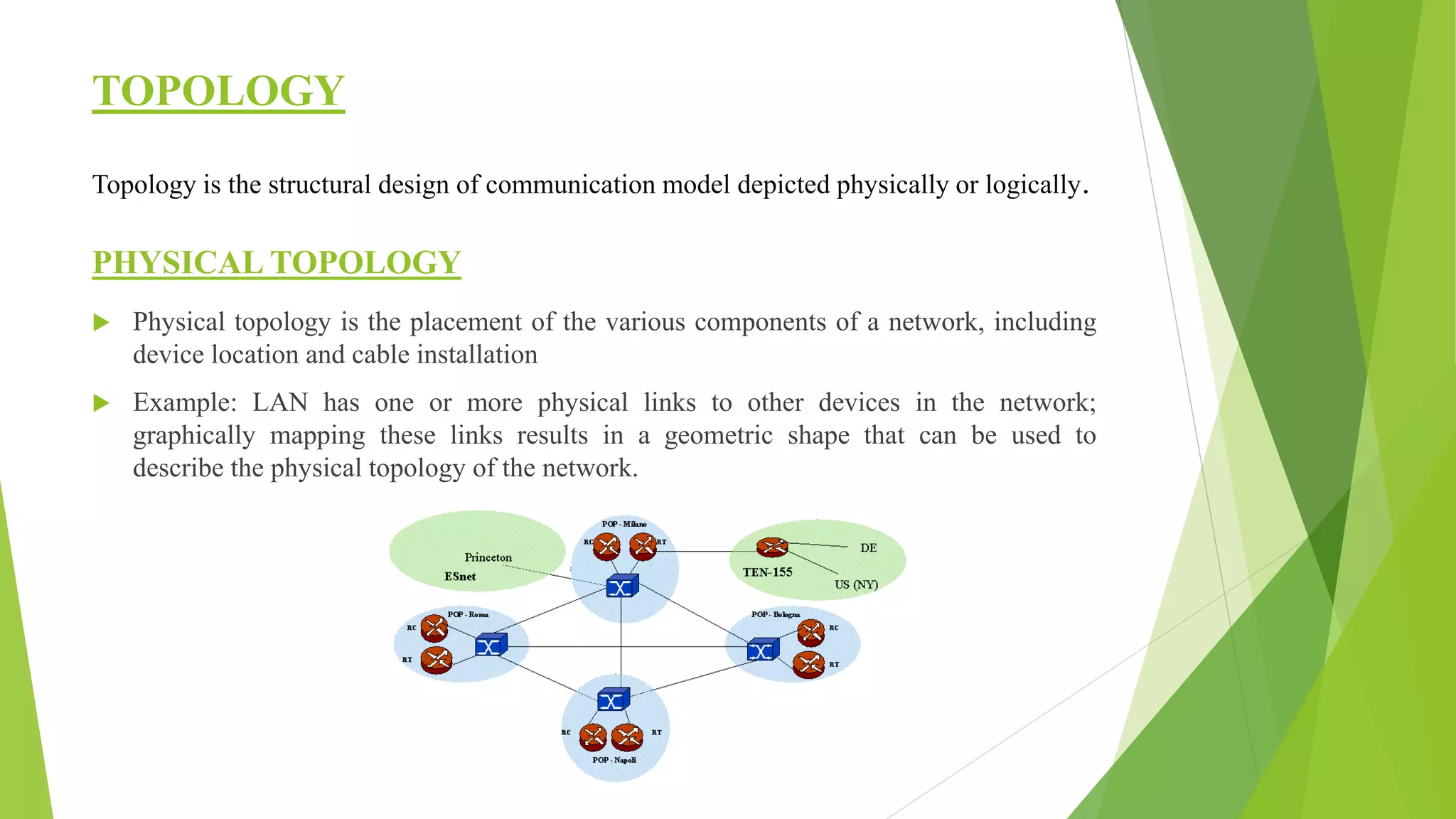
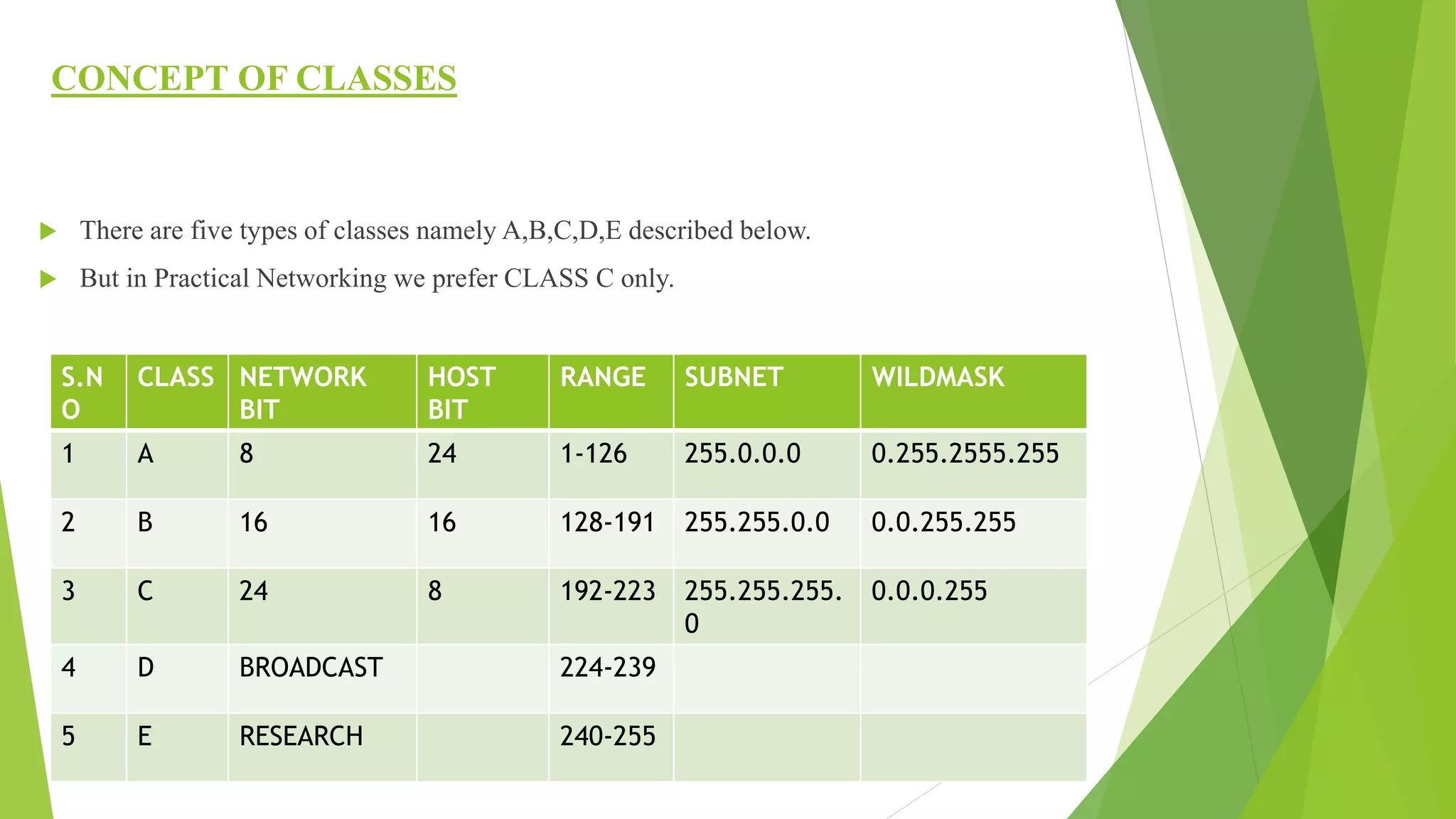
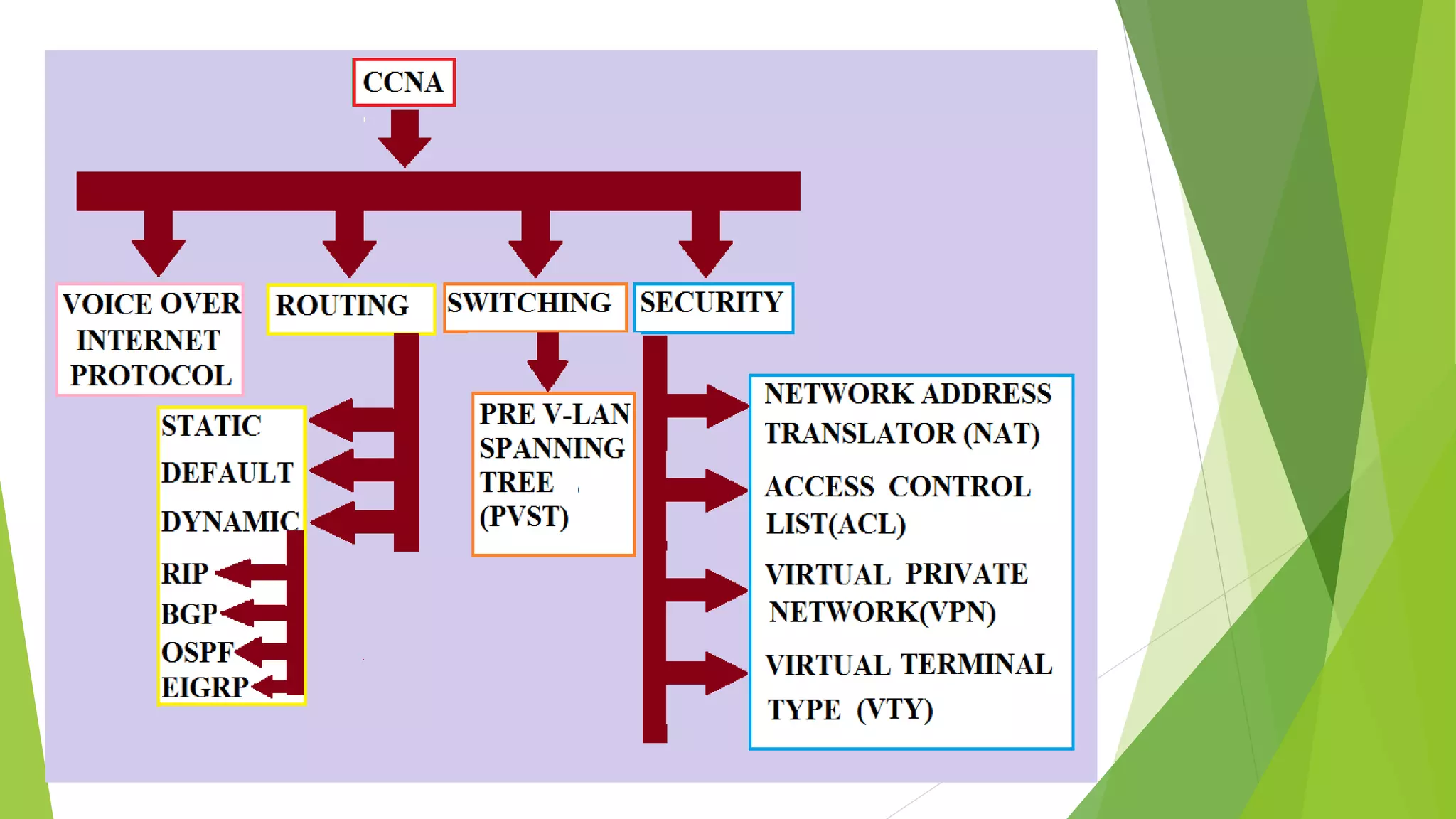
