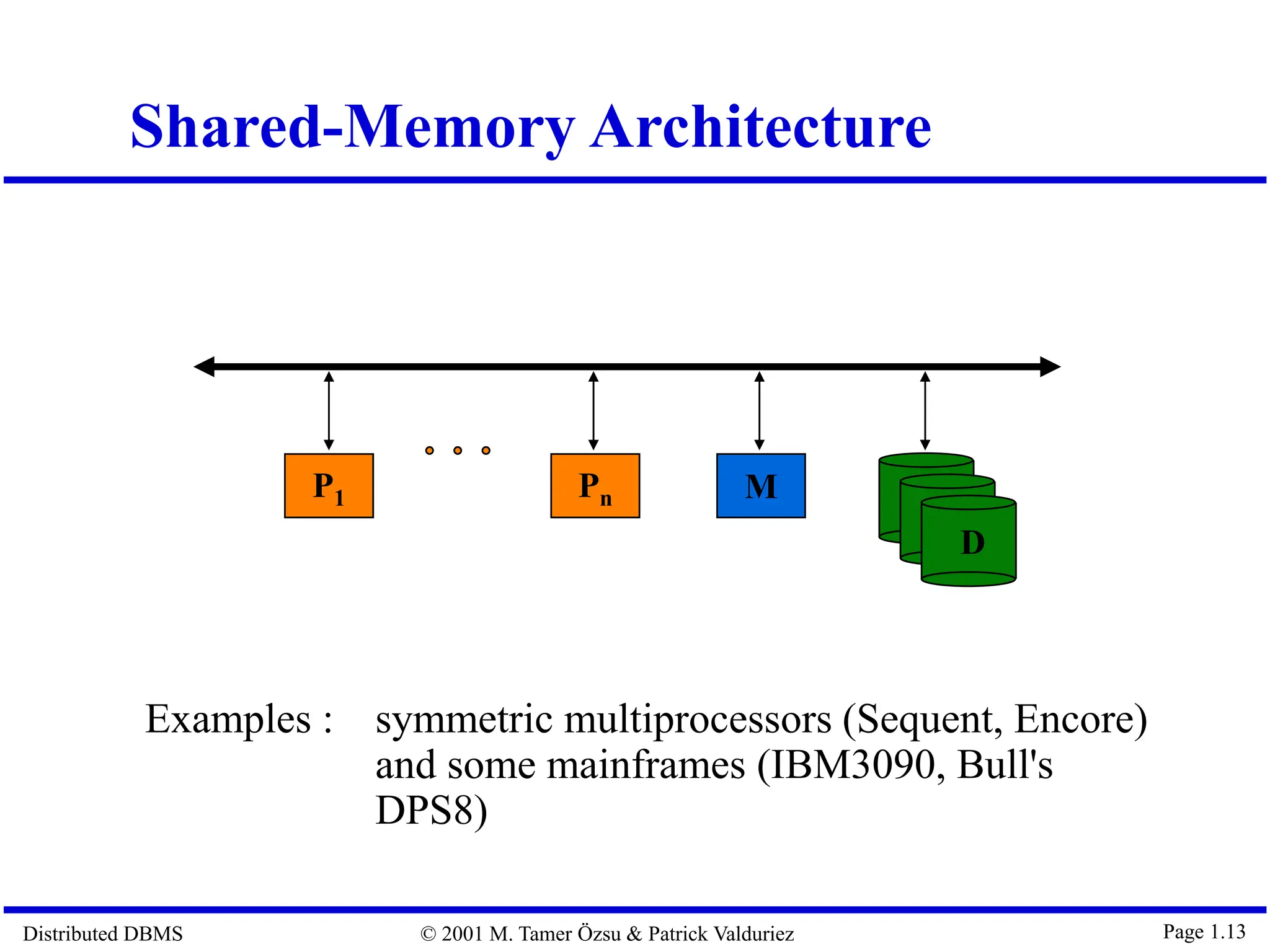
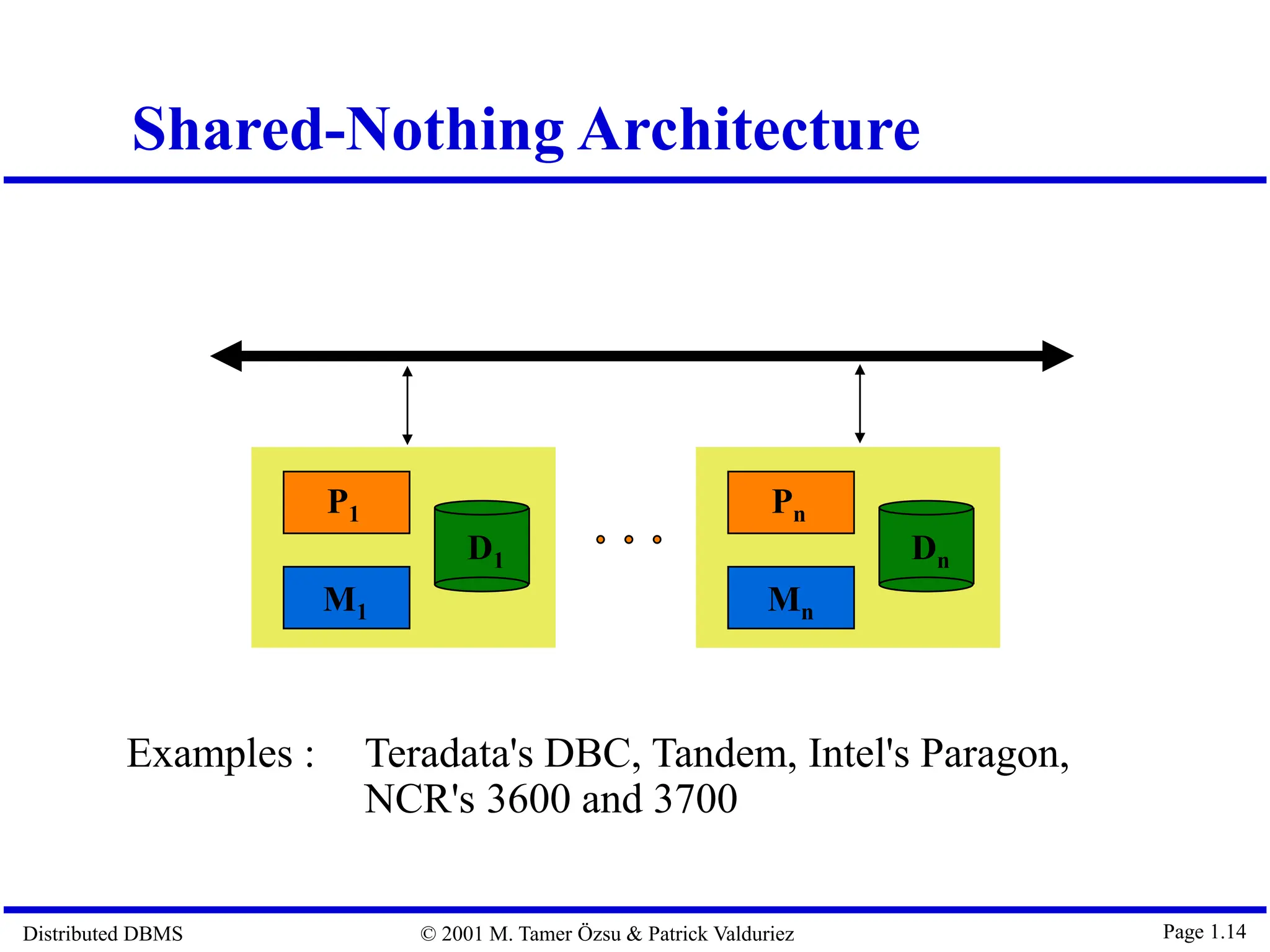
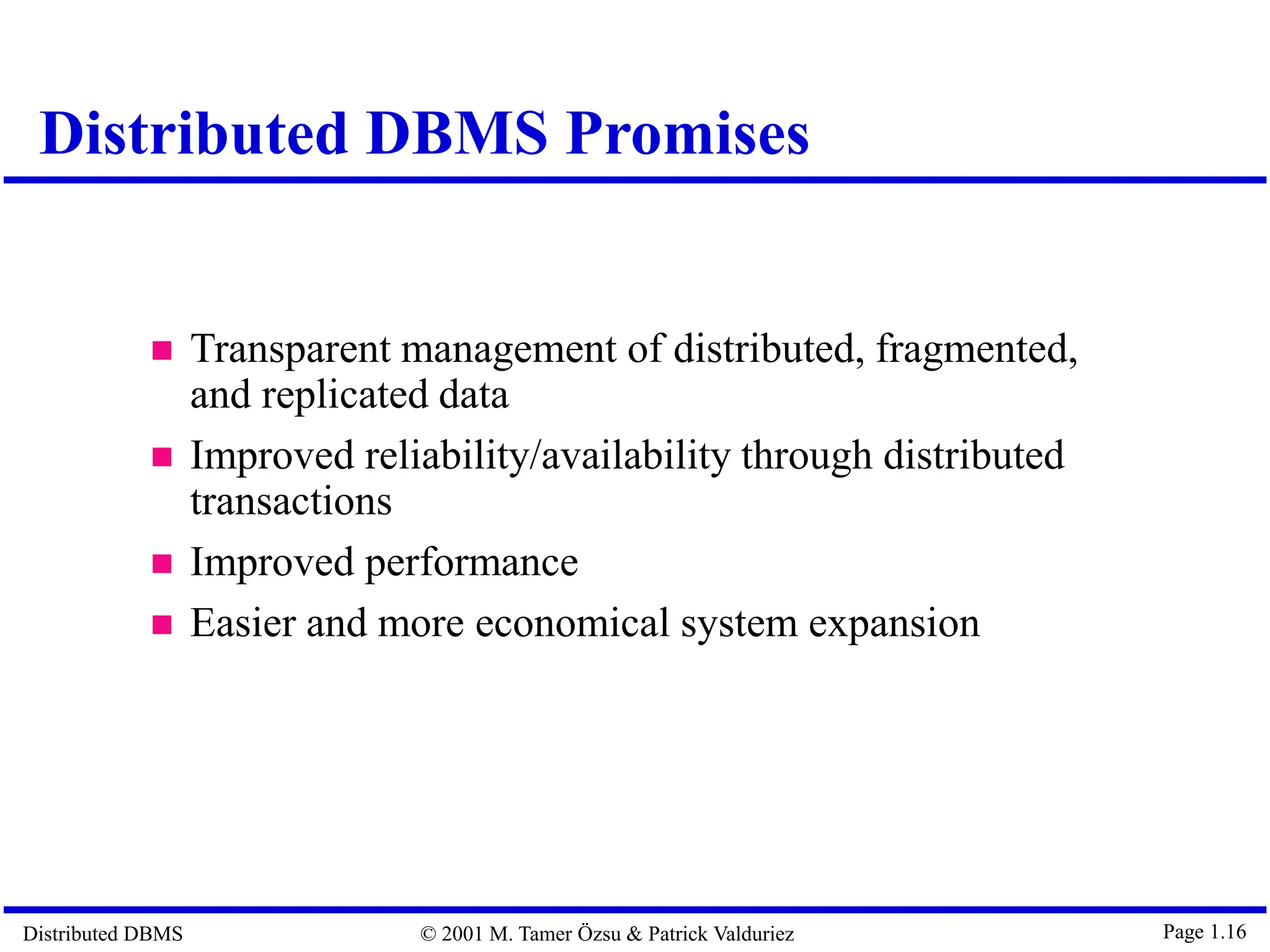
