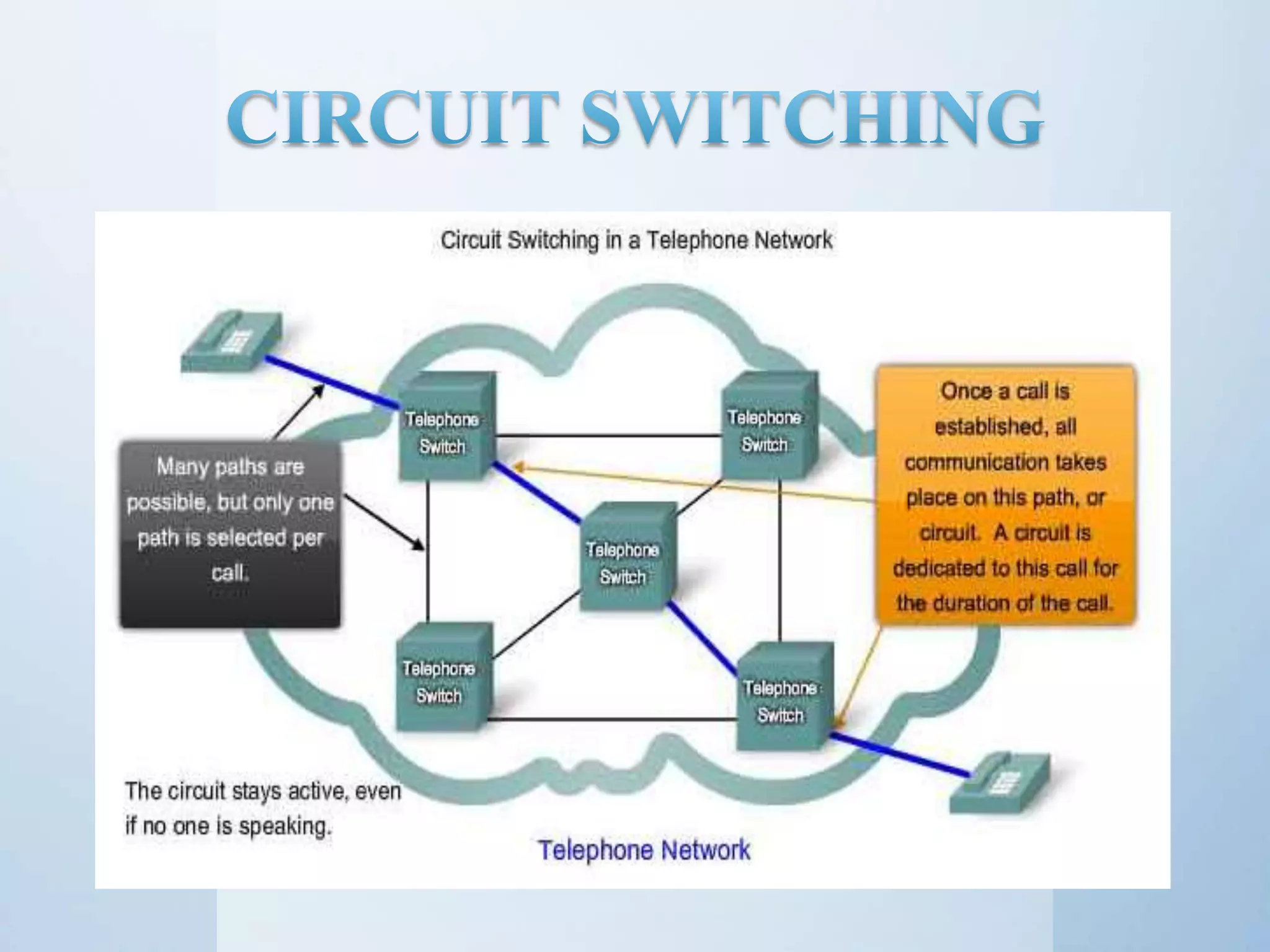
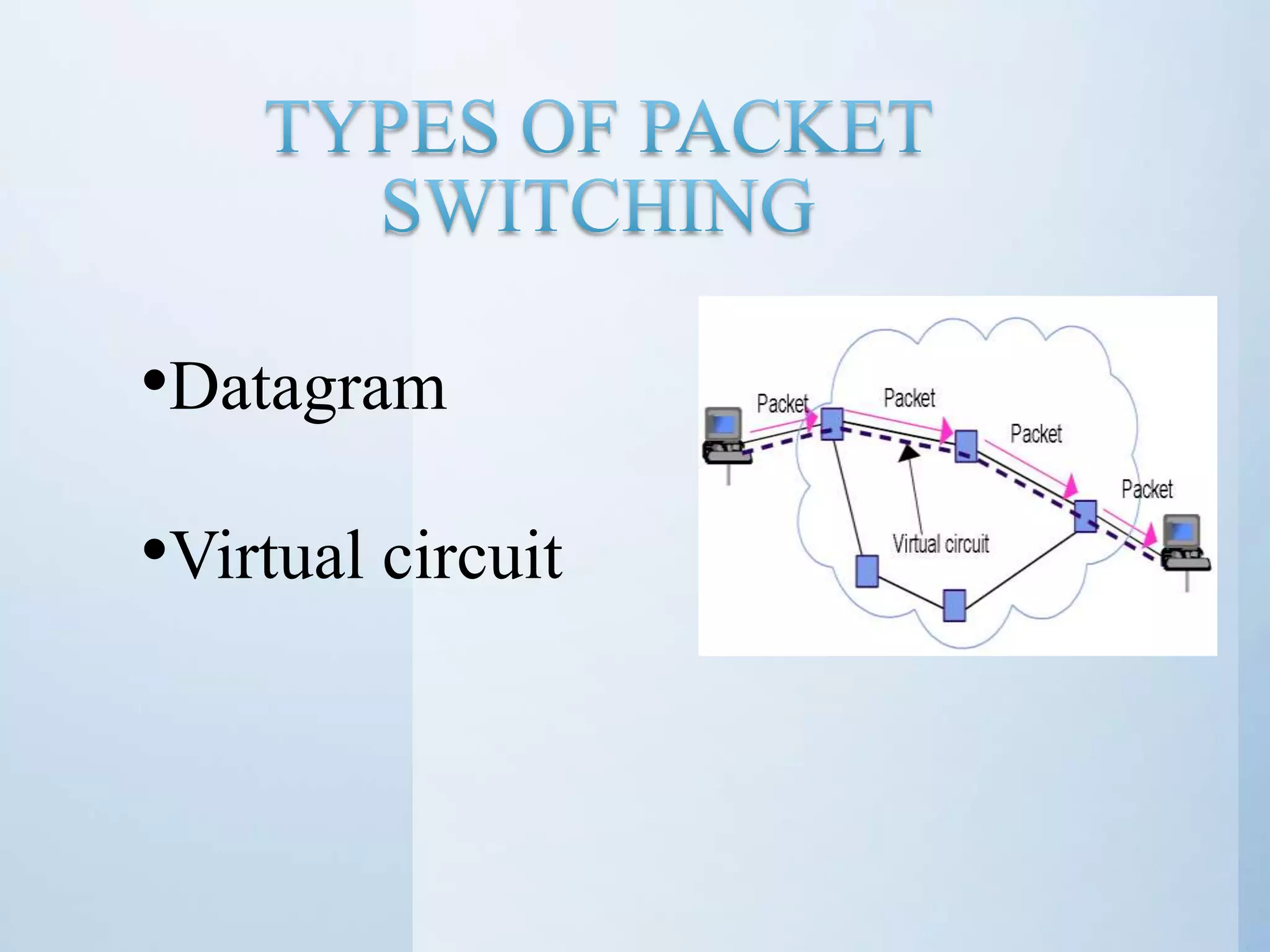
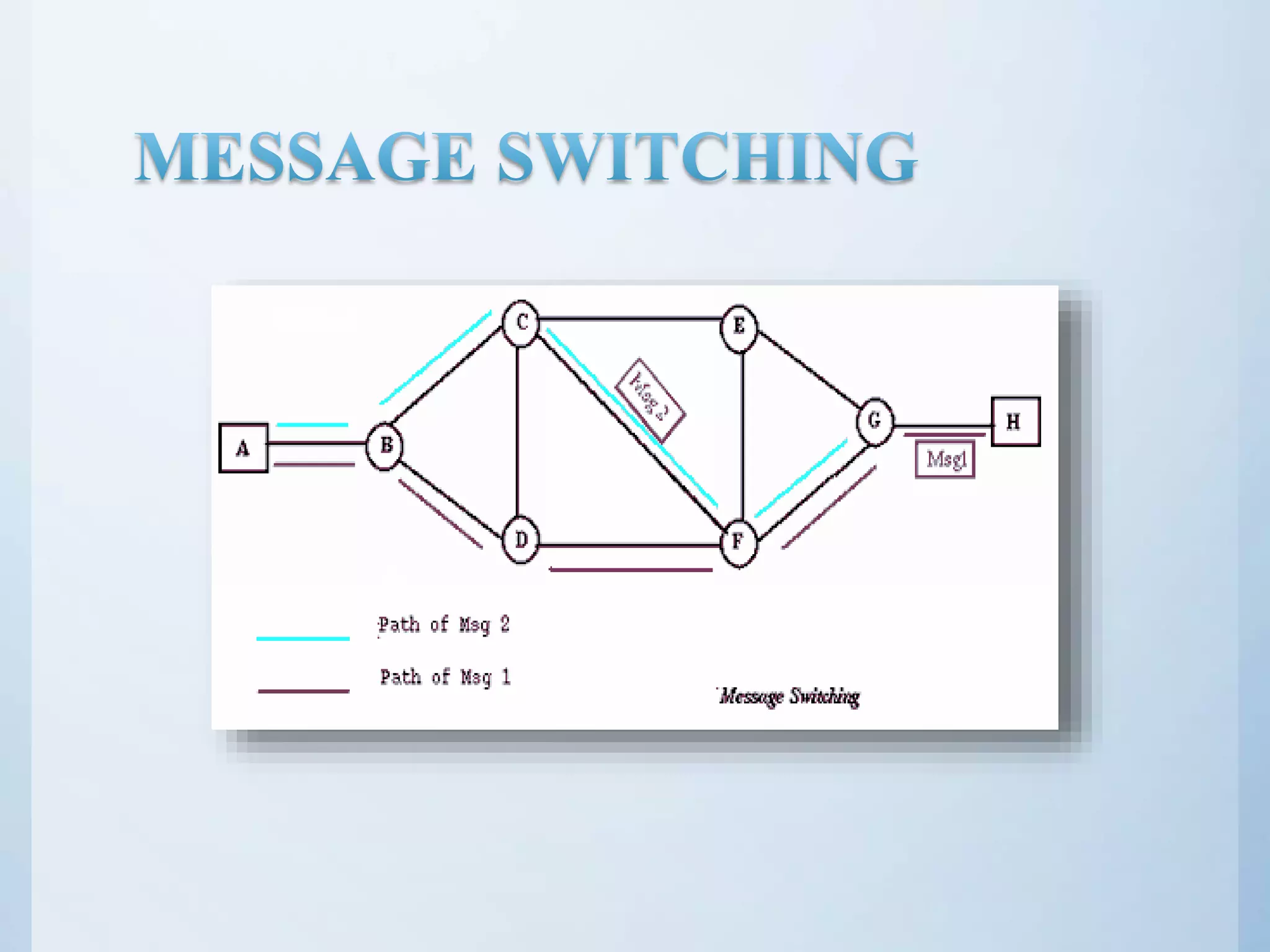
This document discusses different types of network switching: circuit switching, packet switching, and message switching. It describes circuit switching as establishing a dedicated electrical path for communication between two ports. Packet switching breaks communication down into small packets that are routed through the network based on destination addresses. There are two approaches for packet switching - datagram and virtual circuit. Datagram packets can take different paths to the destination while virtual circuit establishes a pre-planned route. Message switching does not establish a dedicated path, and each message is treated independently with the destination address added. The document was submitted by several students to their professor.