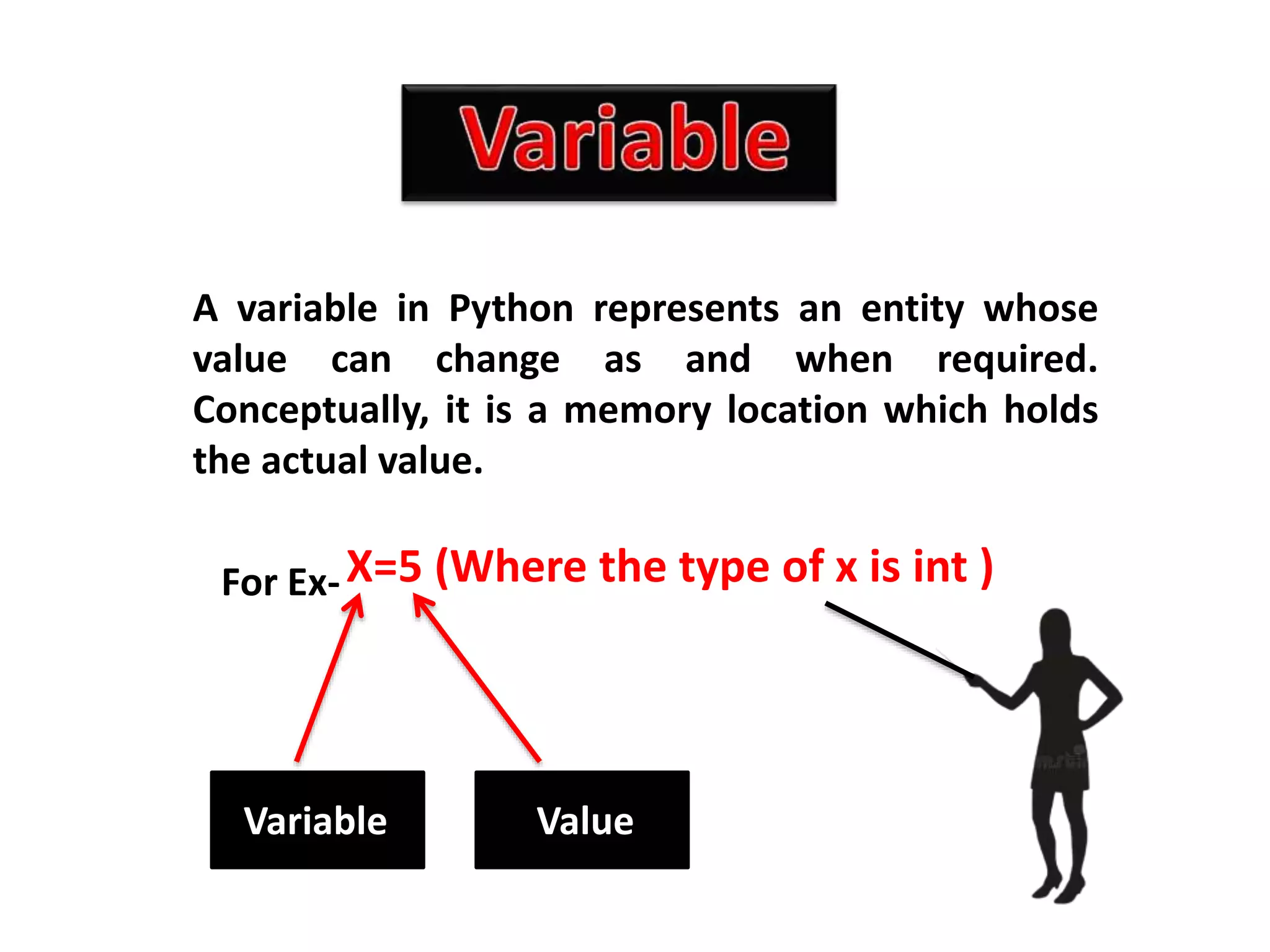
