Downloaded 367 times



A tree is a hierarchical data structure where items are arranged in a sorted sequence. It represents relationships between data items. A tree has a root node at the top with child nodes branching out connected by edges. Each node stores data and links to other nodes. The level of a node indicates its depth from the root with the root being level 0. Siblings are nodes that share the same parent. Leaf nodes have no children while non-terminal nodes have children. The degree of a node is the number of subtrees extending from it.
A tree is a non-linear data structure for hierarchical relationships among data items.
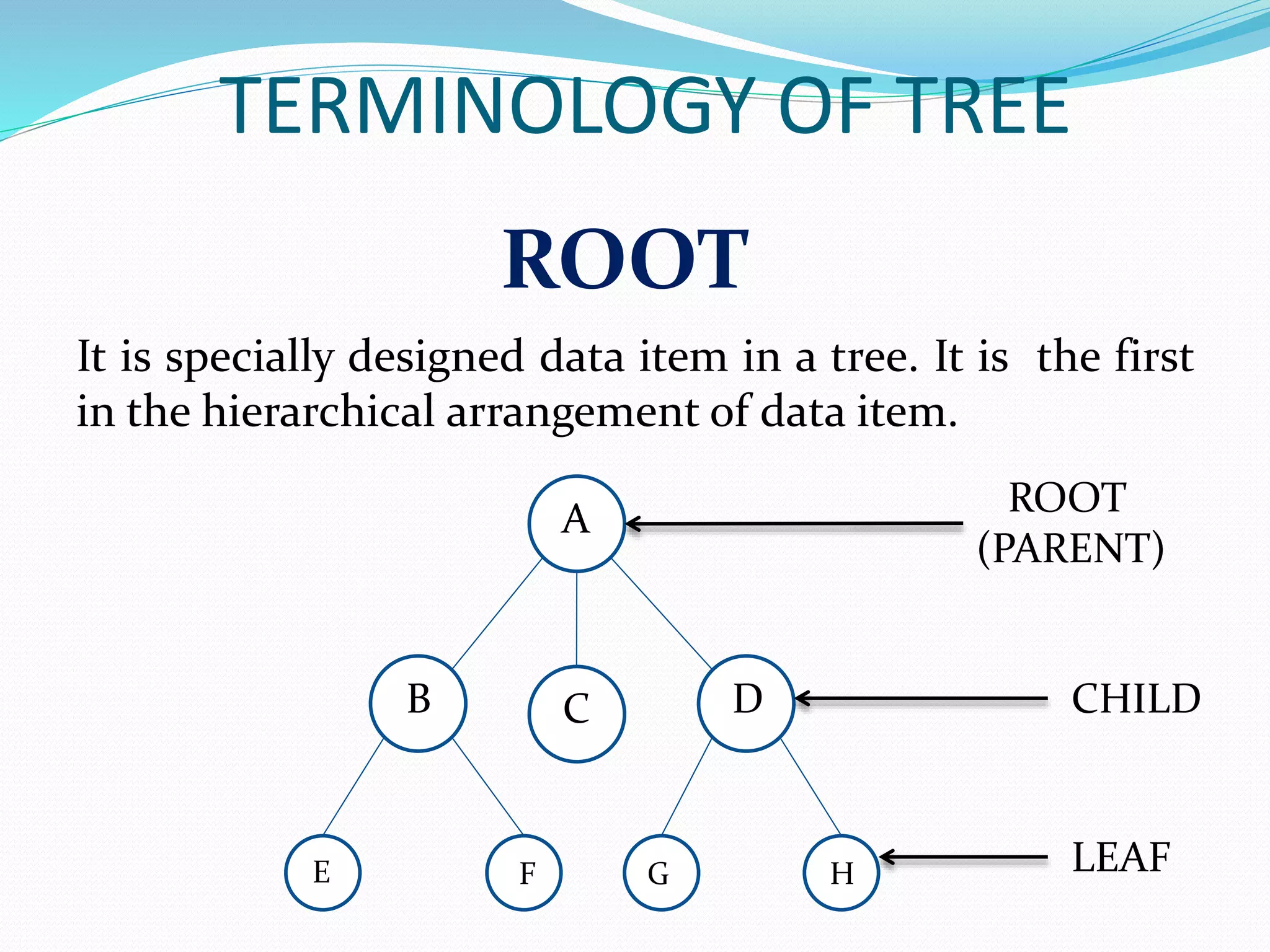
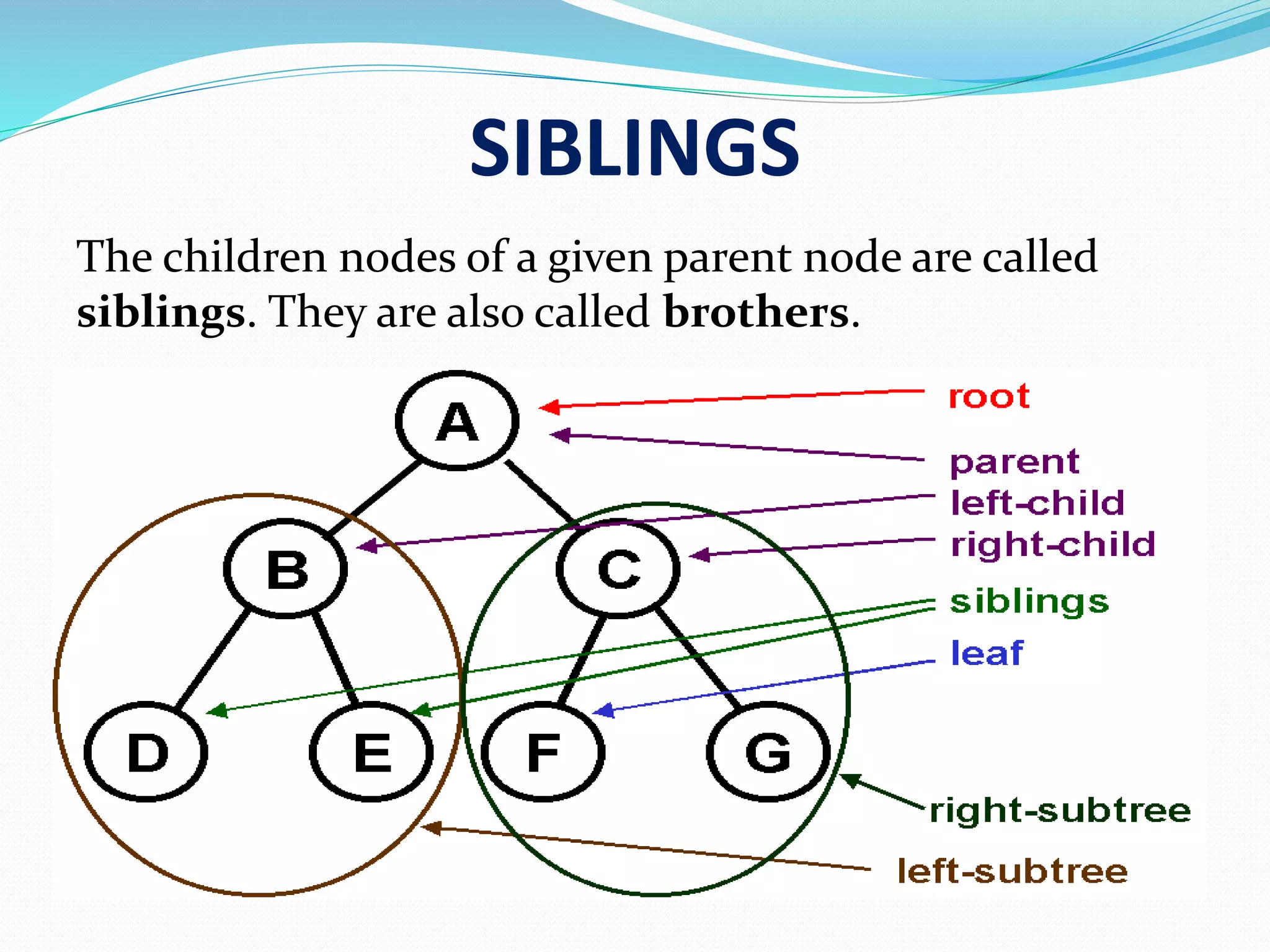
Key terms include ROOT (the top element), CHILD, LEAF, and PARENT that define tree structure.
