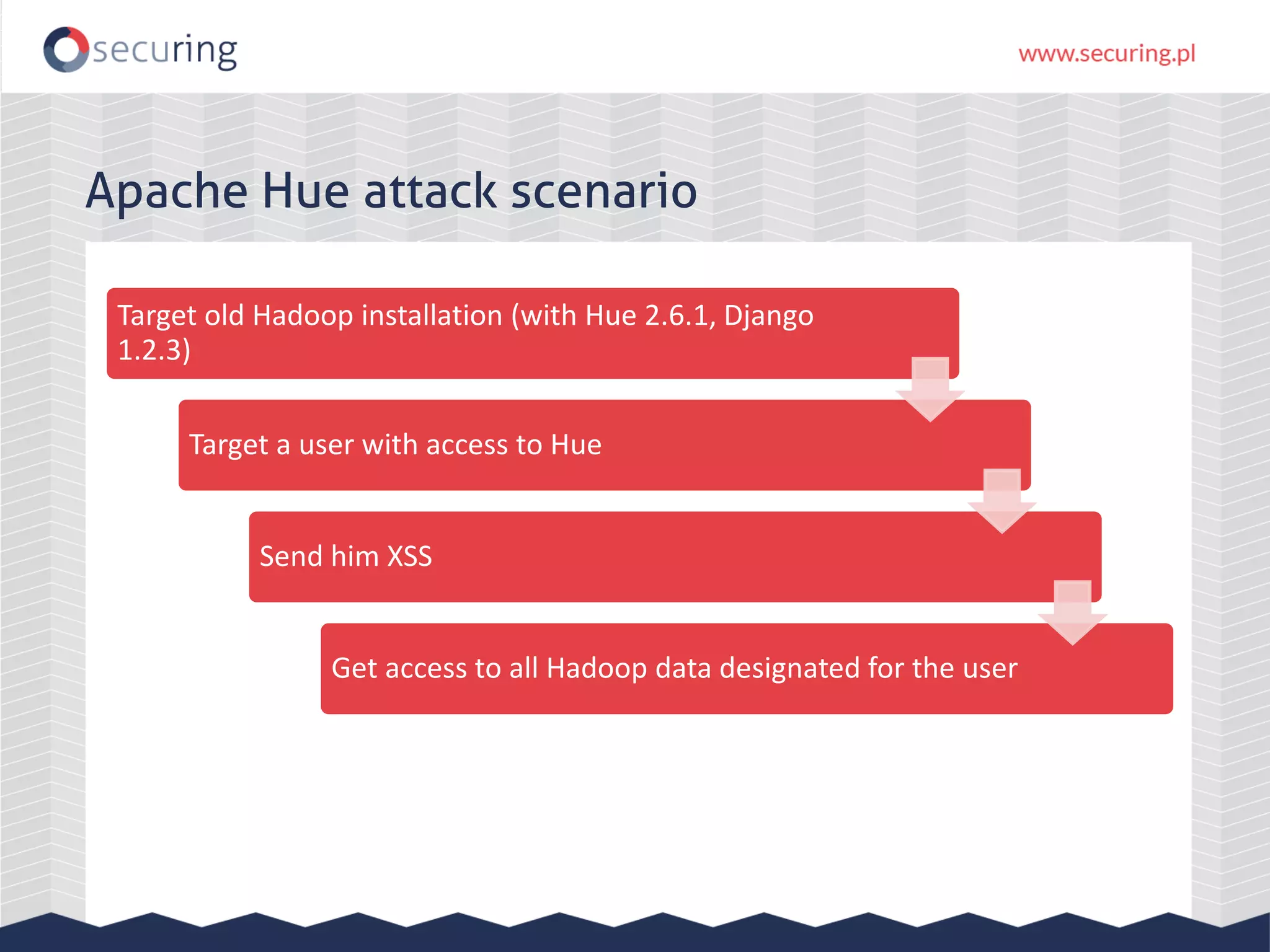
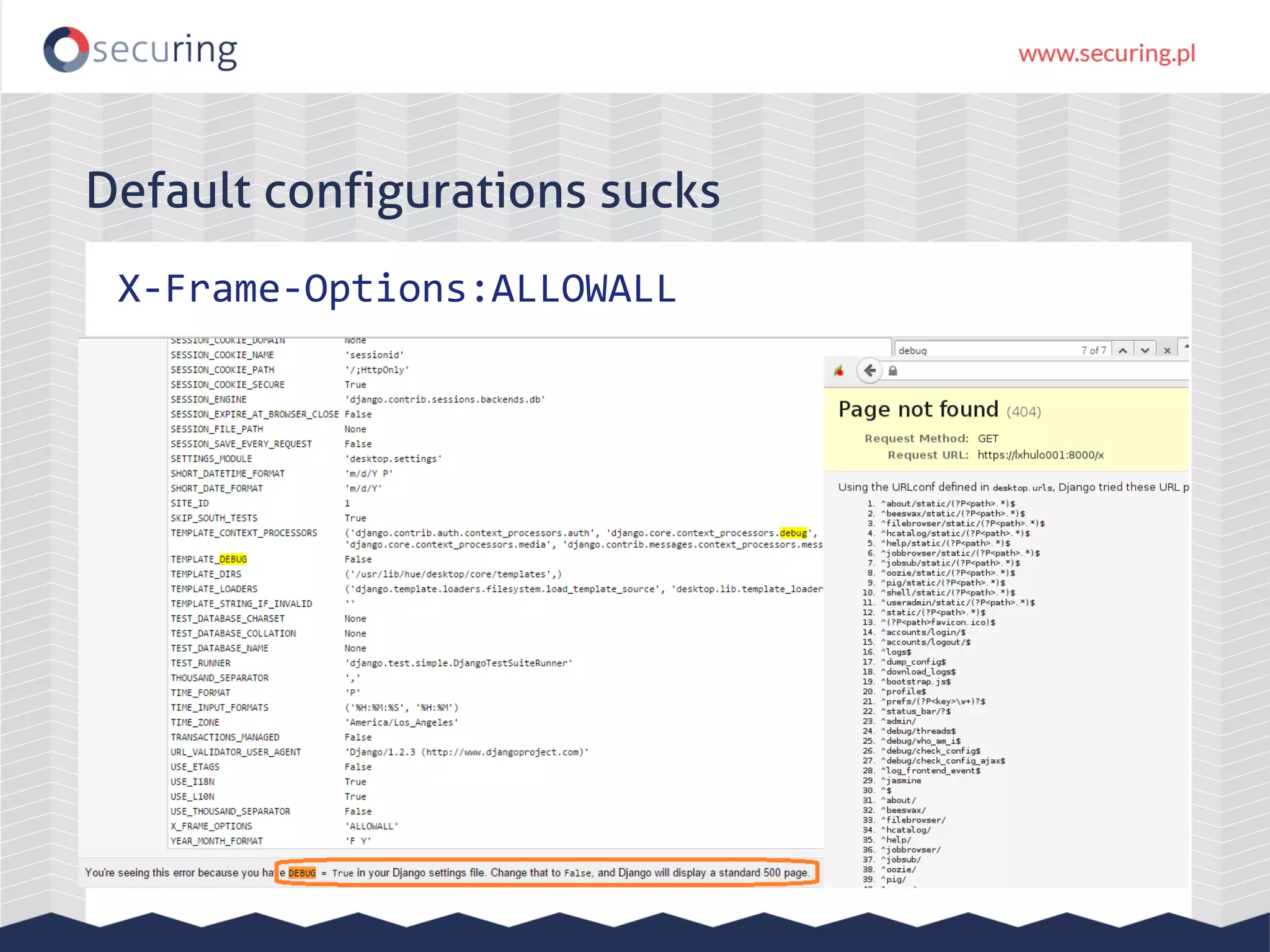
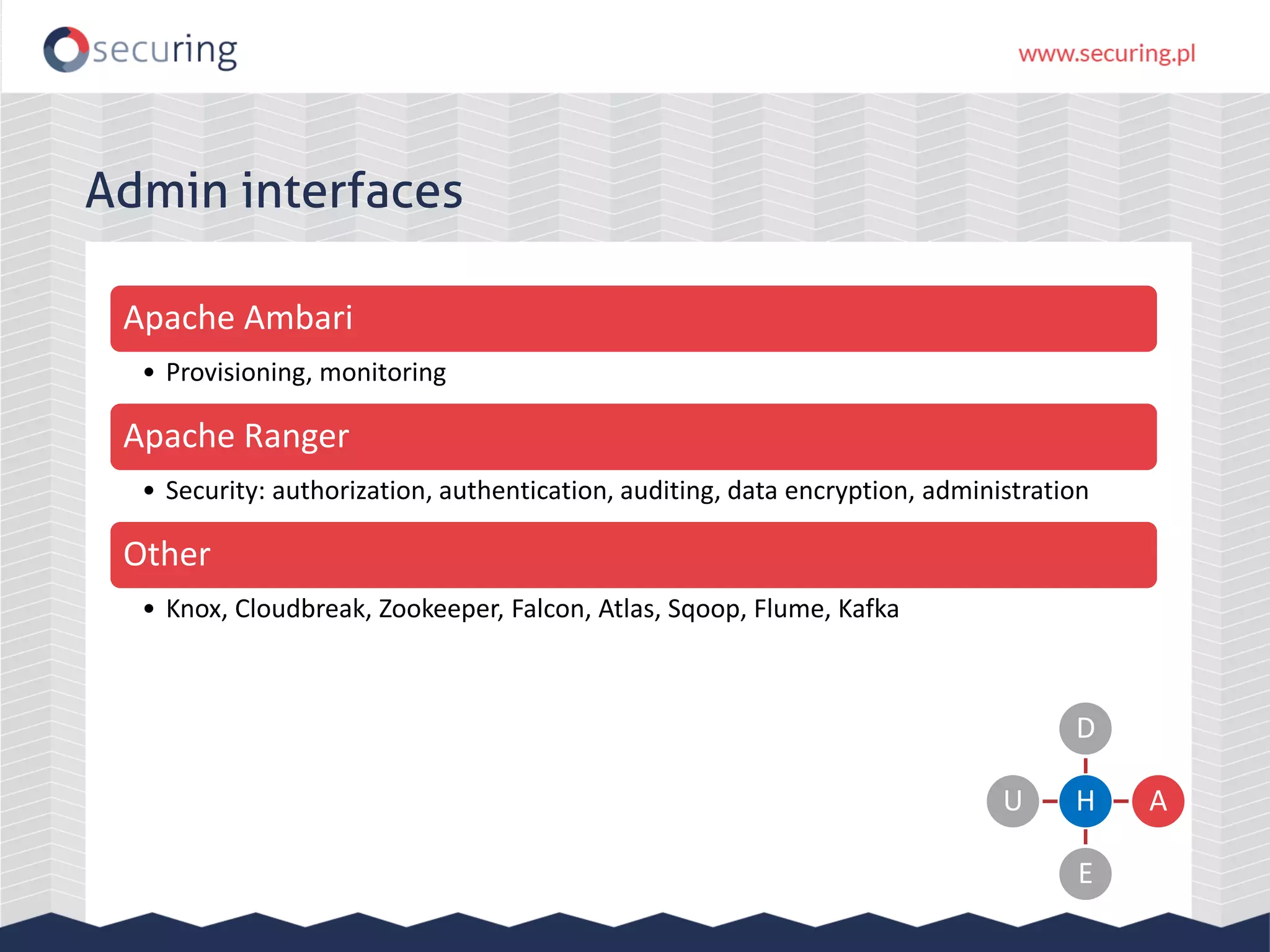
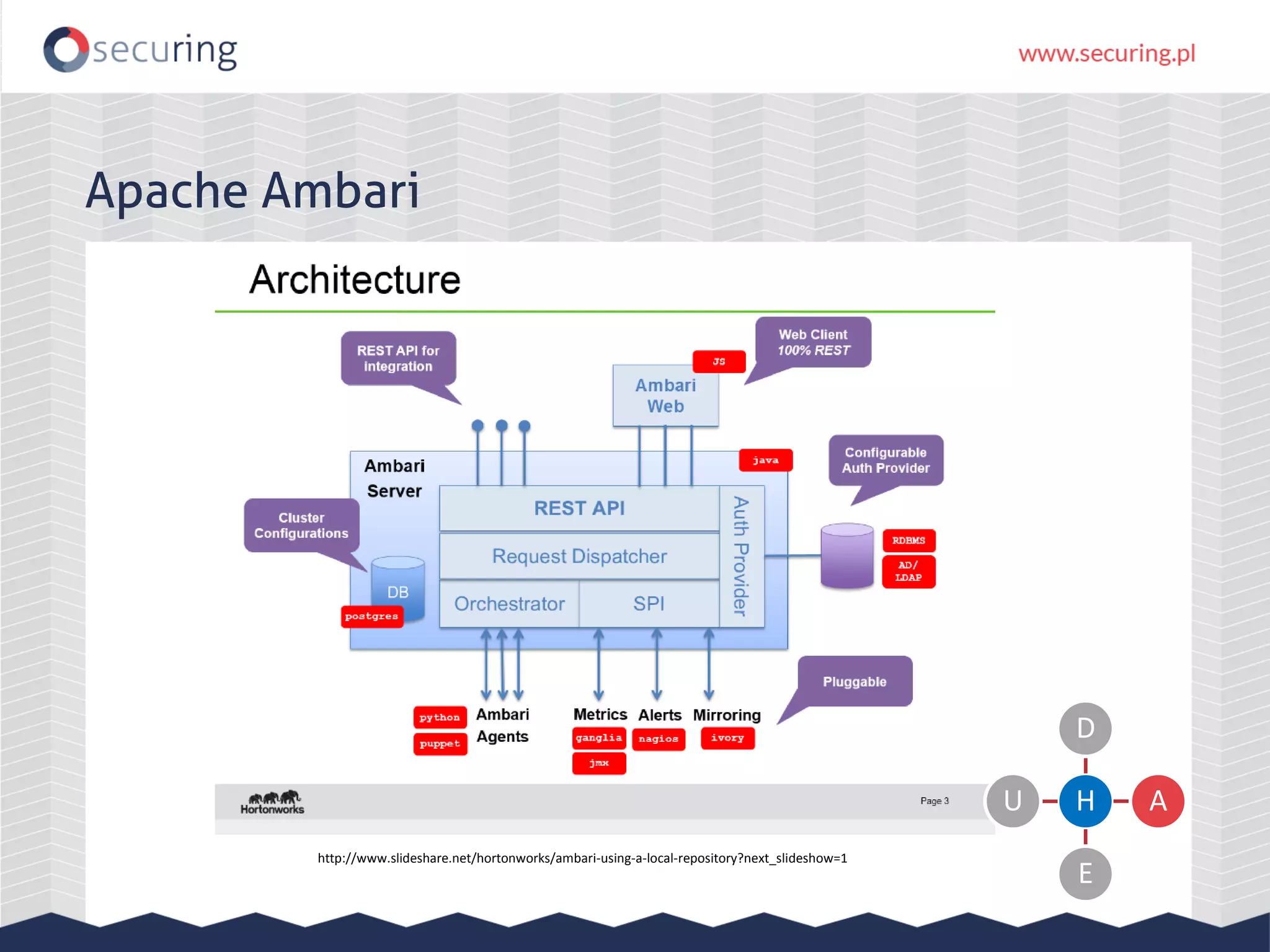
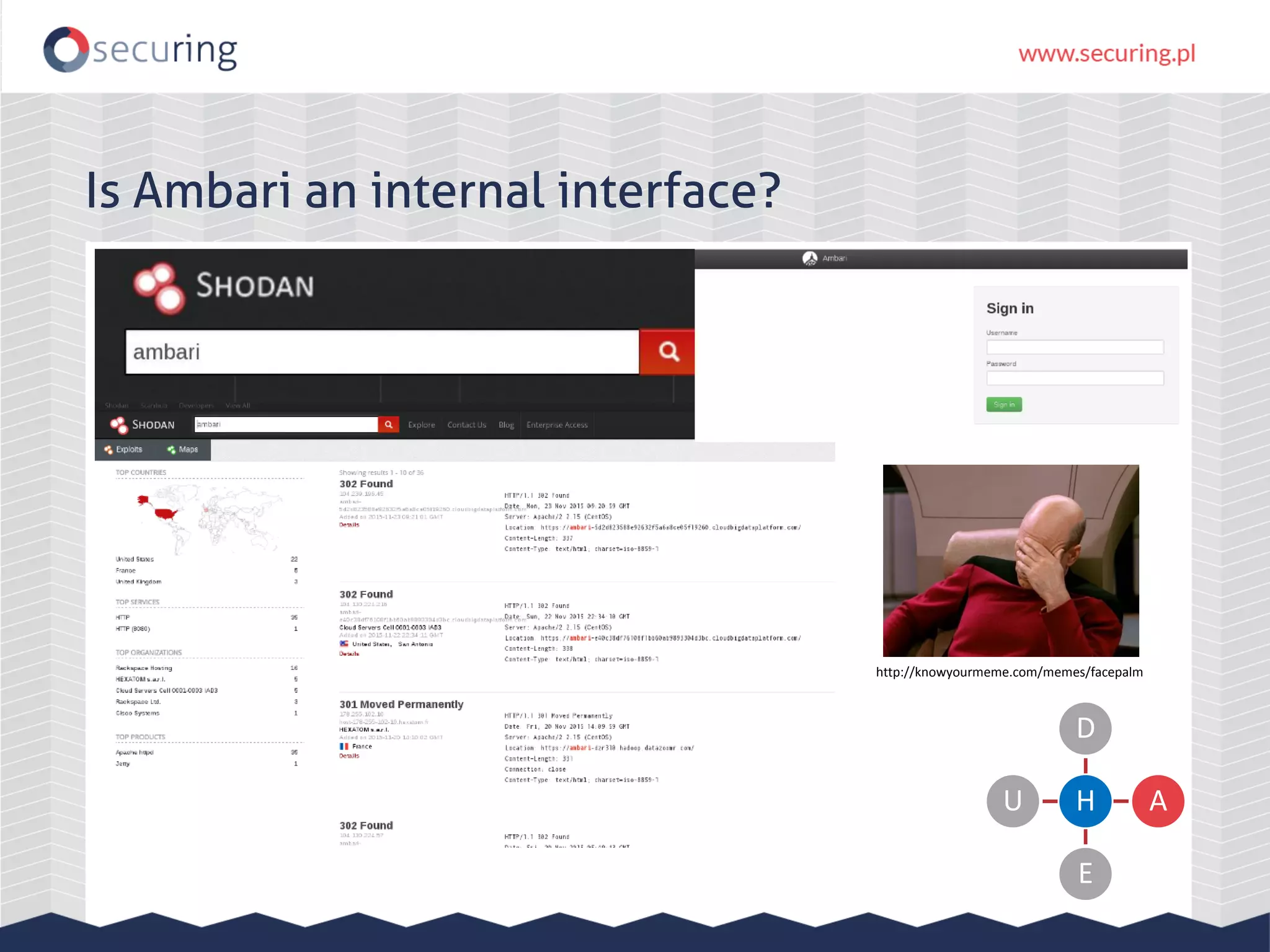
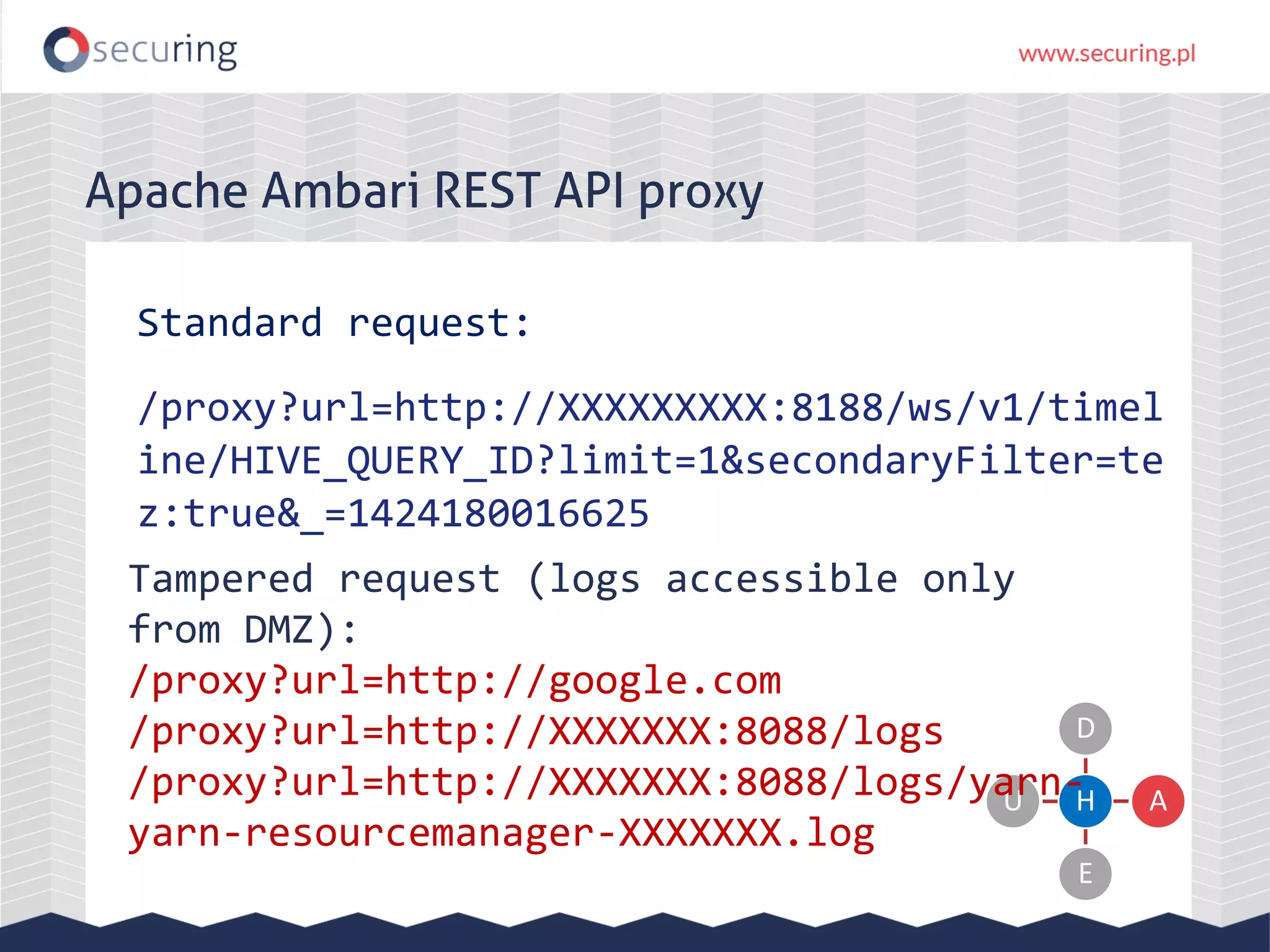
