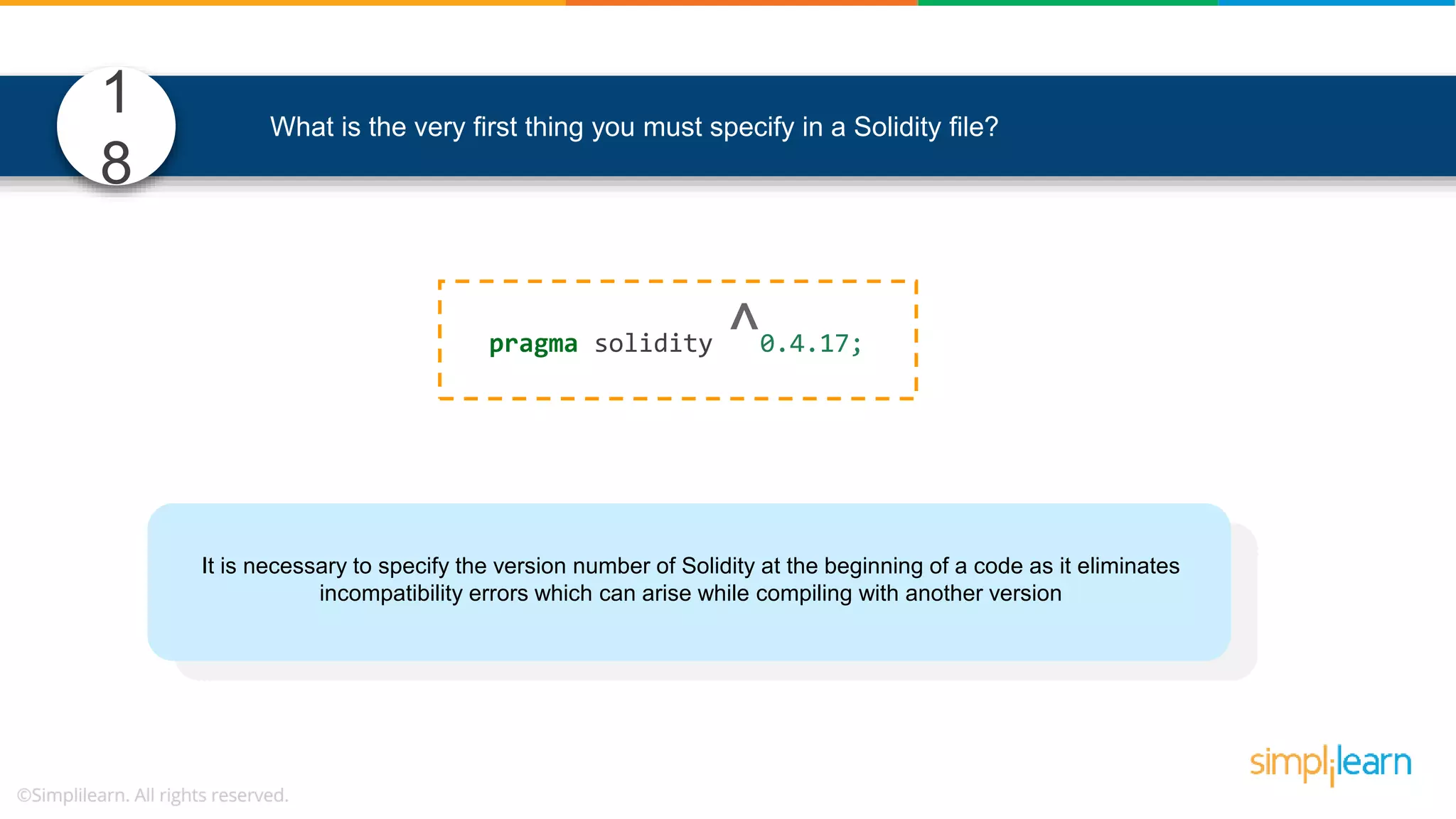


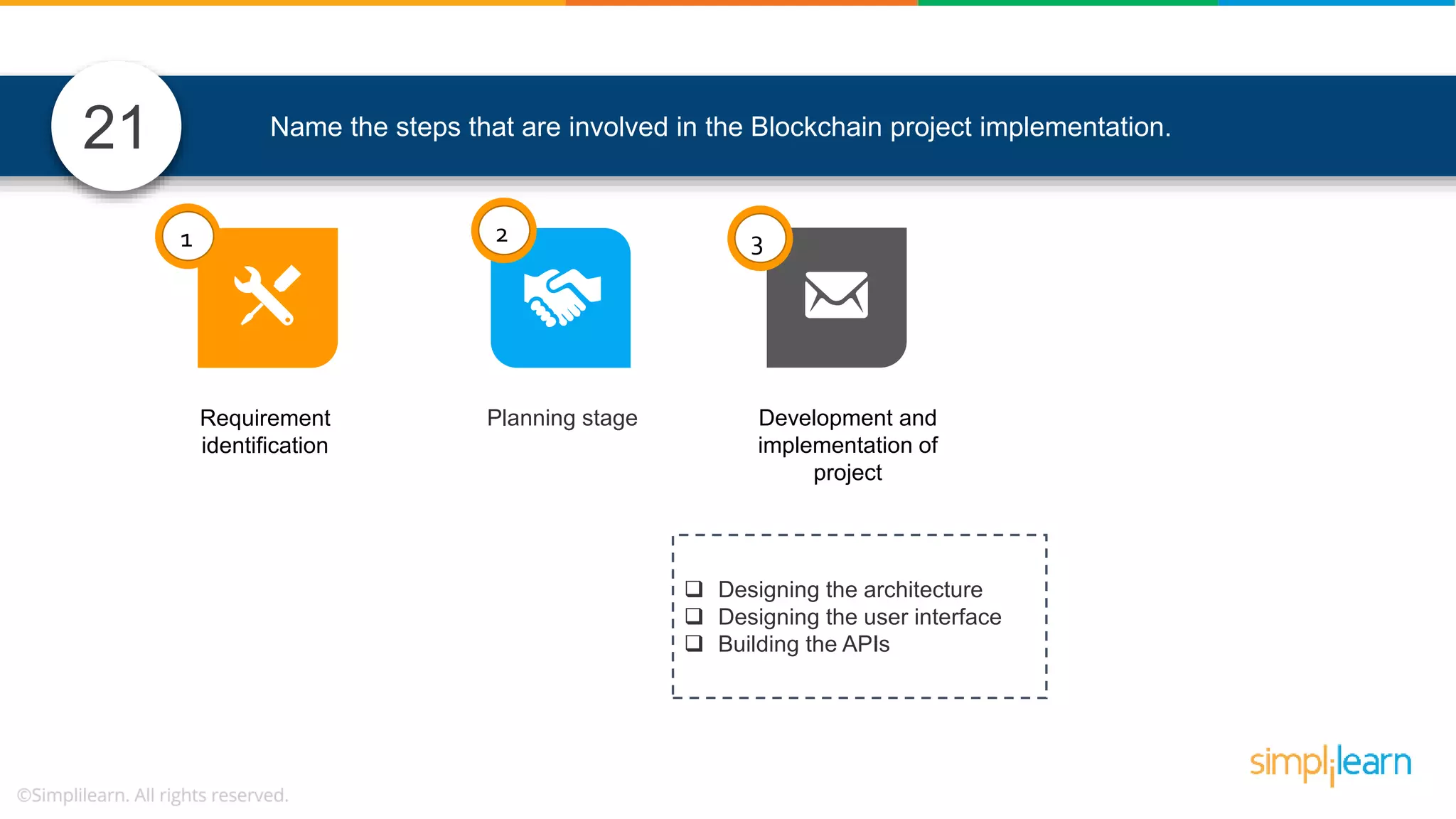
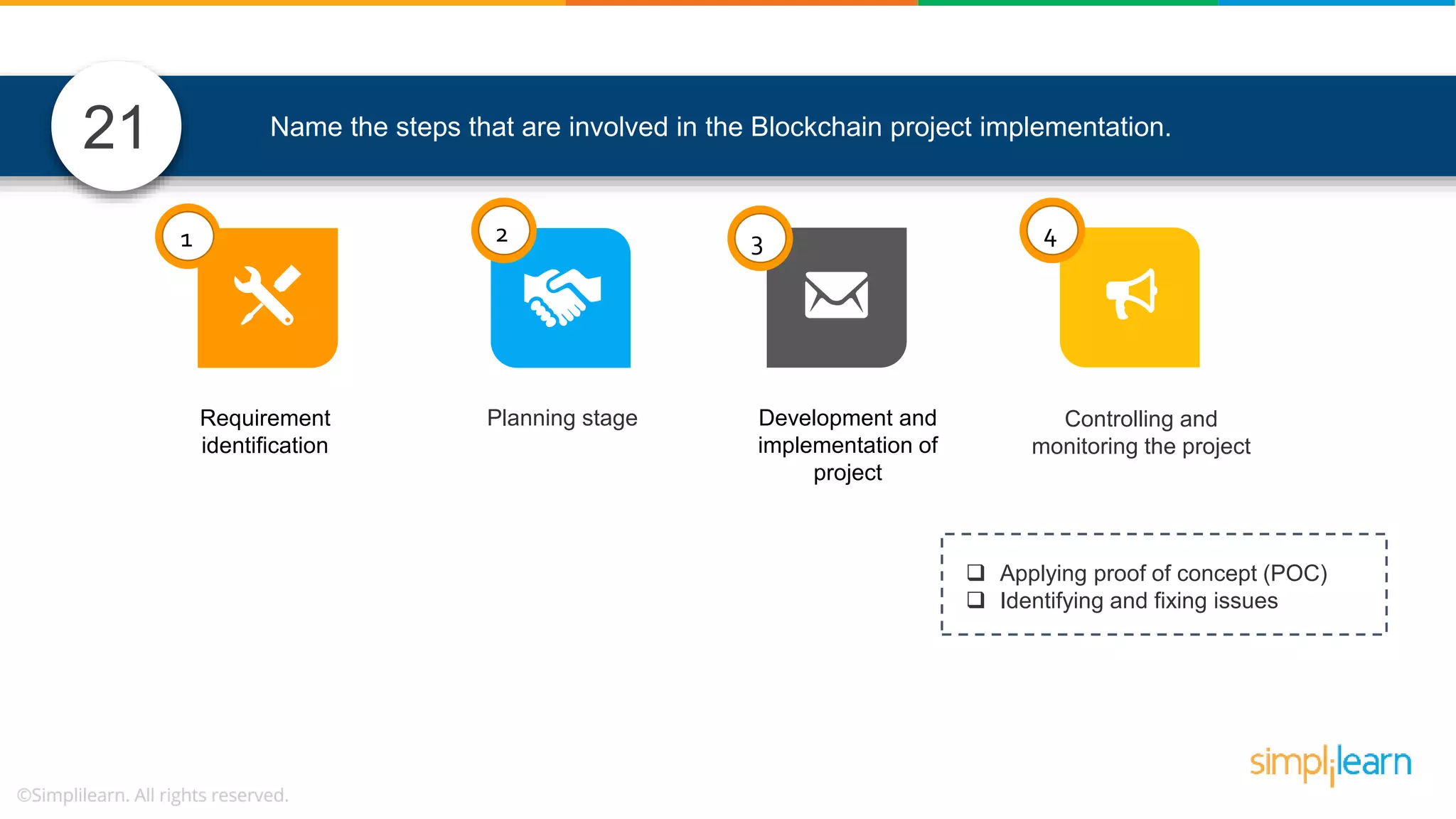
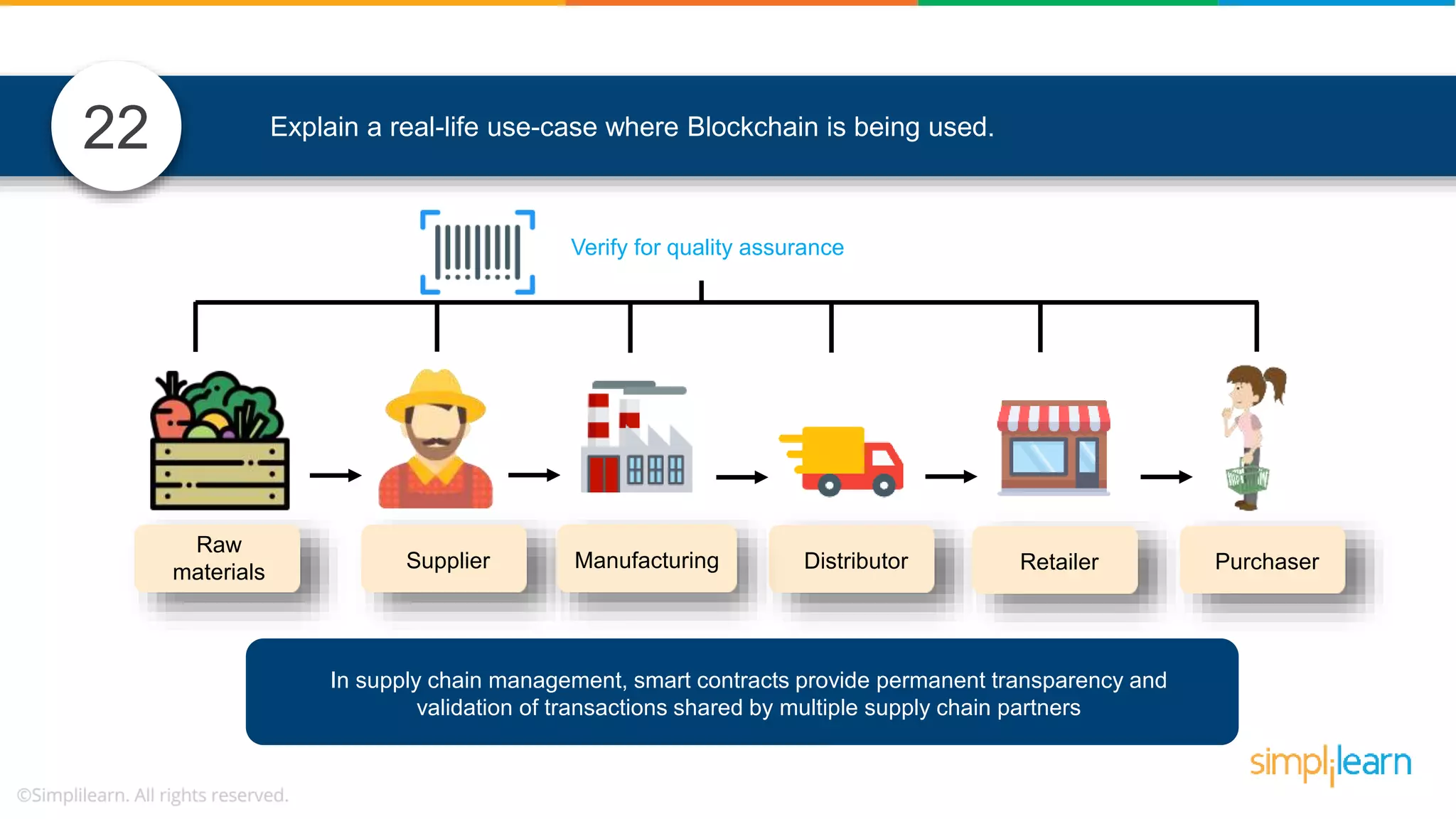

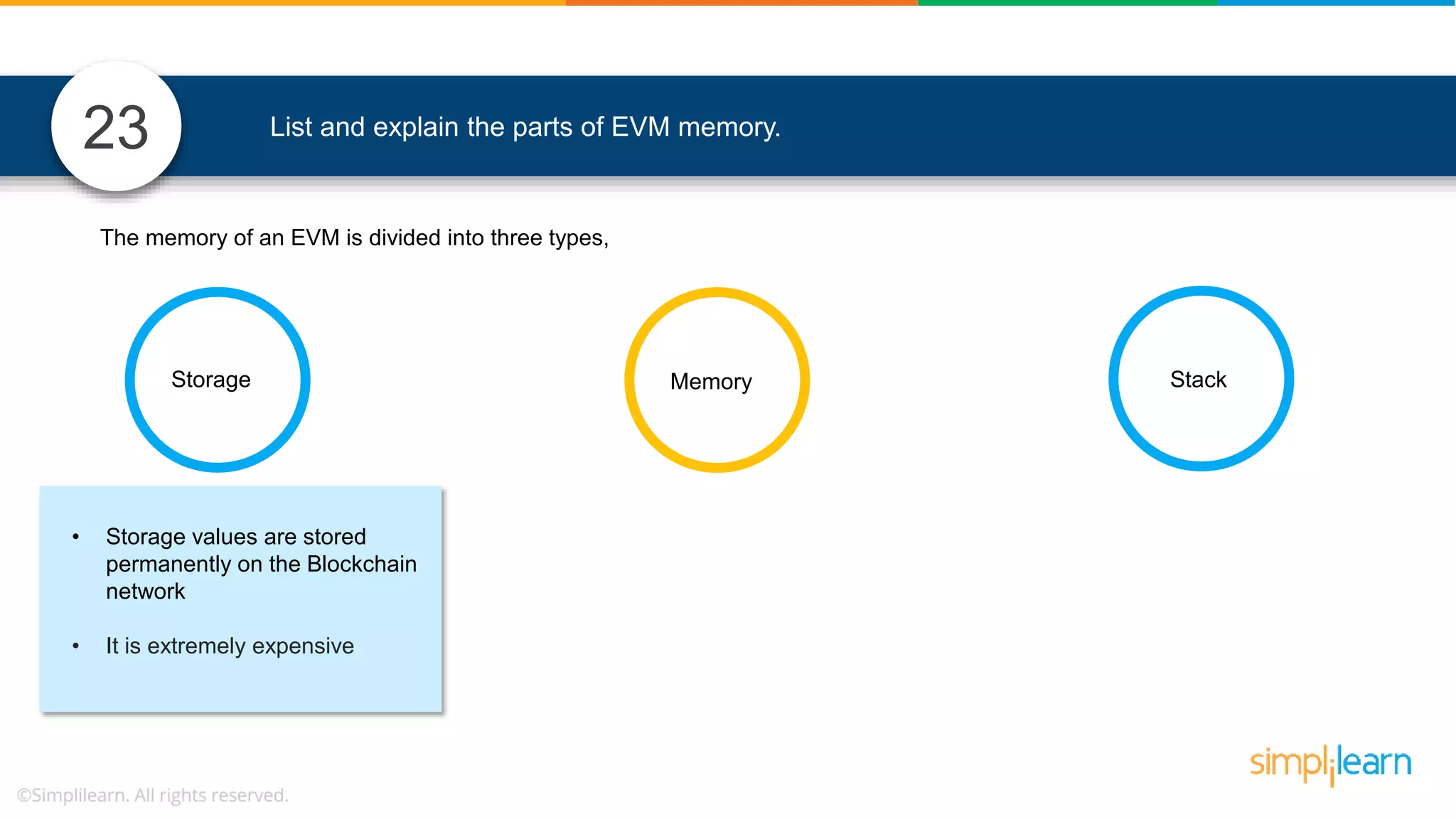
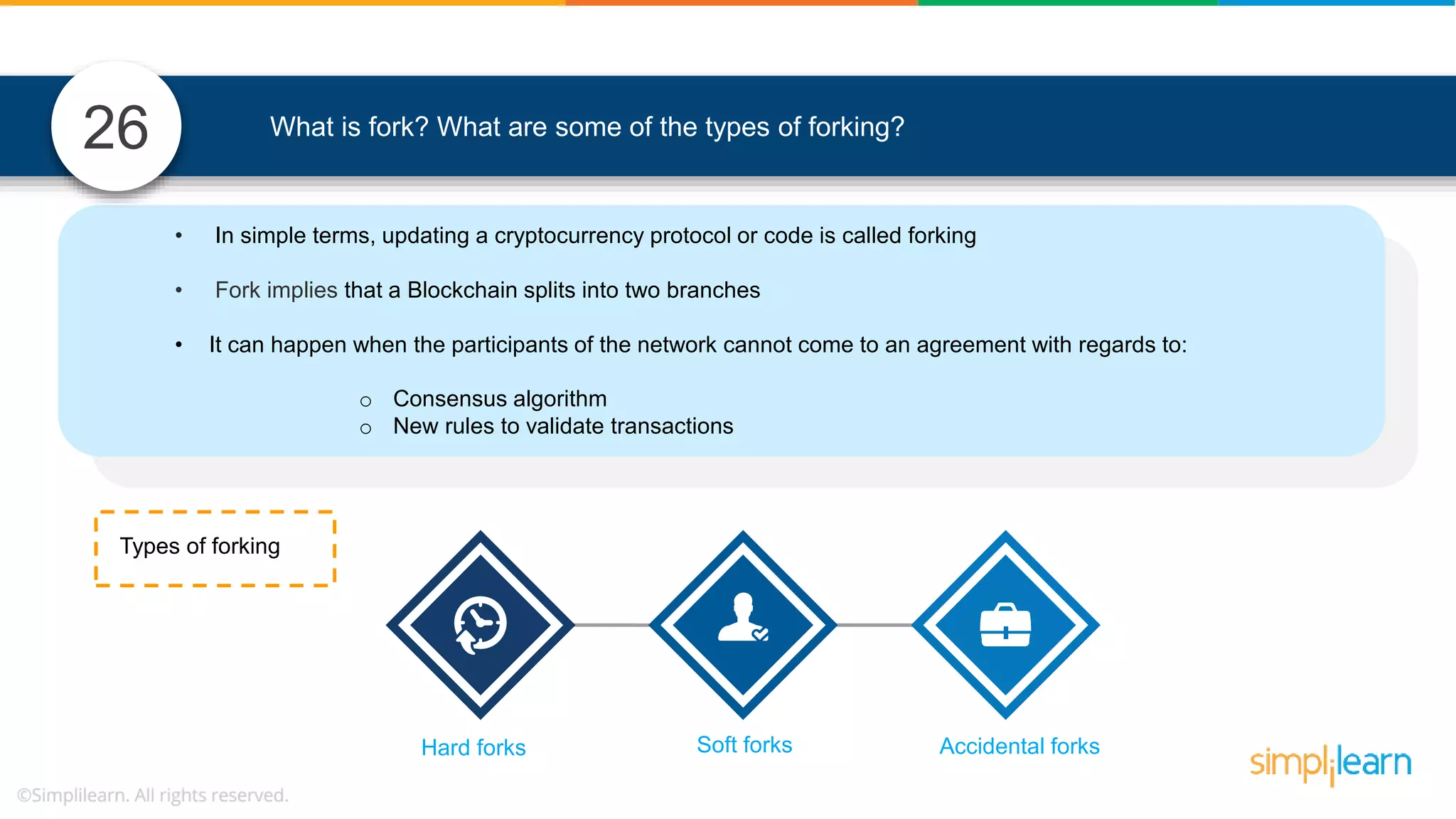

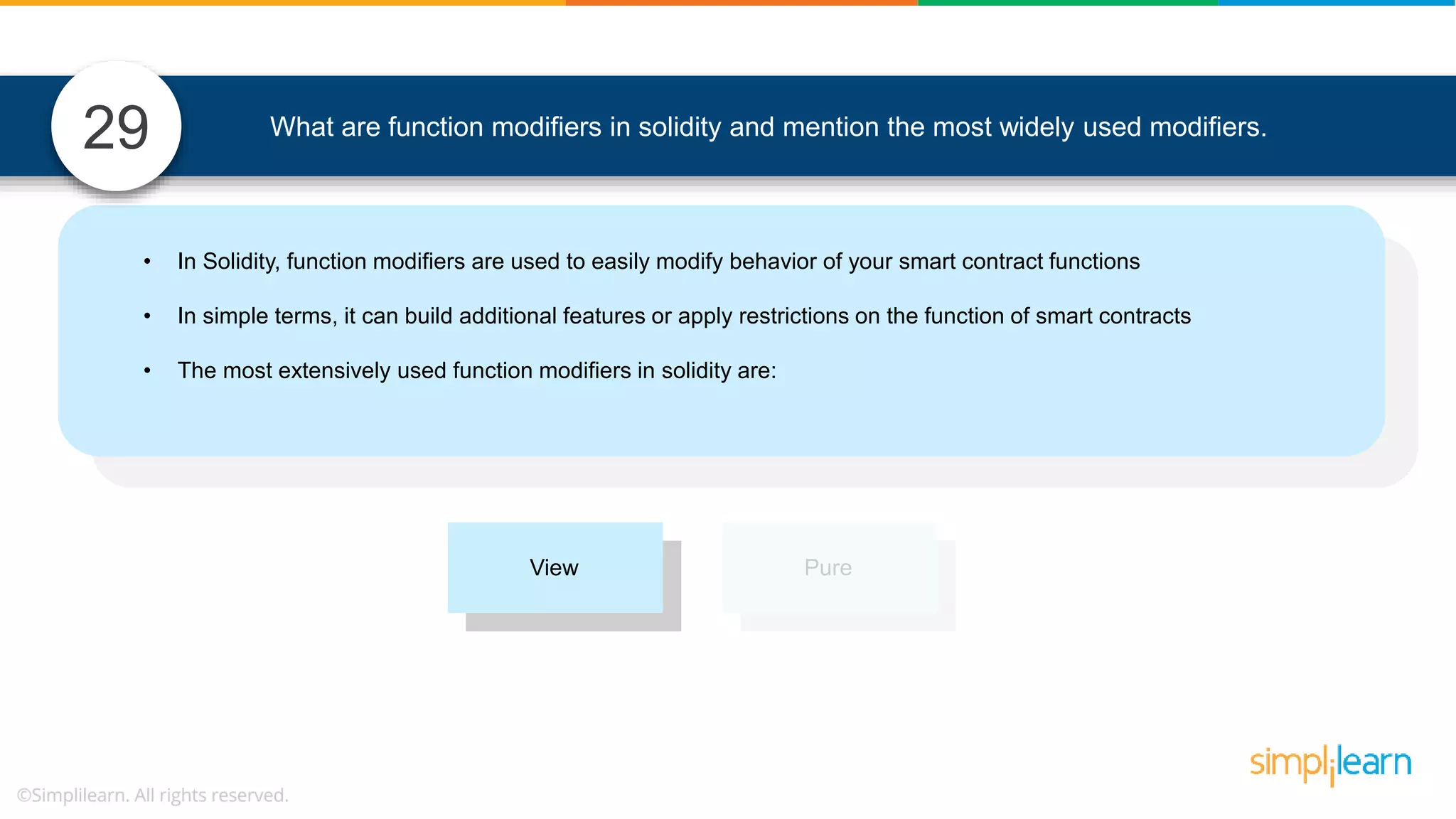
