Download as PDF, PPTX




![Python Collection • List [] • ordered • duplicate elements • mutable • compound data • Tuple () • ordered • duplicate elements • immutable • heterogeneous data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmsanddatastructures-141127063009-conversion-gate01/75/Problem-Solving-with-Algorithms-and-Data-Structures-6-2048.jpg)



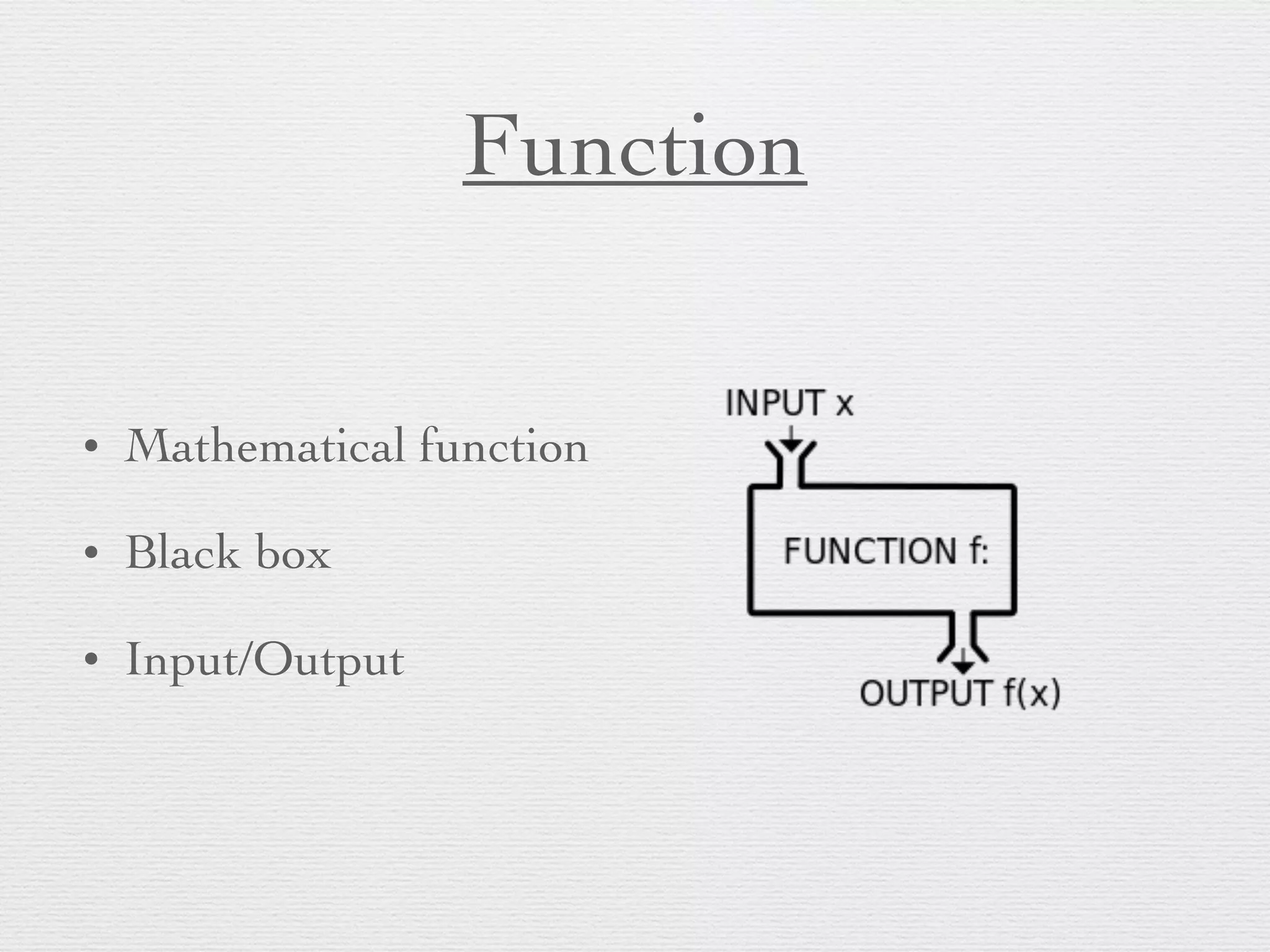


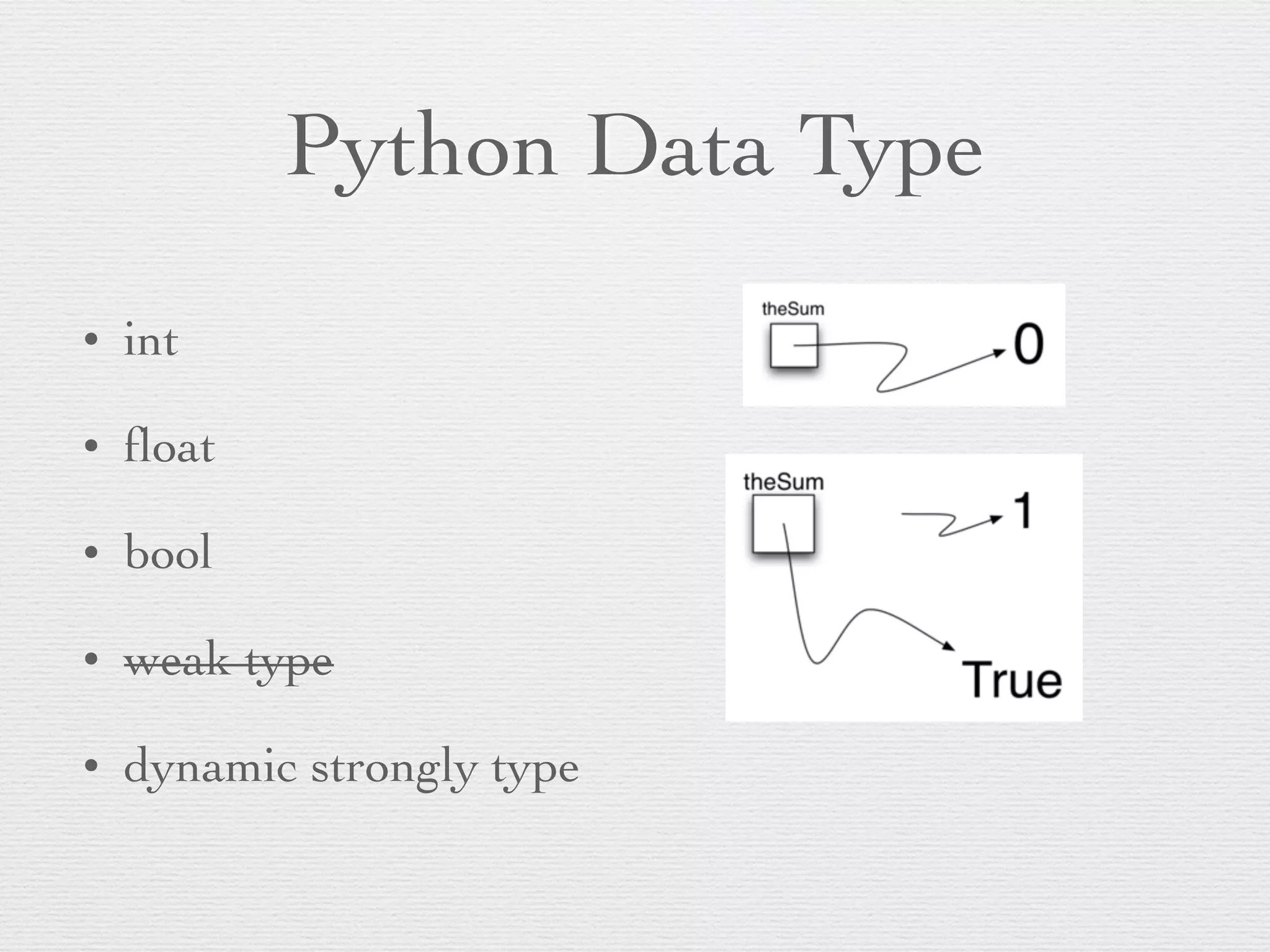
The document discusses problem solving using algorithms and data structures in Python. It covers key concepts like algorithms being step-by-step procedures for calculations, data structures organizing data, and computers providing efficient solutions. Examples include sorting a list of numbers and Python data types like integers, floats, and booleans. Common Python data structures like lists, tuples, sets and dictionaries are described along with control structures like while and for loops. The document also mentions exception handling and functions.





![Python Collection • List [] • ordered • duplicate elements • mutable • compound data • Tuple () • ordered • duplicate elements • immutable • heterogeneous data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmsanddatastructures-141127063009-conversion-gate01/75/Problem-Solving-with-Algorithms-and-Data-Structures-6-2048.jpg)