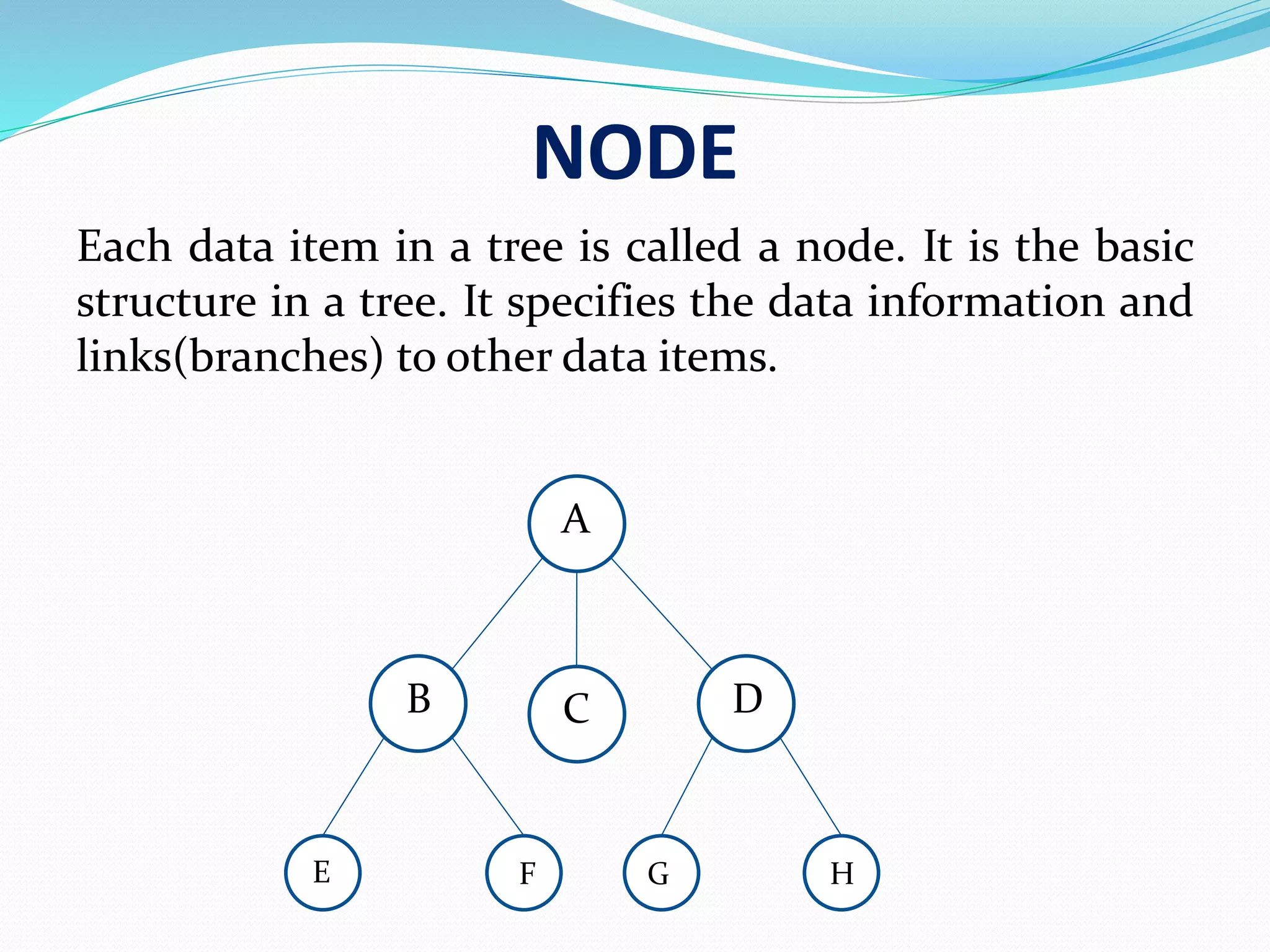
Each data item in a tree is called a node, which includes data and links to other nodes.
