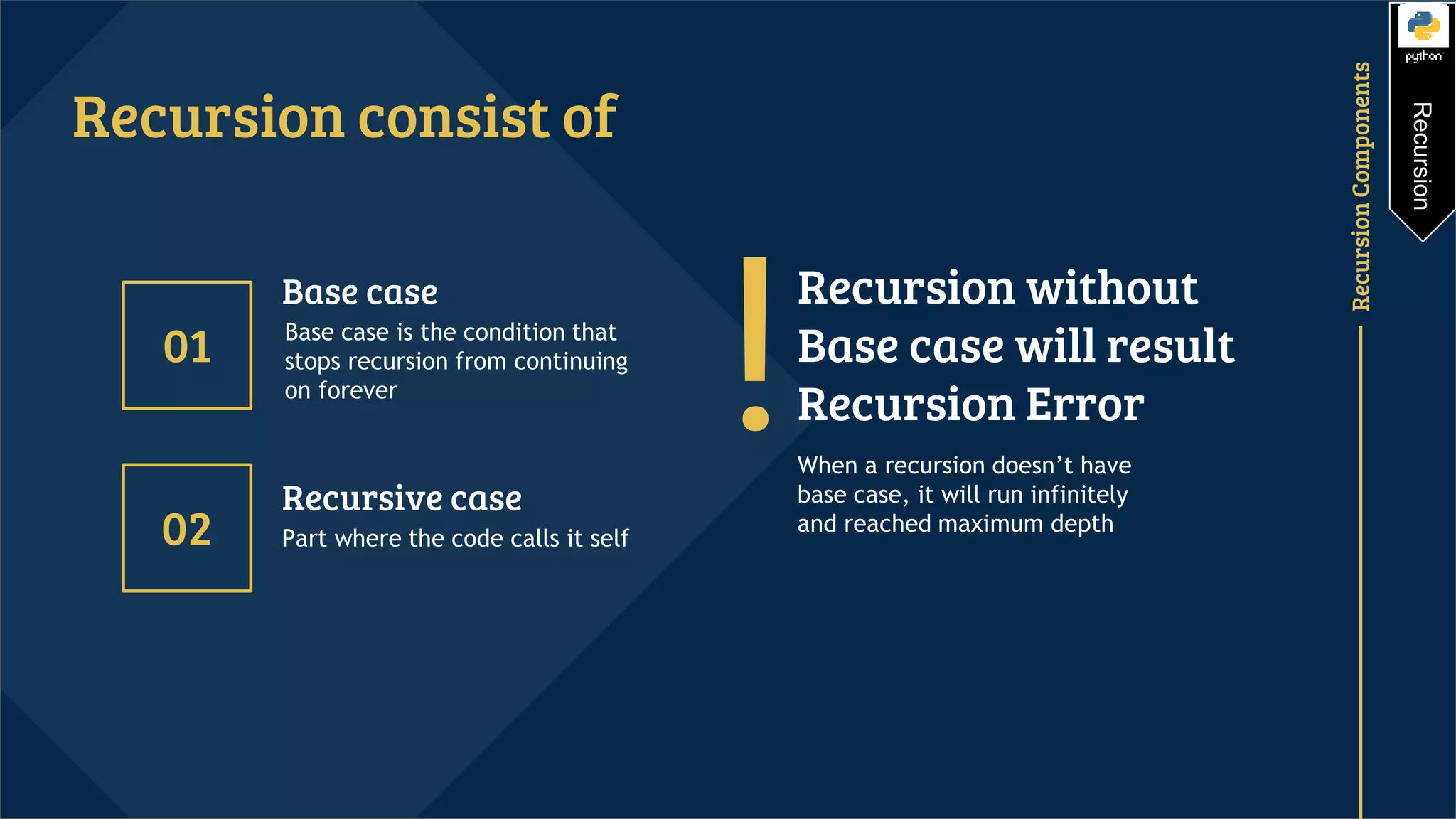
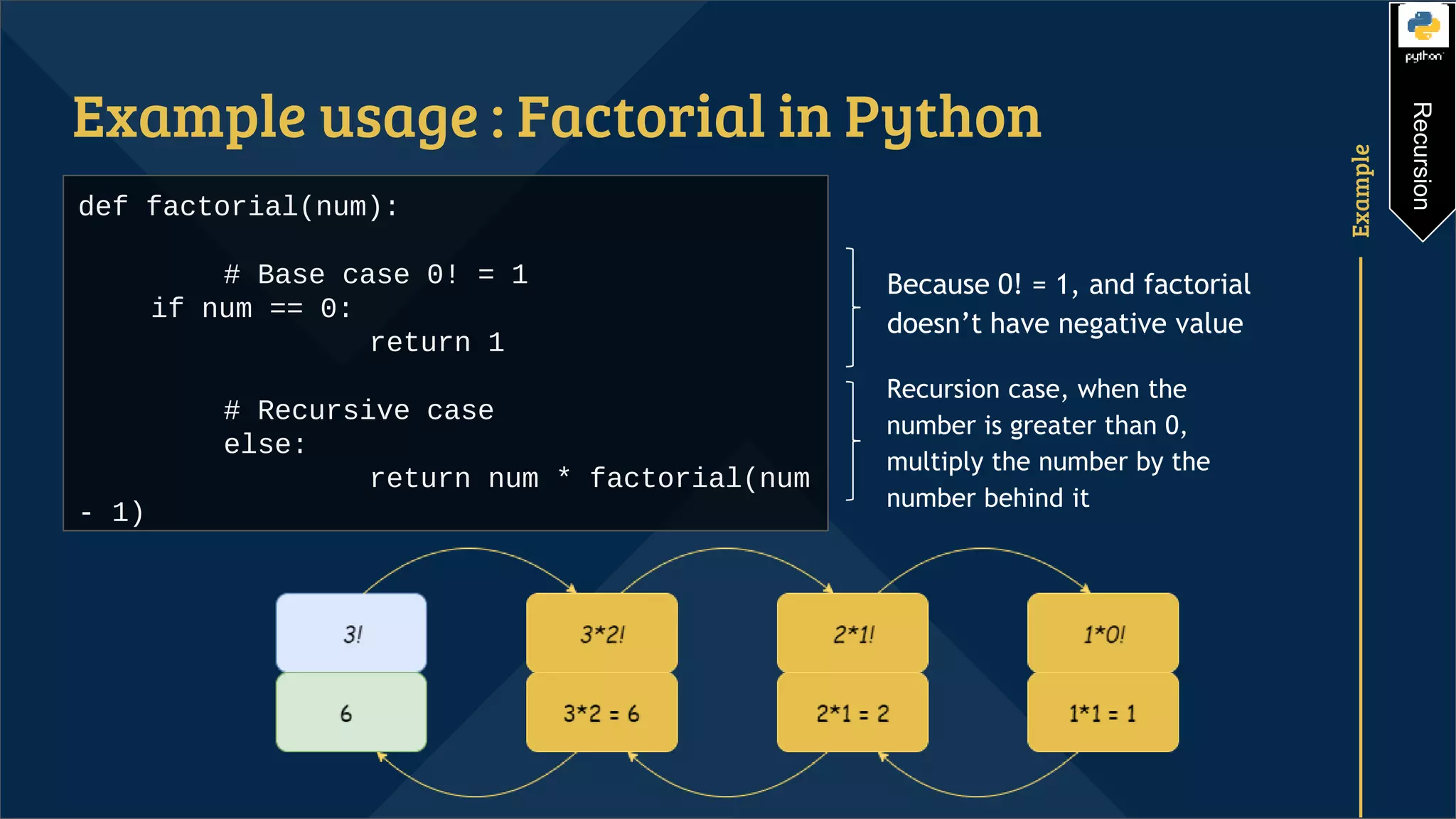
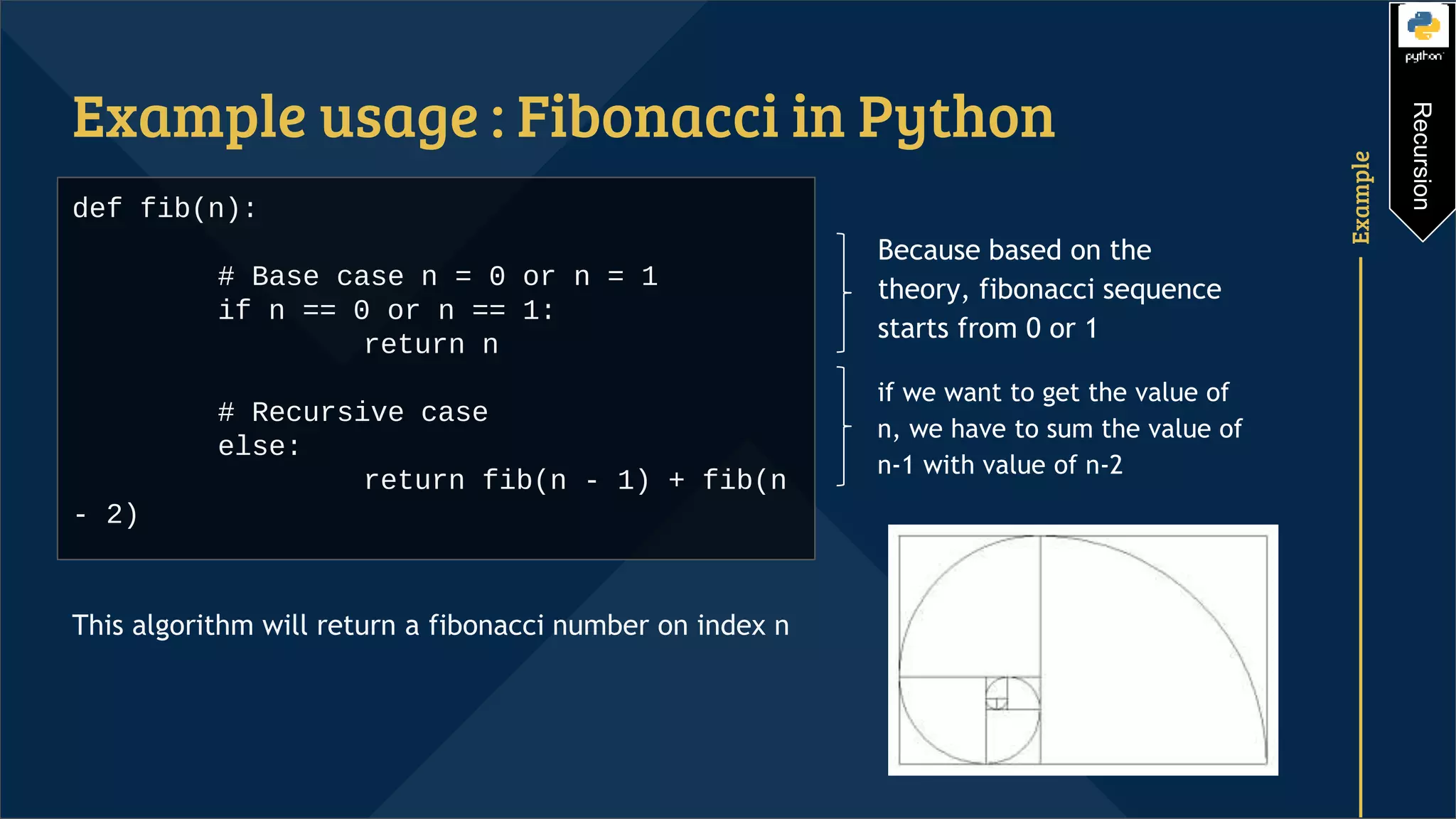
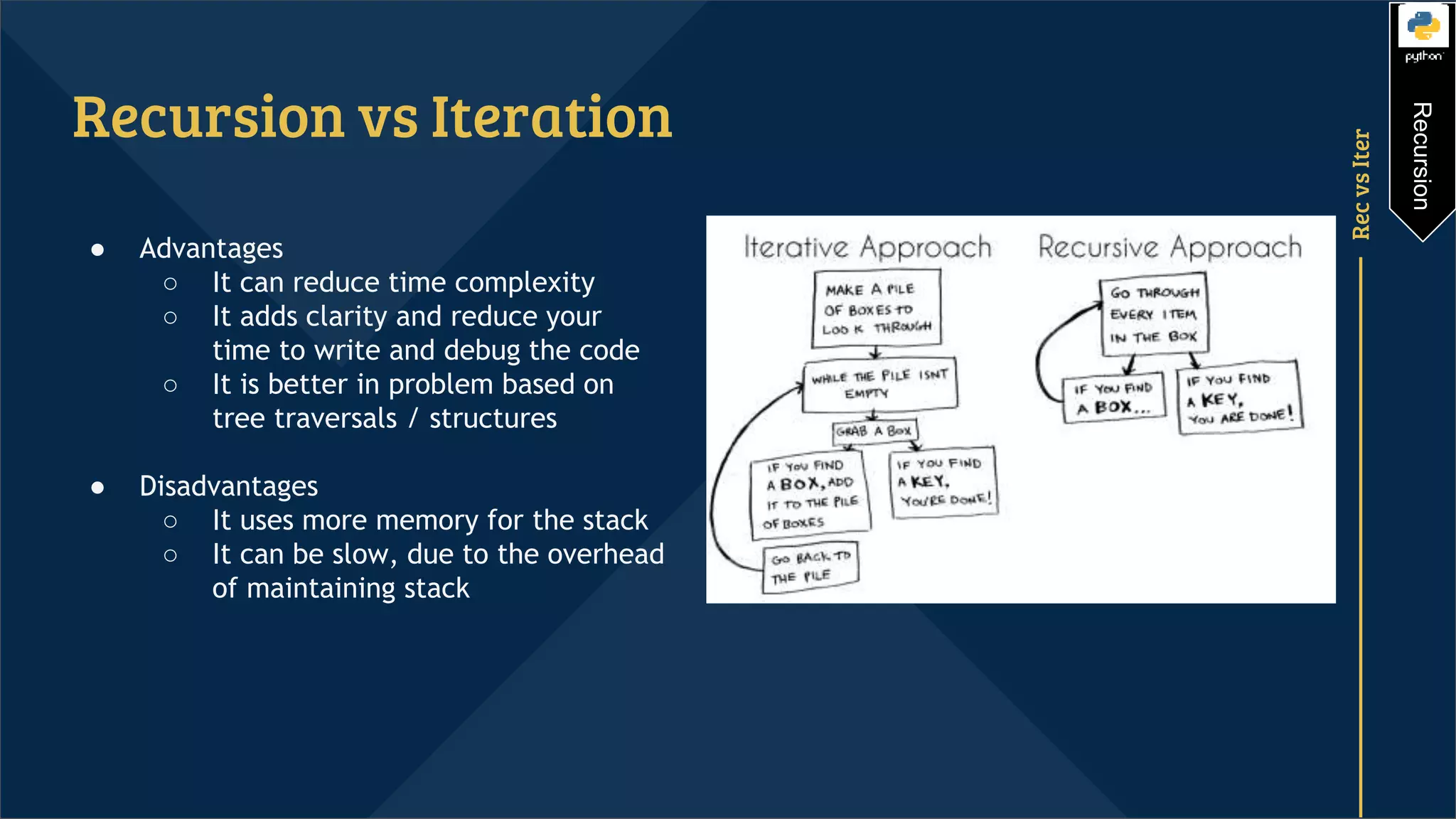
Recursion is a programming technique that involves a function calling itself. It consists of a recursive case where the function calls itself and a base case that stops the recursion. Without a base case, recursion will run infinitely. Examples of using recursion include calculating factorials and Fibonacci sequences by defining the problem in terms of smaller instances of the same problem. Recursion can reduce time complexity but uses more memory than iteration due to the function calls being stored on the stack.