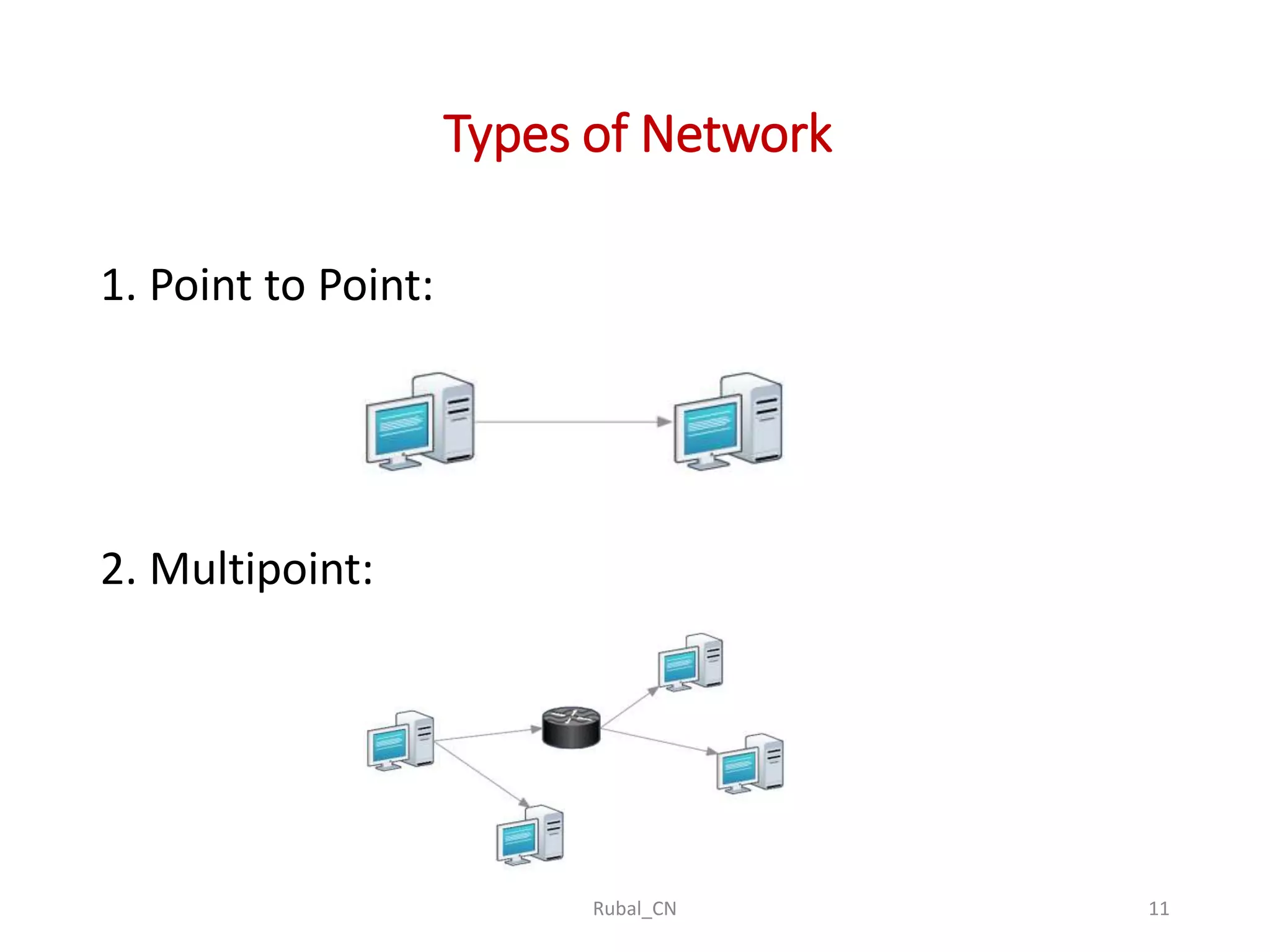
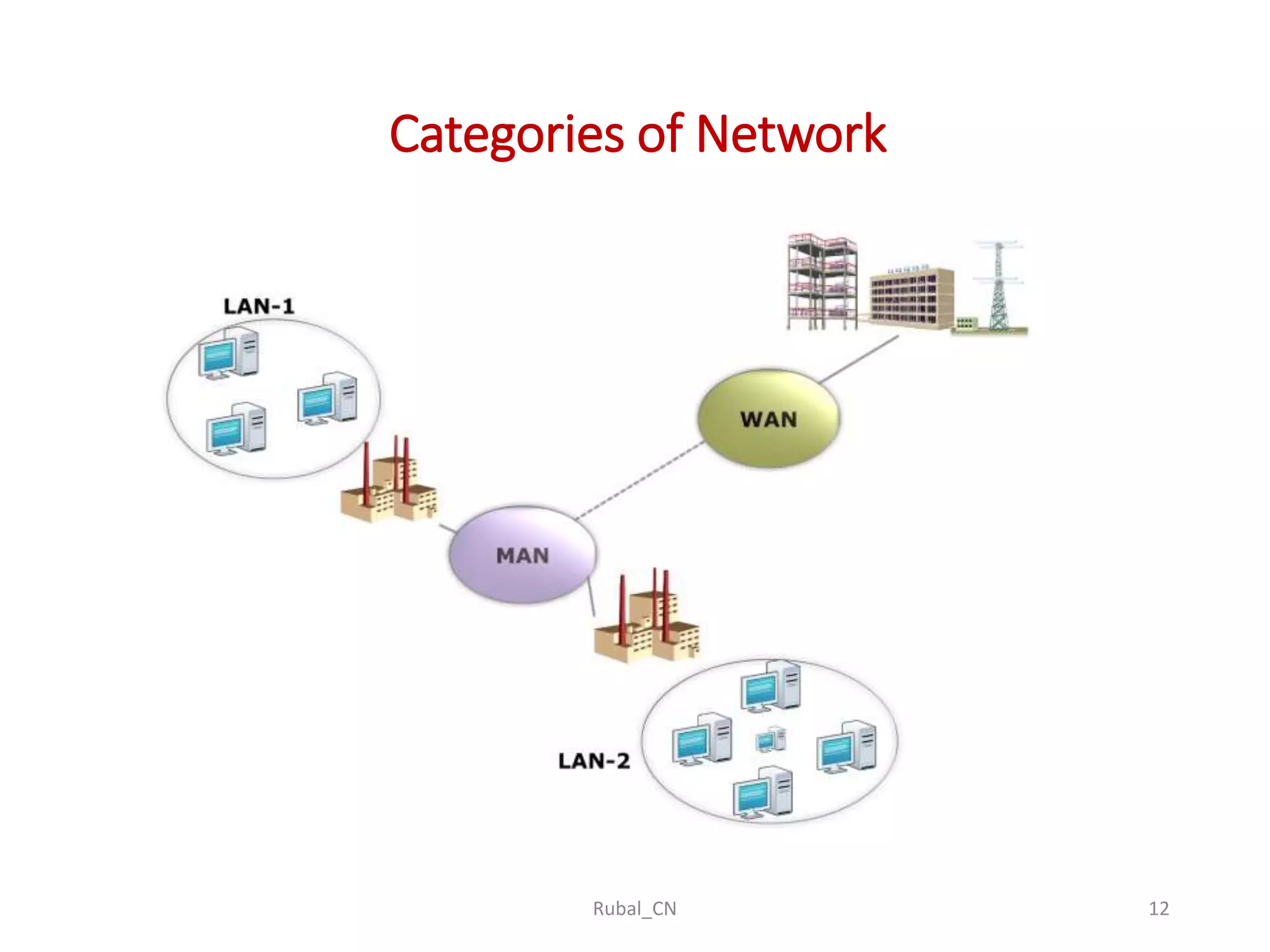
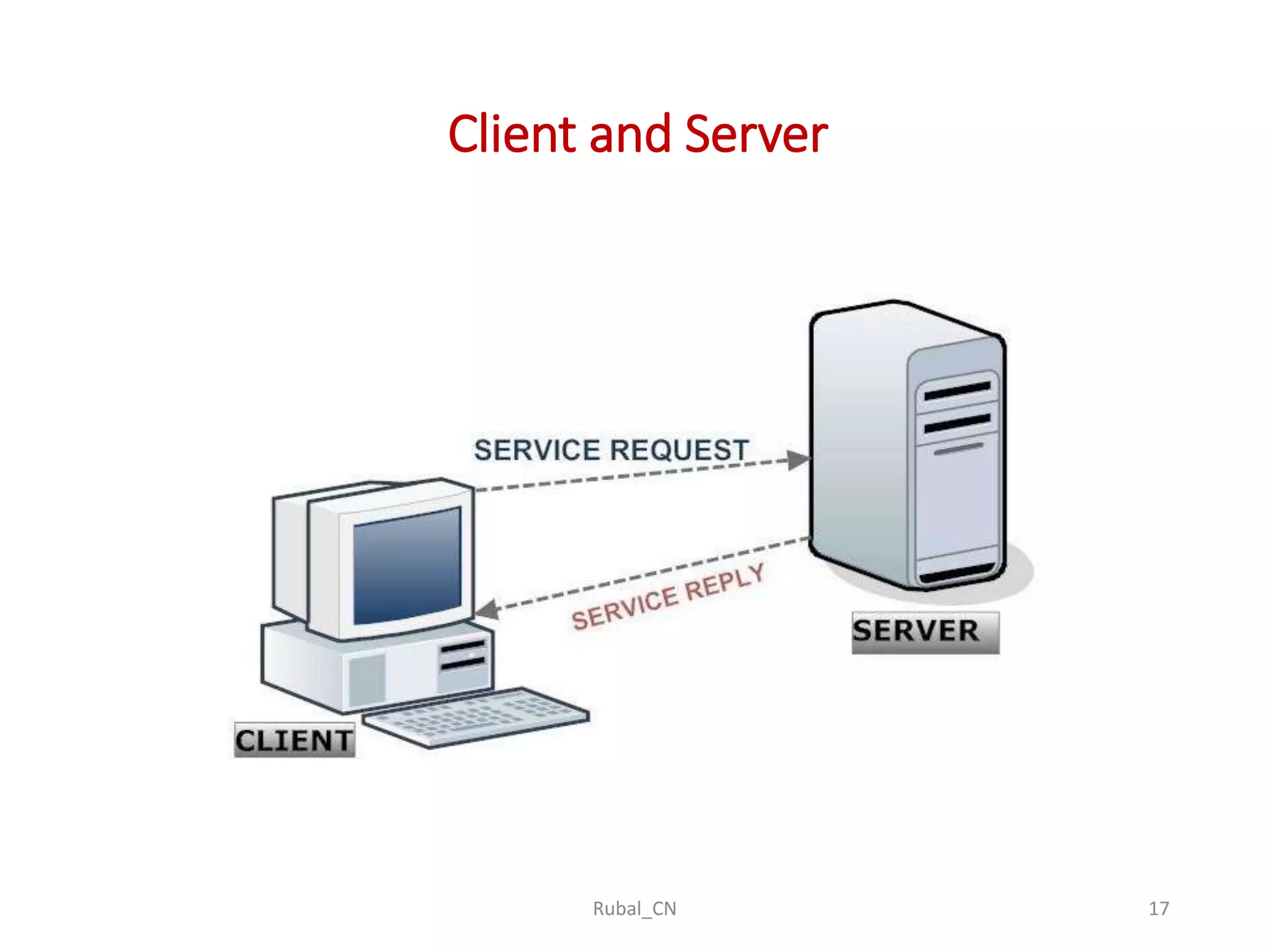