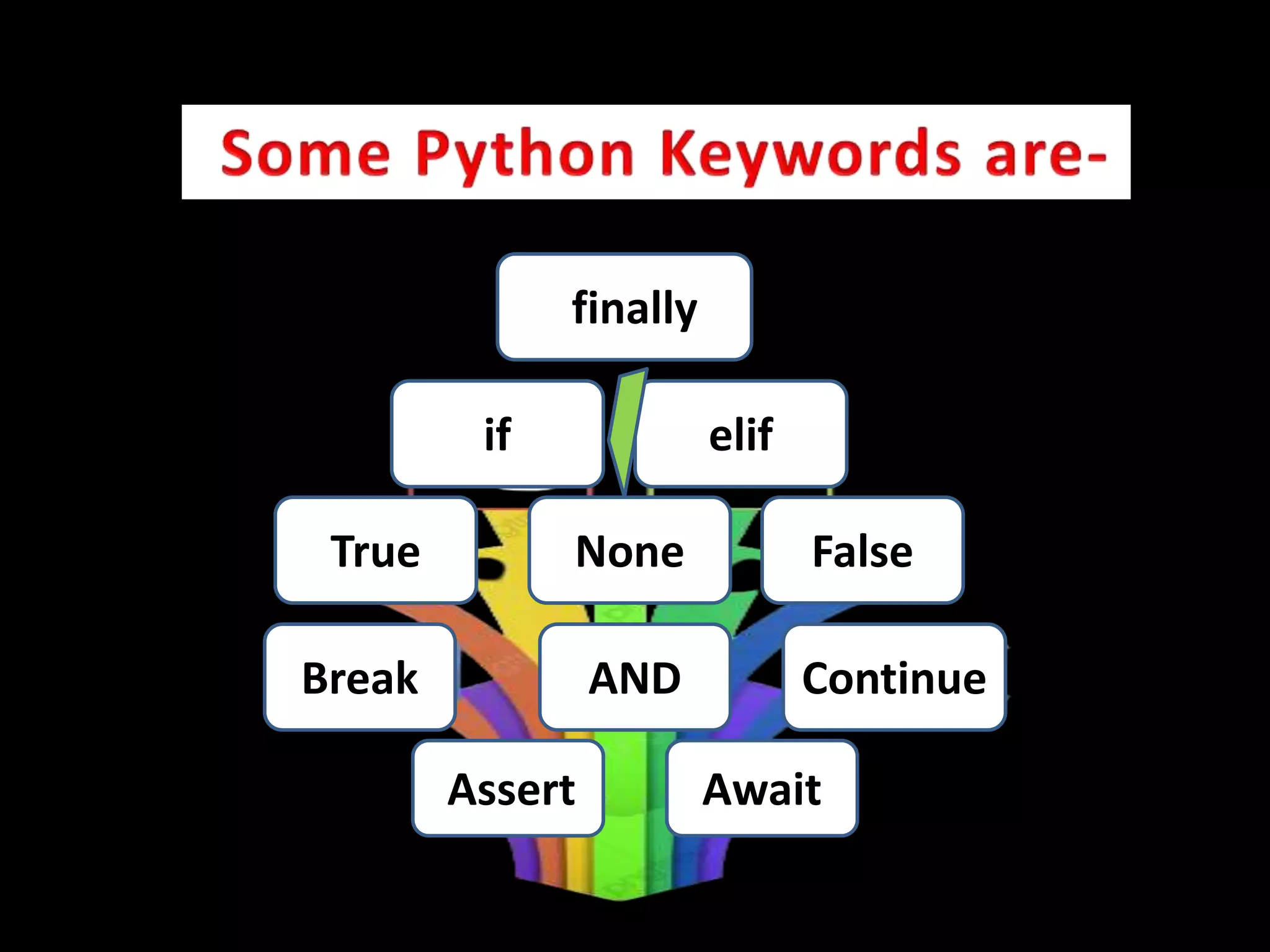
