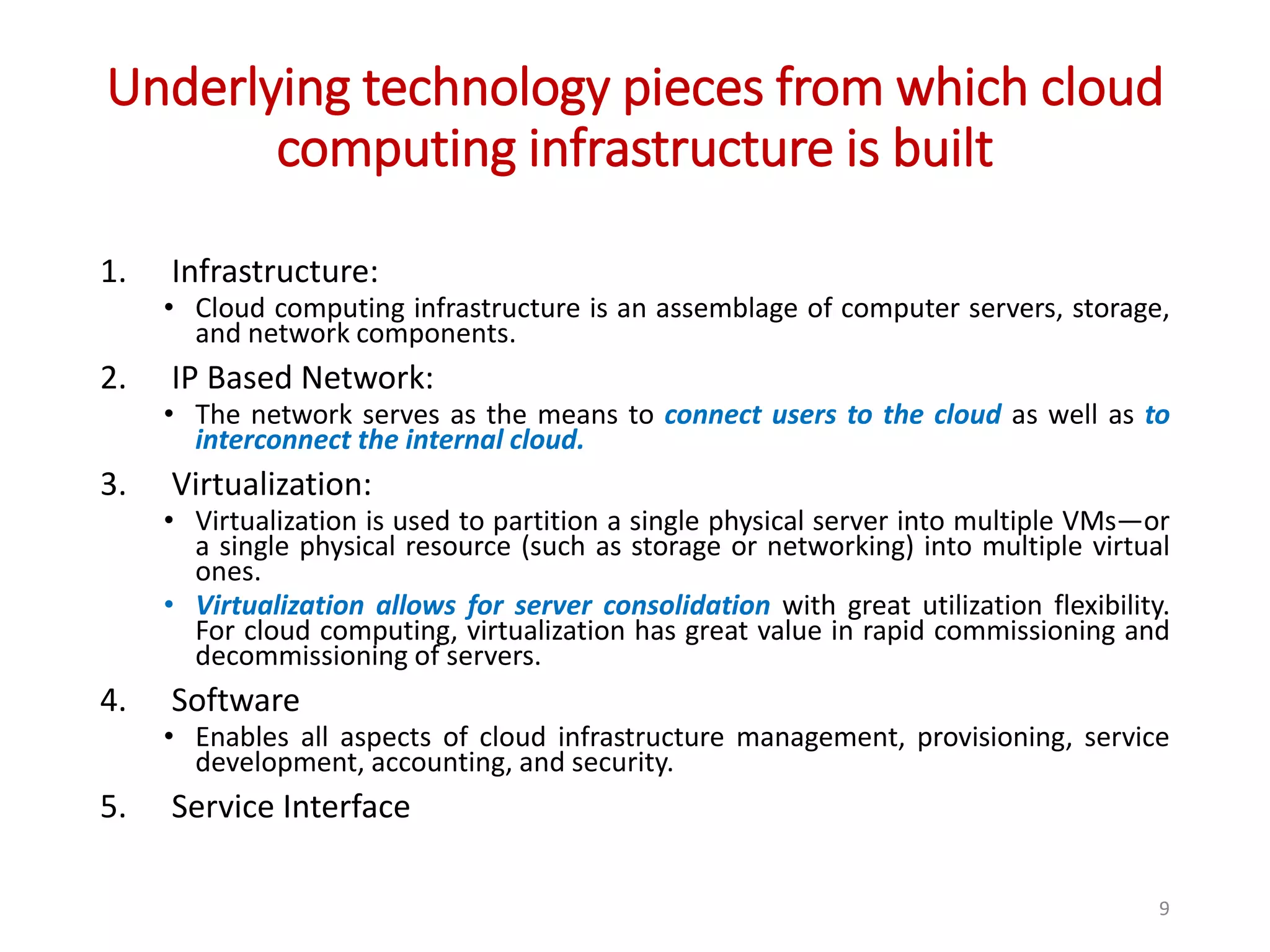
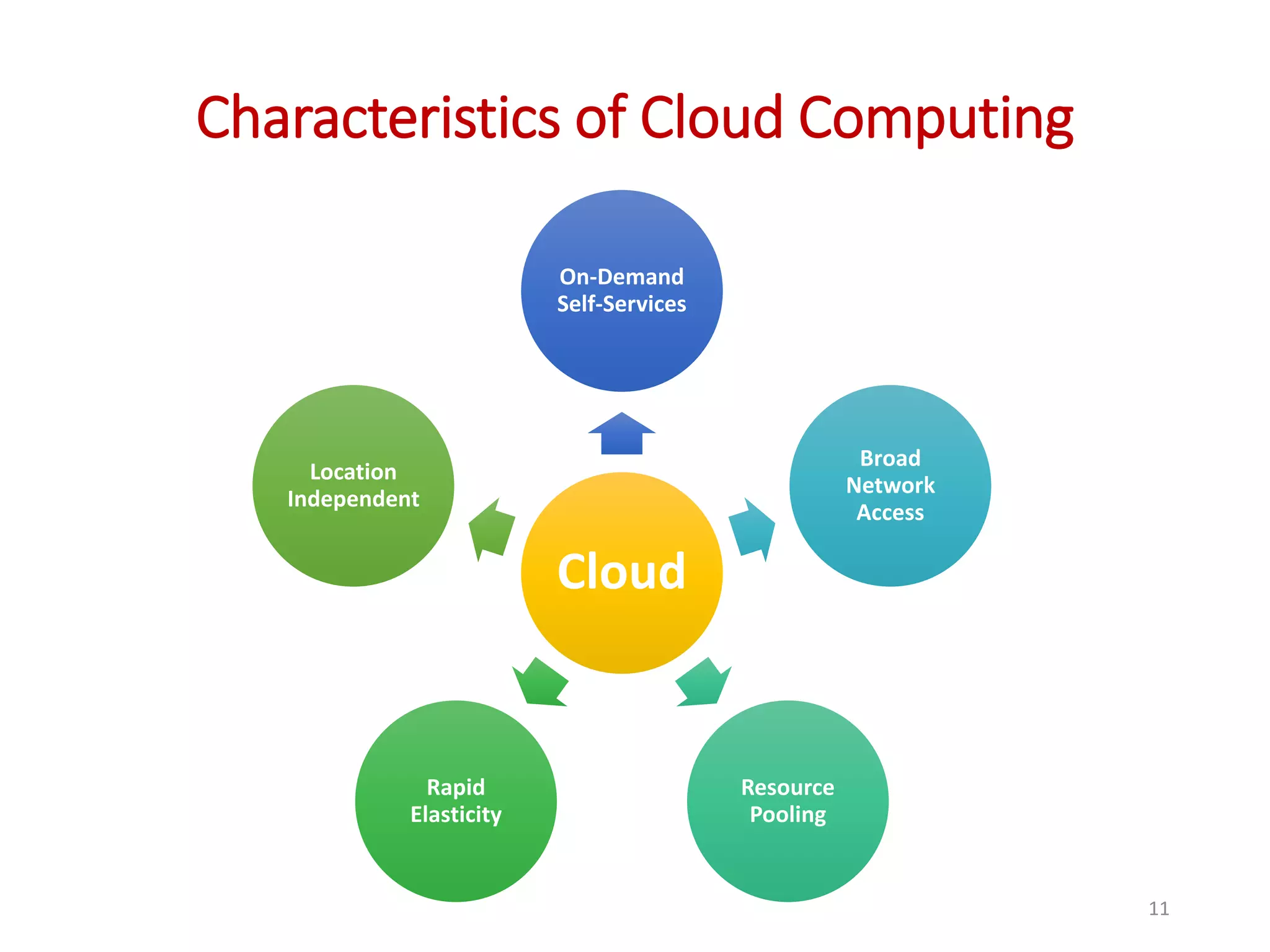
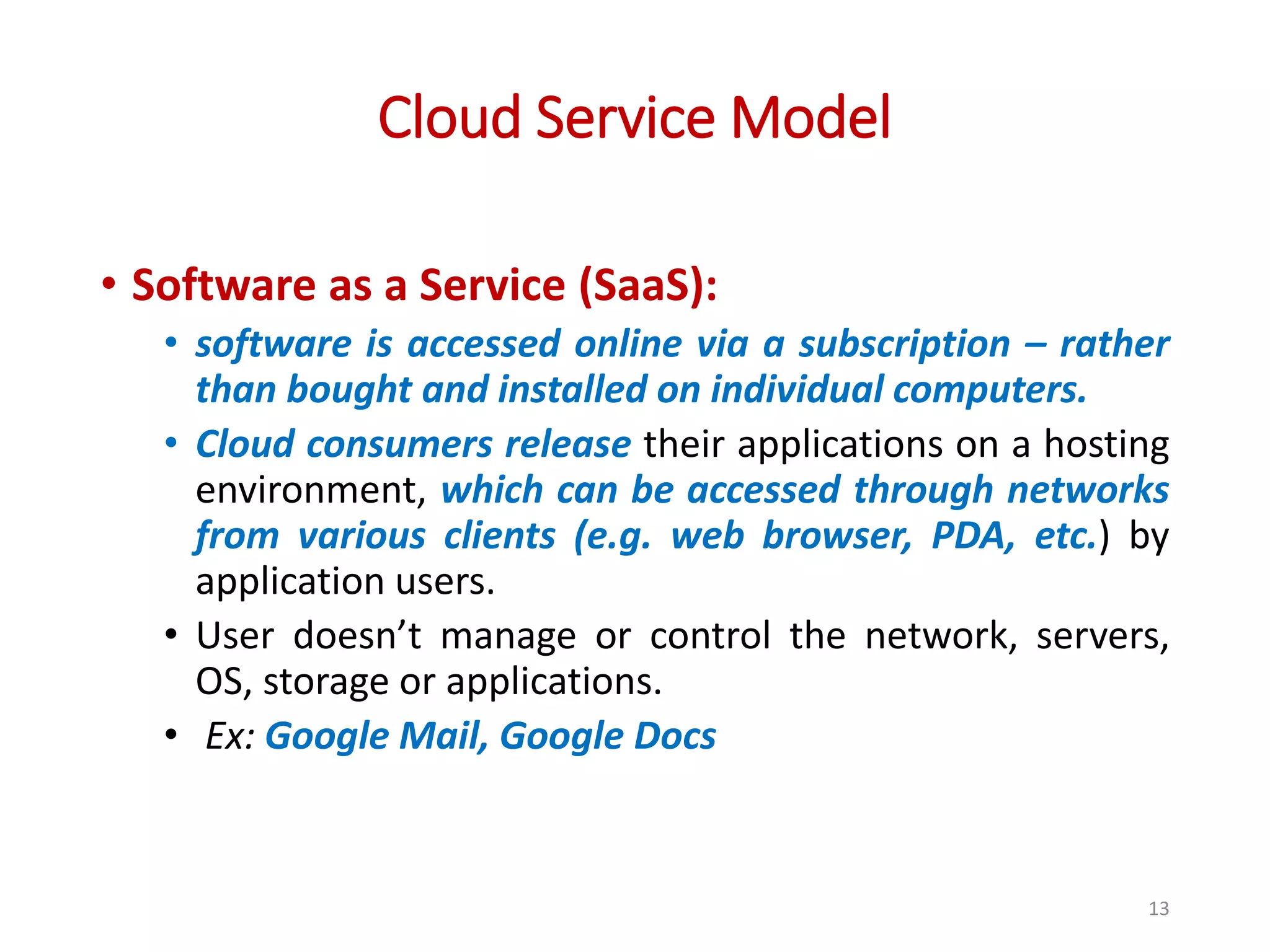
