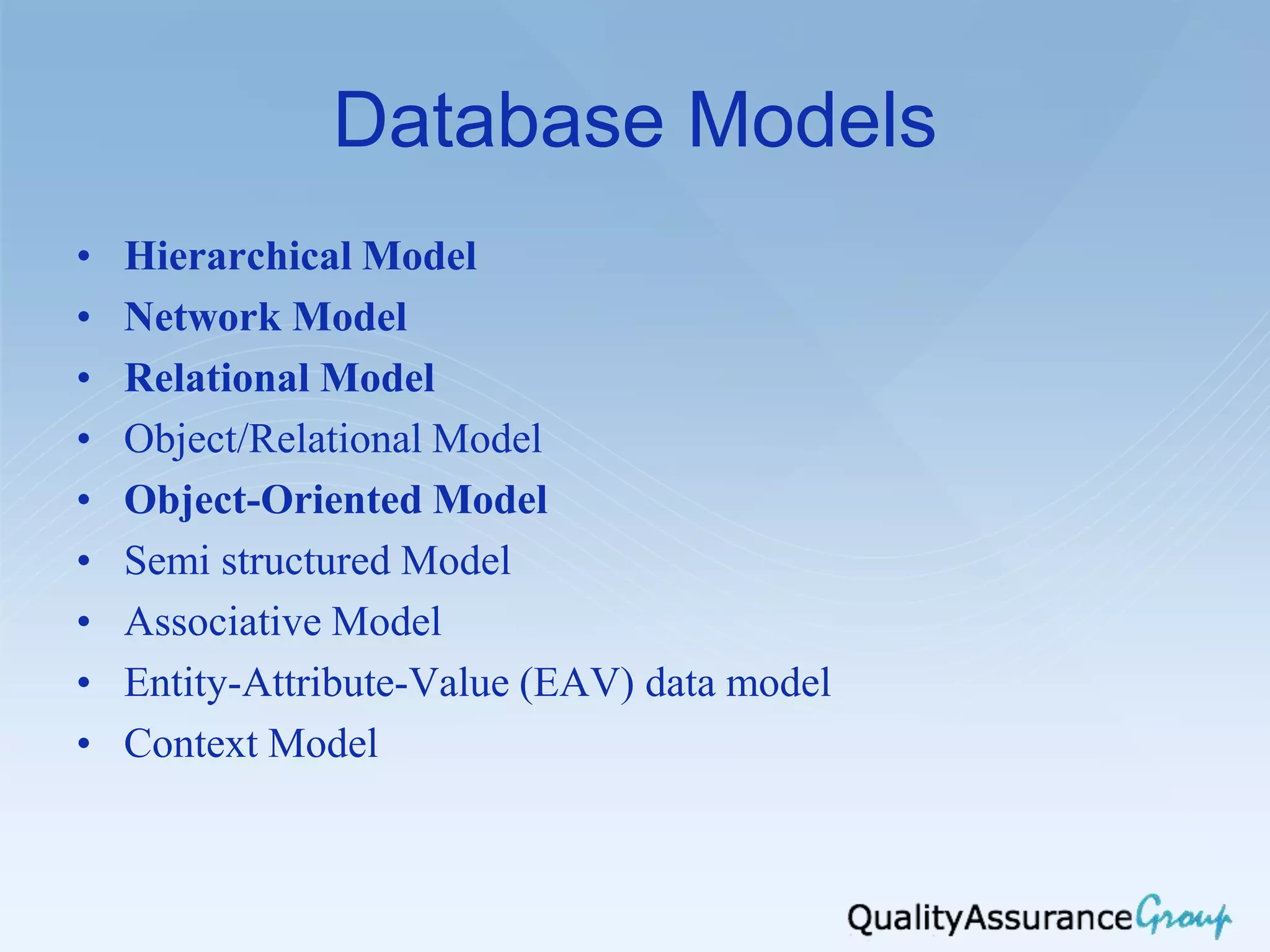
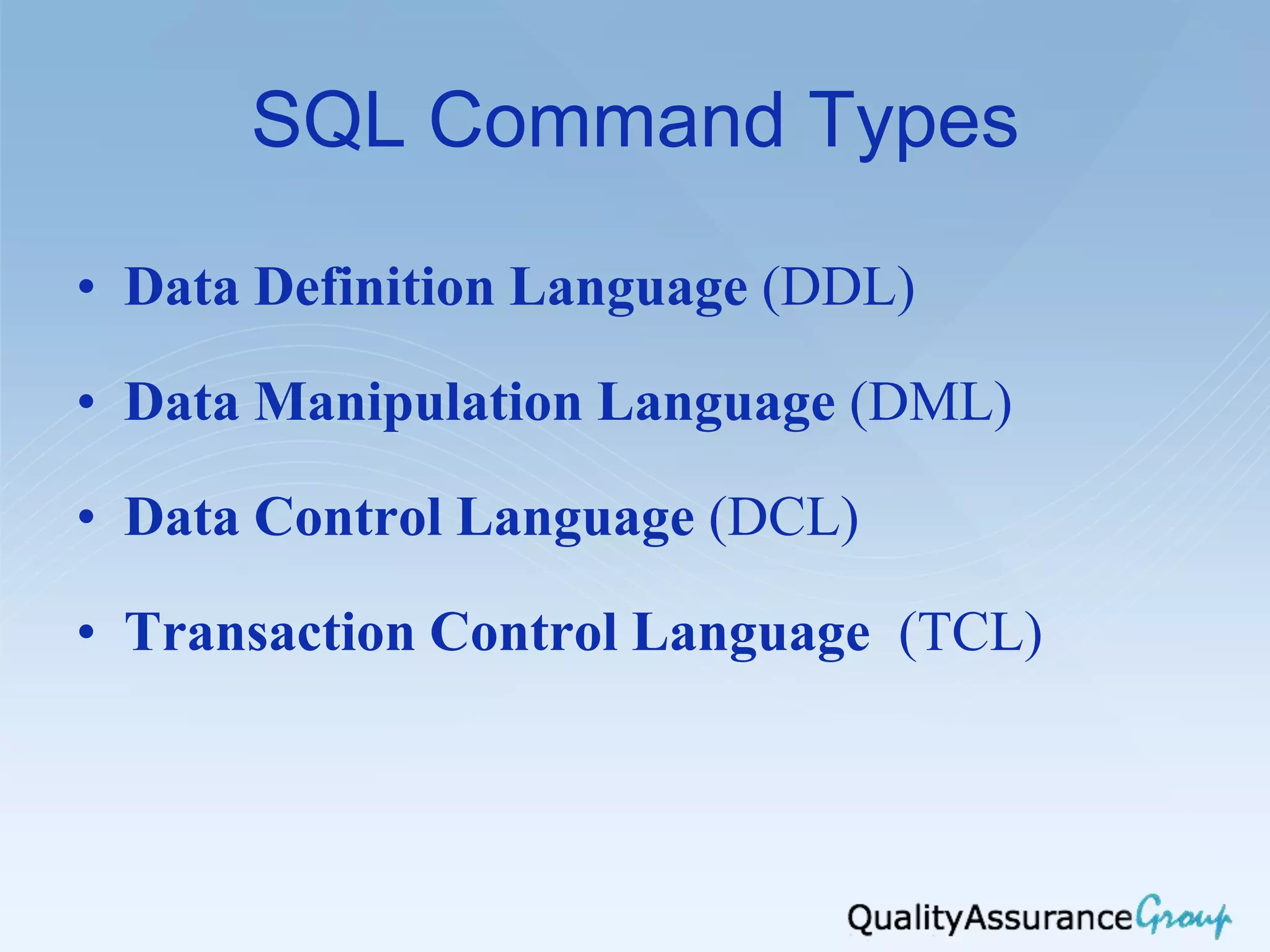
The document outlines the agenda for a workshop on software databases and testing in Lviv, Ukraine in 2013. It covers introduction to database models and keys, SQL commands including SELECT statements, and database testing approaches. Database models discussed include relational, hierarchical, network, object-oriented, and semi-structured models. SQL command types include DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL. Database testing topics include database testing, migration testing, and SQL optimization.