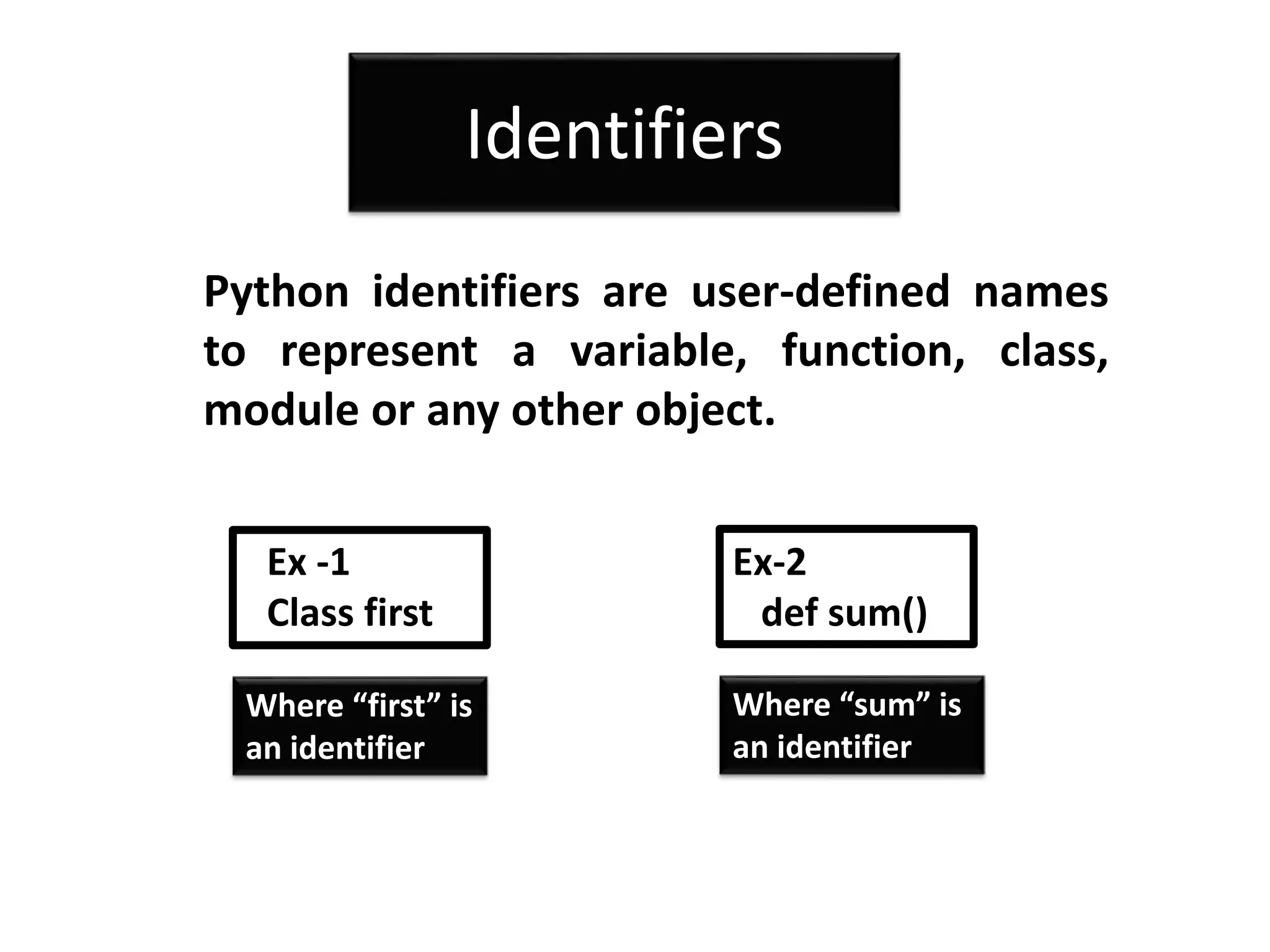
