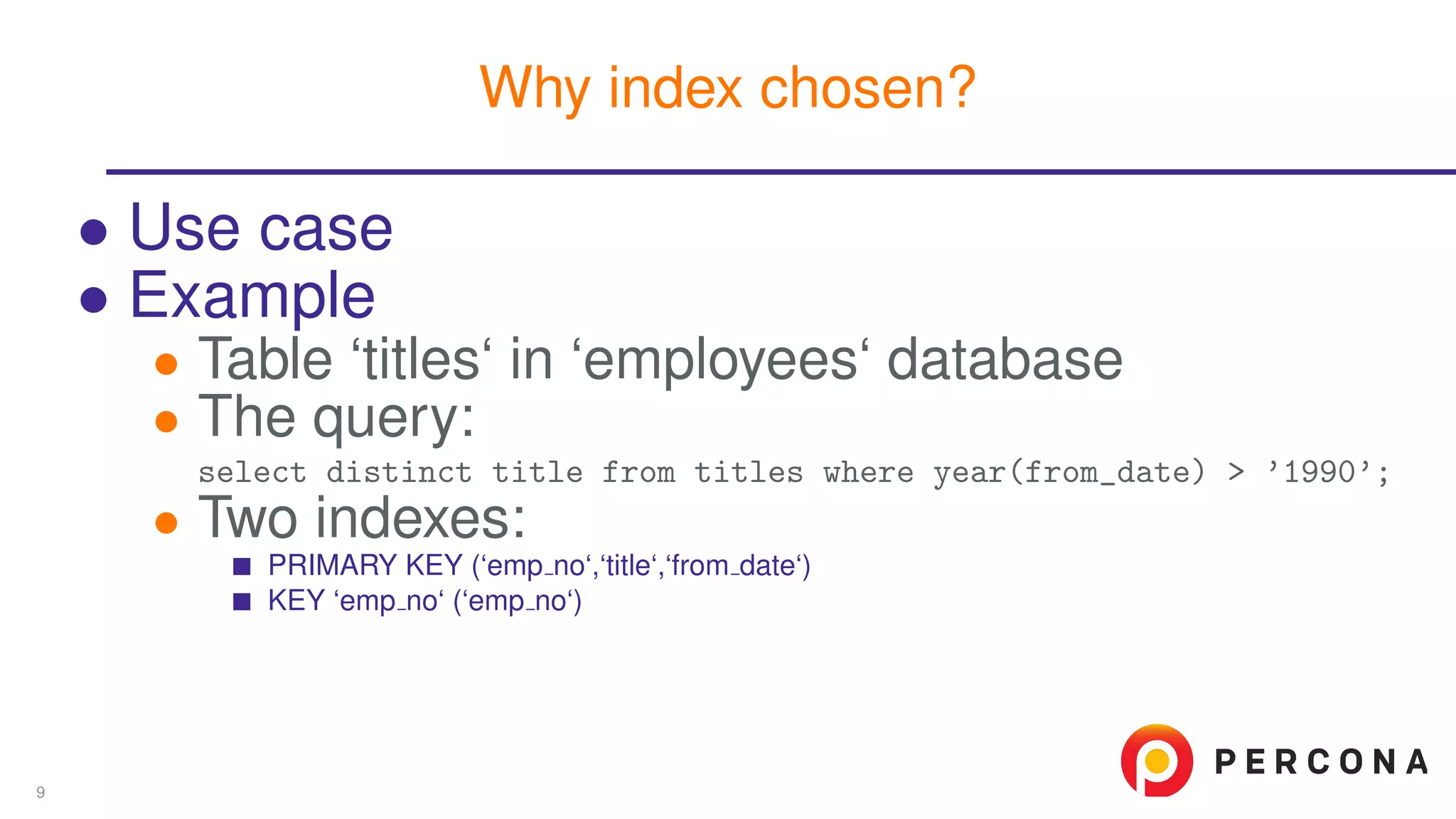
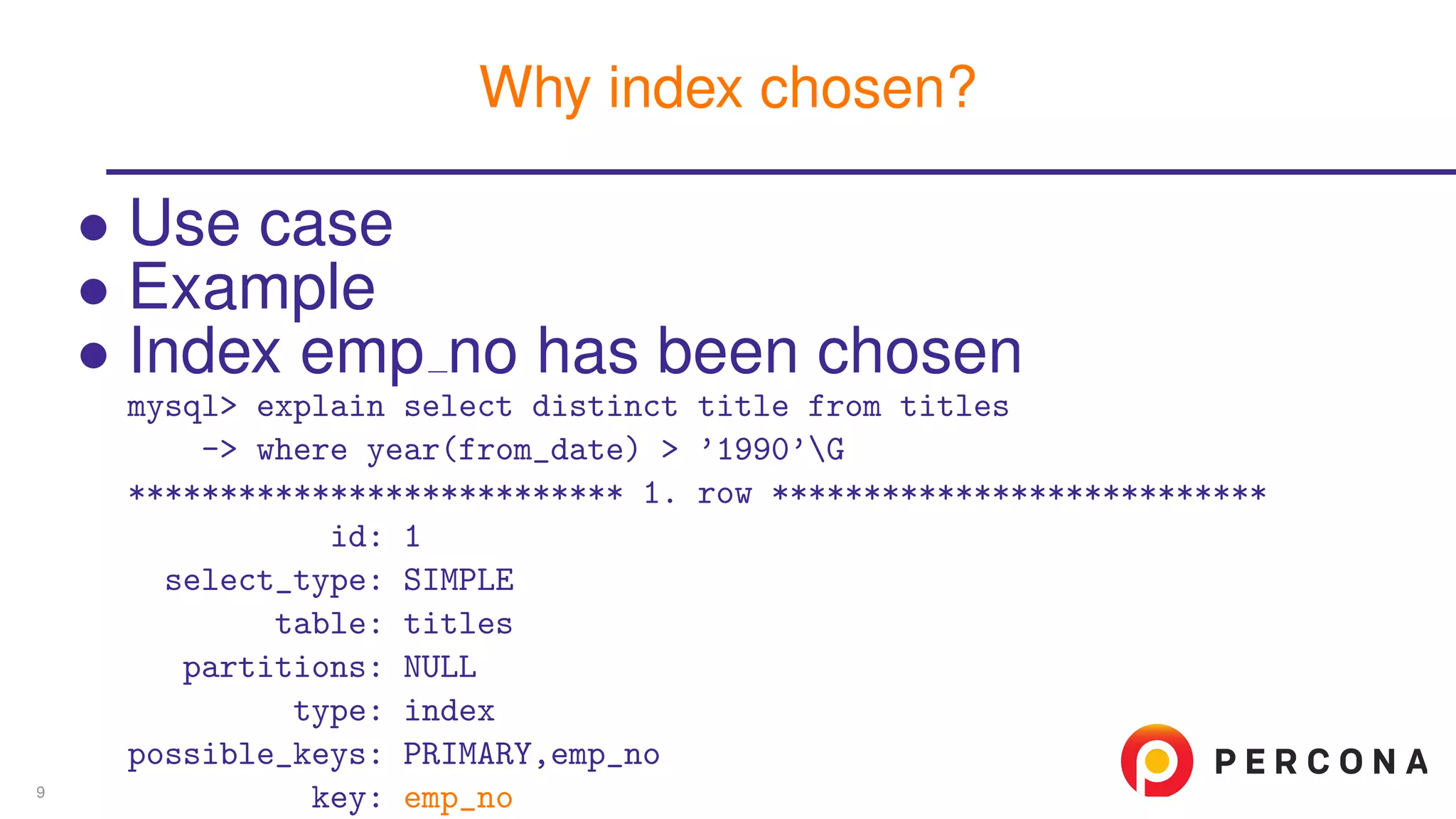
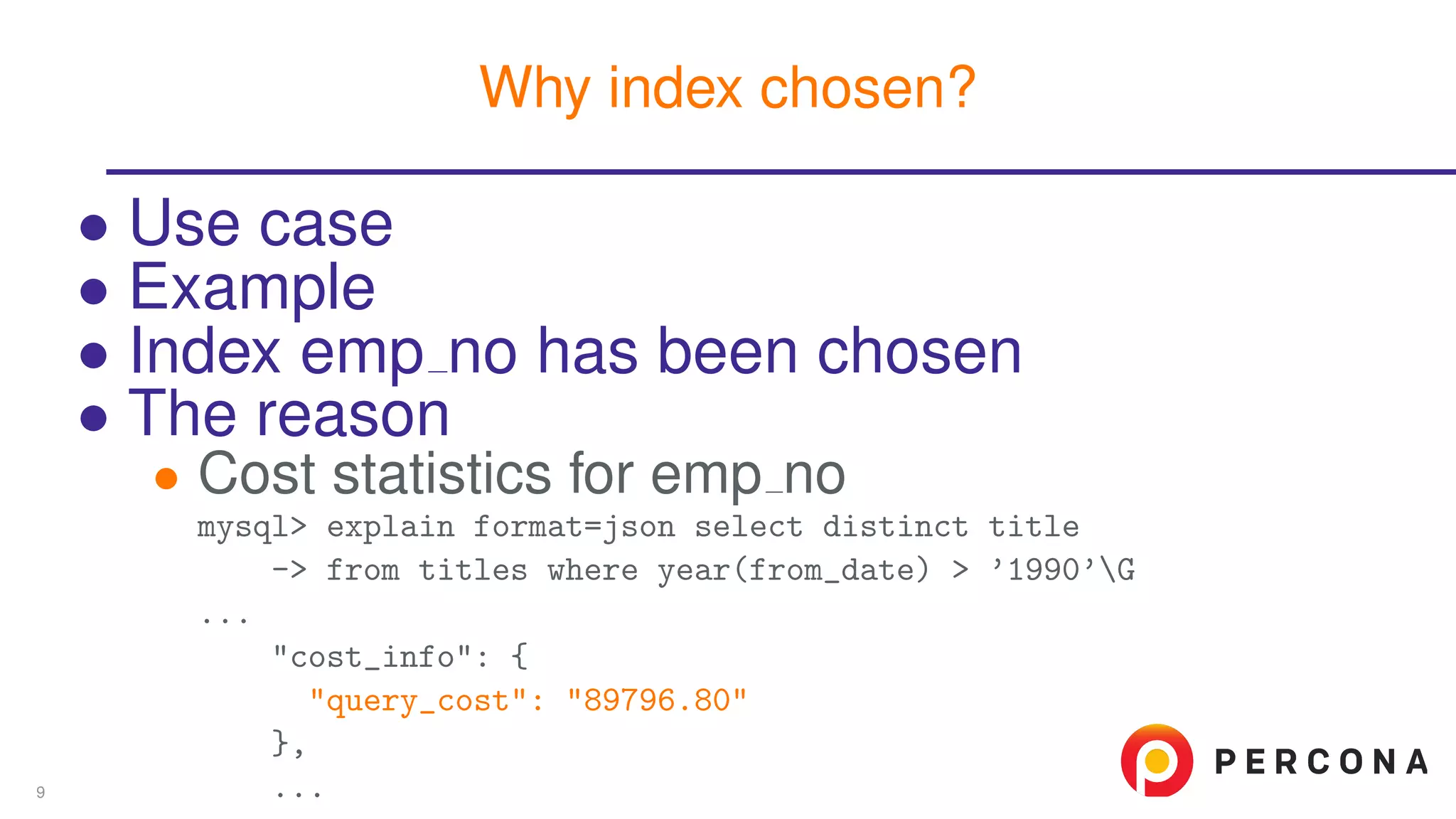
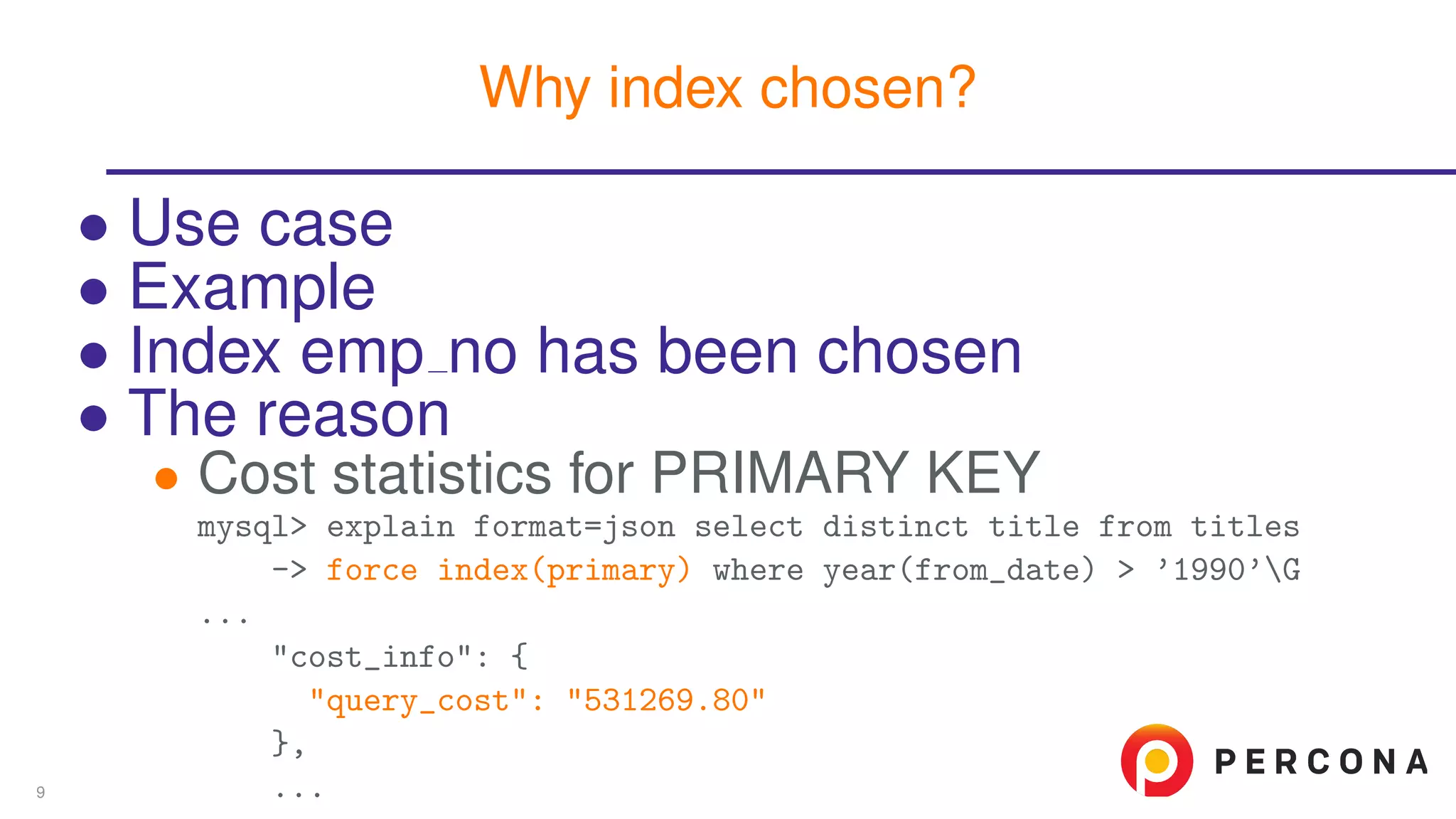
