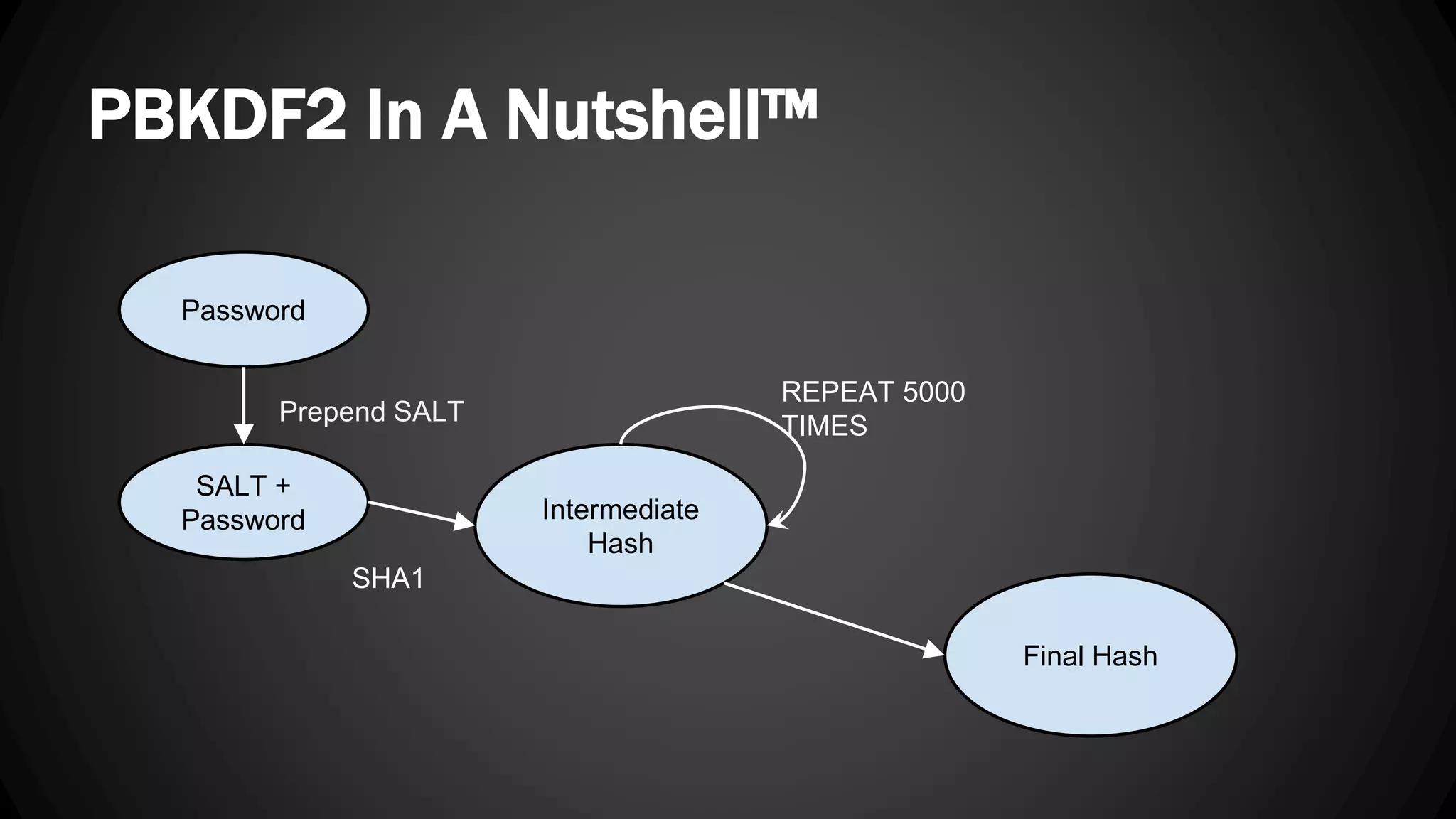
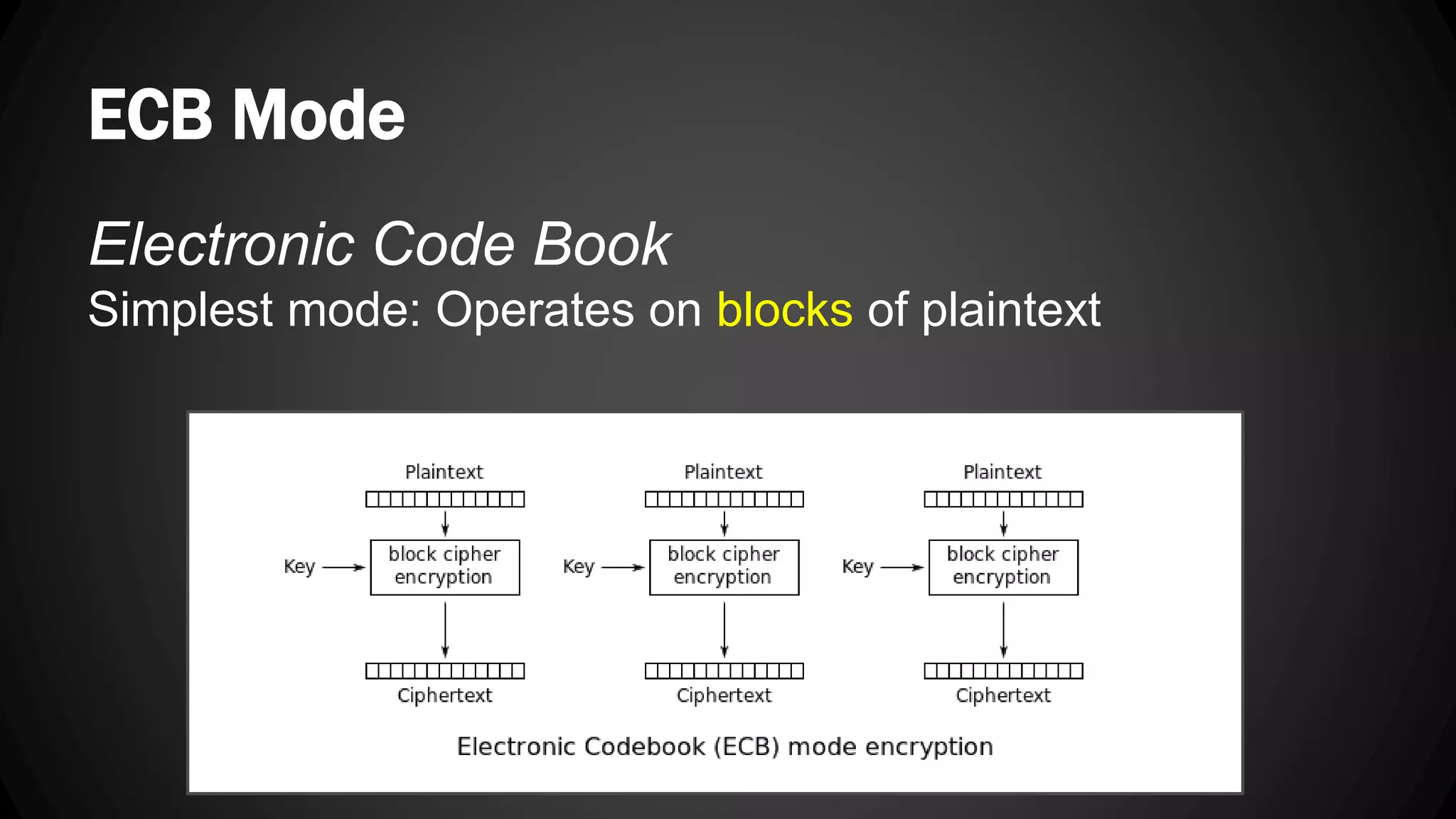
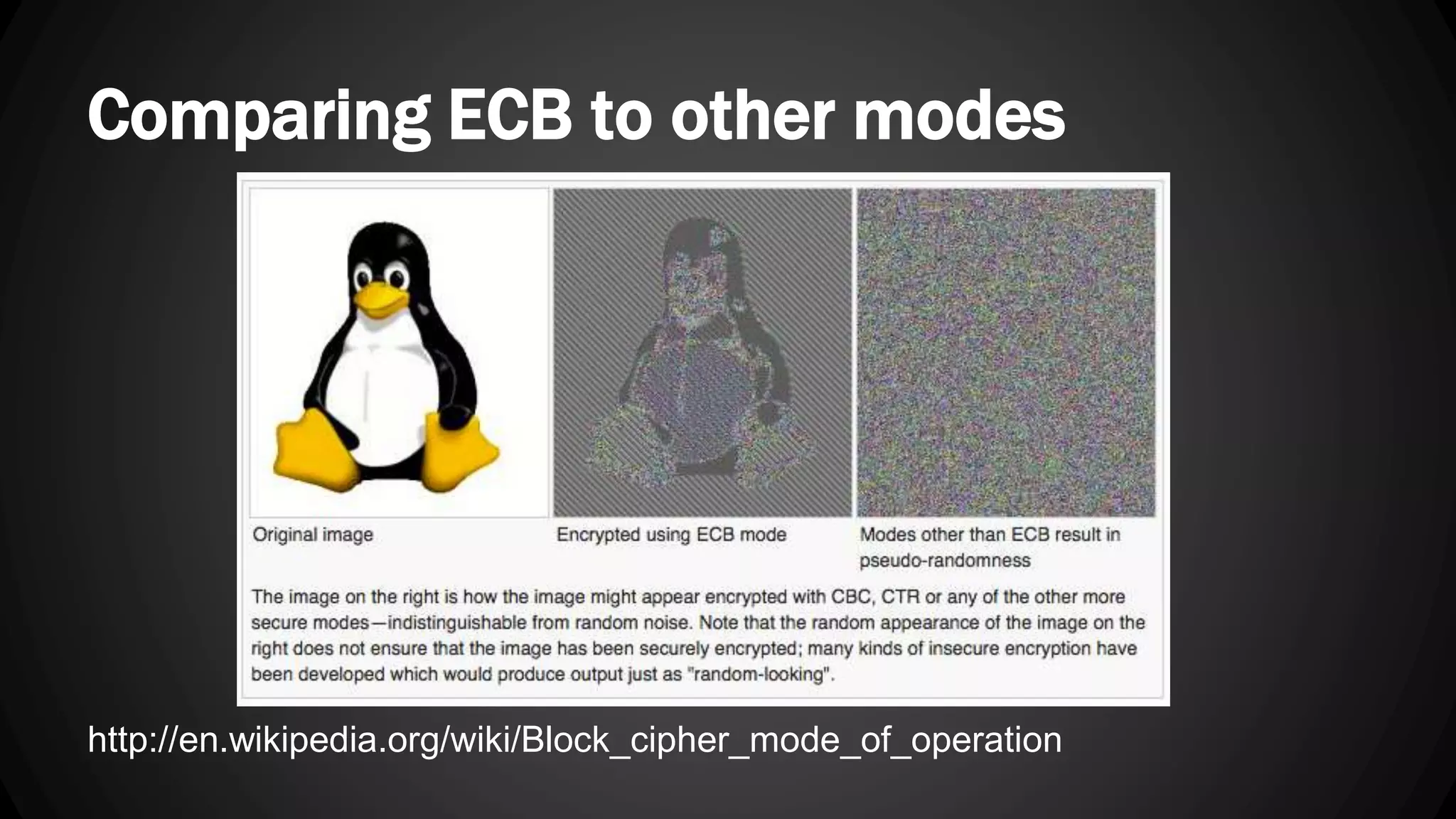
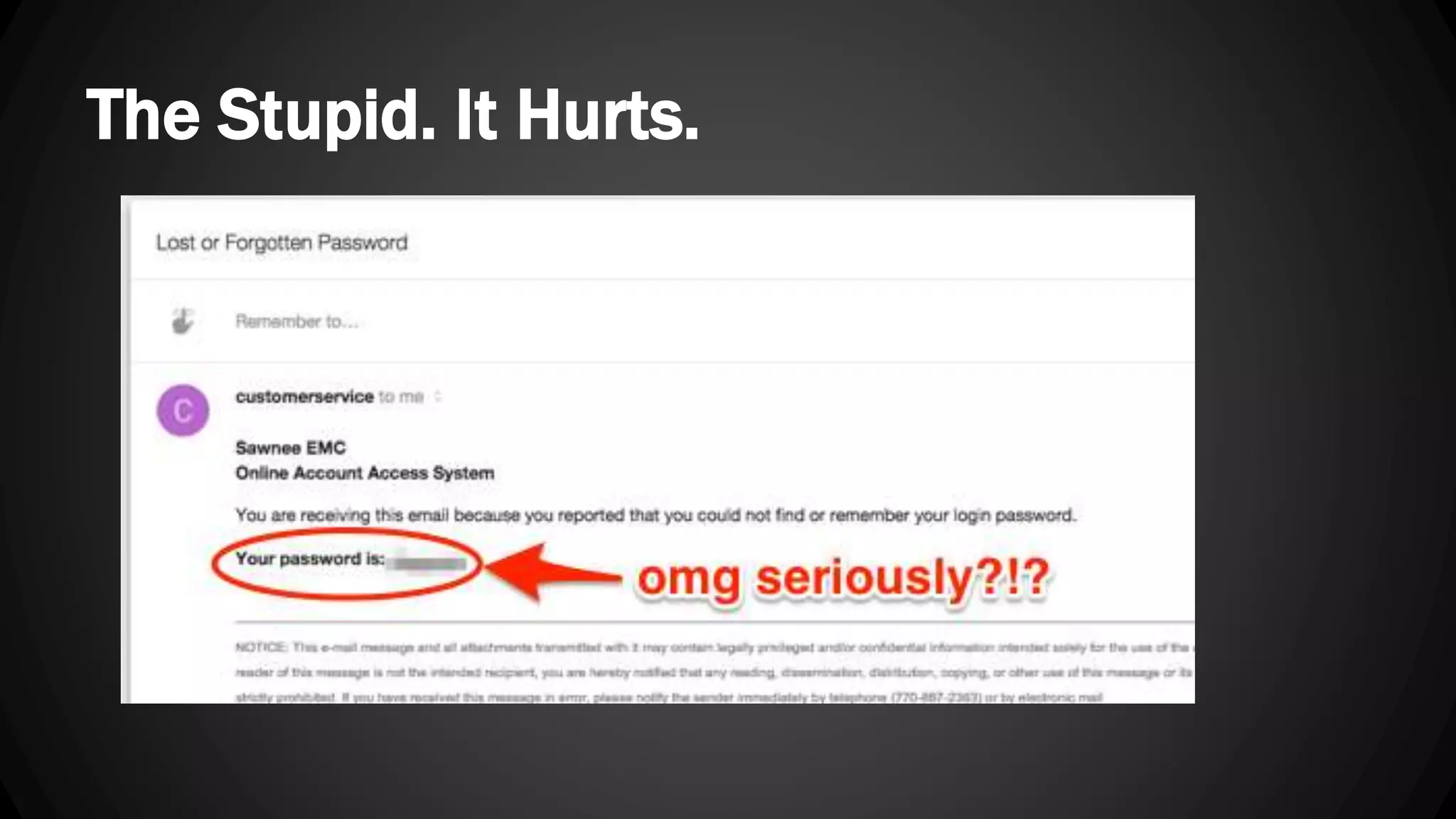
Andy Watson, an employee of Ionic Security, gave a presentation on properly using cryptography in applications. The presentation covered topics such as random number generation, hashing, salting passwords, key derivation functions, symmetric encryption algorithms and common mistakes made with cryptography. The goal was to help people avoid vulnerabilities like unsalted hashes, hardcoded keys, weak random number generation and improper encryption modes.