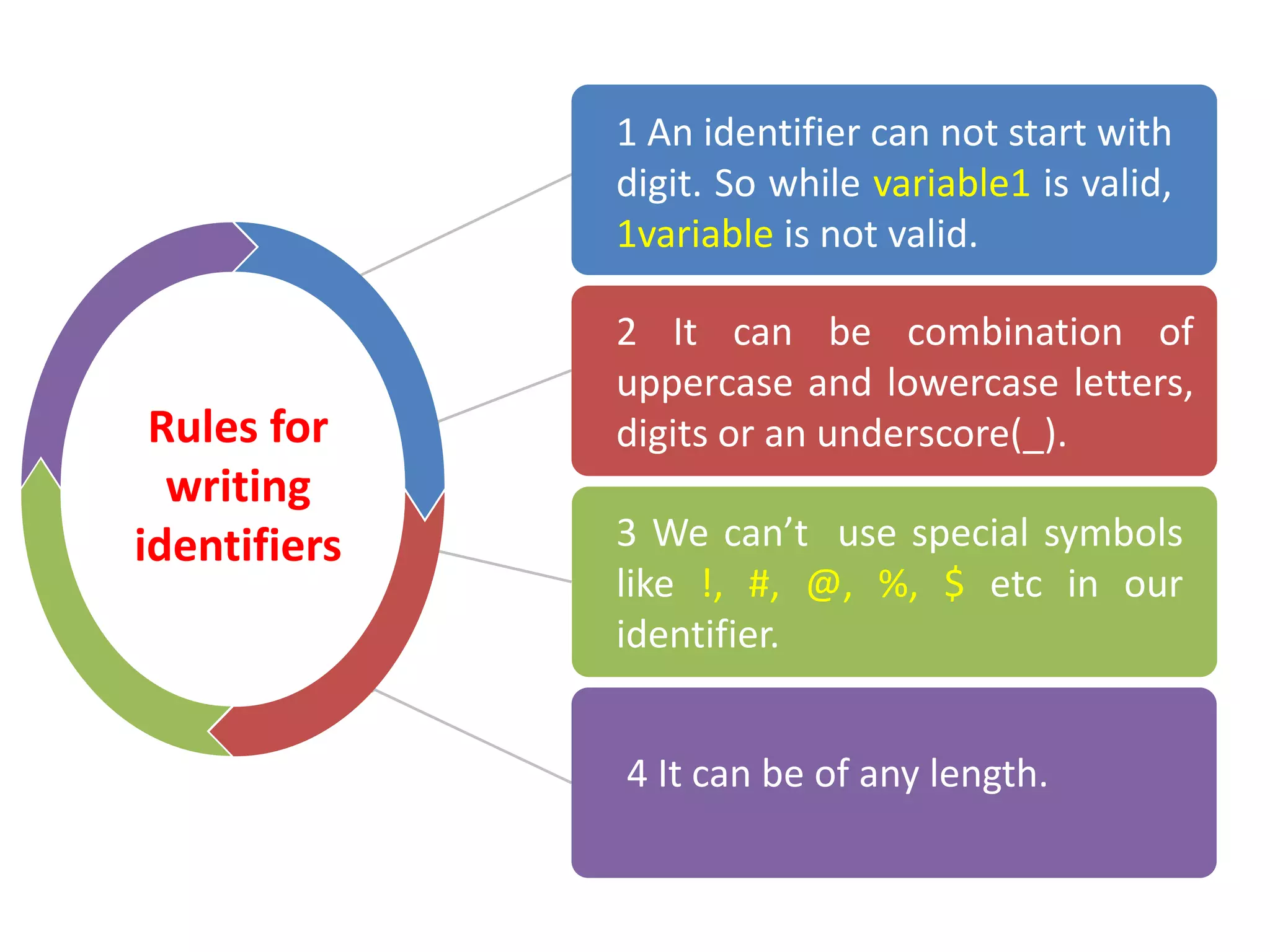
