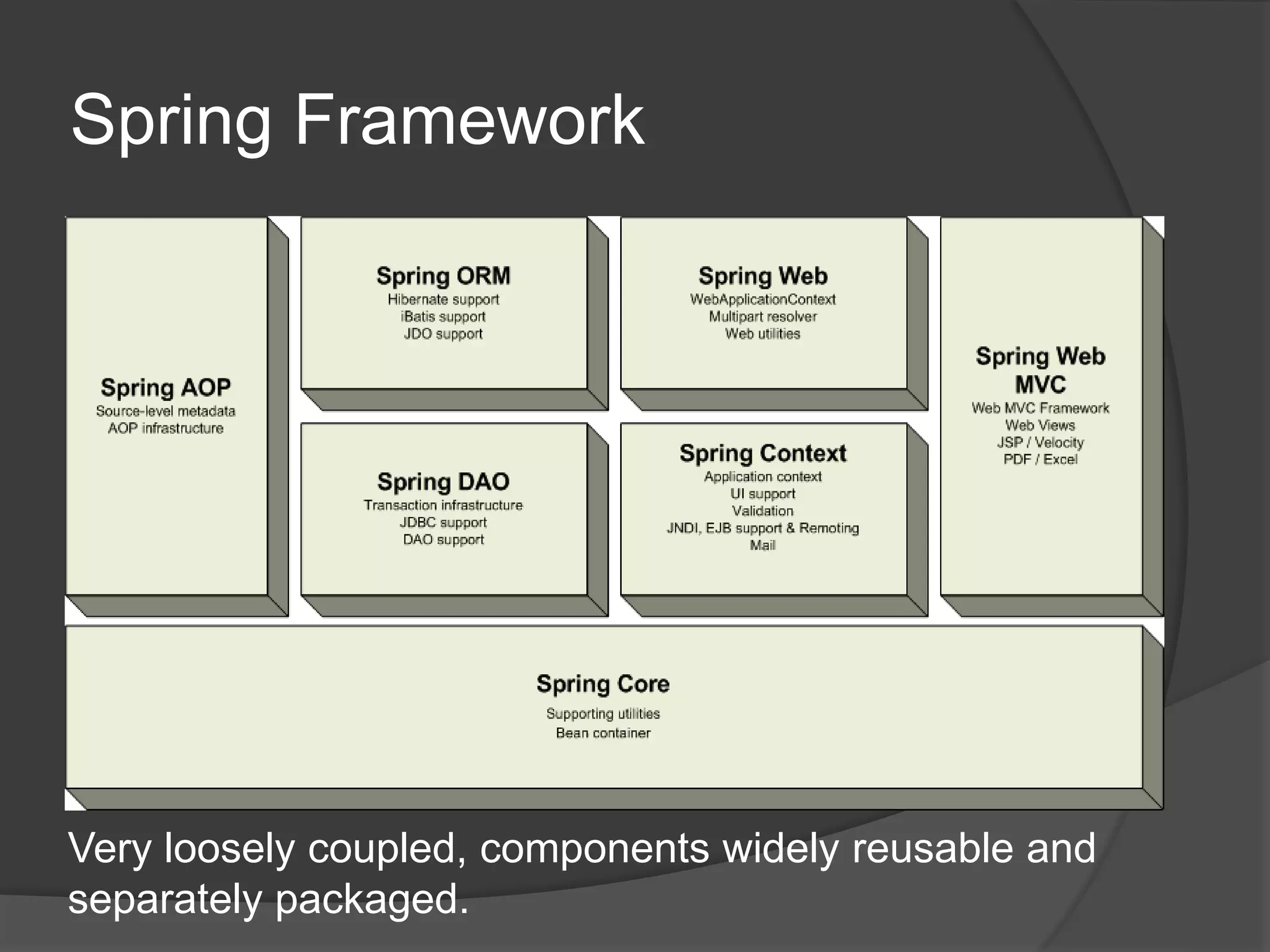
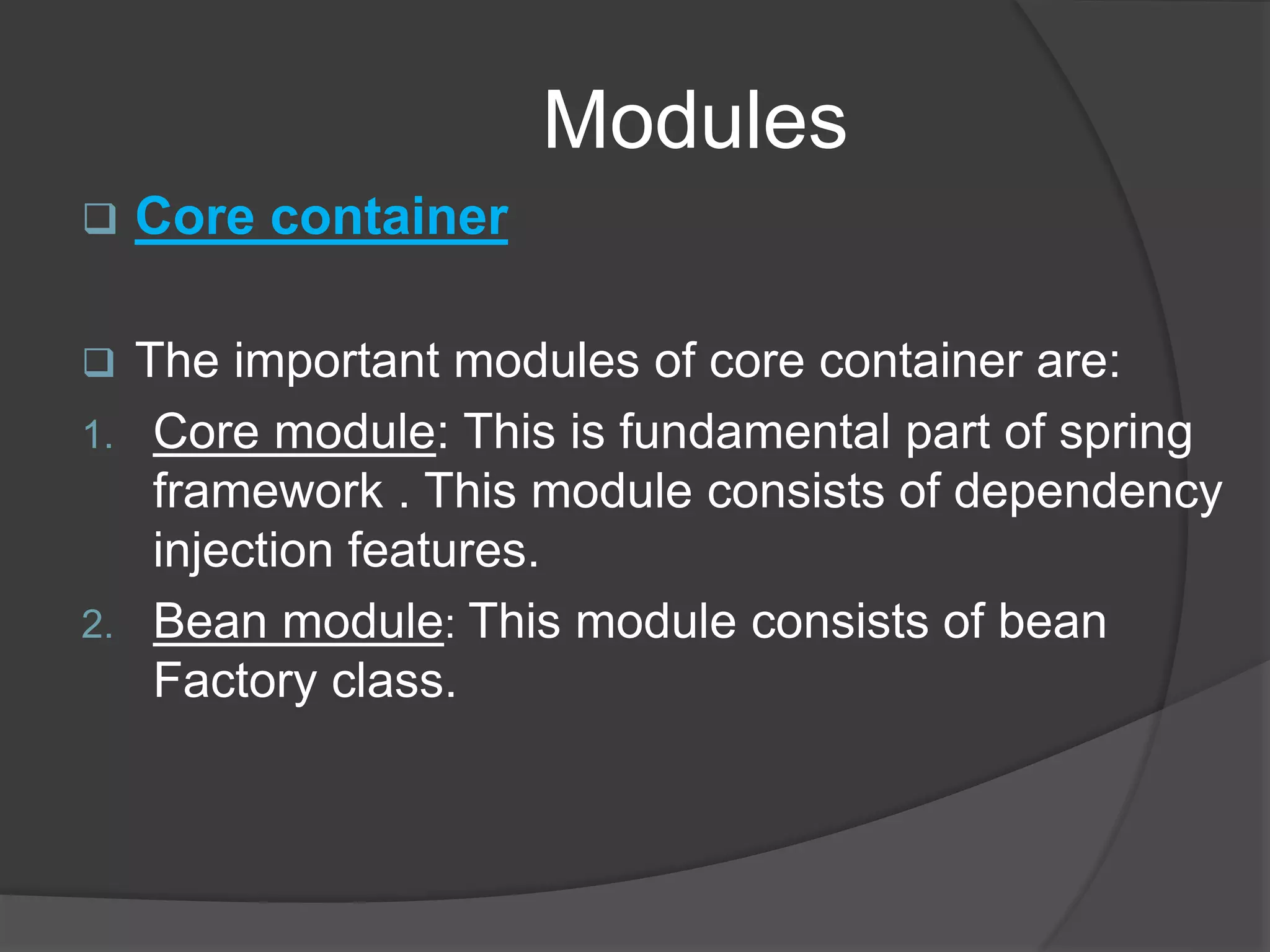
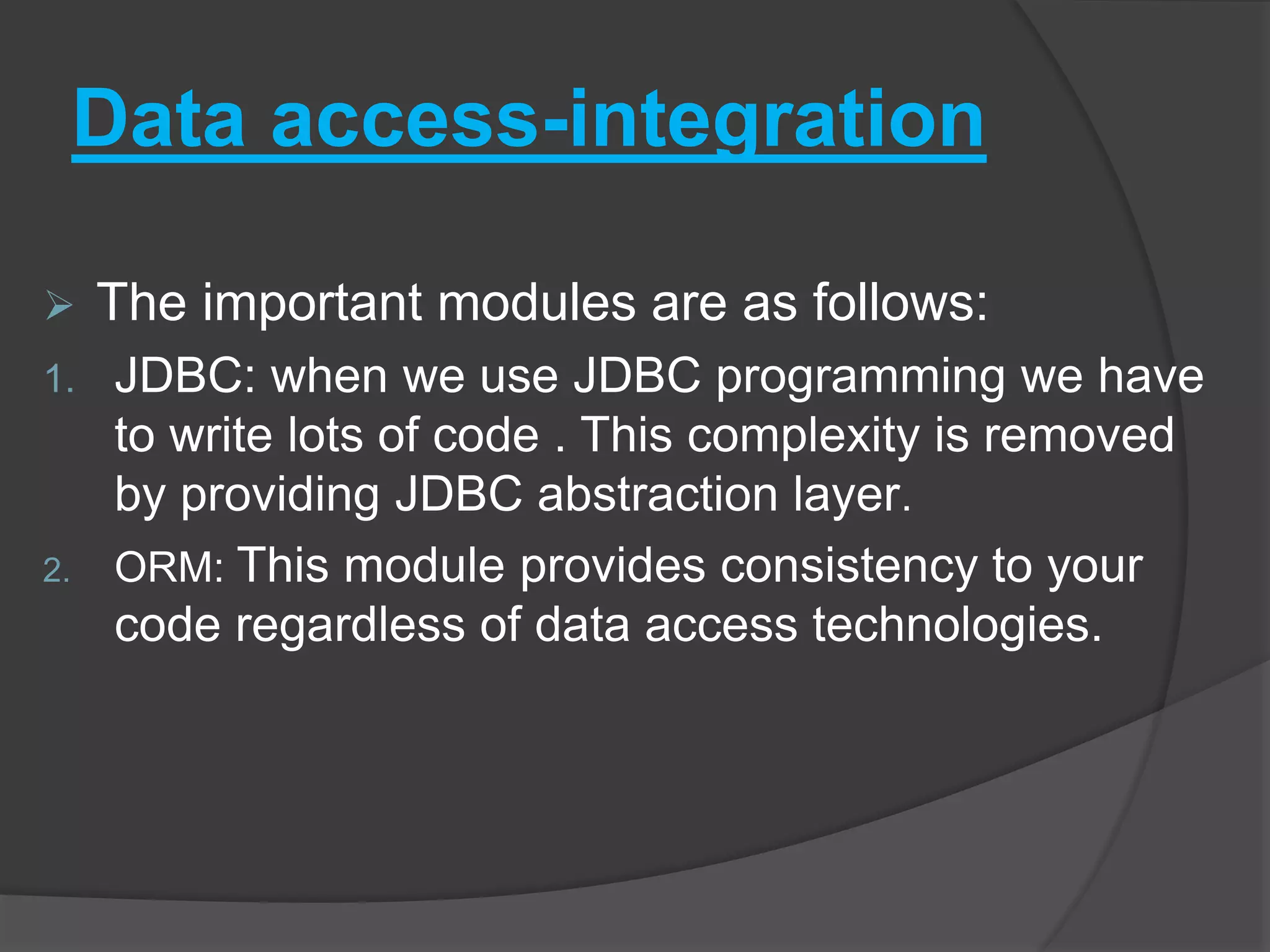
