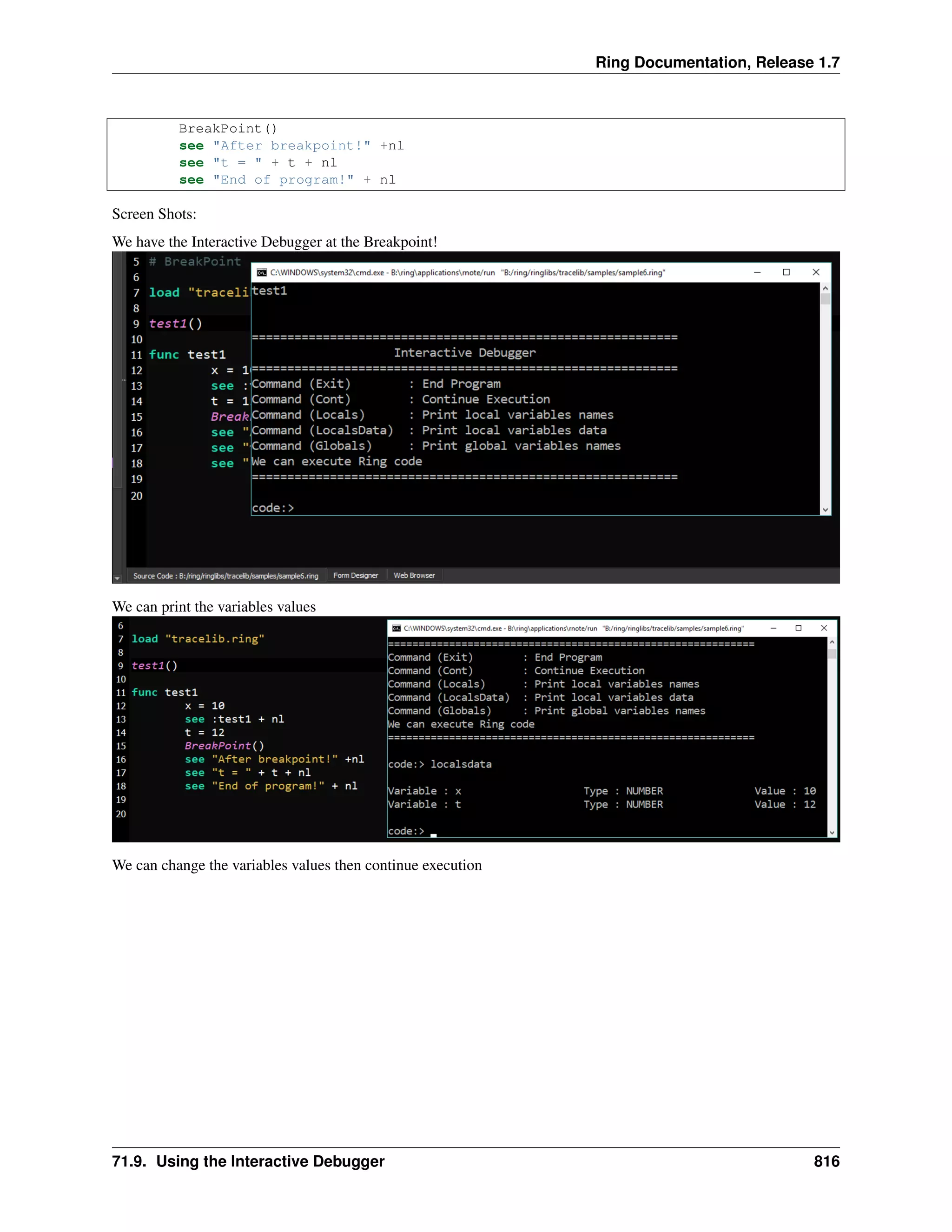
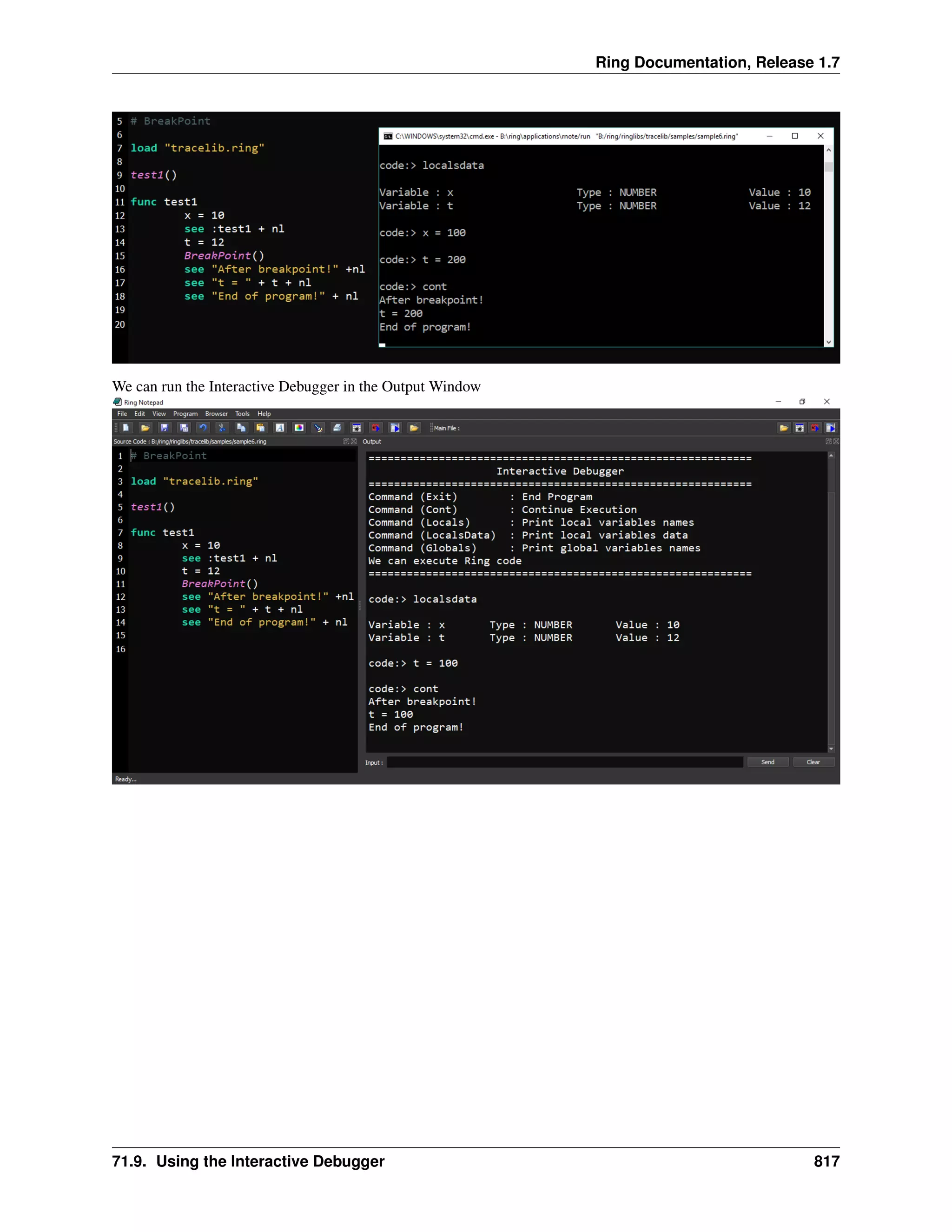
The document discusses embedding Ring programs within other Ring programs using the ringvm library. It describes functions for running Ring code in isolated states to prevent conflicts, executing programs serially, passing variables between states, and running Ring programs from other programs while controlling memory management. The goal is to provide safe integration of Ring programs and applications.


![CHAPTER SEVENTYTWO EMBEDDING RING IN RING In this chapter we will learn about embedding Ring in Ring programs and applications. 72.1 Embedding Ring in Ring without sharing the State From Ring 1.0 we already have functions for embedding Ring in the C language. Also we can execute Ring code inside Ring programs using the eval() function. In this release we provide functions for embedding Ring in Ring programs without sharing the state. Advantages: 1. Quick integration for Ring programs and applications together without conflicts. 2. Execute and run Ring code in safe environments that we can trace. Example: pState = ring_state_init() ring_state_runcode(pState,"See 'Hello, World!'+nl") ring_state_runcode(pState,"x = 10") pState2 = ring_state_init() ring_state_runcode(pState2,"See 'Hello, World!'+nl") ring_state_runcode(pState2,"x = 20") ring_state_runcode(pState,"see x +nl") ring_state_runcode(pState2,"see x +nl") v1 = ring_state_findvar(pState,"x") v2 = ring_state_findvar(pState2,"x") see v1[3] + nl see V2[3] + nl ring_state_delete(pState) ring_state_delete(pState2) Output: Hello, World! Hello, World! 10 20 10 20 818](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/841pdfsamfayedringdoc1-180722102946/75/The-Ring-programming-language-version-1-7-book-Part-85-of-196-7-2048.jpg)