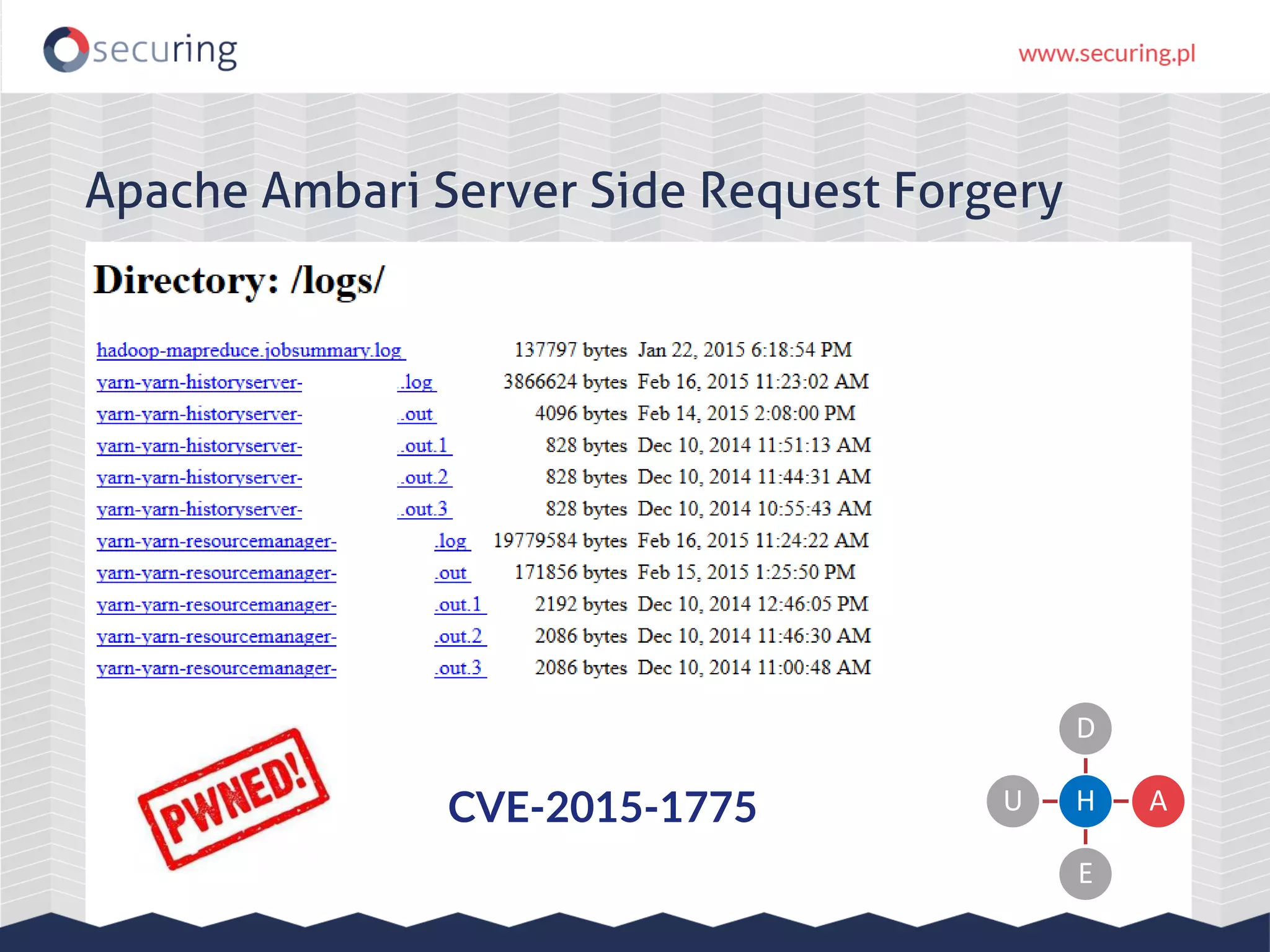
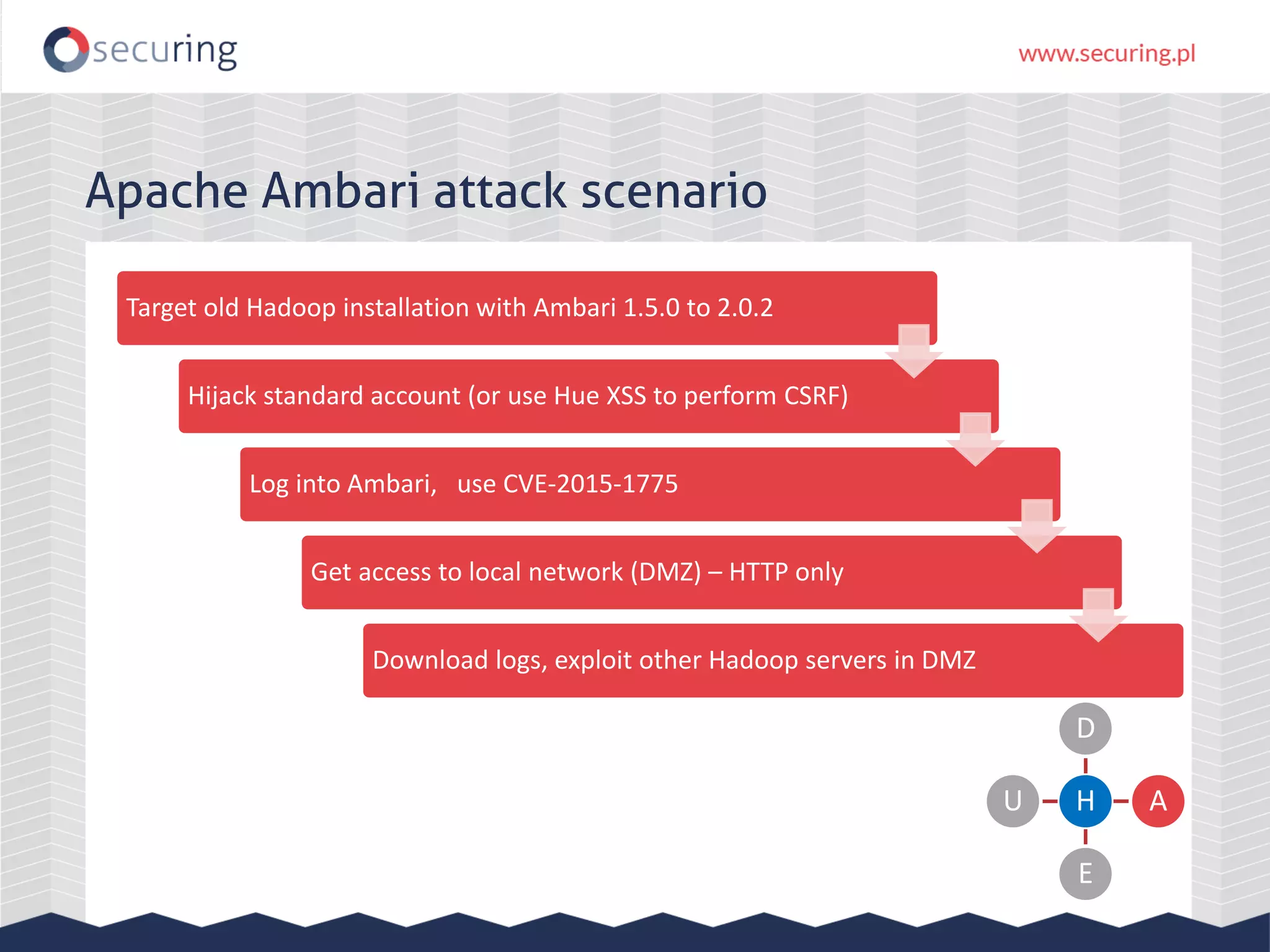
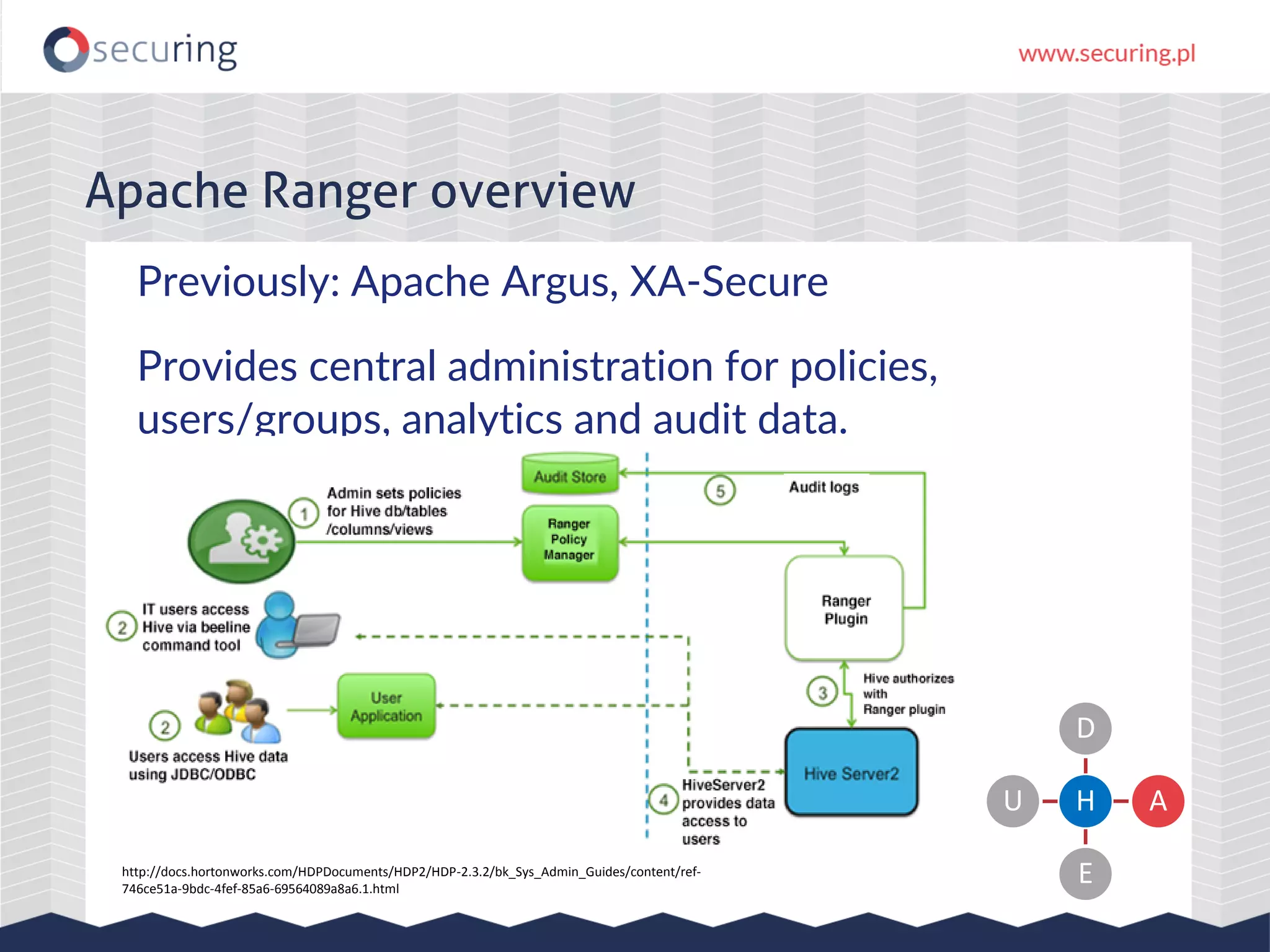
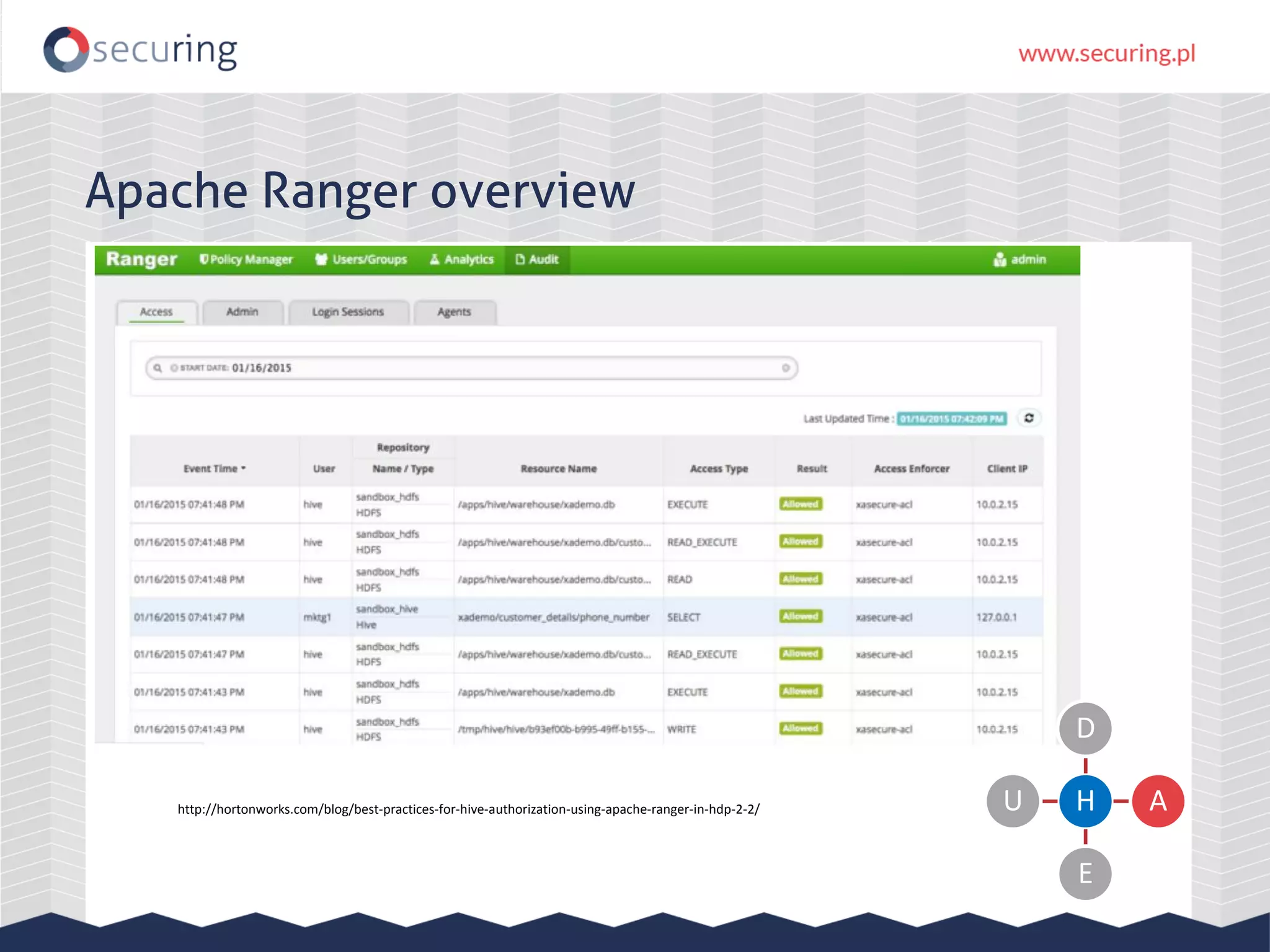
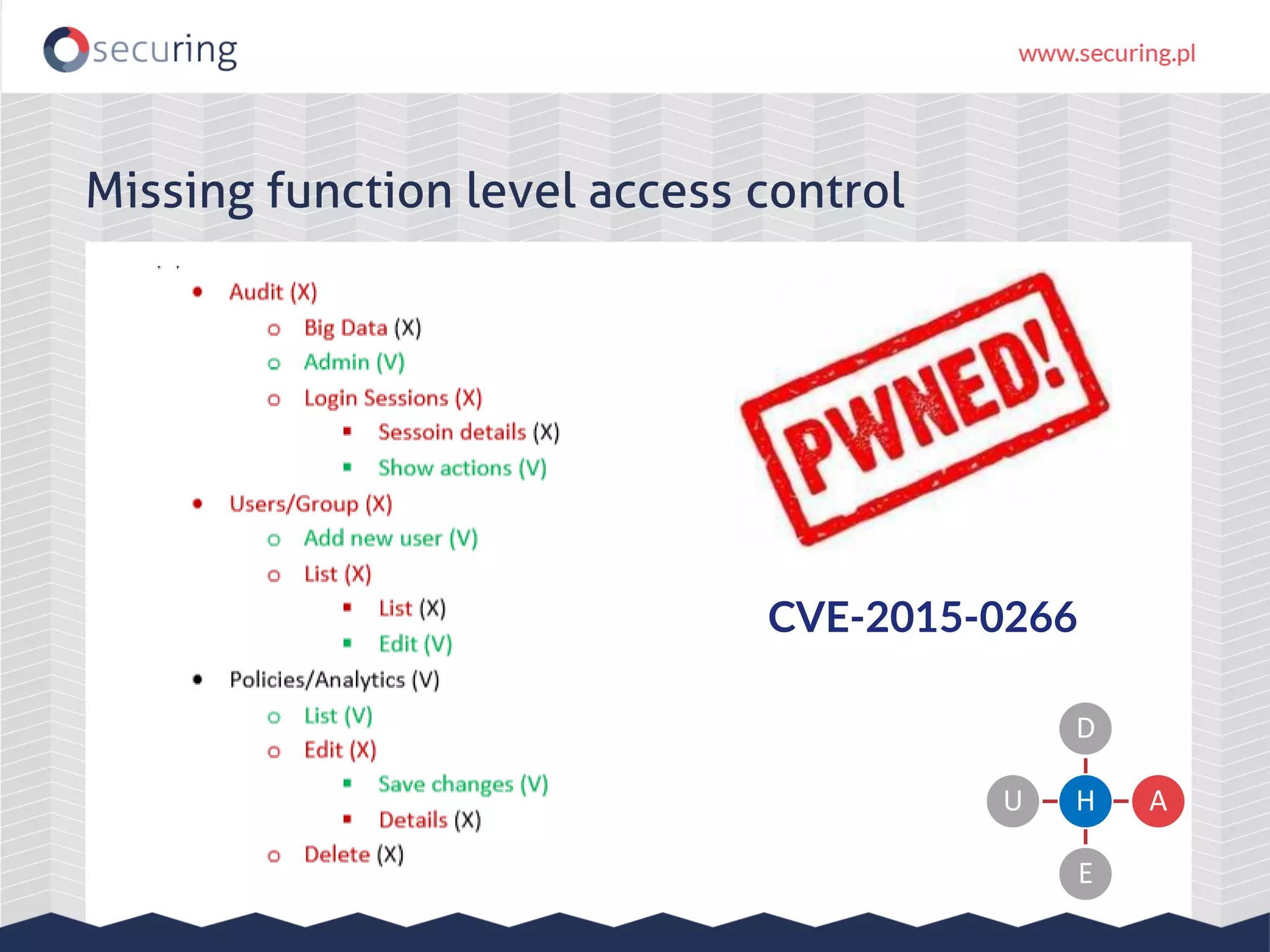
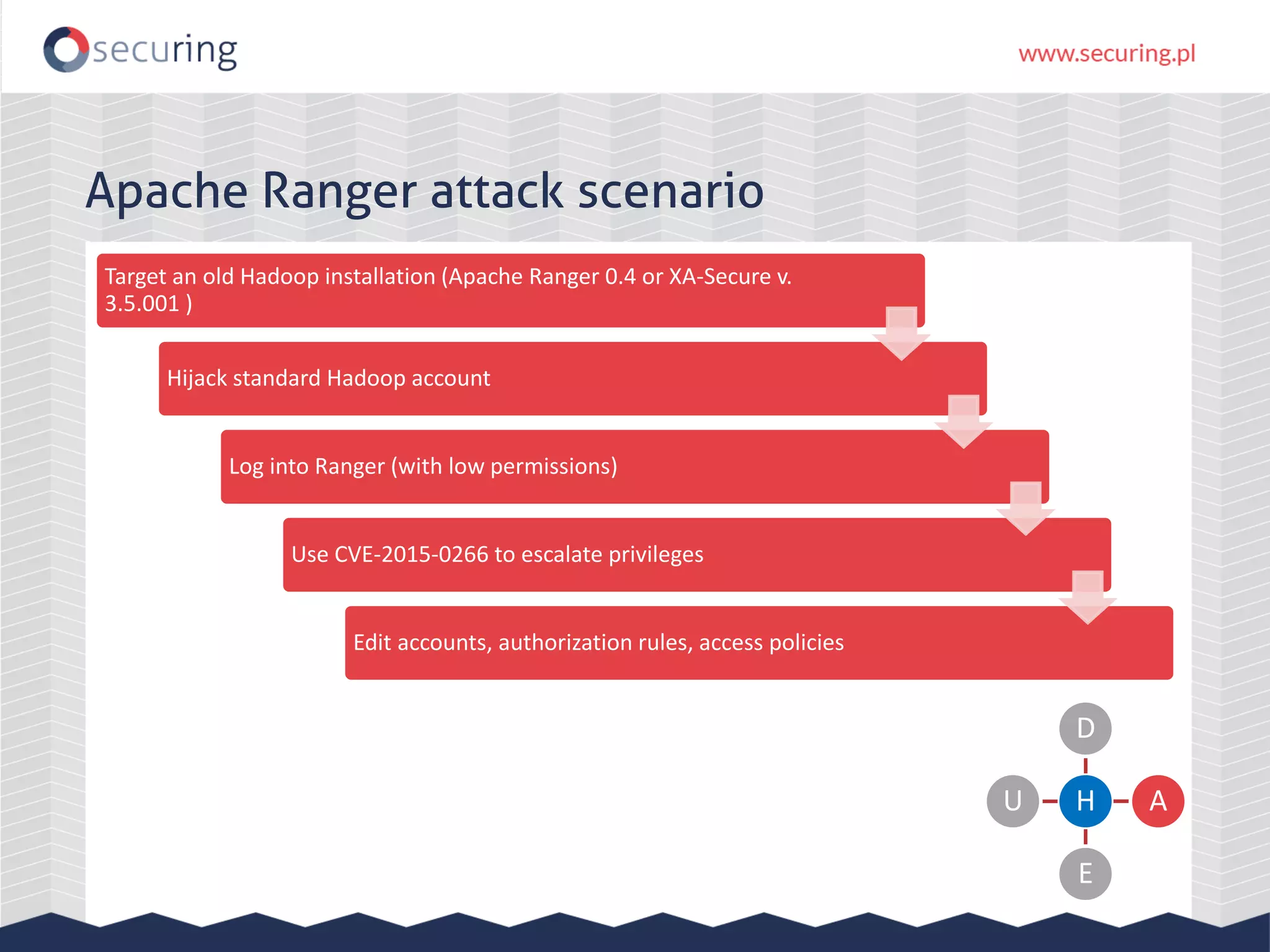
