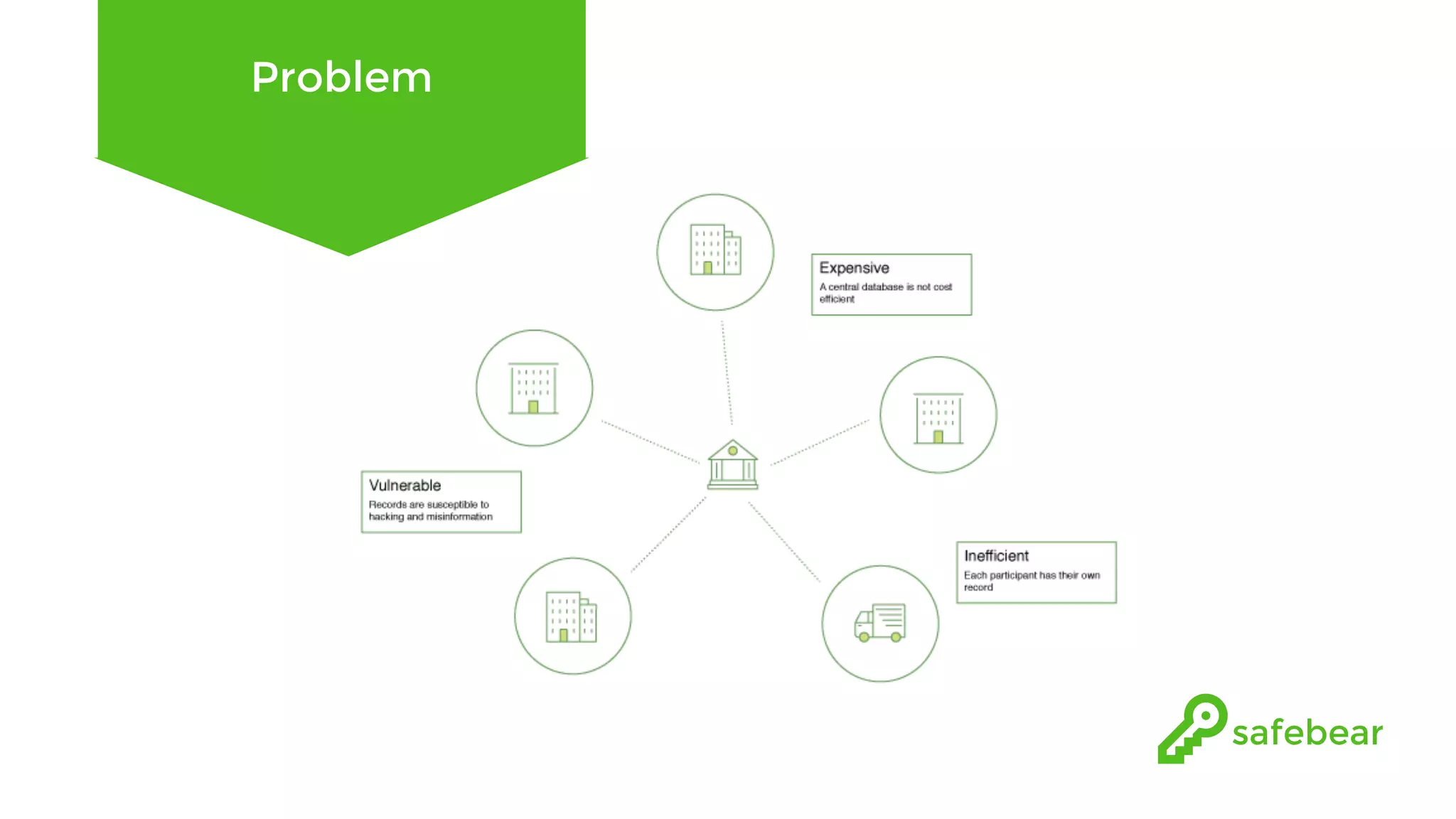
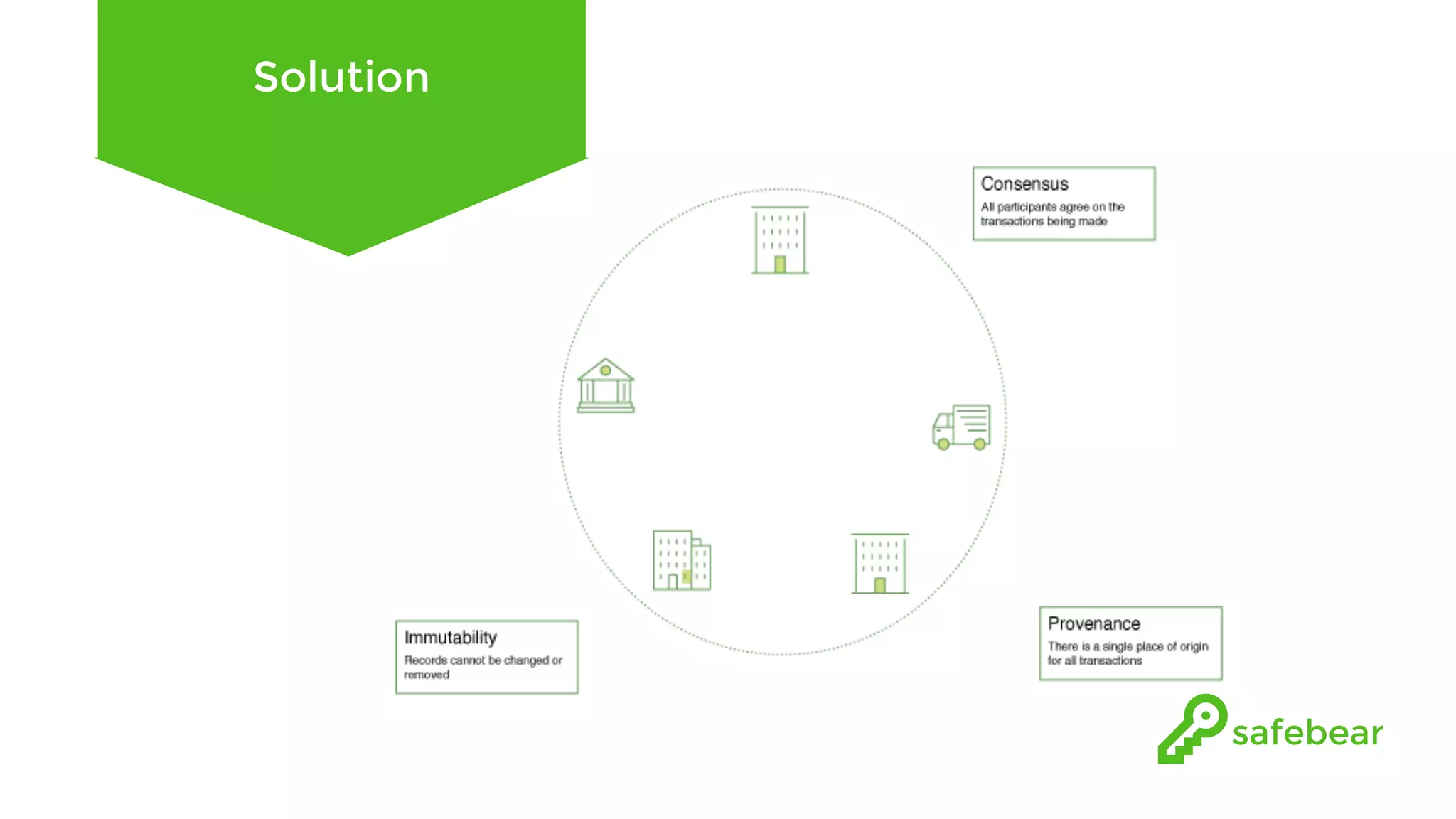
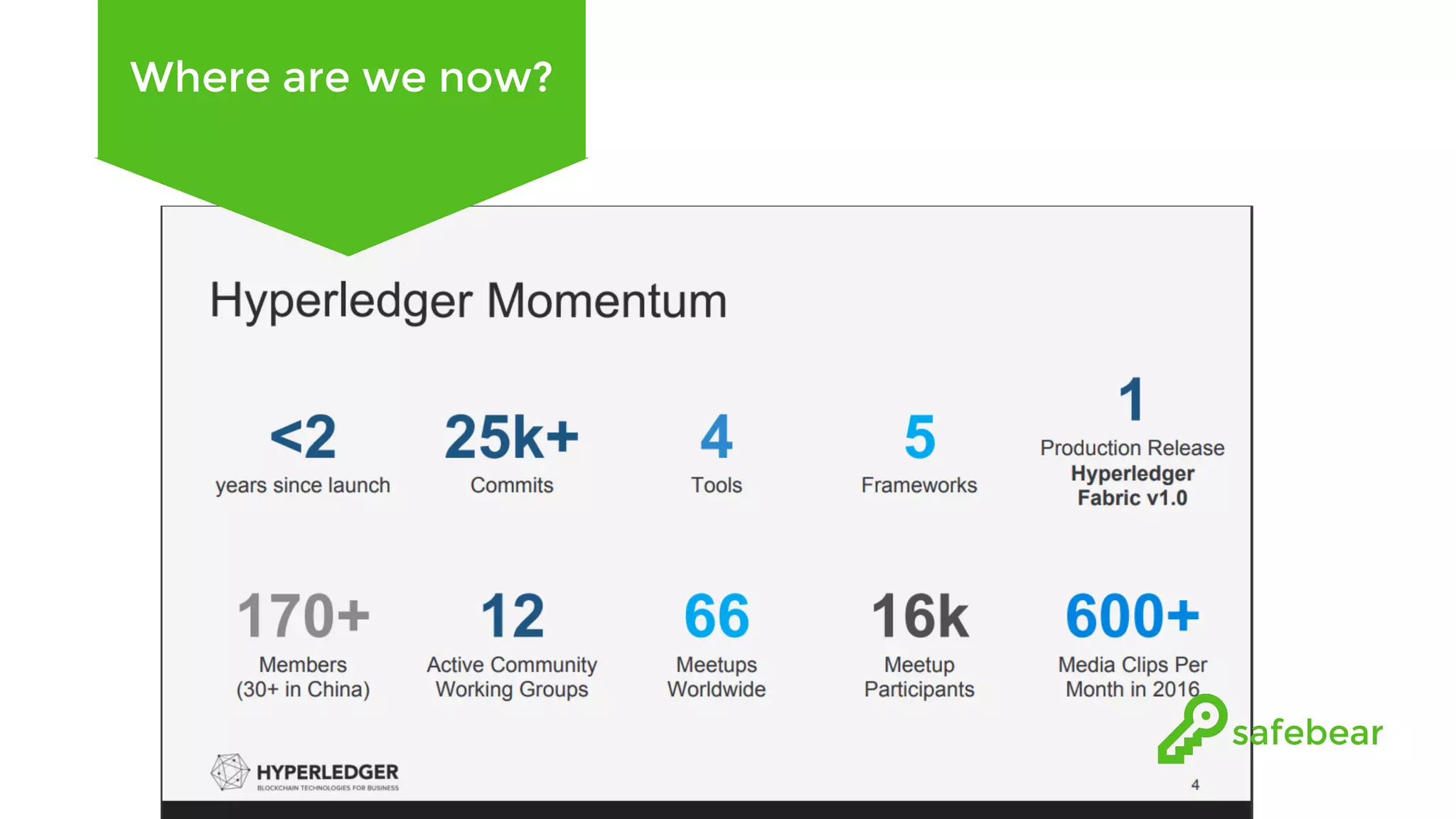