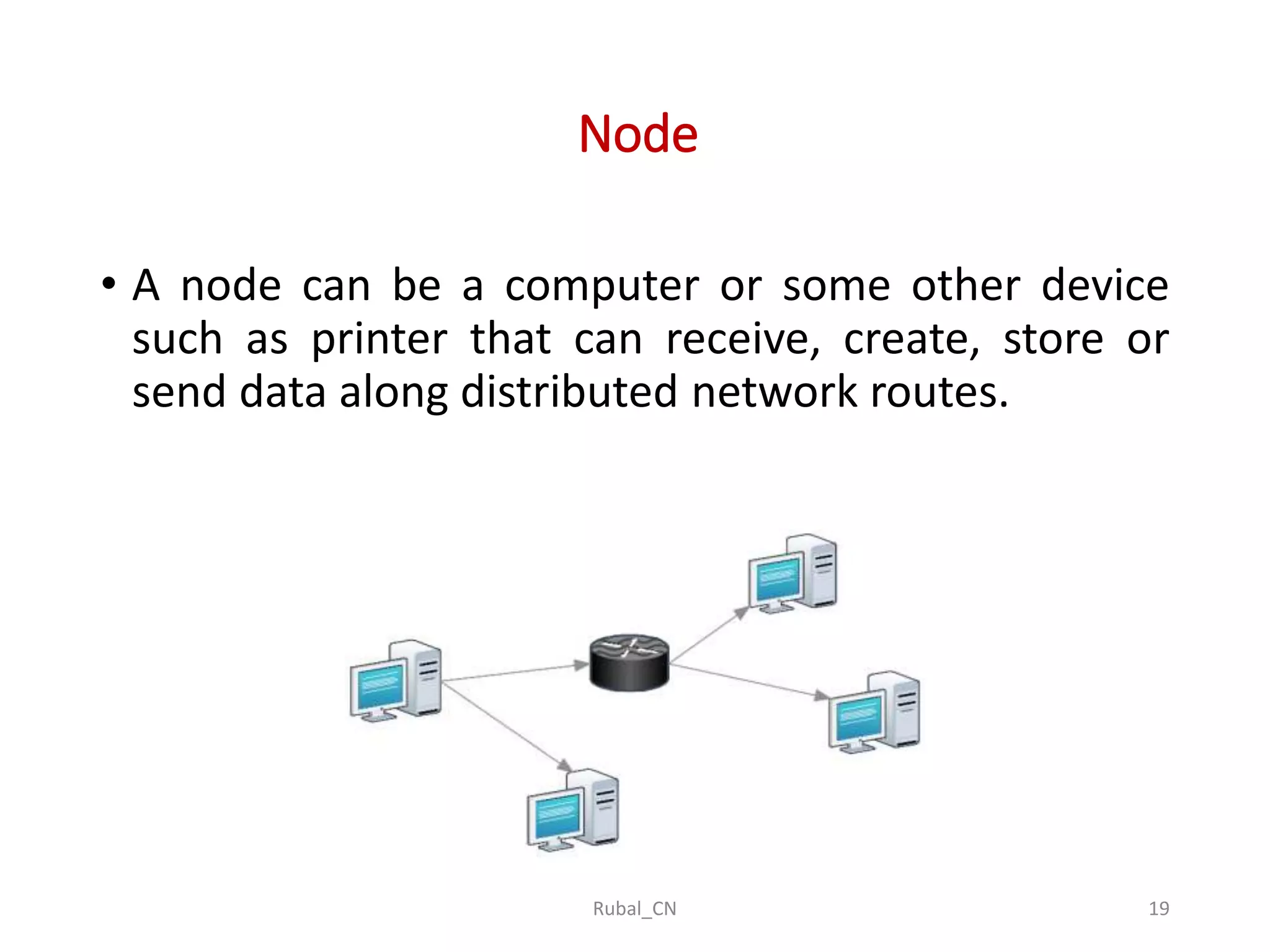
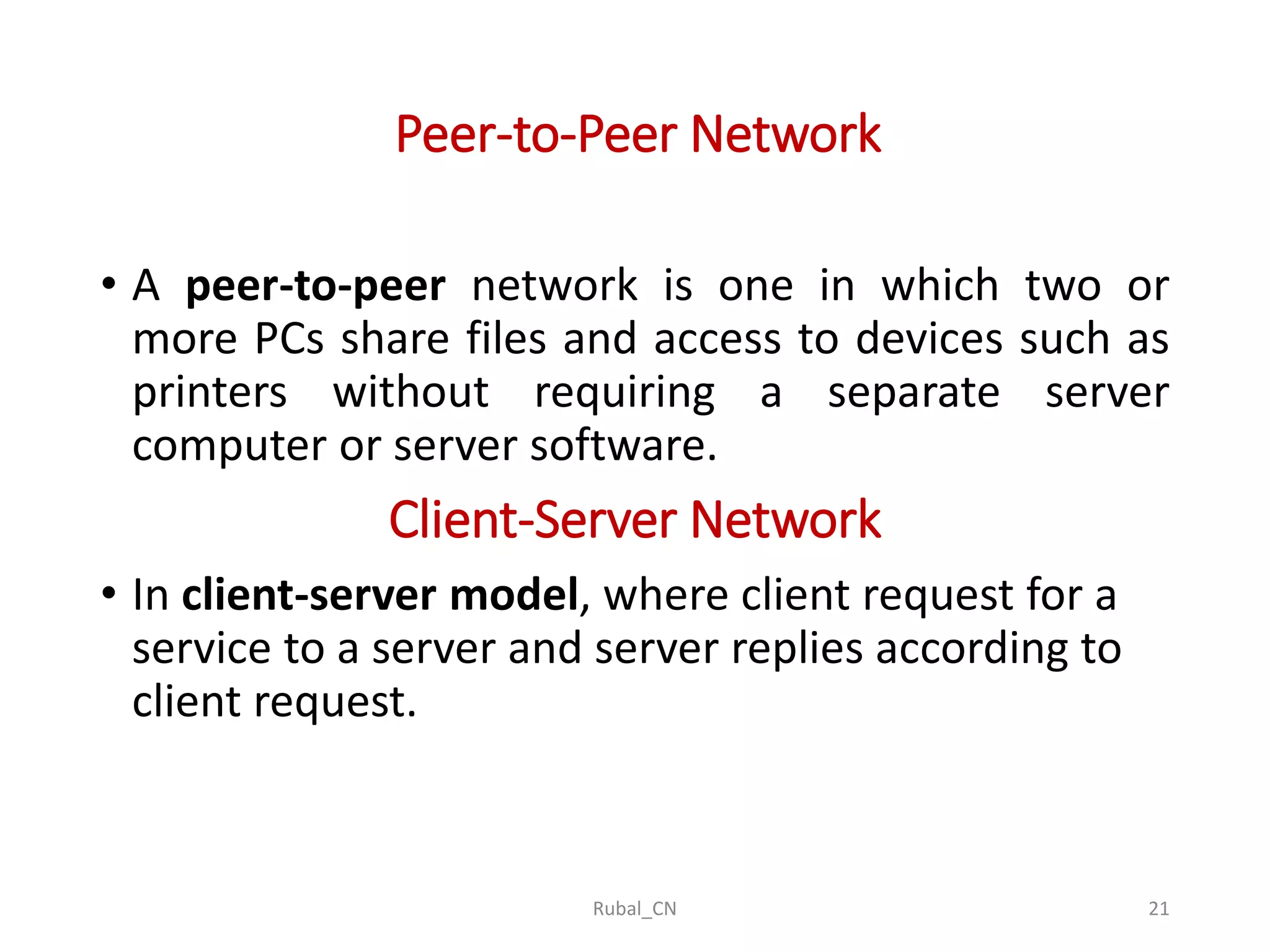
