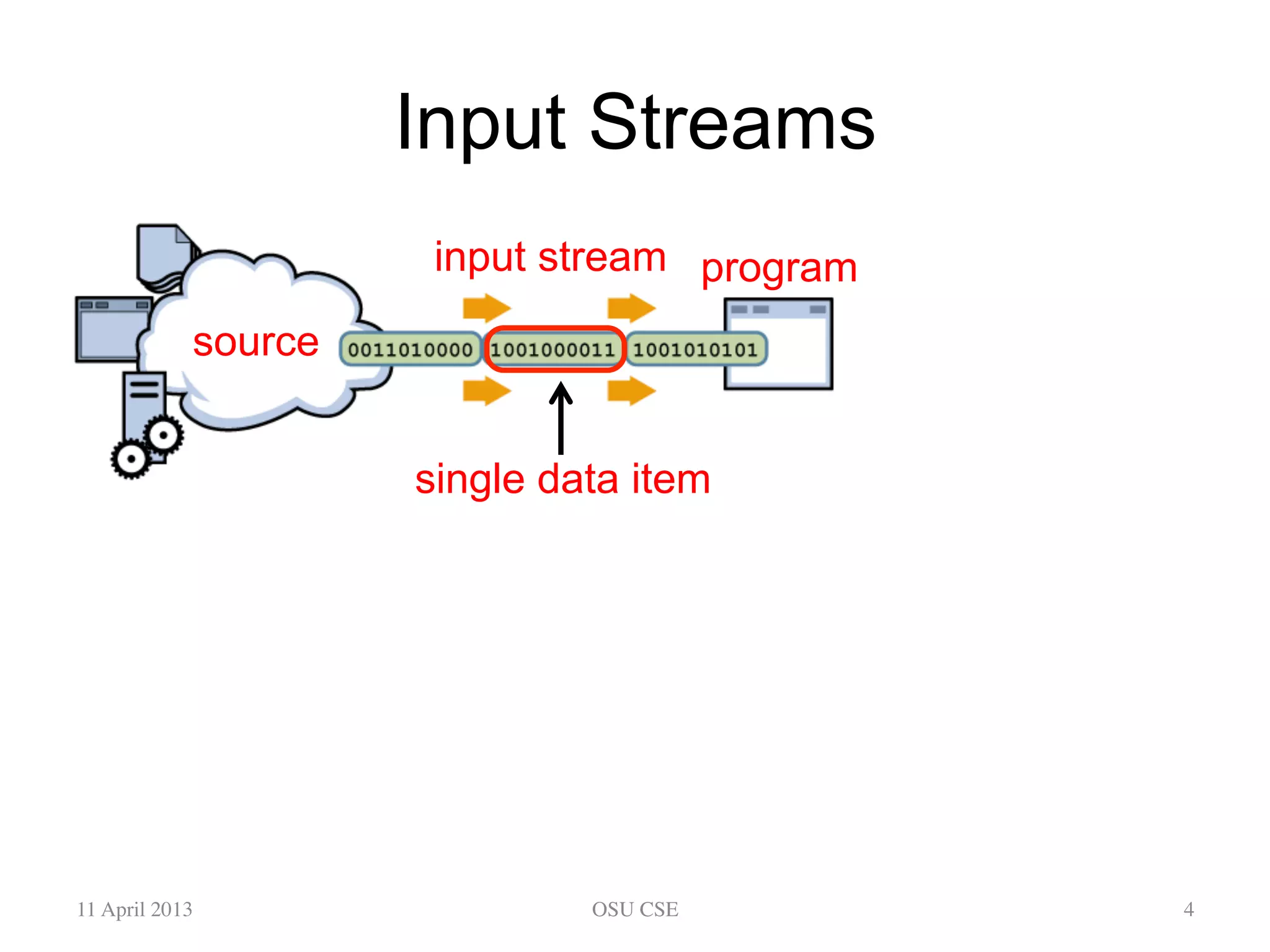
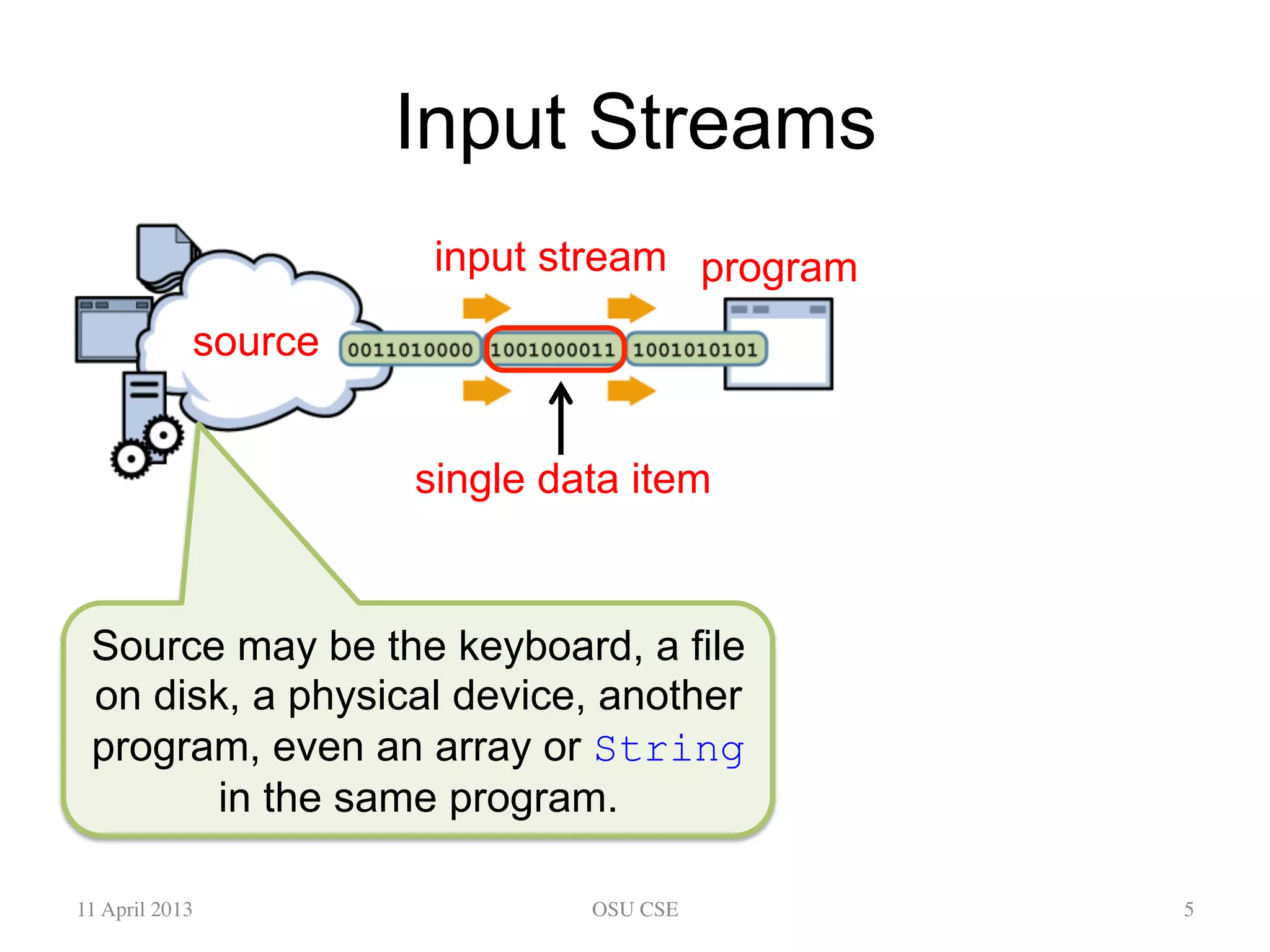
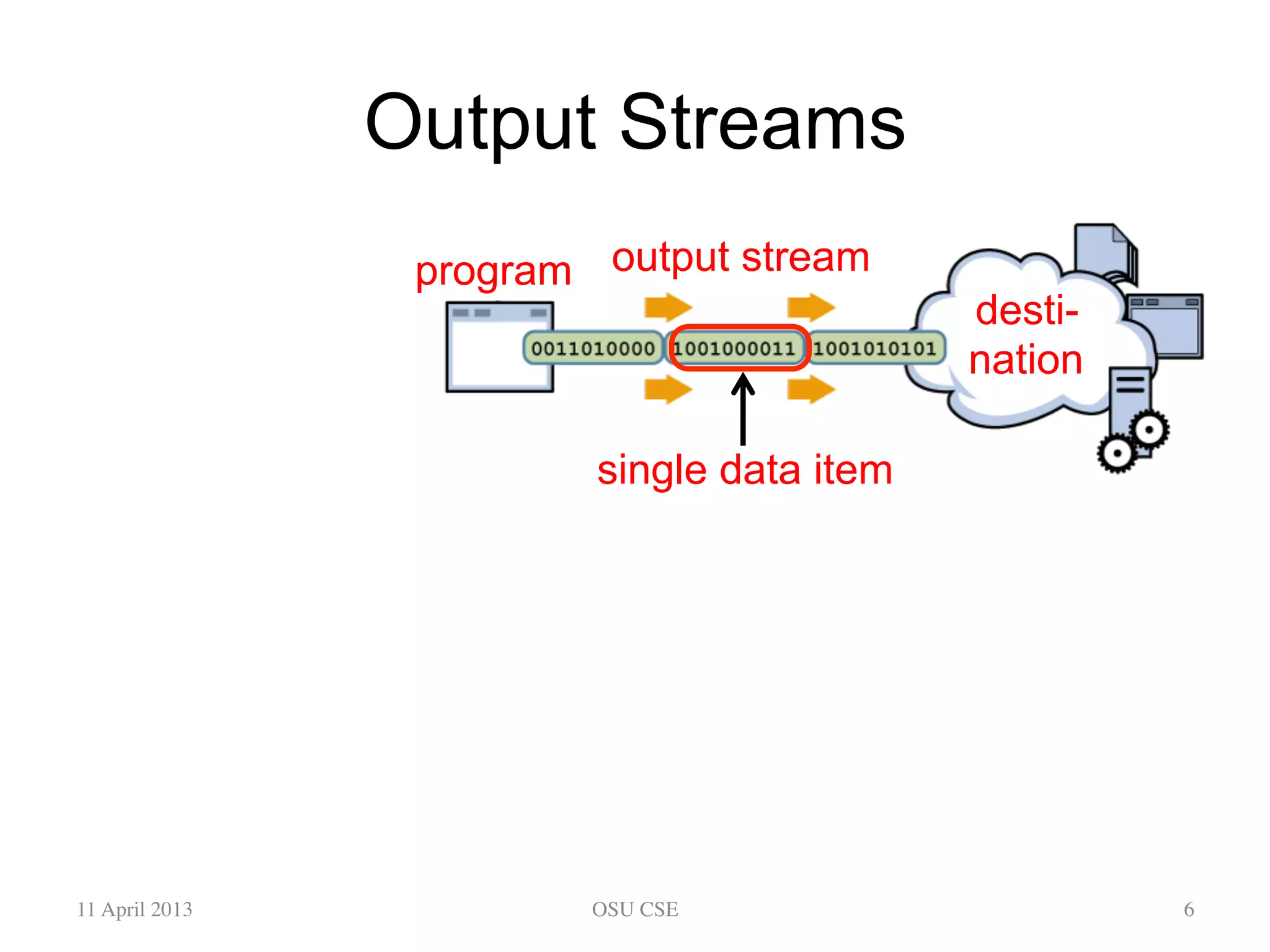
