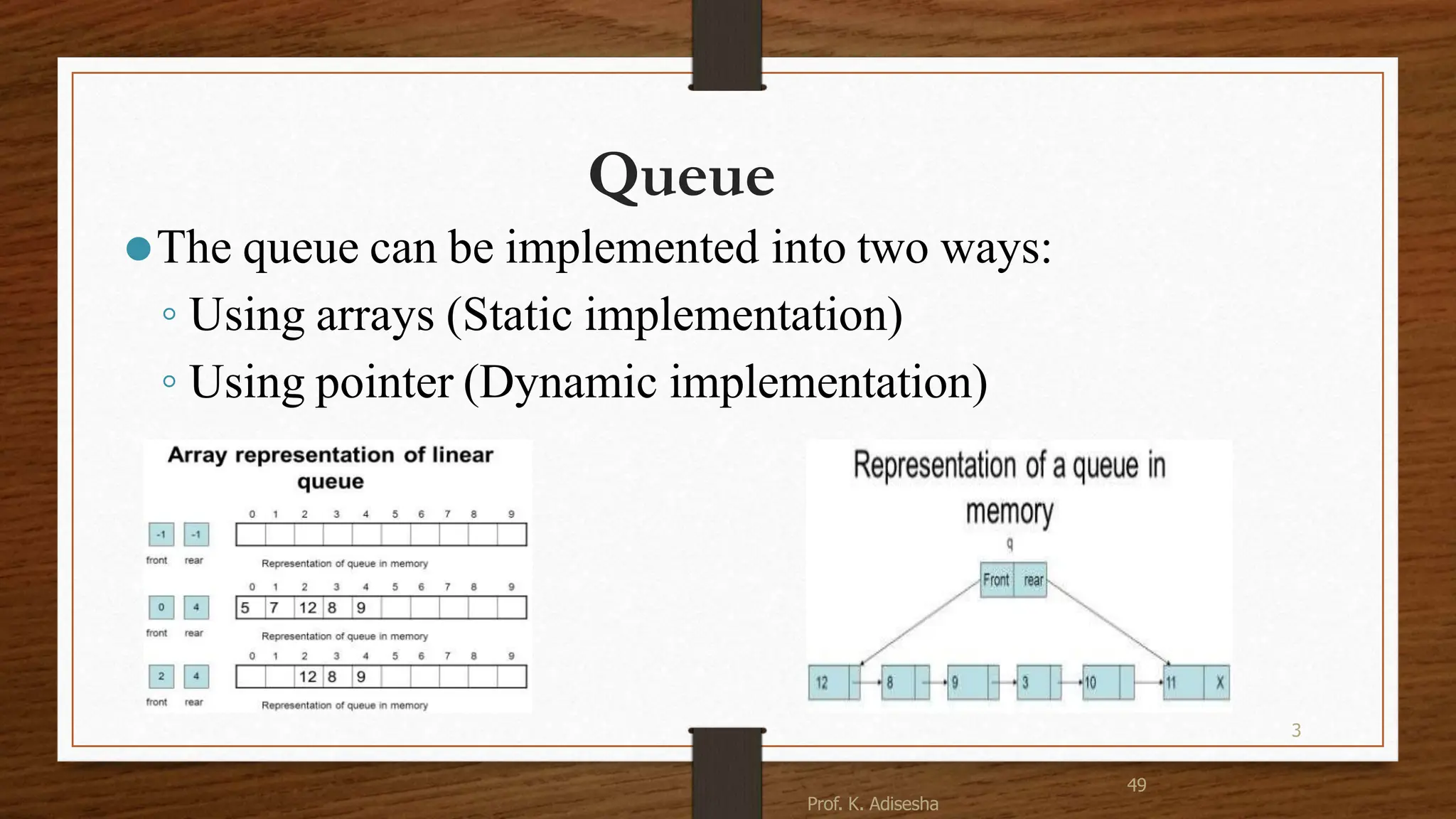
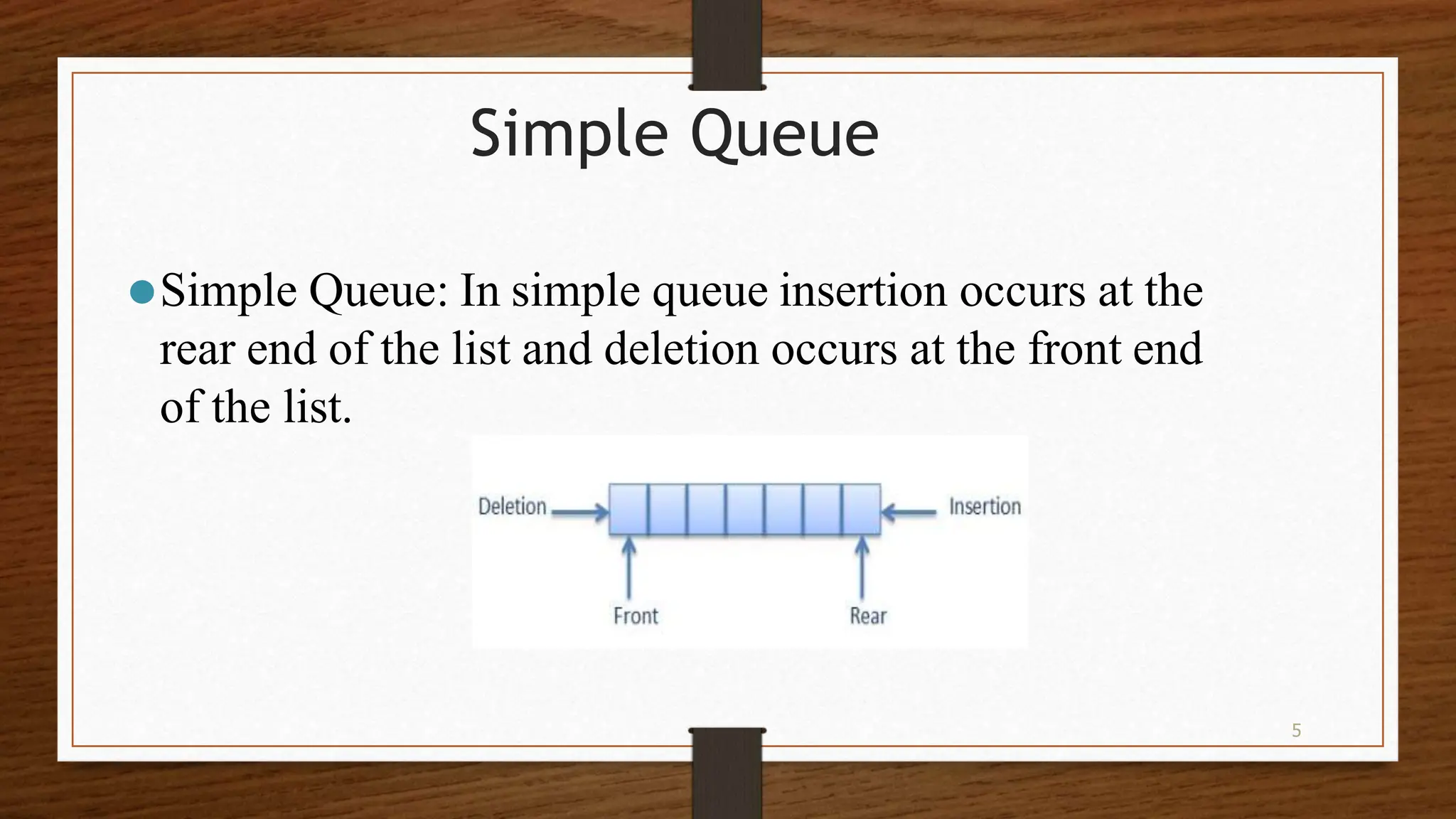
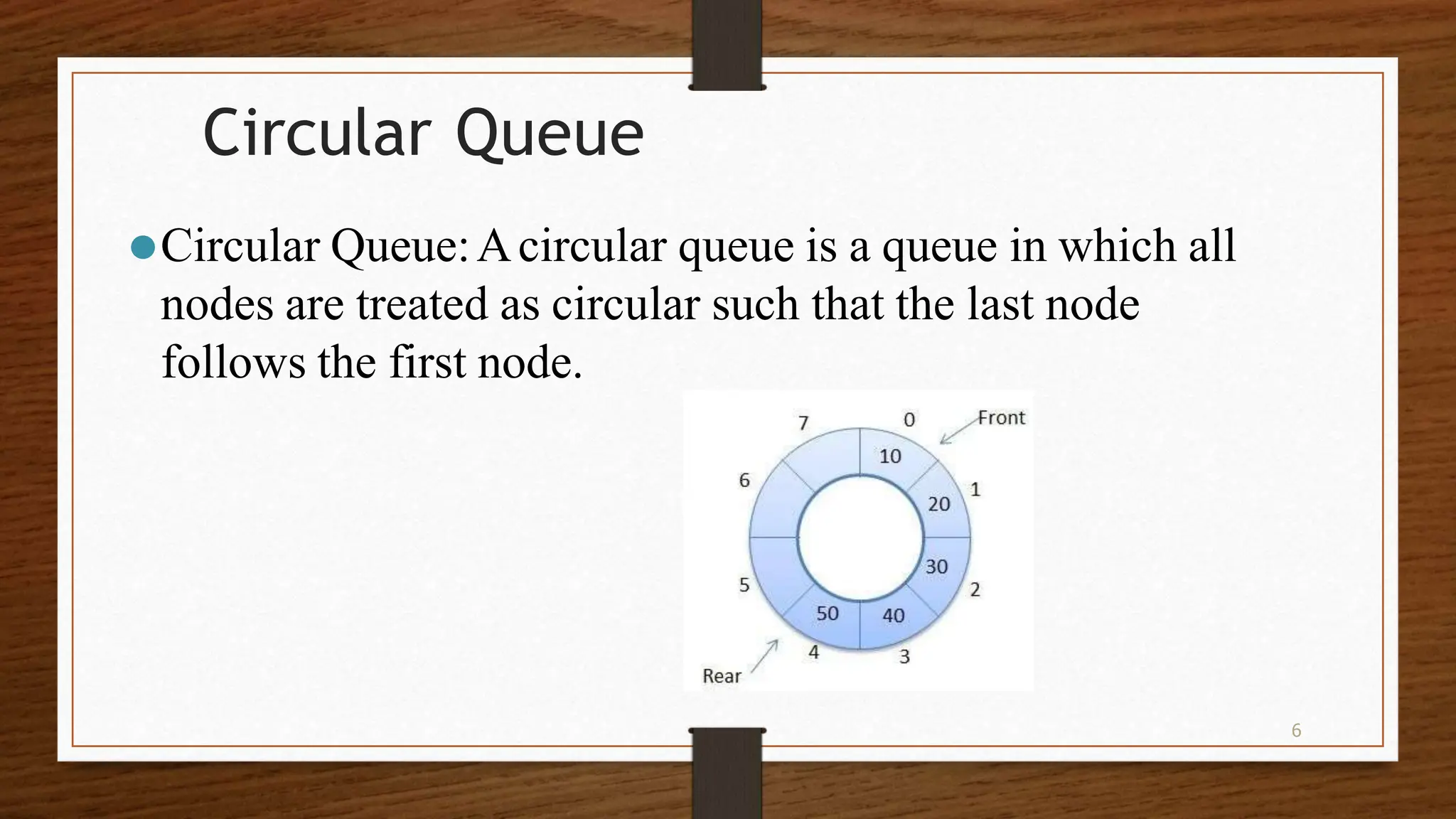
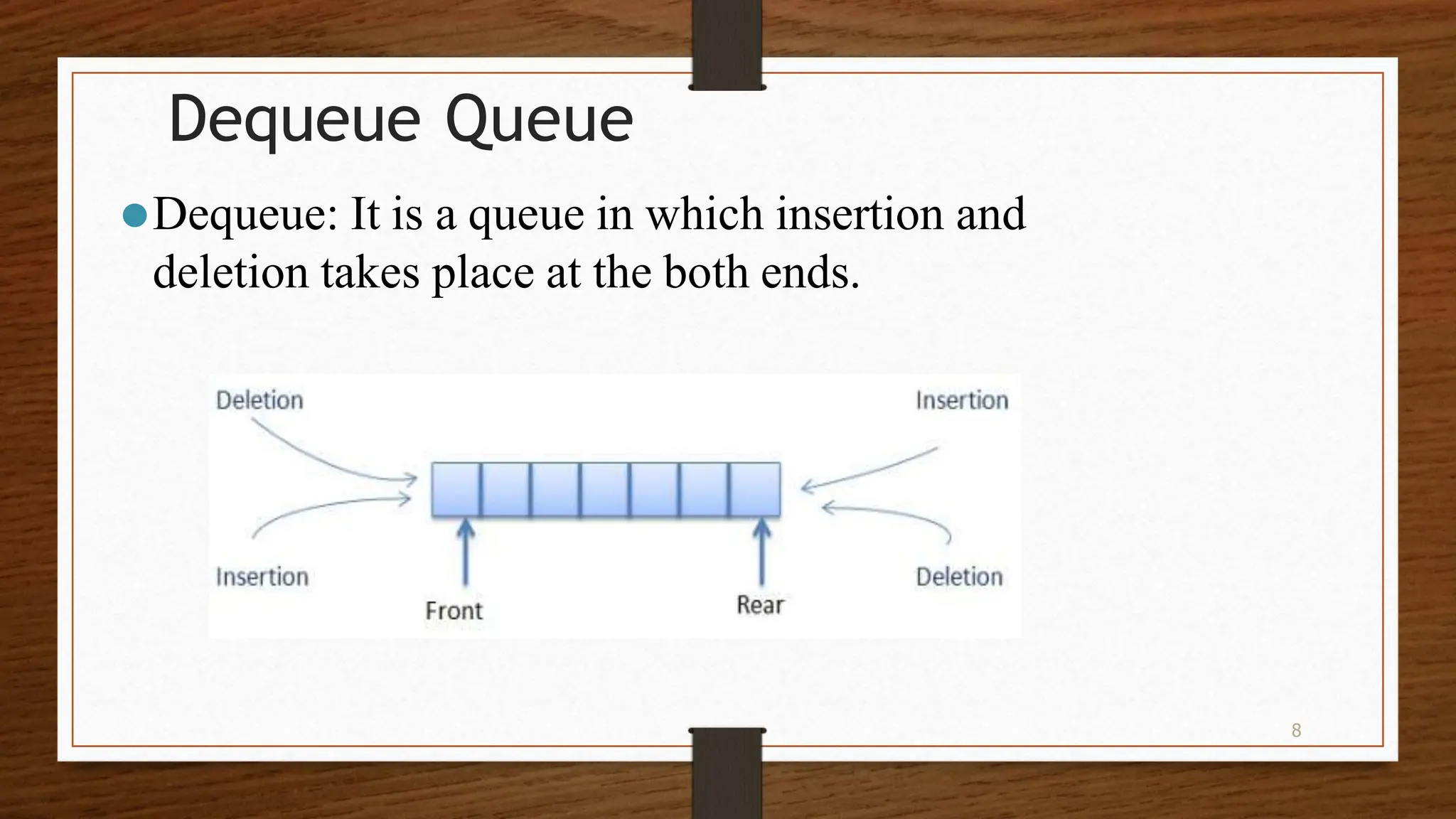
This document discusses queues, which are ordered collections where items are inserted at the rear and removed from the front. There are two main operations: enqueue, which inserts an item at the rear, and dequeue, which removes an item from the front. Queues can be implemented using arrays or pointers. The key types are simple, circular, priority, and dequeue queues. Memory representation uses a