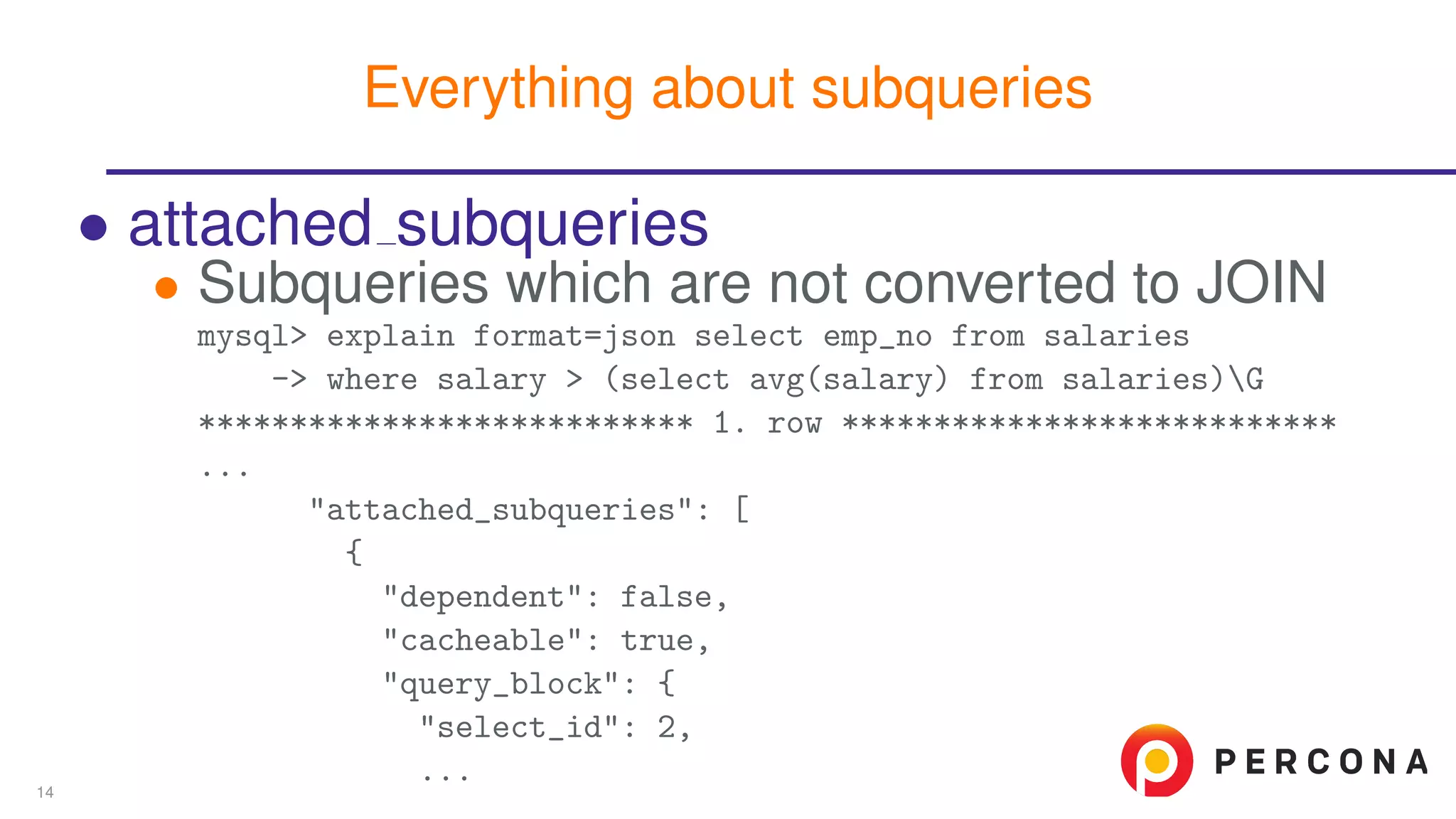
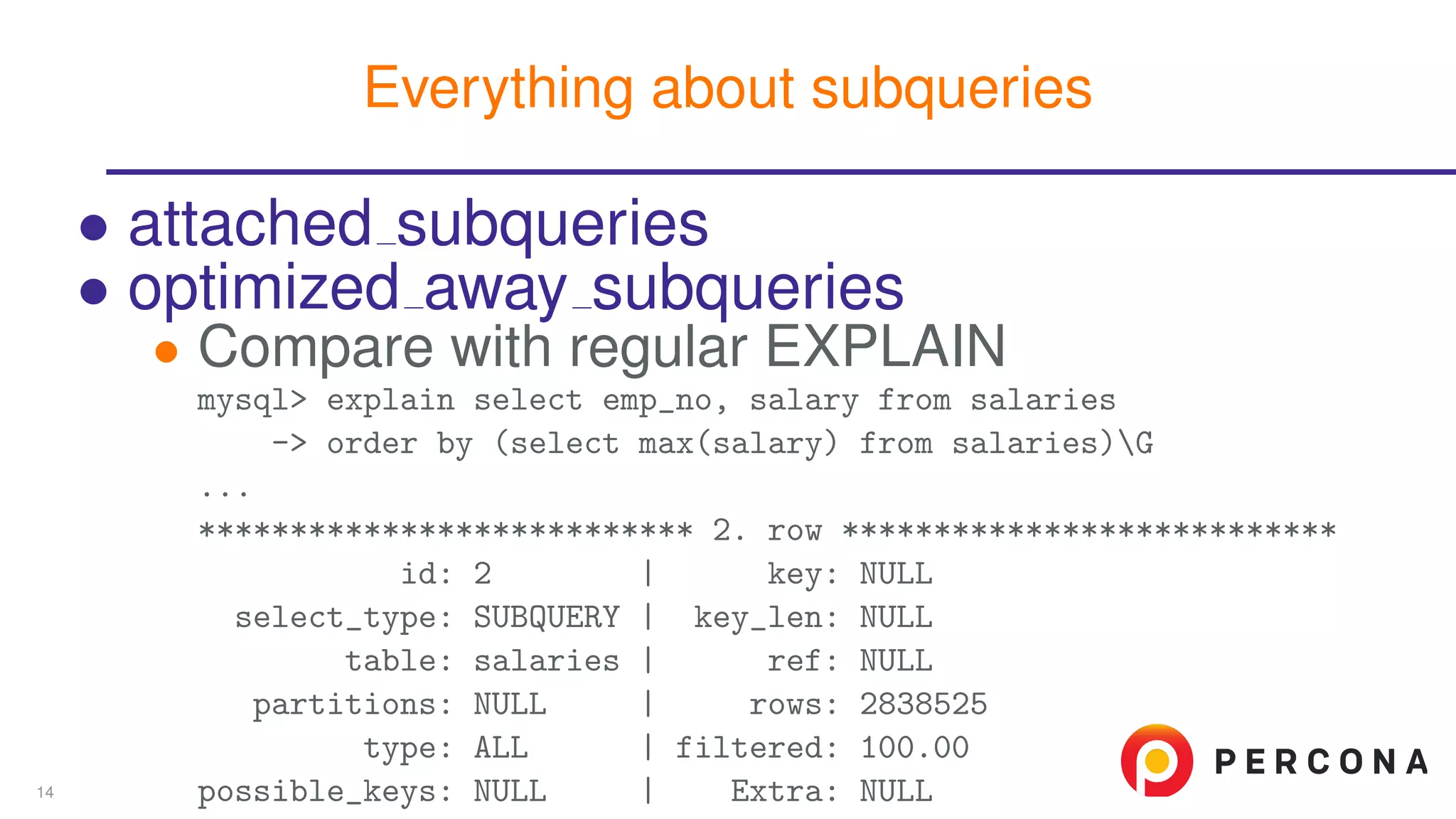
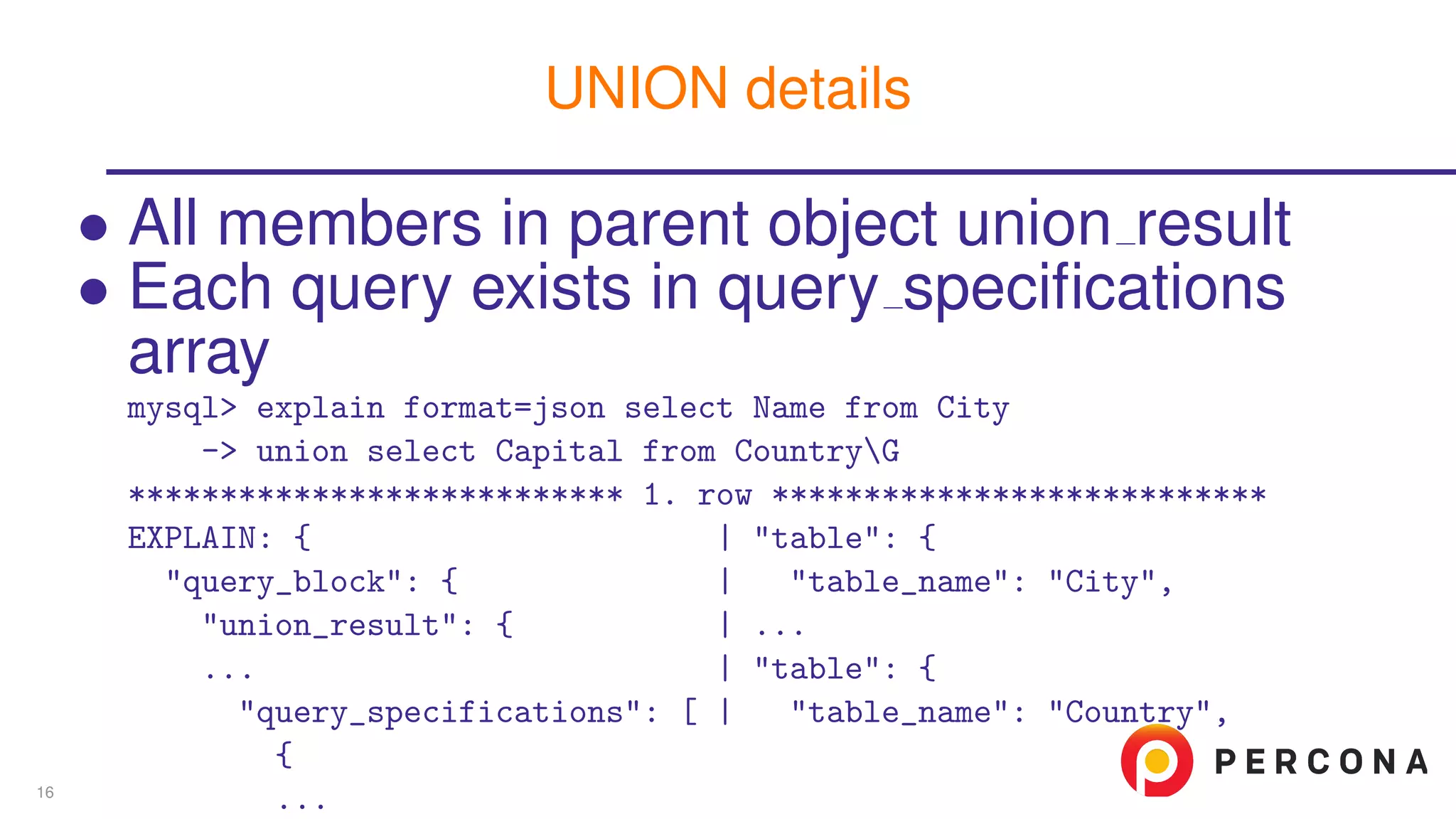
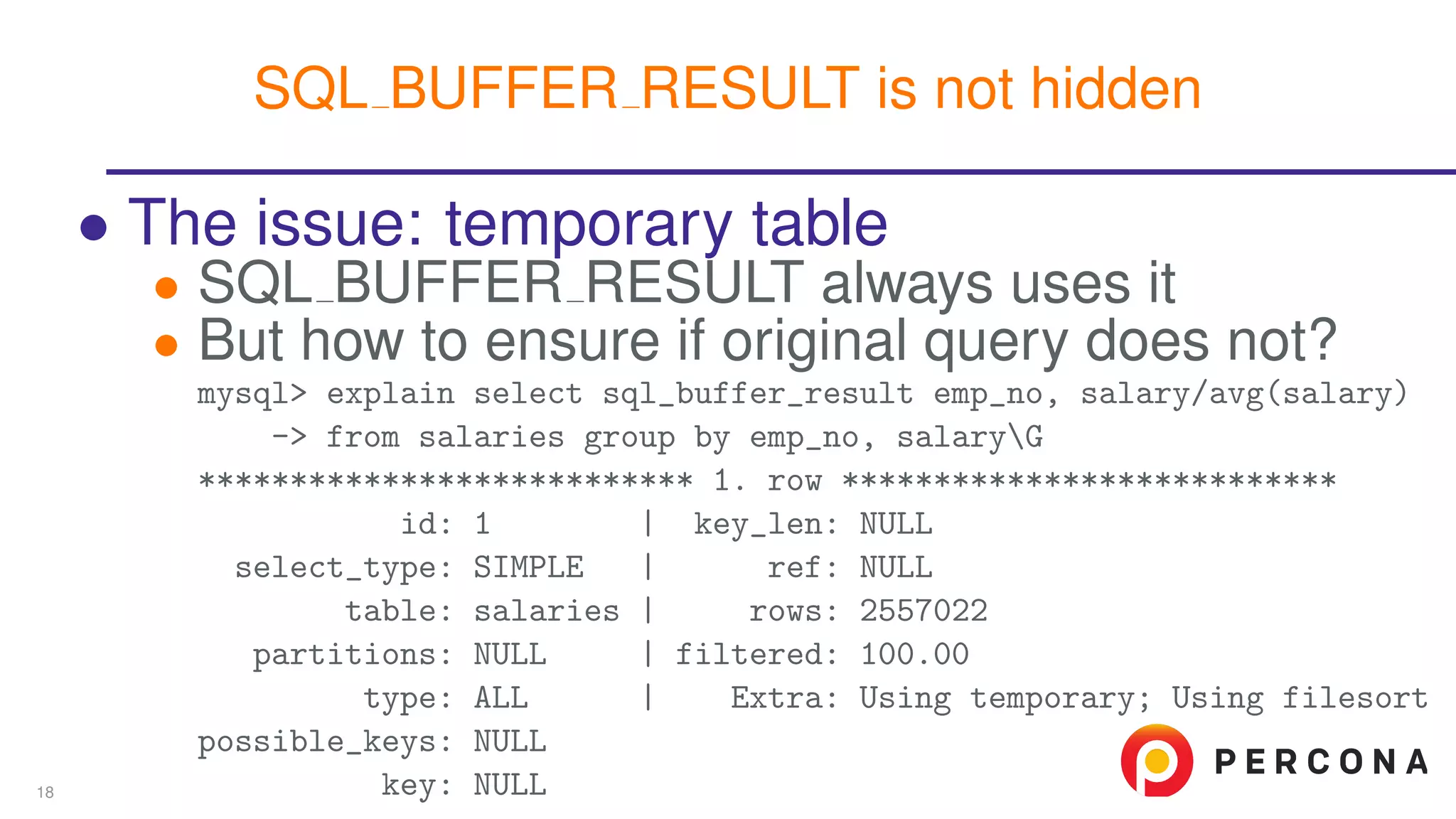
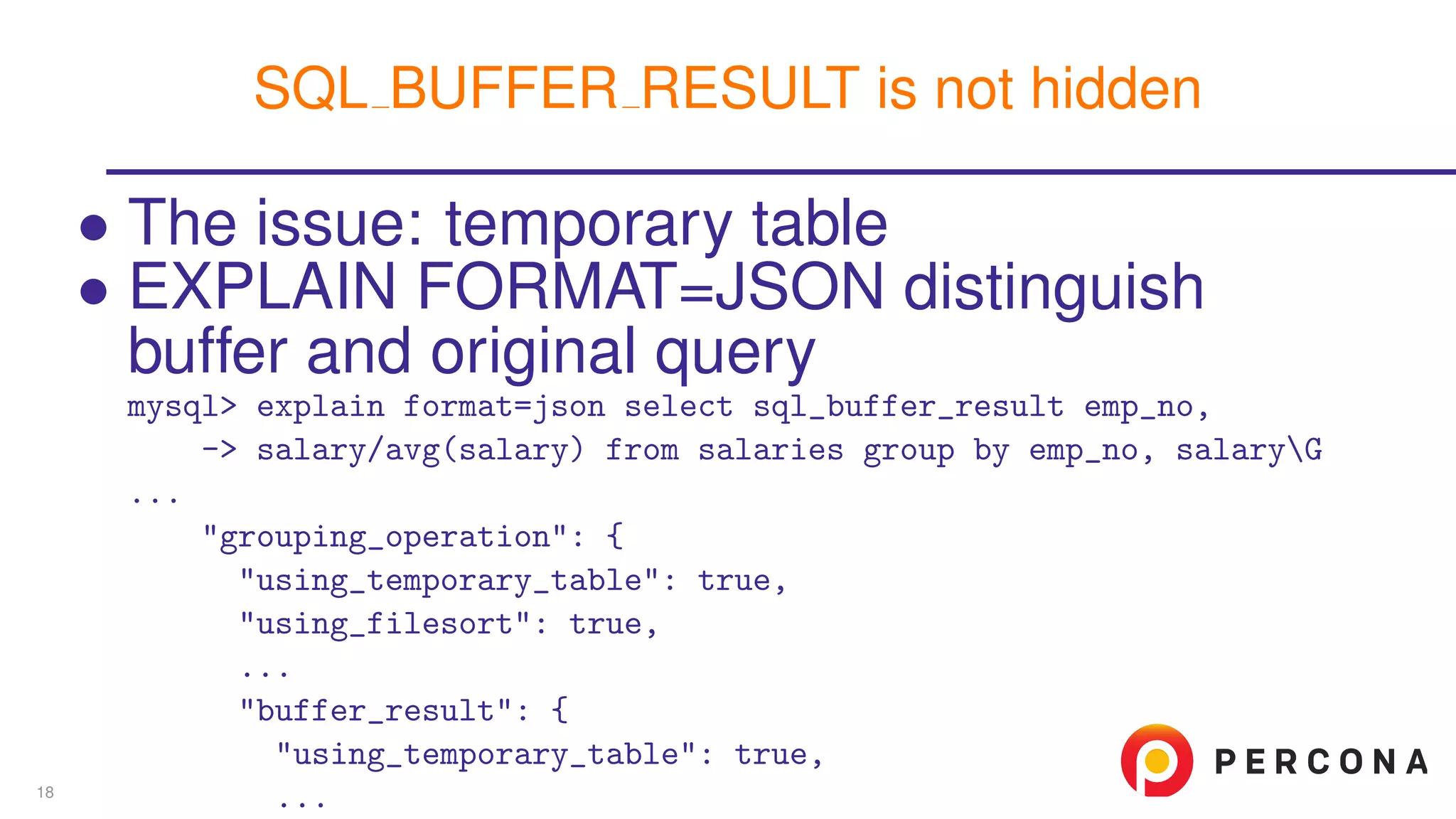