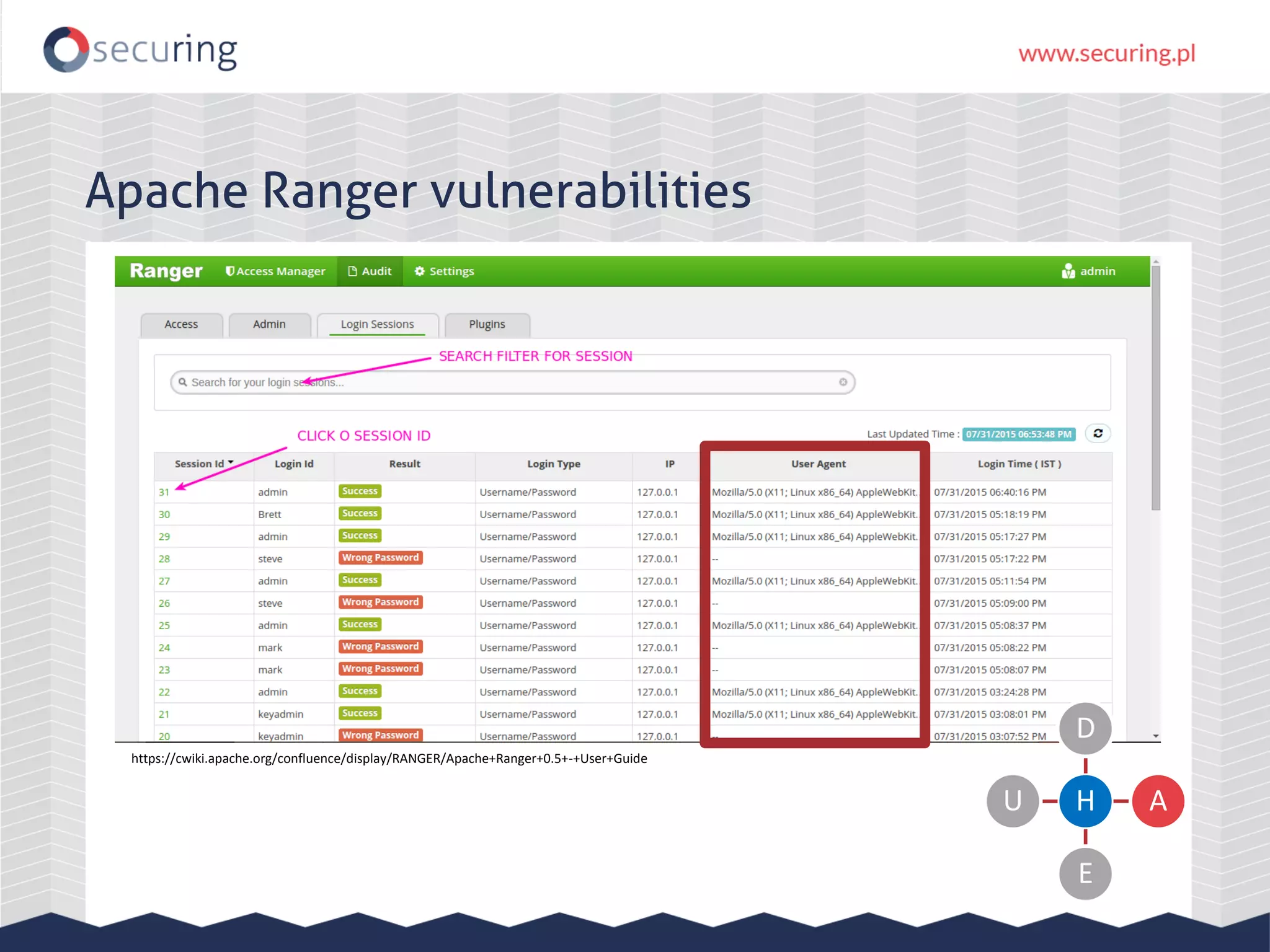
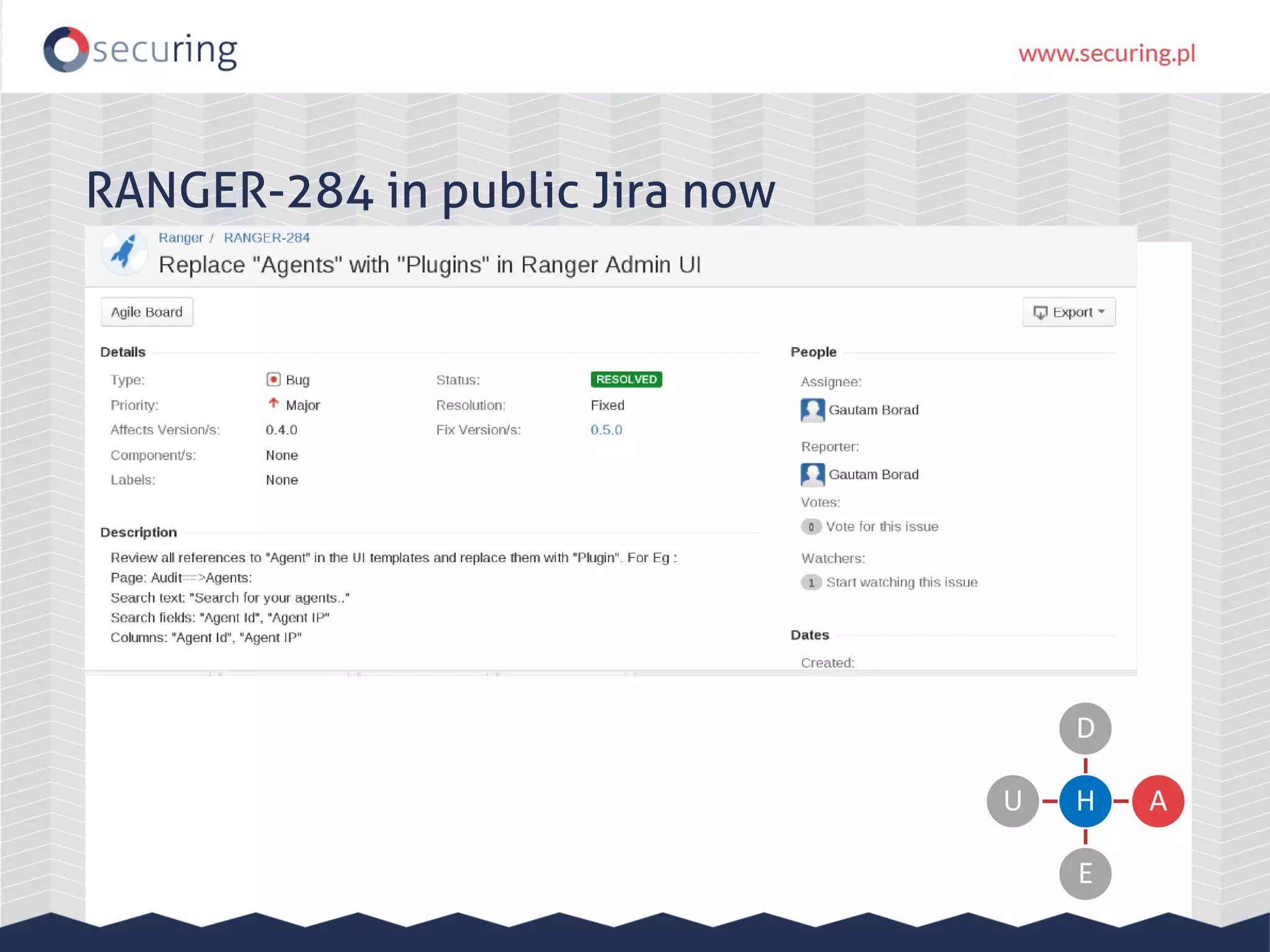
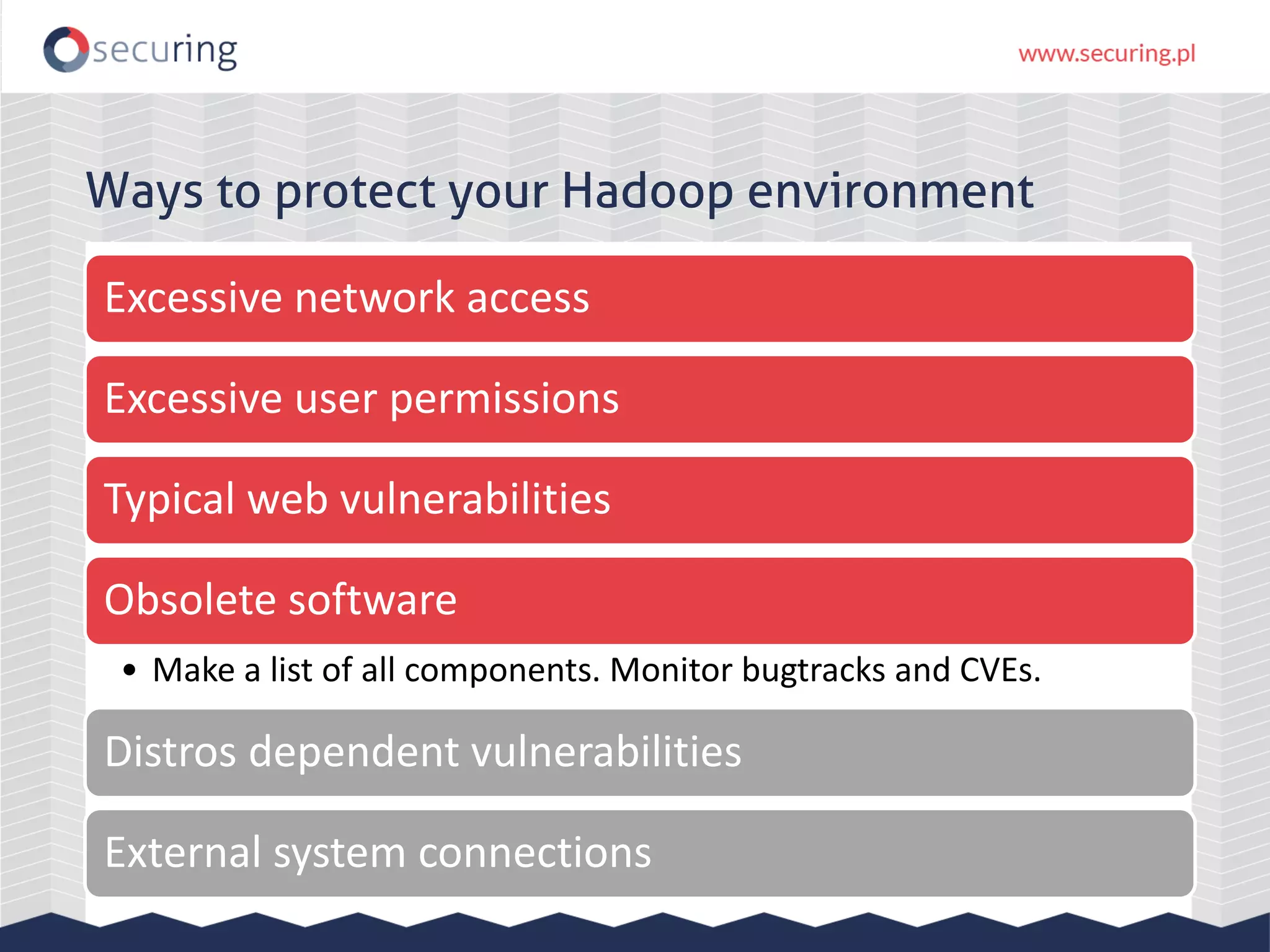
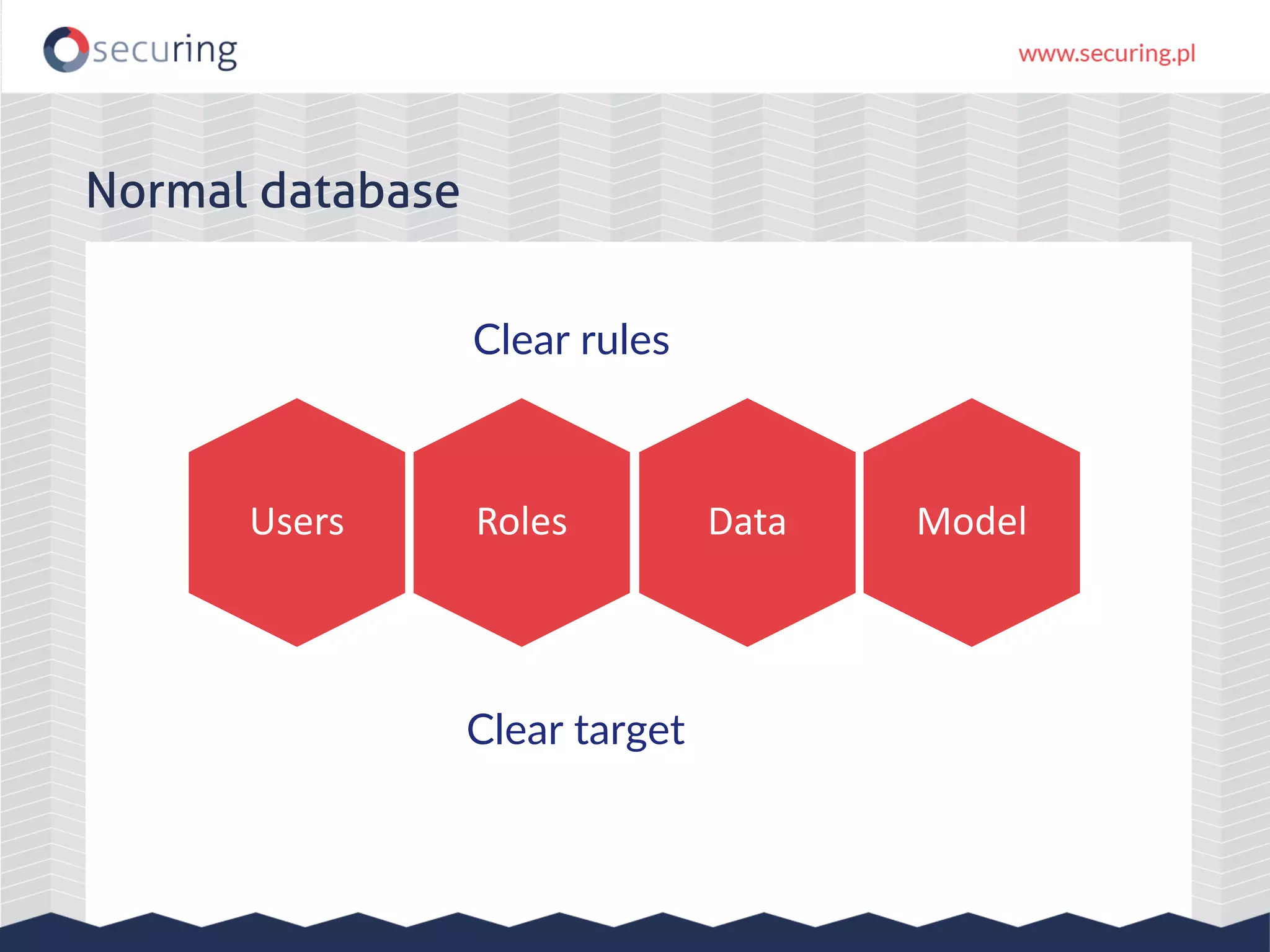
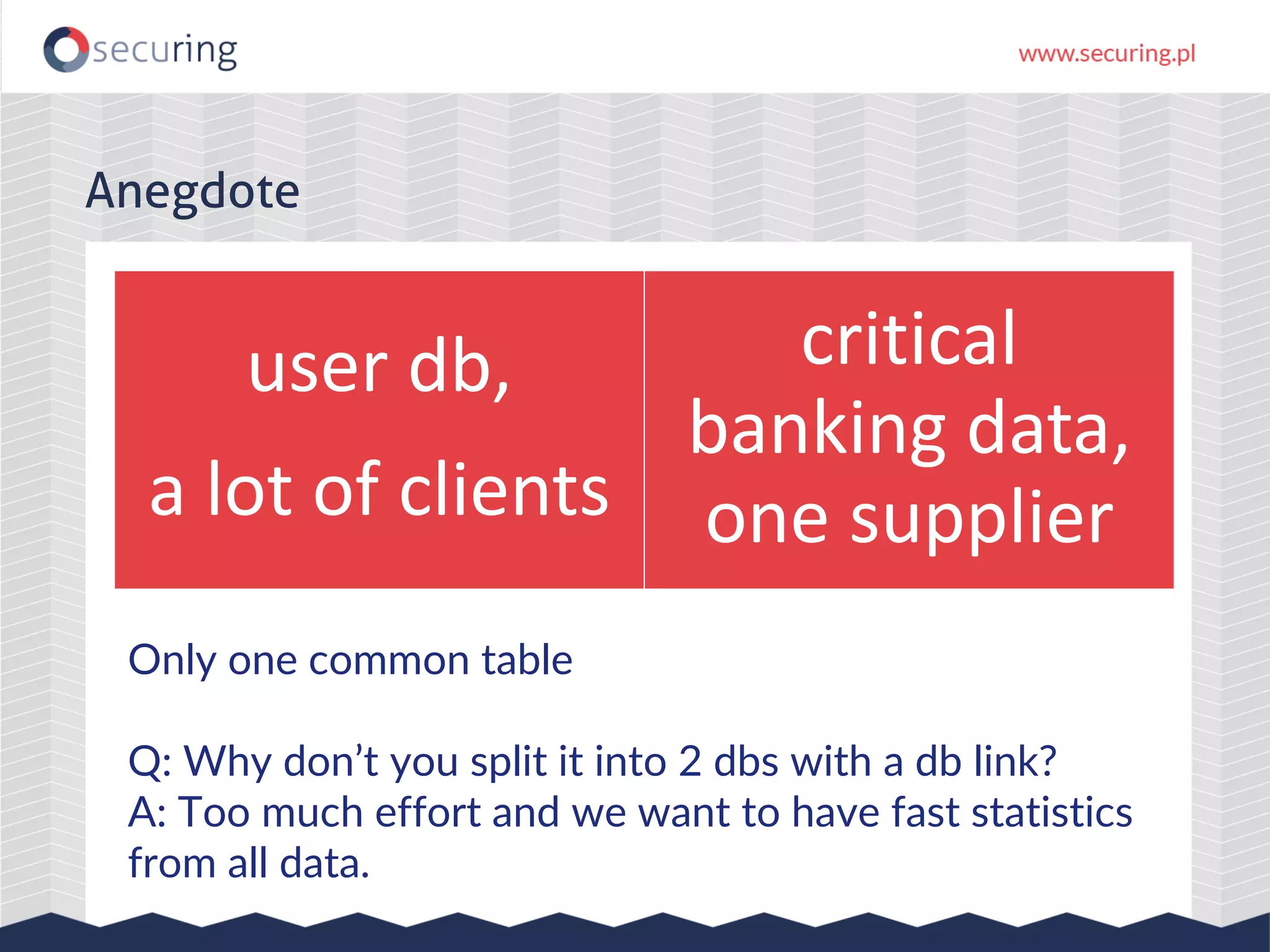
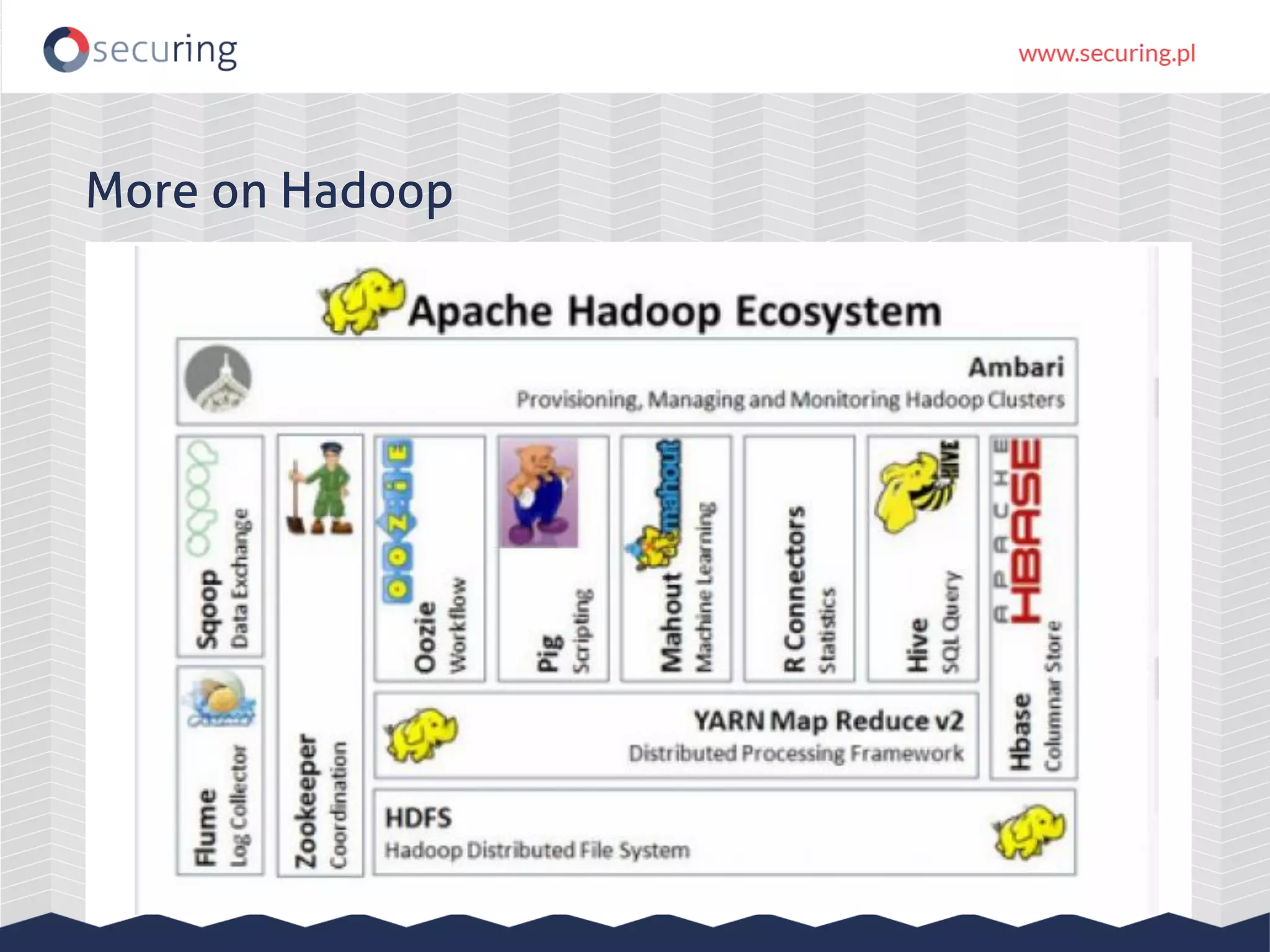