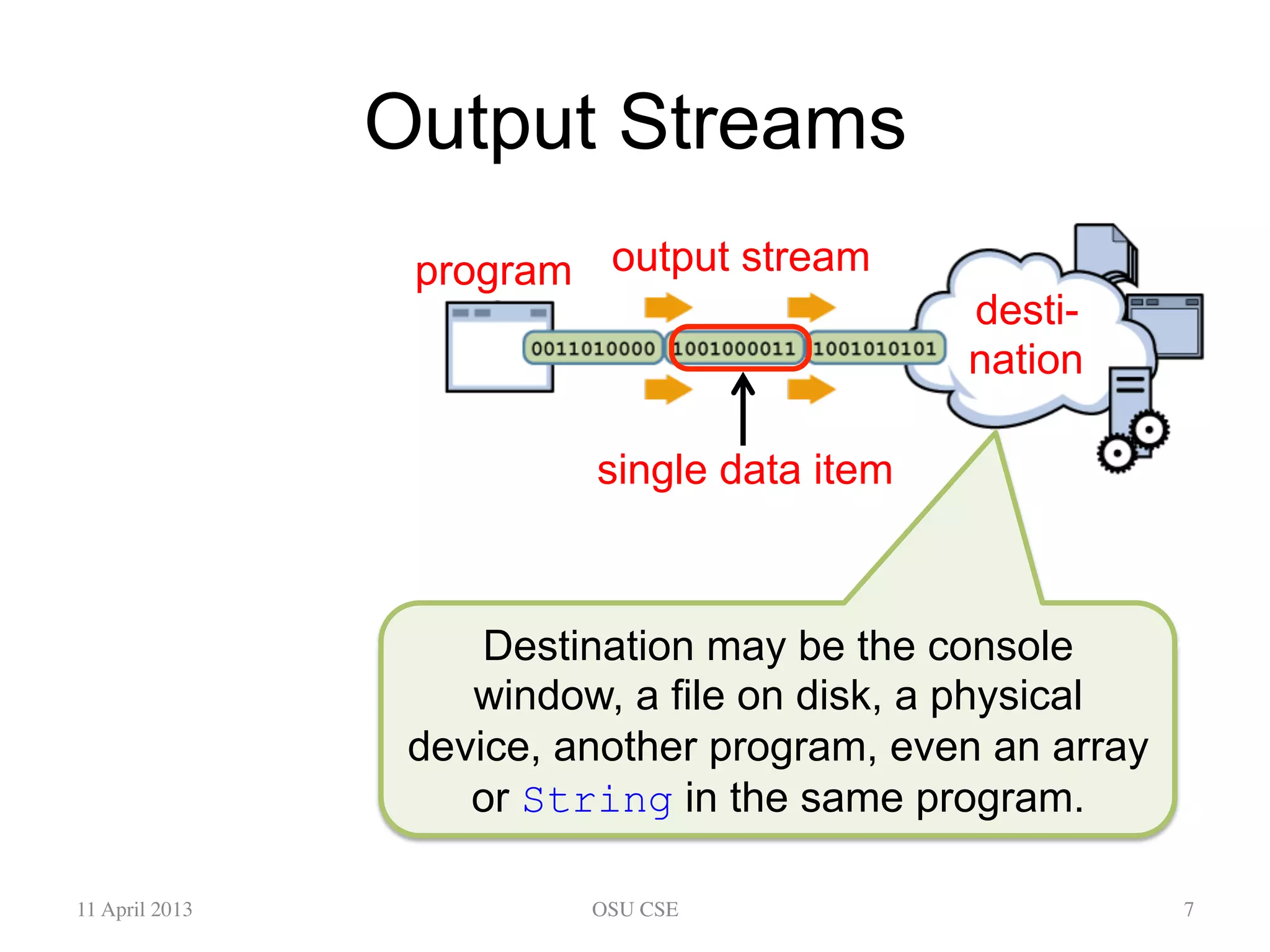
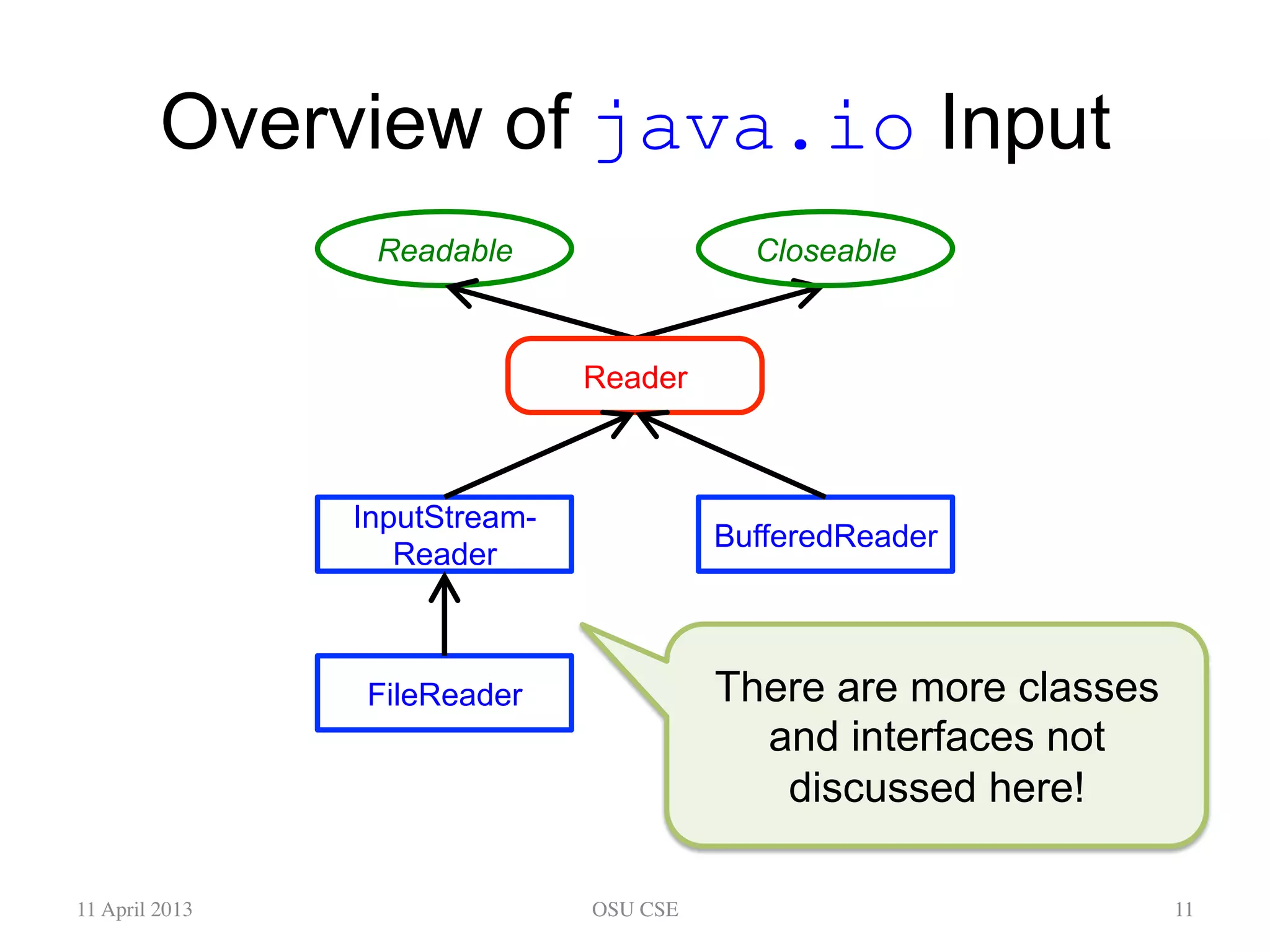
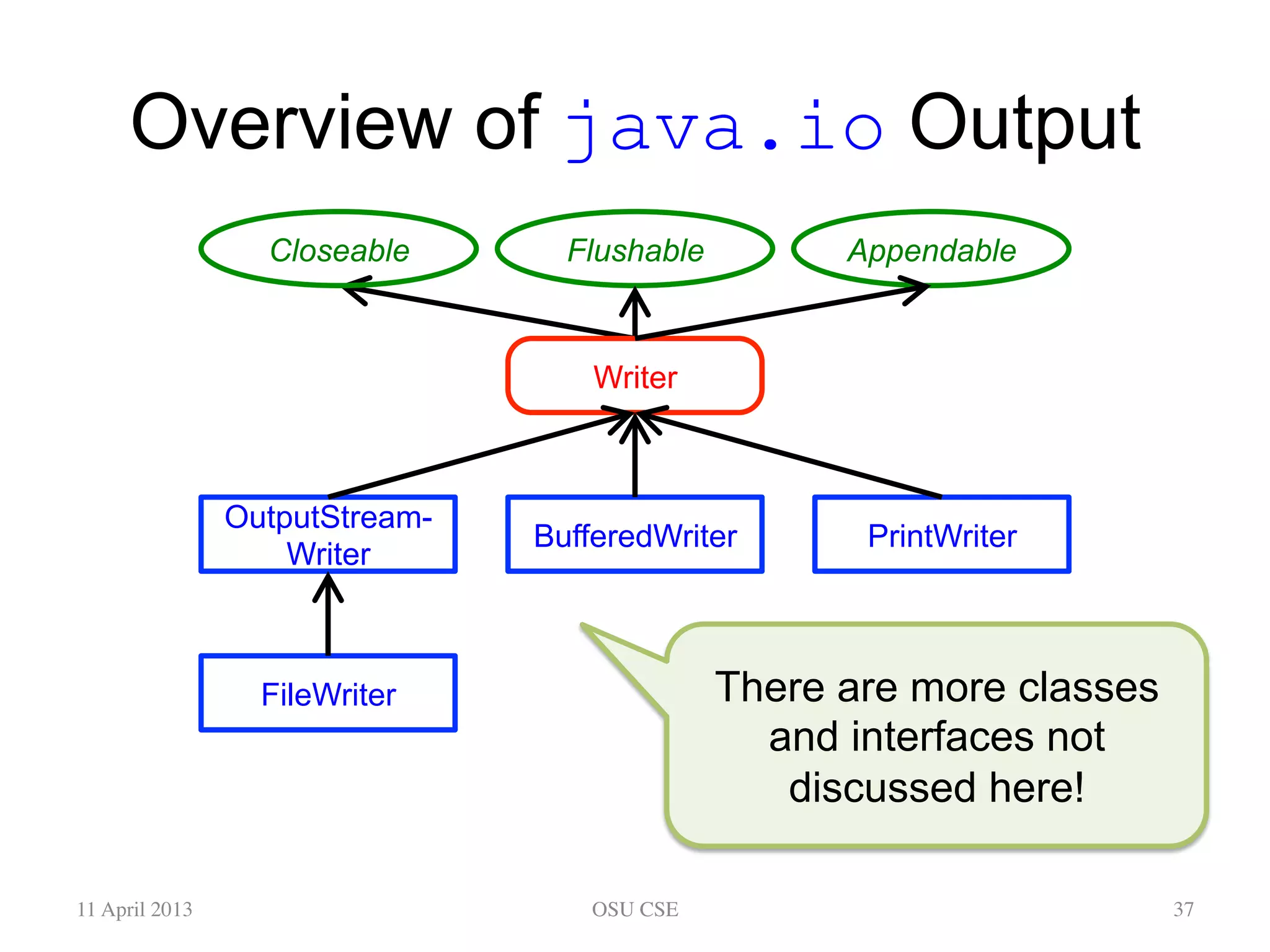
This document provides an overview of input and output streams in Java. It discusses the java.io package and interfaces for reading from and writing to various sources like the keyboard, files, and other programs. It explains how to use classes like BufferedReader and Scanner to read input from the keyboard or a file. It also covers concepts like byte streams, character streams, buffered streams, and detecting end of stream conditions. The document is intended as a beginner's guide for using input/output in Java and compares the approaches using java.io versus alternatives like Scanner from java.util.