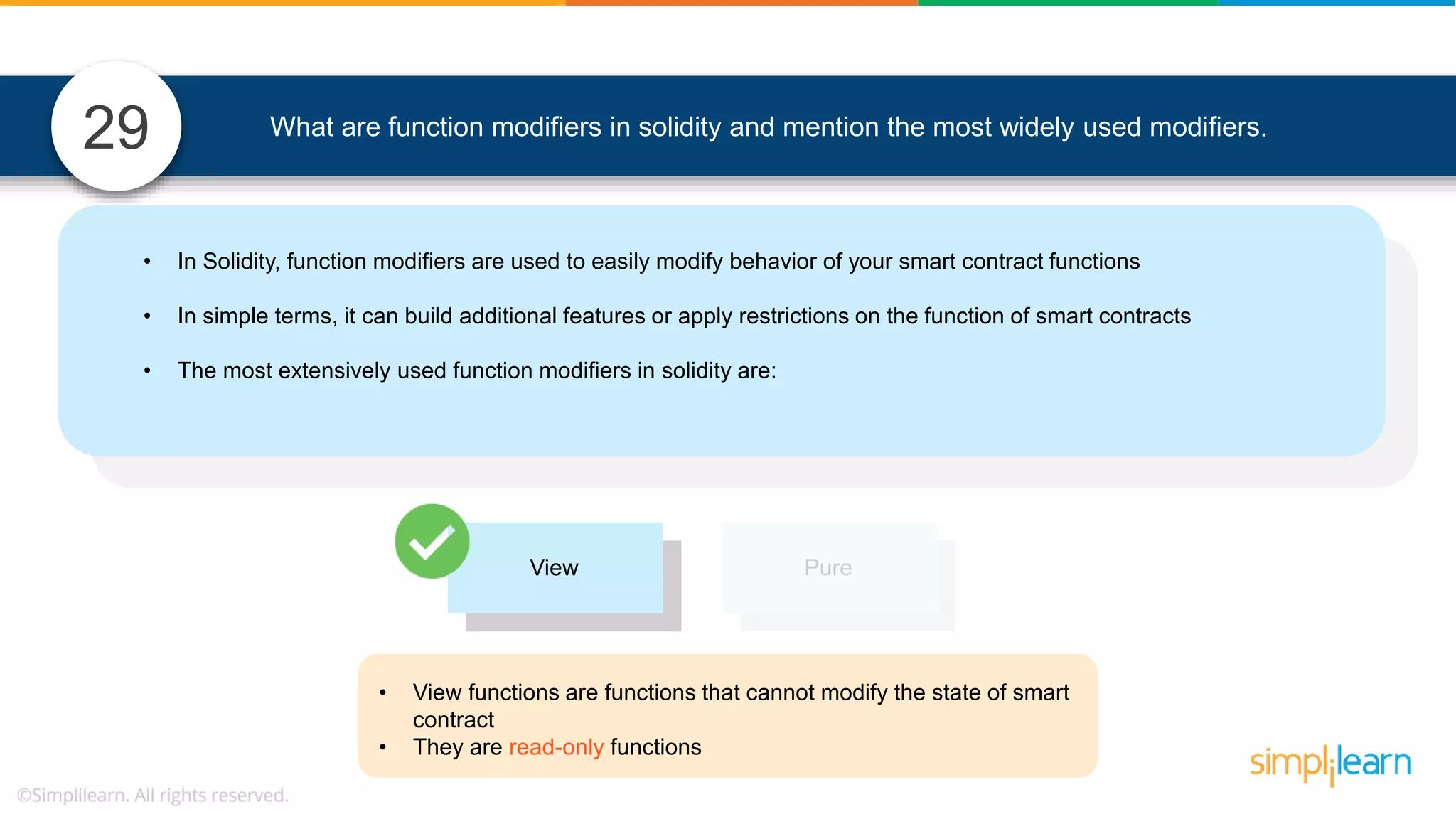
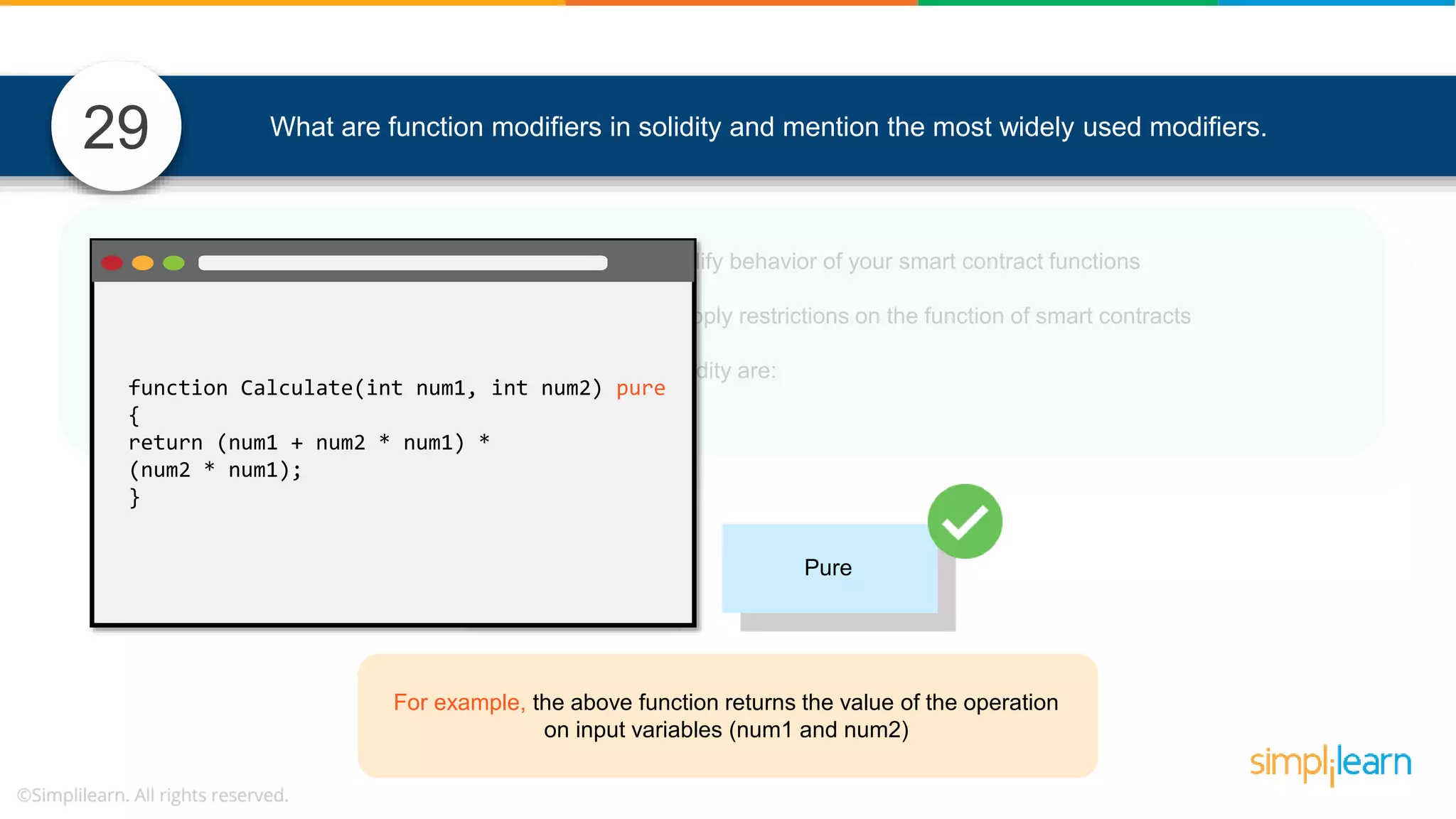
![• In Solidity, function modifiers are used to easily modify behavior of your smart contract functions • In simple terms, it can build additional features or apply restrictions on the function of smart contracts • The most extensively used