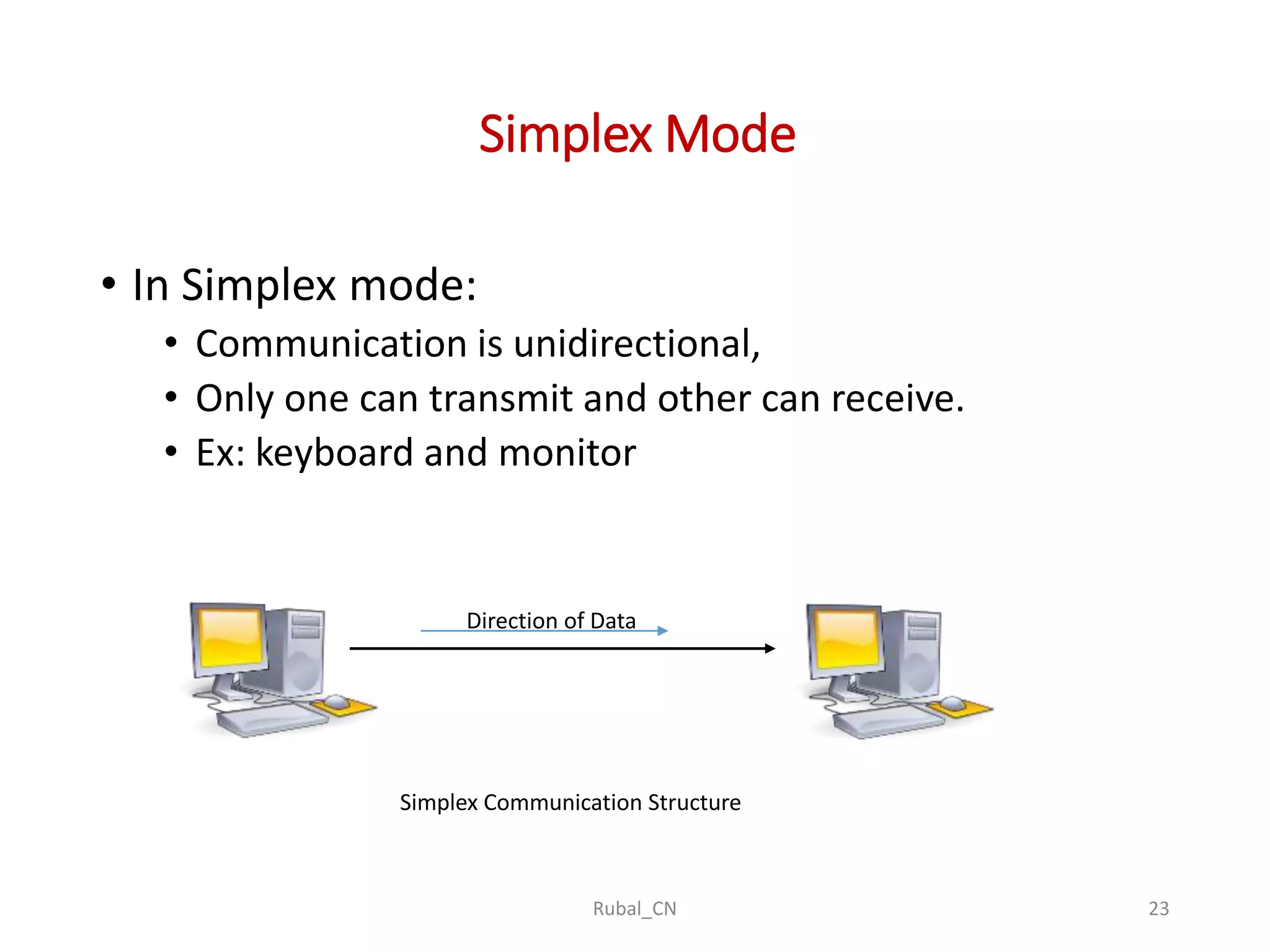
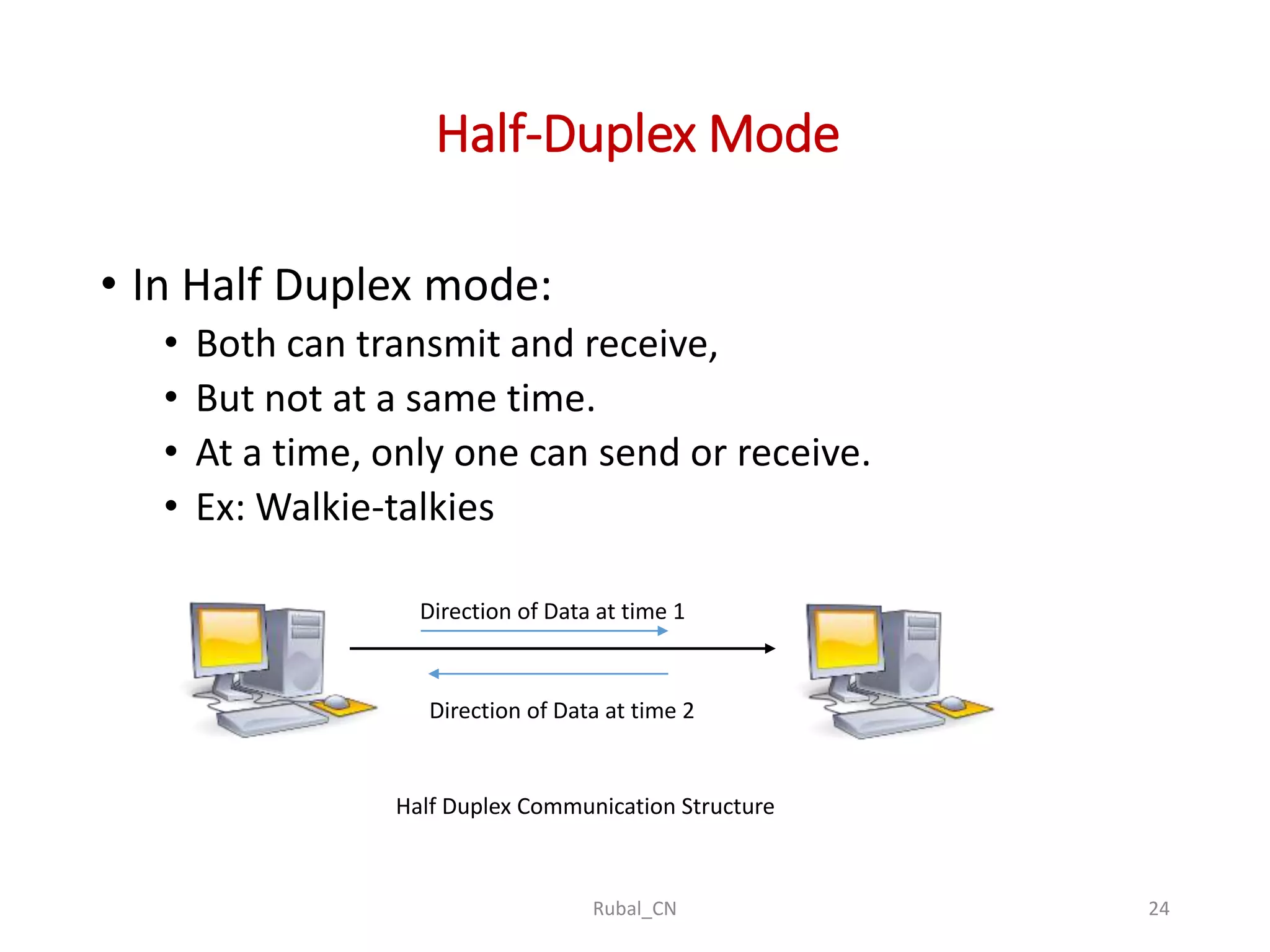
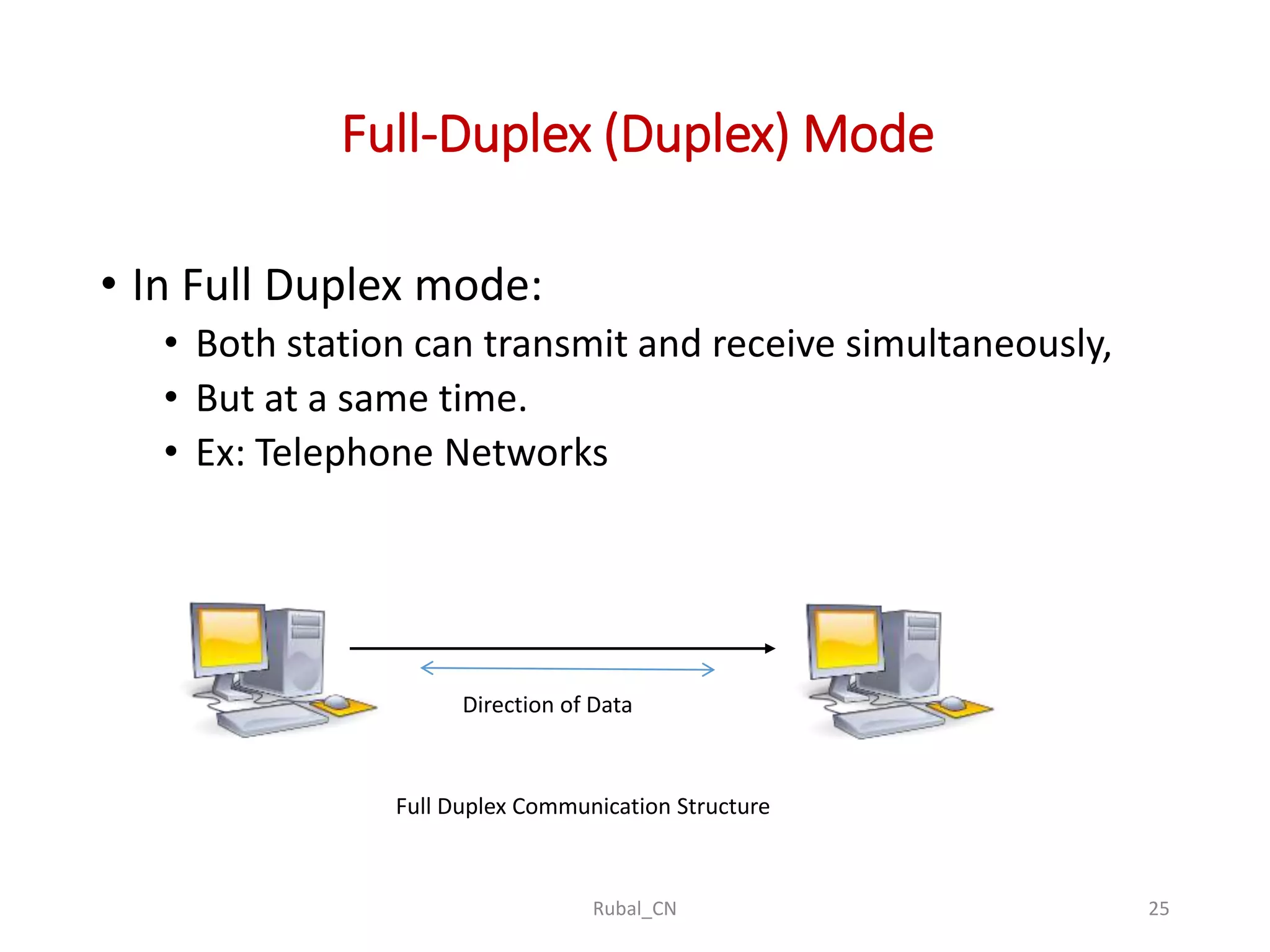
