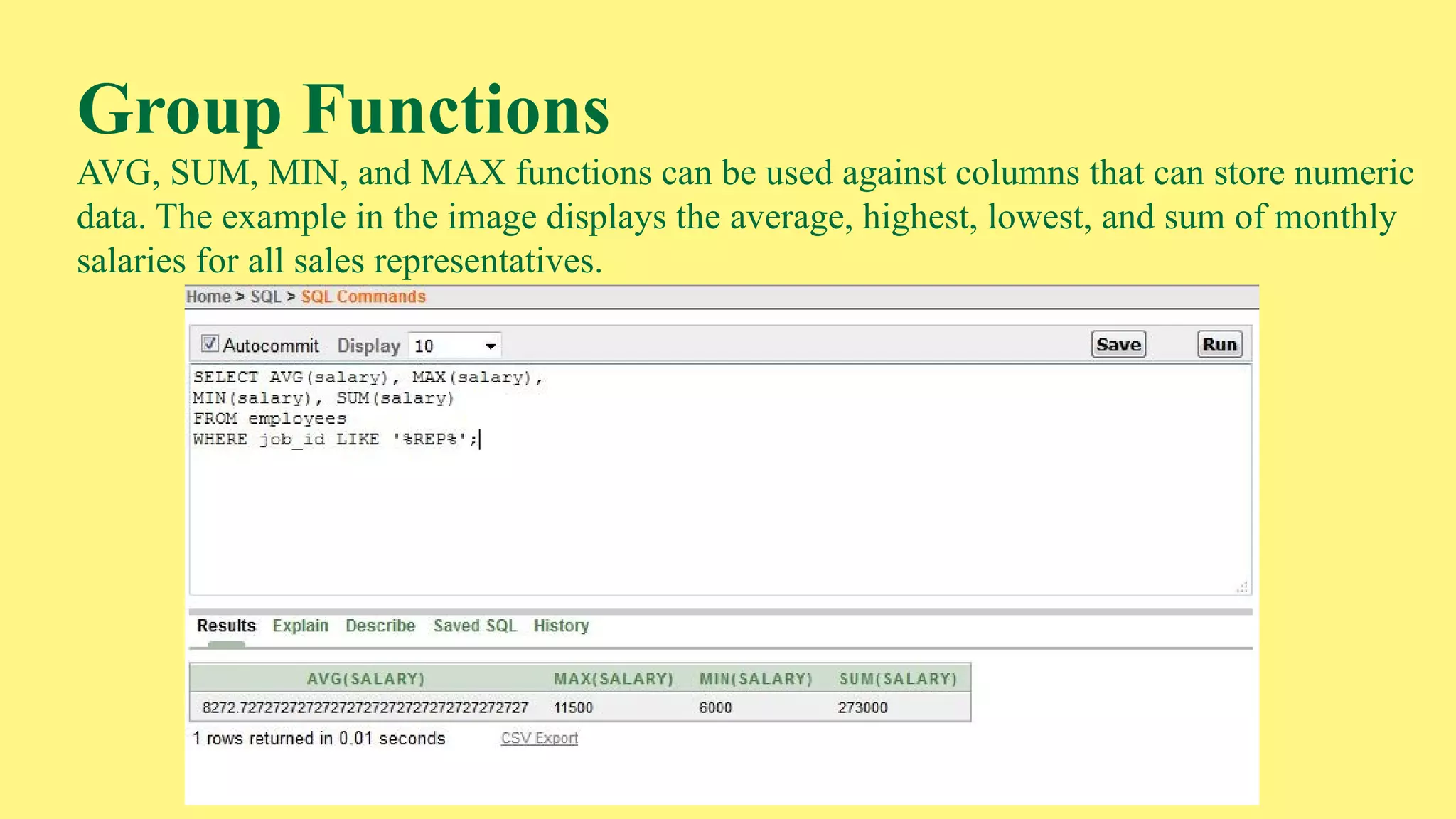
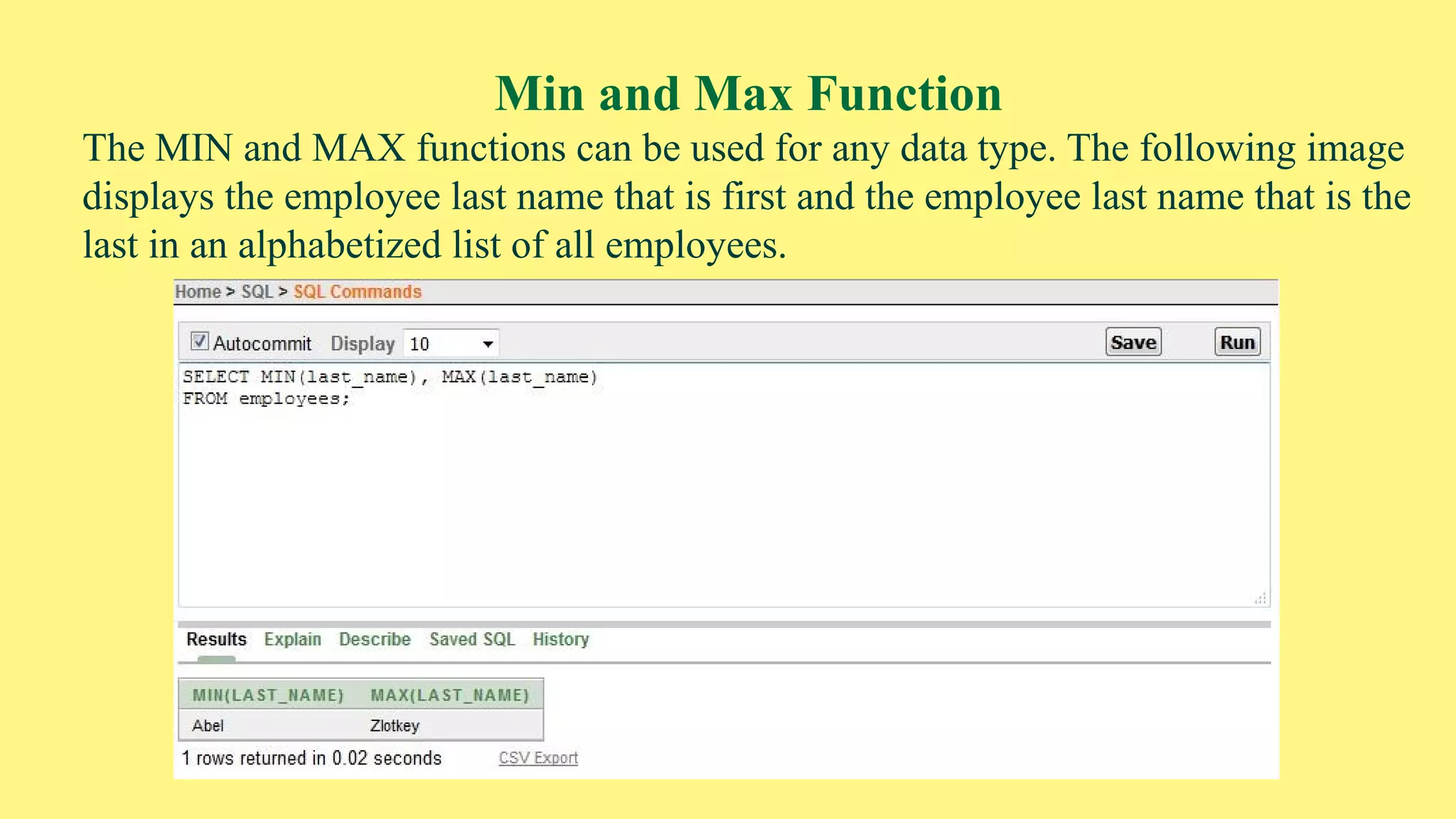
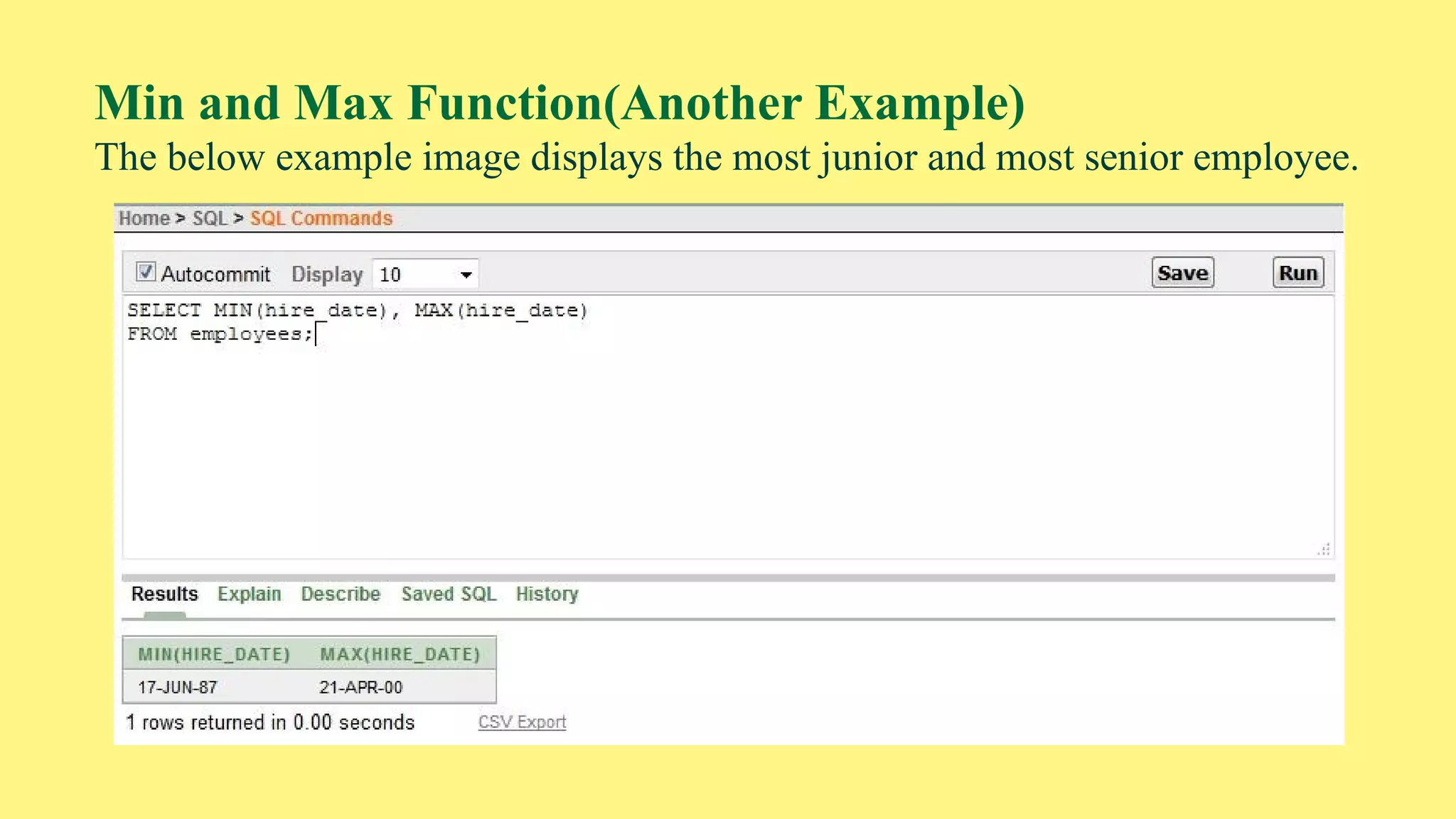
