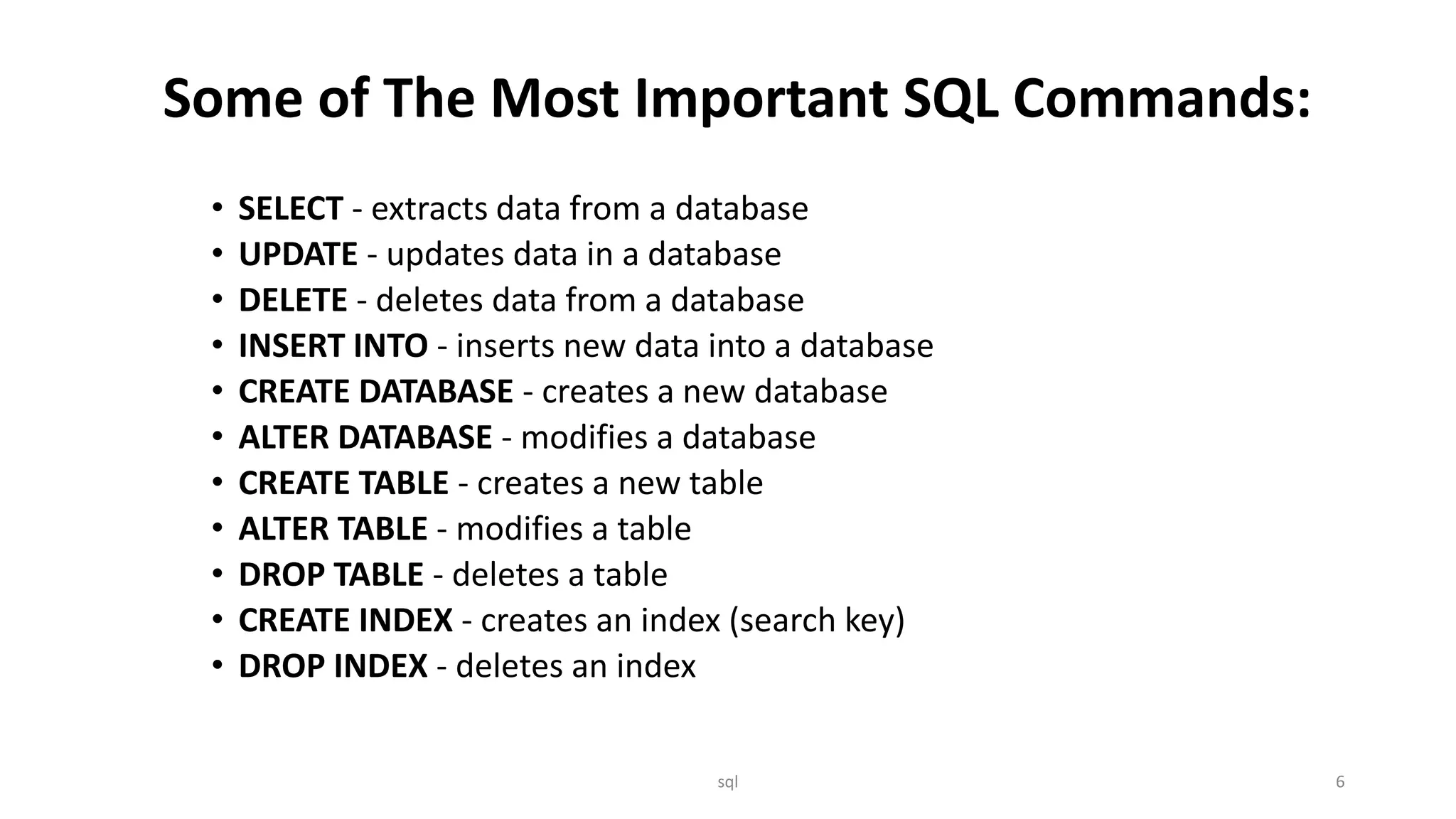
SQL is a standard language used to store, manipulate, and retrieve data in databases. It was influenced by Codd's relational model and is now the most widely used database language. SQL can perform functions like executing queries, retrieving, inserting, updating, and deleting records from databases, and can also create and modify databases, tables, indexes, and views. Common SQL commands include SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT INTO, and CREATE operations. The basic SQL syntax involves SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT statements using keywords, columns, tables, and conditions.