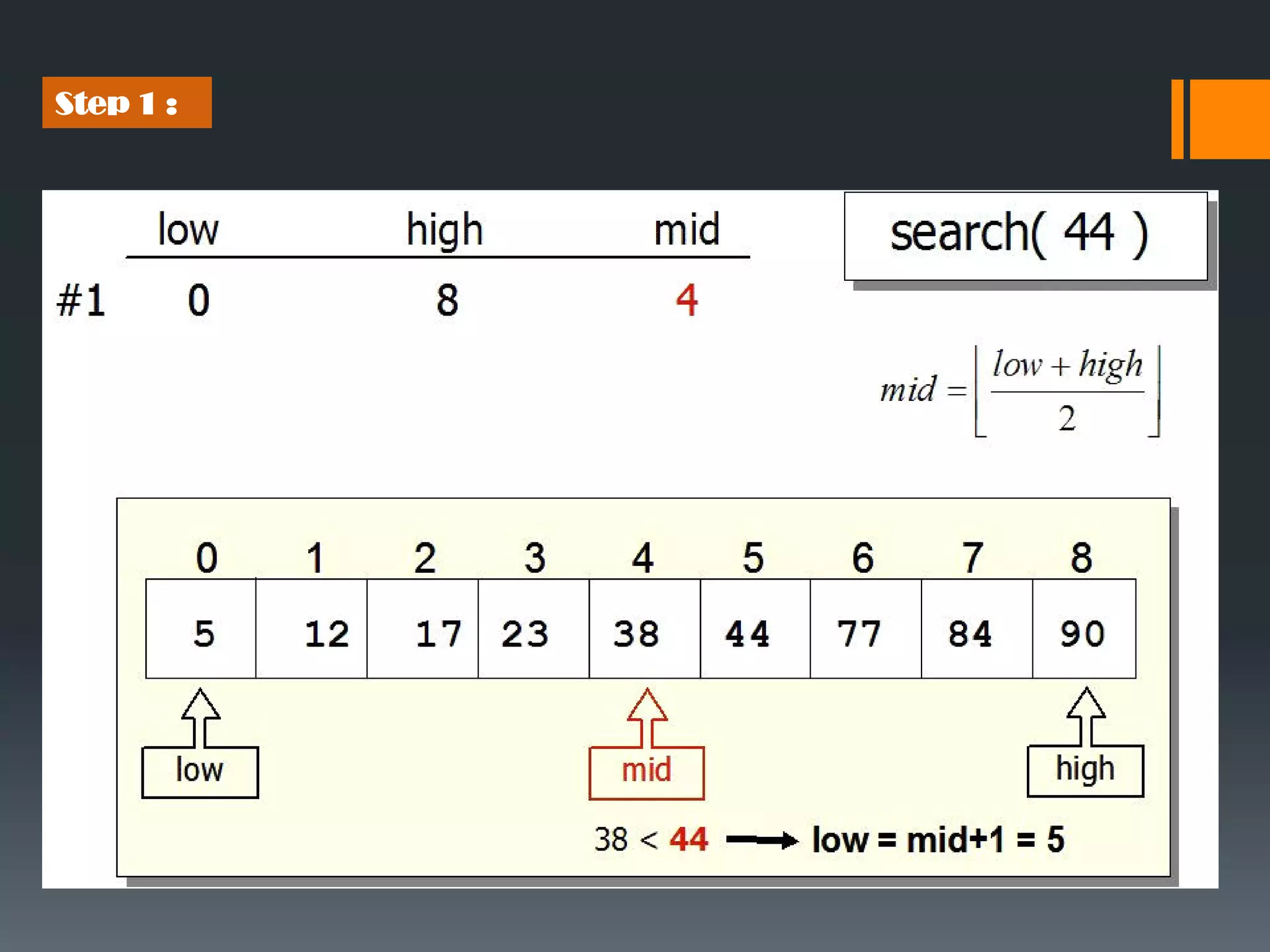
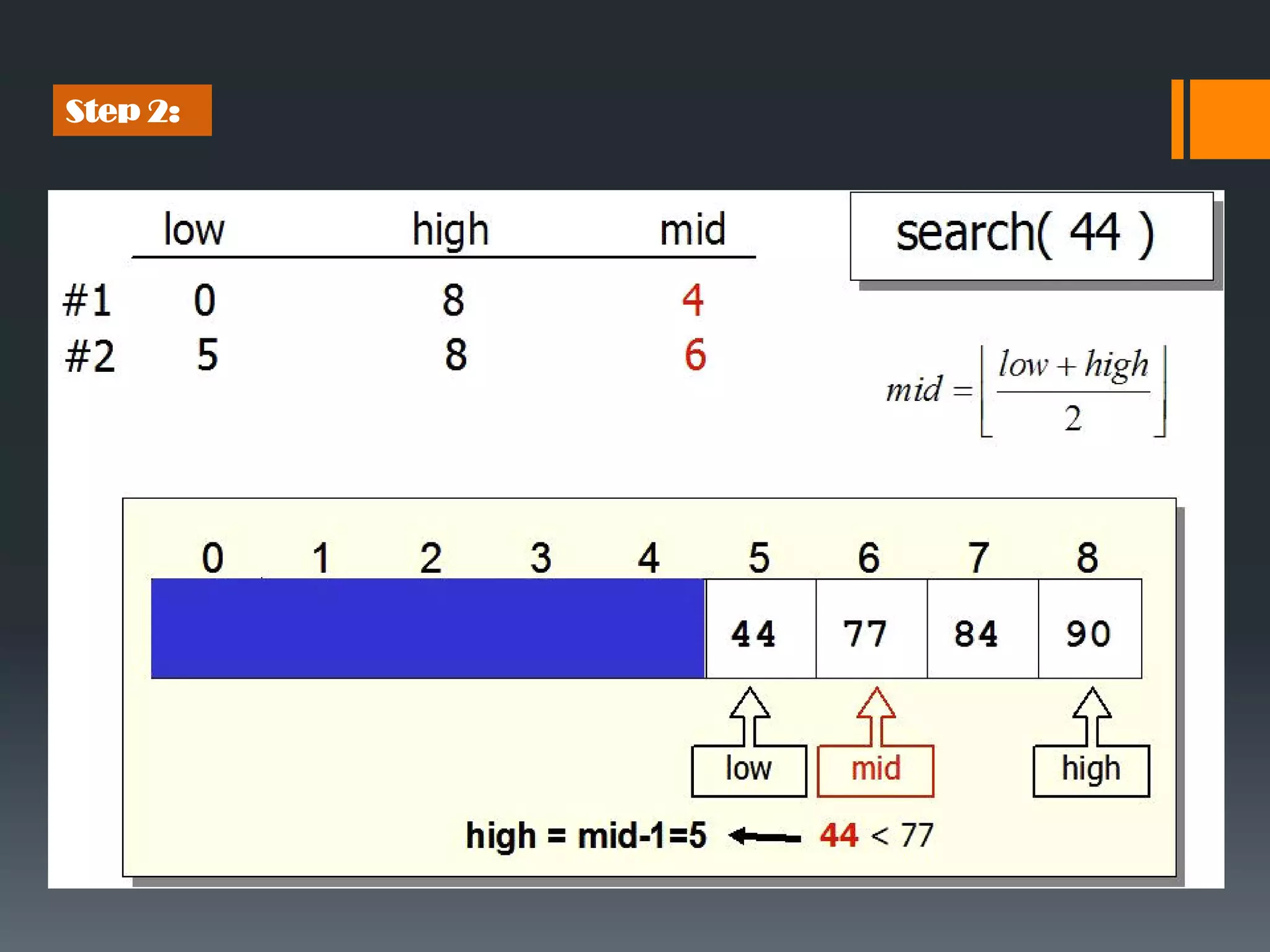
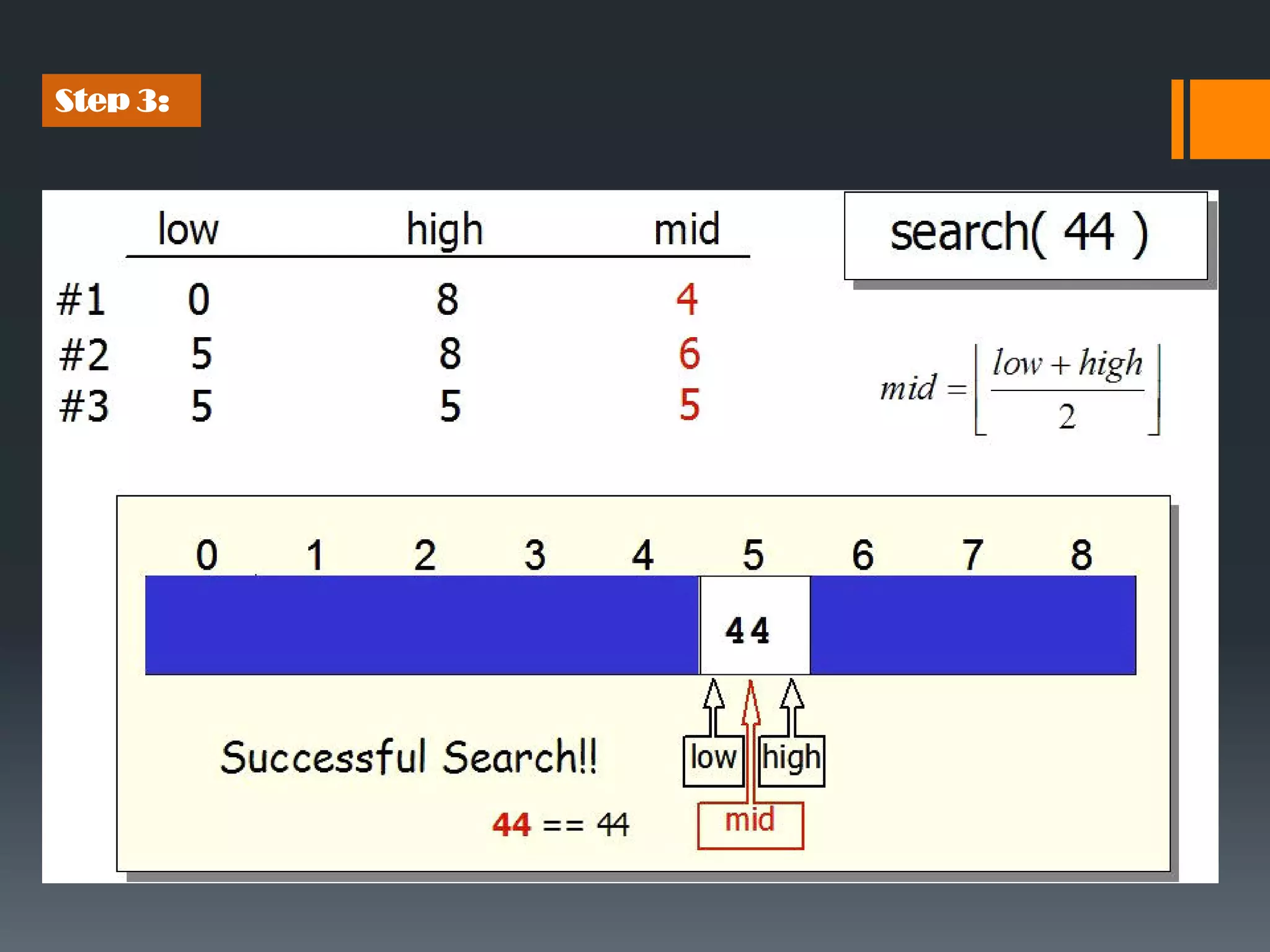
Binary search is an efficient algorithm for finding a target value within a sorted array. It works by repeatedly dividing the search range in half and checking the value at the midpoint. This eliminates about half of the remaining candidates in each step. The maximum number of comparisons needed is log n, where n is the number of elements. This makes binary search faster than linear search, which requires checking every element. The algorithm works by first finding the middle element, then checking if it matches the target. If not, it recursively searches either the lower or upper half depending on if the target is less than or greater than the middle element.