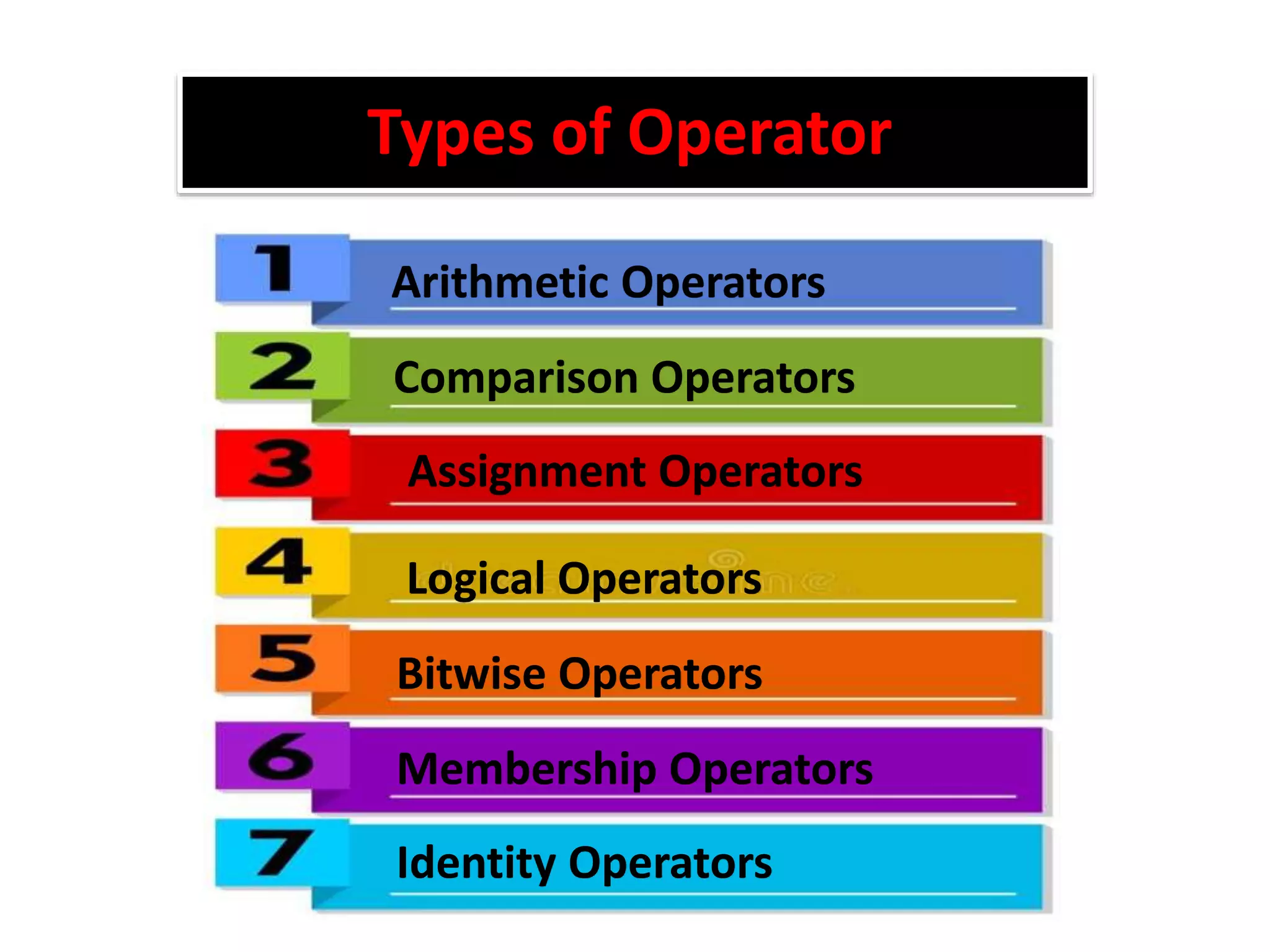