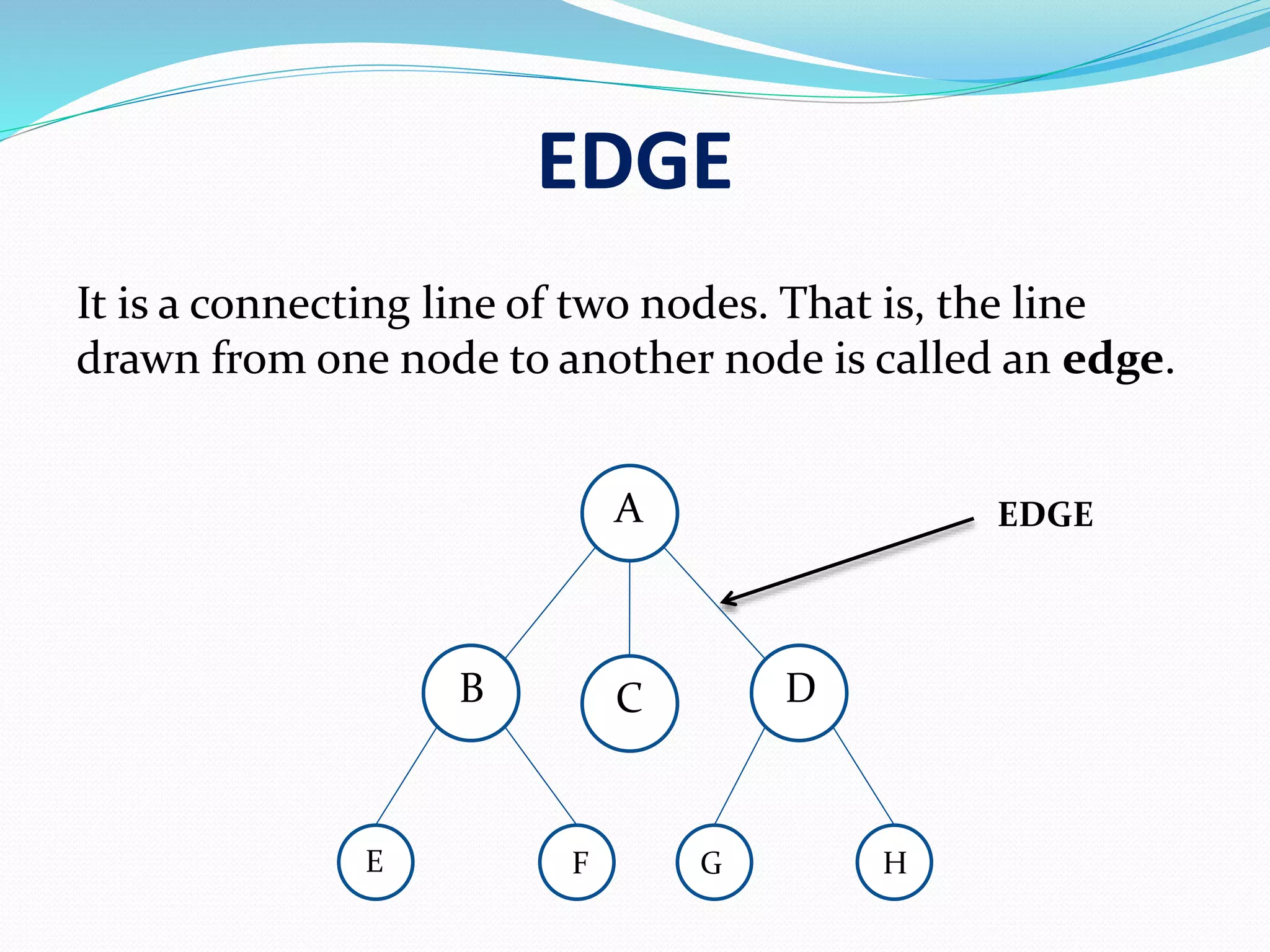
An edge connects two nodes in a tree, represented as the line between them.