function modifiers in solidity are: 29 View Pure For example, this function returns address To simplilearn[msg.sender] without any data being modified function getsimplilearnName() view { return addressTosimplilearn[msg.sender]; } What are function modifiers in solidity and mention the most widely used modifiers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchaininterviewquestionsandanswersblockchaintechnologyinterviewquestionssimplilearn-180905041740/75/Blockchain-Interview-Questions-And-Answers-Blockchain-Technology-Interview-Questions-Simplilearn-63-2048.jpg)


![Write a crowd sale smart contract code in solidity programming language30 function () payable public { require(!crowdsaleClosed); uint amount = msg.value; balanceOf[msg.sender] += amount; amountRaised += amount; tokenReward.transfer(msg.sender, amount / price); emit FundTransfer(msg.sender, amount, true); } Default function to send Values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchaininterviewquestionsandanswersblockchaintechnologyinterviewquestionssimplilearn-180905041740/75/Blockchain-Interview-Questions-And-Answers-Blockchain-Technology-Interview-Questions-Simplilearn-67-2048.jpg)
![Write a crowd sale smart contract code in solidity programming language30 function safeWithdrawal() public afterDeadline { if (!fundingGoalReached) { uint amount = balanceOf[msg.sender]; balanceOf[msg.sender] = 0; if (amount > 0) { if (msg.sender.send(amount)) { emit FundTransfer(msg.sender, amount, false); } else { balanceOf[msg.sender] = amount; }}} Default function of funds withdrawal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchaininterviewquestionsandanswersblockchaintechnologyinterviewquestionssimplilearn-180905041740/75/Blockchain-Interview-Questions-And-Answers-Blockchain-Technology-Interview-Questions-Simplilearn-68-2048.jpg)