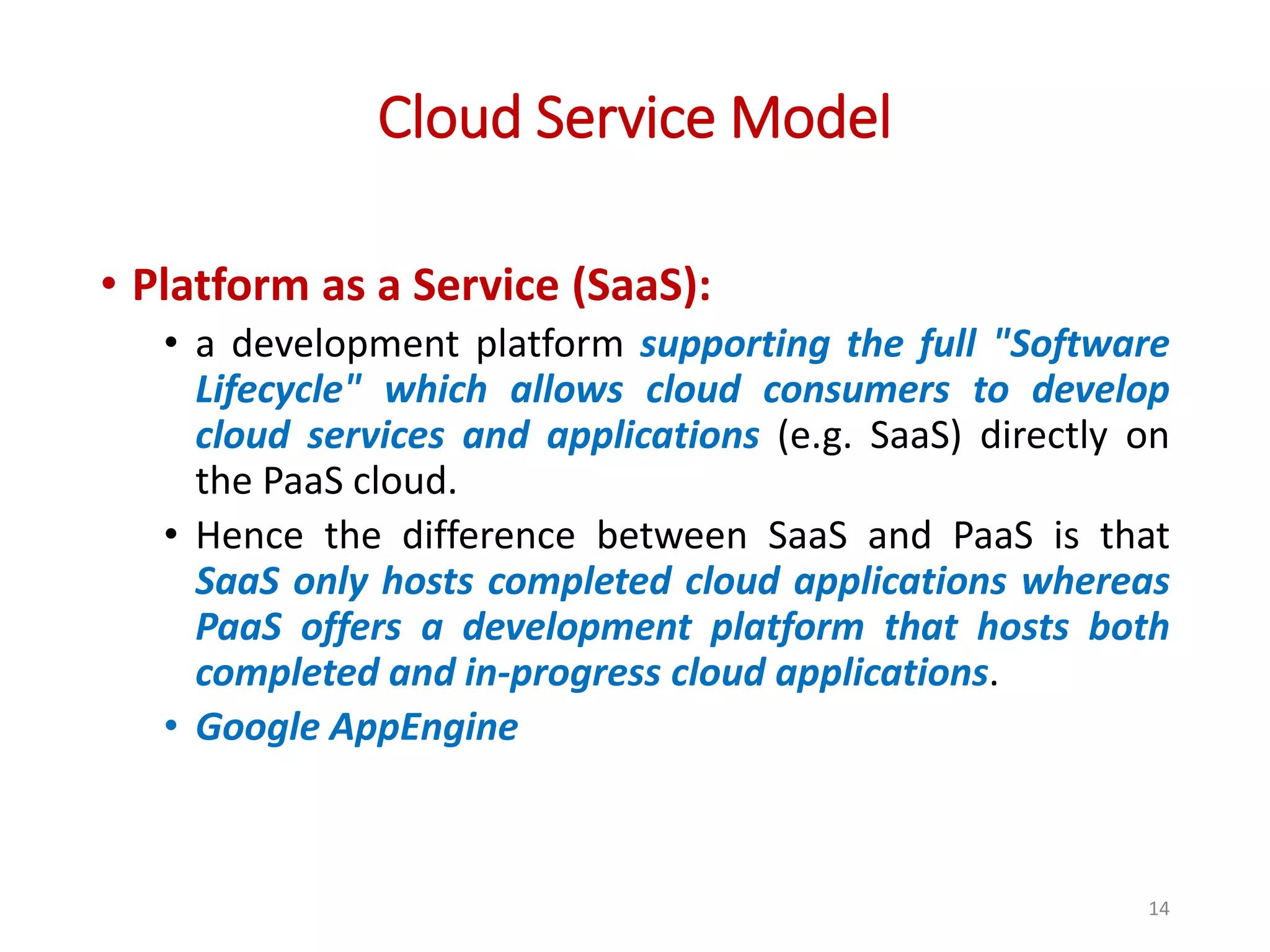
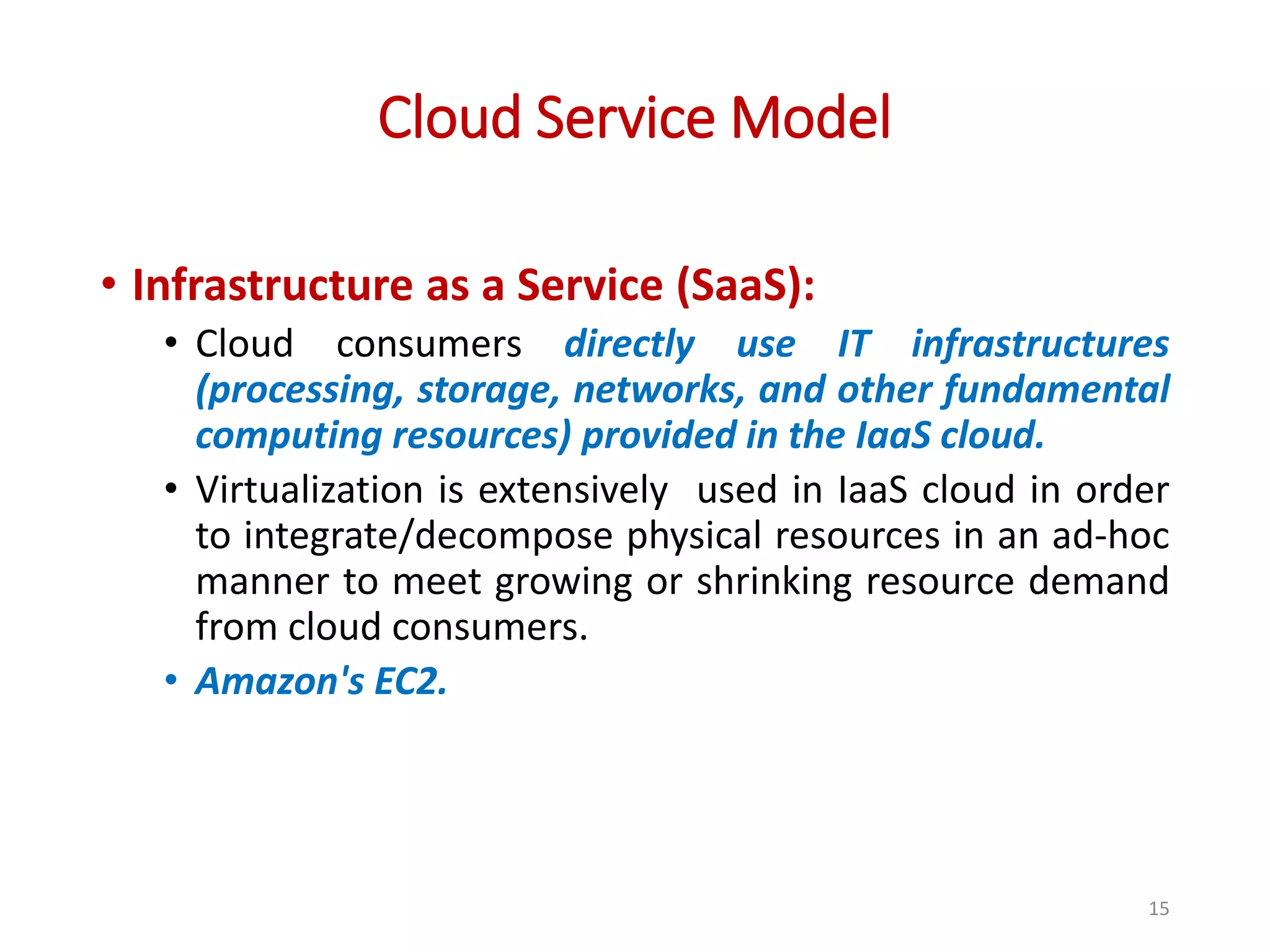
