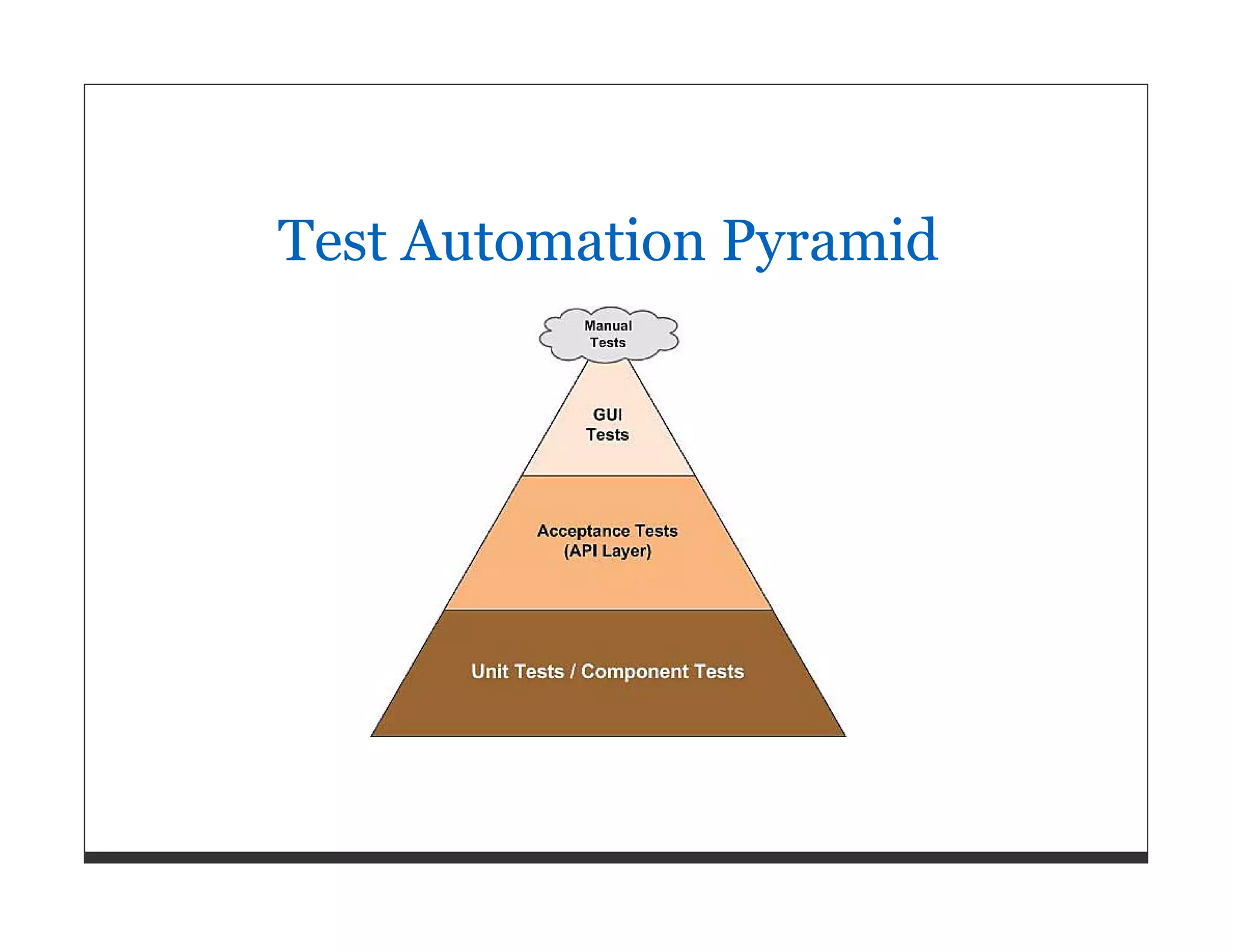
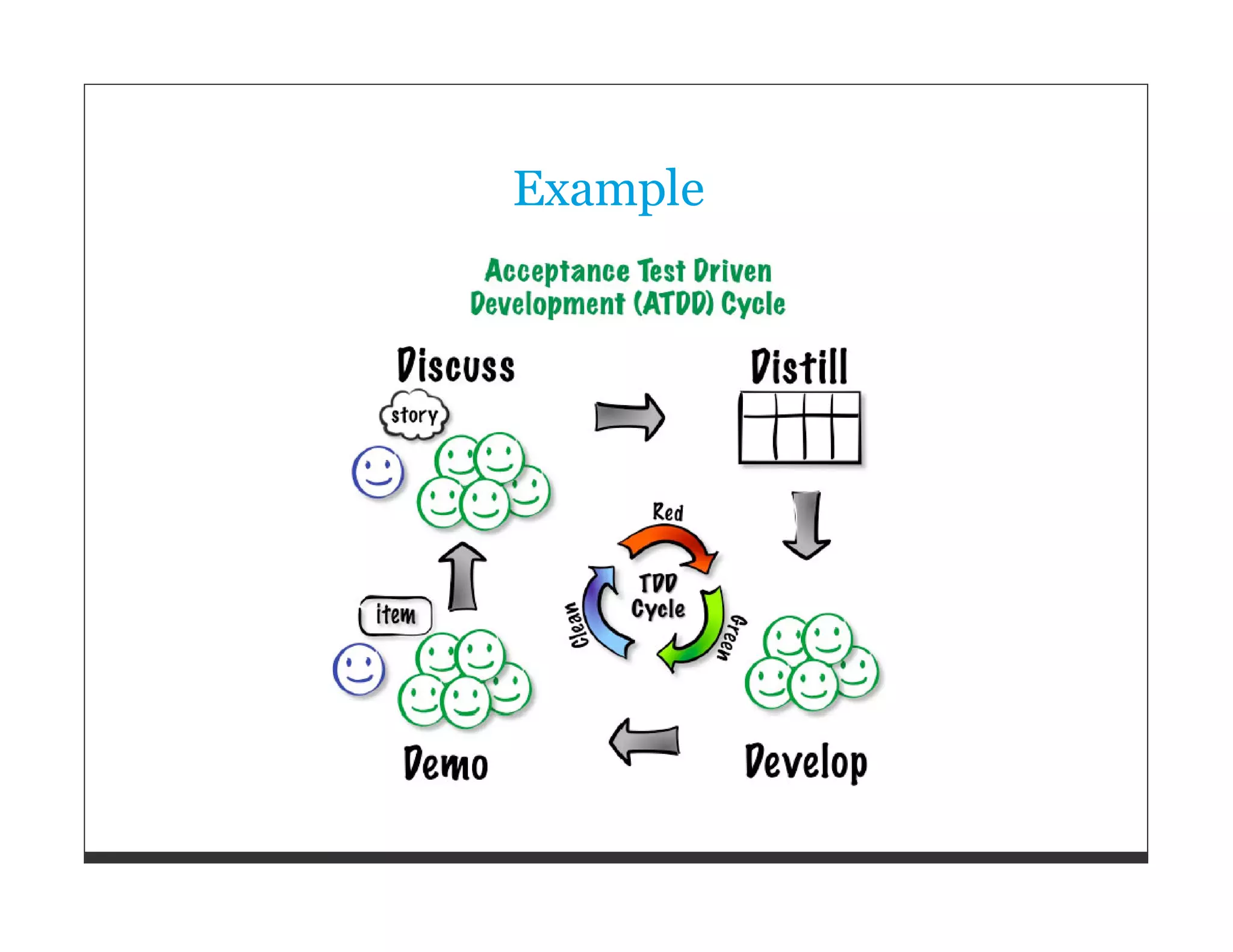
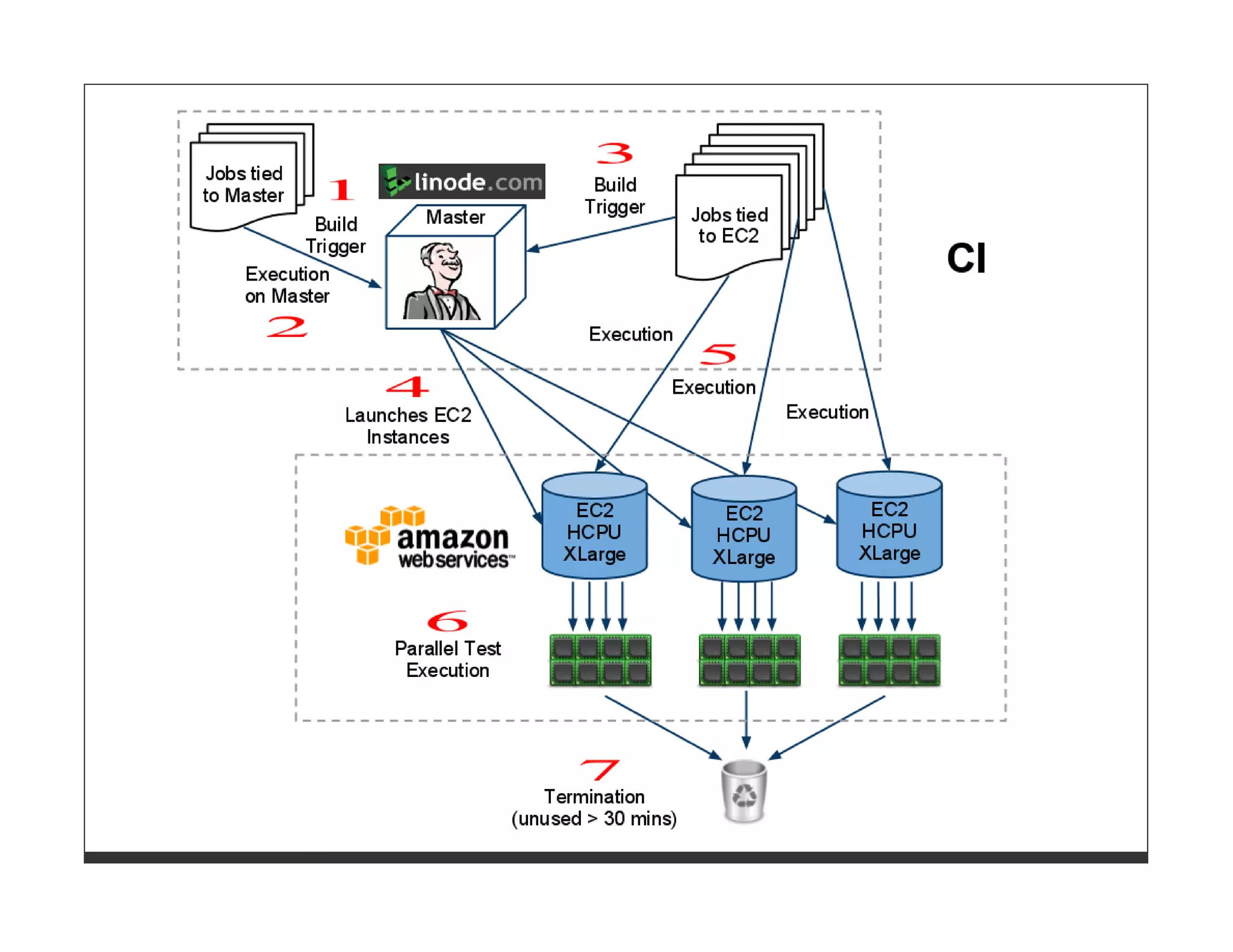
This document provides an overview of software quality and test strategies for Ruby and Rails applications. It discusses the importance of quality, managing quality through setting goals and measuring metrics. It outlines a test strategy template and covers test types, tools, and approaches for unit, integration, acceptance and other types of tests in Ruby/Rails. It also discusses test data management, defect management, and the Ruby/Rails testing ecosystem including various testing frameworks and quality/metrics tools.