![Keyboard Input (SimpleReader) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using SimpleReader: public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleReader input = new SimpleReader1L(); String s = input.nextLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-9-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (SimpleReader) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using SimpleReader: public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleReader input = new SimpleReader1L(); String s = input.nextLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 10 Advice (except for the simplest programs): to guard against the user entering “unexpected” input, read a line at a time into a String and then parse it to see whether it looks like expected.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-10-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-12-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 13 Some methods in java.io throw exceptions (discussed later) under certain circumstances, and you either need to catch them or let them propagate “up the call chain”, like this.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-13-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 14 The variable System.in is a Java standard stream (discussed later), so you may use it without declaring it; but it is a byte stream (discussed later), so you want to wrap it ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-14-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 15 ... in a character stream (discussed later) like this ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-15-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 16 ... and then you want to wrap that character stream in a buffered stream (discussed later), like this, so ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-16-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 17 ... you can read one line at a time into a String, like this.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-17-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 18 The declared types of variables when you use java.io are class types rather than interface types.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-18-2048.jpg)
![Keyboard Input (java.io)to • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 19 This technique of slightly extending features or capabilities of an object by wrapping it inside another object is a popular object-oriented design pattern called the decorator pattern.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-19-2048.jpg)

![An Alternative (java.util) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using Scanner: public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s = input.nextLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-21-2048.jpg)
![An Alternative (java.util) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using Scanner: public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s = input.nextLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 22 Now, main does not declare that it throws IOException; in this sense it is similar to using SimpleReader.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-22-2048.jpg)
![An Alternative (java.util) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using Scanner: public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s = input.nextLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 23 Notice that initialization does not involve layers of wrapping of one object inside another; Scanner also has different constructors so it can be used with files.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-23-2048.jpg)
![An Alternative (java.util) • Here’s some code in main to read input from the keyboard, using Scanner: public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s = input.nextLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 24 The method for reading a line into a String has a different name than for BufferedReader: it is nextLine (like SimpleReader).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-24-2048.jpg)
![End-of-Stream (SimpleReader) public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleReader input = new SimpleReader1L(); while (!input.atEOS()) { s = input.nextLine(); ... } ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-25-2048.jpg)
![End-of-Stream (SimpleReader) public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleReader input = new SimpleReader1L(); while (!input.atEOS()) { s = input.nextLine(); ... } ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 26 SimpleReader has a method to report “at end-of-stream”, and it can tell you this before you read “past the end of the input stream”; similarly, Scanner has method hasNext.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-26-2048.jpg)
![End-of-Stream (java.io) public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); while (s != null) { ... s = input.readLine(); } ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-27-2048.jpg)
![End-of-Stream (java.io) public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); while (s != null) { ... s = input.readLine(); } ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 28 BufferedReader has no method to detect when you cannot read any more input, so you can check it only after you try to read “past the end of the stream”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-28-2048.jpg)
![End-of-Stream (java.io) public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s = input.readLine(); while (s != null) { ... s = input.readLine(); } ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 29 Before checking again, you must try to read another line.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-29-2048.jpg)
![File Input (SimpleReader) • Here’s some code in main to read input from a file, using SimpleReader: public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleReader input = new SimpleReader1L("data/test.txt"); String s = input.nextLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-30-2048.jpg)
![File Input (SimpleReader) • Here’s some code in main to read input from a file, using SimpleReader: public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleReader input = new SimpleReader1L("data/test.txt"); String s = input.nextLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 31 SimpleReader has a constructor from a String, which is the name of the file you want to read from.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-31-2048.jpg)
![File Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from a file, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-32-2048.jpg)
![File Input (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to read input from a file, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); String s = input.readLine(); ... input.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 33 Now, you wrap a BufferedReader around a FileReader (which has a constructor from a String, which is the name of the file you want to read from).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-33-2048.jpg)

![Console Output (SimpleWriter) • Here’s some code in main to write output to the console, using SimpleWriter: public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleWriter output = new SimpleWriter1L(); output.print("foo"); output.println(" and bar"); ... output.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-35-2048.jpg)
![Console Output (SimpleWriter) • Here’s some code in main to write output to the console, using SimpleWriter: public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleWriter output = new SimpleWriter1L(); output.print("foo"); output.println(" and bar"); ... output.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 36 Both print and println are available, and the latter should be used to output the line separator string for the current “platform” (i.e., the system the Java program is running on).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-36-2048.jpg)
![Console Output (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to write output to the console, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) { ... System.out.print("foo"); System.out.println(" and bar"); ... } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-38-2048.jpg)
