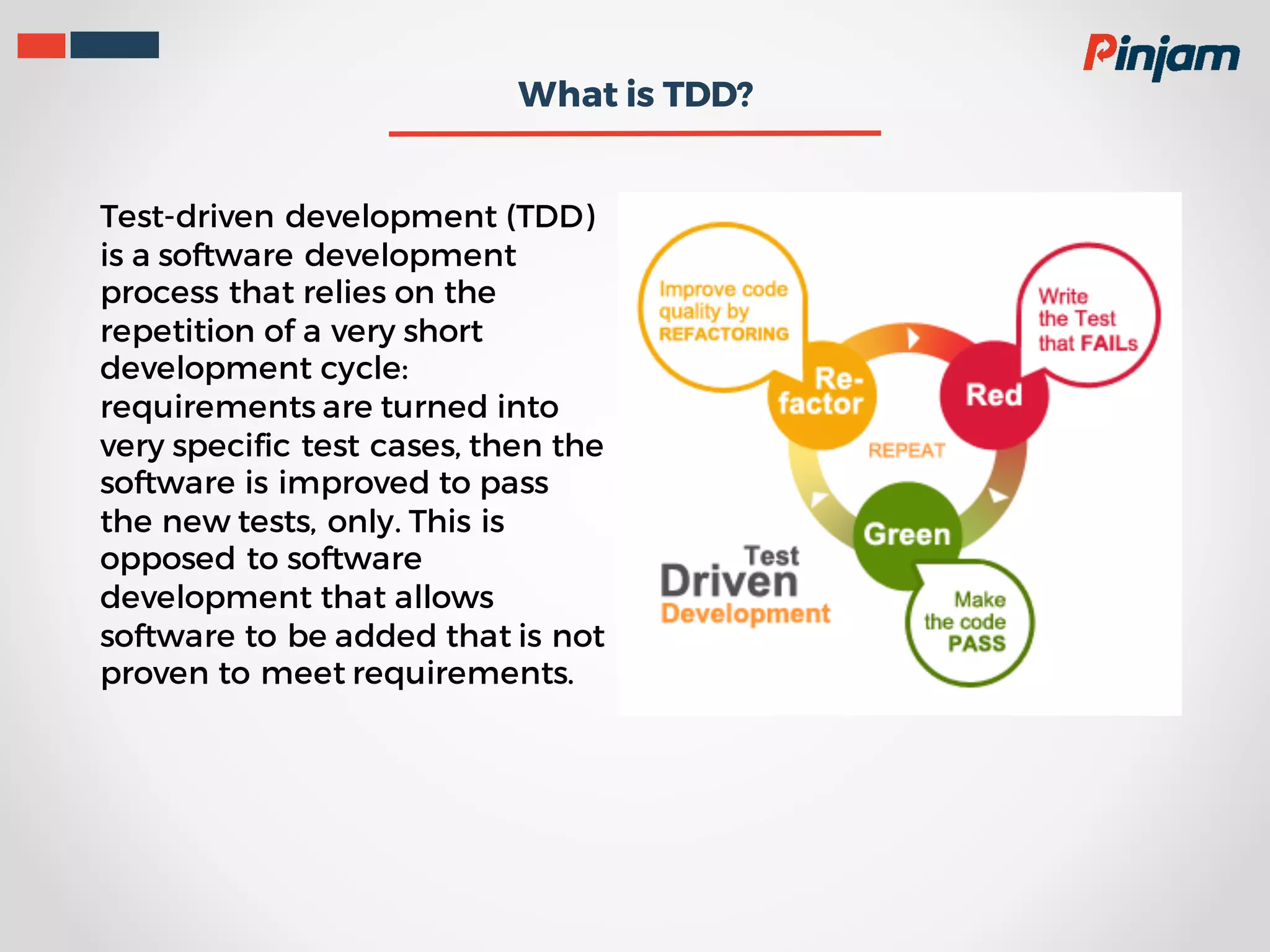
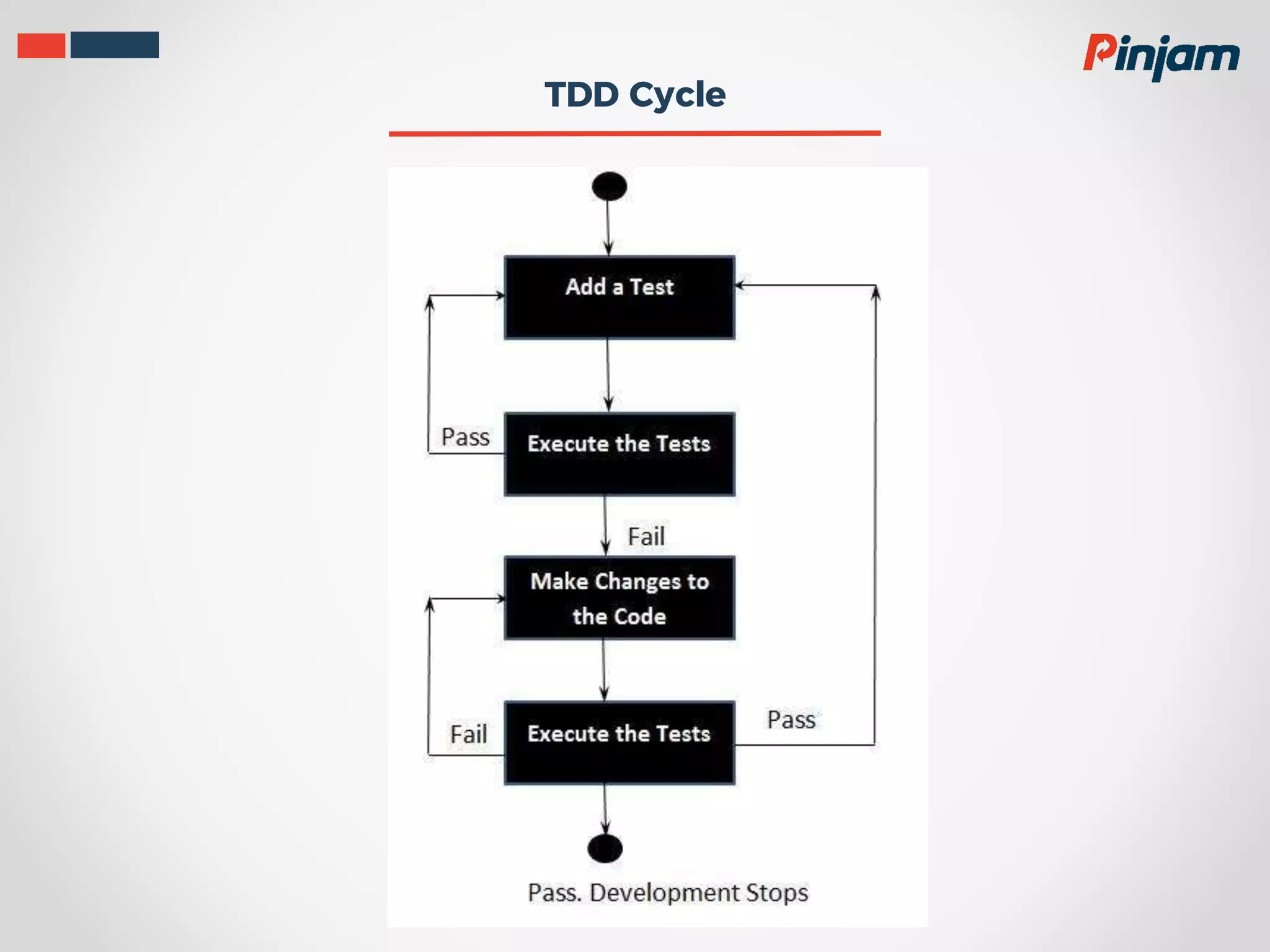
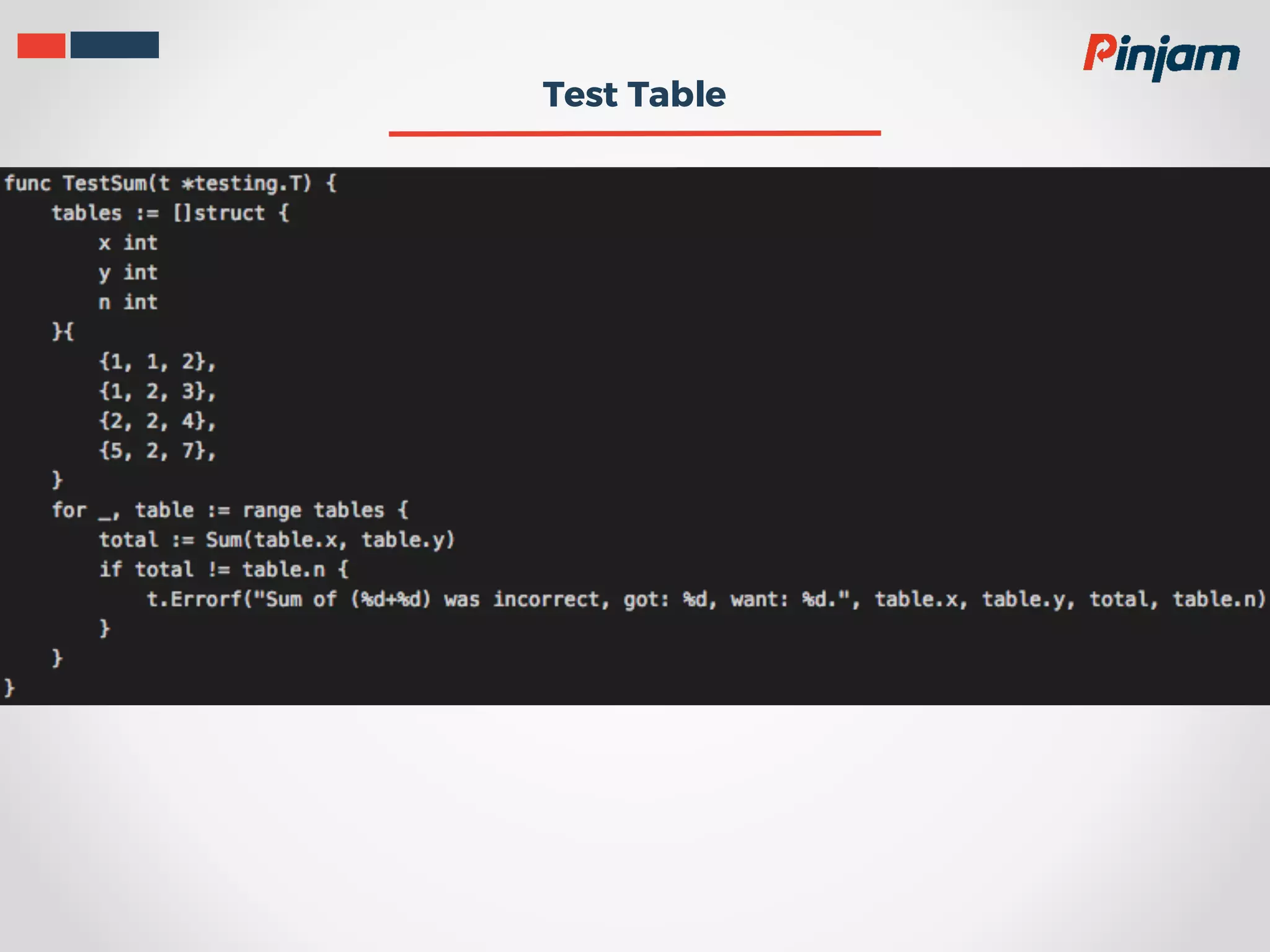
Test-driven development (TDD) is a process where test cases are created to validate requirements before functional code is written. The primary goals of TDD are to help specify requirements and design and to produce clean, bug-free code through a short development cycle of writing tests then code to pass those tests. Good unit tests for TDD should run fast, isolate dependencies, clearly define their scope, not require special setup, and clearly indicate their intention. In Golang, the testing package and go test command provide tools for writing and running tests, and go test can measure test coverage.