linear array and front/rear pointers. Enqueue increments rear and inserts at that index, while dequeue removes from front and increments front if not last element. Queues have applications in operating systems, scheduling, and simulation.






![11 Queue Insertion Operation (ENQUEUE): ⚫ ALGORITHM: ENQUEUE (QUEUE, REAR, FRONT, ITEM) QUEUE is the array with N elements. FRONT is the pointer that contains the location of the element to be deleted and REAR contains the location of the inserted element. ITEM is the element to be inserted. Step 1: if REAR = N-1 then [Check Overflow] PRINT “QUEUE is Full or Overflow” Exit [End if] Step 2: if FRONT = NULL then [Check Whether Queue is empty] FRONT = -1 REAR = -1 else REAR = REAR + 1 [Increment REAR Pointer] Step 3: QUEUE[REAR] = ITEM [Copy ITEM to REAR position] Step 4: Return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-240327163434-29fc80fd/75/Queue-data-structures-and-operation-on-data-structures-11-2048.jpg)
![12 Queue Deletion Operation (DEQUEUE) ALGORITHM: DEQUEUE (QUEUE, REAR, FRONT, ITEM) QUEUE is the array with N elements. FRONT is the pointer that contains the location of the element to be deleted and REAR contains the location of the inserted element. ITEM is the element to be inserted. Step 1: if FRONT = NULL then [Check Whether Queue is empty] PRINT “QUEUE is Empty or Underflow” Exit [End if] Step 2: ITEM = QUEUE[FRONT] Step 3: if FRONT = REAR then [if QUEUE has only one element] FRONT = NULL REAR = NULL else FRONT = FRONT + 1 [Increment FRONT pointer] Step 4: Return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-240327163434-29fc80fd/75/Queue-data-structures-and-operation-on-data-structures-12-2048.jpg)