![Console Output (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to write output to the console, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) { ... System.out.print("foo"); System.out.println(" and bar"); ... } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 39 System.out is another Java standard stream (discussed later), which you neither declare nor close; both print and println are available.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-39-2048.jpg)
![Console Output (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to write output to the console, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) { ... System.out.print("foo"); System.out.println(" and bar"); ... } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 40 It is fine to use System.out for console output, but there are potential problems using (unwrapped) System.in for keyboard input.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-40-2048.jpg)
![File Output (SimpleWriter) • Here’s some code in main to write output to a file, using SimpleWriter: public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleWriter output = new SimpleWriter1L("data/test.txt"); output.print("foo"); output.println(" and bar"); ... output.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-41-2048.jpg)
![File Output (SimpleWriter) • Here’s some code in main to write output to a file, using SimpleWriter: public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleWriter output = new SimpleWriter1L("data/test.txt"); output.print("foo"); output.println(" and bar"); ... output.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 42 SimpleWriter has a constructor from a String, which is the name of the file you want to write to.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-42-2048.jpg)
![File Output (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to write output to a file, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter( new BufferedWriter ( new FileWriter("data/test.txt"))); output.print("foo"); output.println(" and bar"); ... output.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-43-2048.jpg)
![File Output (java.io) • Here’s some code in main to write output to a file, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter( new BufferedWriter ( new FileWriter("data/test.txt"))); output.print("foo"); output.println(" and bar"); ... output.close(); } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 44 PrintWriter is needed for convenient output, and is added as yet another wrapper—to get print and println.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-44-2048.jpg)




![Example • Here’s the overall structure of an example main in a simple application that reads input from a file, using java.io: public static void main(String[] args) { // Code to open file // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-49-2048.jpg)
![Example: Opening a File public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader input; try { input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error opening file"); return; } // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-50-2048.jpg)
![Example: Opening a File public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader input; try { input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error opening file"); return; } // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 51 Now, main does not declare that it throws IOException if it (always) catches the exception.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-51-2048.jpg)
![Example: Opening a File public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader input; try { input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error opening file"); return; } // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 52 This variable must be declared (but not initialized) here, so it is in scope later where the code reads from the file—if the file is opened successfully.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-52-2048.jpg)
![Example: Opening a File public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader input; try { input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error opening file"); return; } // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 53 The try block contains the code that might throw an IOException ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-53-2048.jpg)
![Example: Opening a File public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader input; try { input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error opening file"); return; } // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 54 ... which this constructor might throw, e.g., if the file does not exist.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-54-2048.jpg)
![Example: Opening a File public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader input; try { input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error opening file"); return; } // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 55 The catch block states the exception it handles, and is executed iff code in the try block throws that exception (which is called e in the catch block).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-55-2048.jpg)
![Example: Opening a File public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader input; try { input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error opening file"); return; } // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 56 Here, the code prints an error message to System.err, another Java standard stream (discussed later), and “aborts” main by returning from it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-56-2048.jpg)
![Example: Opening a File public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader input; try { input = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("data/test.txt")); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error opening file"); return; } // Code to read from file // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 57 In either case (even after the catch block, if it did not return as it does here), execution proceeds with the next statement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-57-2048.jpg)
![Example: Reading From a File public static void main(String[] args) { // Code to open file try { String s = input.readLine(); while (s != null) { ... s = input.readLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error reading from file"); } // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-58-2048.jpg)
![Example: Reading From a File public static void main(String[] args) { // Code to open file try { String s = input.readLine(); while (s != null) { ... s = input.readLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error reading from file"); } // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 59 We need this try-catch because the method readLine might throw an IOException.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-59-2048.jpg)
![Example: Reading From a File public static void main(String[] args) { // Code to open file try { String s = input.readLine(); while (s != null) { ... s = input.readLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error reading from file"); } // Code to close file } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 60 As before, even after the catch block (which in this case does not end with a return), execution proceeds with the next statement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-60-2048.jpg)
![Example: Closing a File public static void main(String[] args) { // Code to open file // Code to read from file try { input.close(); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error closing file"); } } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-61-2048.jpg)
![Example: Closing a File public static void main(String[] args) { // Code to open file // Code to read from file try { input.close(); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Error closing file"); } } 11 April 2013 OSU CSE 62 We need this try-catch because even the method close might throw an IOException.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32-140322013311-phpapp02/75/sasasasasasas-62-2048.jpg)