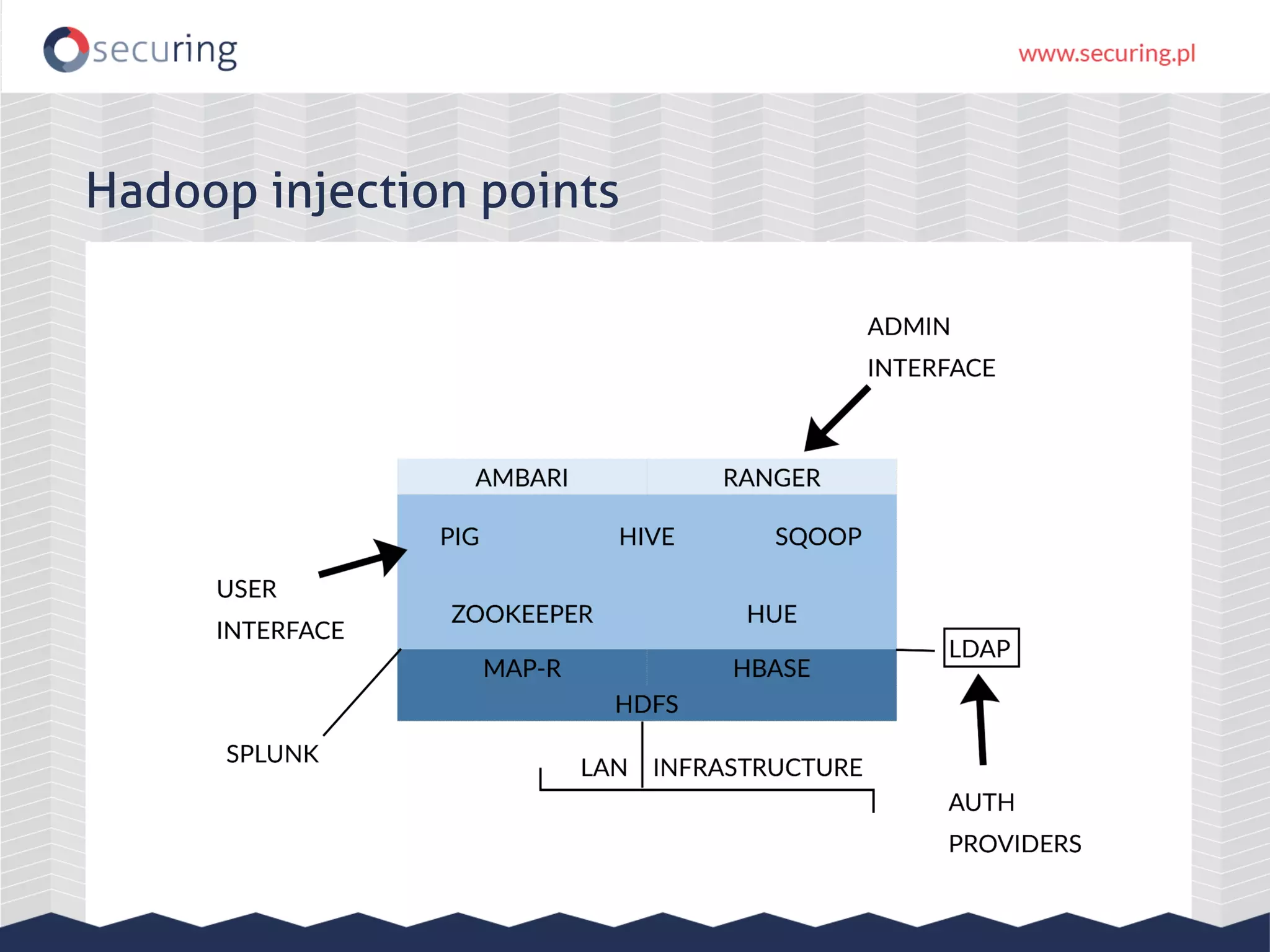
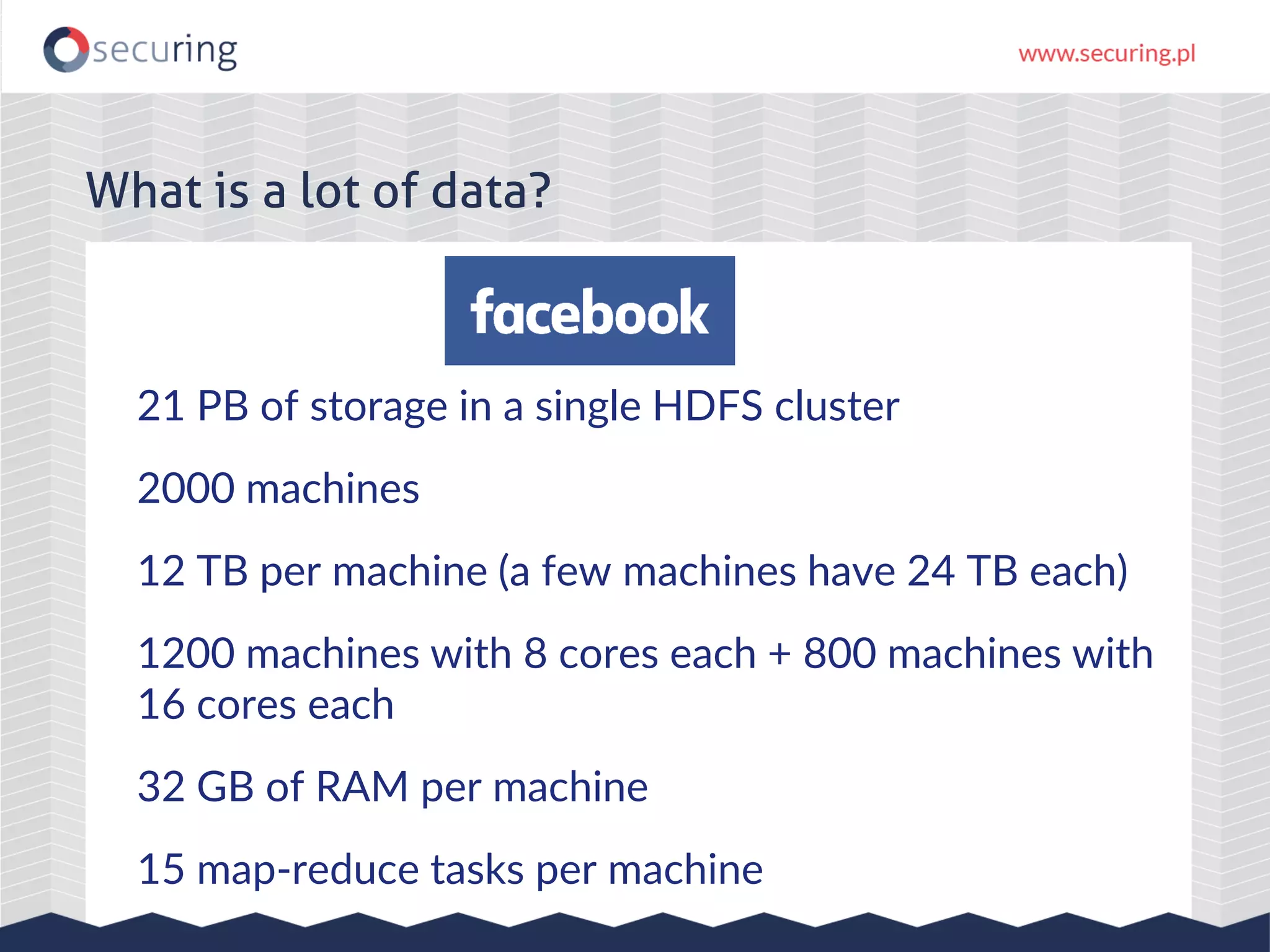
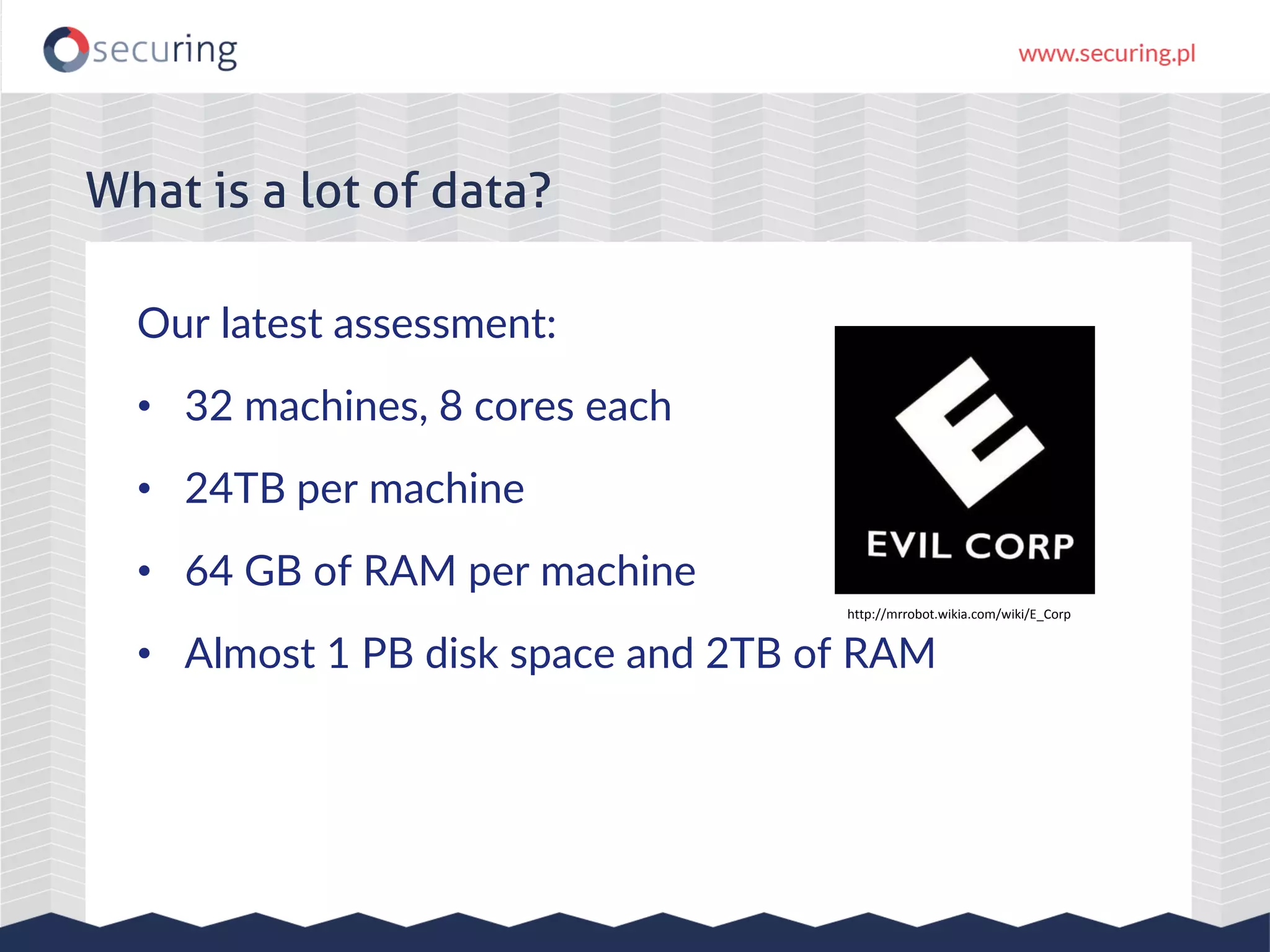
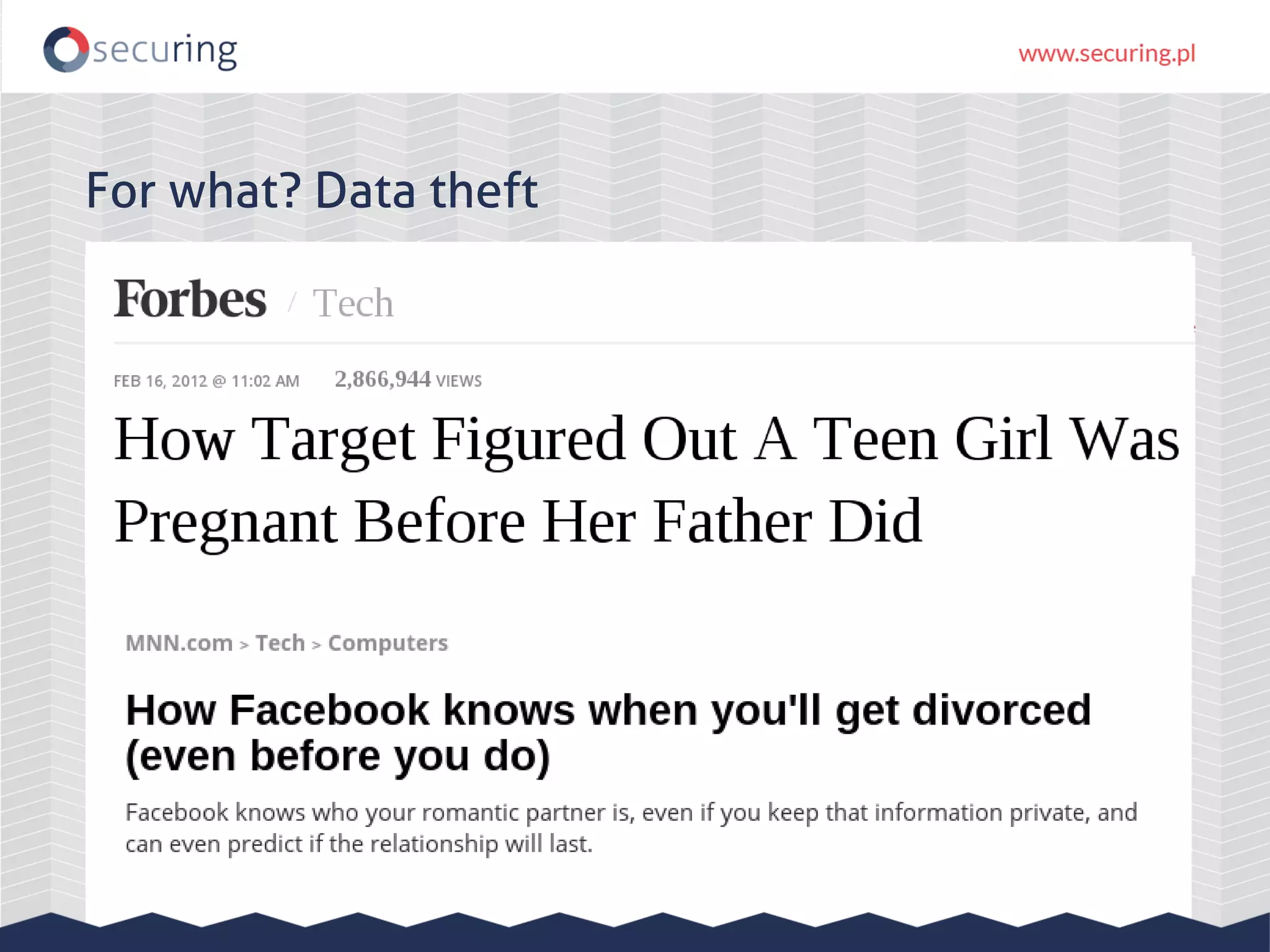
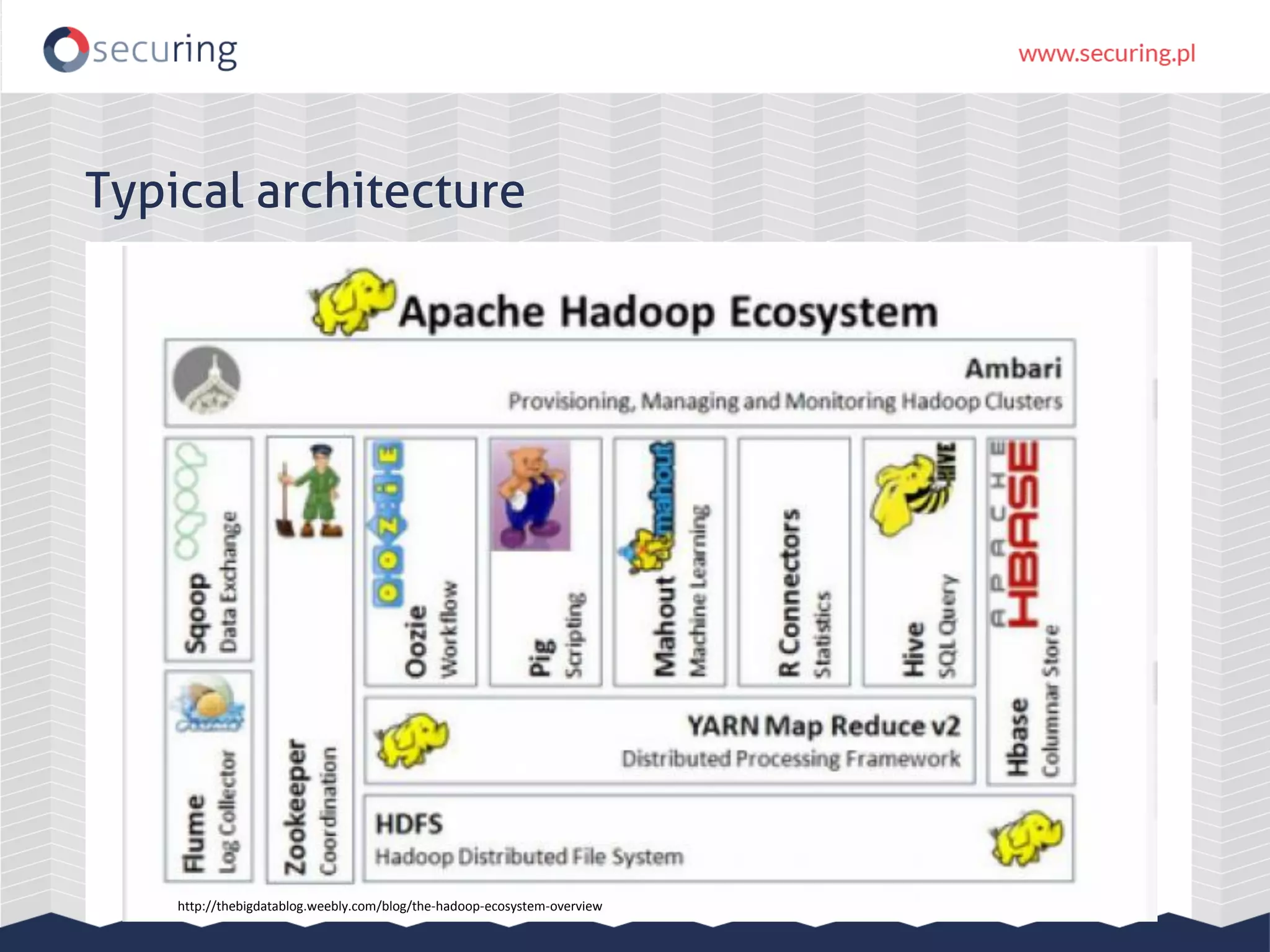
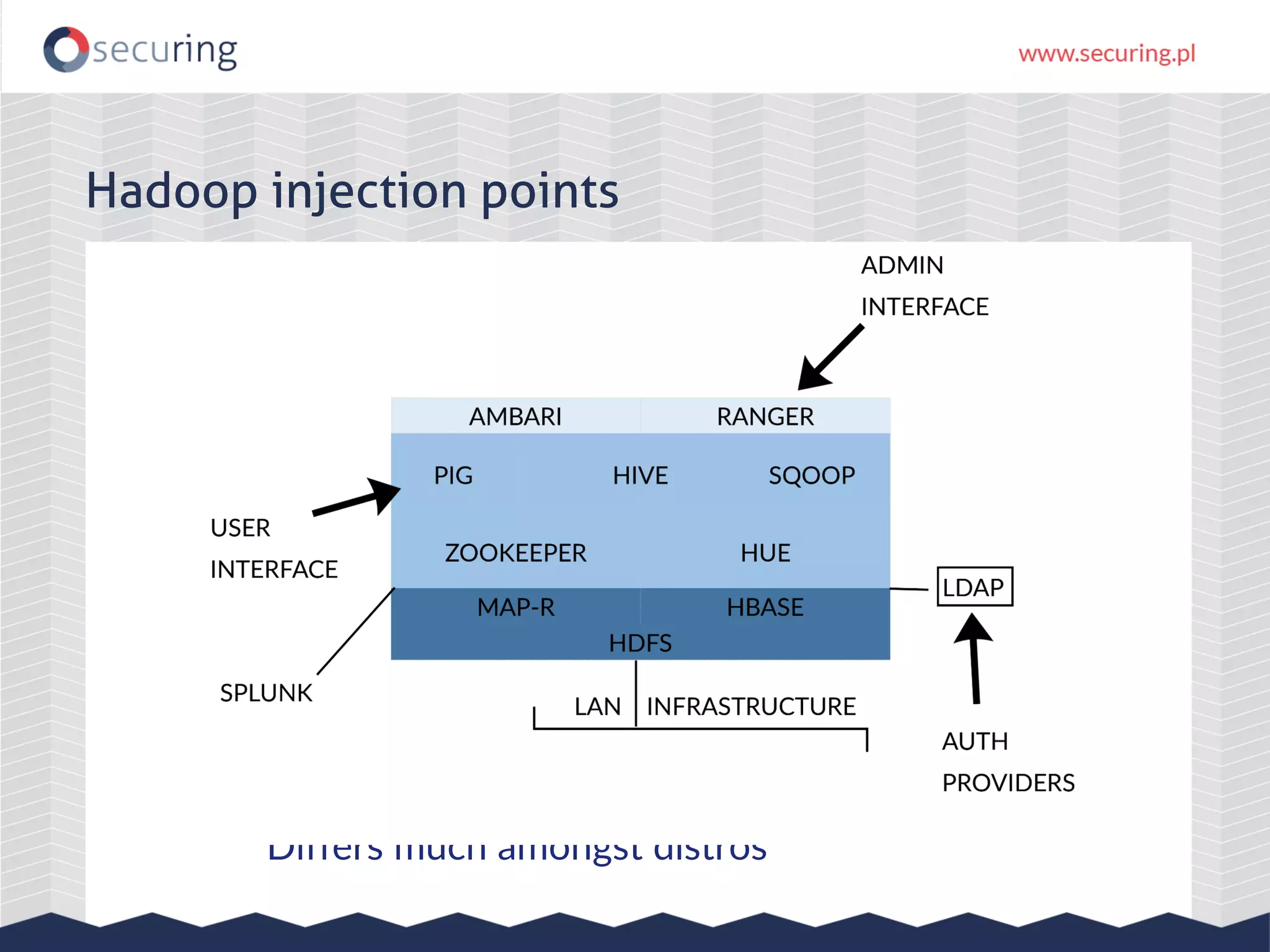
