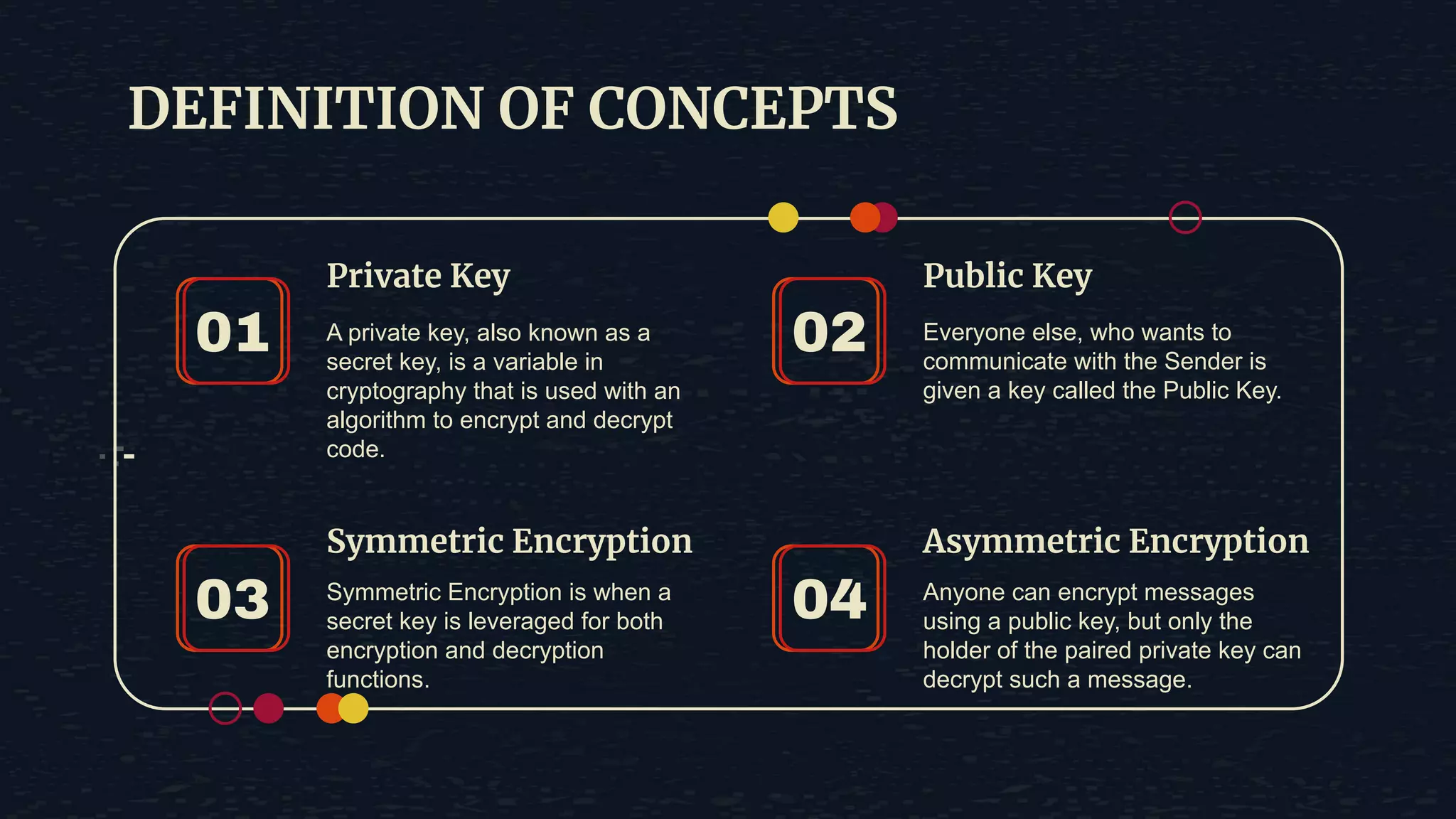
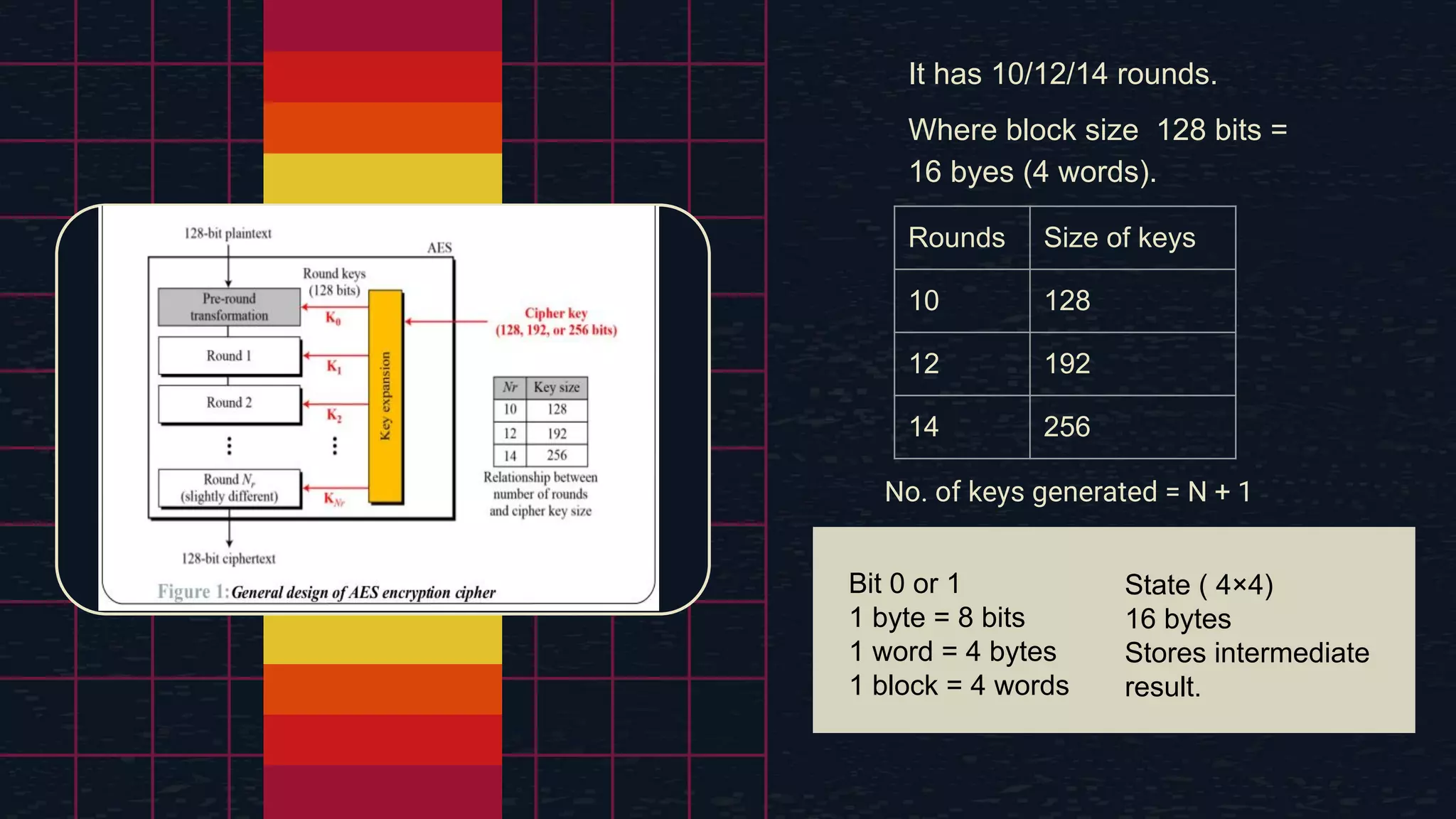
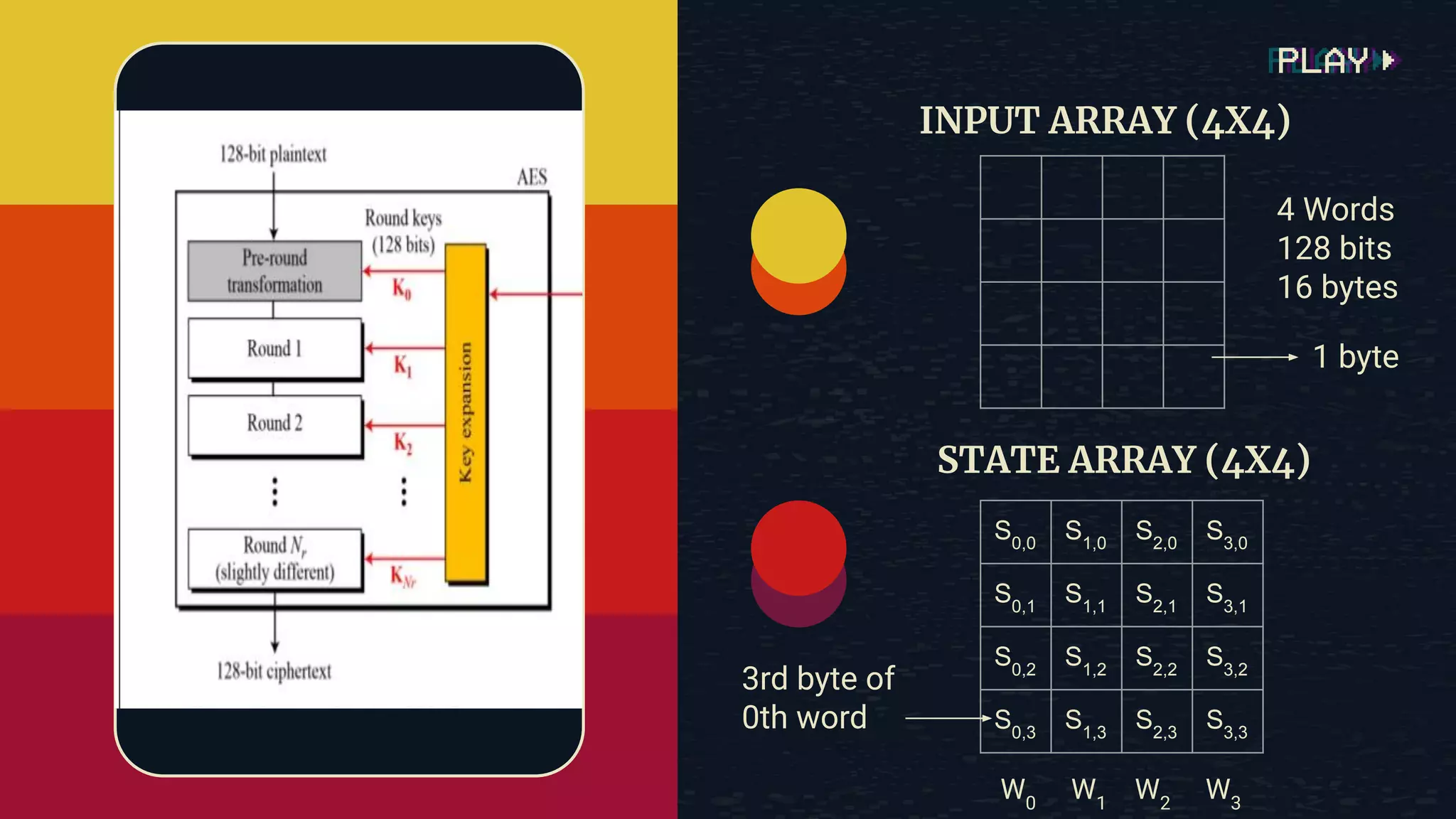
