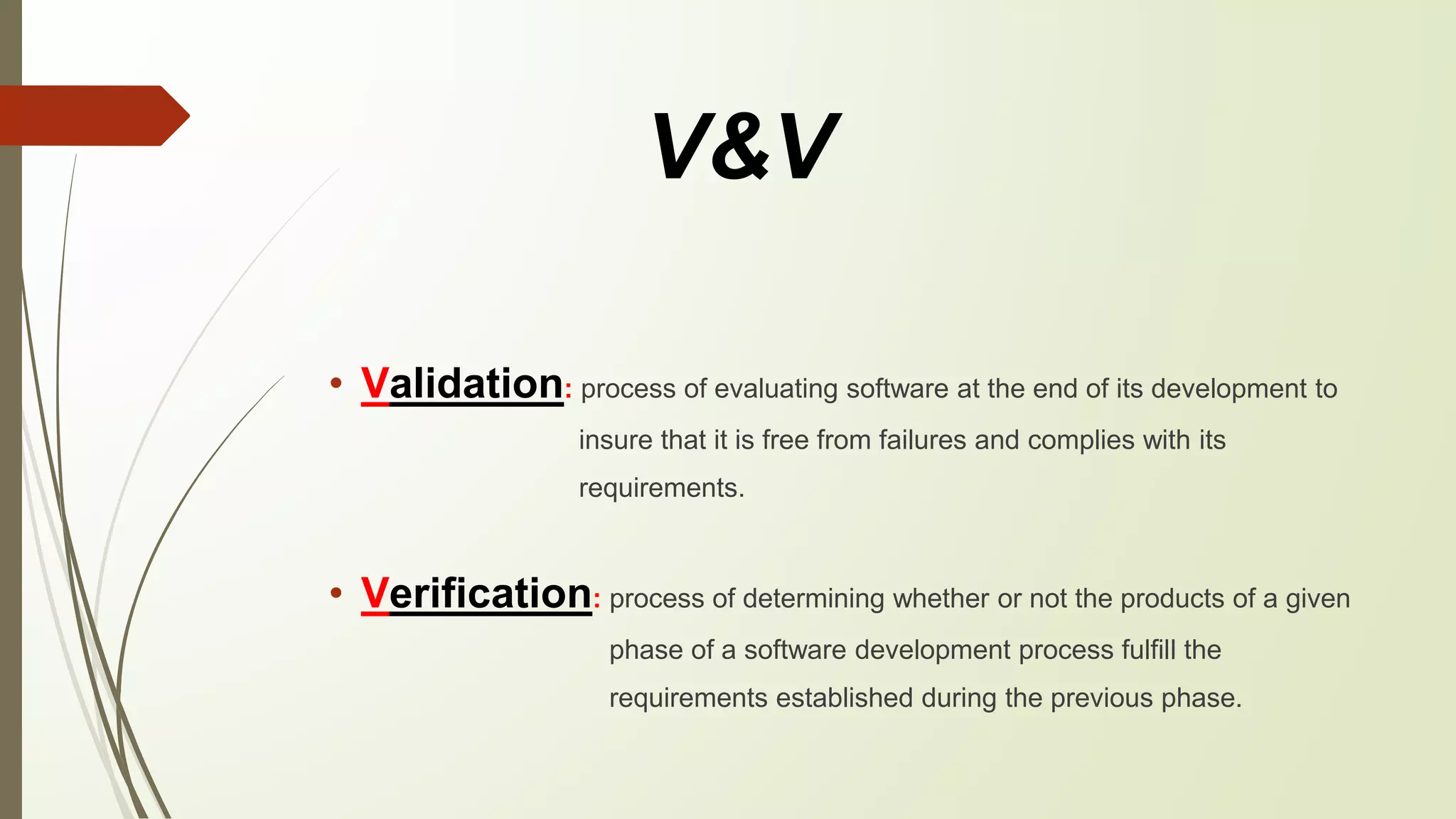
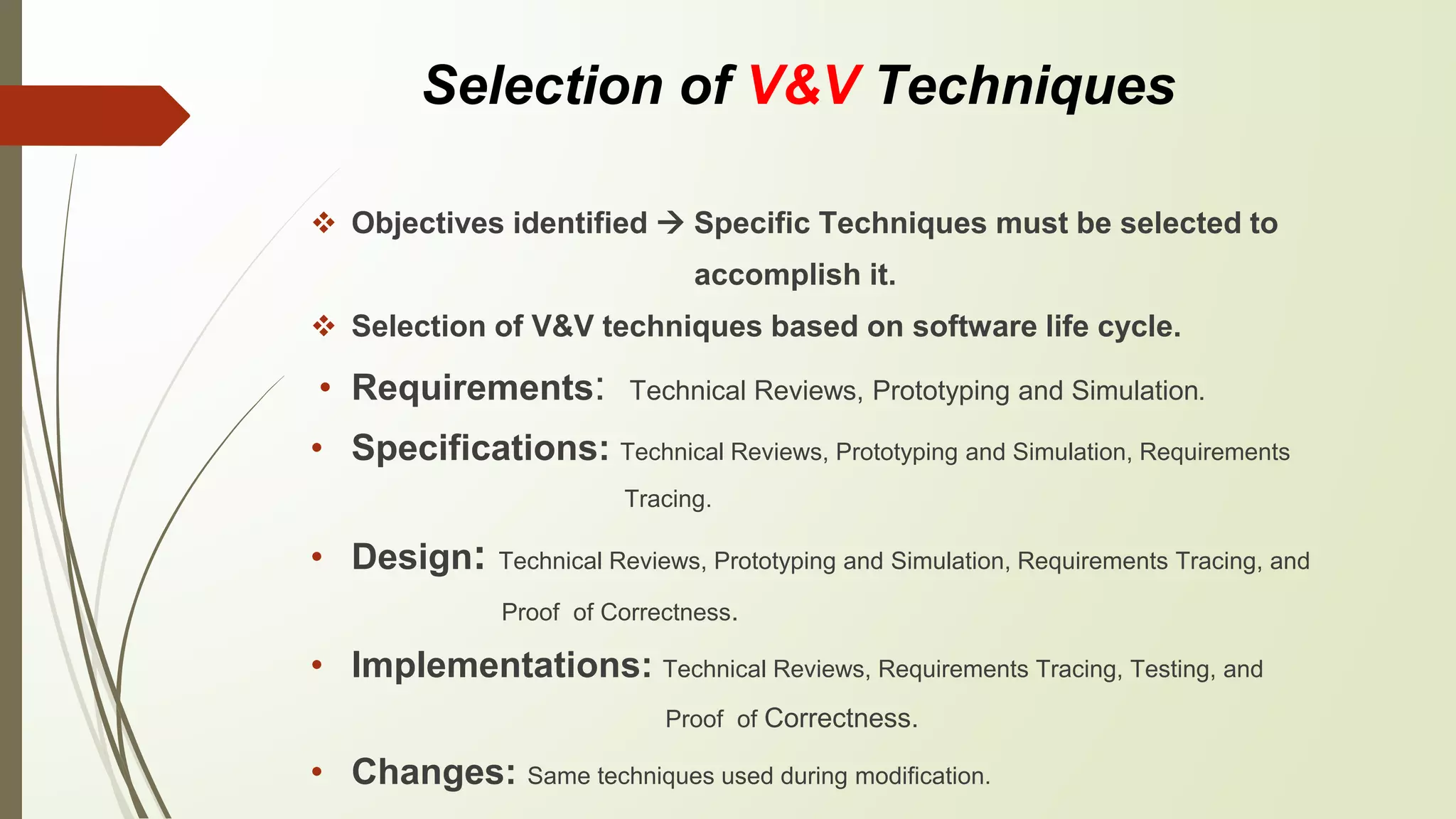
This document discusses software validation and verification (V&V) and the selection process. It defines validation as evaluating software at the end of development to ensure it is free of failures and meets requirements. Verification is determining if each development phase meets the requirements of the previous phase. It then outlines objectives of V&V like correctness and performance. Approaches covered include technical reviews, testing, proof of correctness, simulation and prototyping, and requirements tracing. The document also discusses limitations of V&V and selection of techniques based on software lifecycle phases like requirements, specifications, design, and implementation.