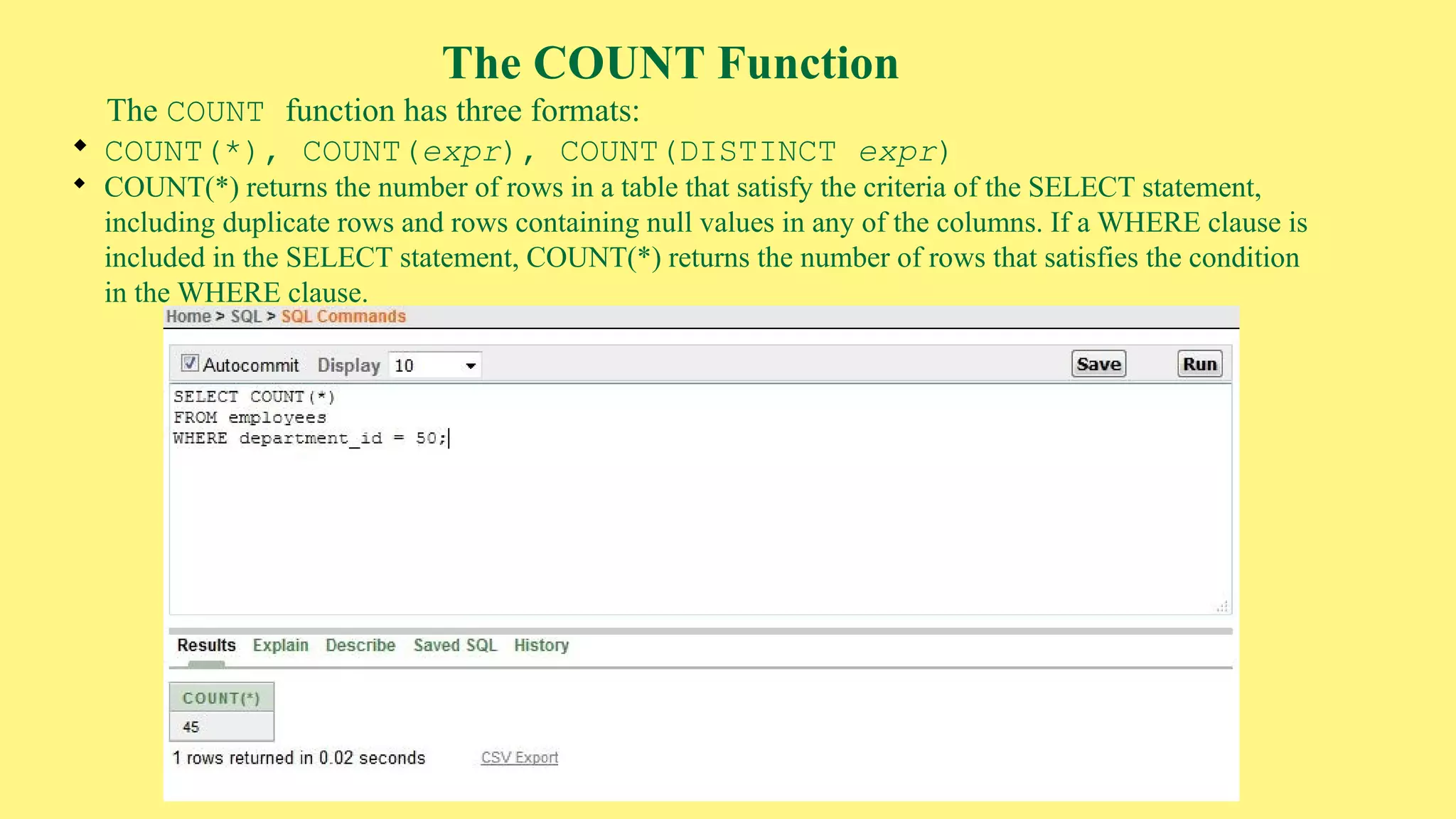
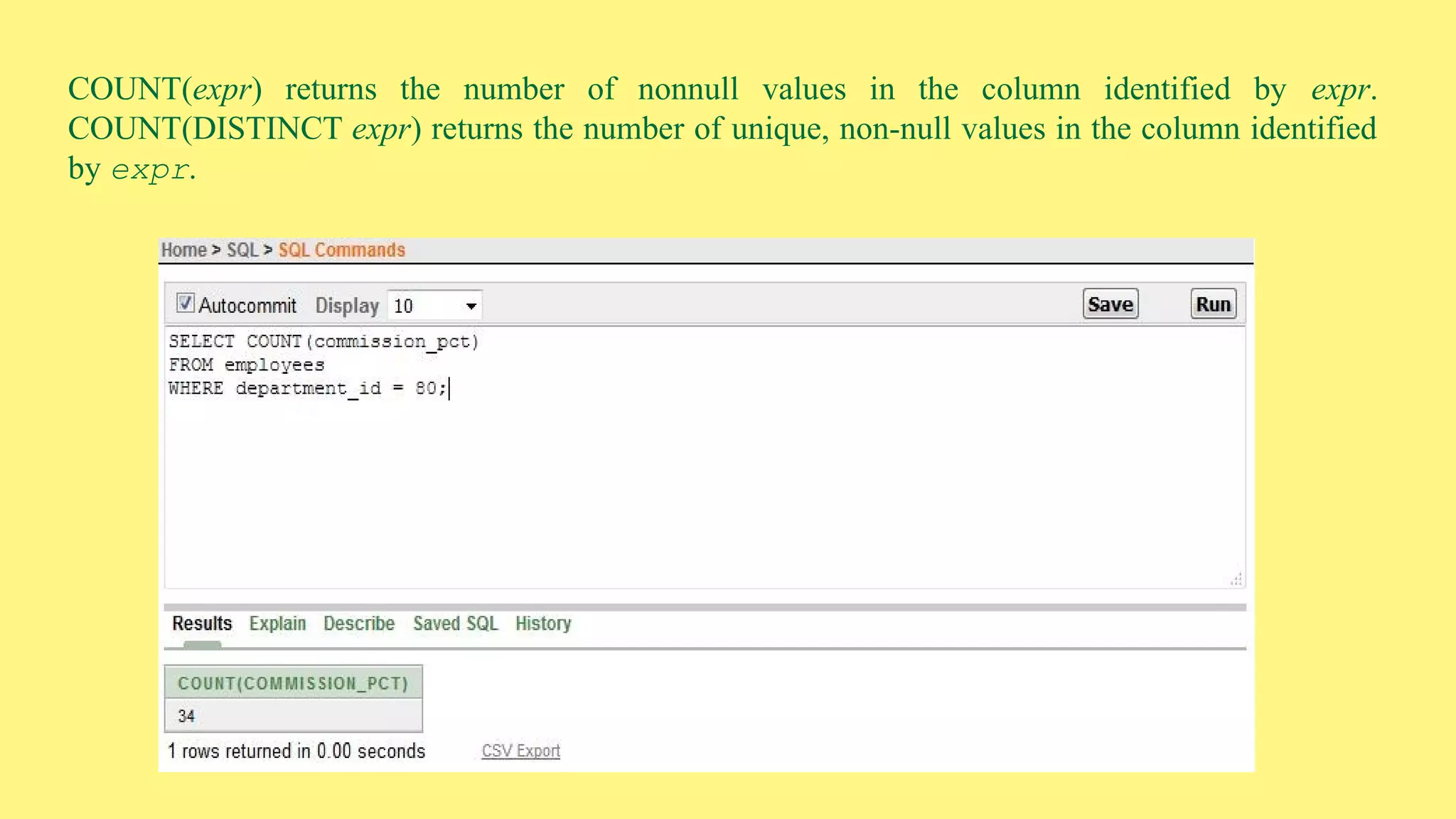
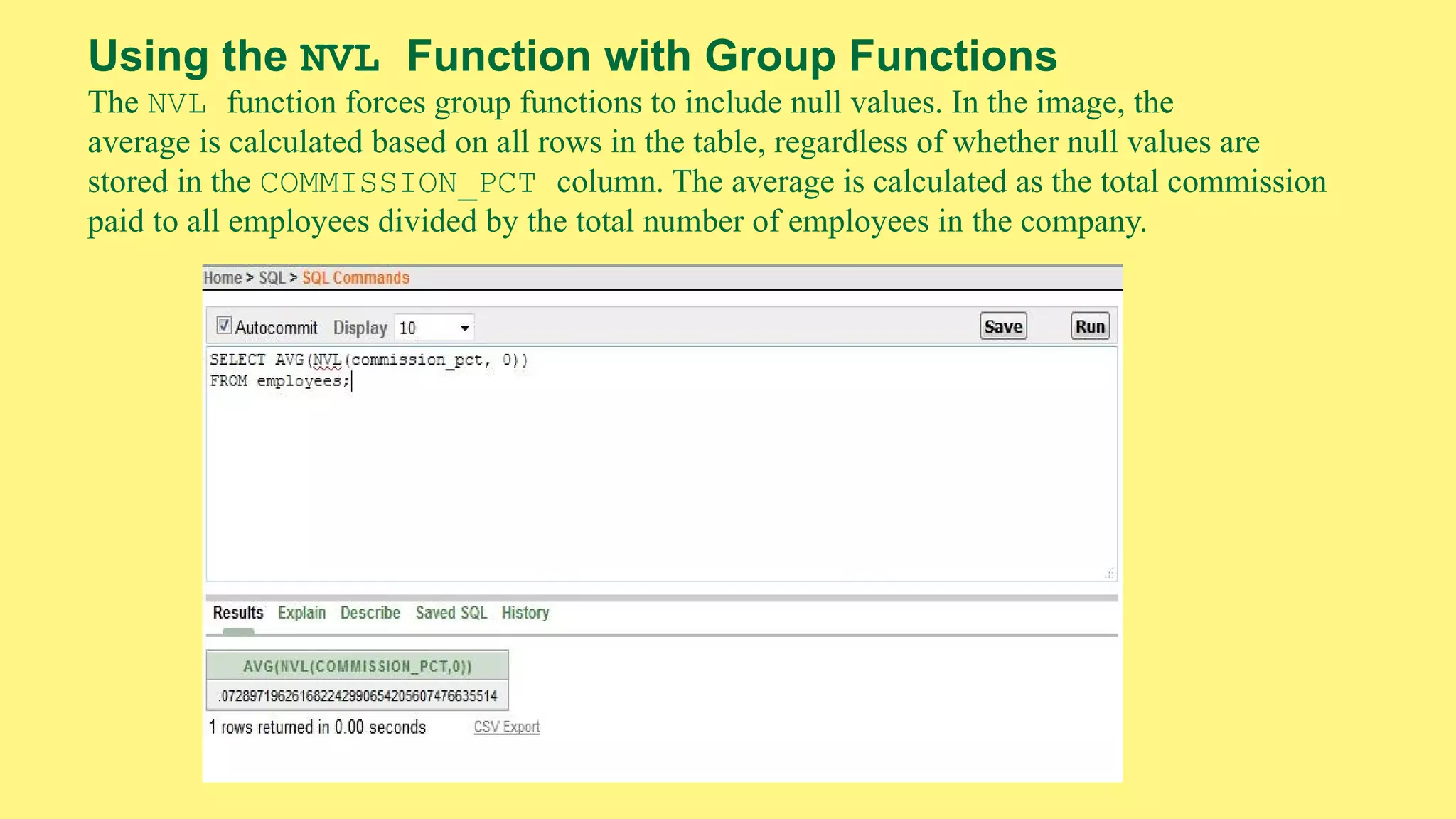