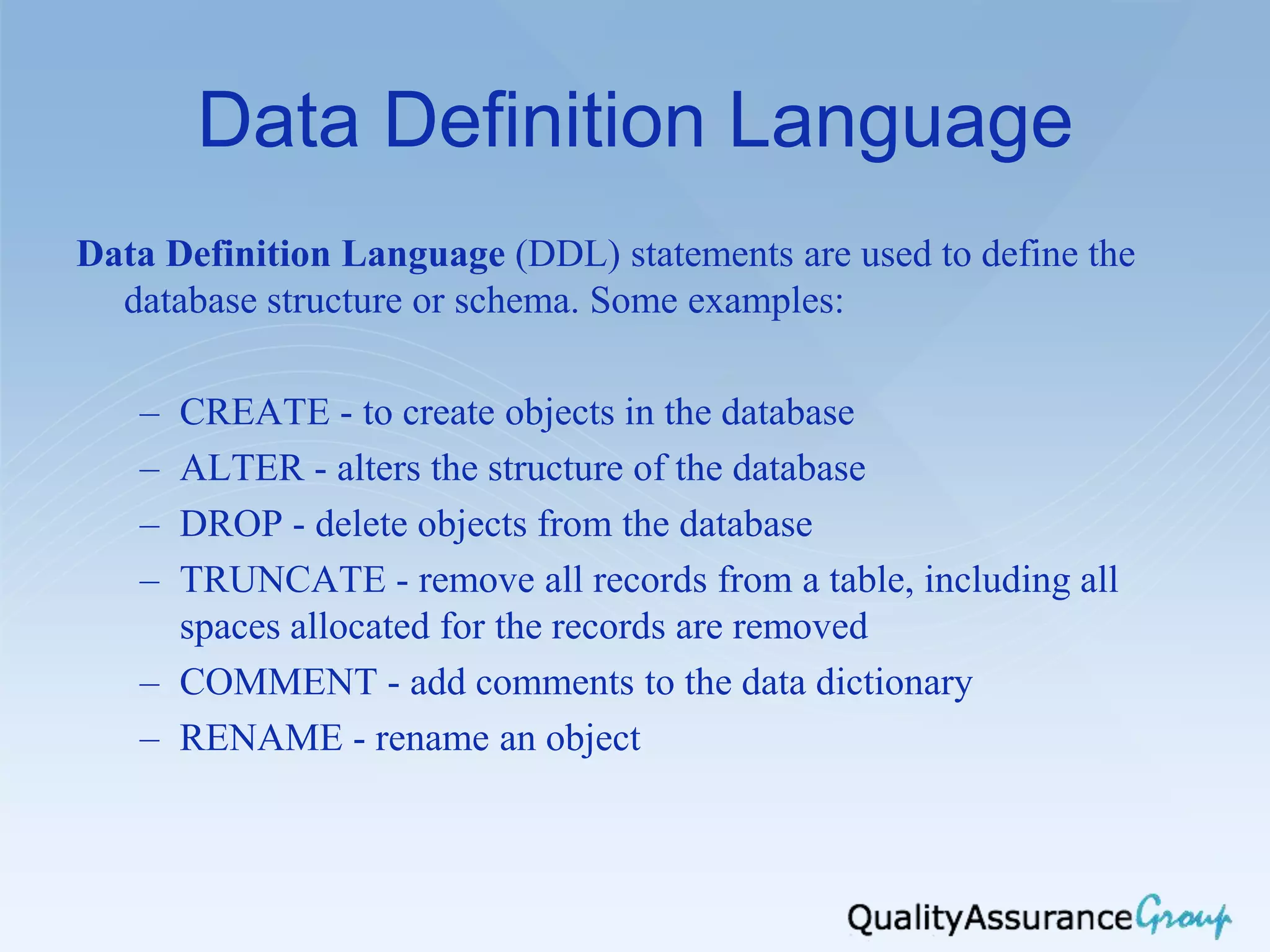


![SQL Select SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] columnname1 [,columnname2] FROM tablename1 [,tablename2] [WHERE condition] [ and|or condition...] [GROUP BY column-list] [HAVING conditions] [ORDER BY column-list [ASC | DESC] ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qagroupsoftwaredbandtesting-26june2013-130626140801-phpapp01/75/Software-Database-and-Testing-12-2048.jpg)