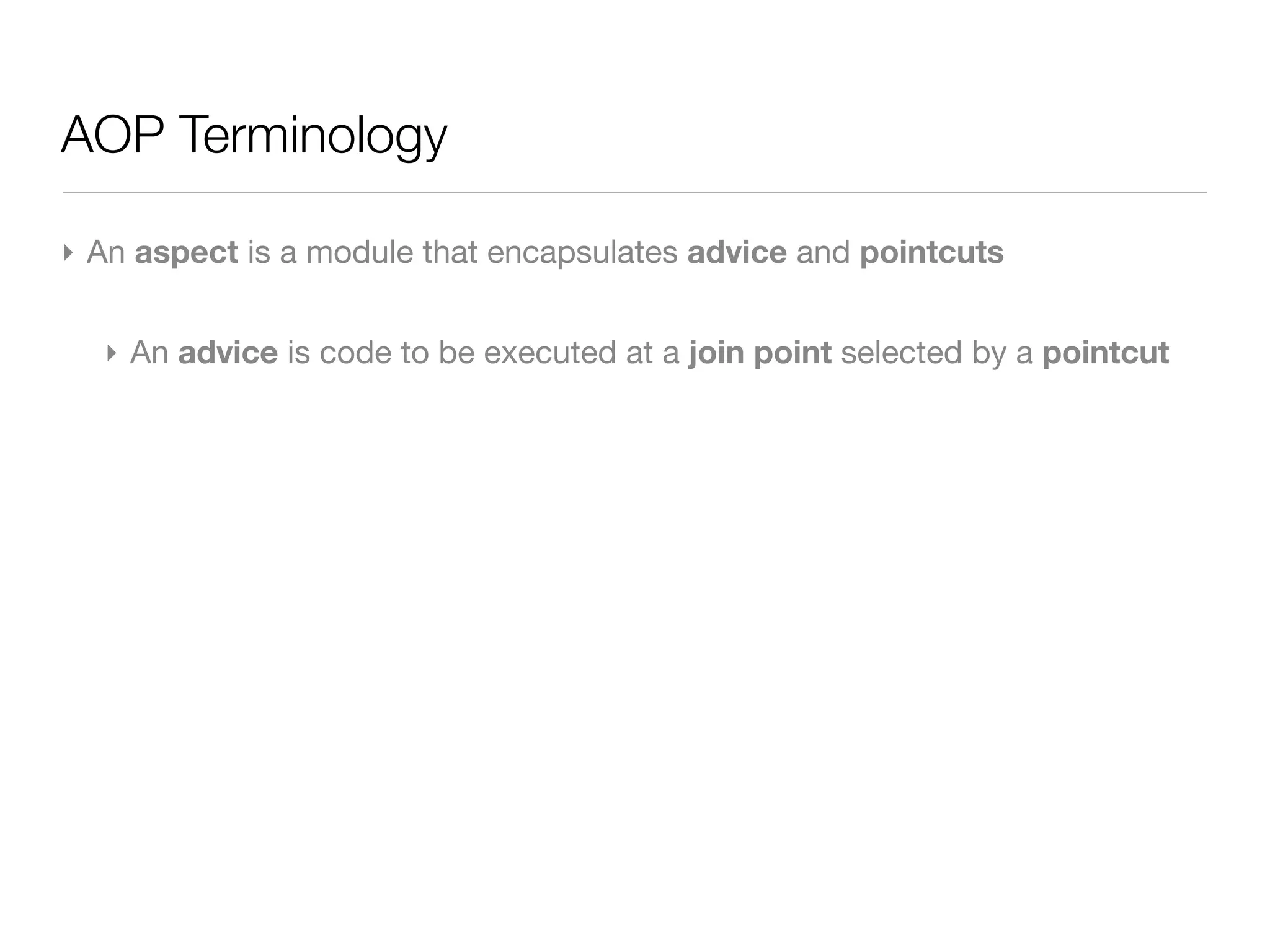
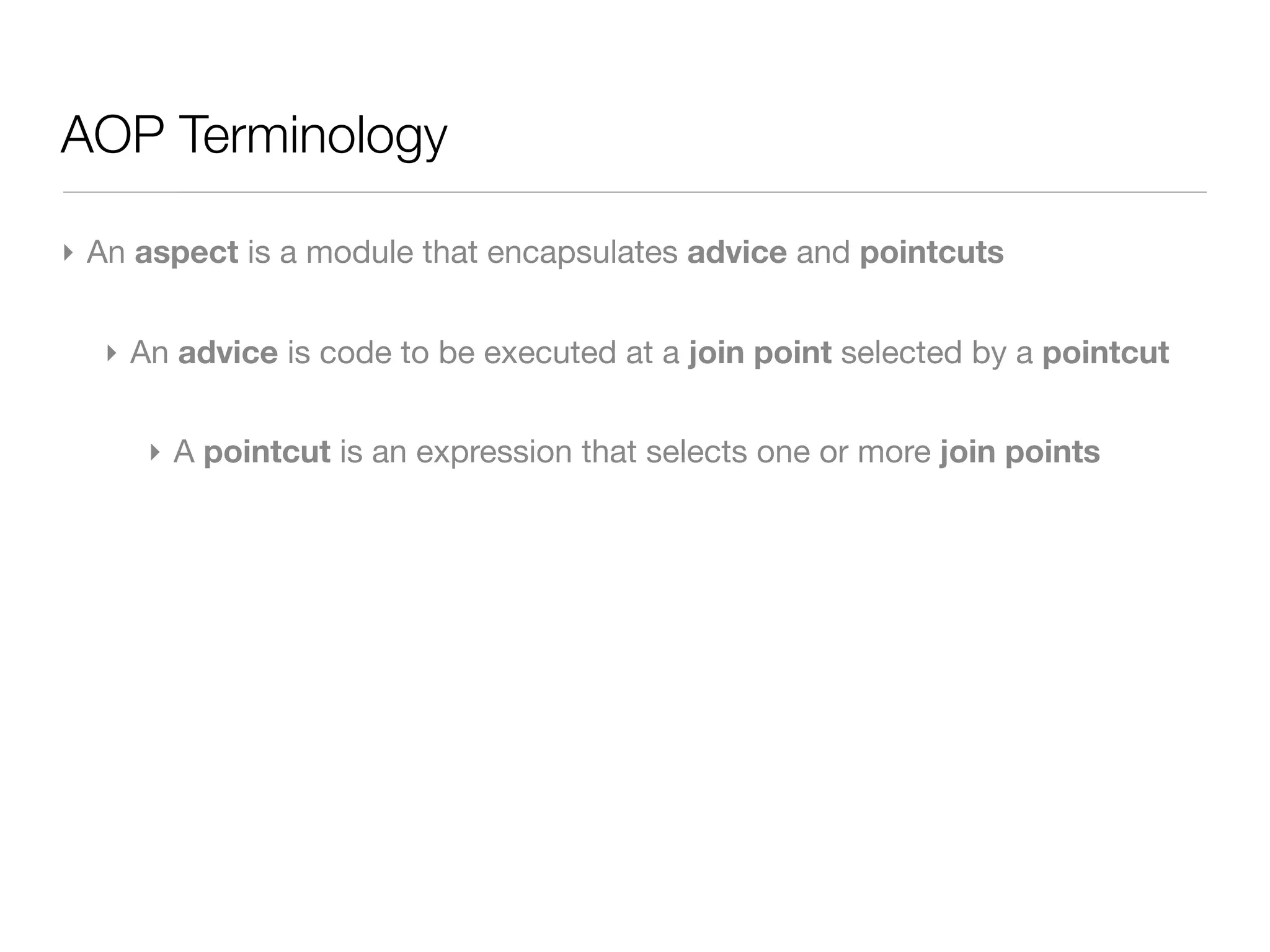
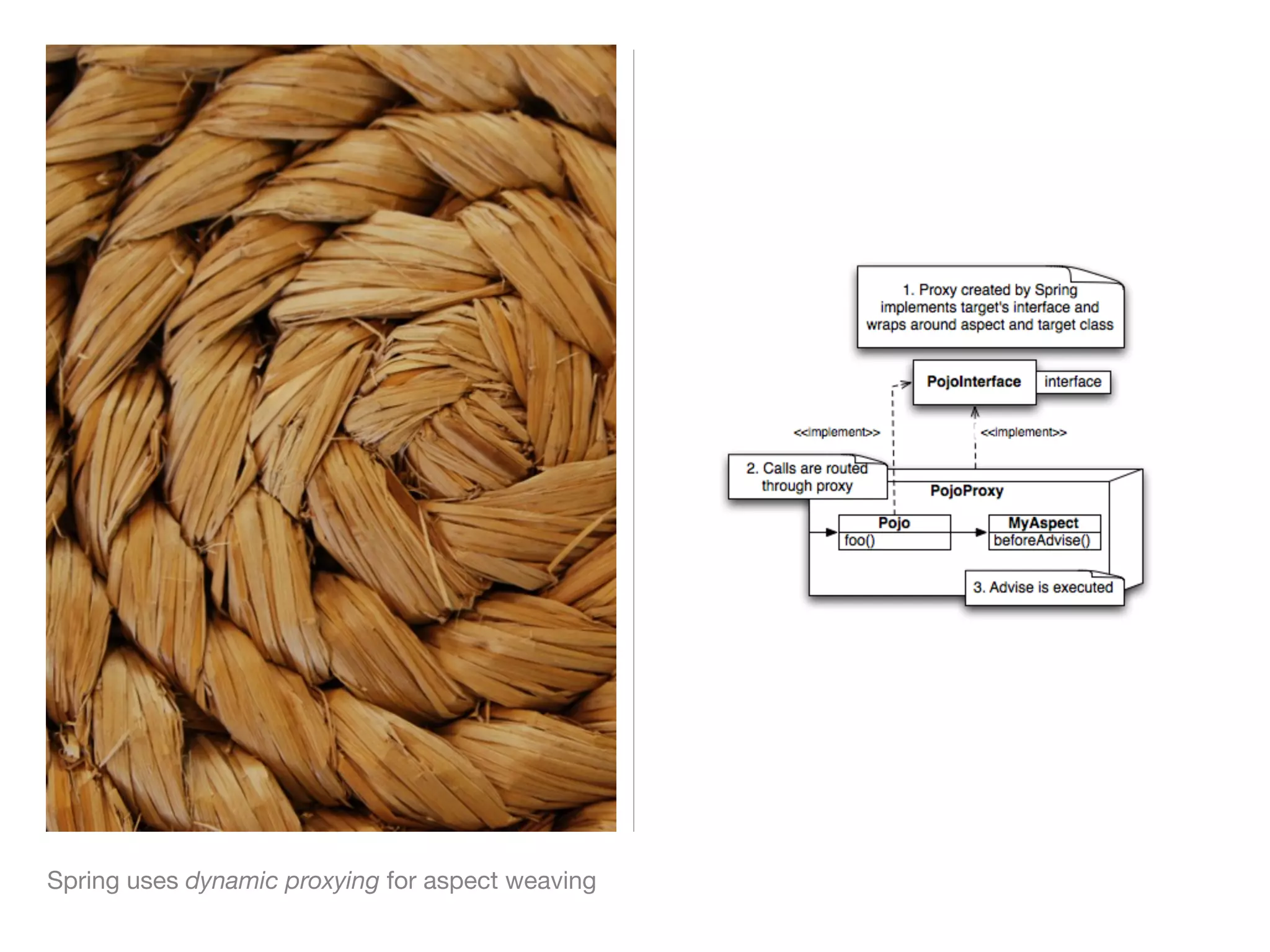