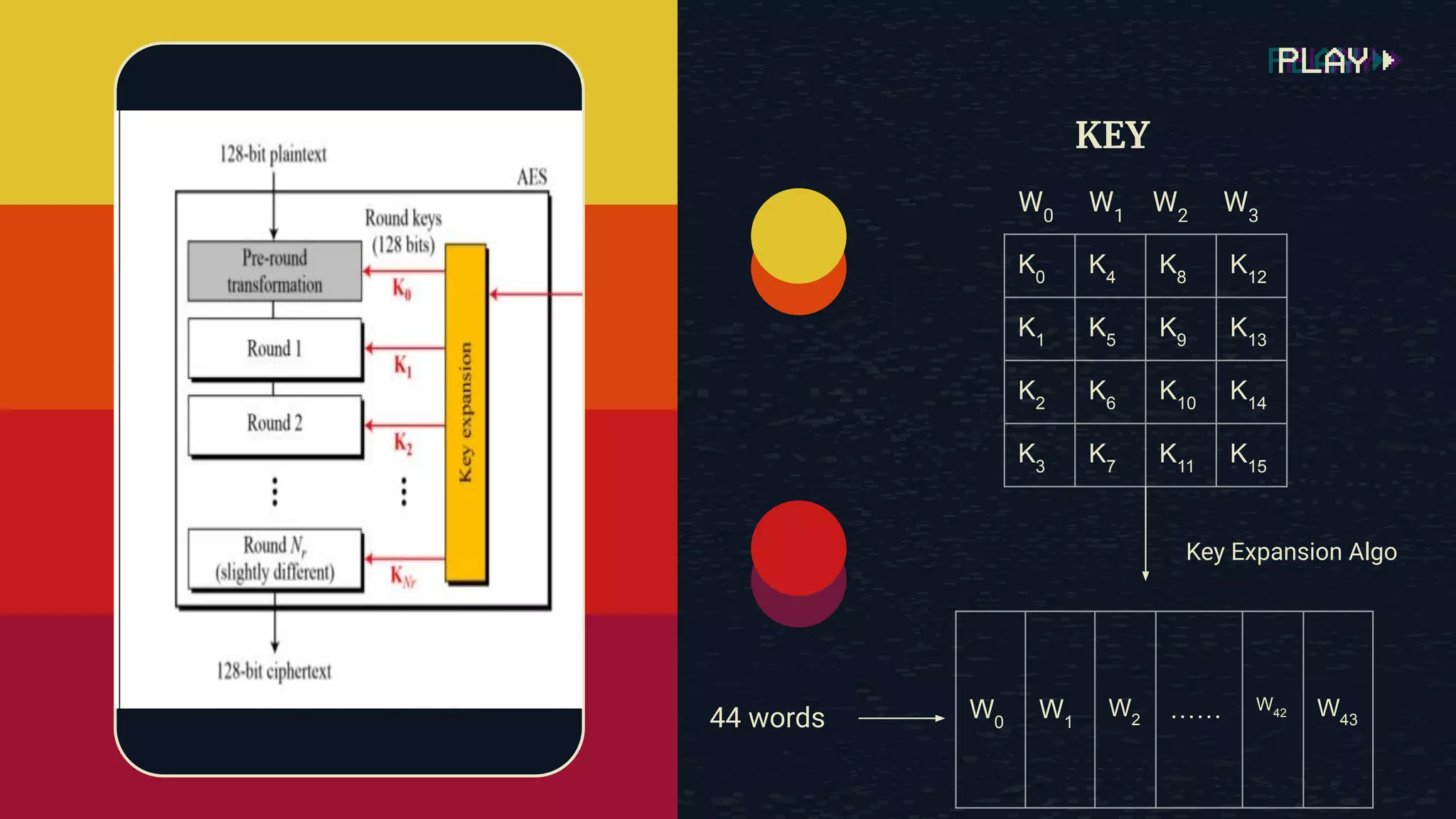
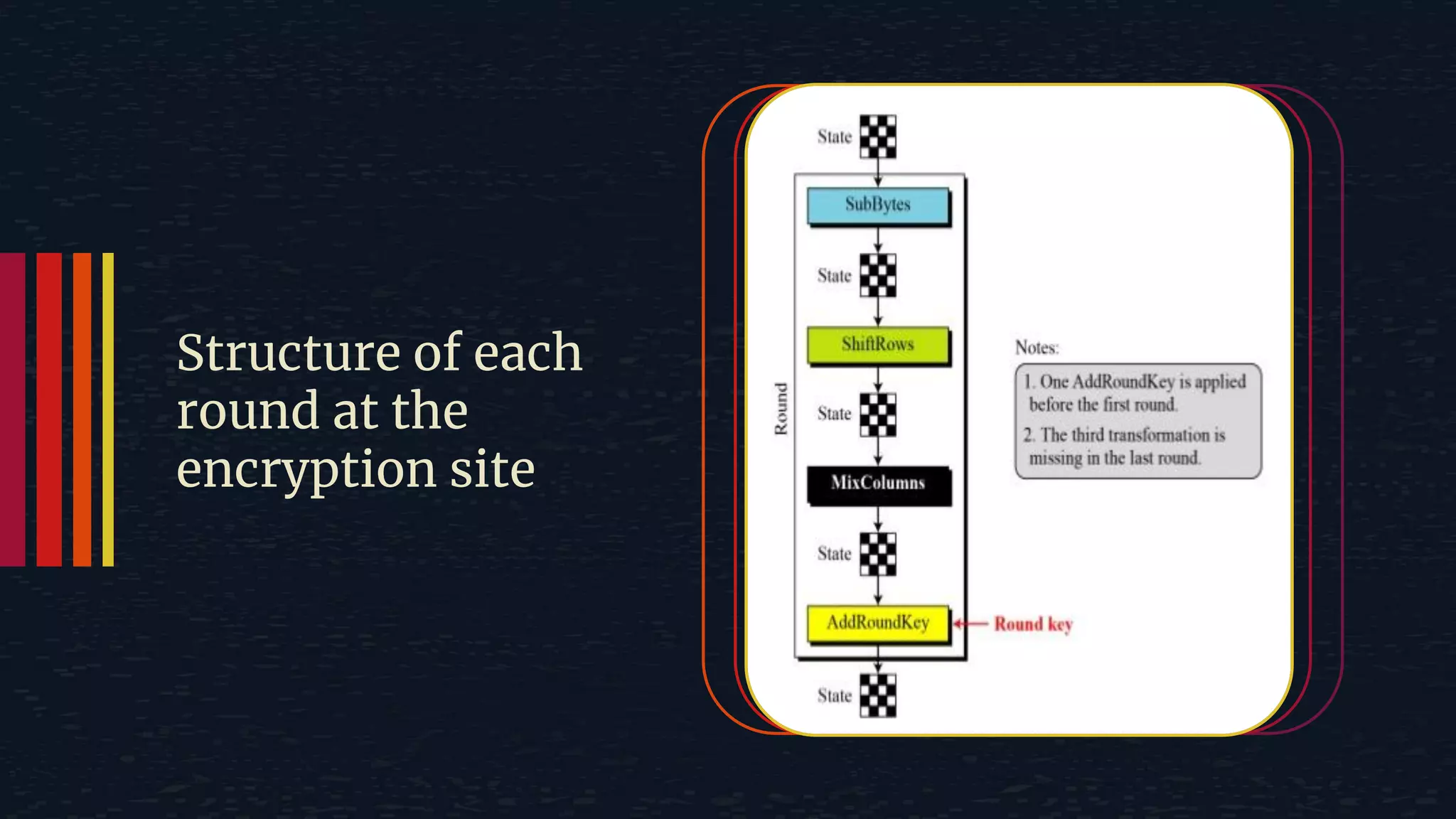
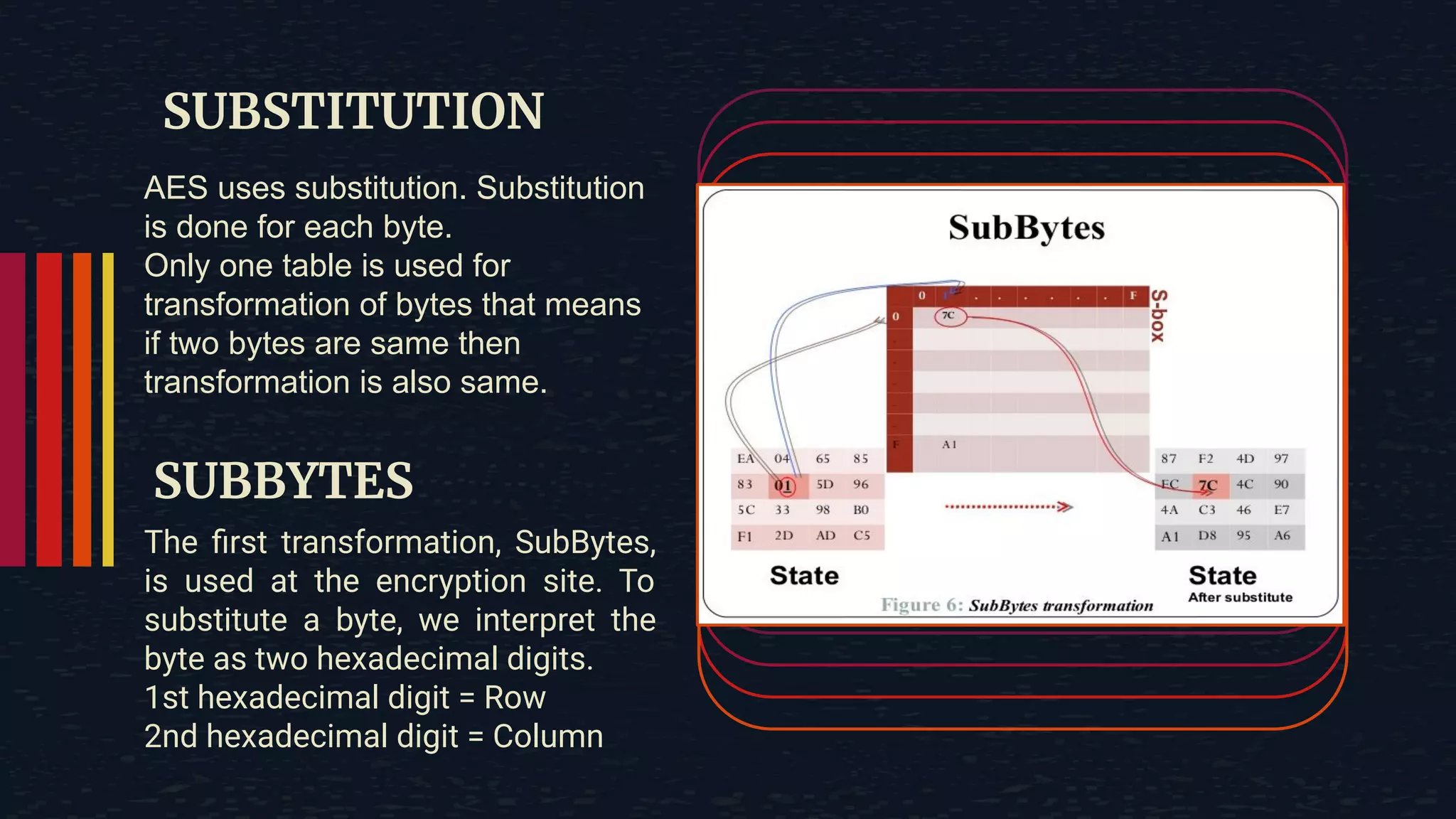