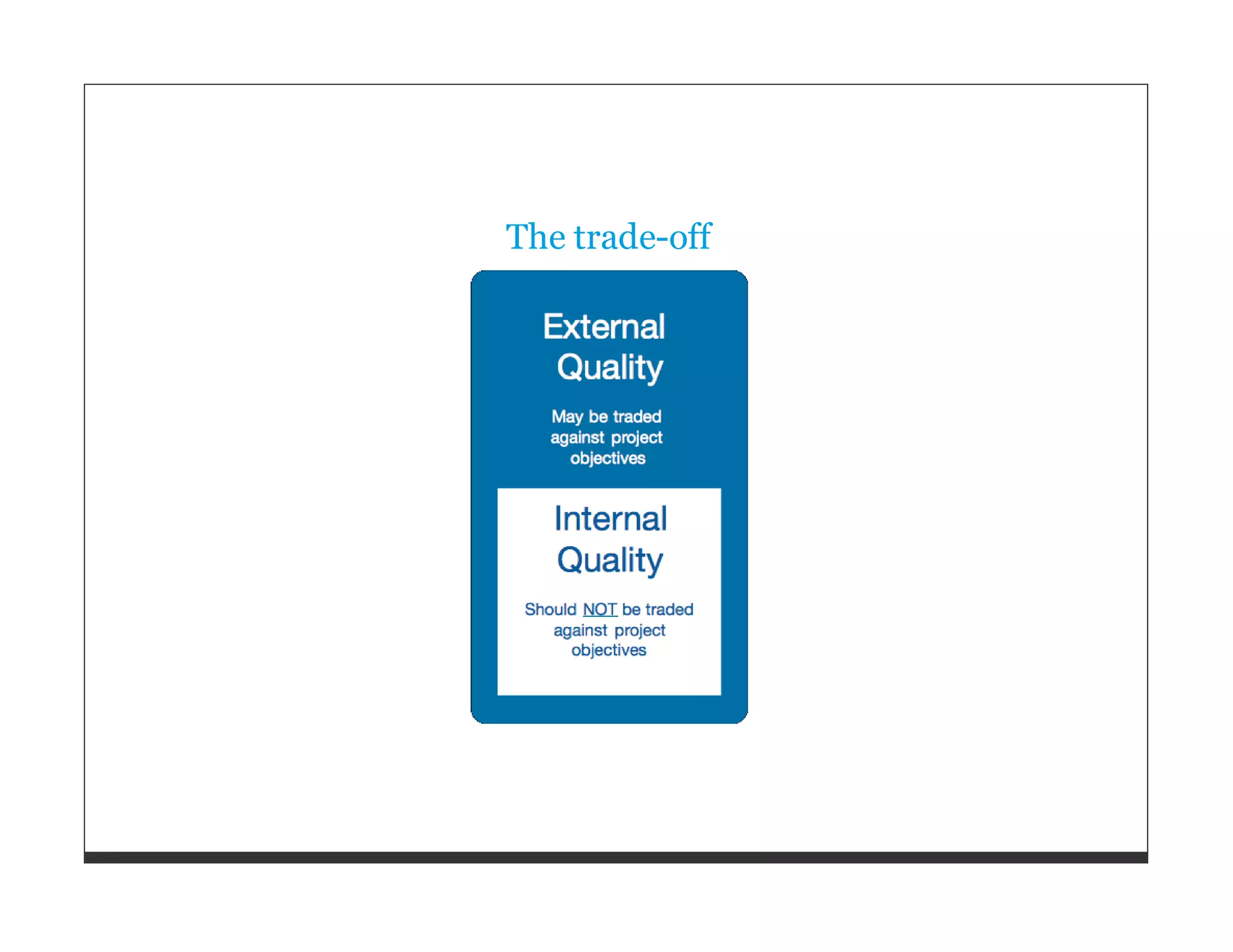
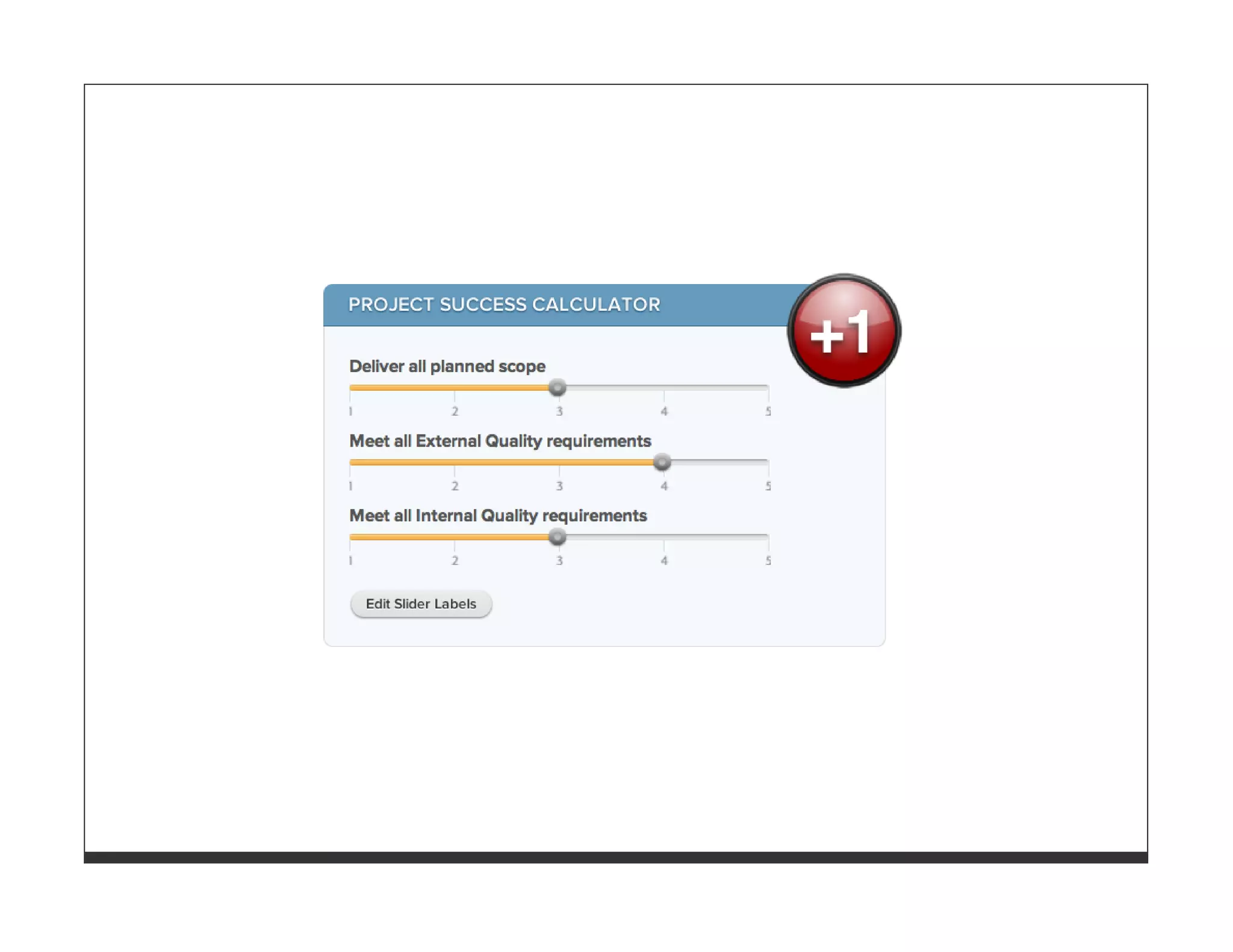
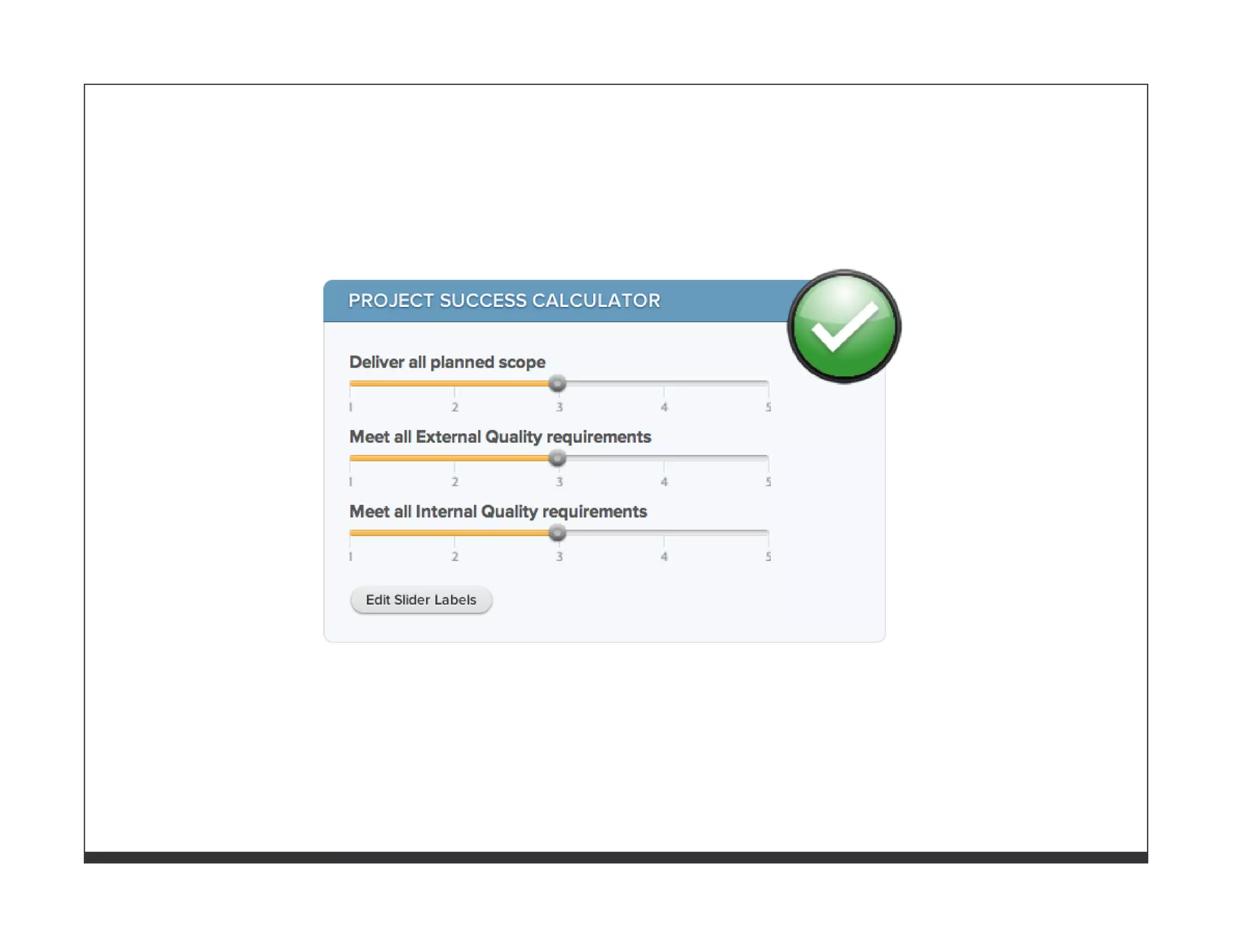
