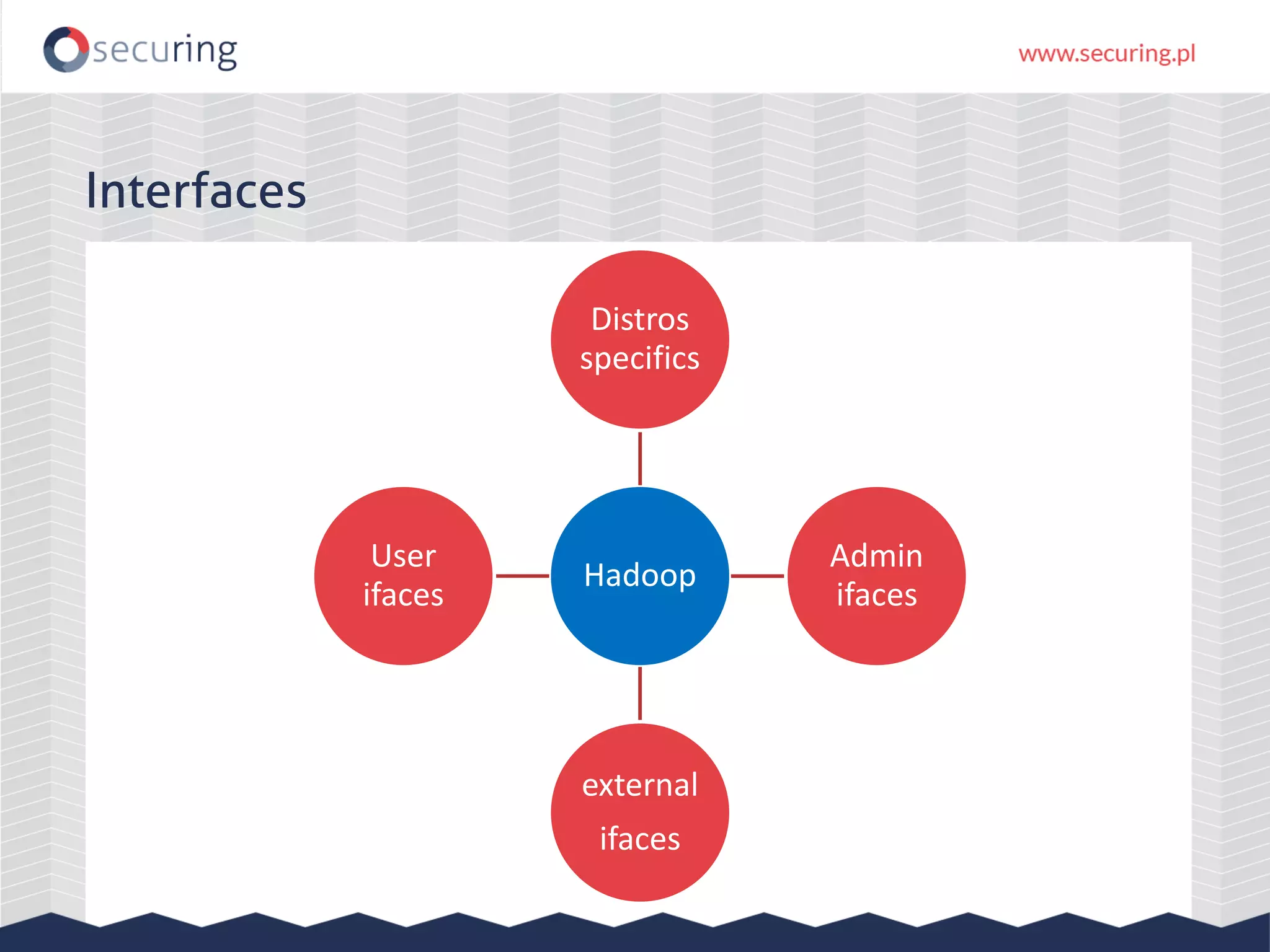
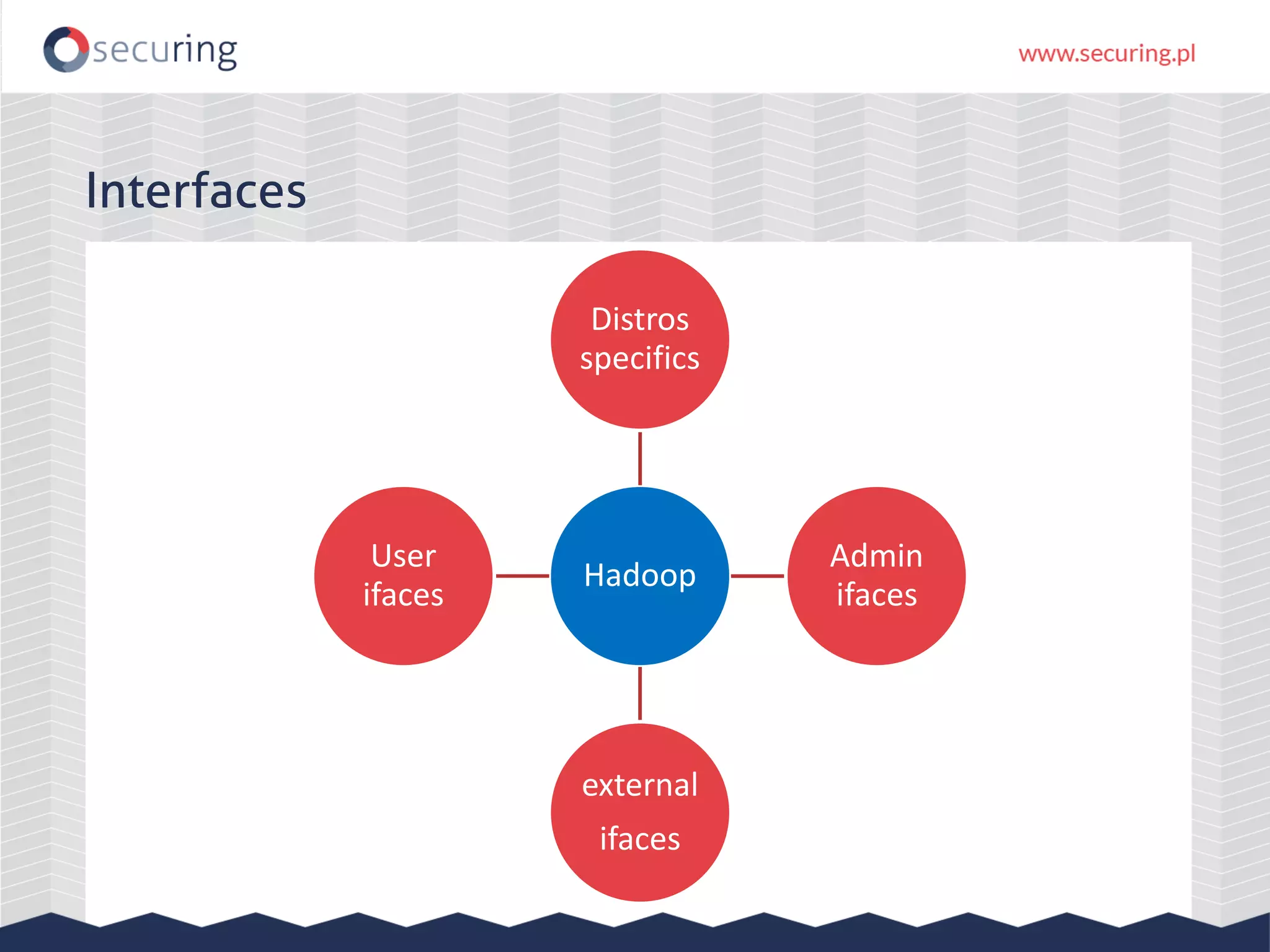
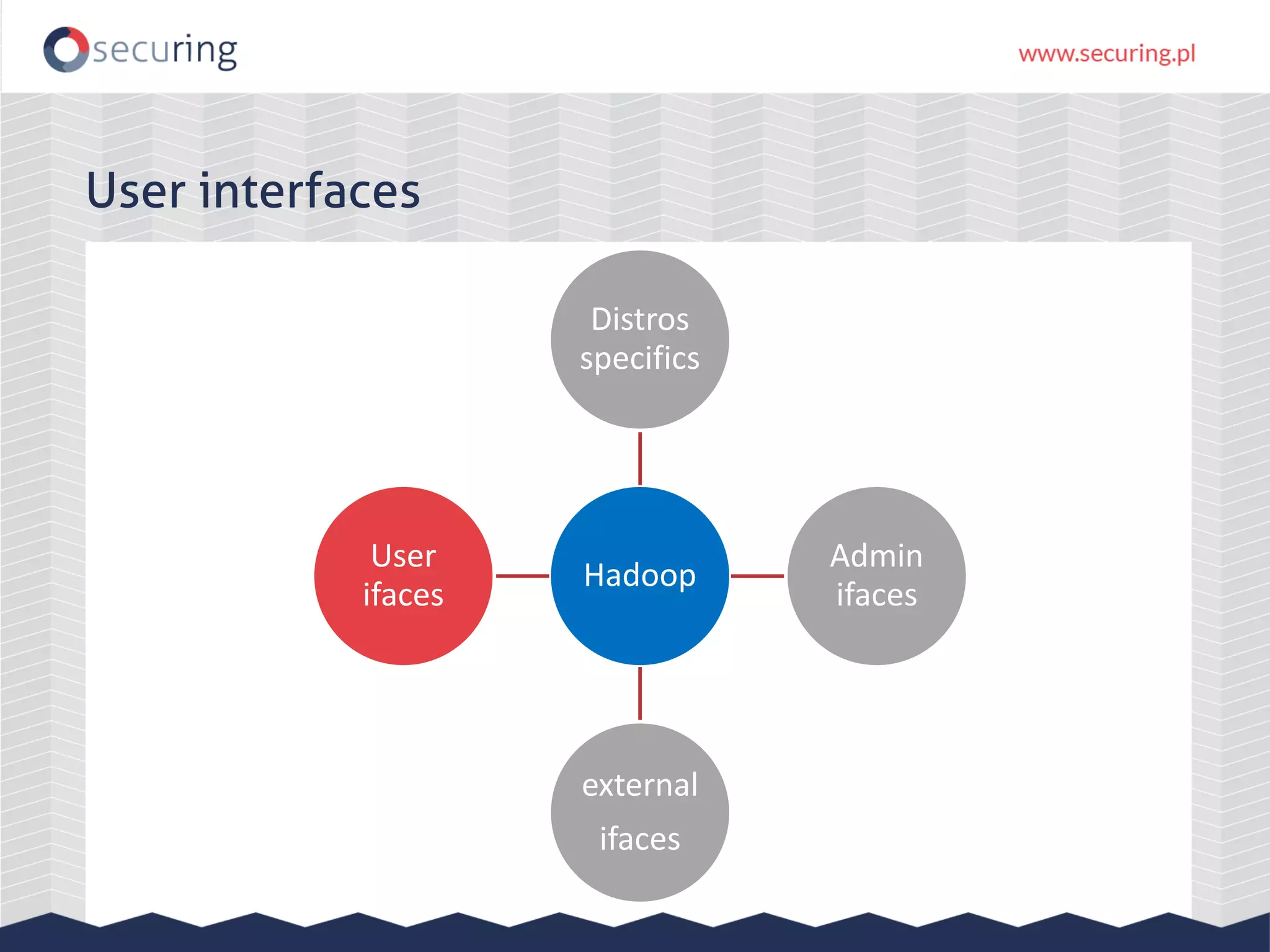
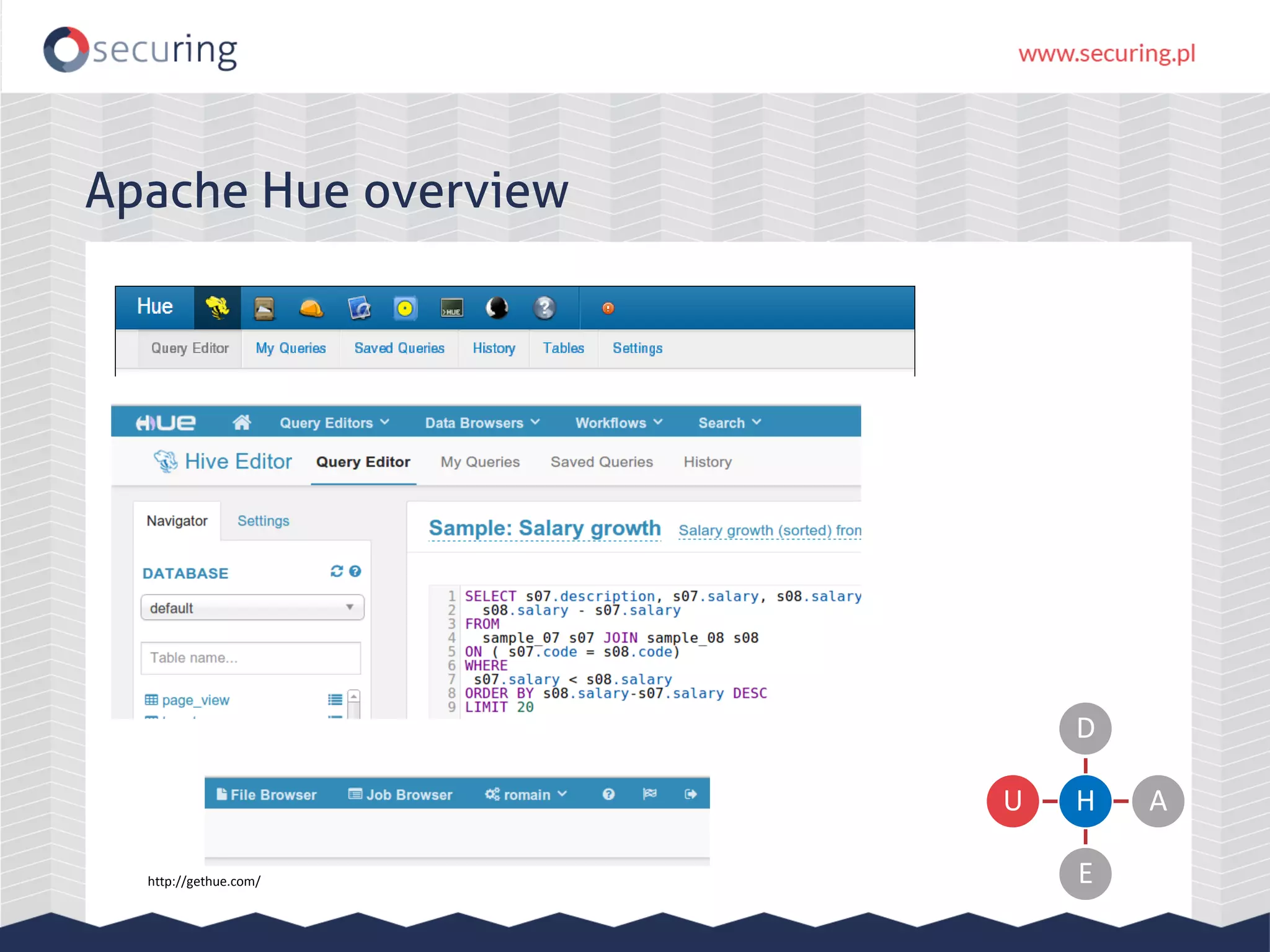
The document discusses vulnerabilities and security concerns associated with Hadoop and big