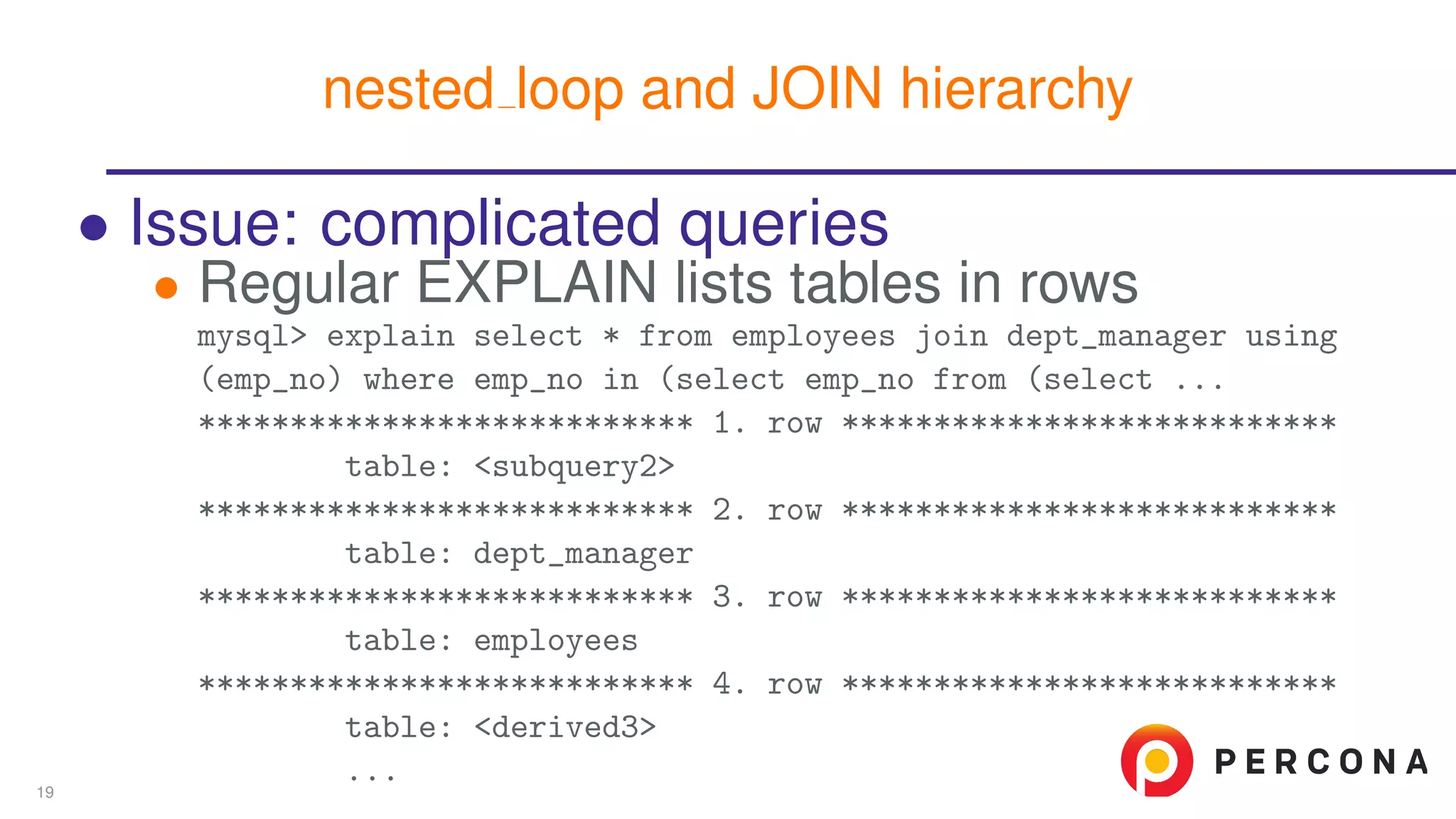
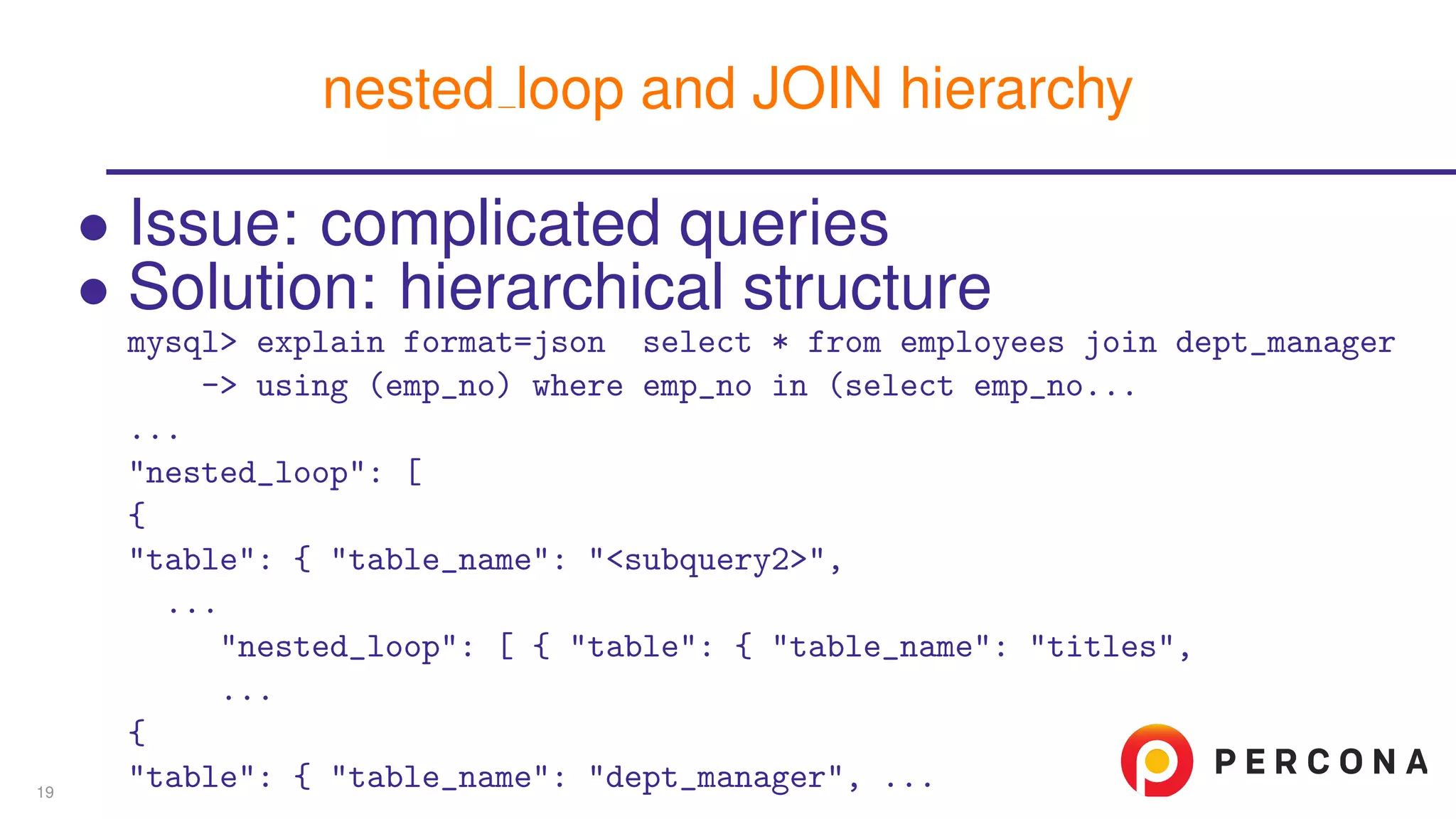
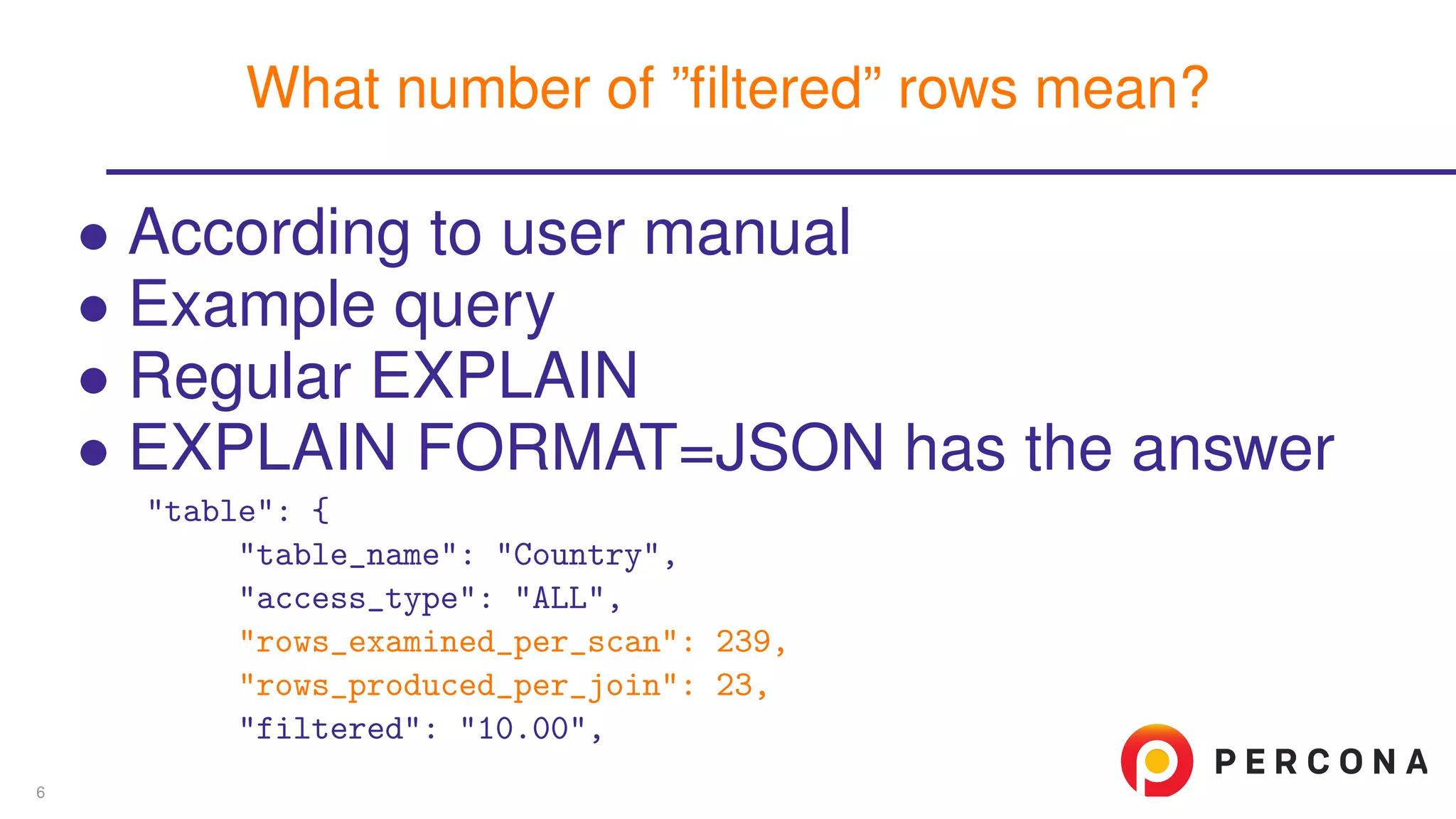
The document discusses the benefits and features of using the 'EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSON' command in MySQL for query optimization, including its structured view that provides detailed insights into query execution, such as filtering information and index usage. It highlights specific use cases, examples, and innovations introduced in MySQL version 5.6, as well as troubleshooting techniques involving temporary tables. The content also emphasizes how the JSON format offers machine-readable output that aids in understanding complex queries and performance metrics.








