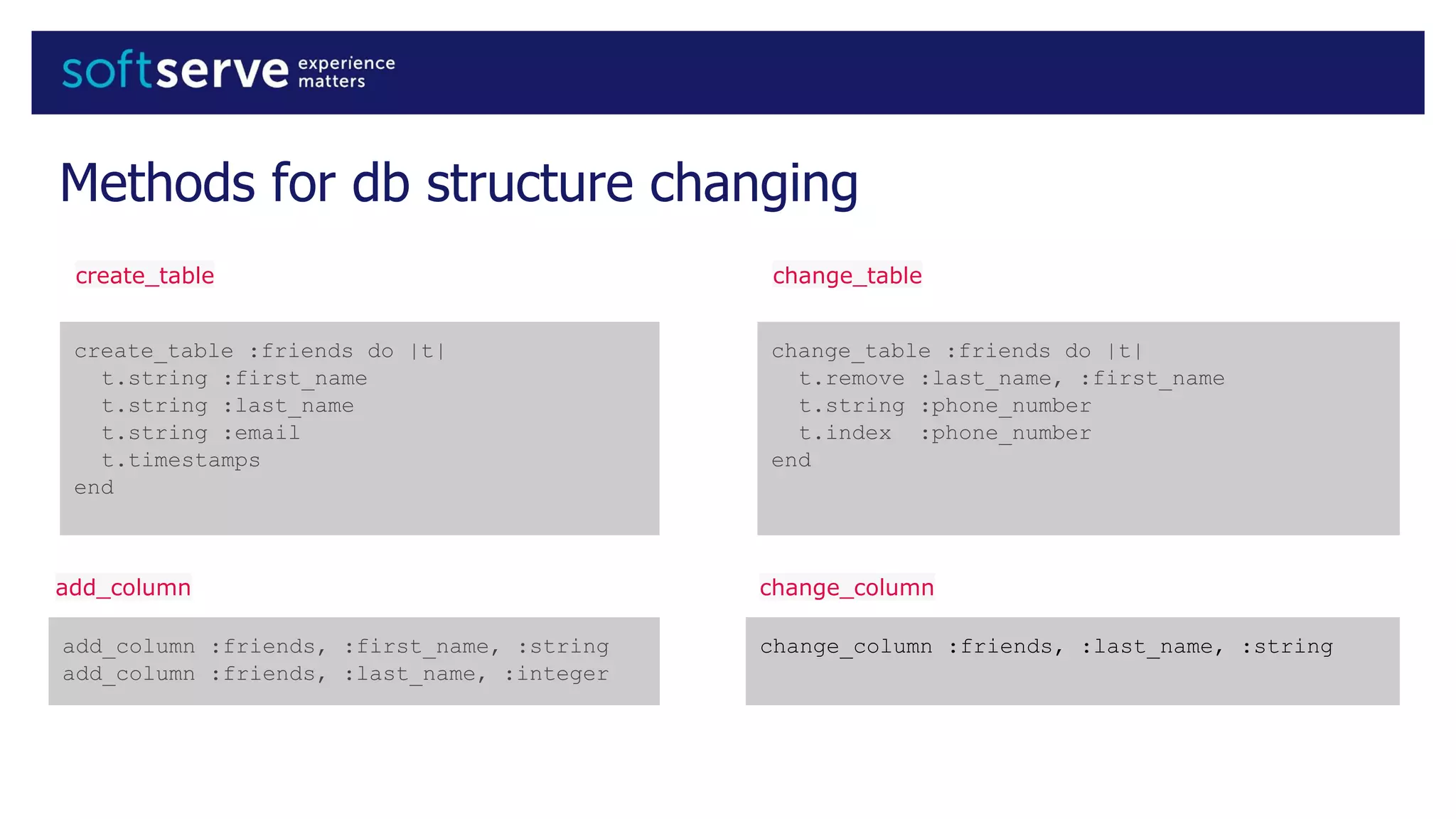
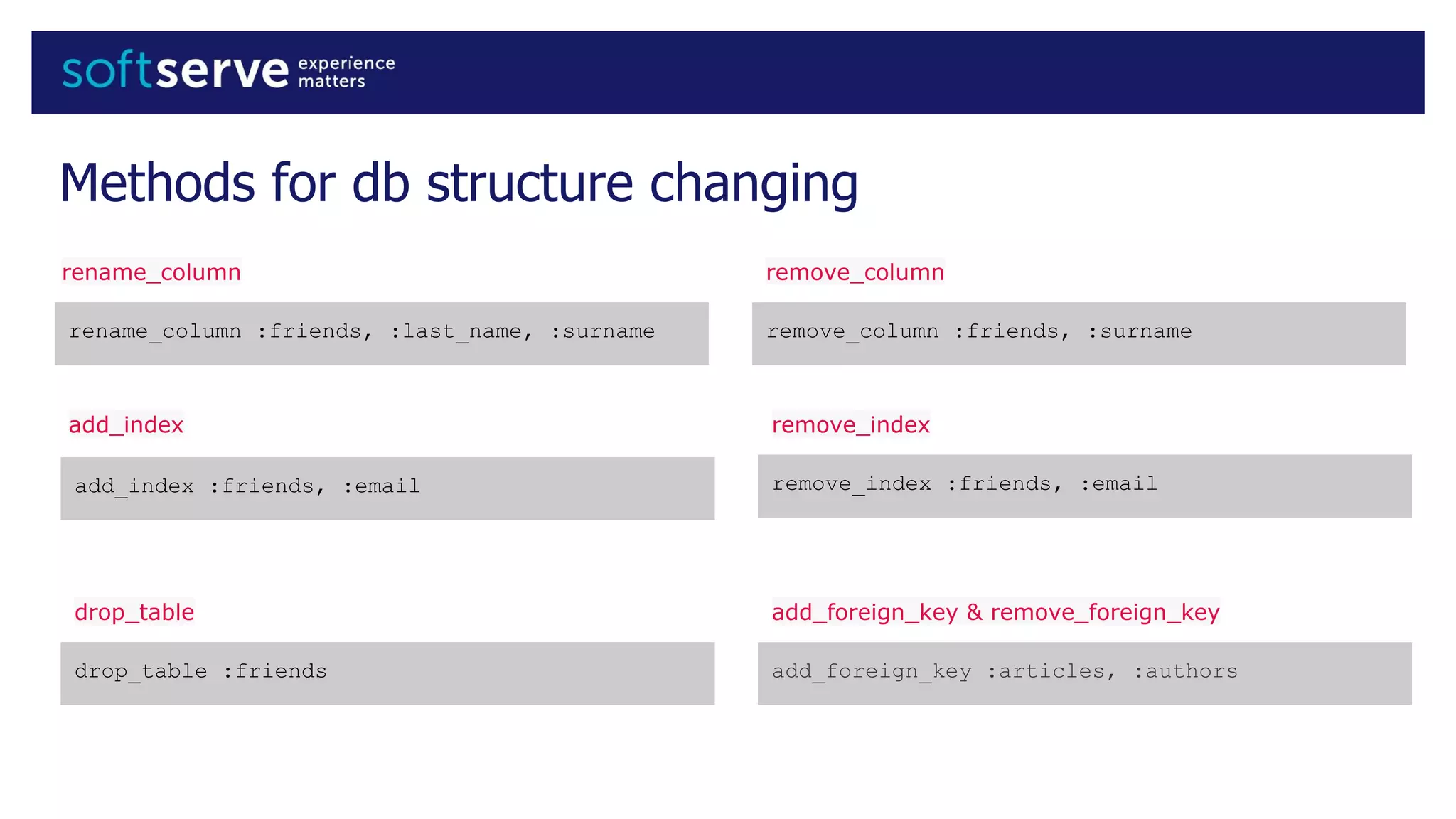
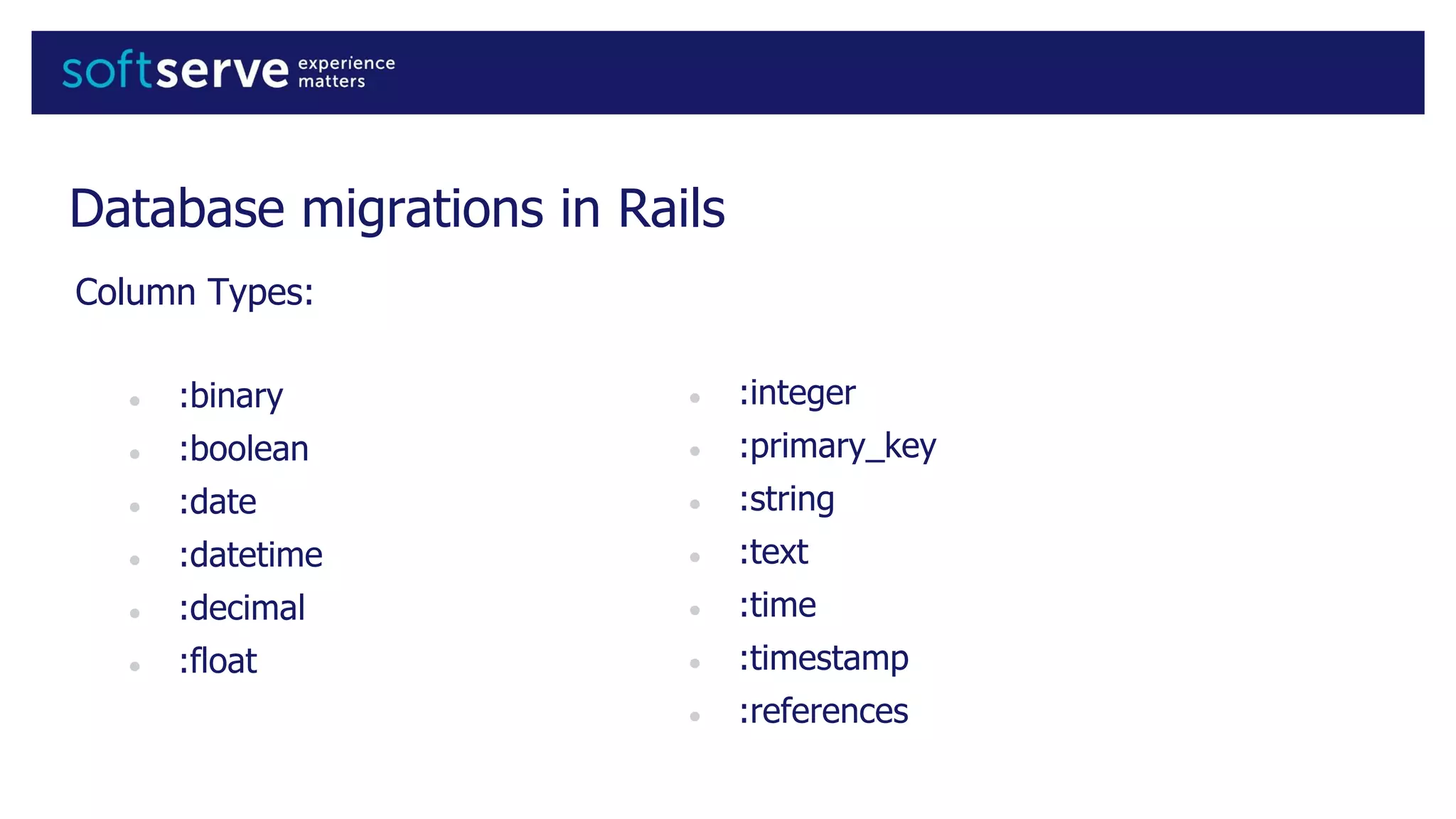
