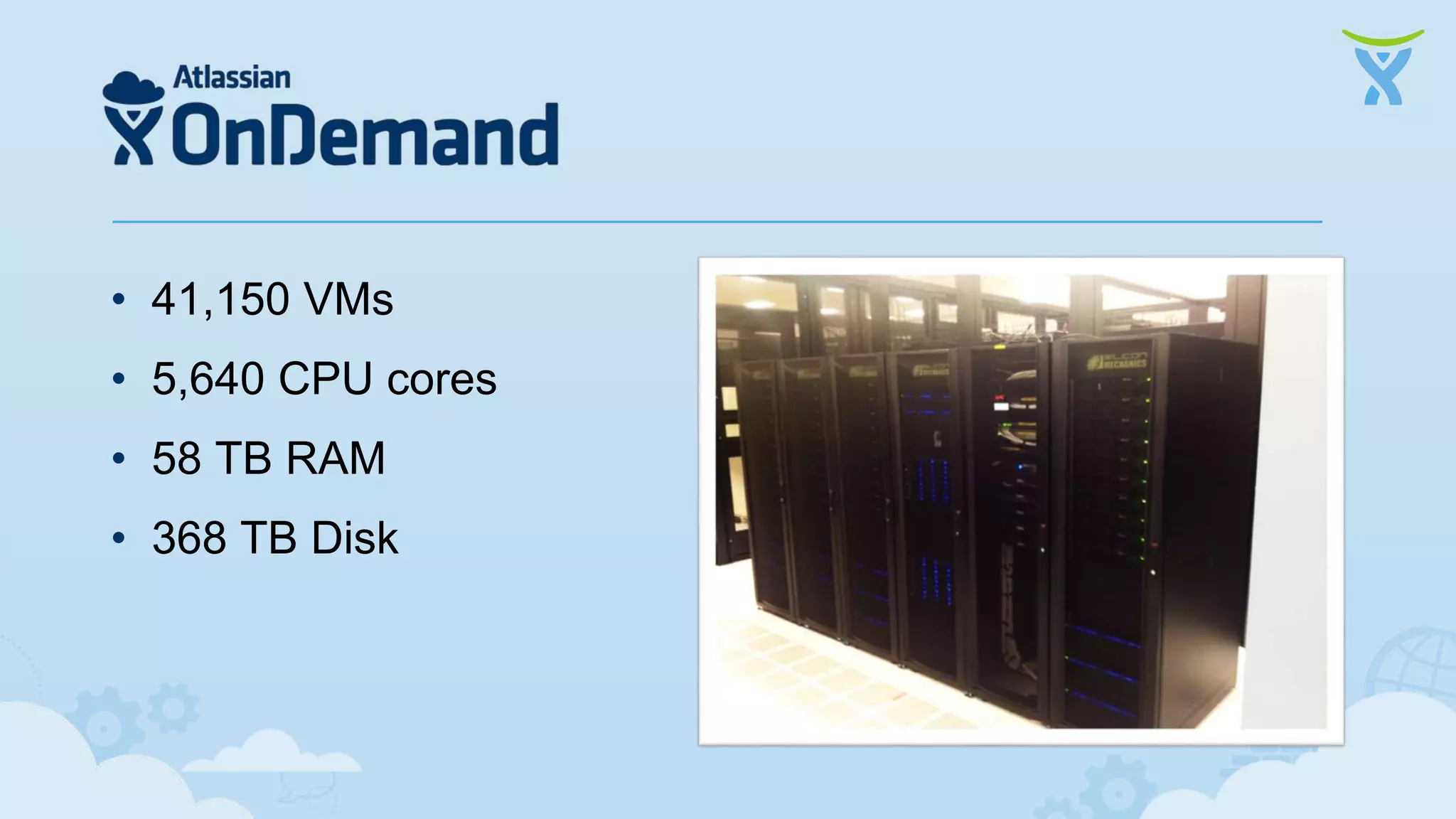
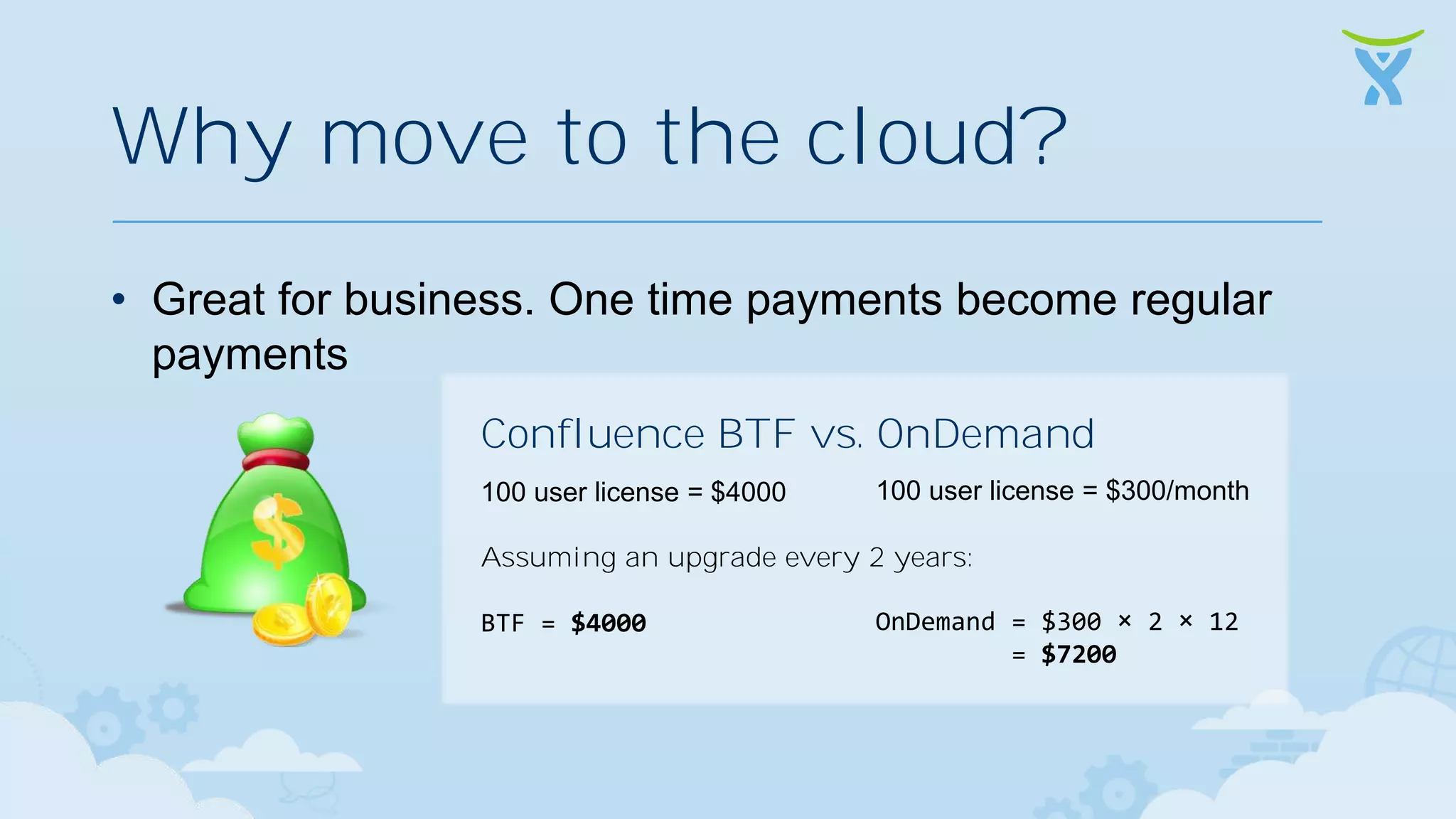
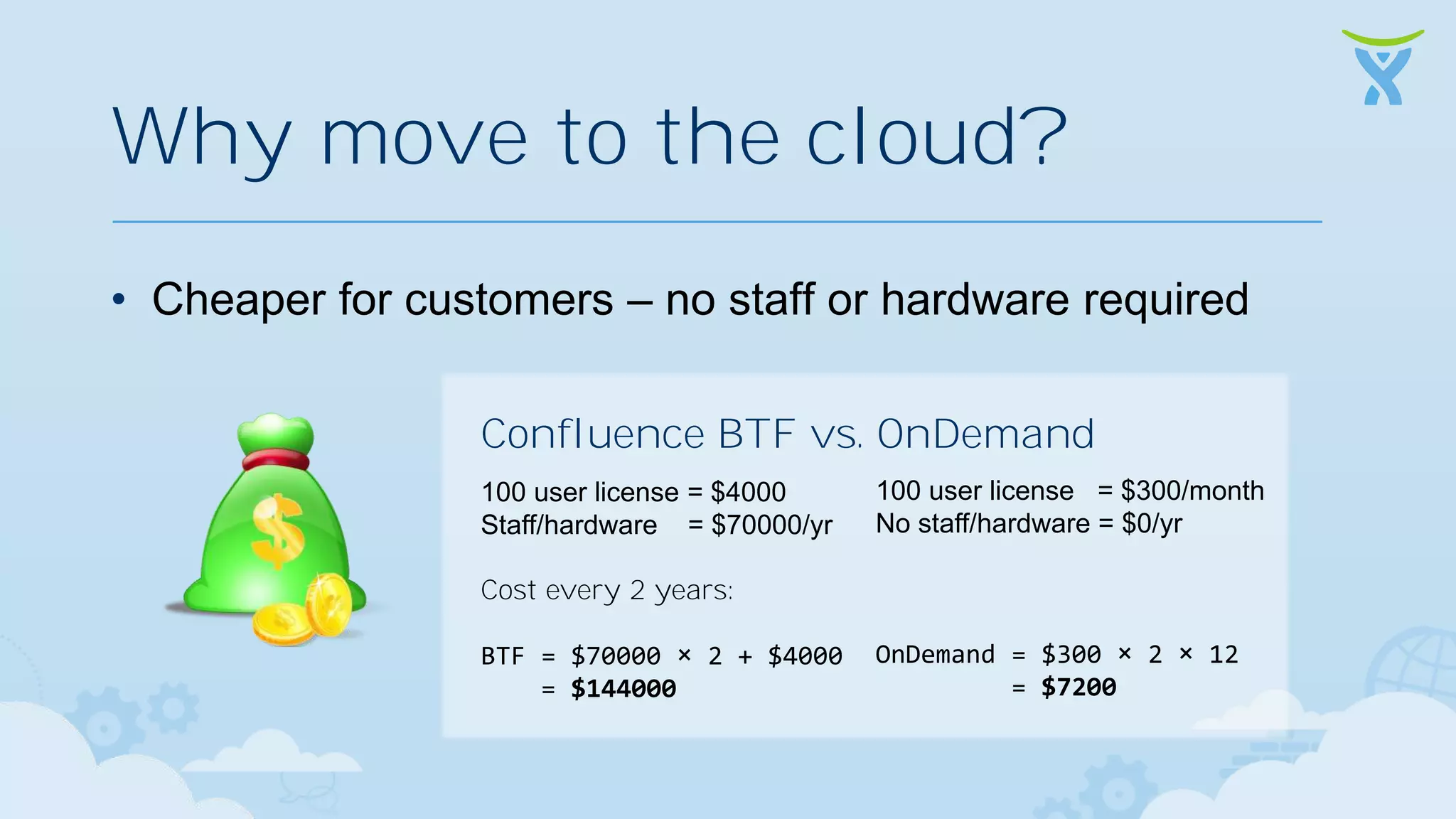