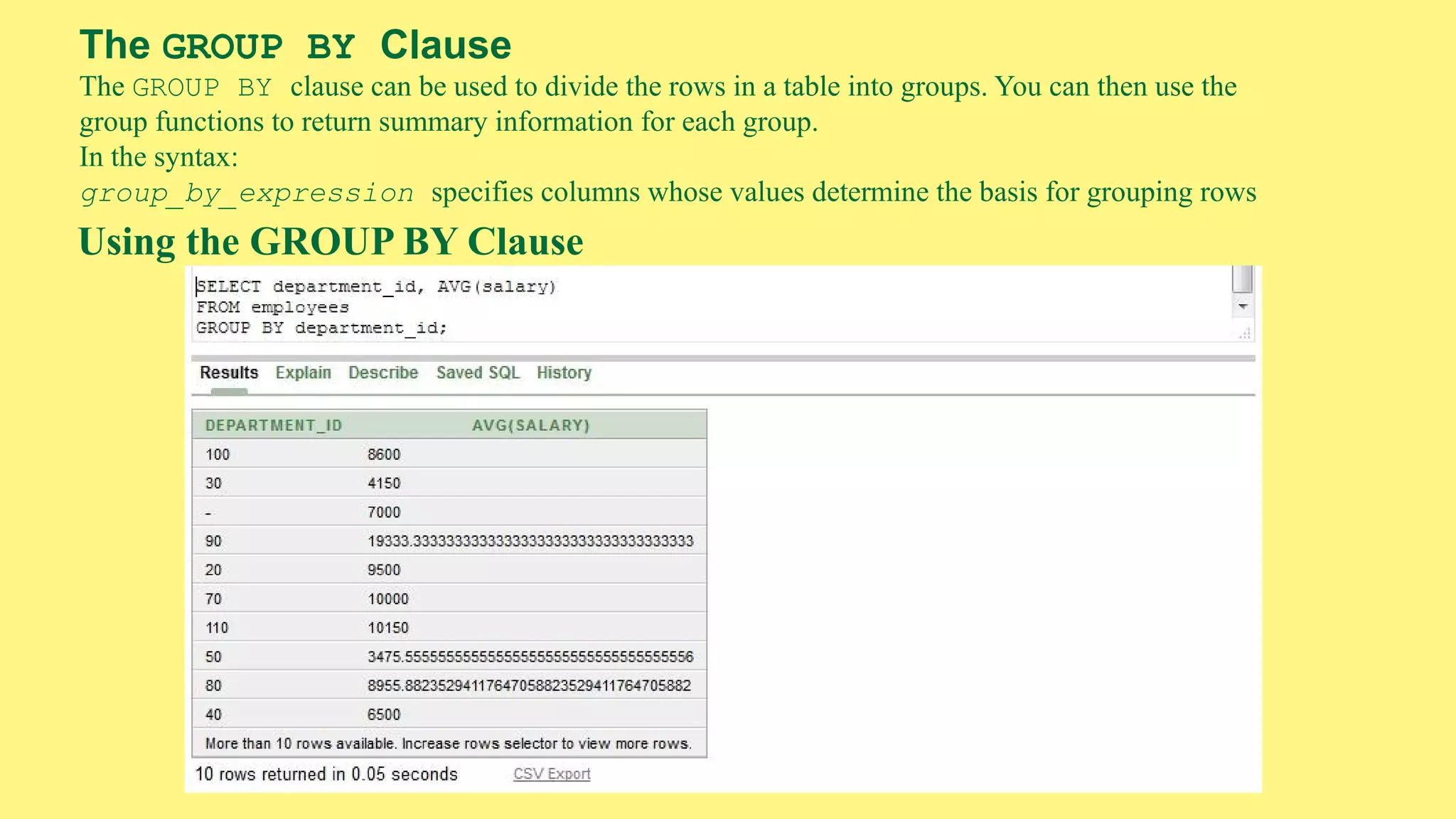
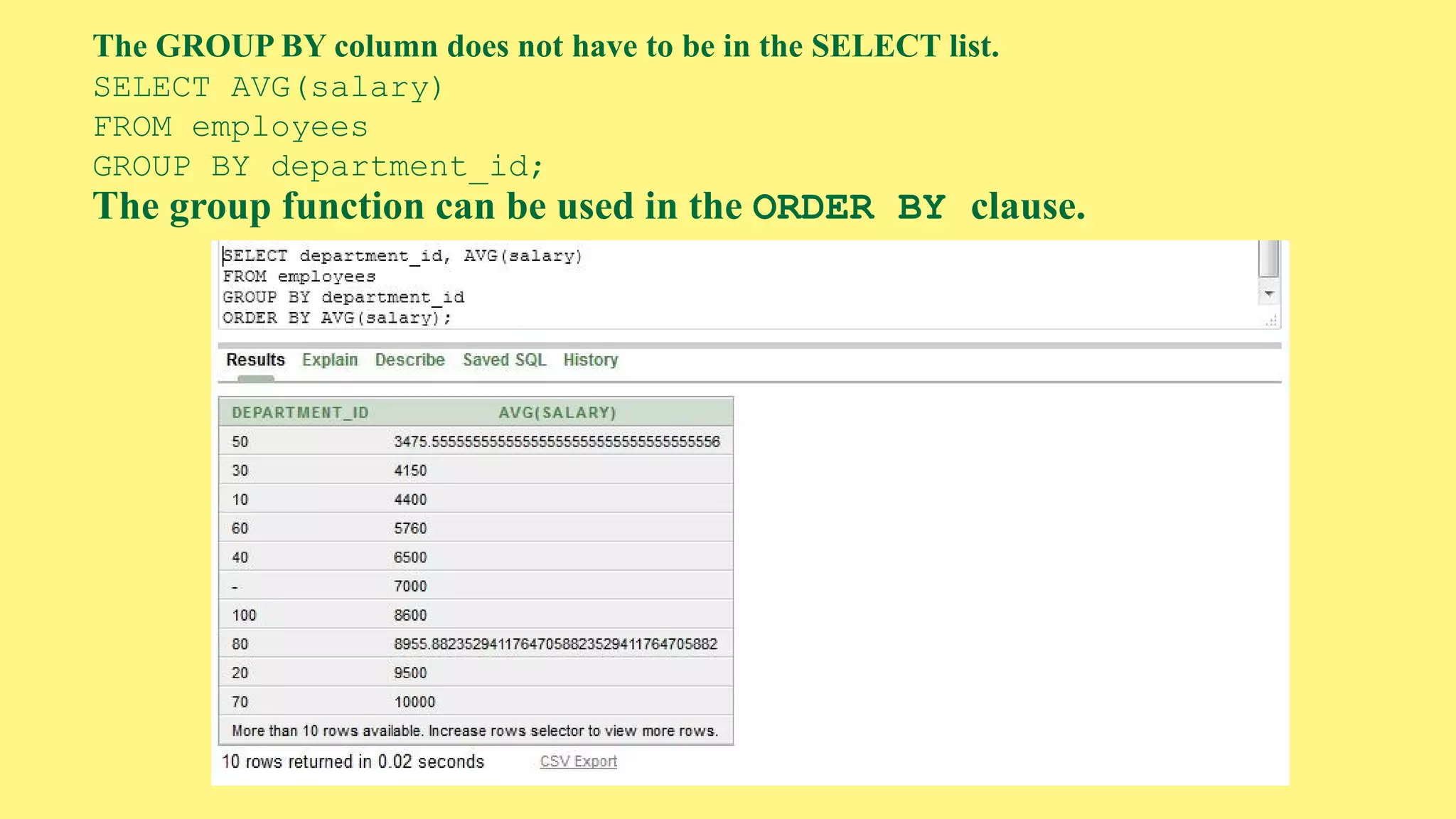
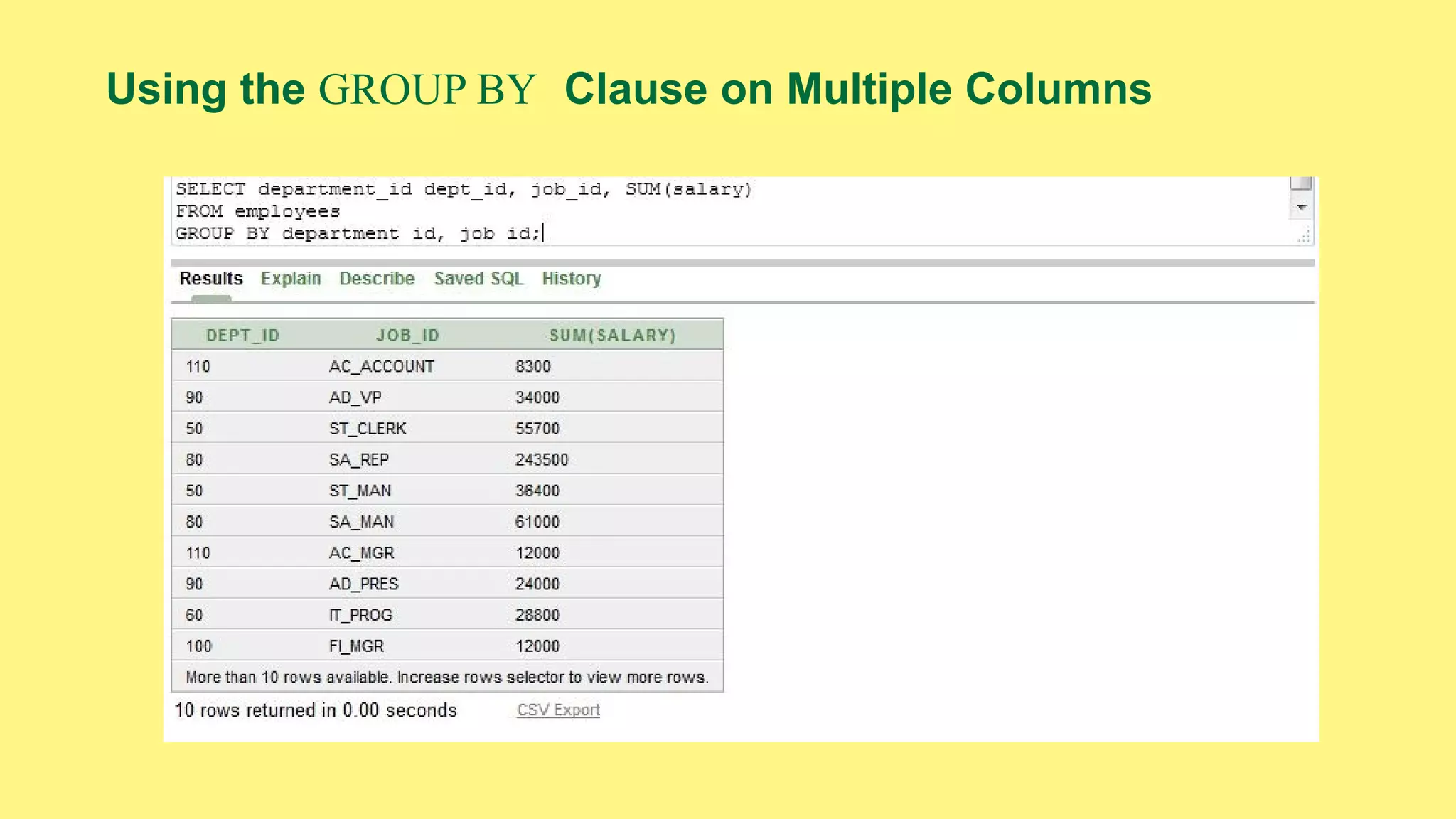