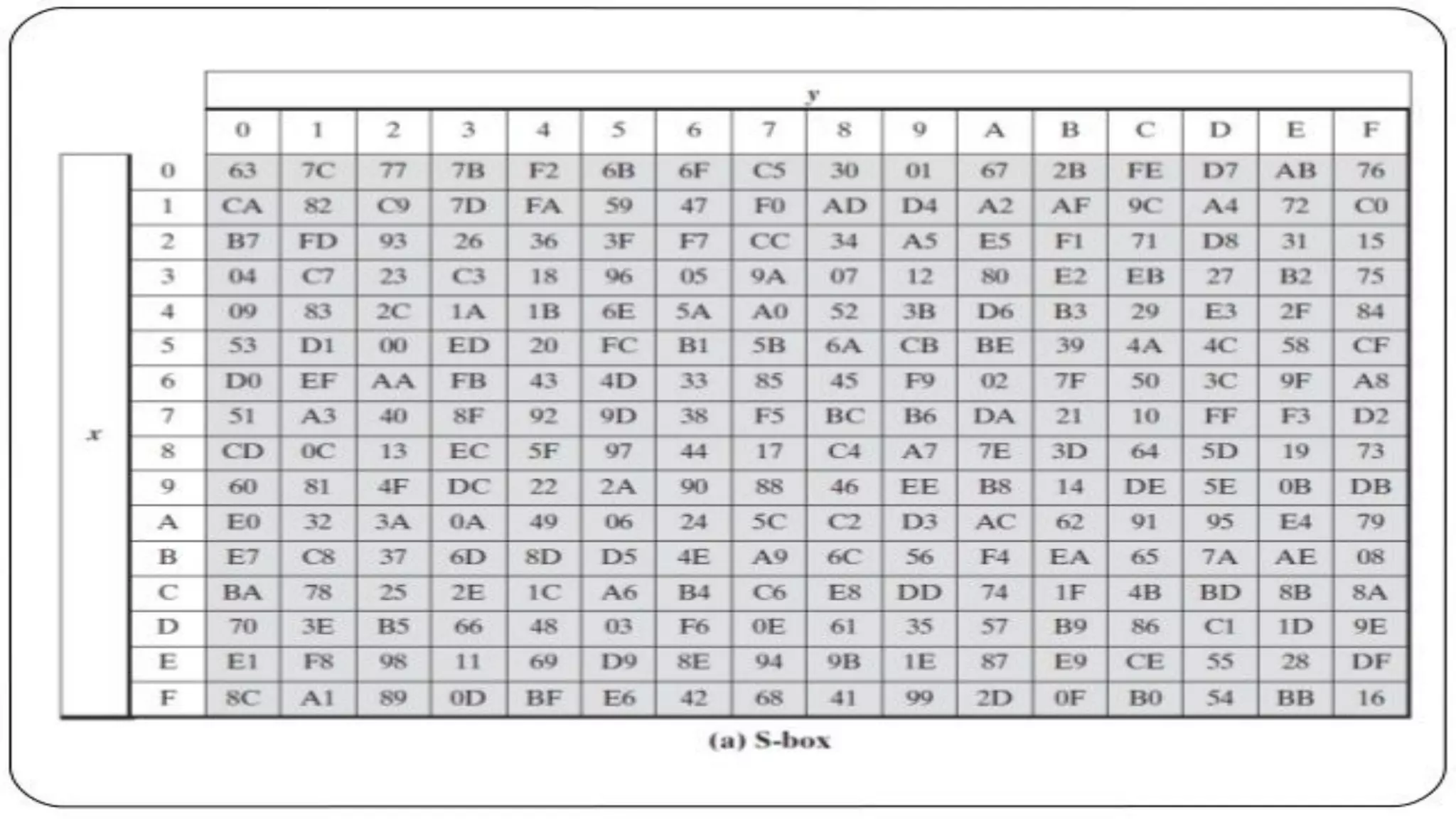
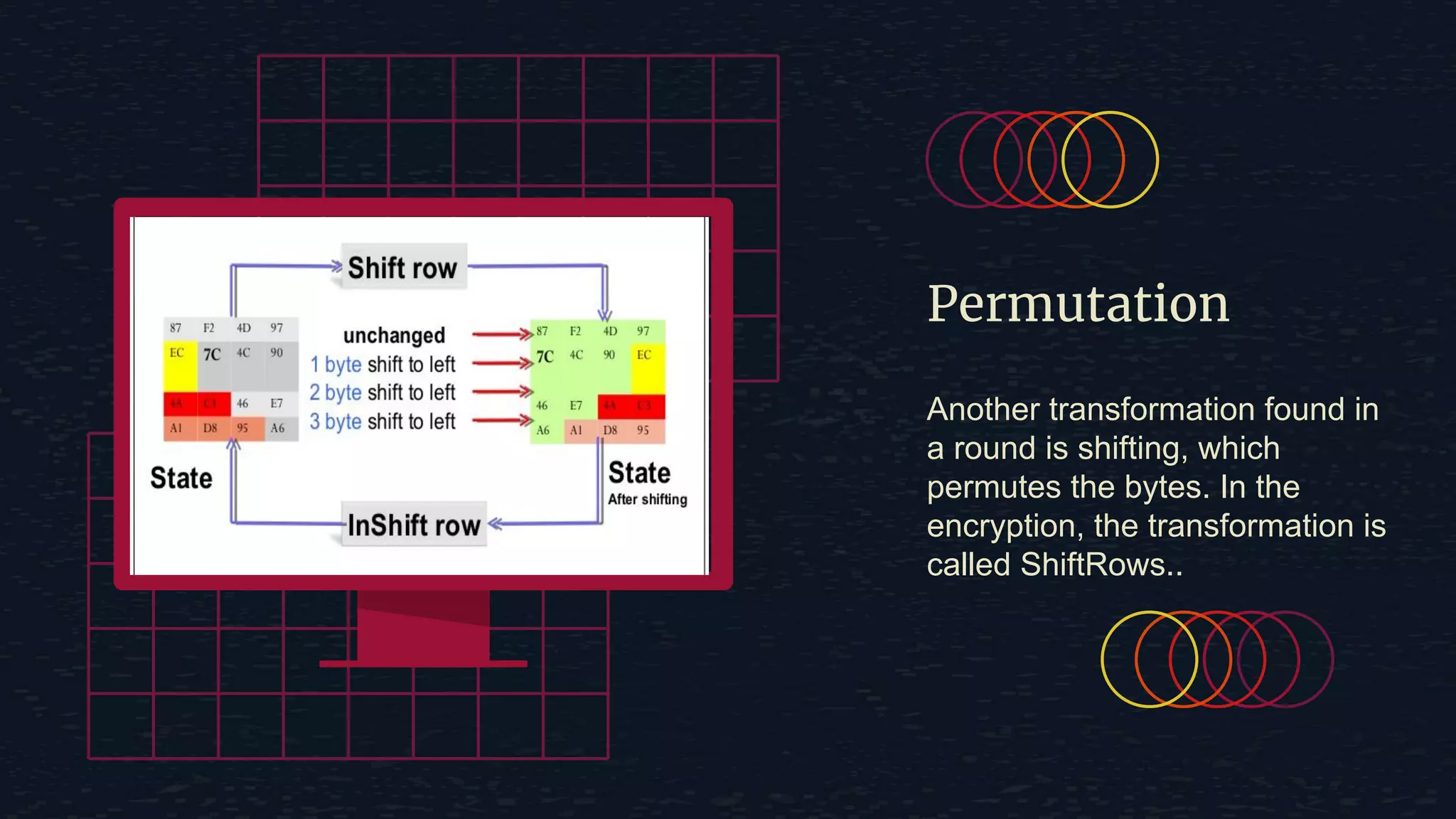
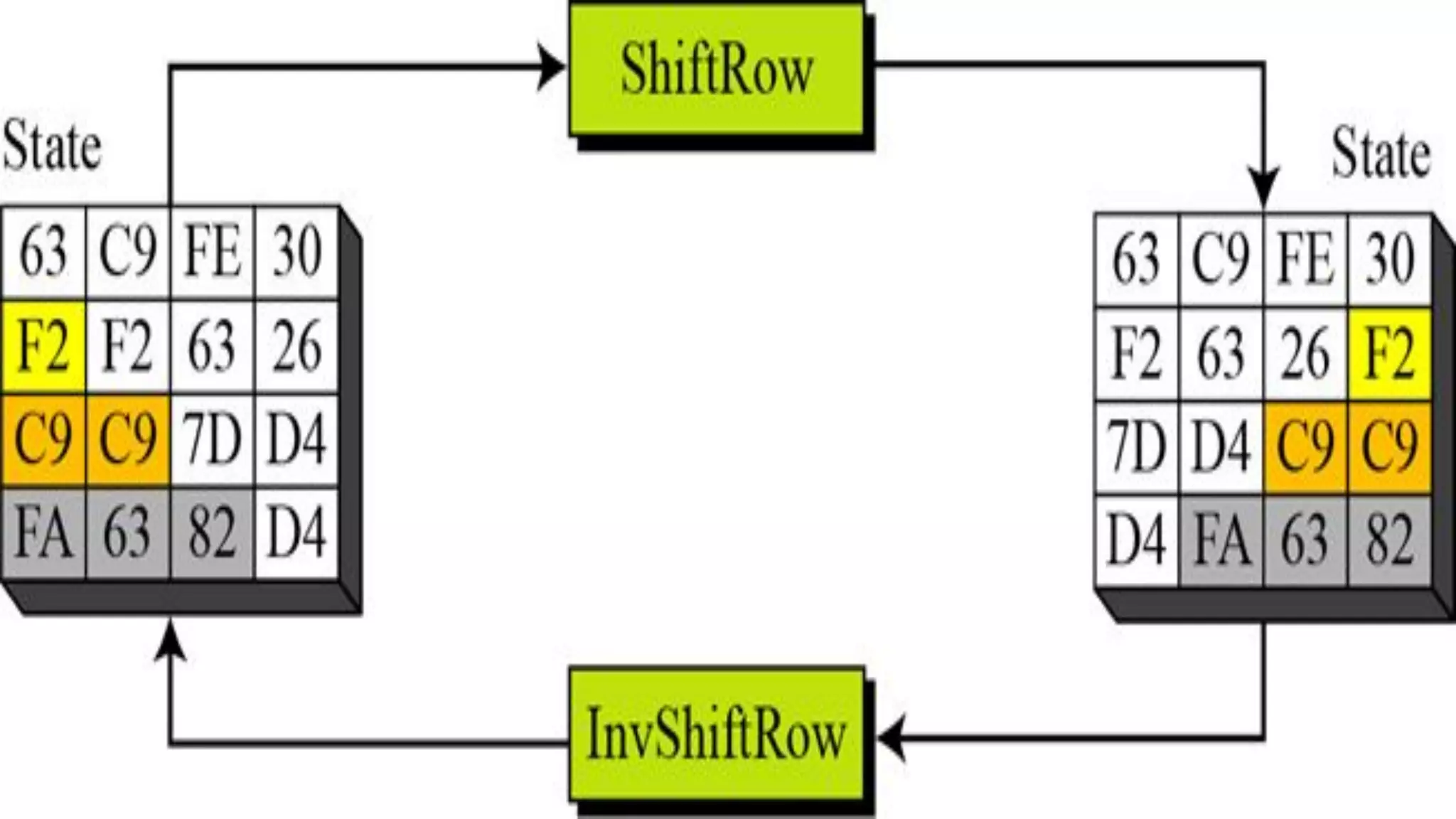
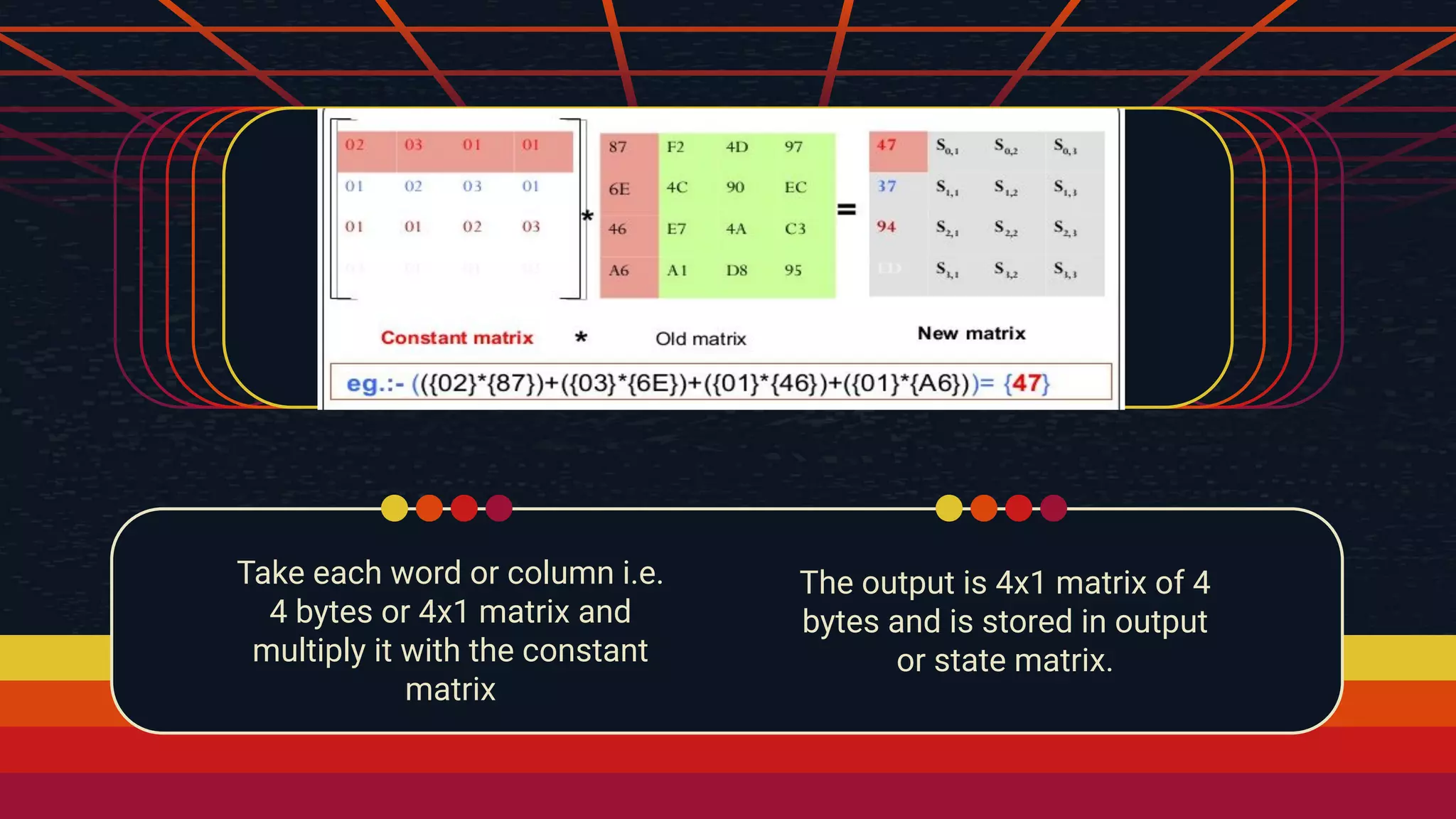