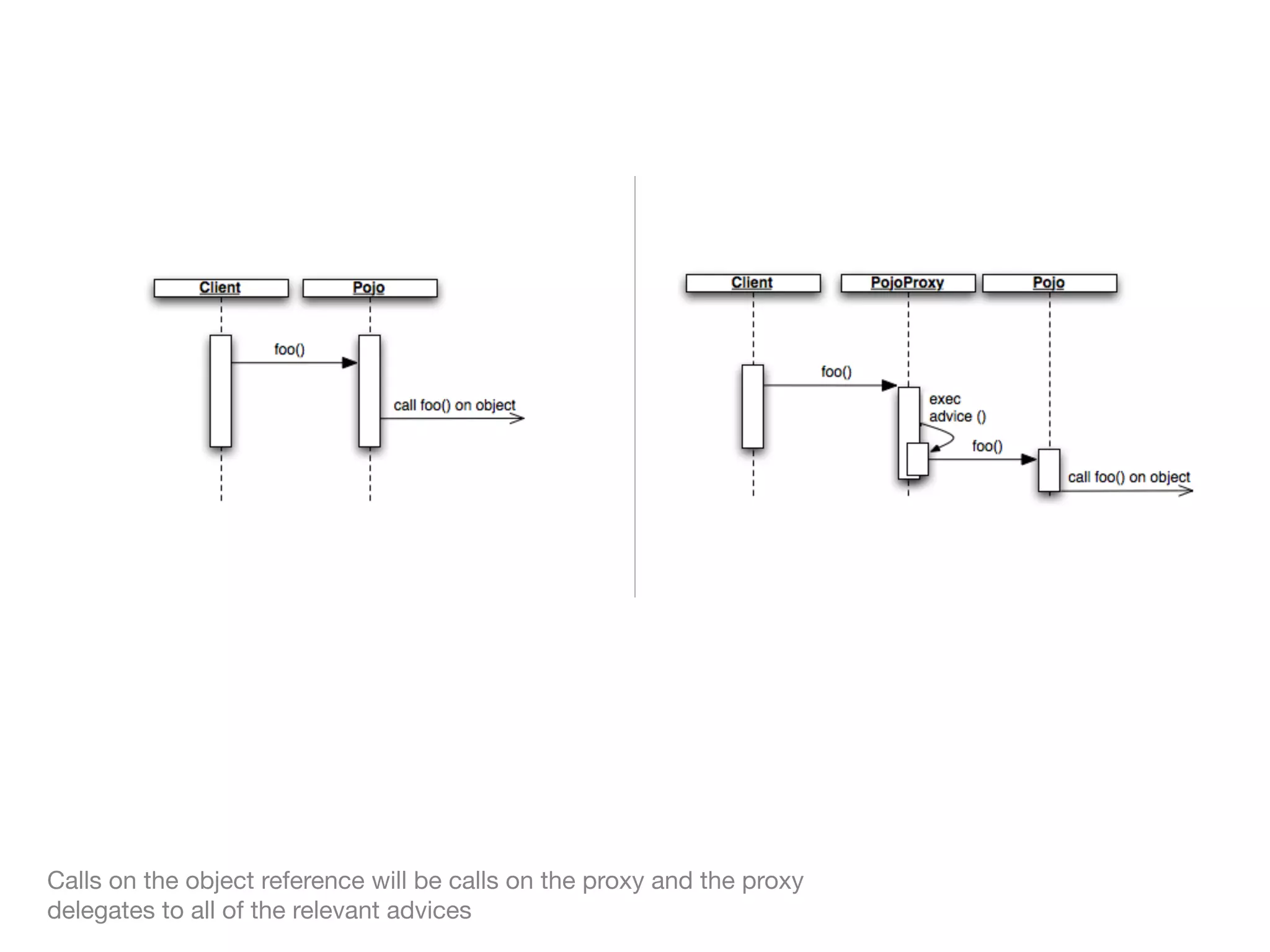
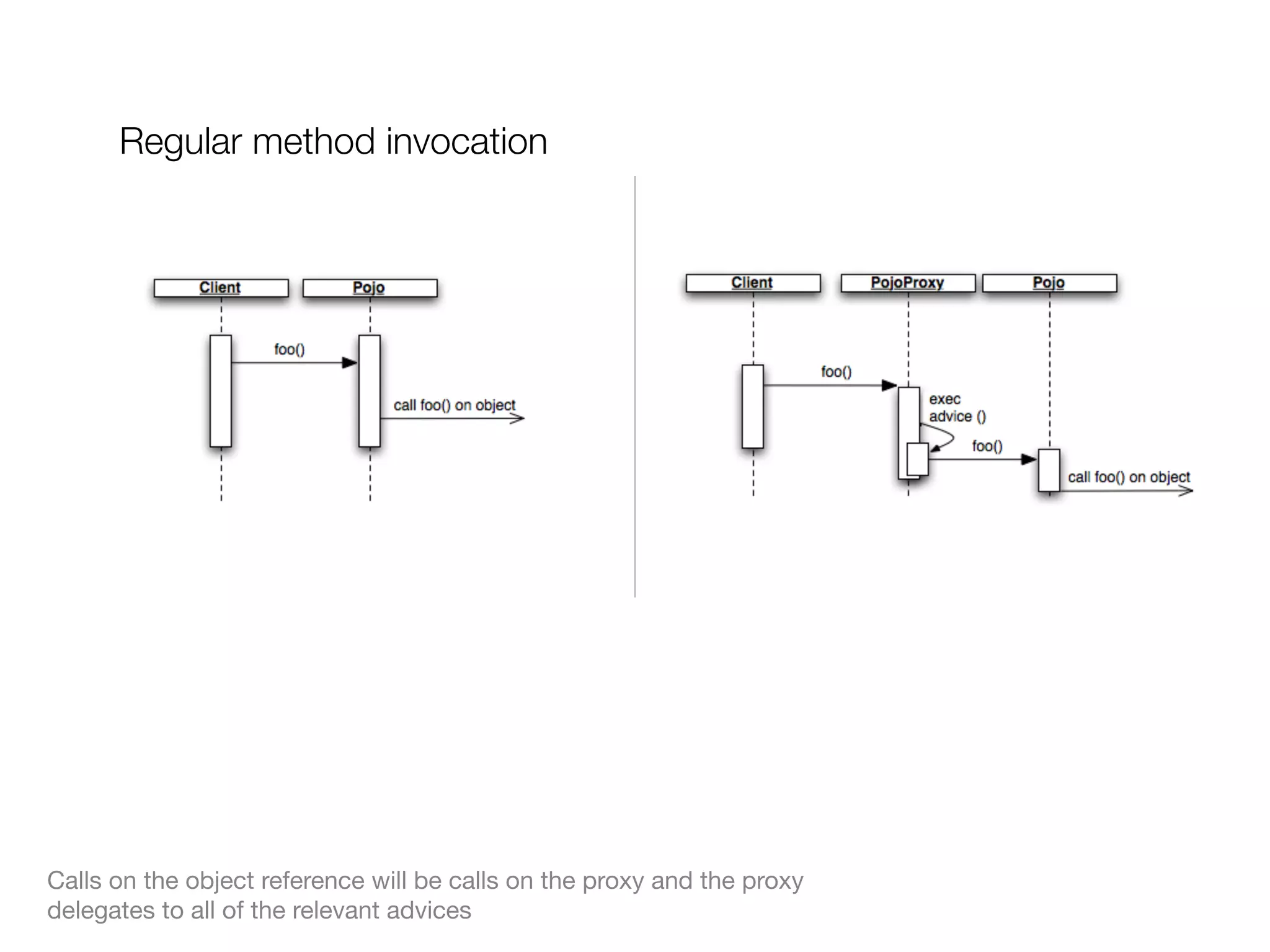