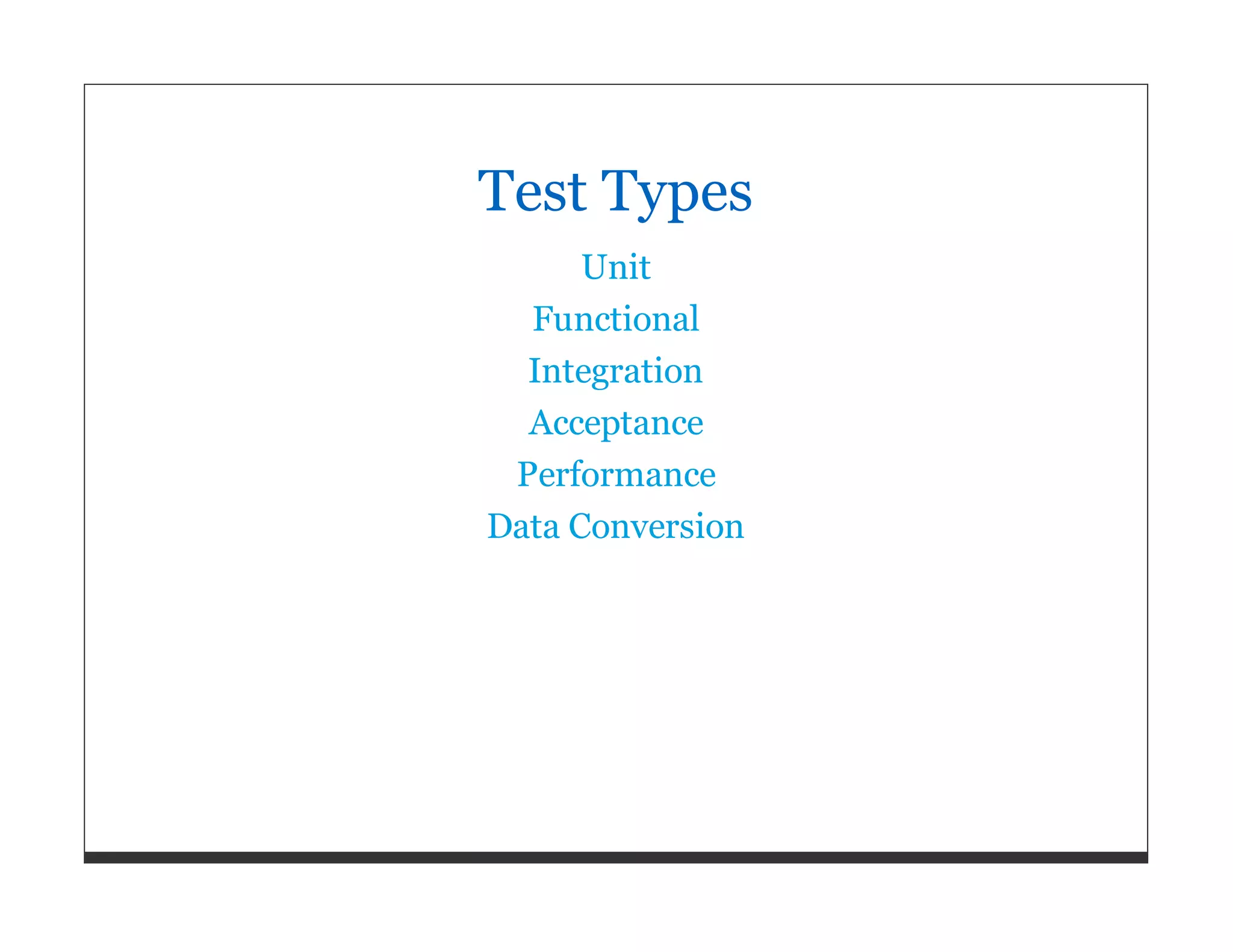








































![WHATS_BEST[:god] = "Write your own !"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarequalityandteststrategy-110615025631-phpapp01/75/Software-Quality-and-Test-Strategies-for-Ruby-and-Rails-Applications-80-2048.jpg)