![ALGORITHM (Recursive) recursivebinarysearch(int A[], int first, int last, int key) if last<first index=-1 else int mid = (first + last) / 2 if key=A[mid] index=mid else if key<A[mid] index= recursivebinarysearch(A, first, mid – 1, key) else index= recursivebinarysearch(A, mid + 1, last, key) return index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/binarysearch-160621081757/75/Binary-Search-Design-Analysis-of-Algorithms-7-2048.jpg)


![CORRECTNESS OF BINARY SEARCH Lemma: For all n>=0, if BinarySearch(E, first , last, k) is called, and the size is (last-first+1)=n and E[first], …E[last] are in ascending order, then it returns -1 if k doesn’t occur in E within the range first, … last and it returns index such that k=E[index] otherwise PROOF BY INDUCTION Base case: n = last − first + 1 = 0 The array is empty, so first = last + 1 Line 1 i.e. (first > last) is true , line 2 is reached and the algorithm correctly returns -1. Therefore, the element is not present in the array. Inductive step: For n>0, assume that the binary search(E, first, last ,k) satisfies the lemma on size k such that 0<=k<n, and first and the last are any indexes such that k=last-first+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/binarysearch-160621081757/75/Binary-Search-Design-Analysis-of-Algorithms-10-2048.jpg)