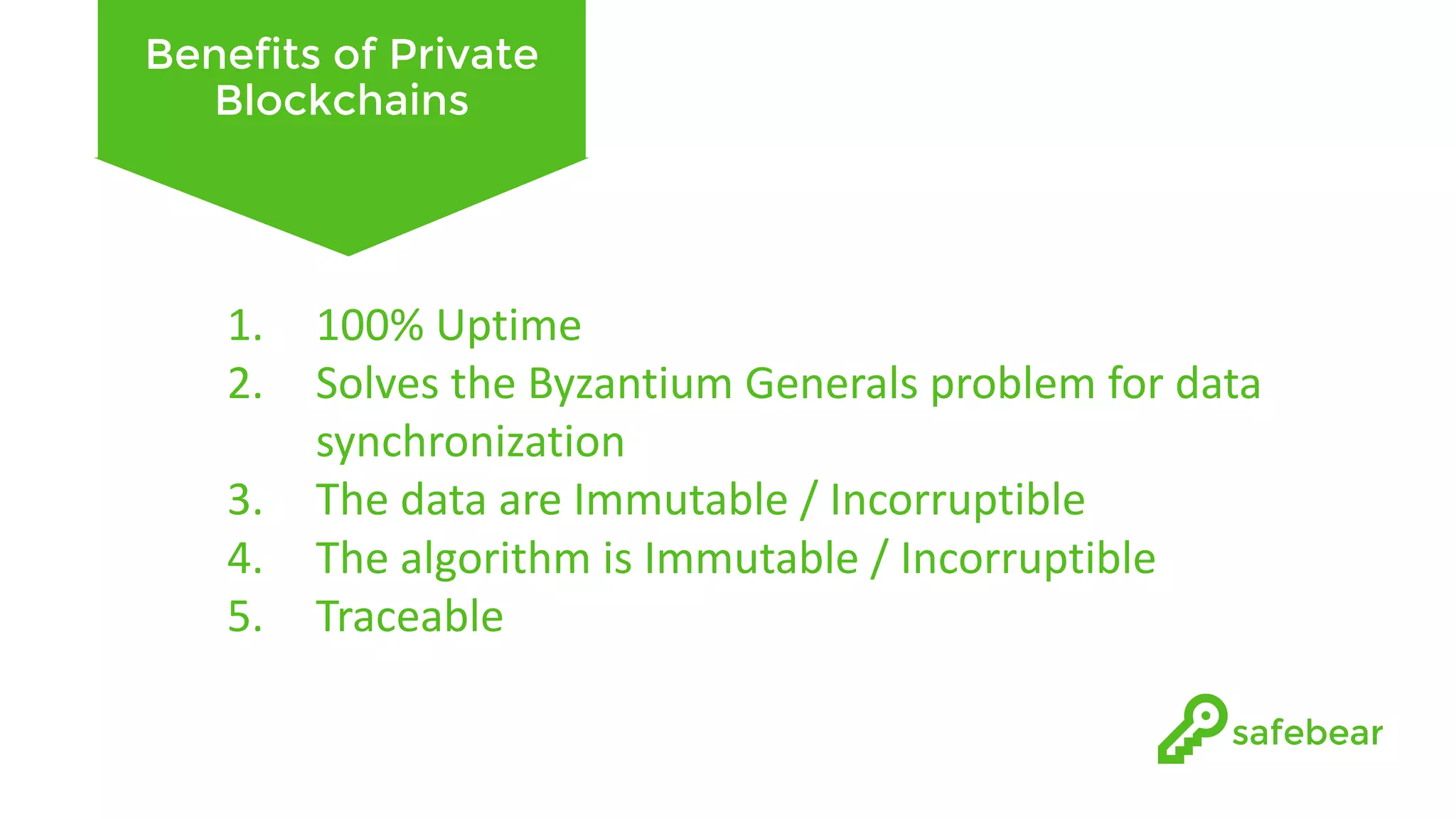
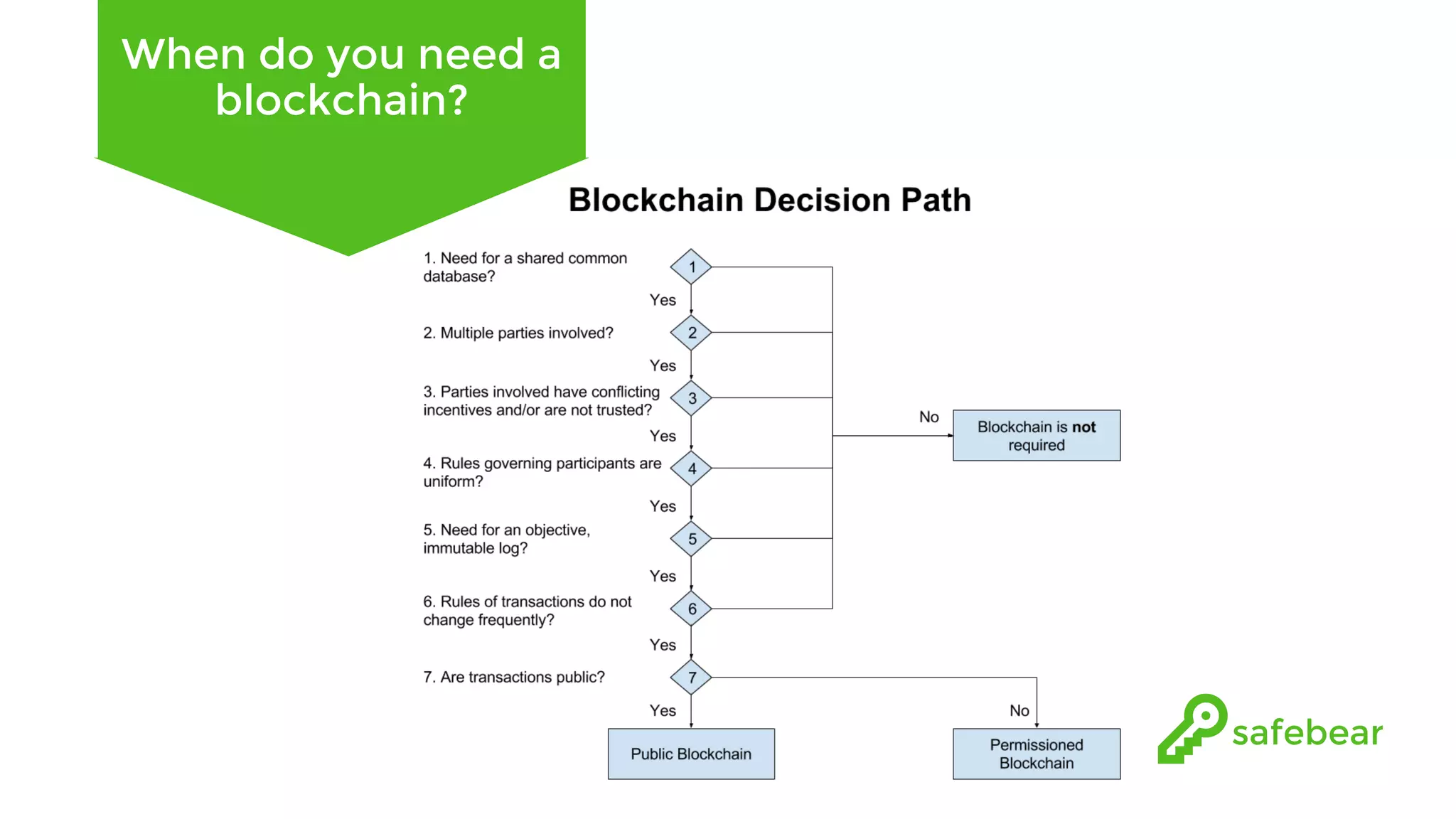
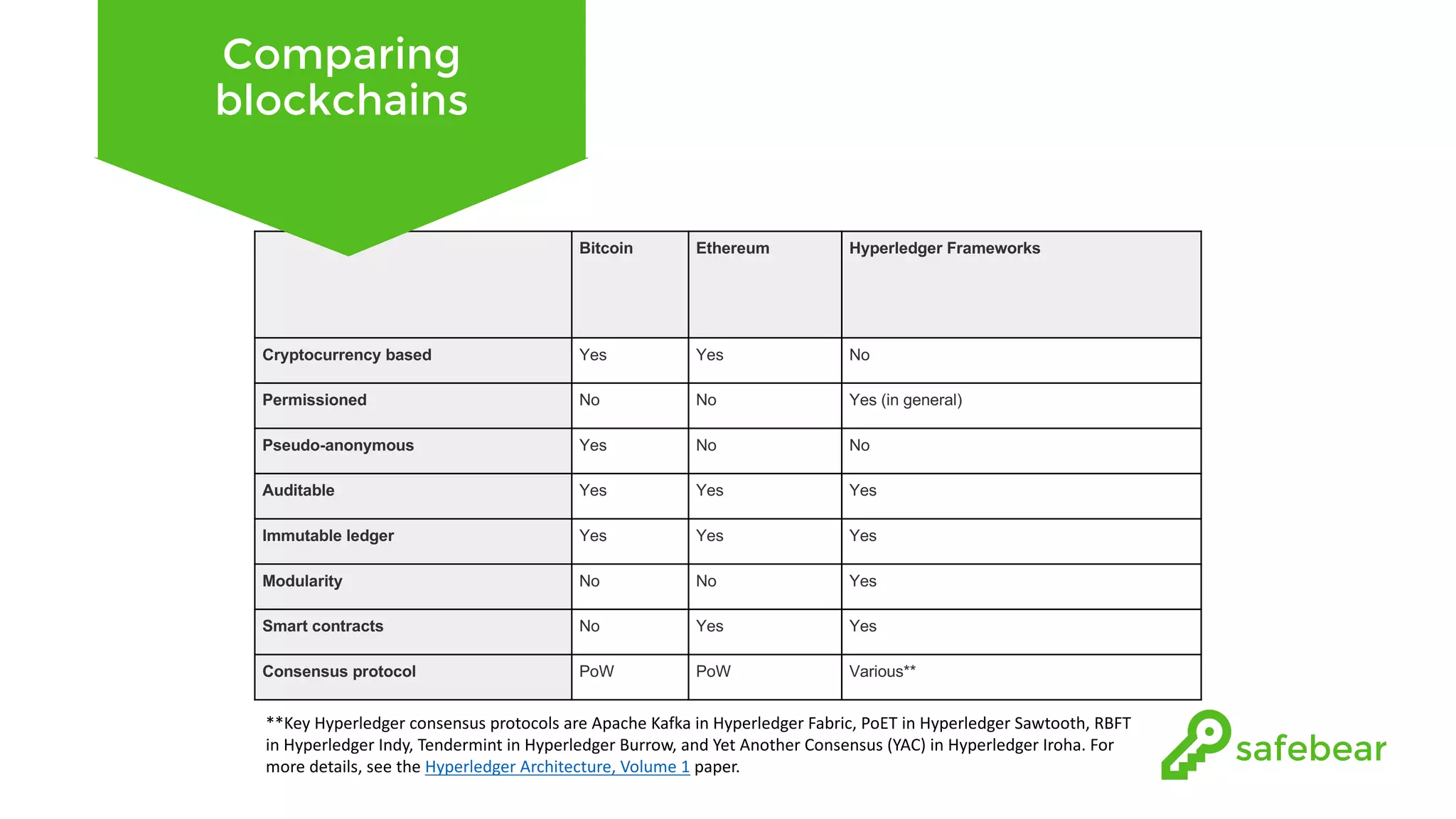
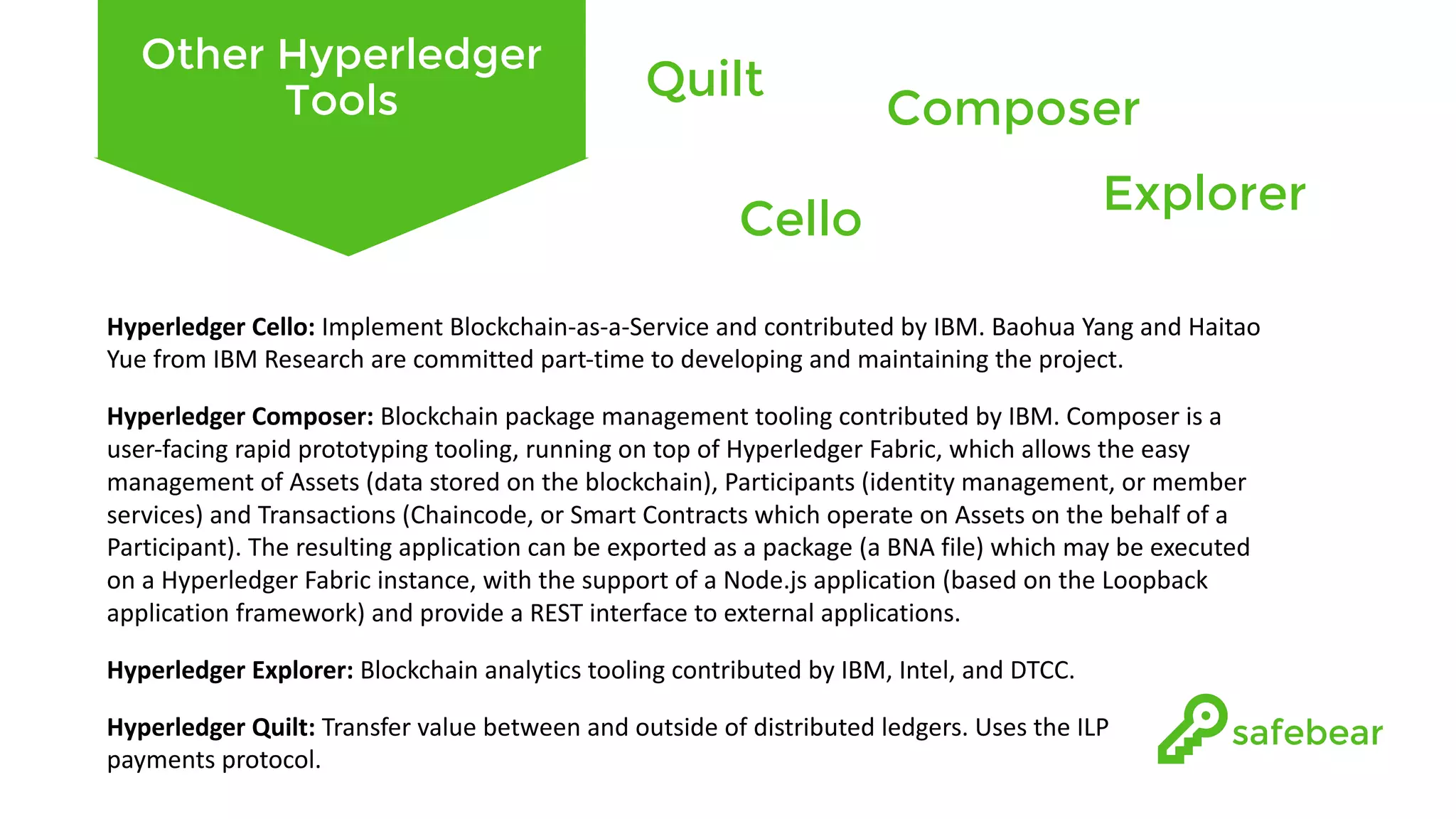
