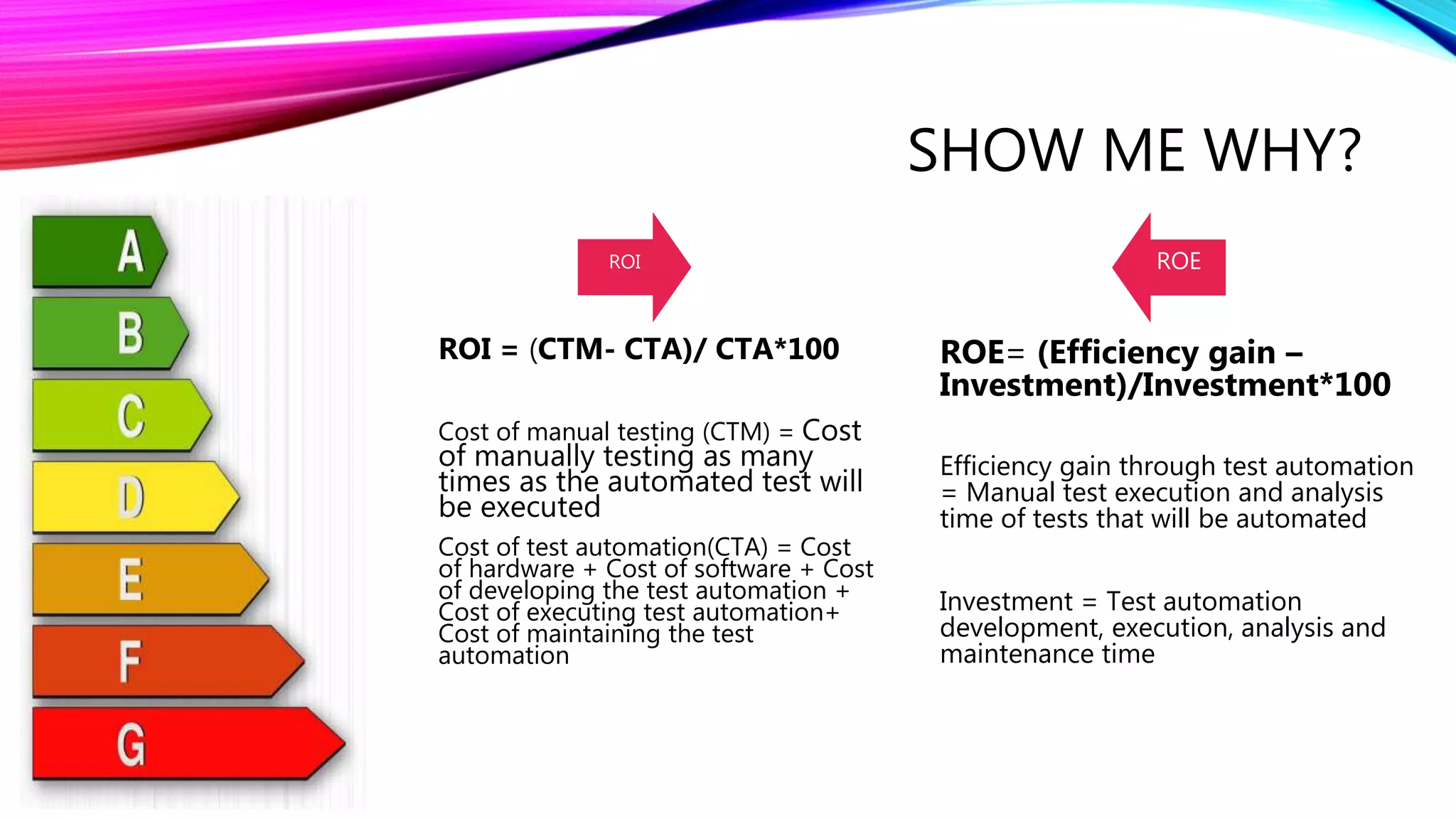
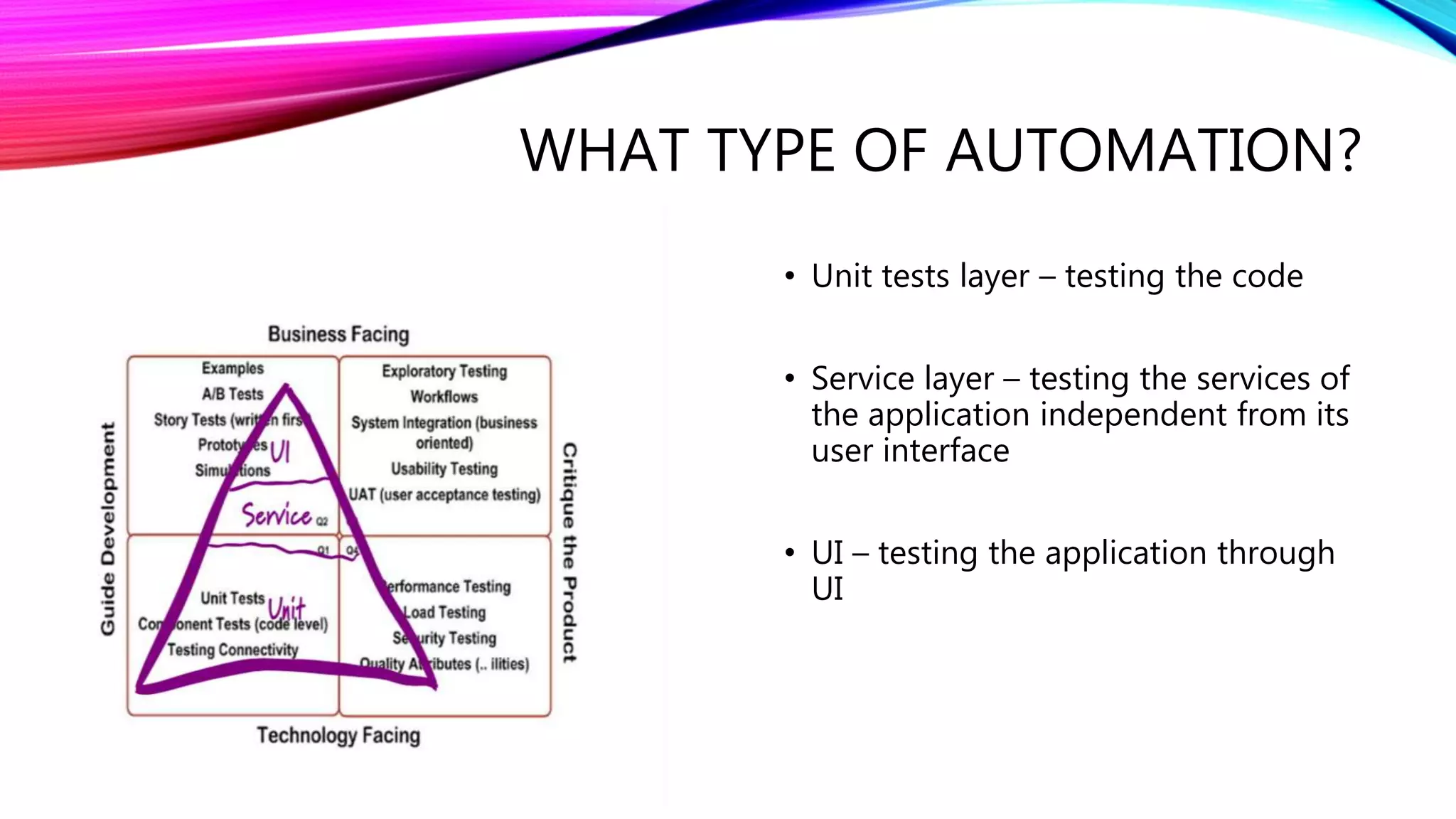
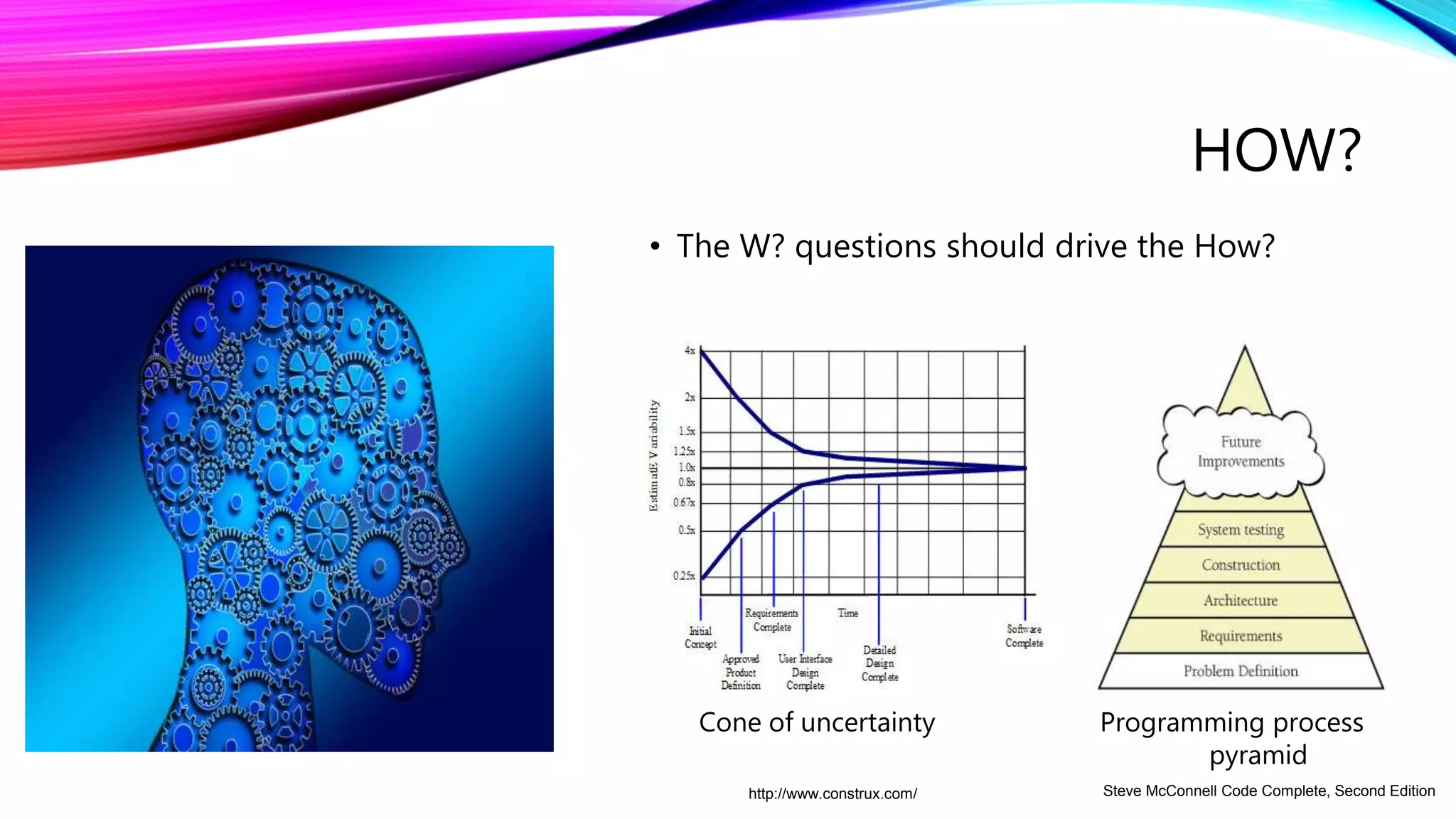
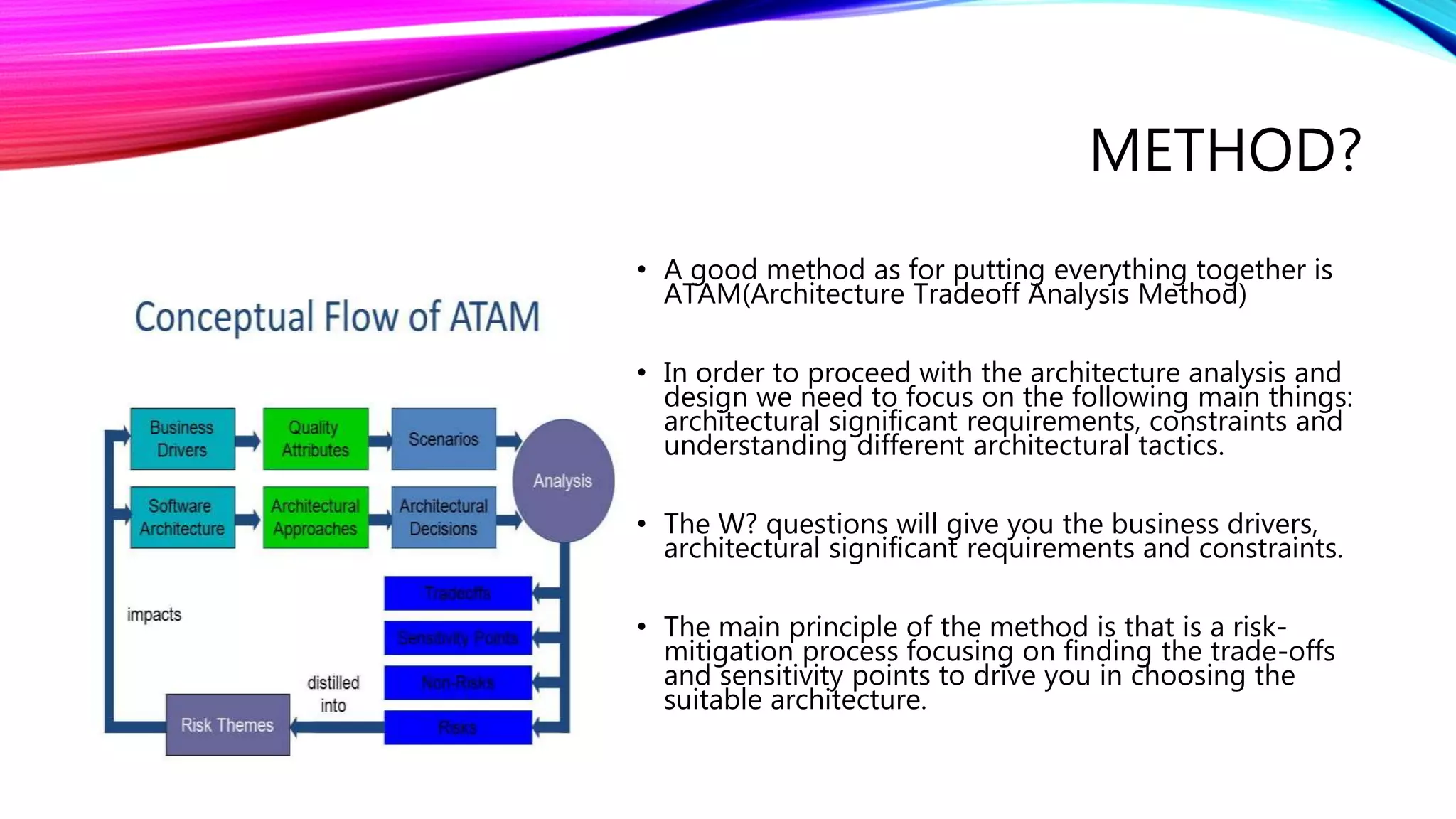