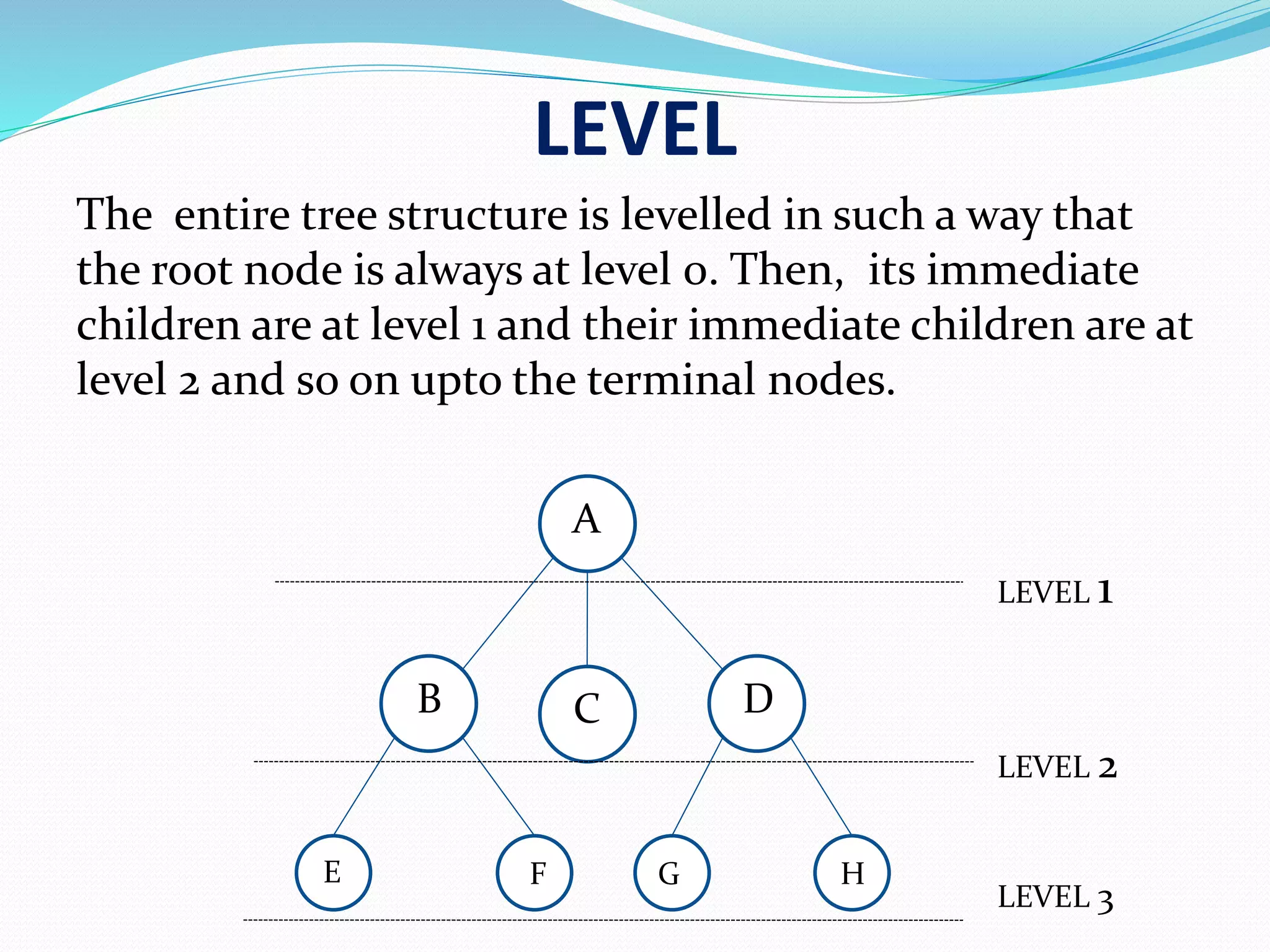
Tree structure levels: ROOT at level 0, children at level 1, grandchildren at level 2, etc.