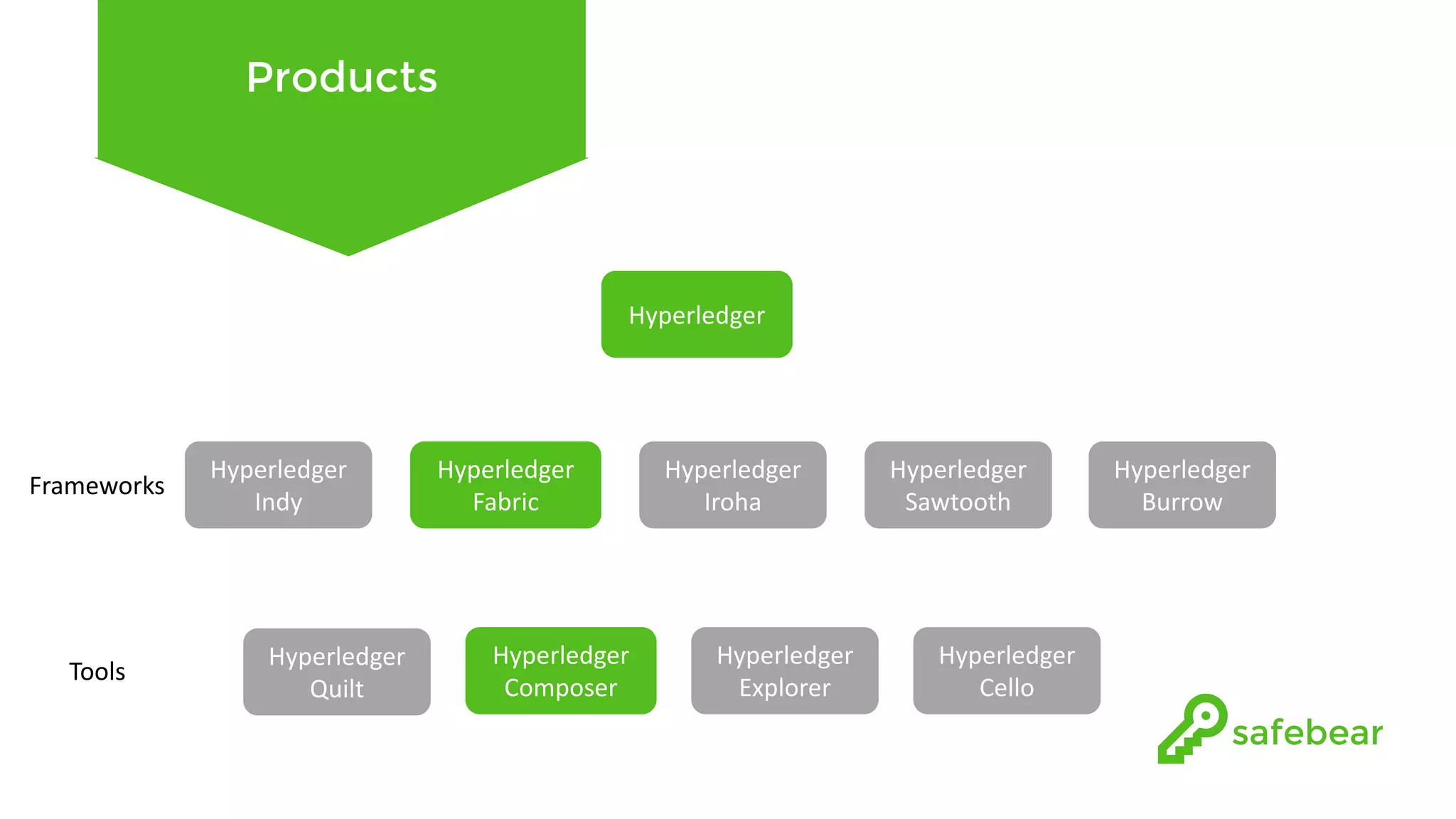
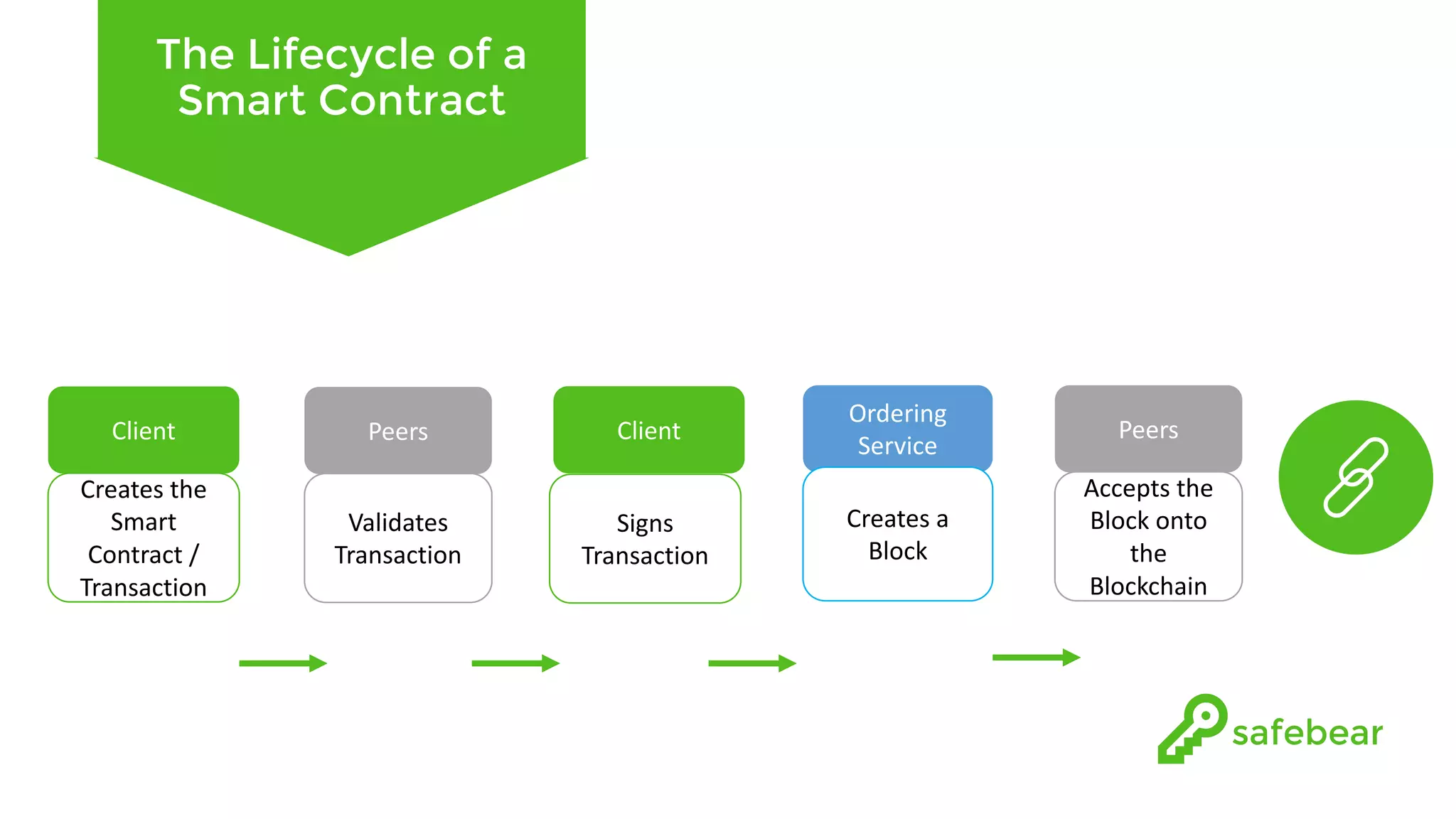
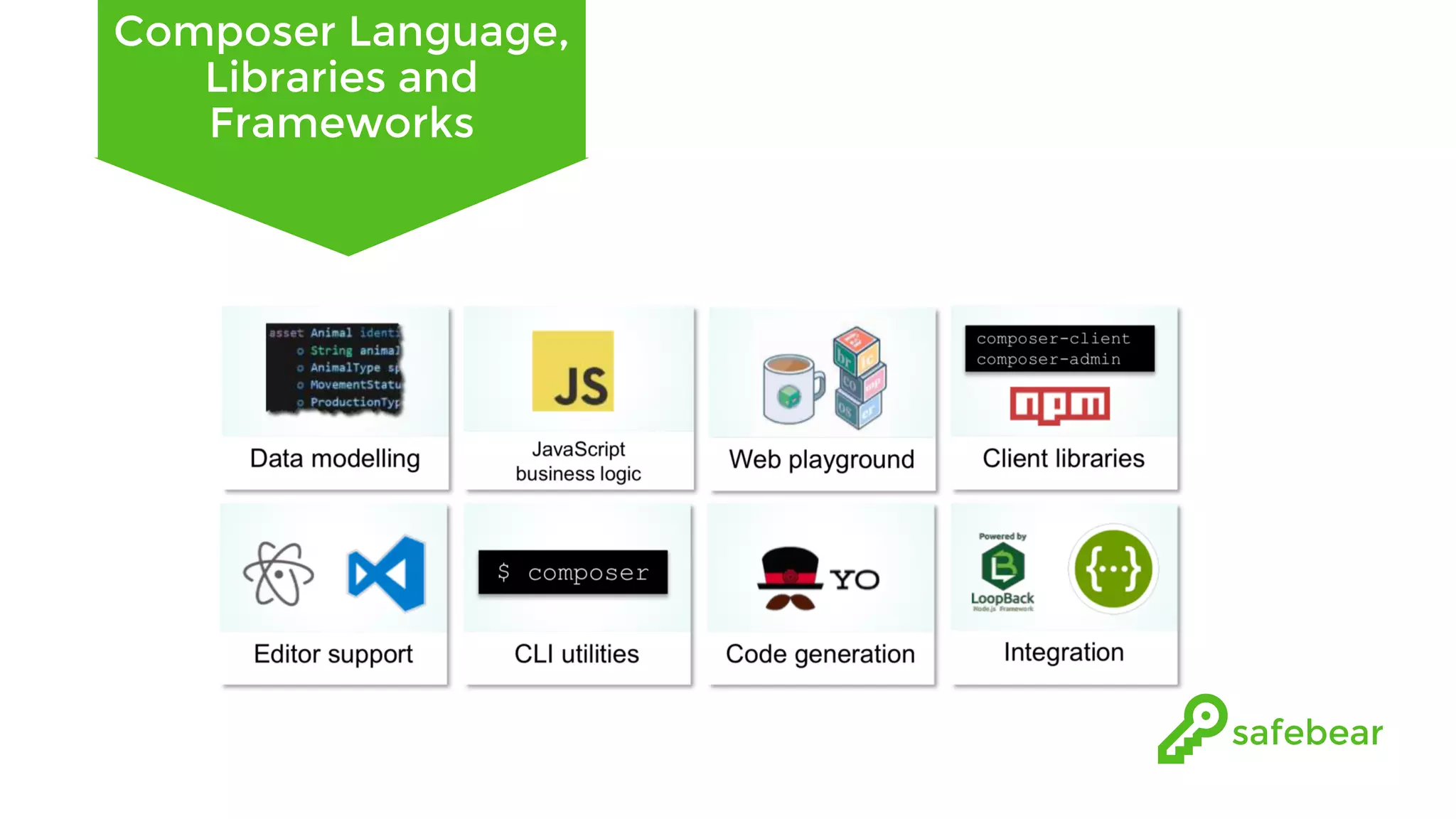