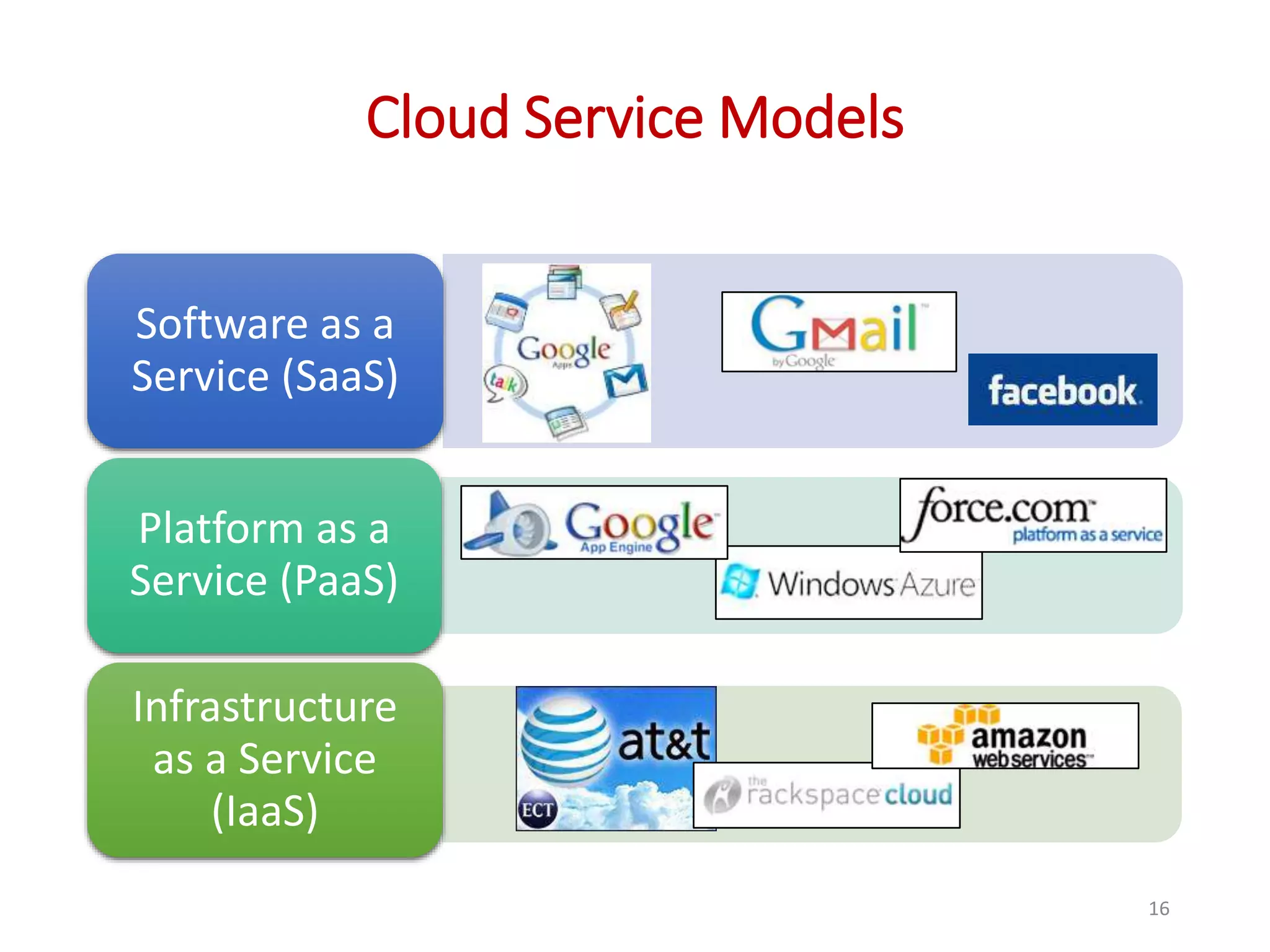
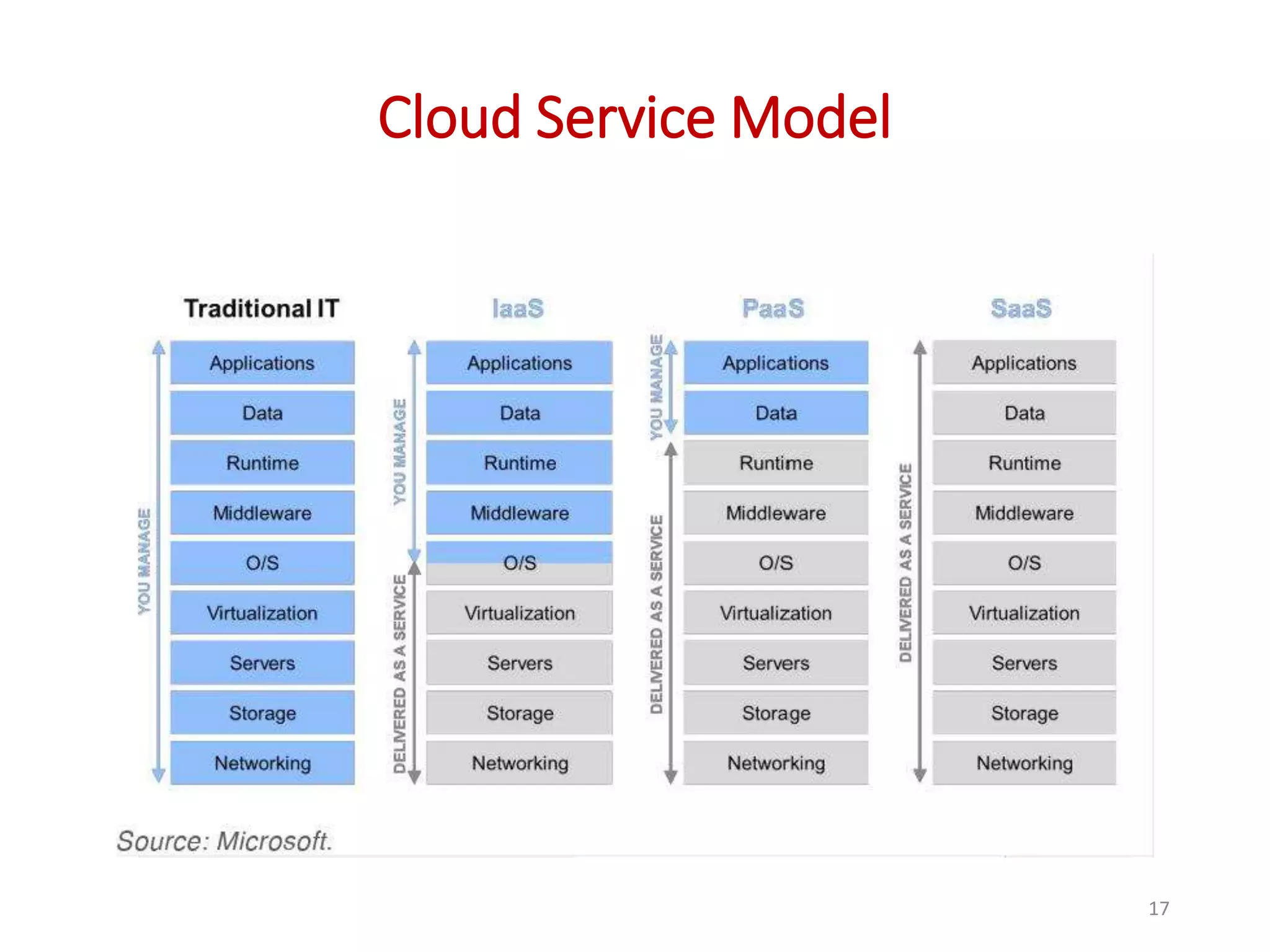
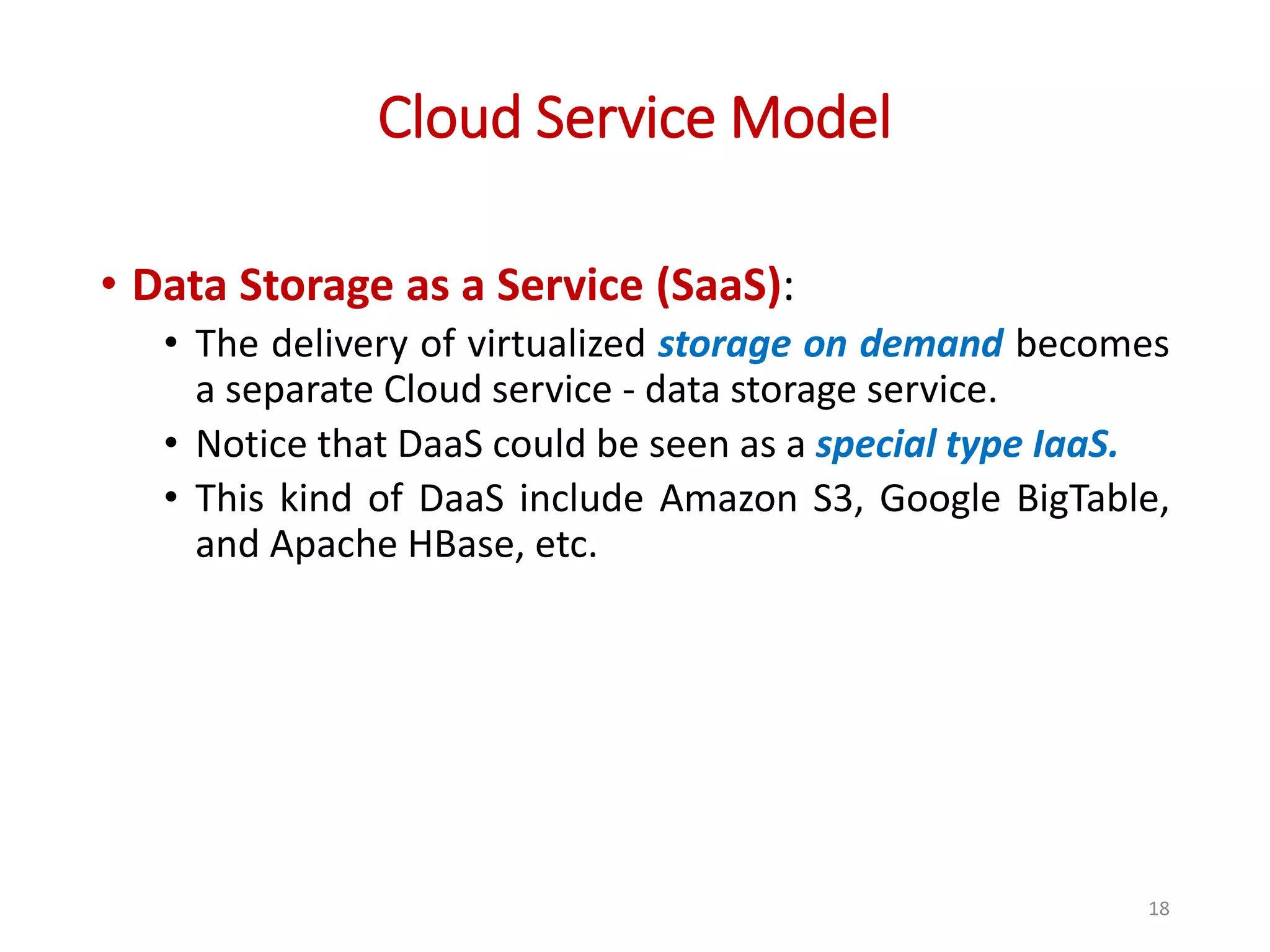
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, detailing its characteristics, service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), and deployment models (private, community, public, and hybrid clouds). It emphasizes the significance of virtualization in enabling cloud services, highlighting its role in resource sharing, scalability, and flexibility. Additionally, the document discusses real-world applications of cloud services and the complexities of security in a virtualized environment.