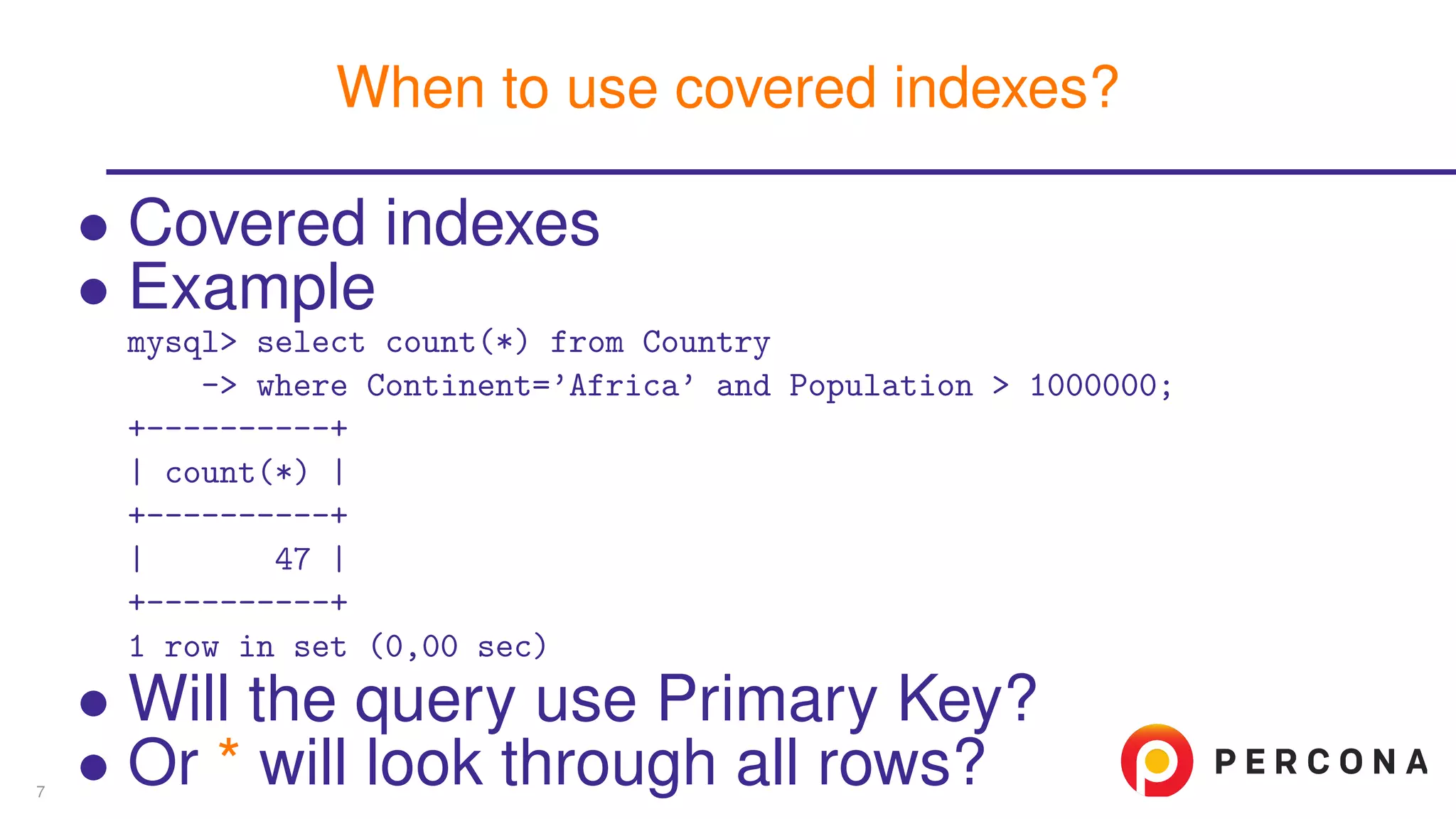
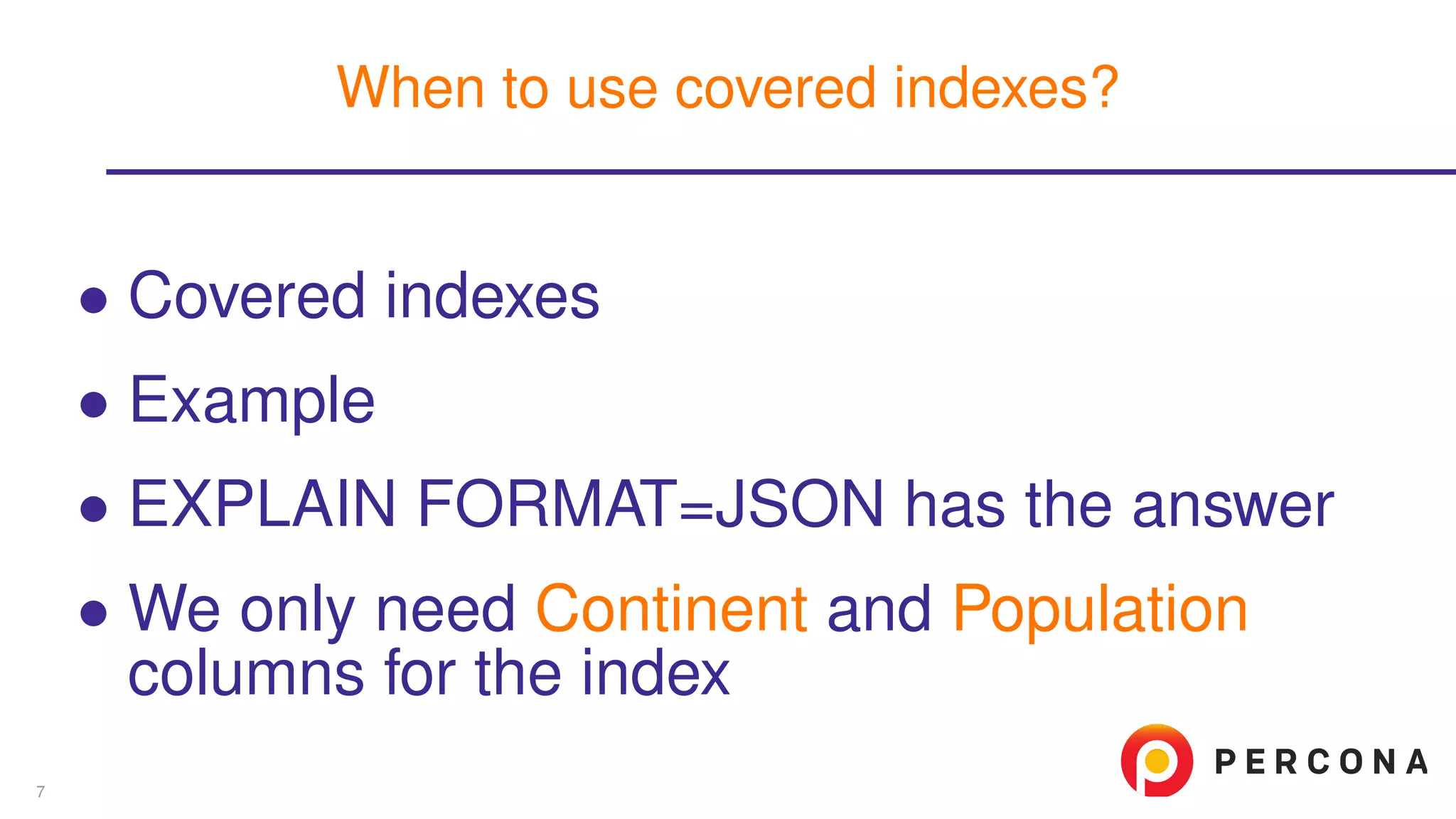
![• Covered indexes • Example • EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSON has the answer mysql> explain format=json select count(*) from Country -> where Continent=’Africa’ and Population > 1000000G *************************** 1. row *************************** ... "used_columns": [ "Continent", "Population" ], ... When to use covered indexes? 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/explainjson-160426141343/75/Why-Use-EXPLAIN-FORMAT-JSON-12-2048.jpg)