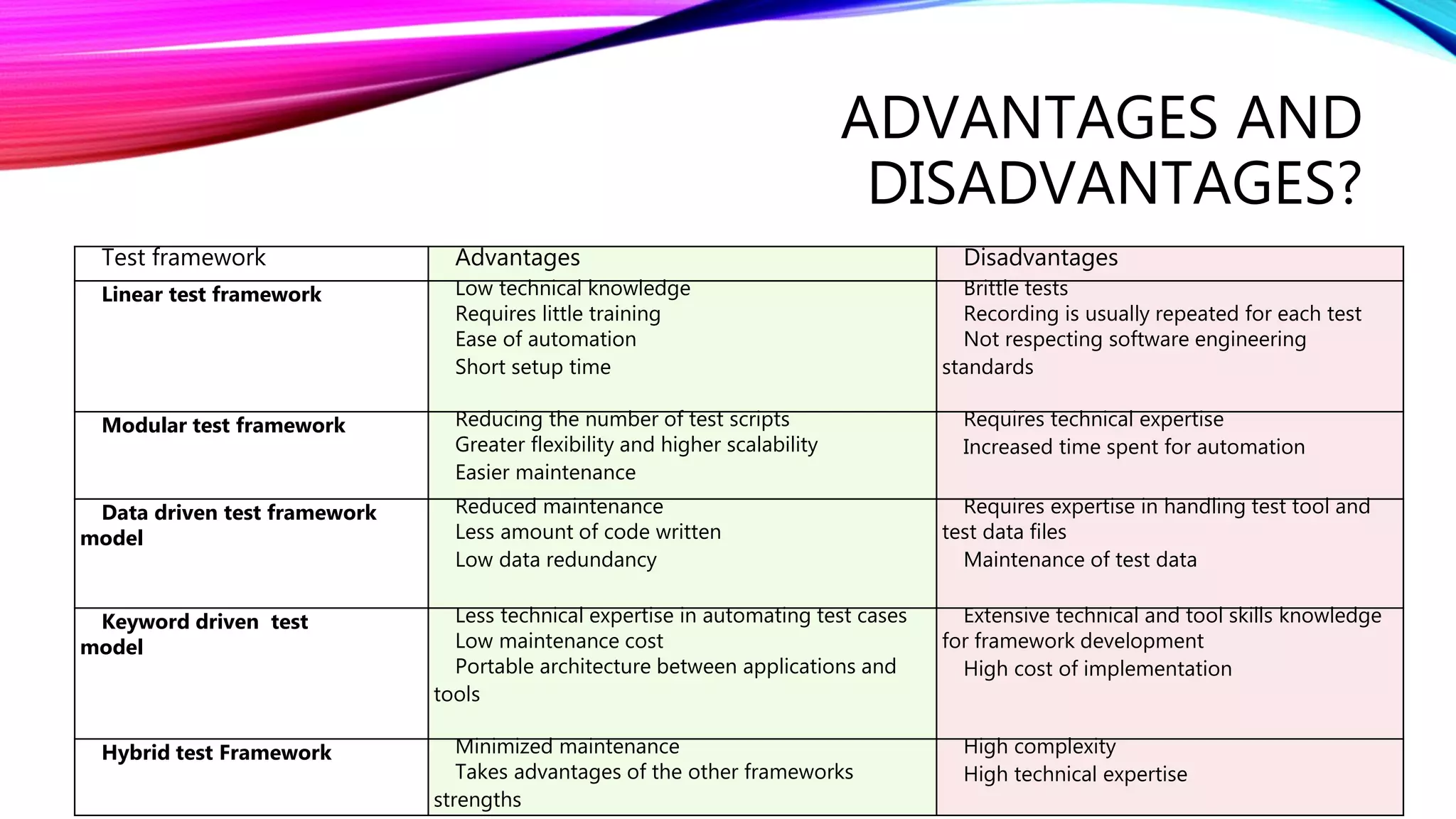
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to successful test automation projects, emphasizing strategic planning, stakeholder involvement, and adapting to evolving software requirements. It discusses the importance of assessing current testing statuses, determining the return on investment (ROI), and identifying the right skills for automation. Additionally, it explores various types of testing, frameworks, input/output expectations, and the need for accurate metrics for continuous improvement in test automation.