Children of the same parent node are referred to as siblings in a tree structure.
Terminal nodes have degree zero (leaves), while non-terminal nodes have a degree greater than zero.
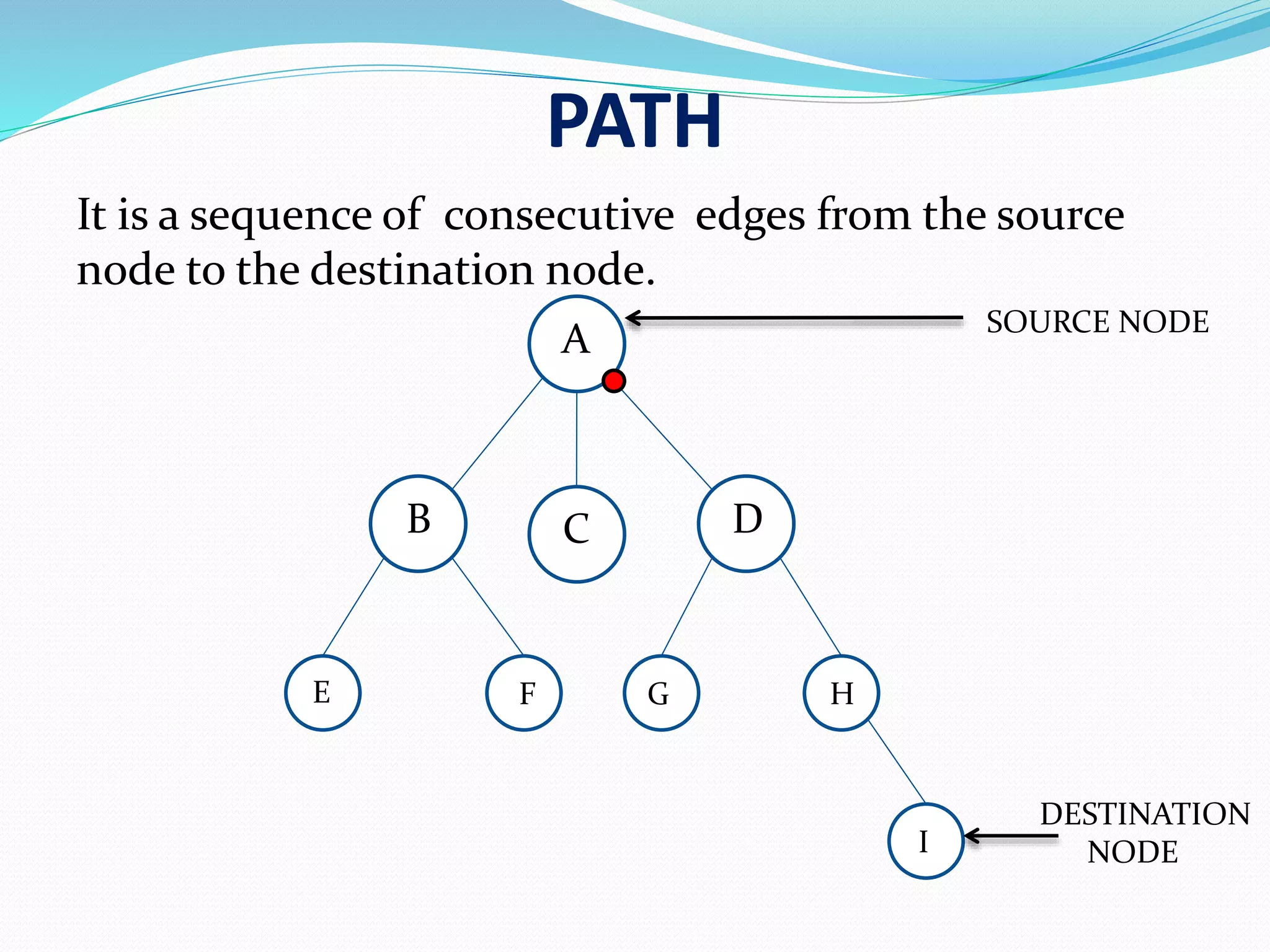
A path is a sequence of edges connecting a source node to a destination node.