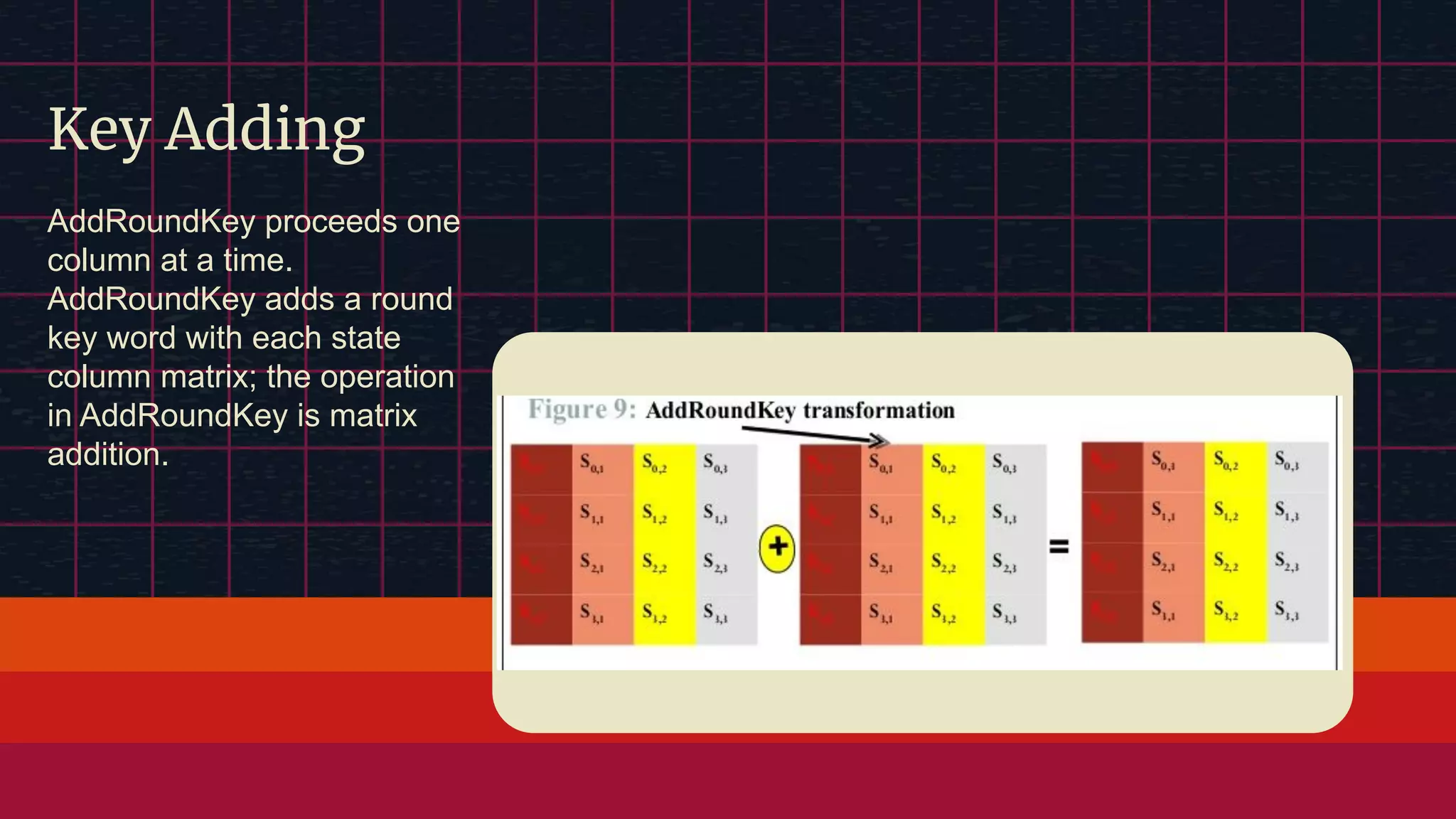
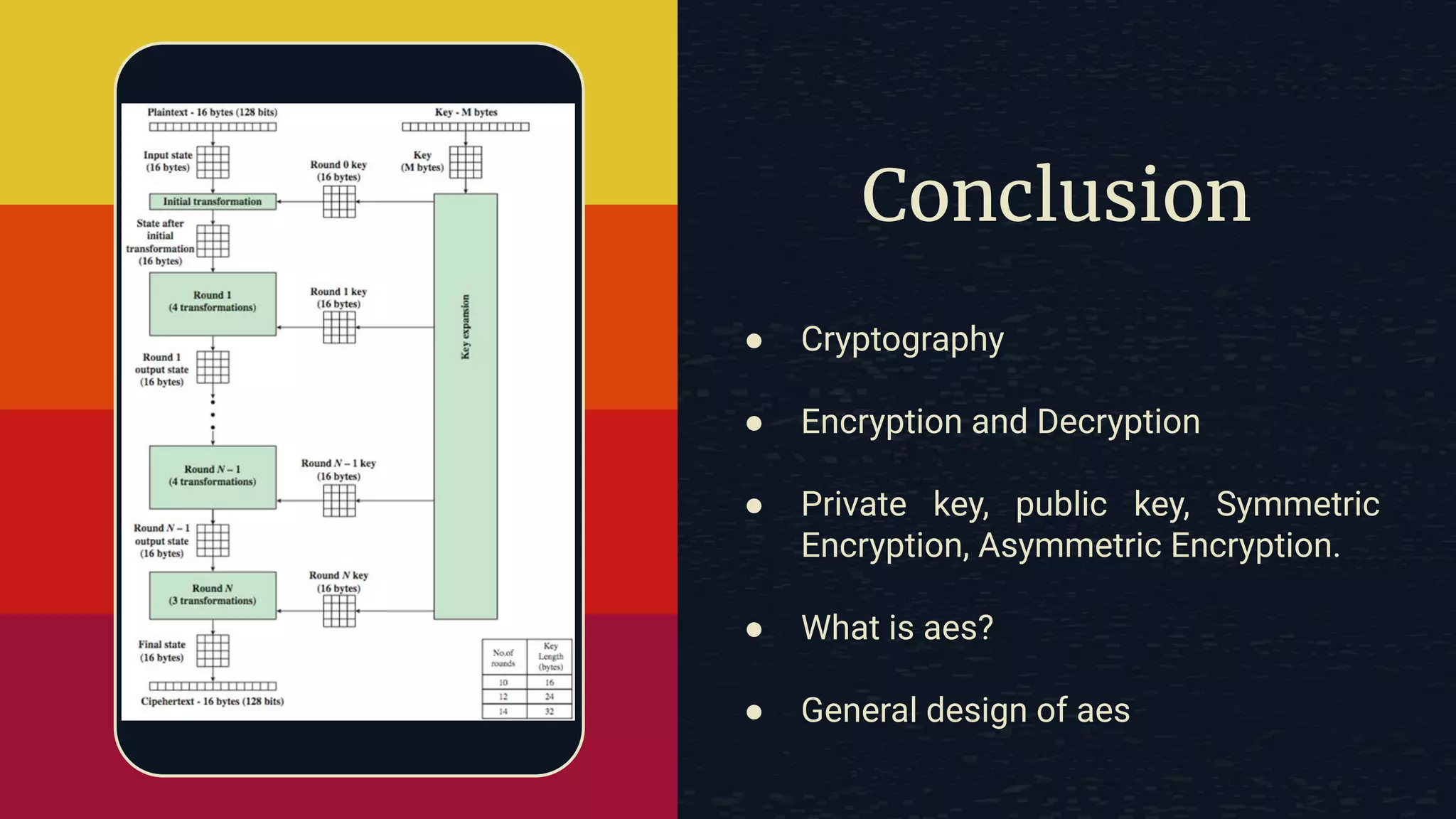
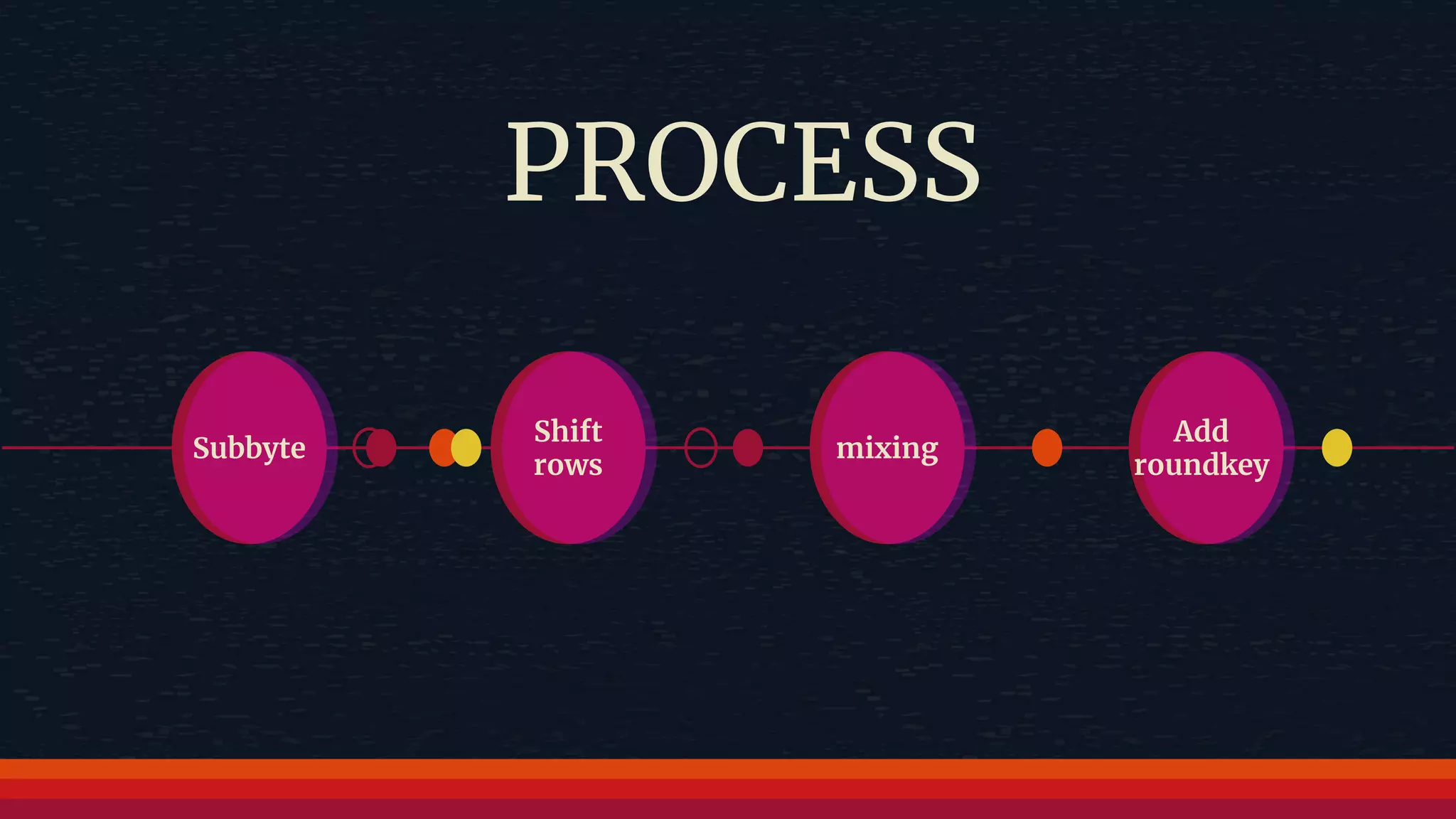
The document provides an overview of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), a symmetric block cipher algorithm used by the U.S. government for protecting classified information. It explains key concepts such as encryption and decryption, private and public keys, and the differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Additionally, it outlines the AES process, including transformations like substitution, permutation, and mixing, as well as the overall structure of encryption rounds.