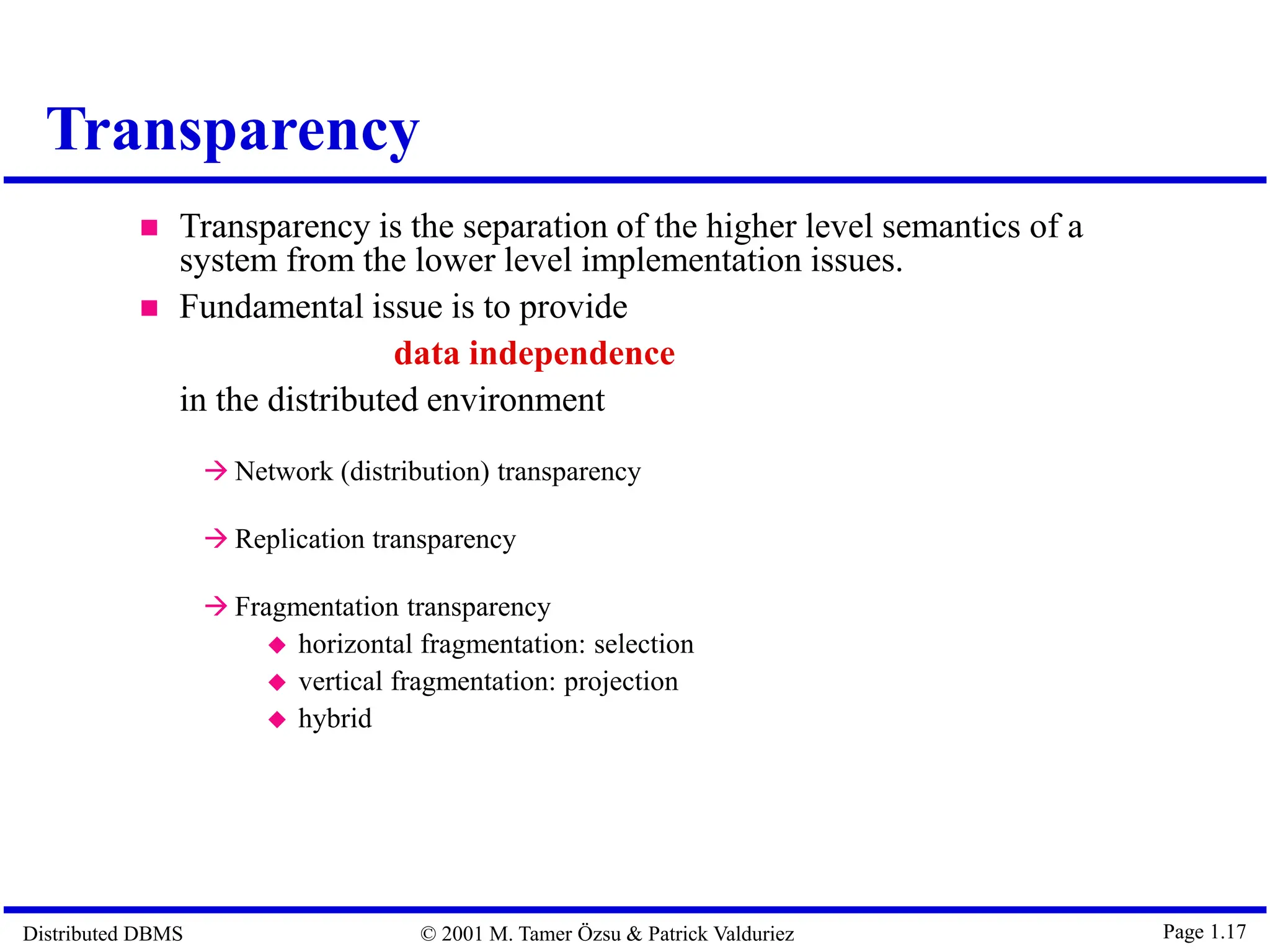
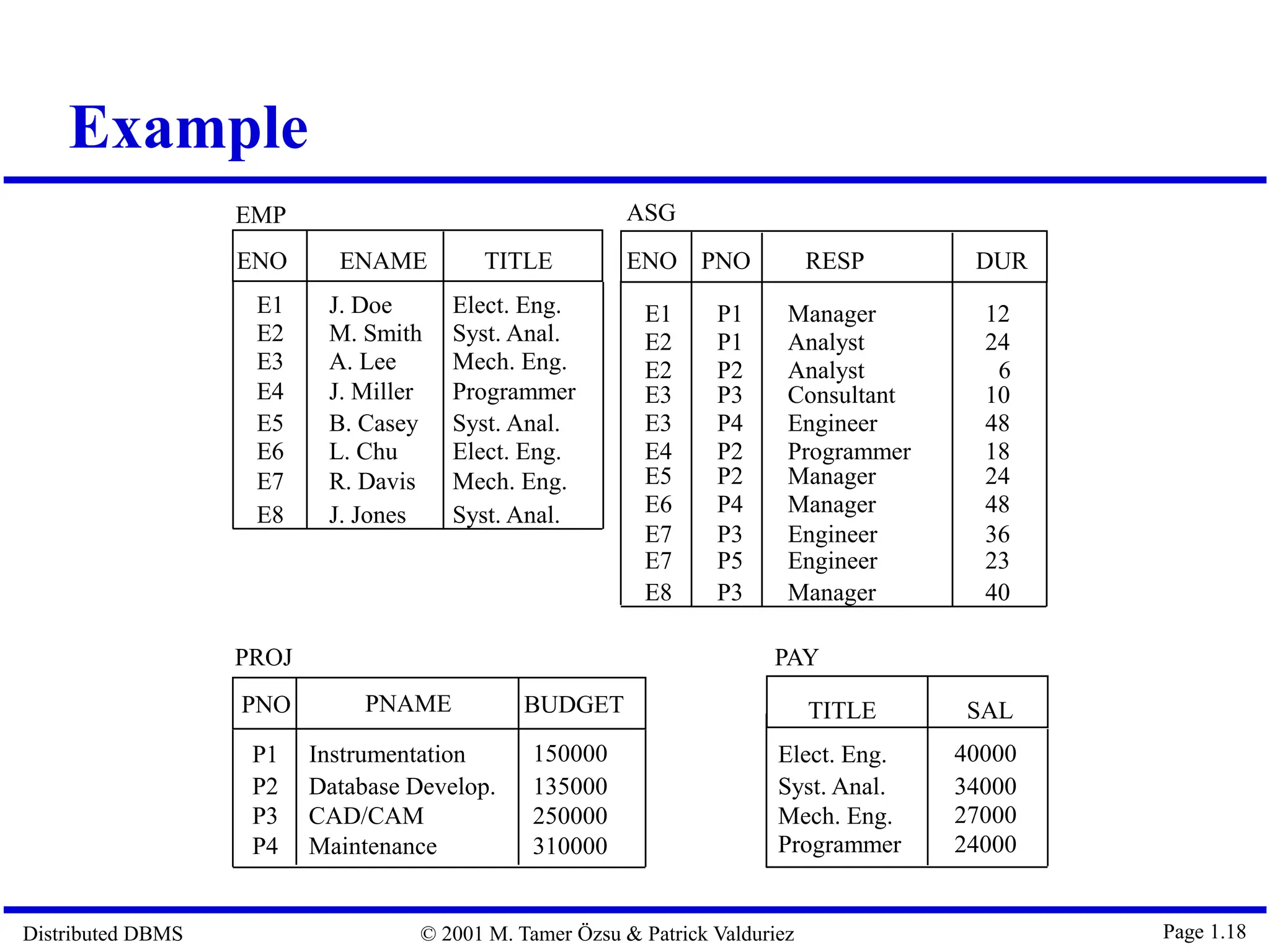
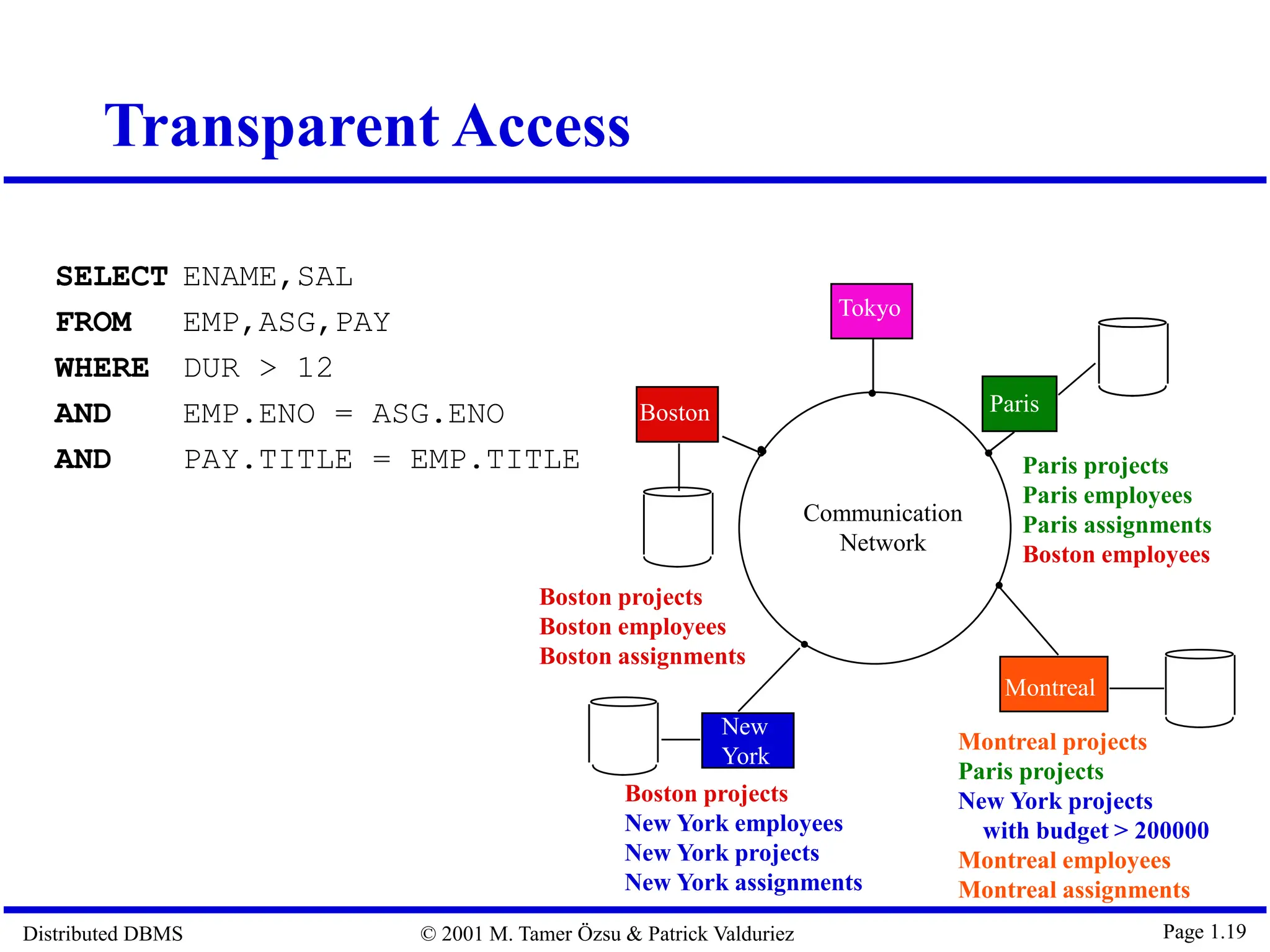
The document outlines distributed database management systems (DDBMS), explaining their architecture, design, and transaction management. It emphasizes the advantages of DDBMS, such as improved reliability, performance, and easier system expansion, while addressing transparency in data management. Additionally, it contrasts DDBMS with centralized systems and highlights various applications of distributed databases in decentralized organizational structures.