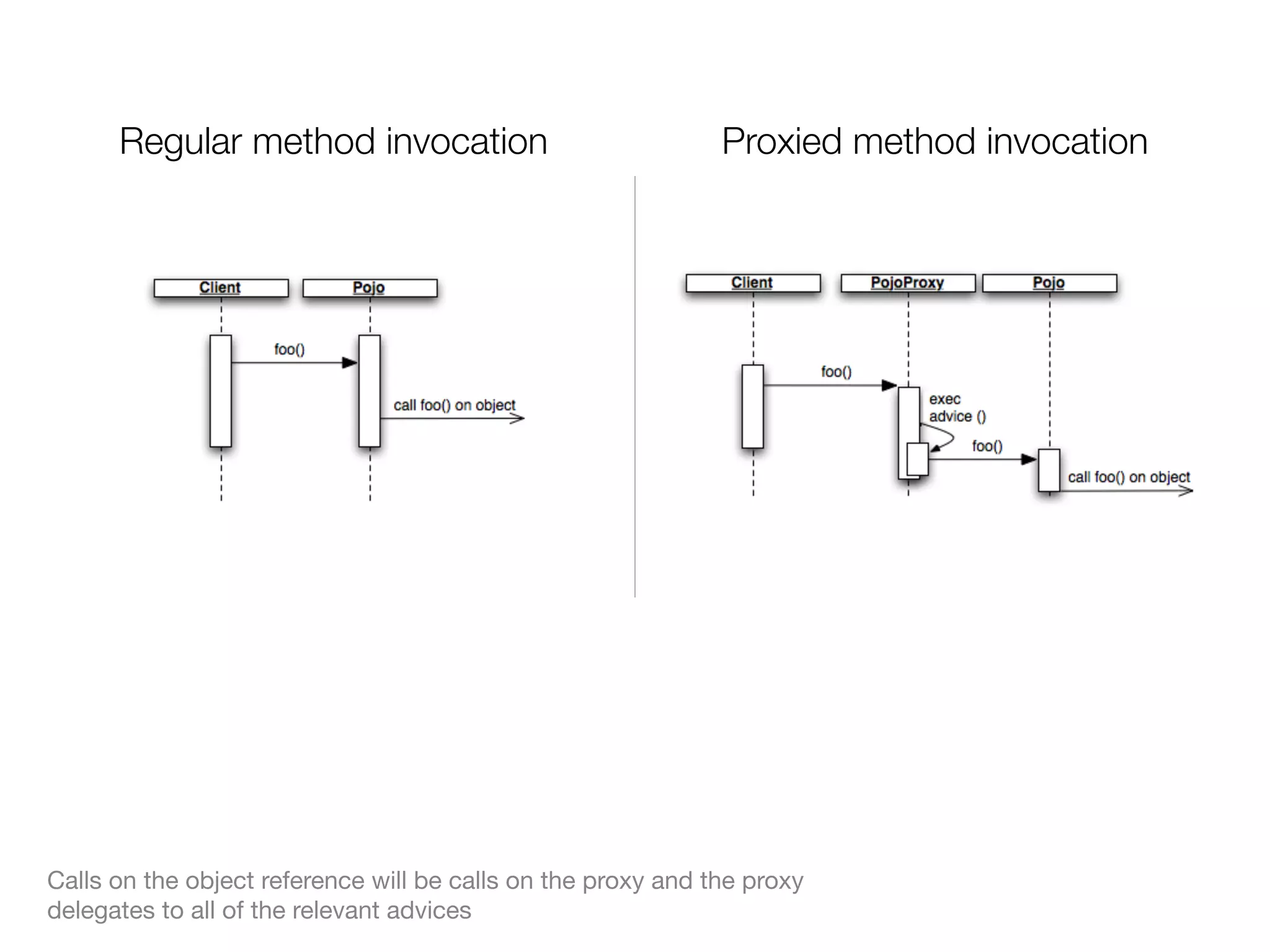
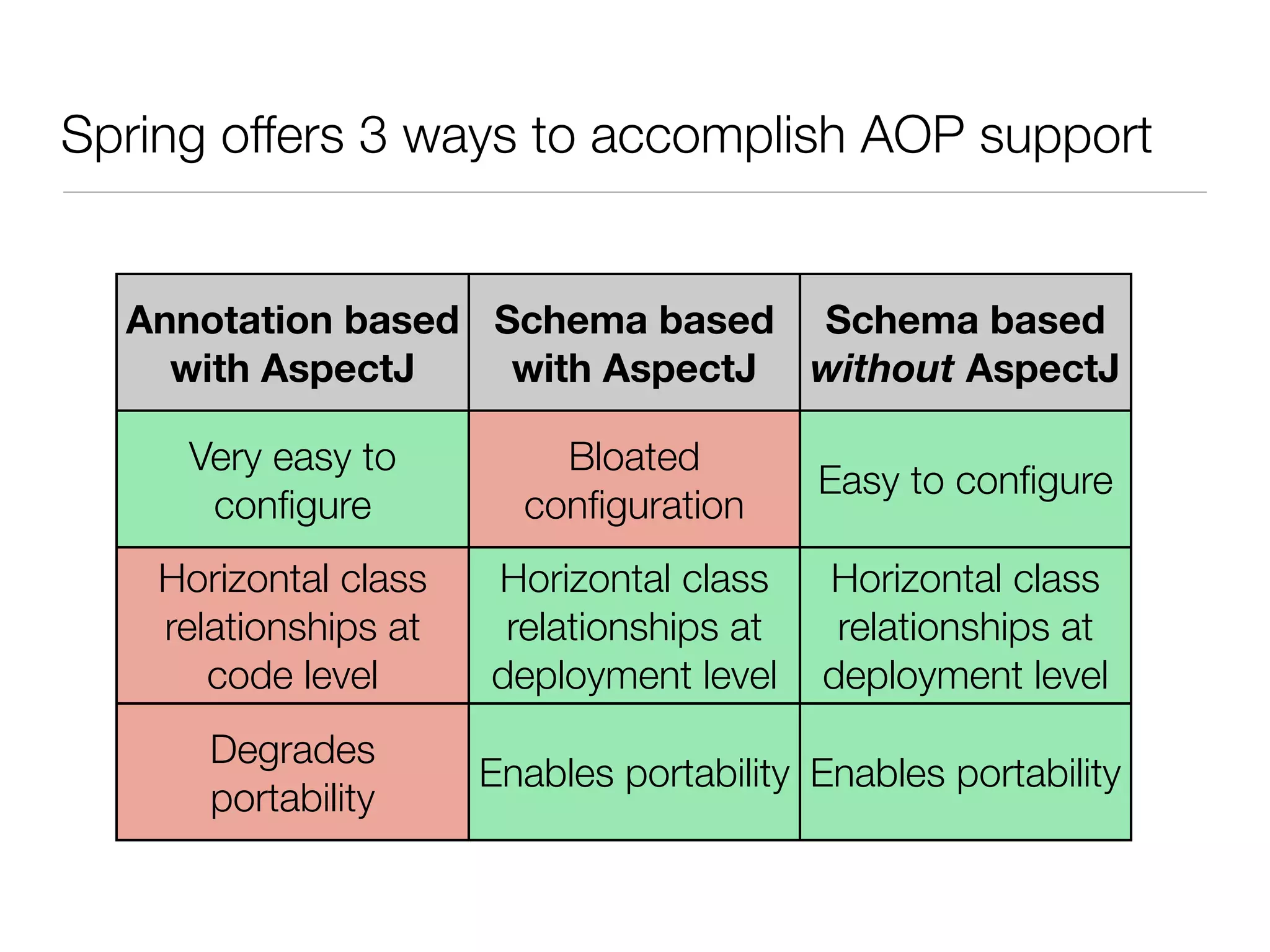
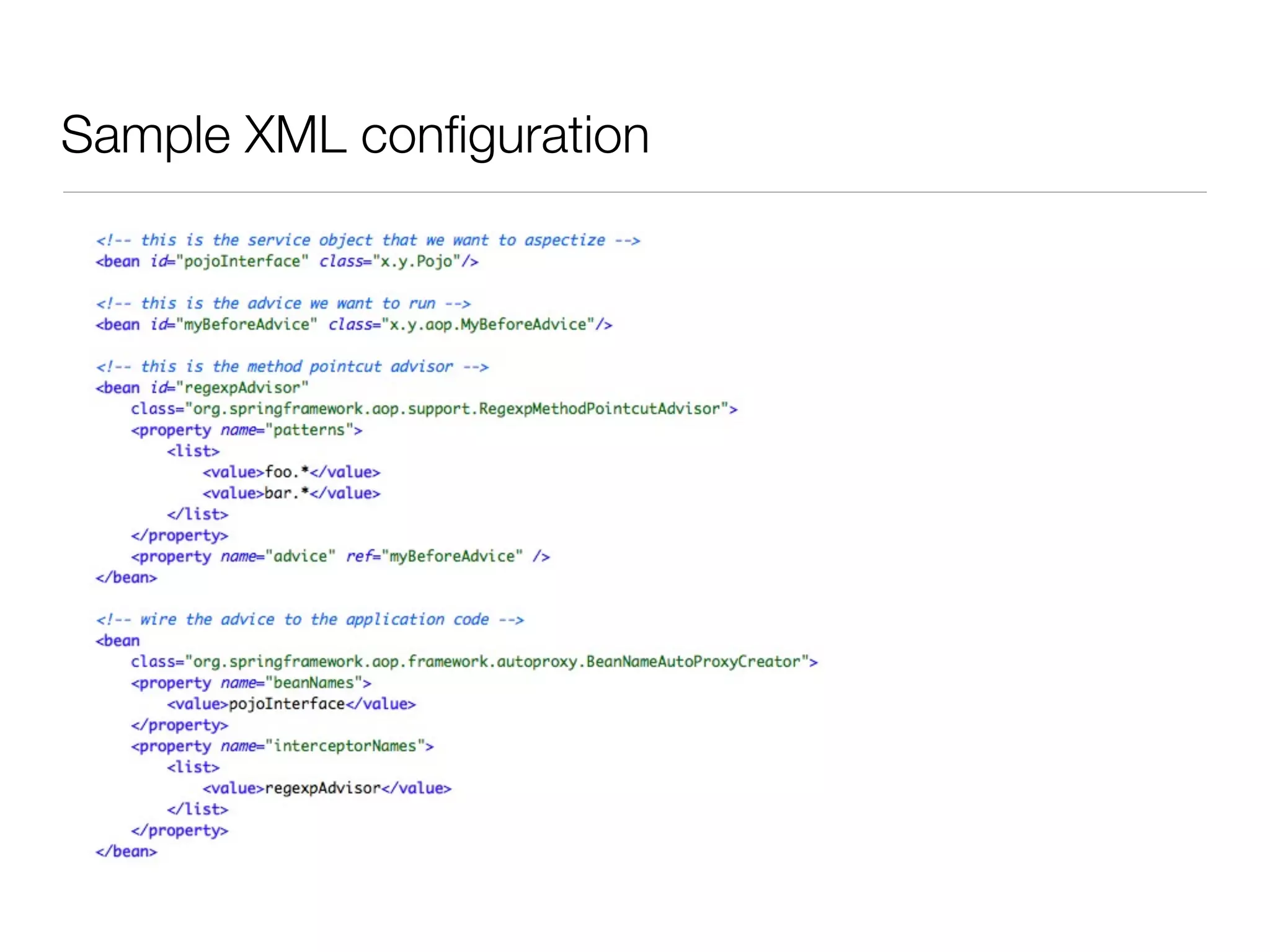