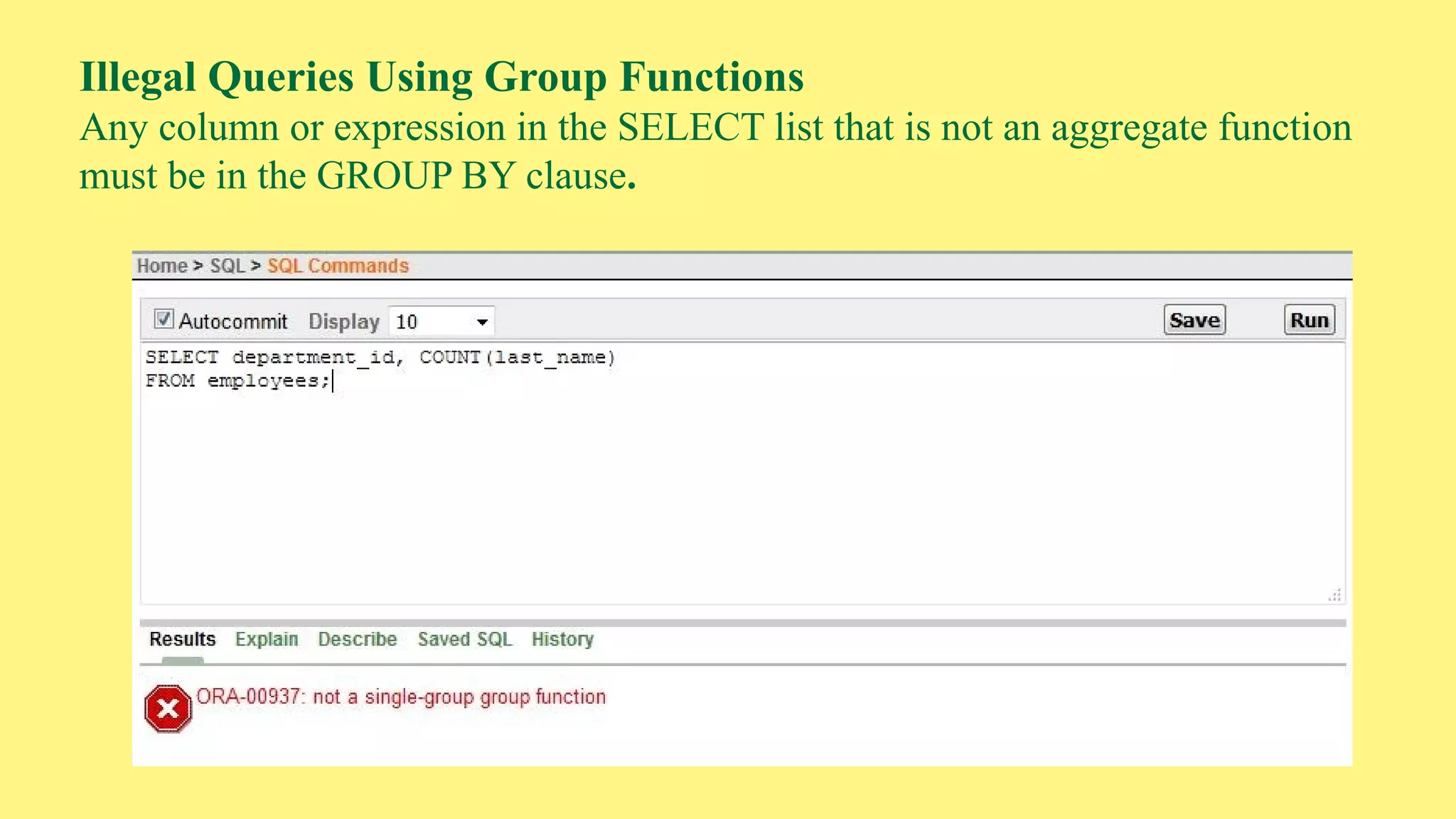
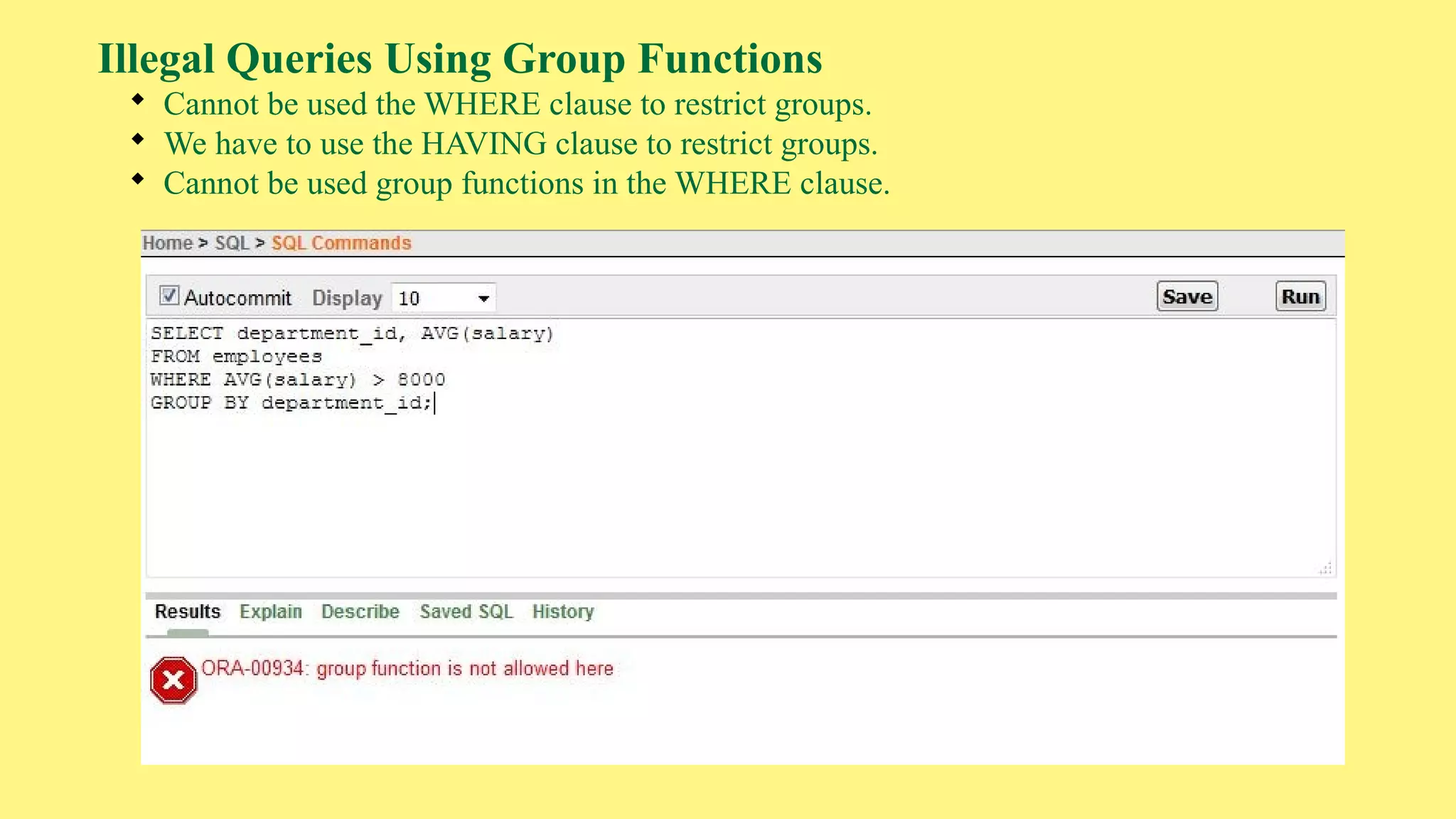
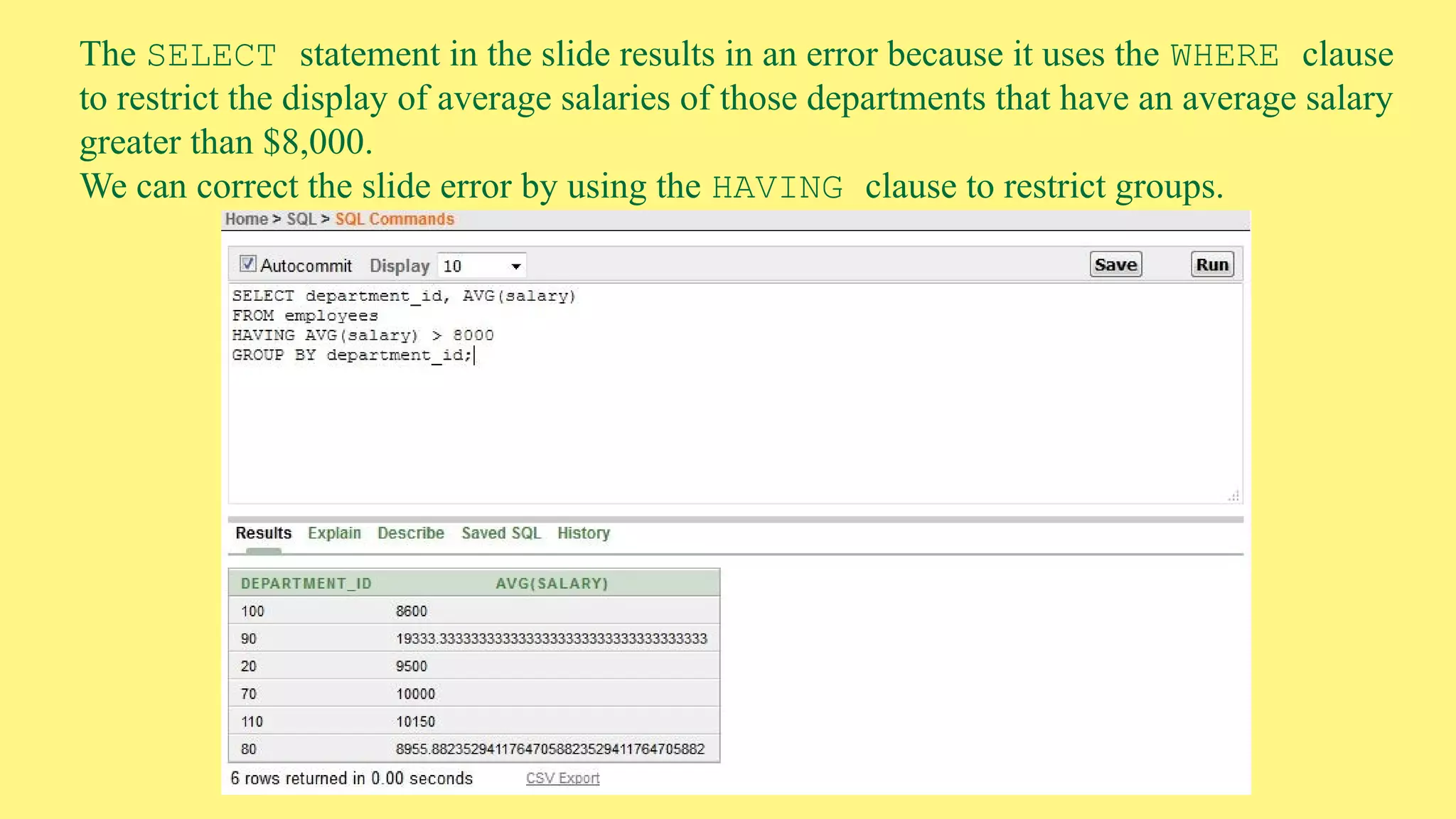
