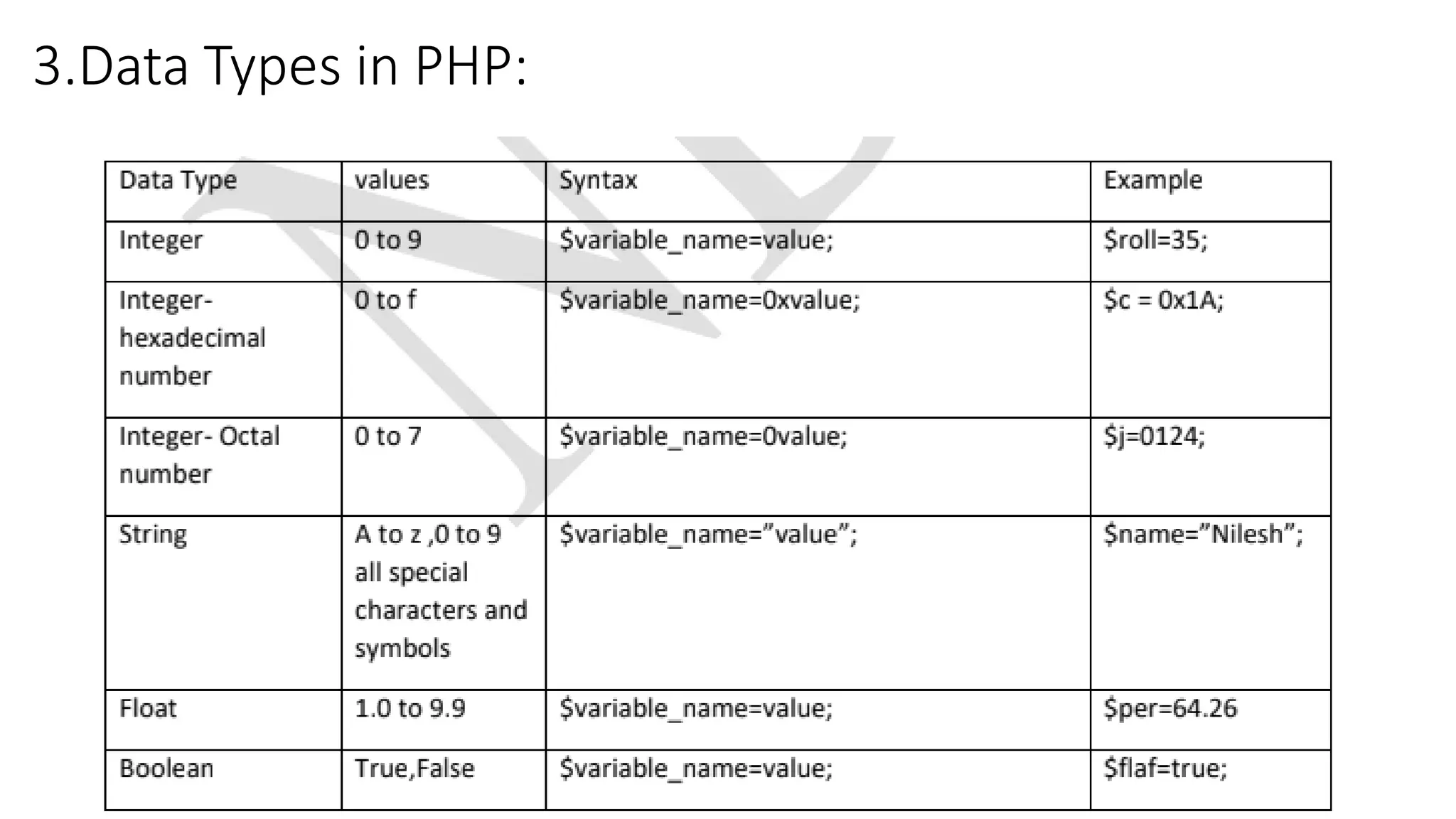
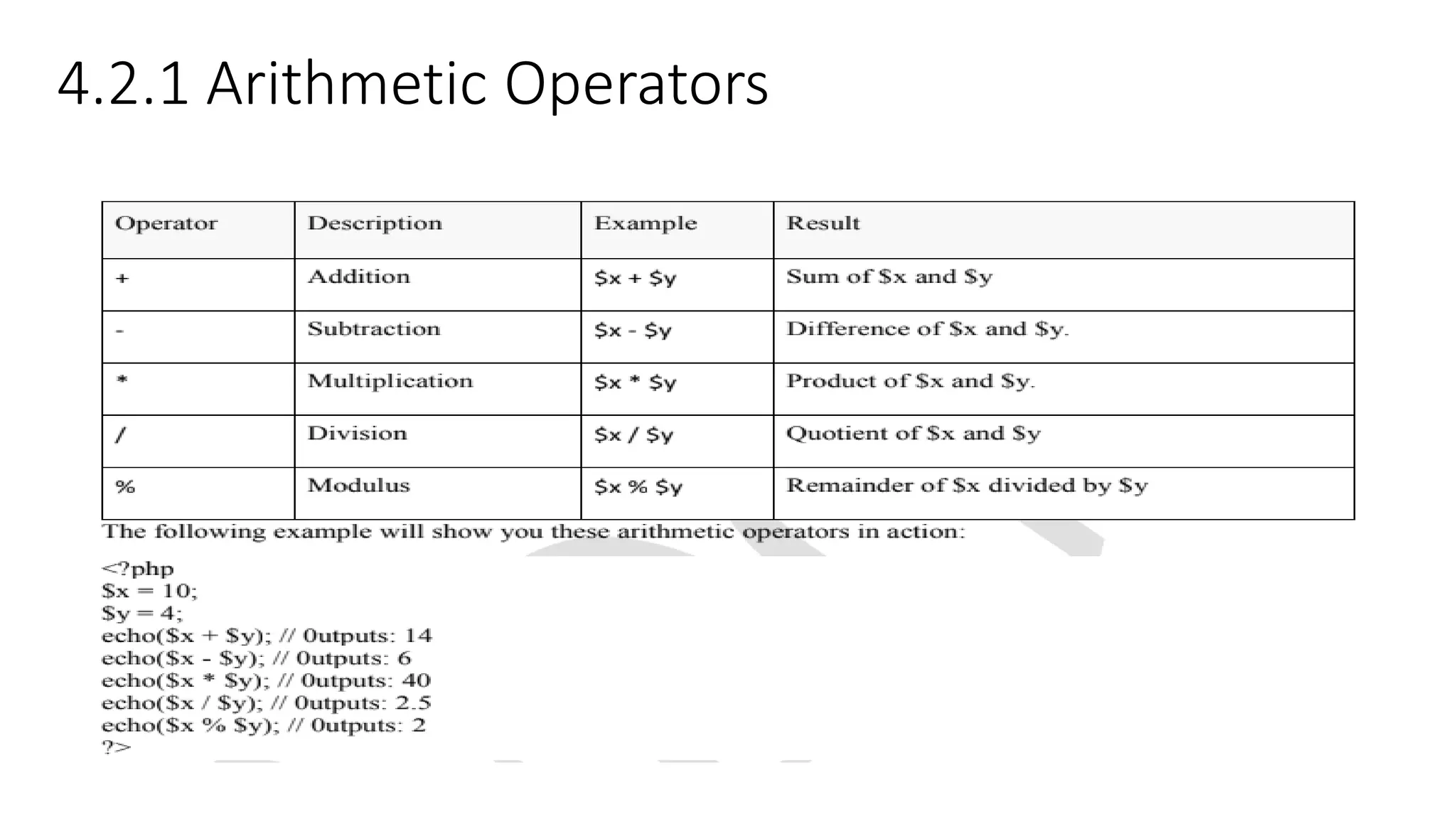
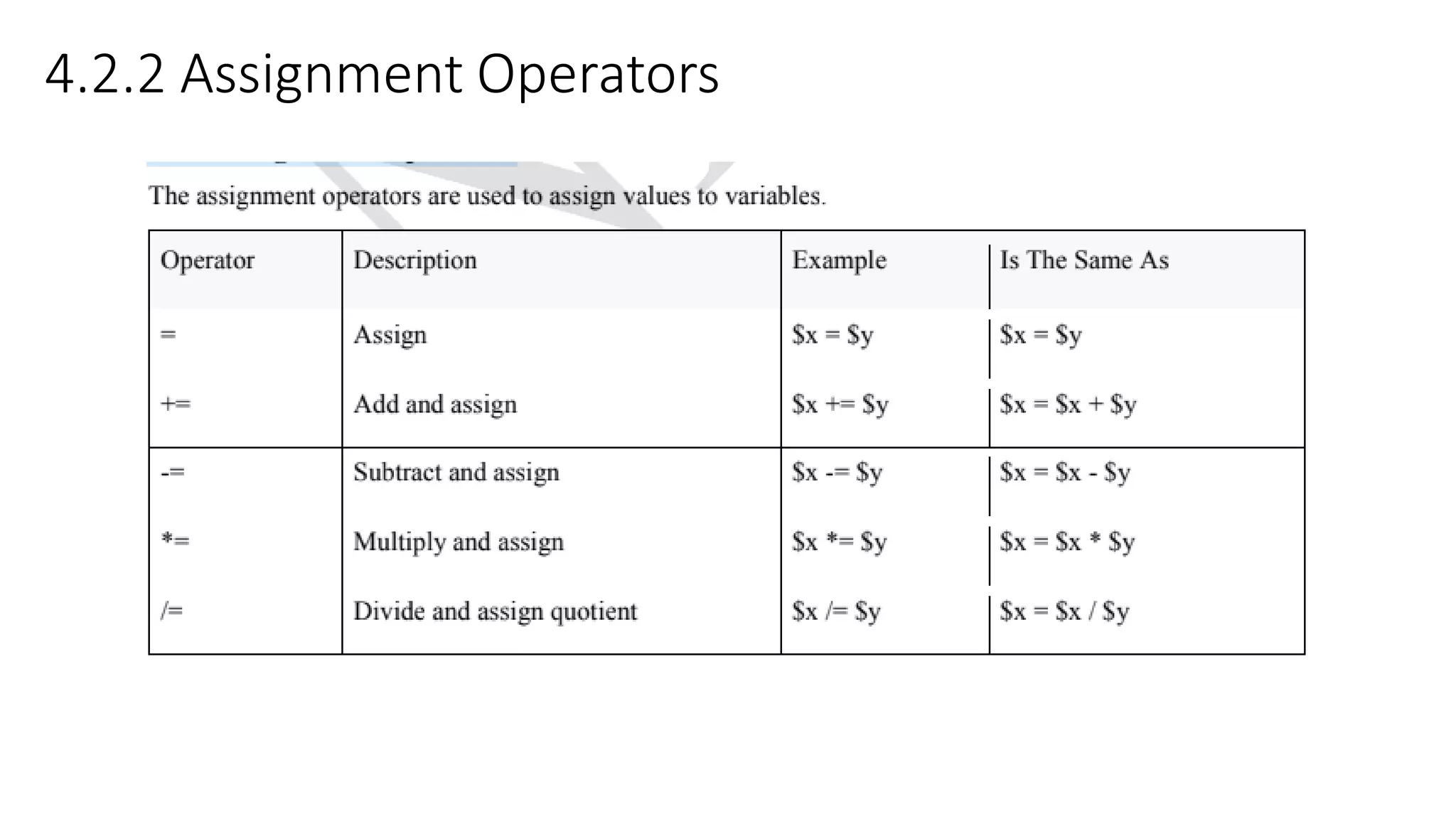