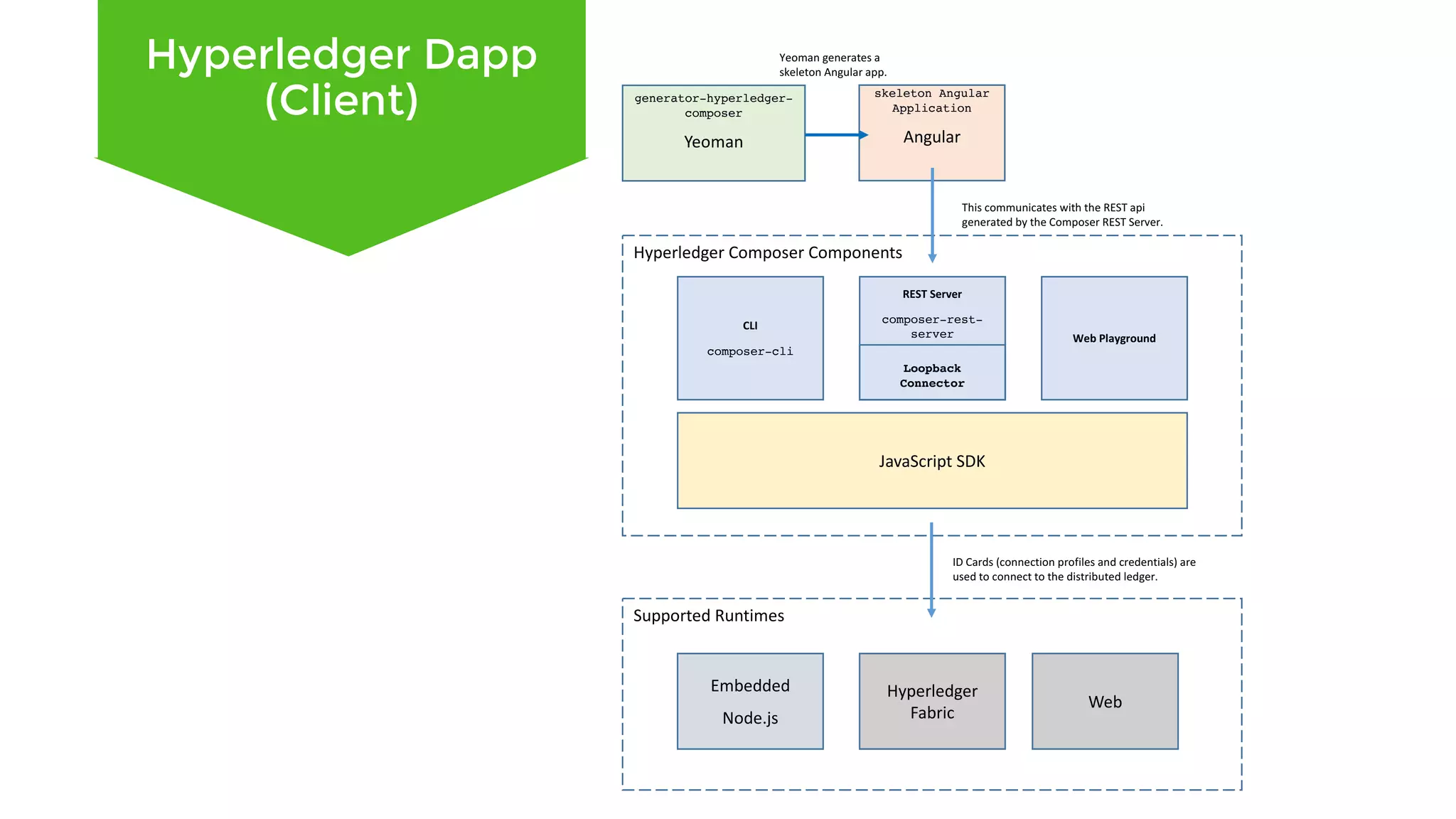
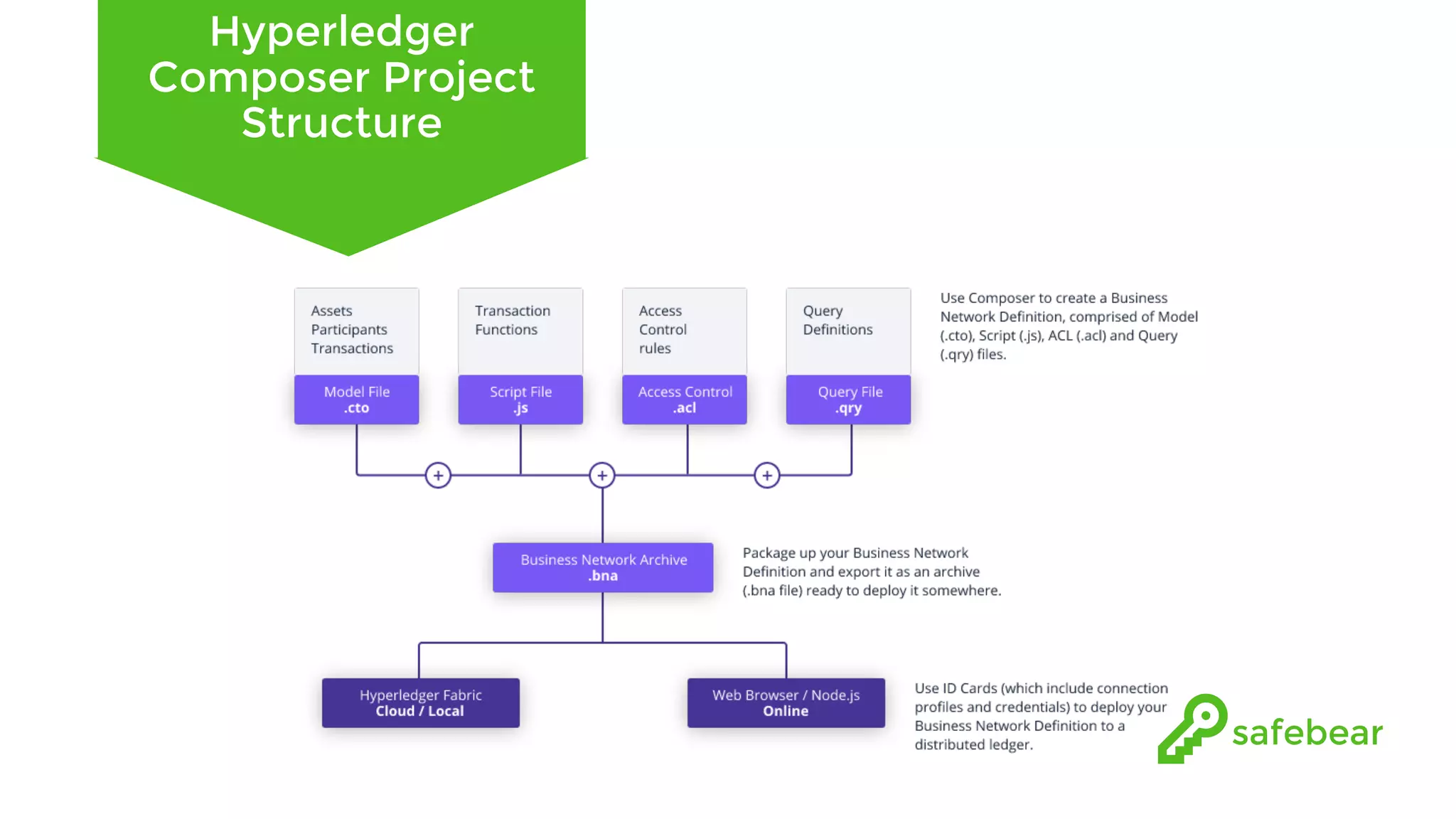
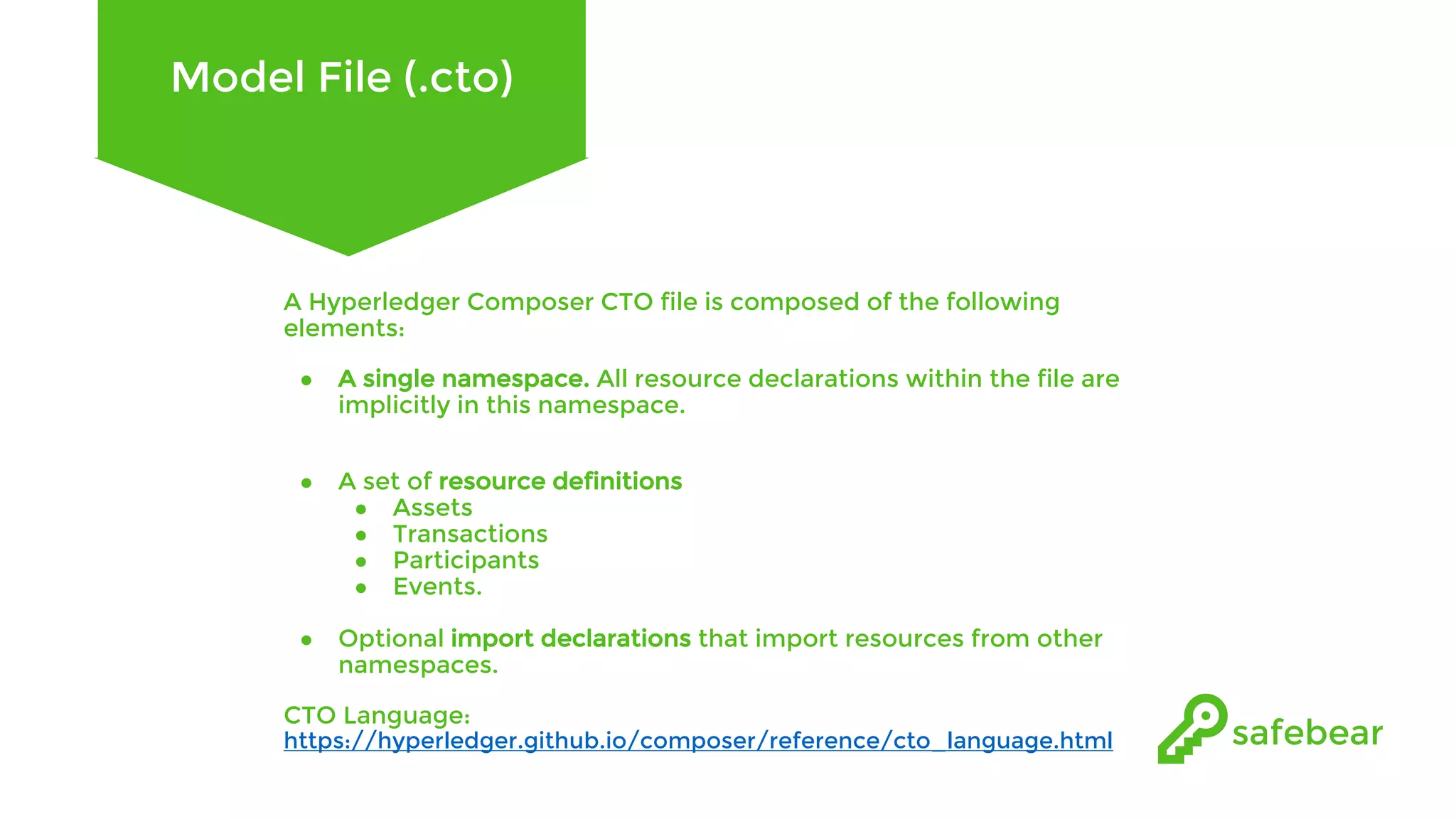