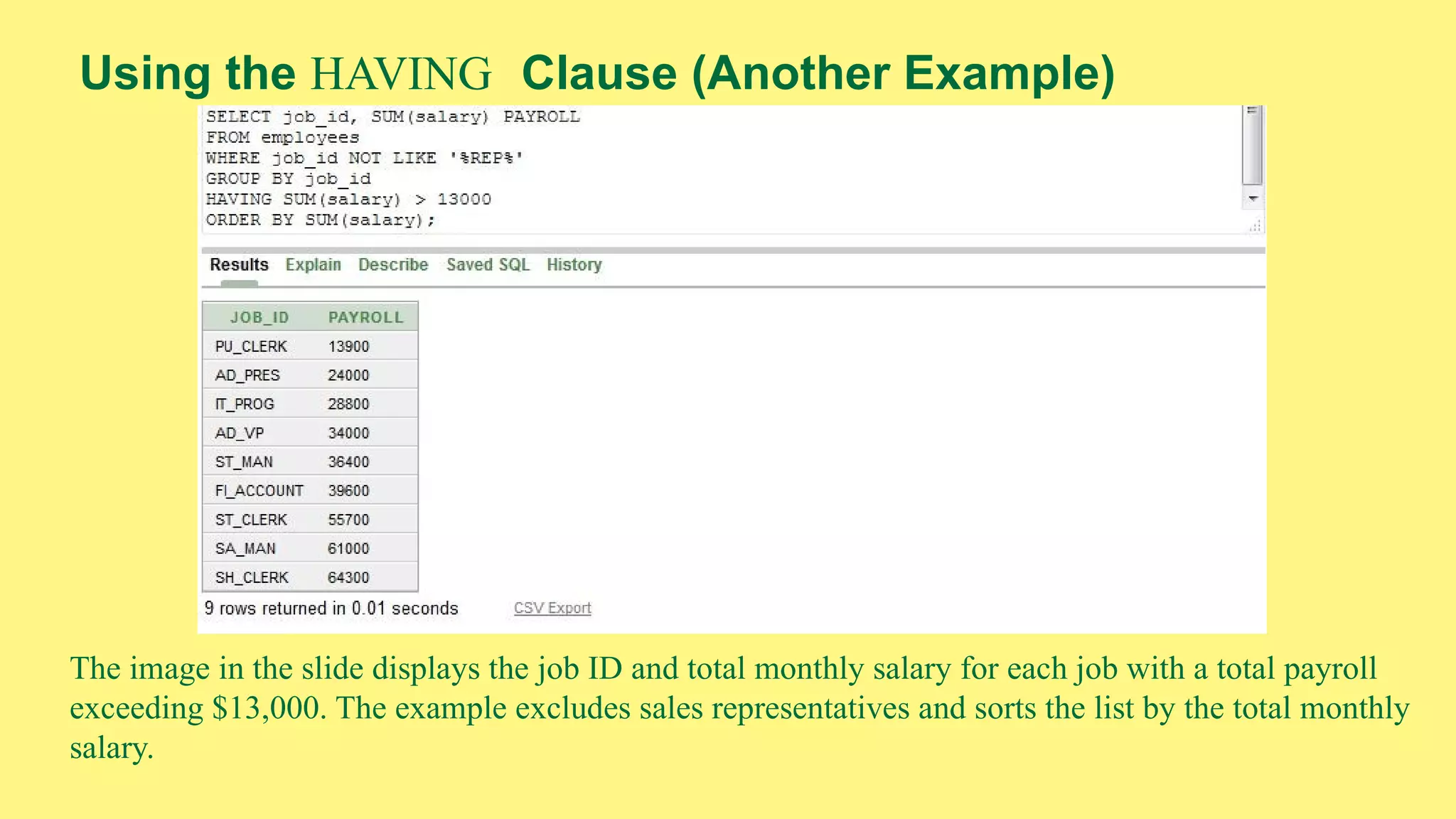
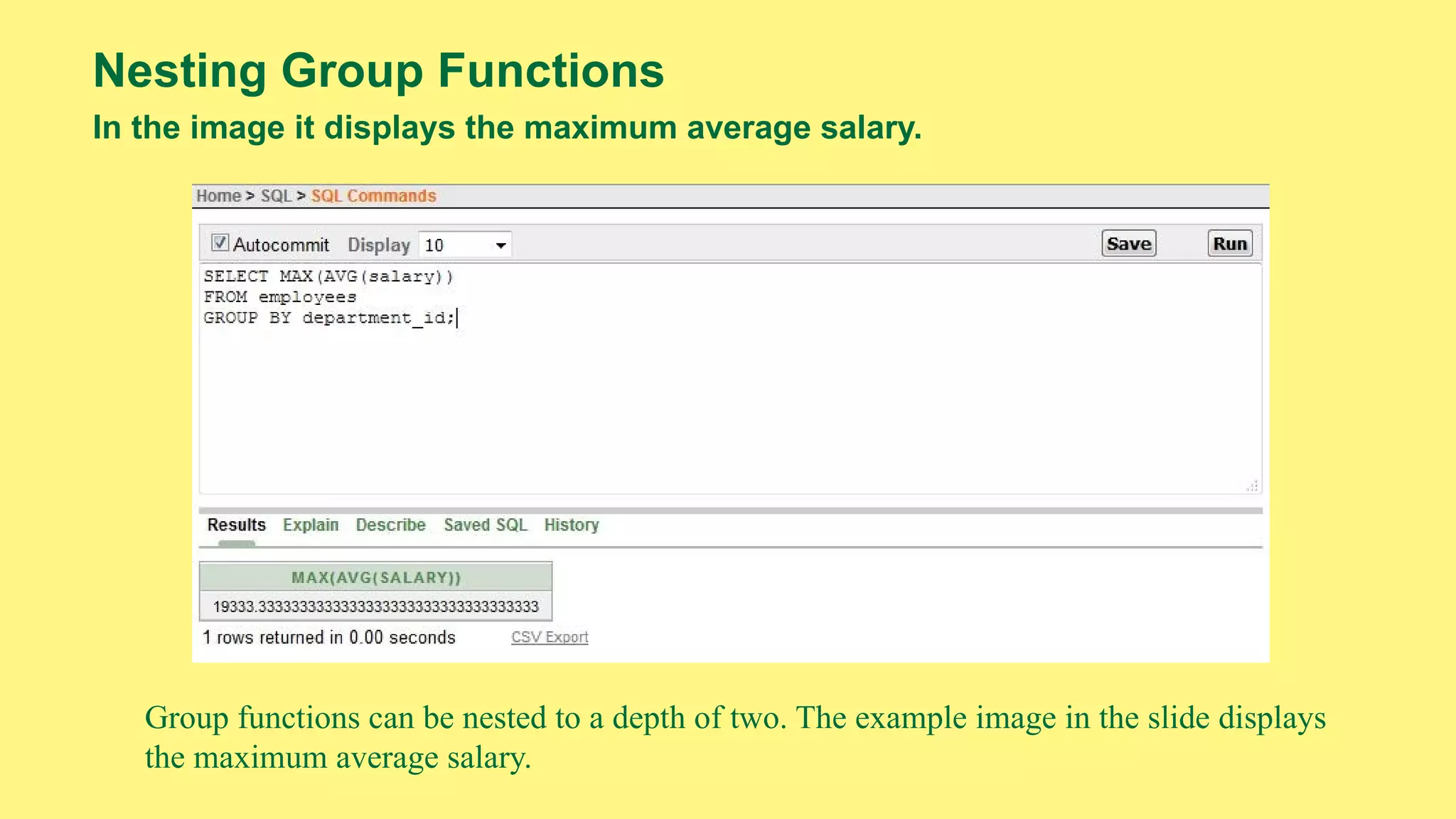
The document provides an overview of group functions in database management systems, including types such as avg, count, min, and max. It details how these functions operate on numeric data, describes the count function variations, and explains the use of the NVL and GROUP BY clauses. Additionally, it highlights limitations regarding the use of WHERE and HAVING clauses with group functions.