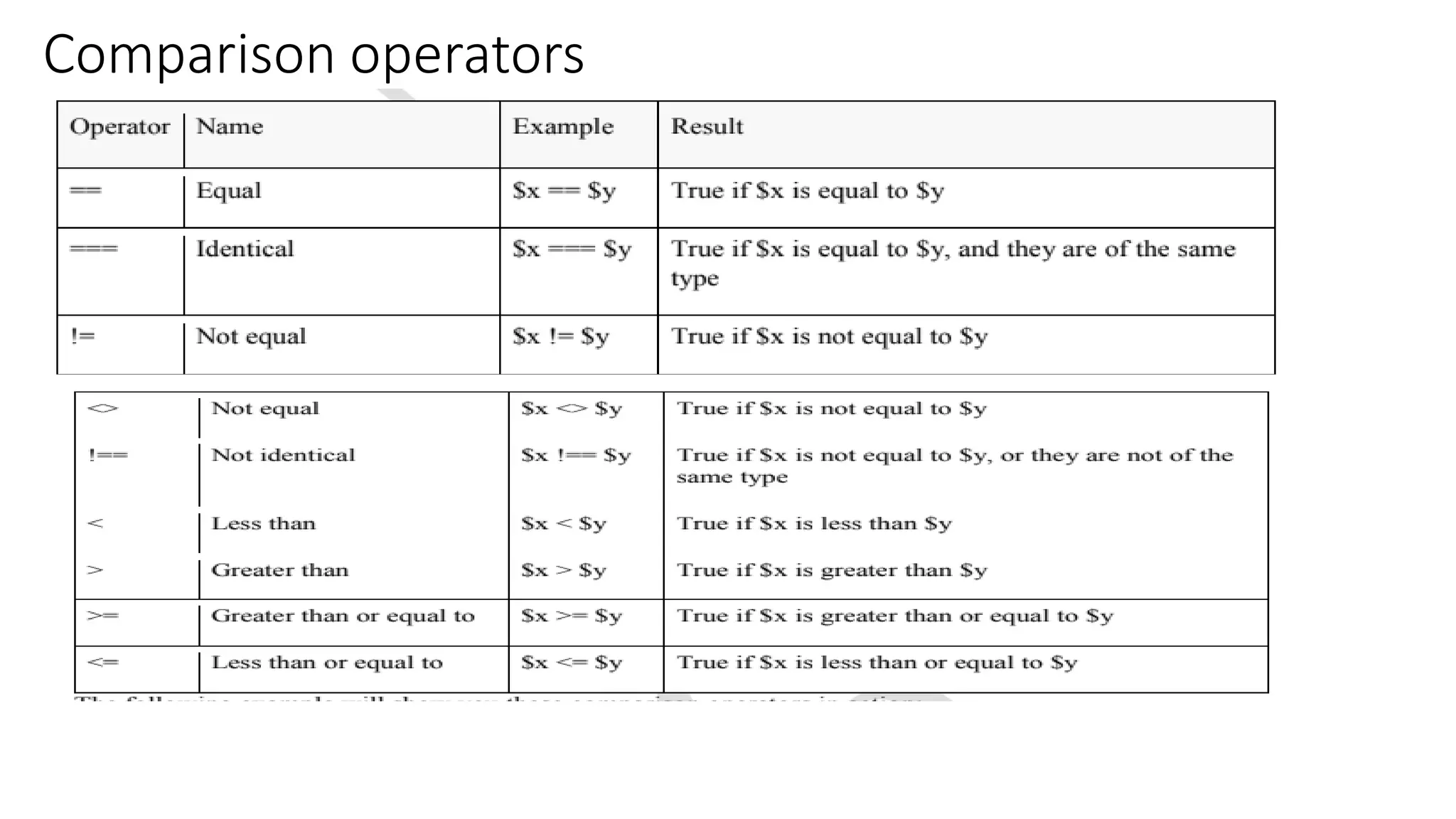
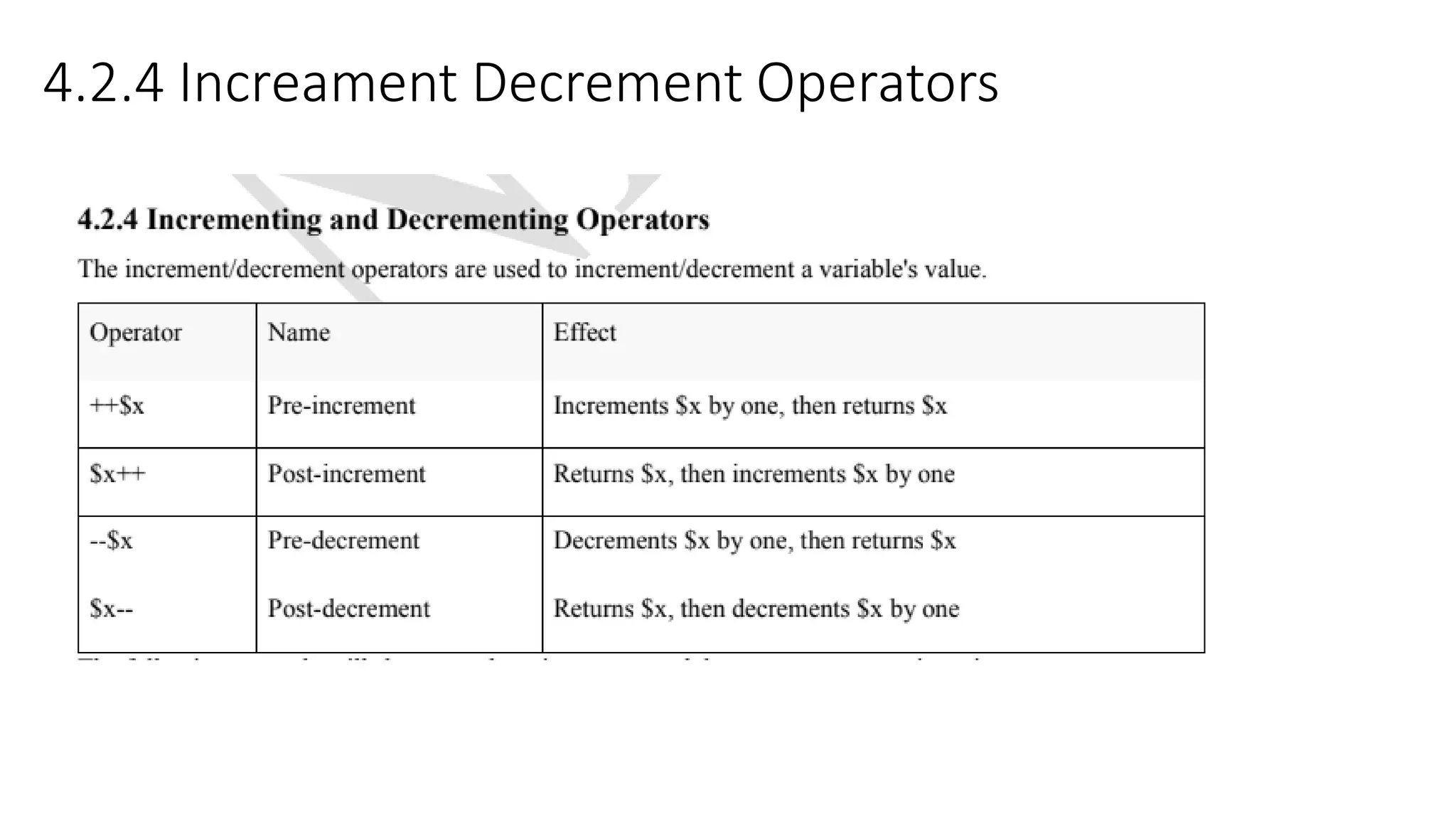
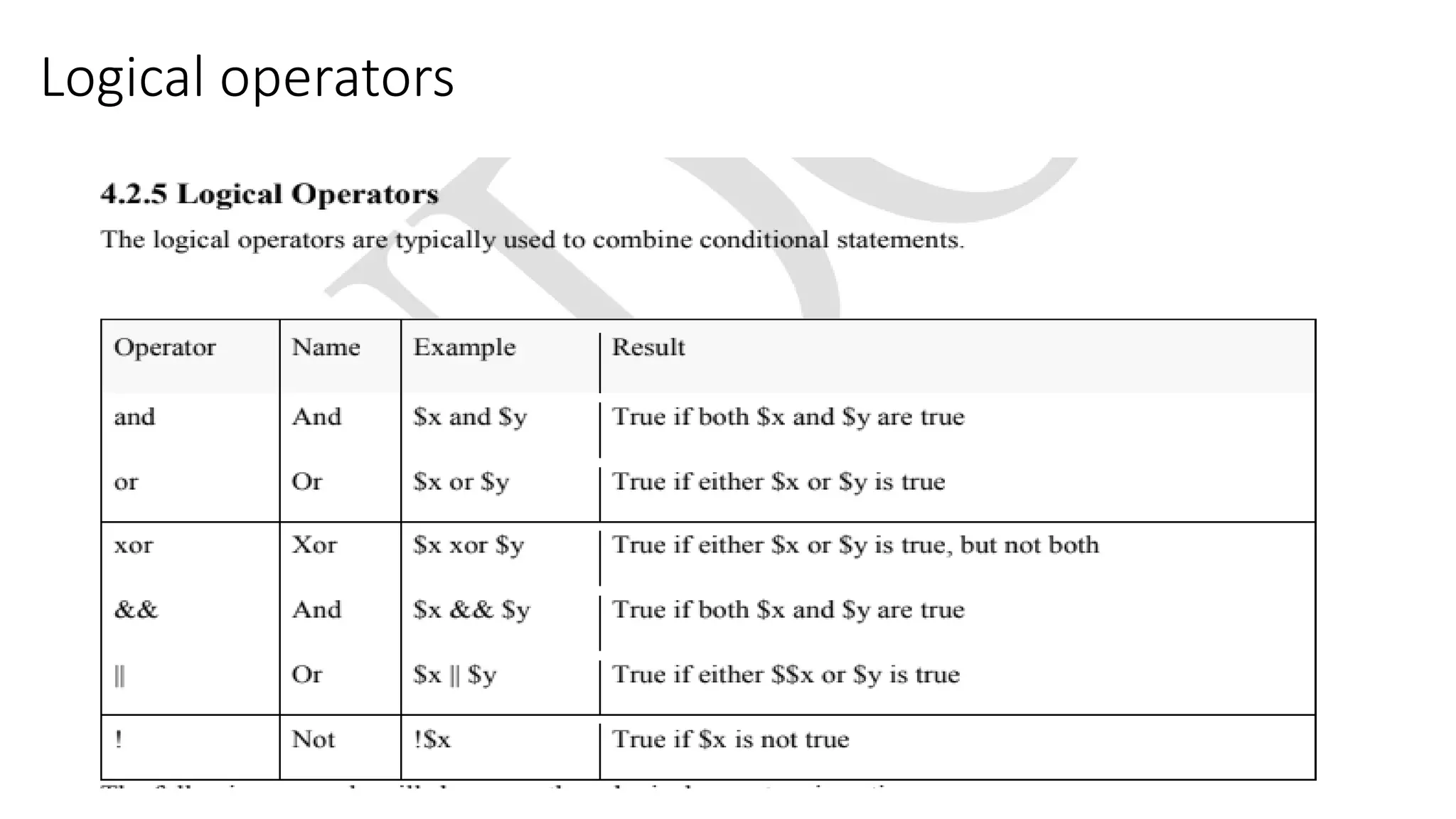
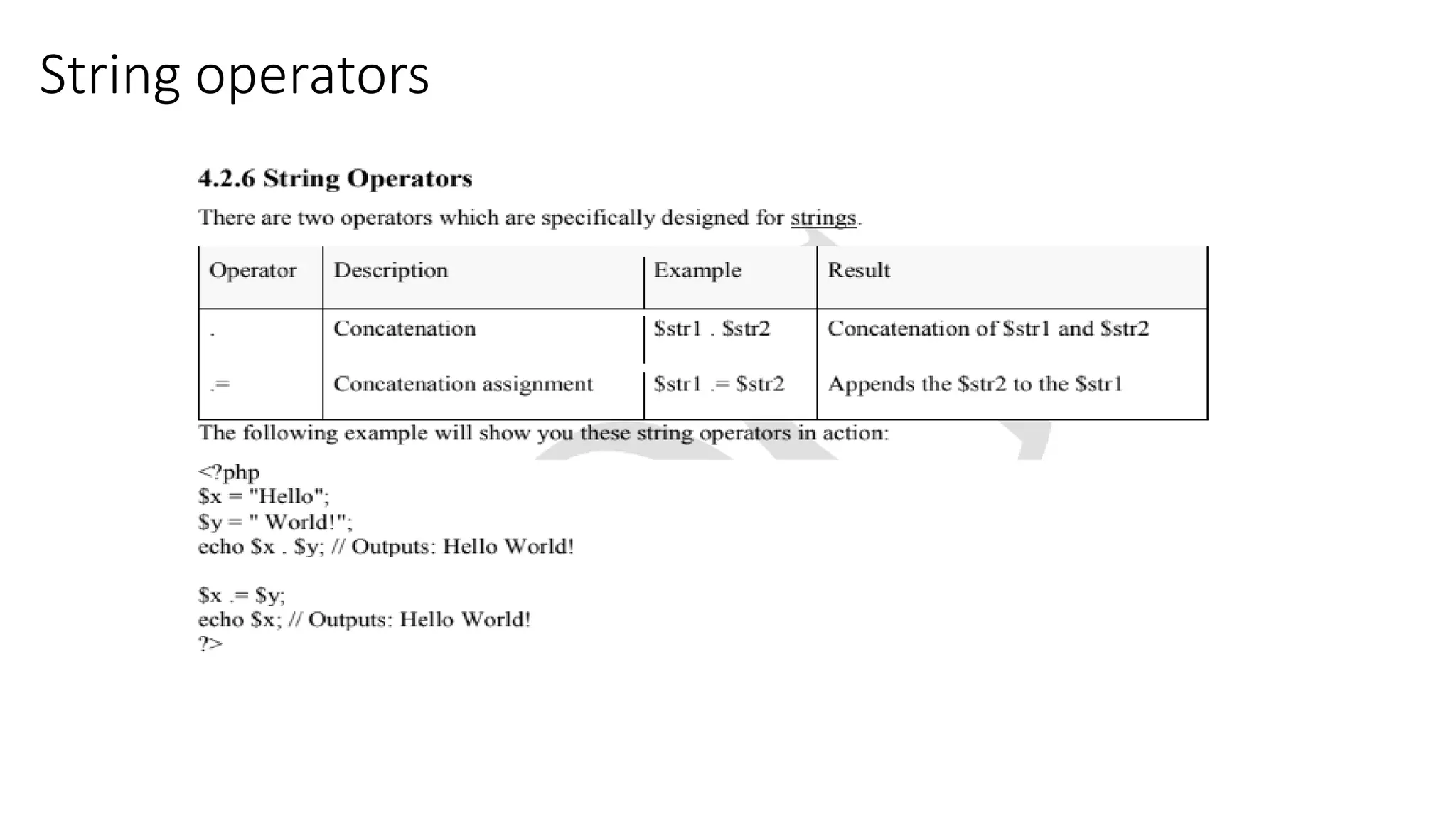
This document provides an overview of PHP including: 1. A brief history of PHP including its origins and versions. PHP was created in 1994 and has evolved through versions like PHP/FI, PHP3, PHP5, and PHP7. 2. Descriptions of core PHP features like being open source, developing dynamic web applications, and supporting various databases. 3. Explanations of PHP syntax including tags, variables, naming conventions, constants, data types, and operators like arithmetic, assignment, comparison, increment/decrement, logical, and string operators. 4. Sections on specific PHP concepts like variables, constants, data types, expressions, and different types of operators. Variables are declared with