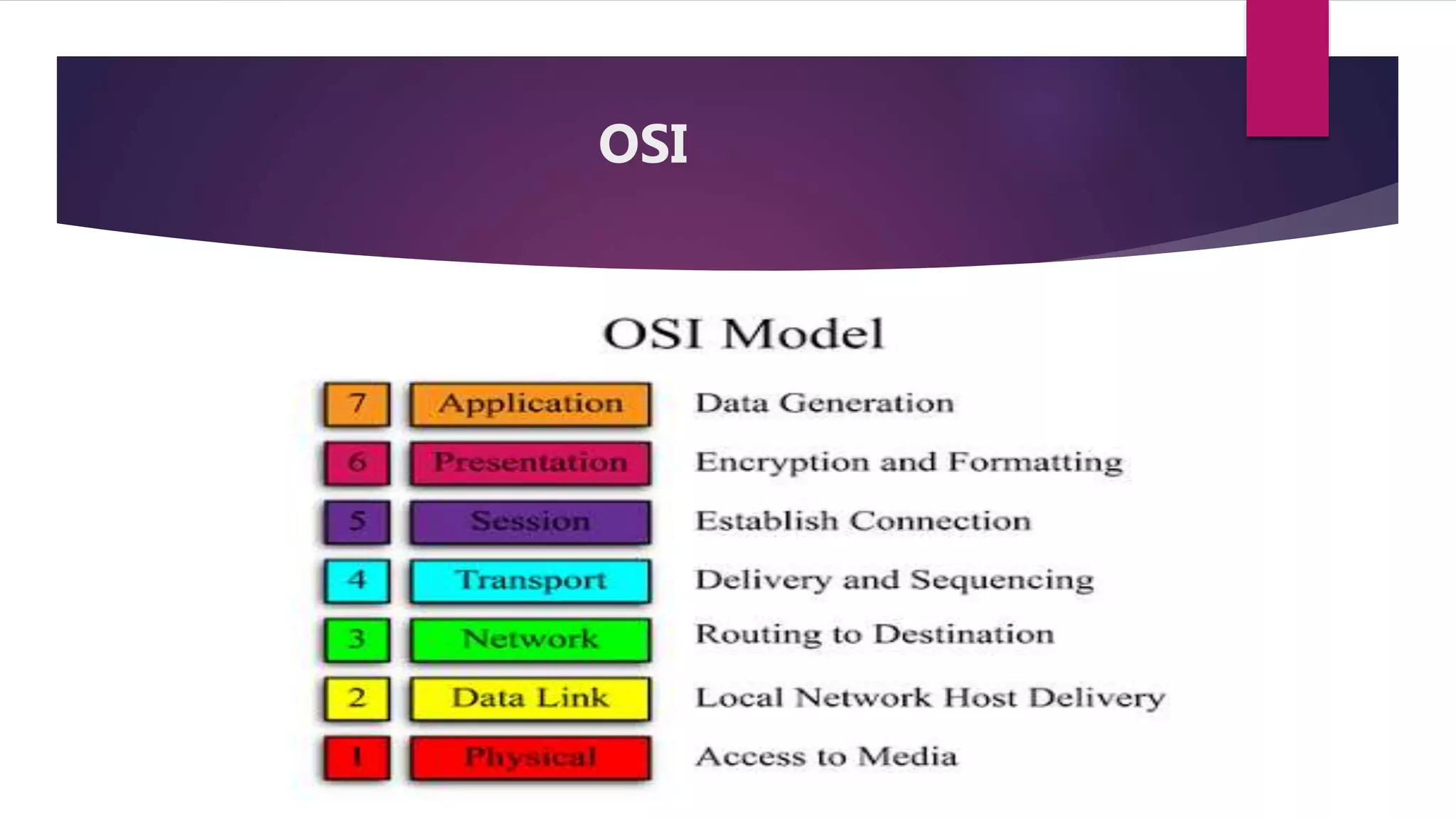
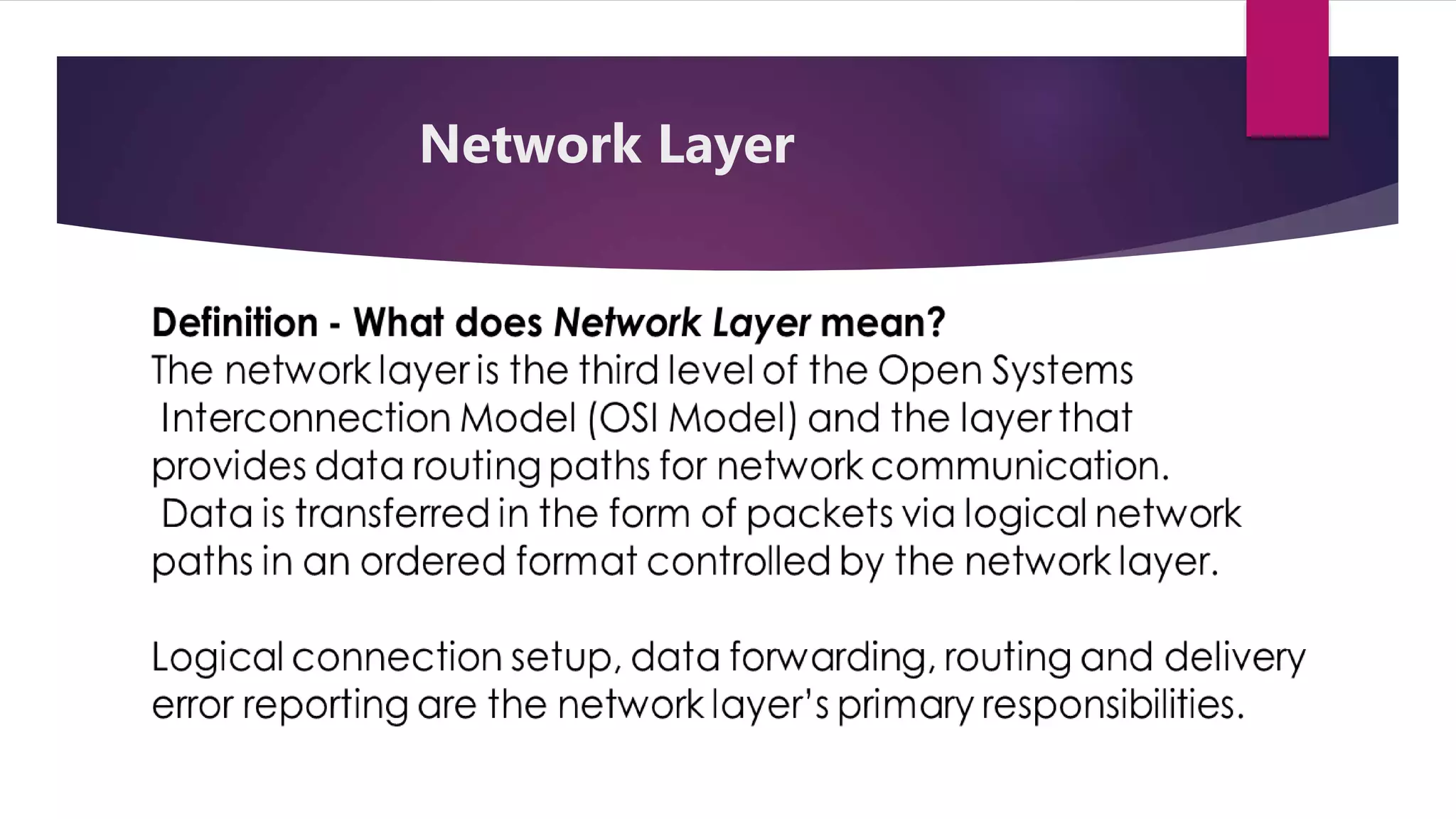
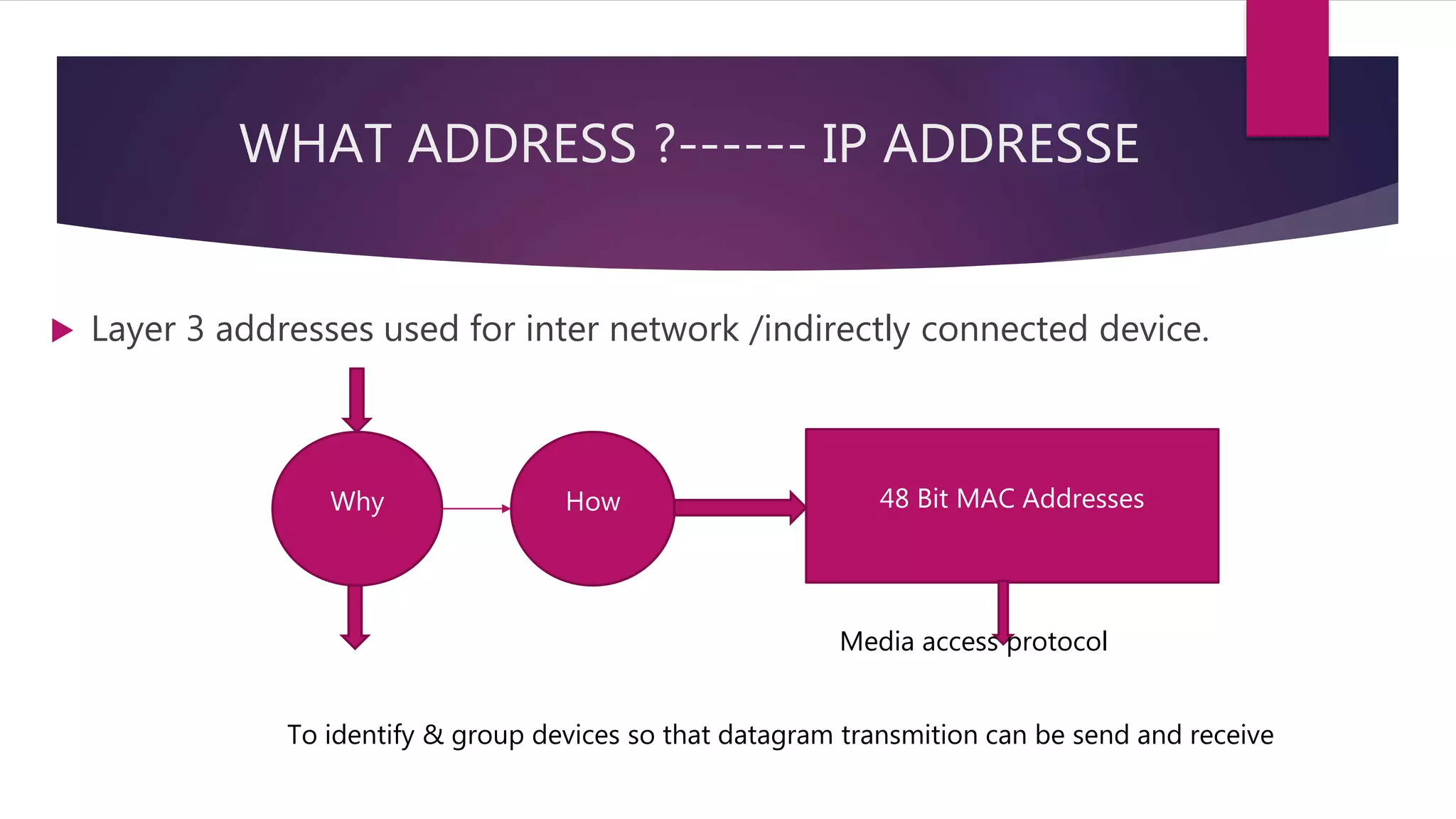