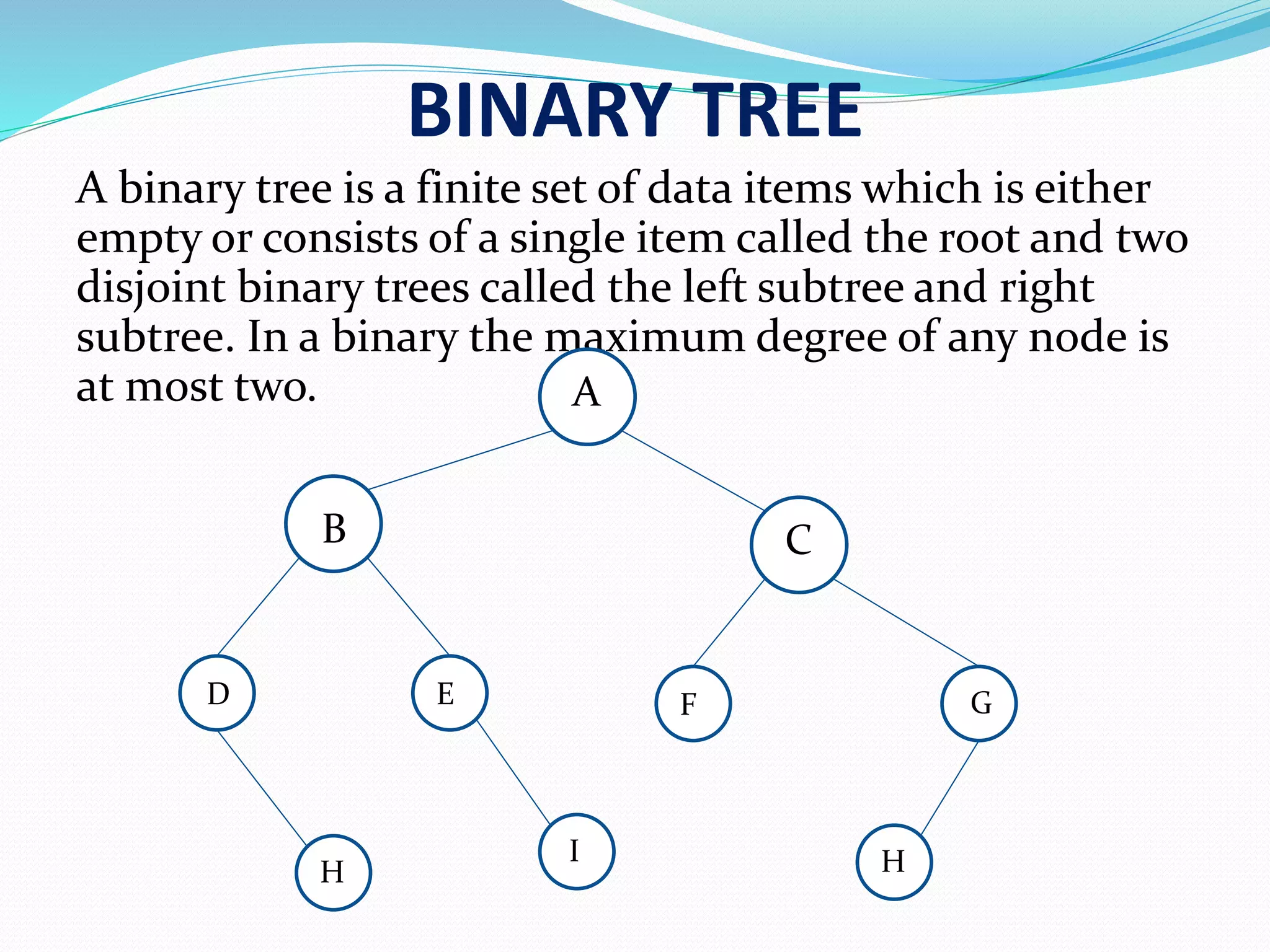
A binary tree consists of a root node and up to two disjoint subtrees, with nodes having a max degree of two.