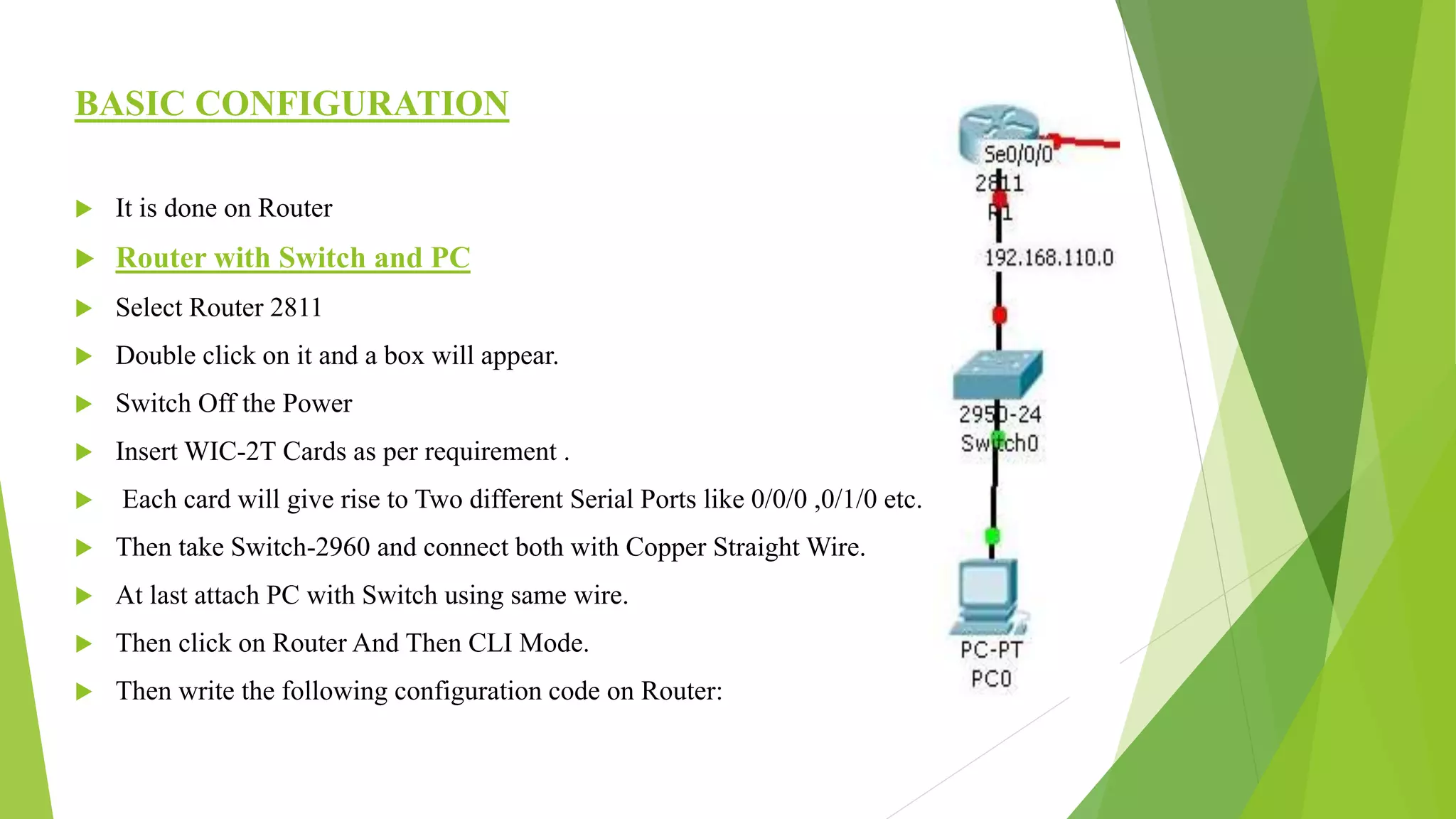
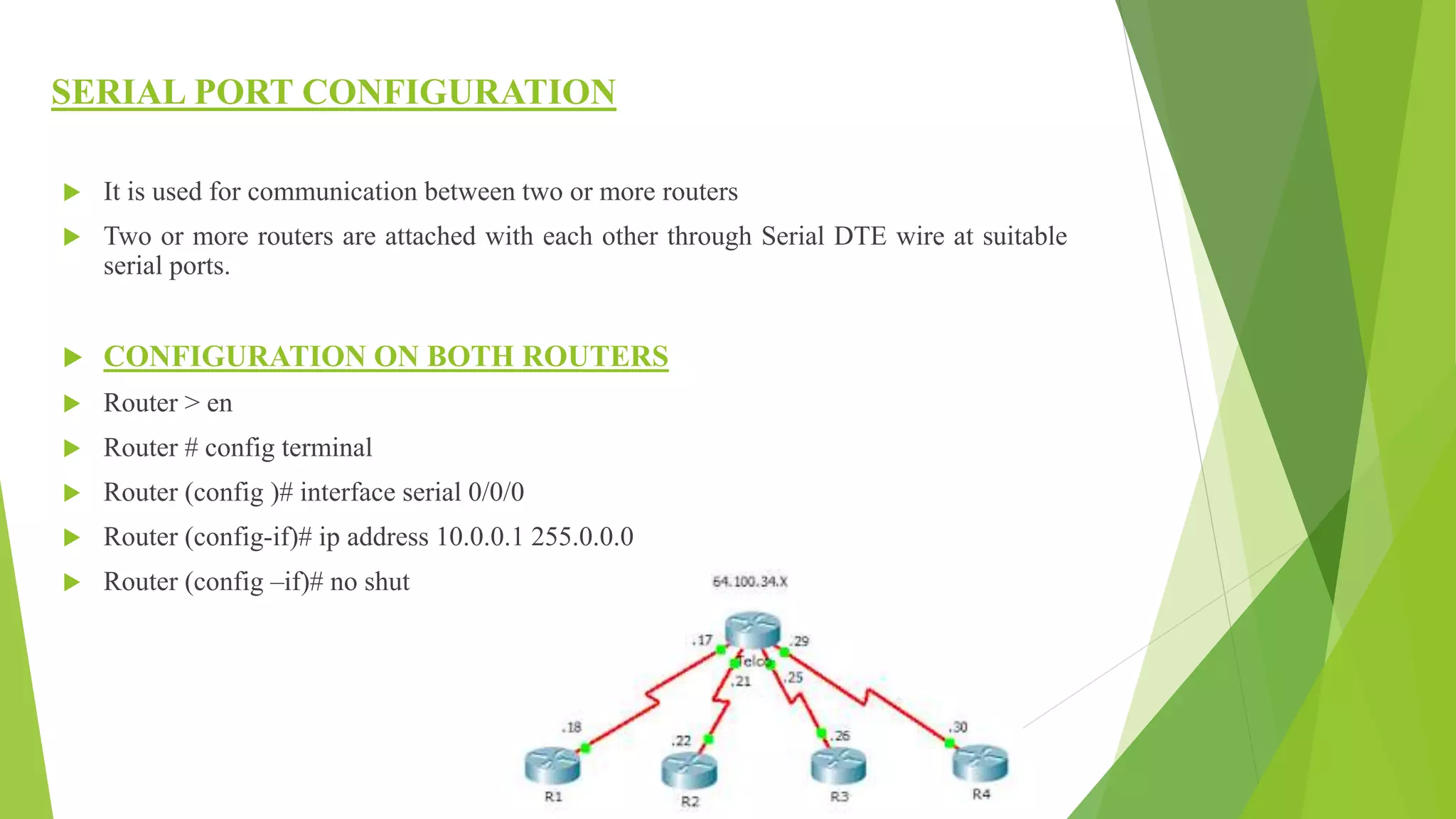
The document provides a comprehensive overview of networking principles, including basic concepts such as topologies, protocols, and routing technologies. It covers topics from physical and logical topologies to advanced networking involving routers, switches, IP addressing, and subnetting, as well as security measures such as ACLs and VPNs. The content is aimed at educating readers on various networking environments and configurations, primarily using Cisco equipment and protocols.