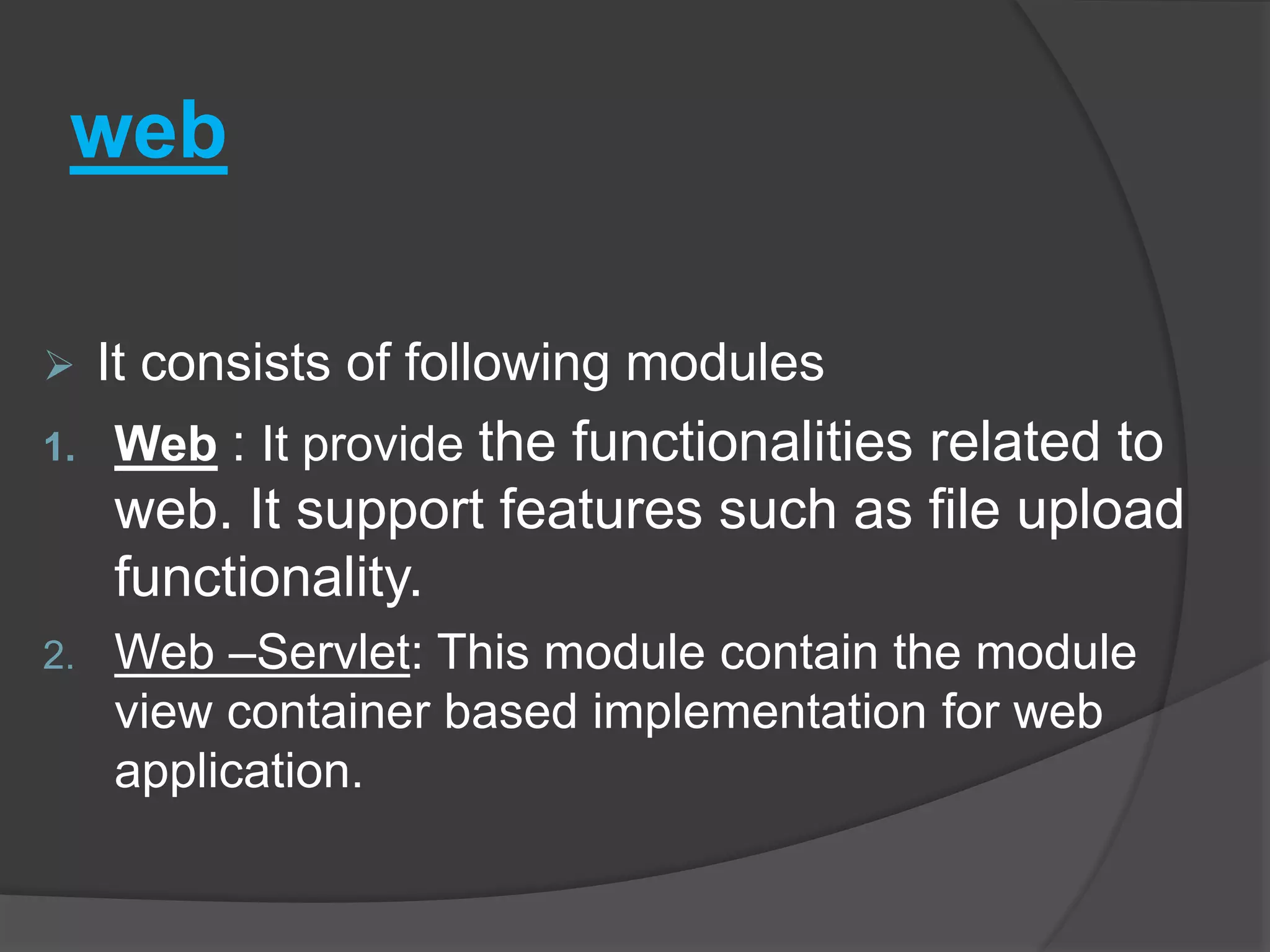
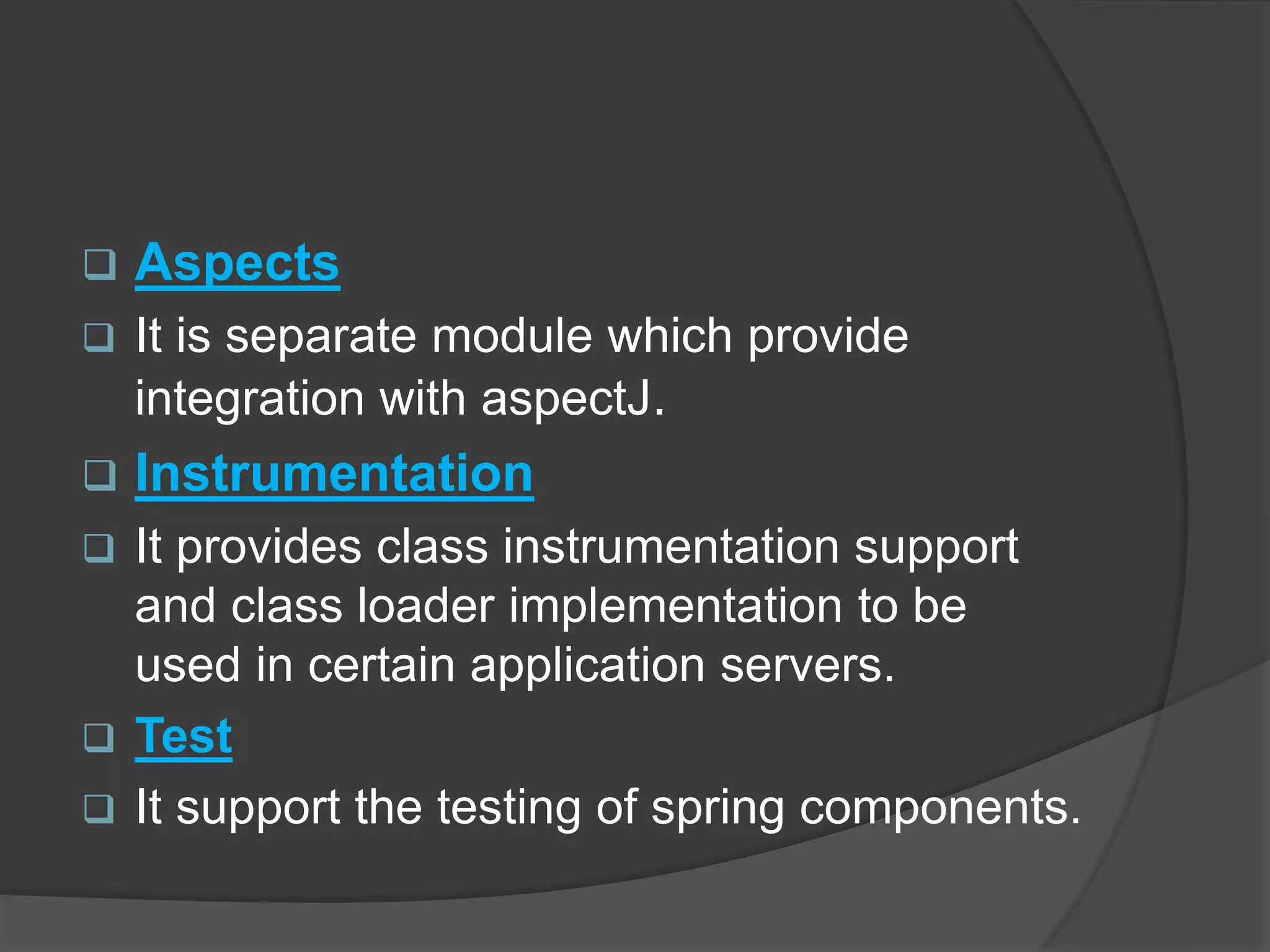
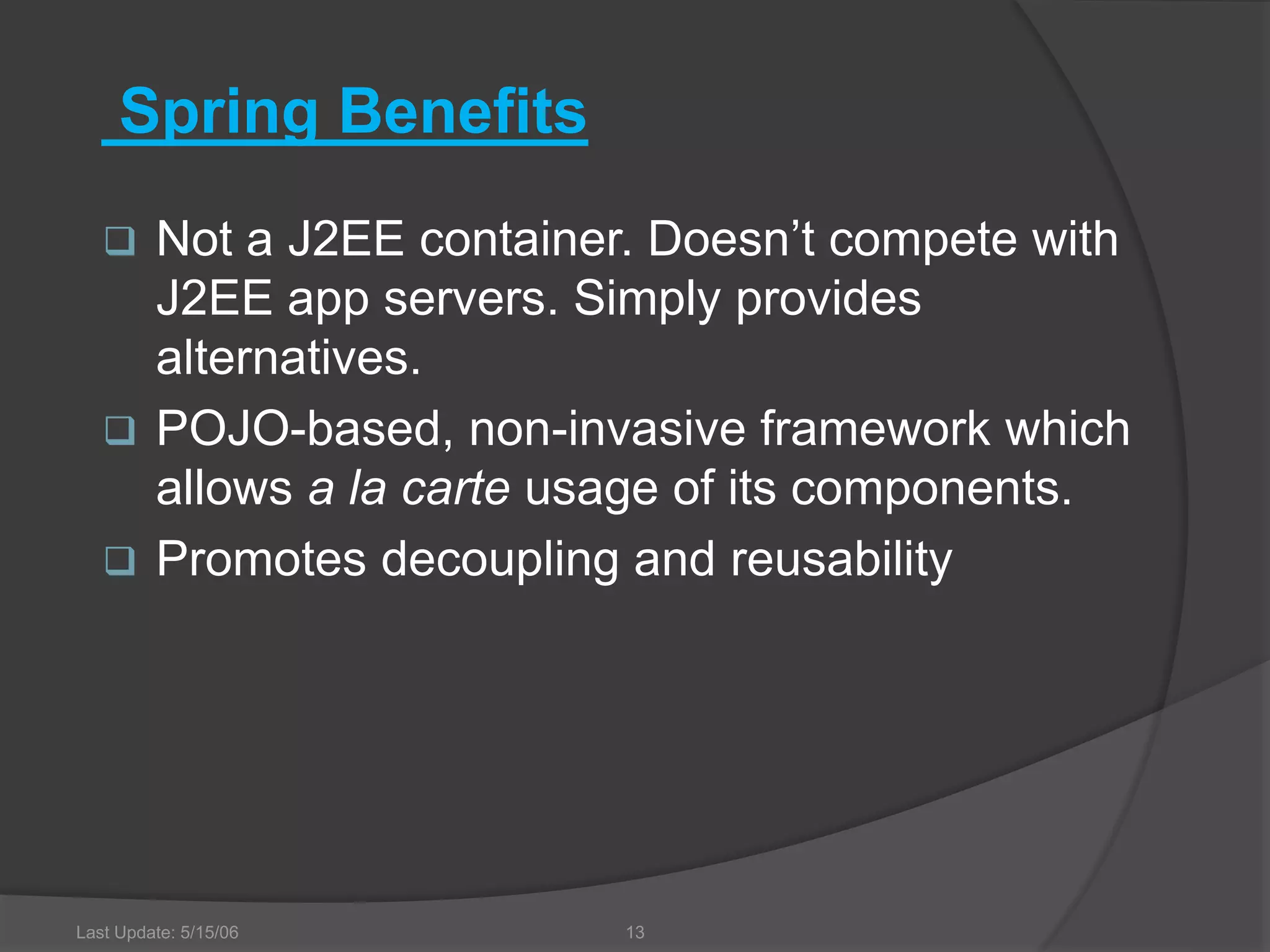
Spring architecture includes around 20 modules grouped into the core container, data access/integration, aspects oriented programming, and instrumentation. The core container's important modules are core, bean, and context. Data access modules include JDBC, ORM, OXM, and transaction management. Spring benefits include being non-invasive, promoting decoupling and reusability, and reducing coding effort through implicit patterns.