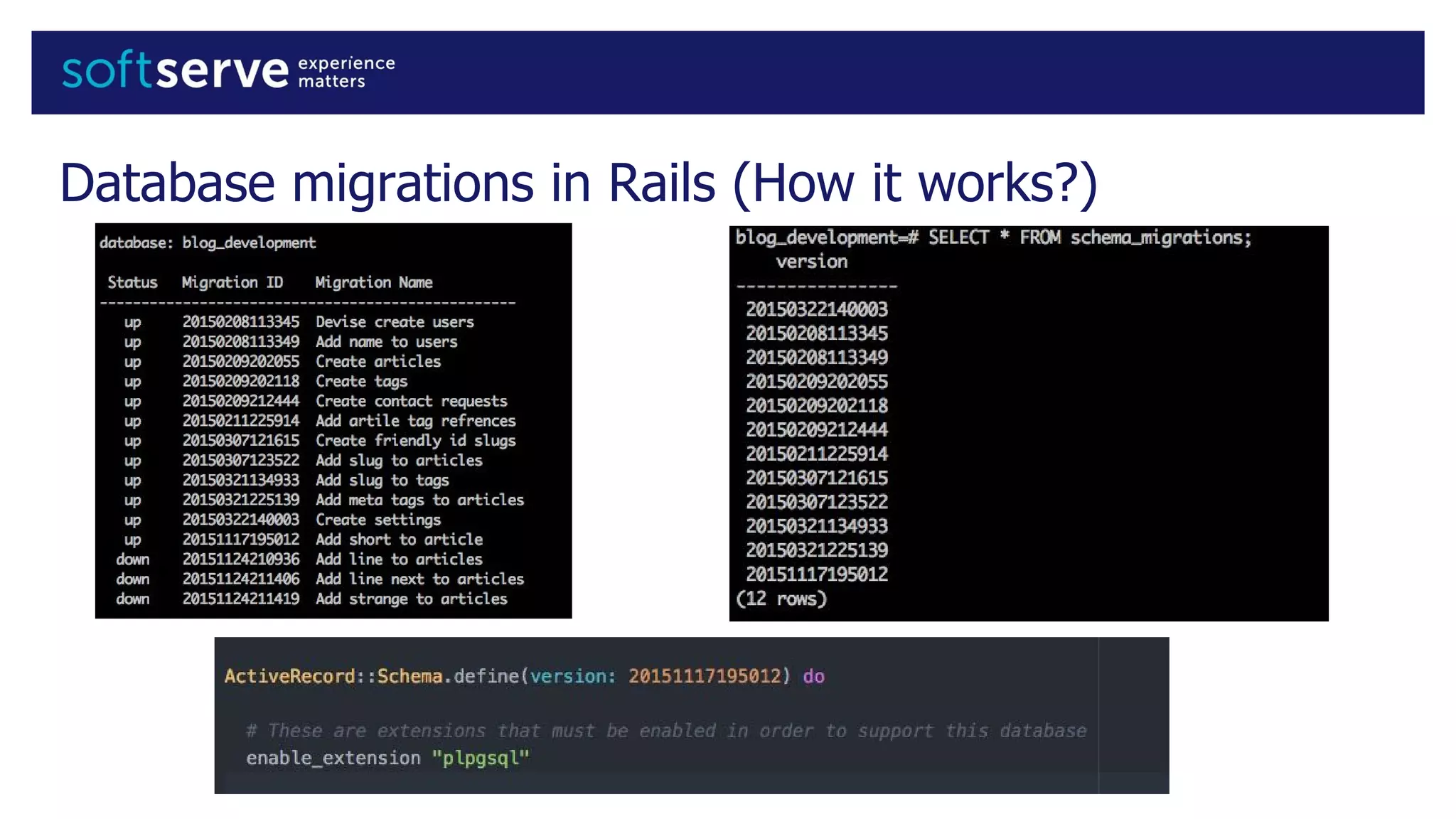
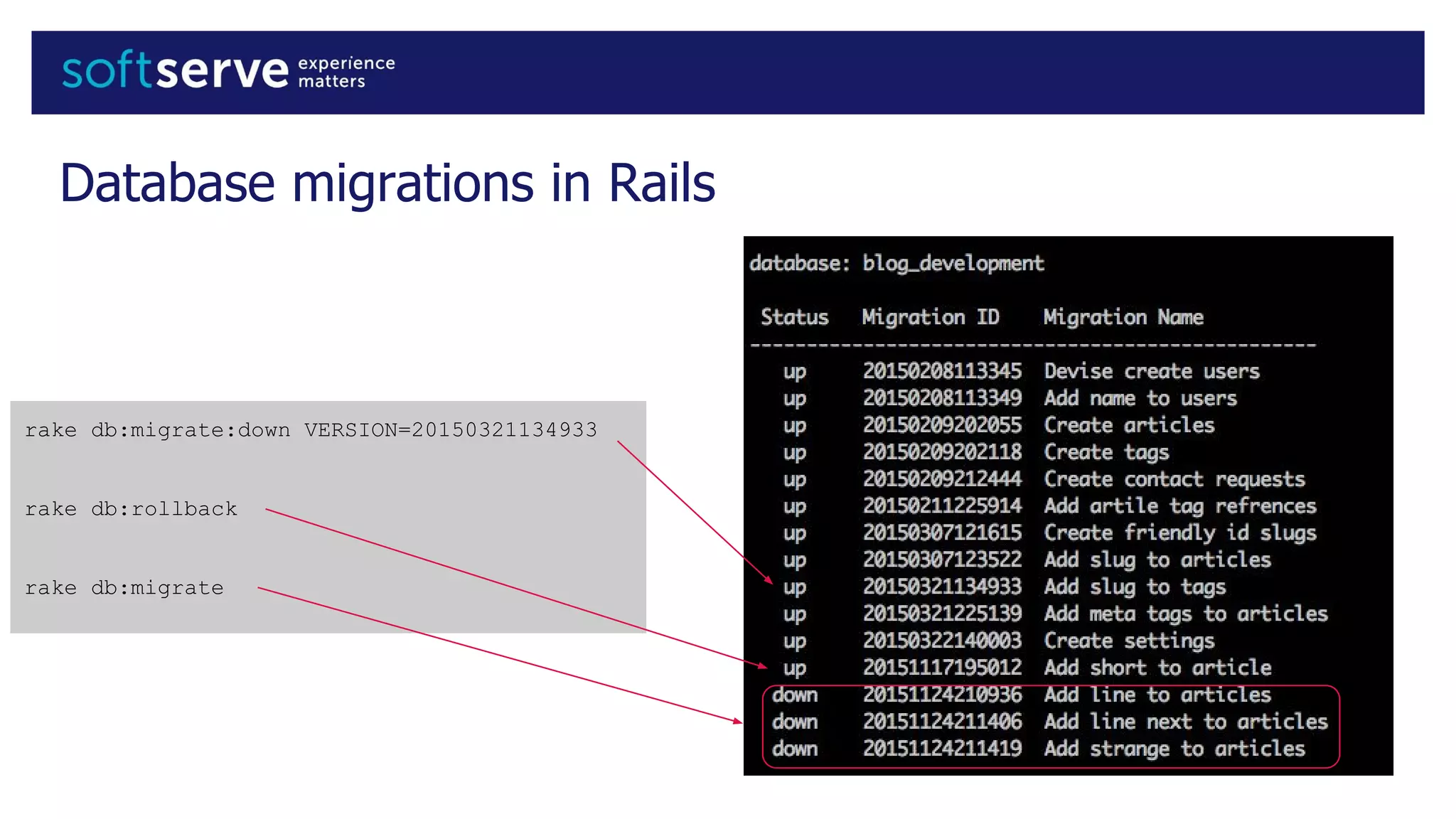
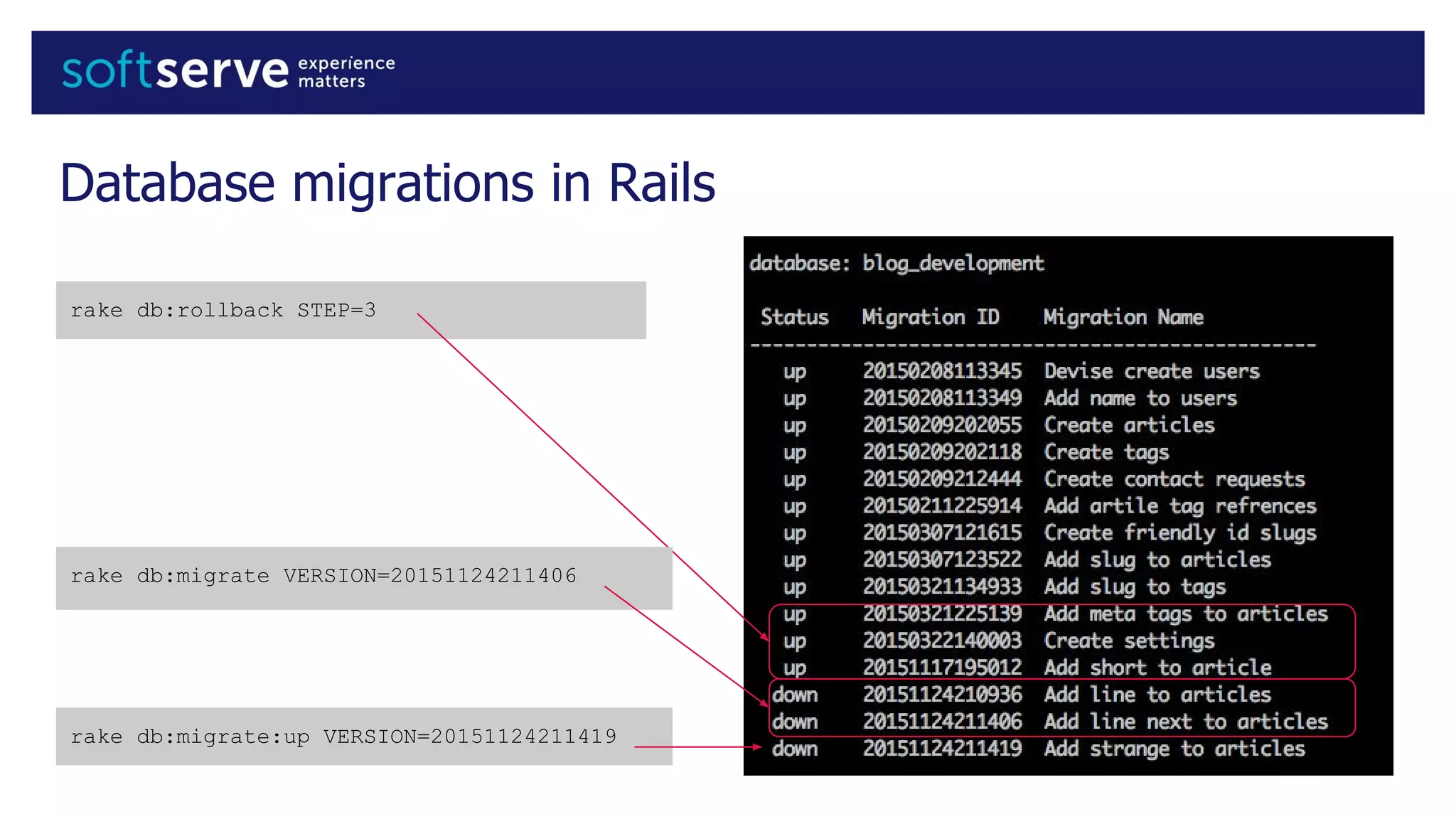
Database migrations allow incremental and reversible changes to a database schema. In Rails, migrations are Ruby classes that describe changes to database tables. Common migration methods add, remove, or change columns or tables. Migrations are run with Rake tasks like db:migrate and can be rolled back. Best practices include using the change method, enforcing defaults in migrations, and keeping schema.rb under version control.