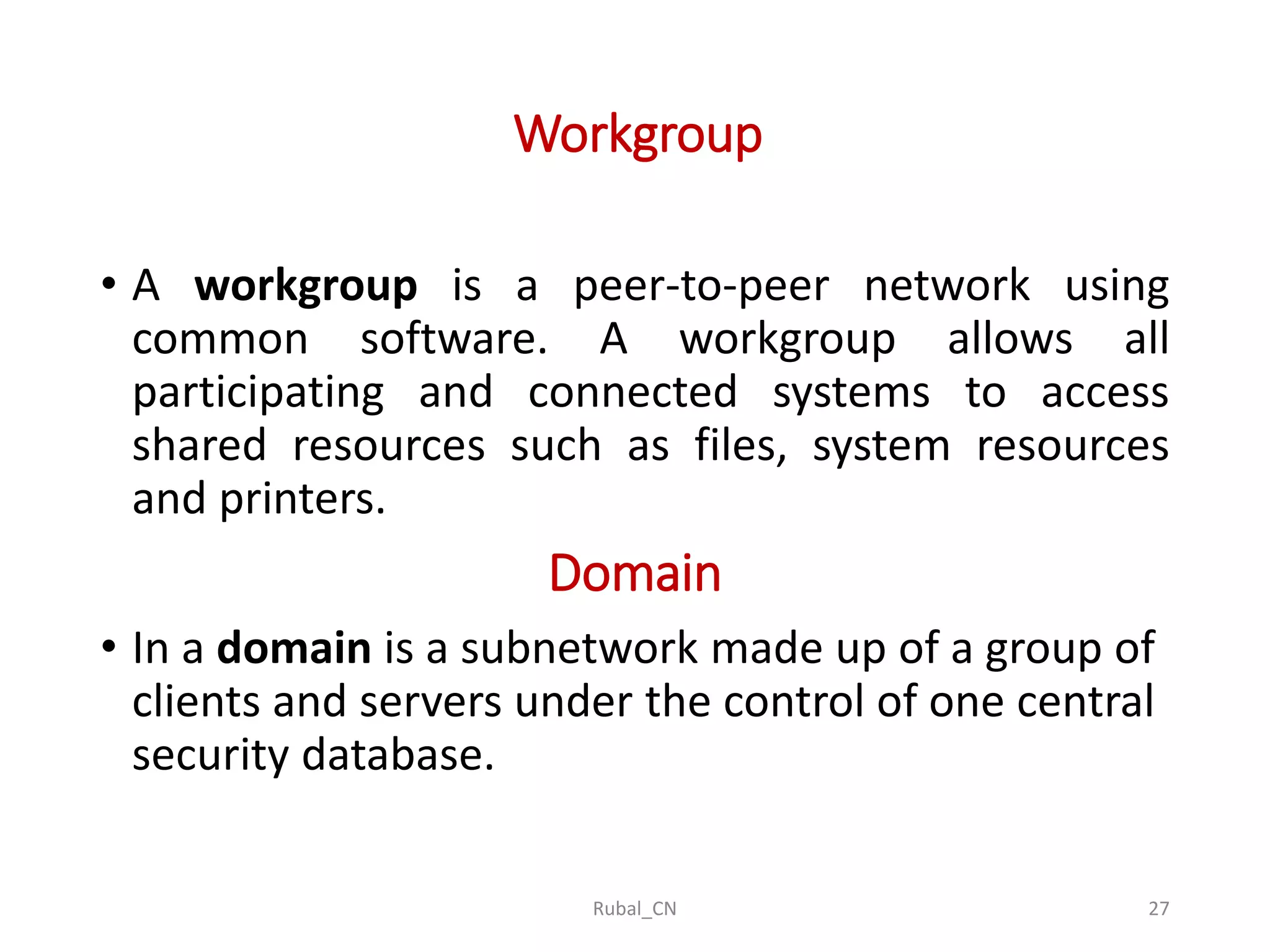
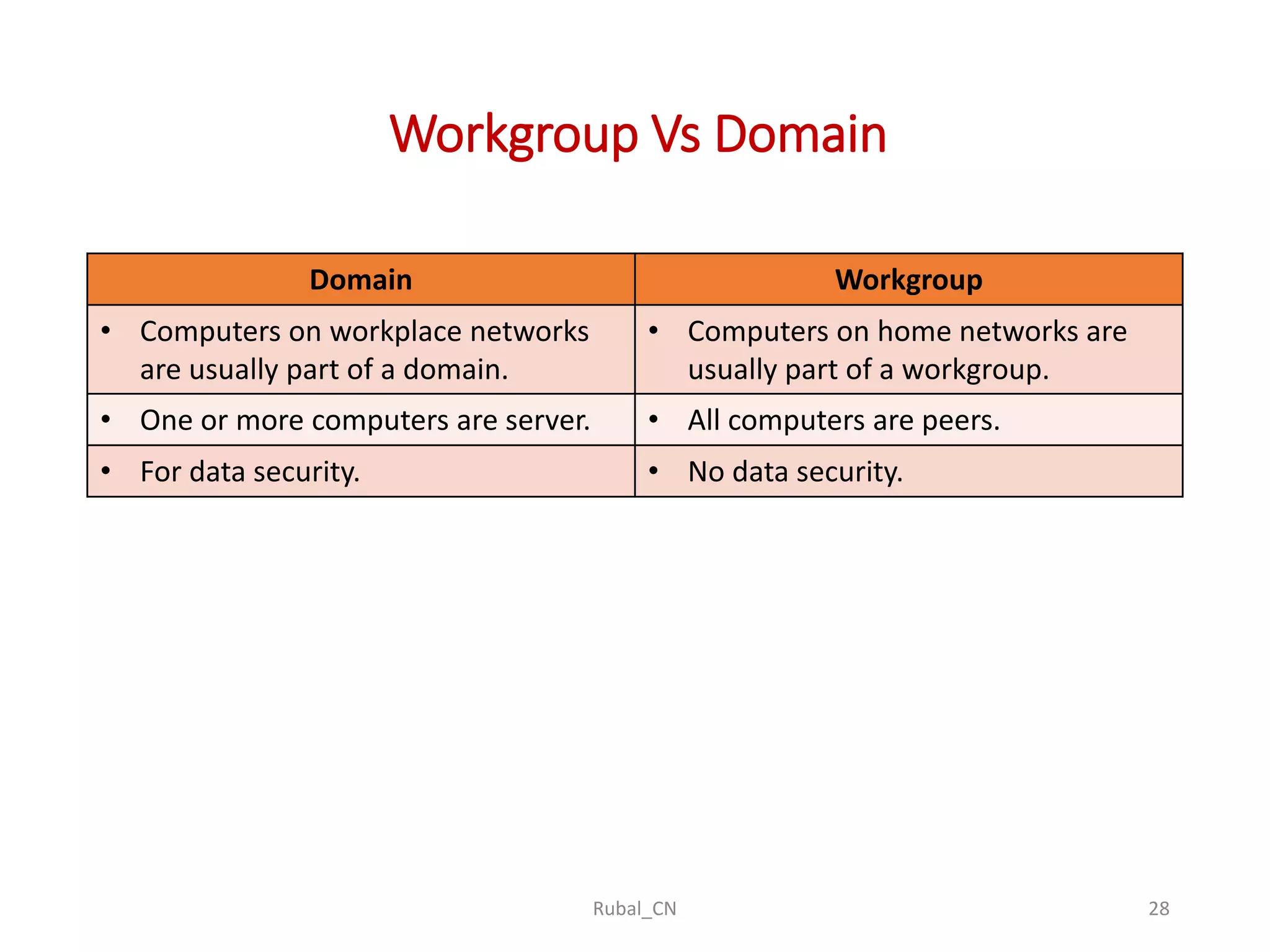
The document provides an overview of computer networks, covering their definition, advantages, and key components such as nodes, hosts, and network types. It discusses various networking models, including peer-to-peer and client-server architectures, as well as data flow modes (simplex, half-duplex, and full duplex). The document also distinguishes between workgroup and domain networks, highlighting their applications in different environments.