![Ring Documentation, Release 1.7 ring_state_runcode(pState,"? x") # Pass Number ring_state_setvar(pState,"x",100) ring_state_runcode(pState,"? x") # Pass List ring_state_setvar(pState,"x",["one","two","three"]) ring_state_runcode(pState,"? x") # Pass Object # We can't pass the Ring Object (win) # Because Objects store pointers to the Class Information # And the class is related to the Parent Ring Environment # And the sub Ring environment can't access it # But we can pass C pointers like win.pObject ring_state_setvar(pState,"x",win.pObject) # Now we create the object again but using the same C pointer # So we have access to the Same window in the parent Ring enviroment ring_state_runcode(pState," new qWidget { pObject = x setwindowtitle('Message from the Sub Ring Environment') } ") ring_state_delete(pState) 72.4 ring_state_new() and ring_state_mainfile() Using ring_state_new() and ring_state_mainfile() we can run Ring programs from Ring programs But unlike ring_state_main(), Here we can control when to delete the Ring state! This is important when we run GUI programs from GUI programs Because they will share the GUI Library (RingQt), And In this case the caller will call qApp.Exec() So the sub program, will not stop and will return to the Main program Here deleting the State of the sub programs will lead to a problem when we run the sub program events So keeping the state is important for sub GUI programs hosted in GUI programs. Example: load "guilib.ring" func main new qApp { win = new qWidget() { setWindowTitle("Test ring_state_mainfile()") resize(400,400) move(100,100) btn = new qPushButton(Win) { settext("test") setclickevent("mytest()") } show() } exec() } 72.4. ring_state_new() and ring_state_mainfile() 820](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/841pdfsamfayedringdoc1-180722102946/75/The-Ring-programming-language-version-1-7-book-Part-85-of-196-9-2048.jpg)