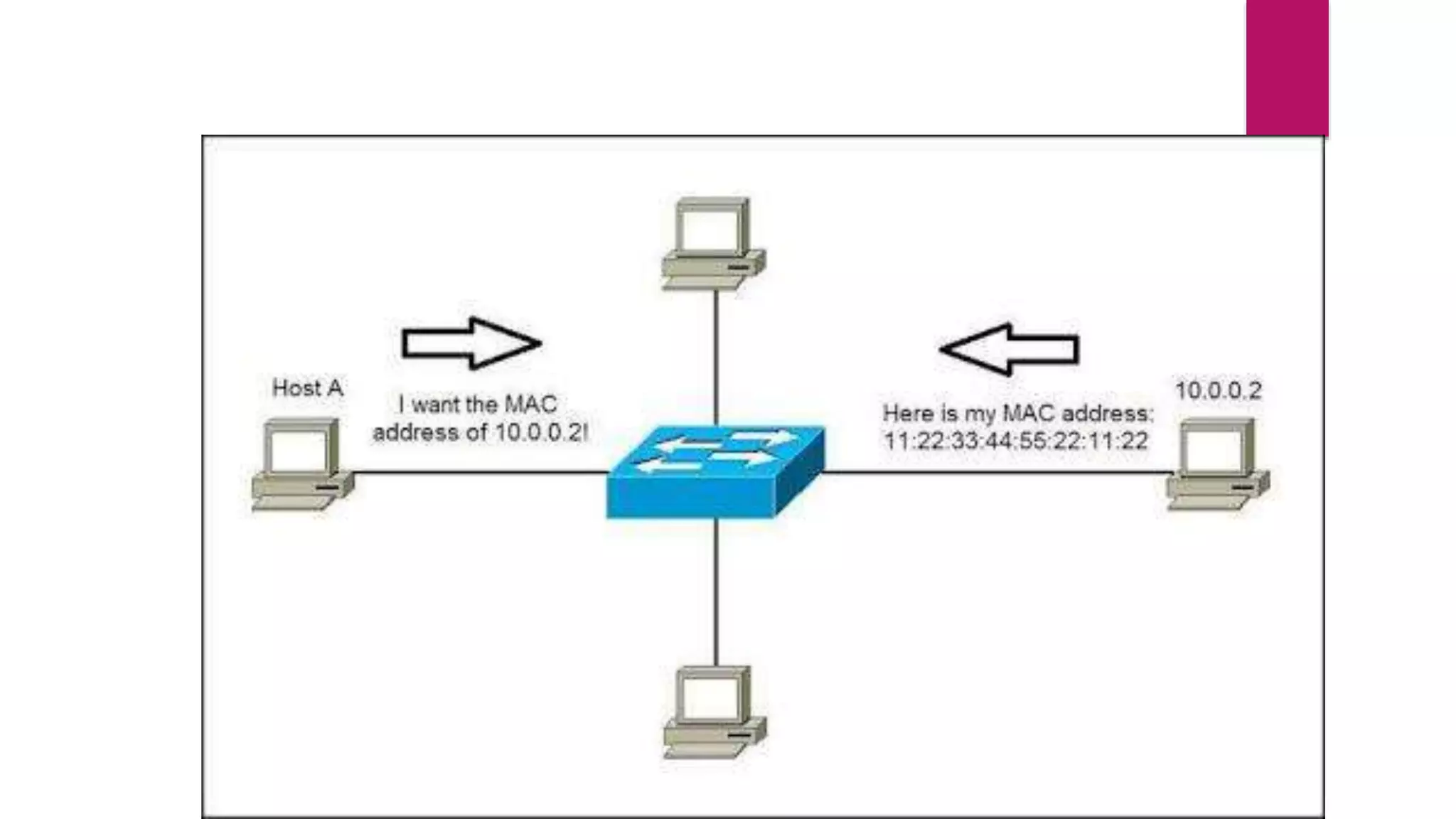
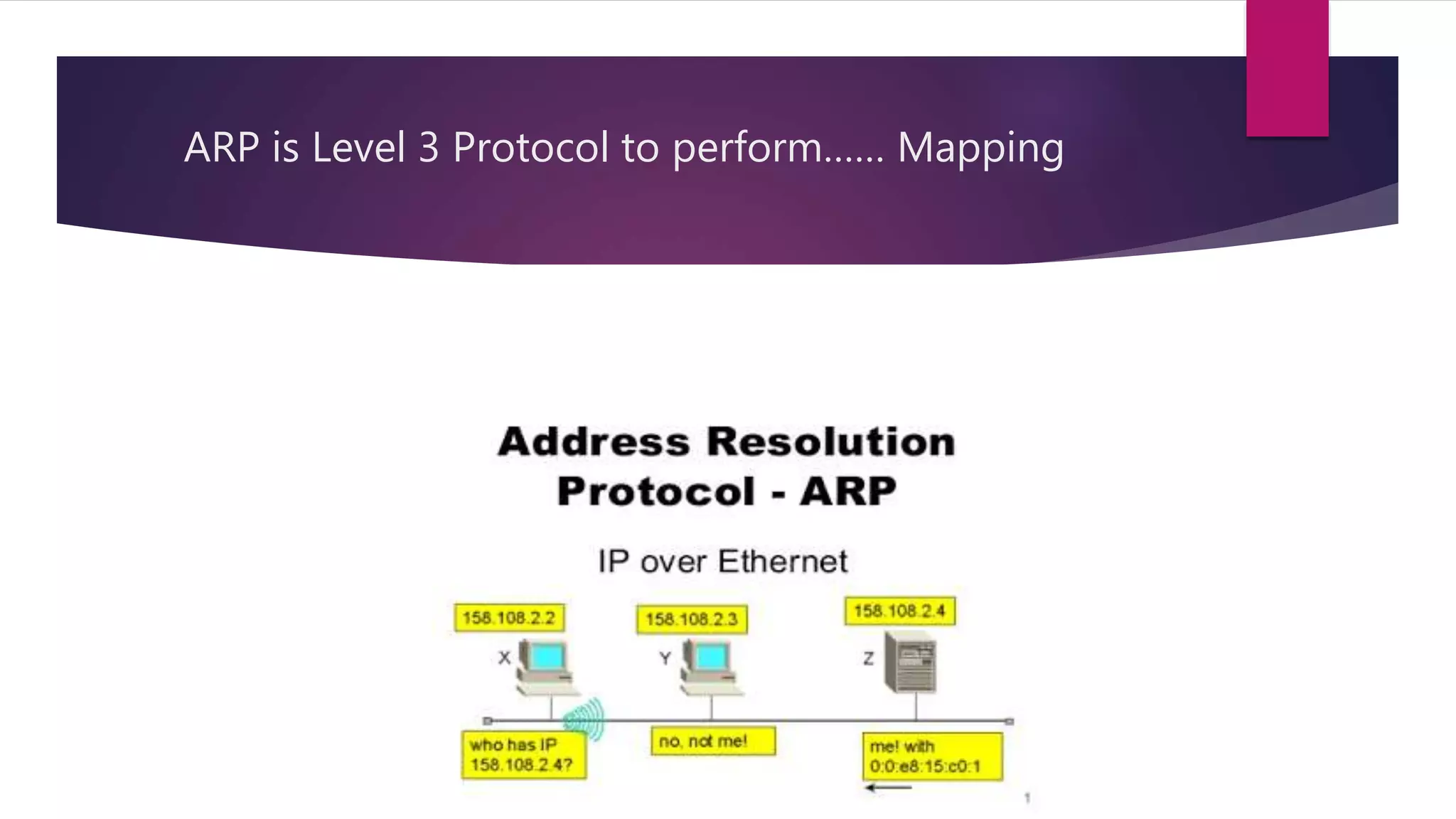
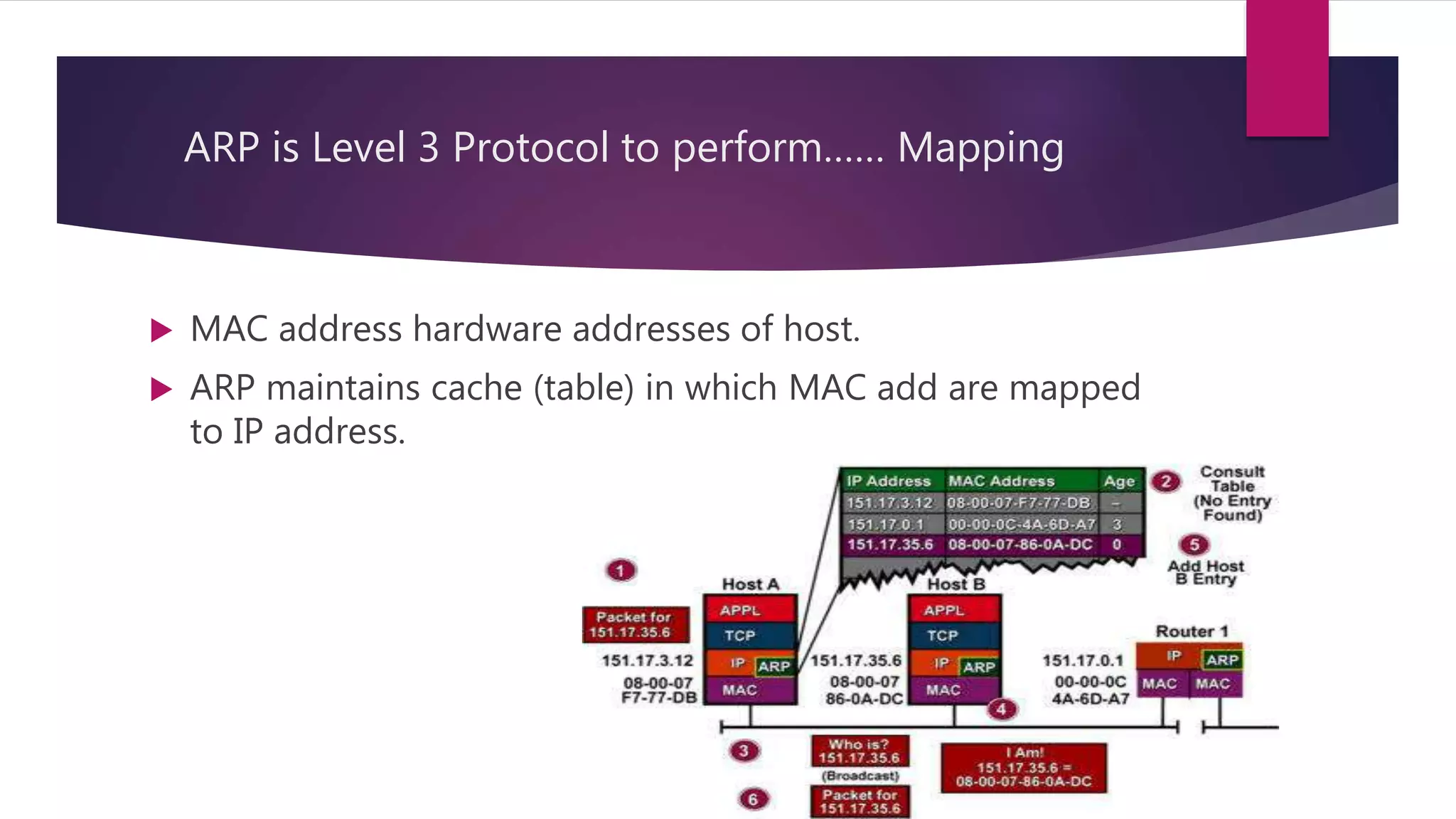
The document discusses address resolution protocol (ARP) which maps logical IP addresses to physical MAC addresses on a local area network. It explains that ARP broadcasts a request to find the MAC address associated with a given IP address, and the device with that IP address responds with its MAC. This dynamic address mapping is stored in an ARP cache for future use. It also describes how different network protocols may use ARP or similar methods to perform address mapping between logical and physical addresses.