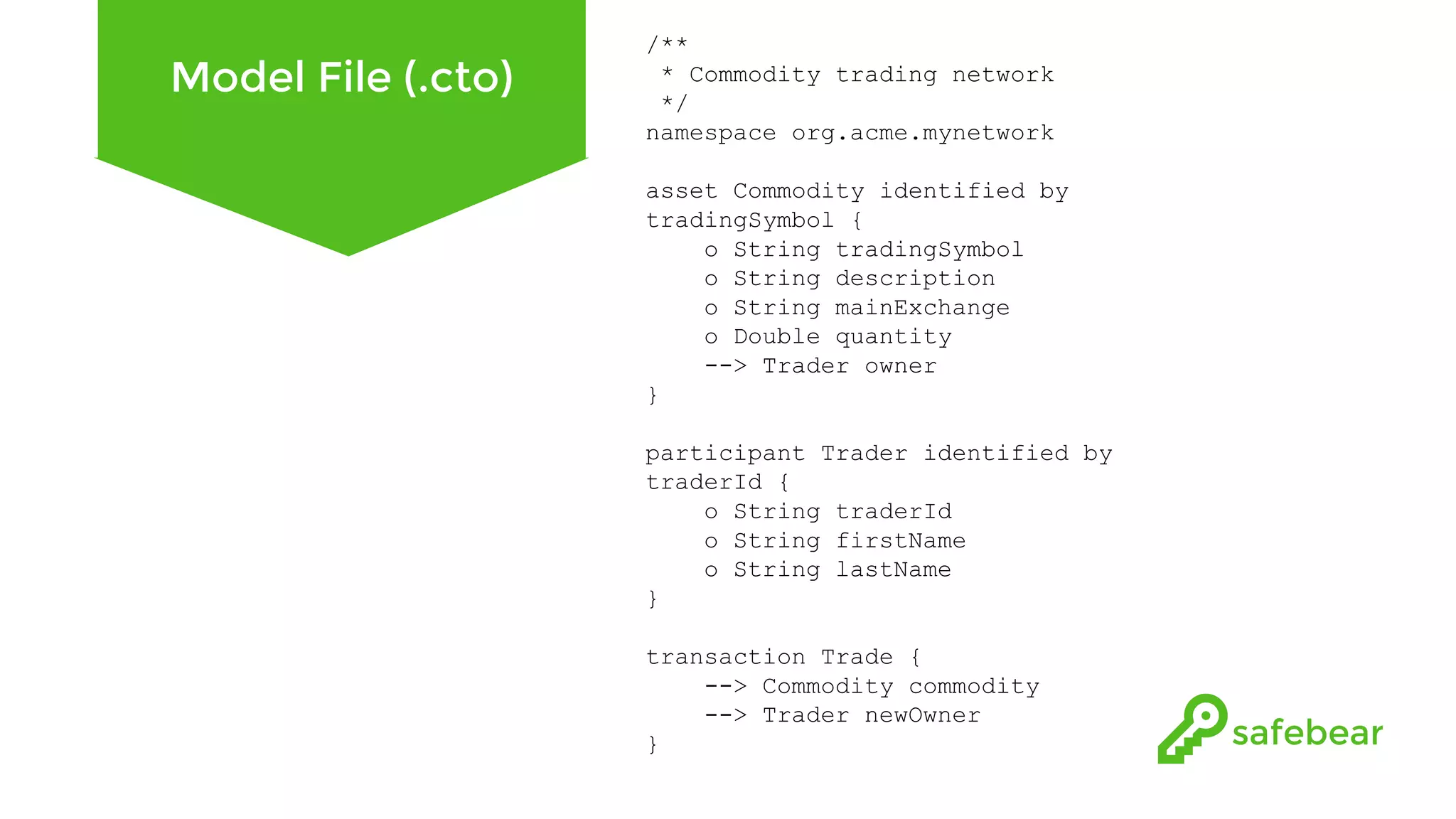
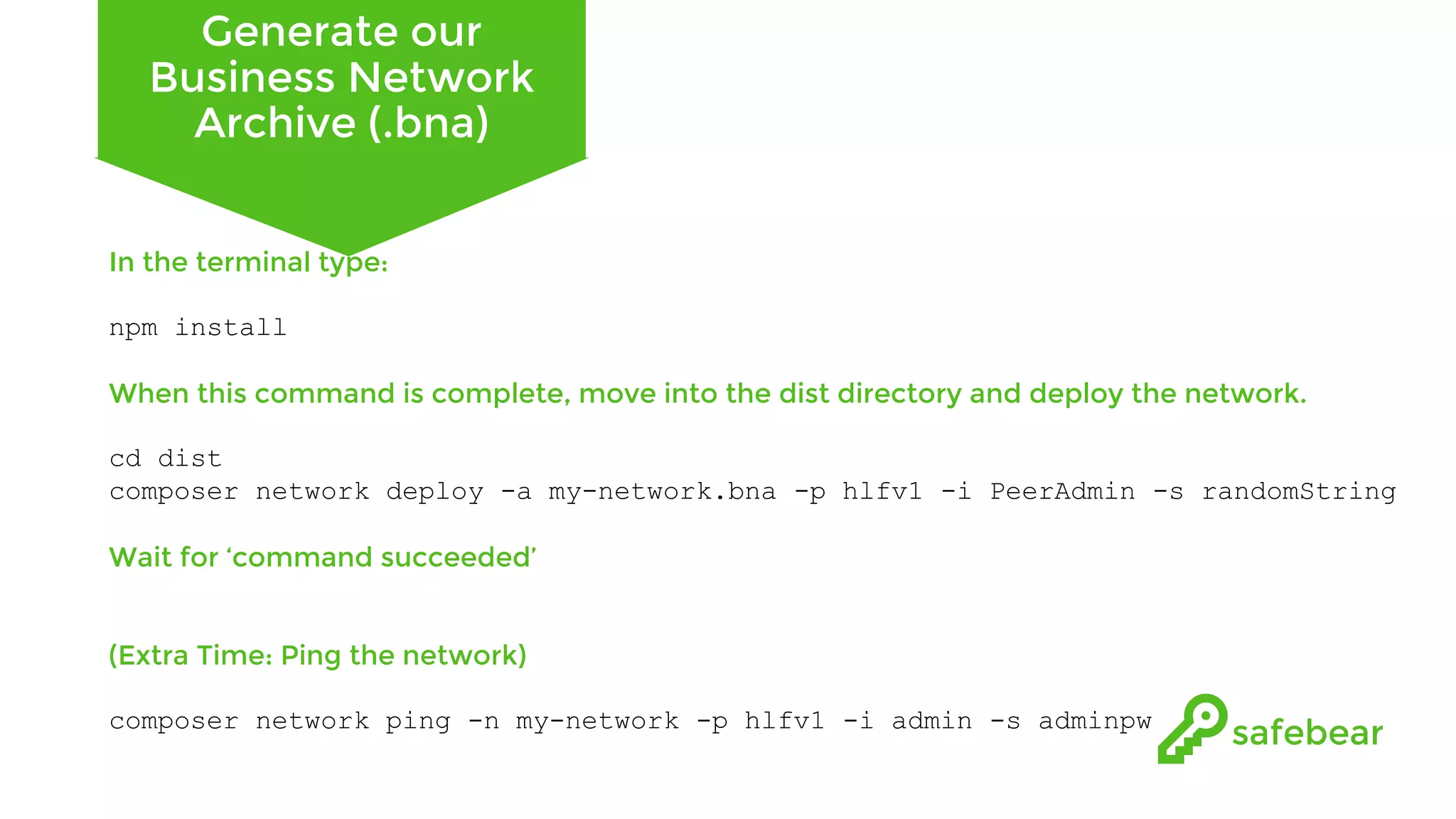
The document outlines the development and features of Hyperledger, a collaborative blockchain project initiated by the Linux Foundation in December 2015. It discusses Hyperledger Fabric, its benefits, consensus protocols, various tools, and functionalities like smart contracts, identity management, and access control. Additionally, it provides technical details on setting up a commodity trading network using Hyperledger Composer and related components.