data environments, emphasizing hacker techniques and common weaknesses. It outlines various injection points, common misconfigurations, and attack scenarios, particularly related to Apache Hue, Ambari, and Ranger. Recommendations for improving security include strict user permissions, regular pentesting, and keeping software components updated.












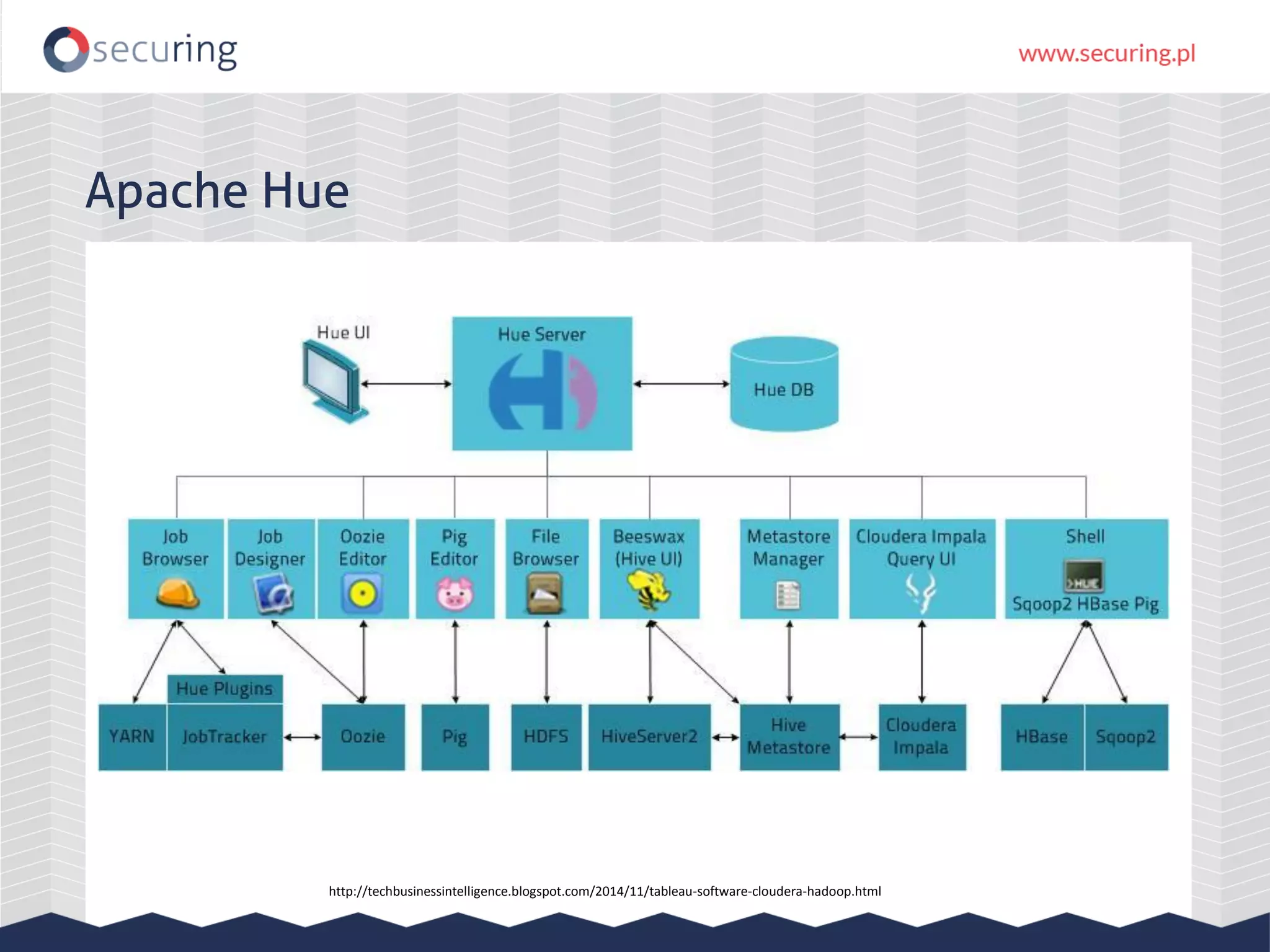




![Apache Hue DOM XSS var _anchor = $("a[name='" + decodeURIComponent(window.location.hash.subs tring(1)) + "']").last(); Payload: URL/help/#<img src="x" onerror="alert(1)"> H D A E U](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zeronights-151203141333-lva1-app6892/75/Big-problems-with-big-data-Hadoop-interfaces-security-44-2048.jpg)