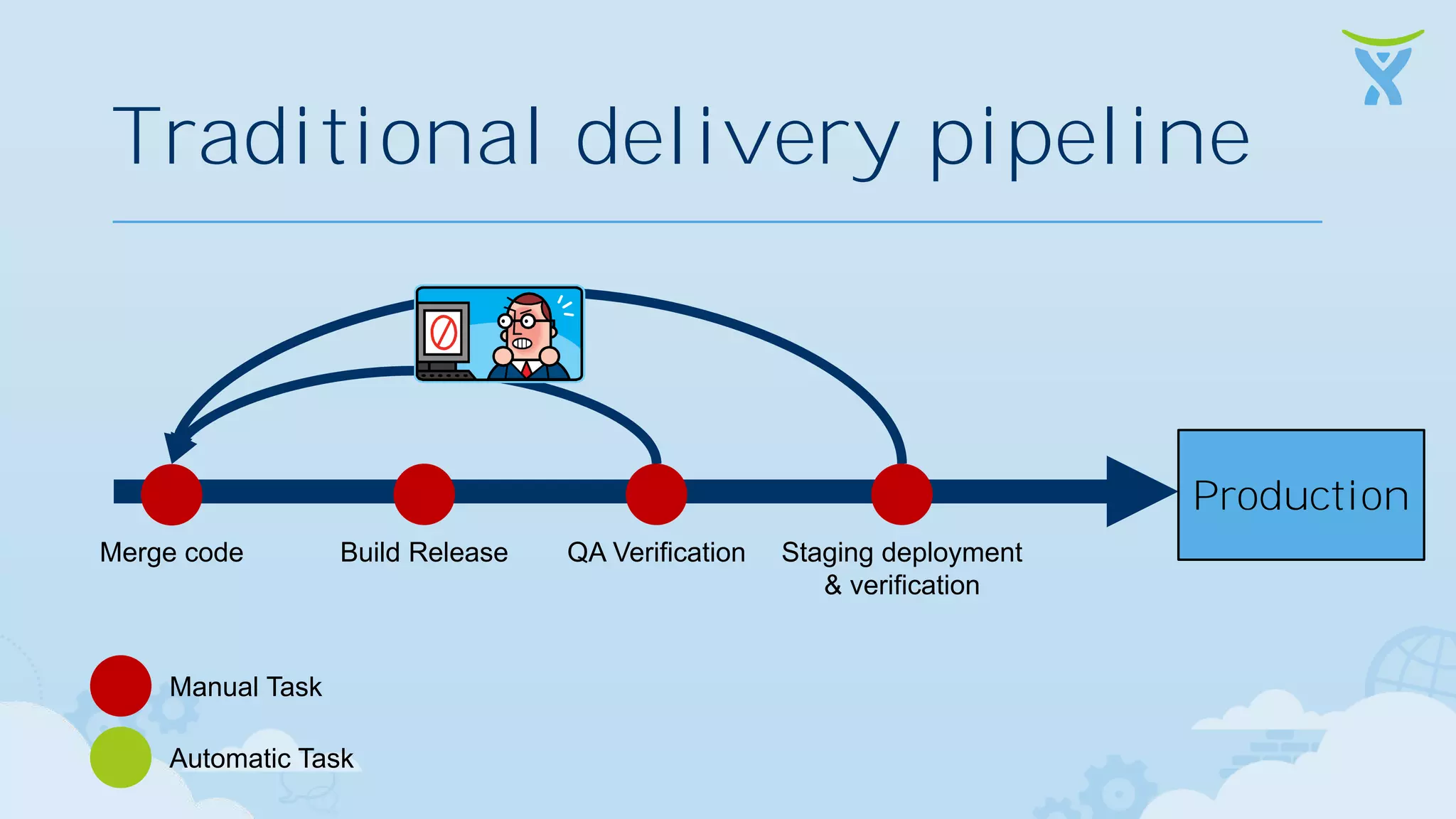
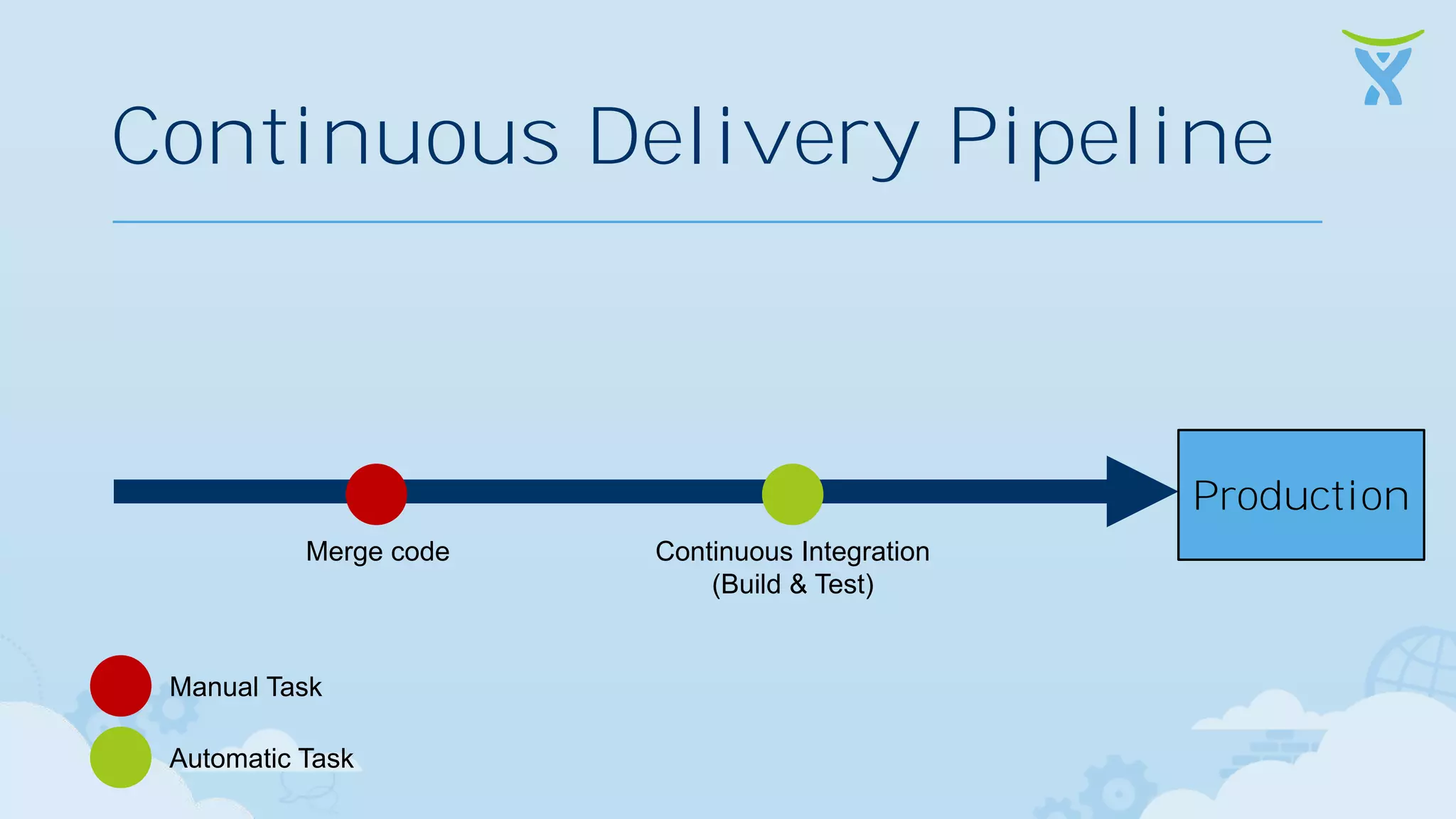
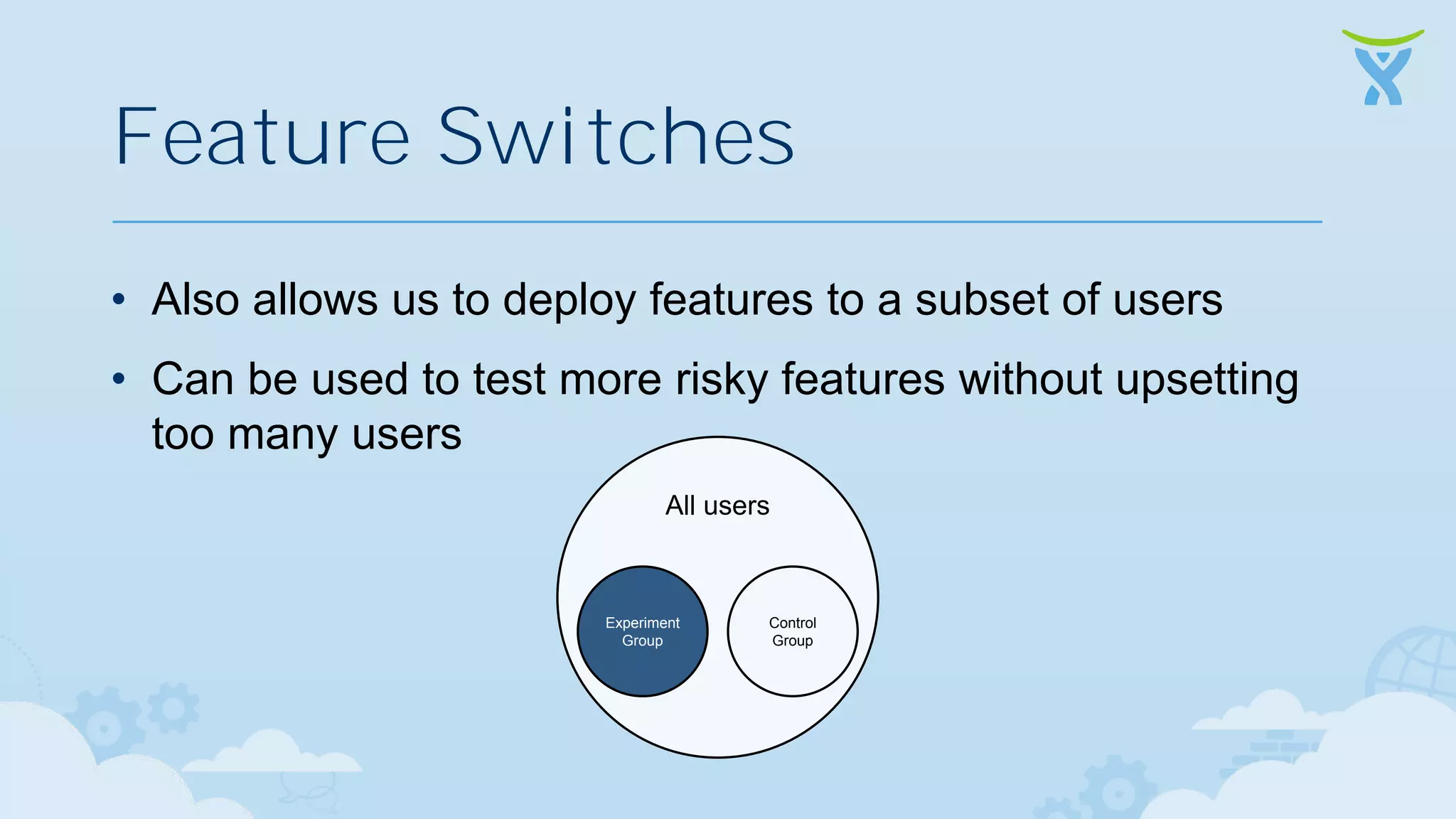