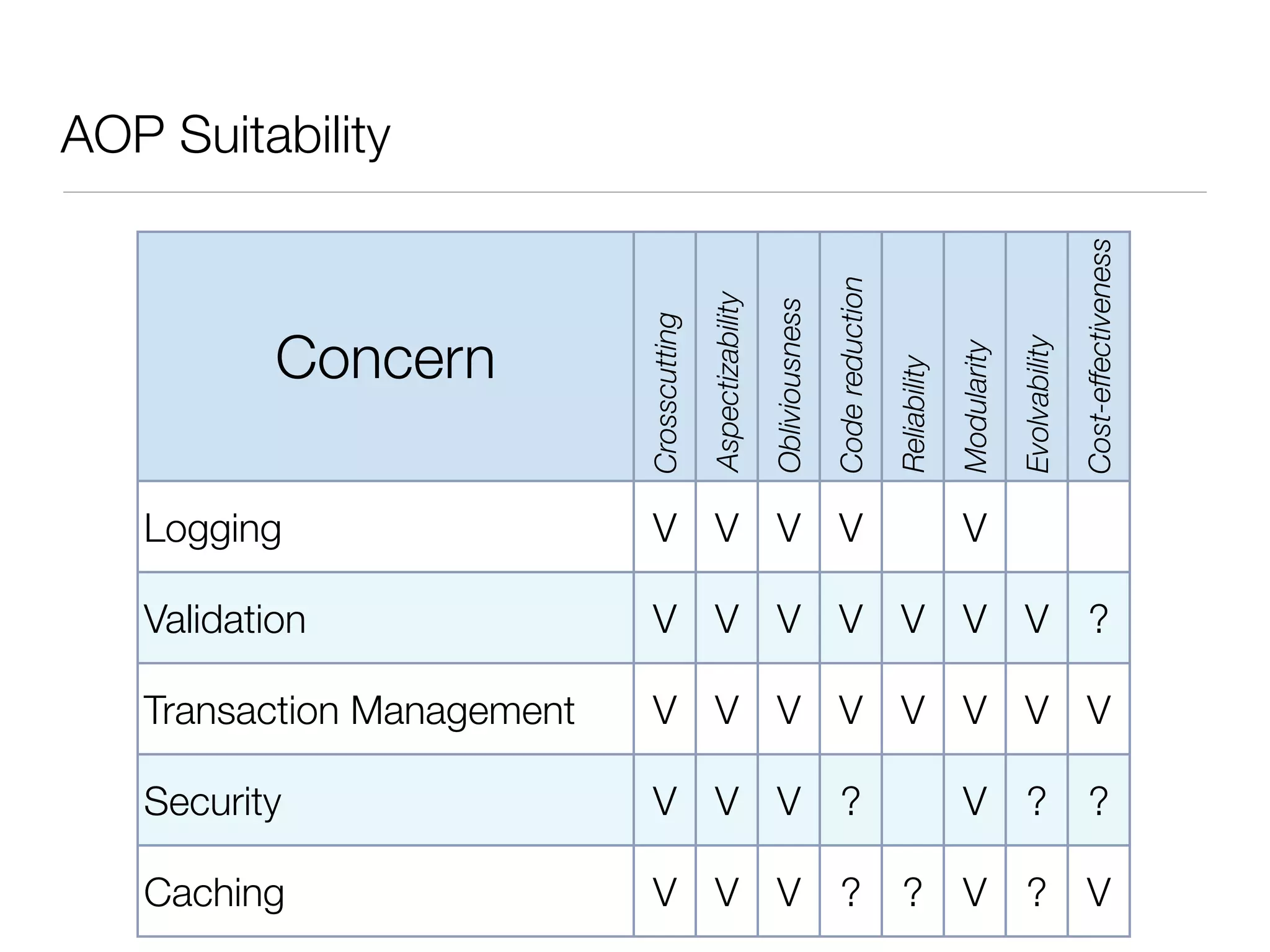
The document discusses aspect-oriented programming (AOP) with Spring, highlighting its benefits in modularizing cross-cutting concerns like logging, validation, and security. It explains key AOP concepts such as aspects, advice, pointcuts, and join points, and explores different methods for implementing AOP in Spring, including annotation and schema-based configurations. The document also addresses the advantages and drawbacks of using Spring AOP, providing insights into its suitability for various applications.