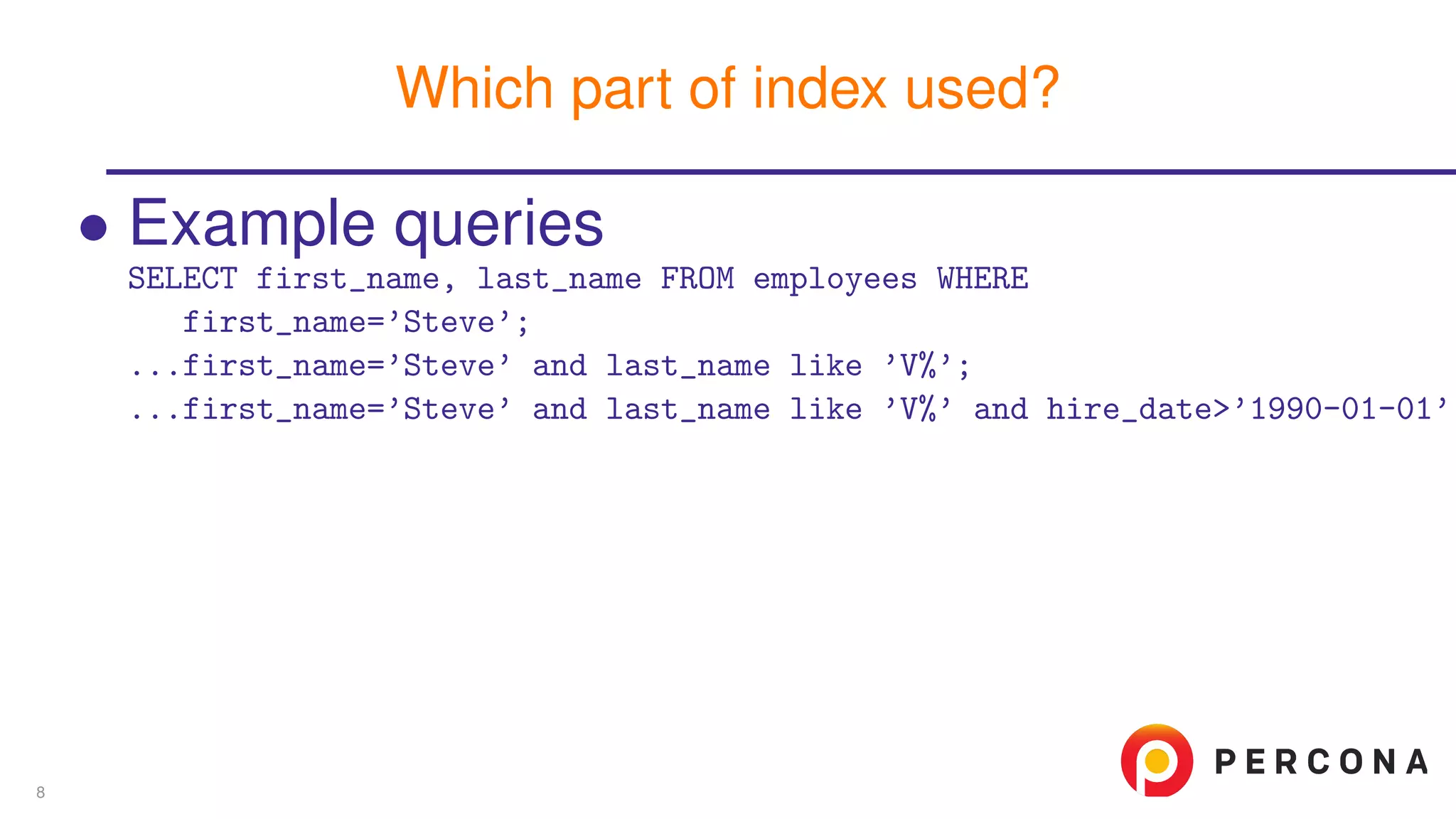
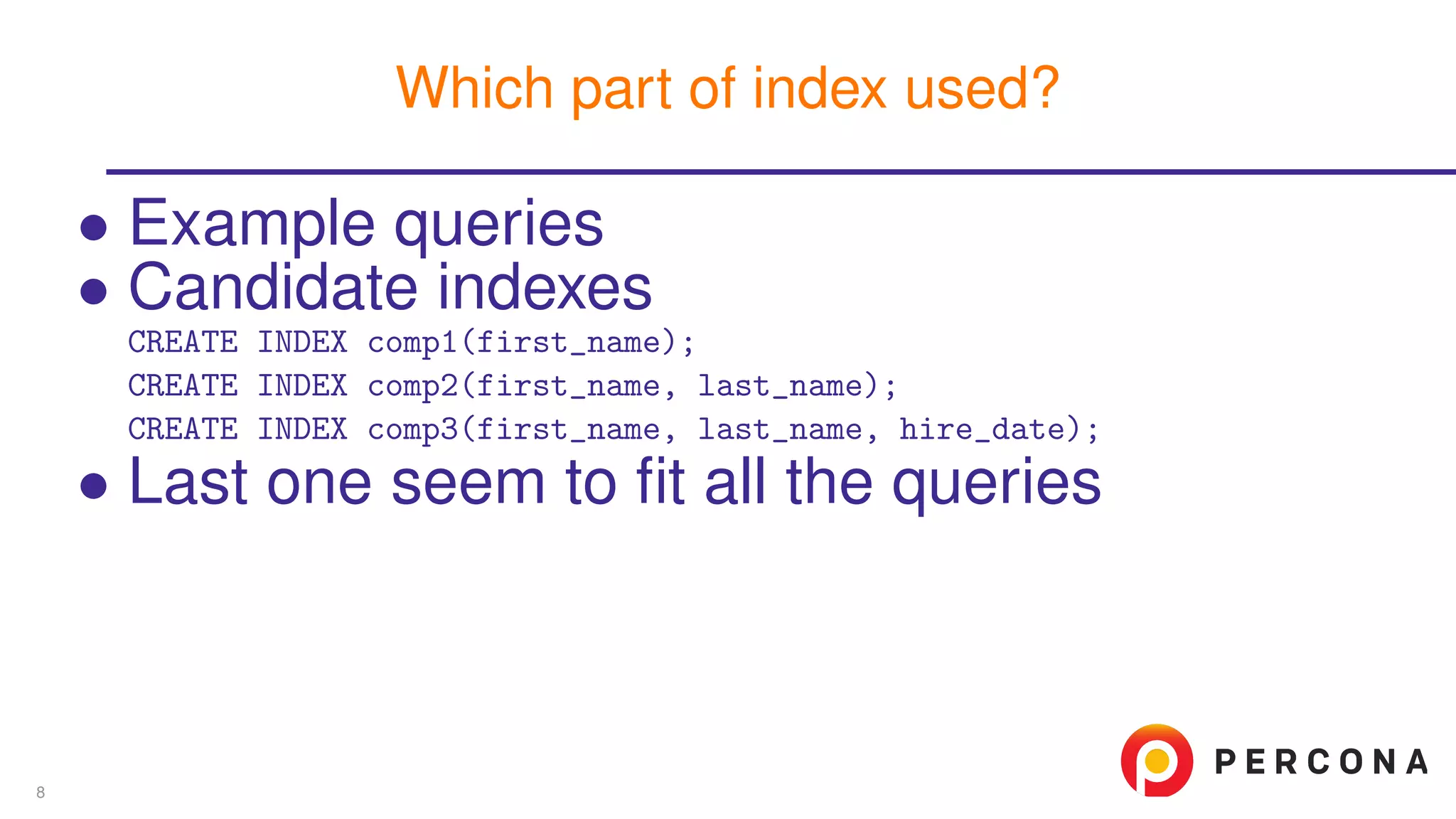
![• Example queries • Candidate indexes • Index effectiveness mysql> explain format=json SELECT first_name, last_name FROM employees -> WHERE first_name=’Steve’ and last_name like ’V%’ -> and hire_date > ’1990-01-01’G *************************** 1. row *************************** EXPLAIN: { ... "used_key_parts": [ "first_name", "last_name" ], Which part of index used? 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/explainjson-160426141343/75/Why-Use-EXPLAIN-FORMAT-JSON-16-2048.jpg)