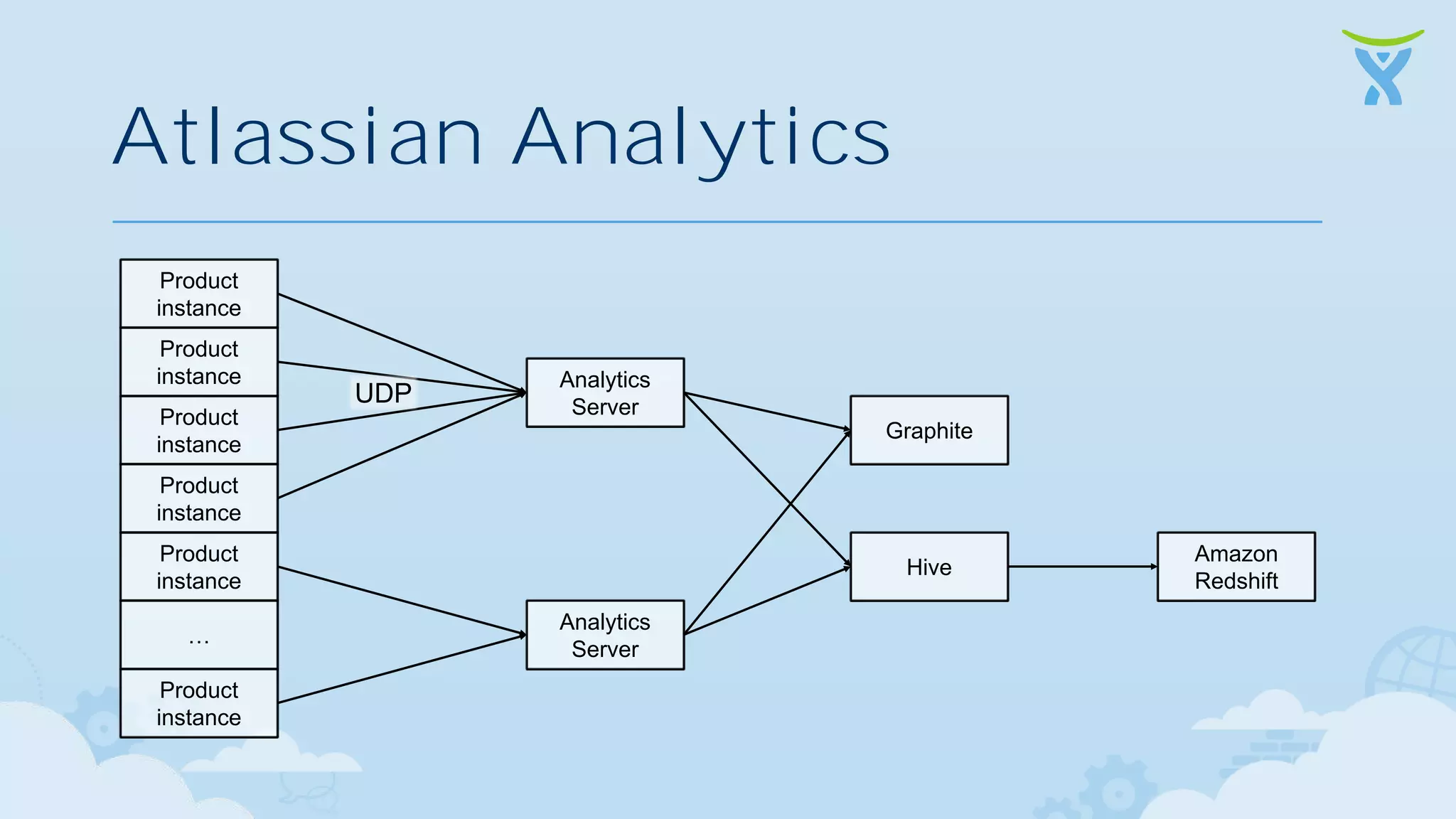
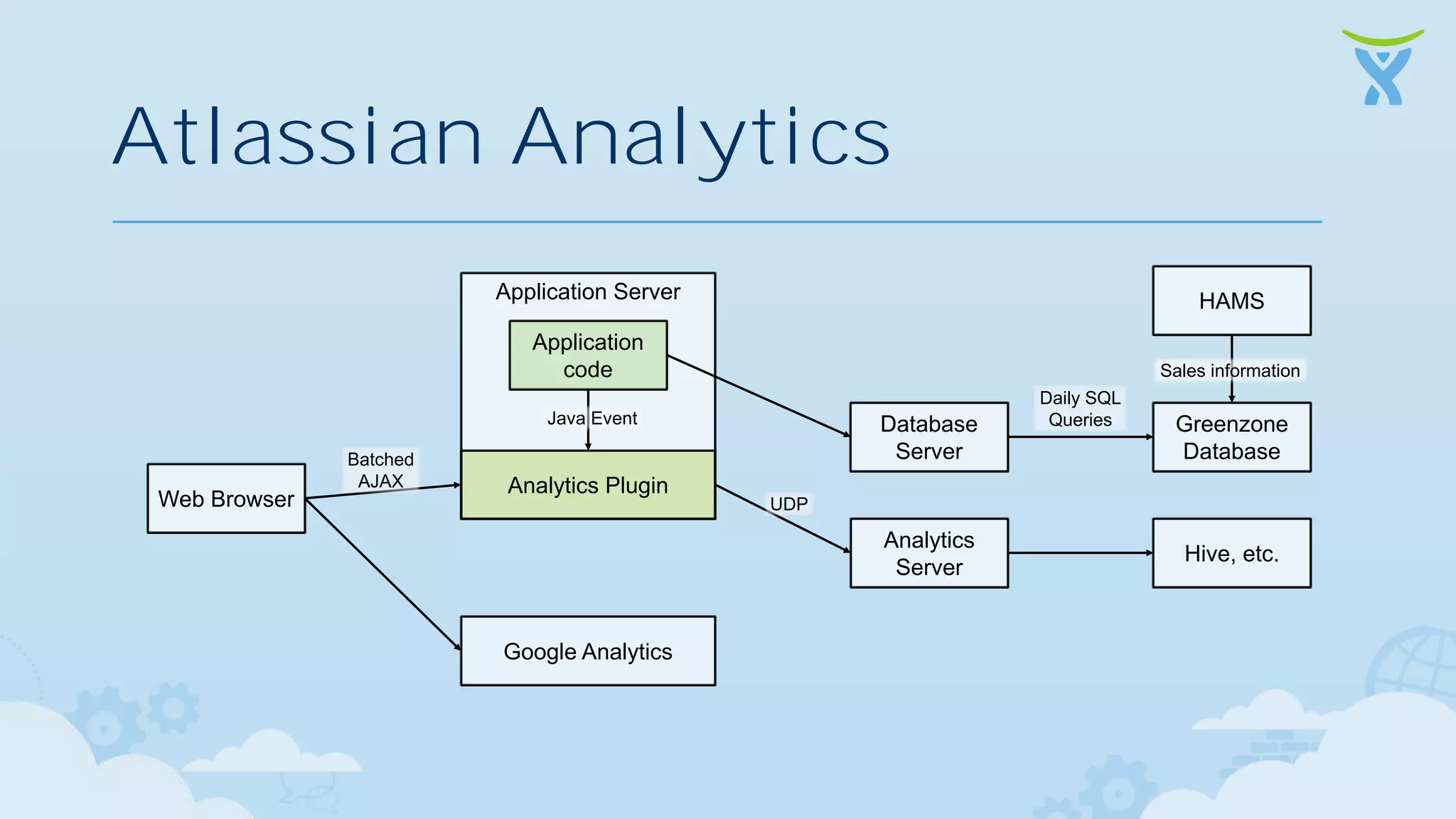
The document discusses 3 key ways that developing software for the cloud differs from traditional approaches: 1. Incremental delivery, with frequent small releases of new features rather than large periodic releases. 2. Increased automation, including automated testing and continuous integration/deployment pipelines to support more agile development and deployment. 3. Analytics of usage data to inform product decisions and ensure features are valuable to users. Developing with the cloud in mind requires rethinking processes to focus on agility, automation and data-driven insights.