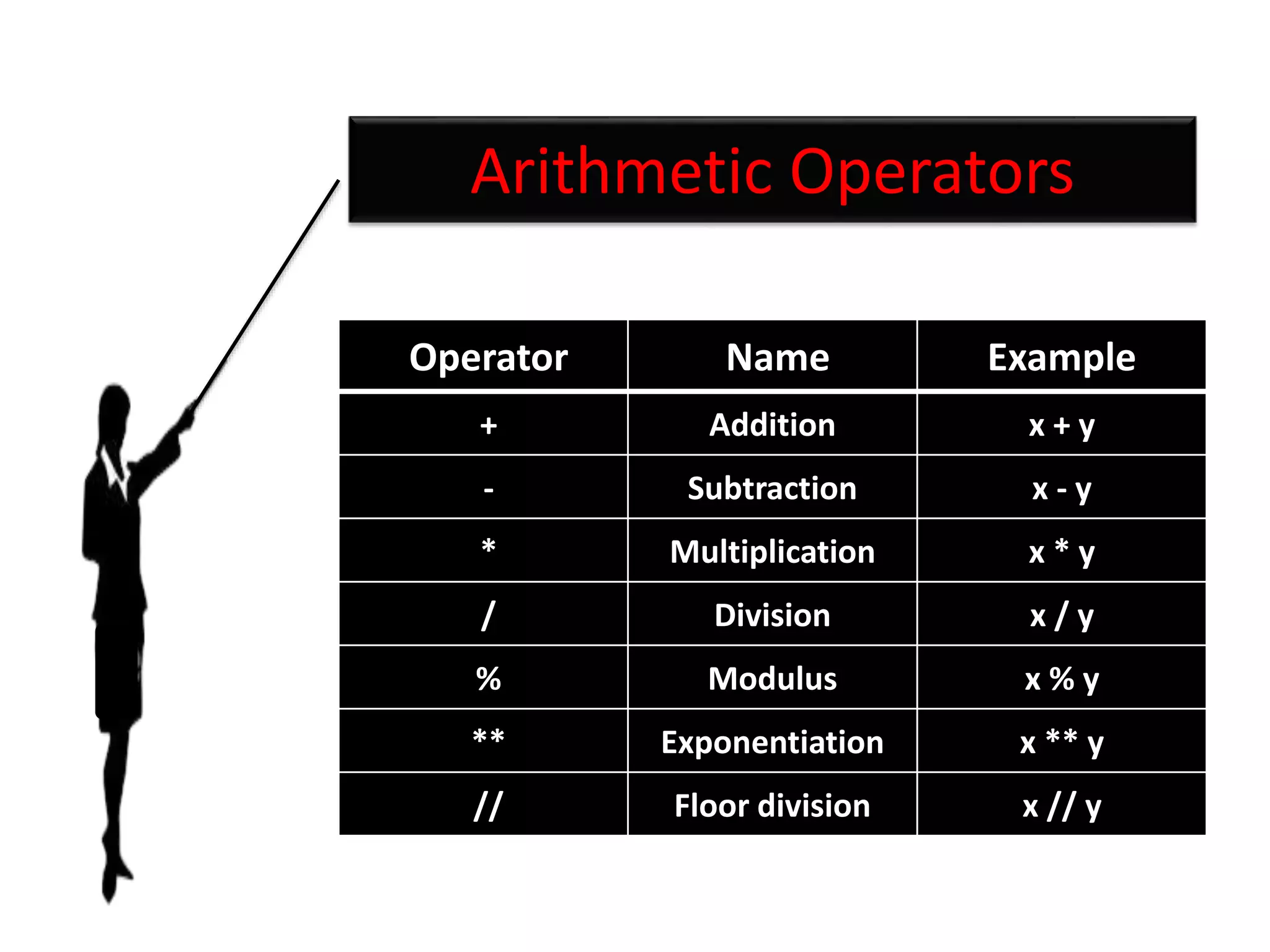
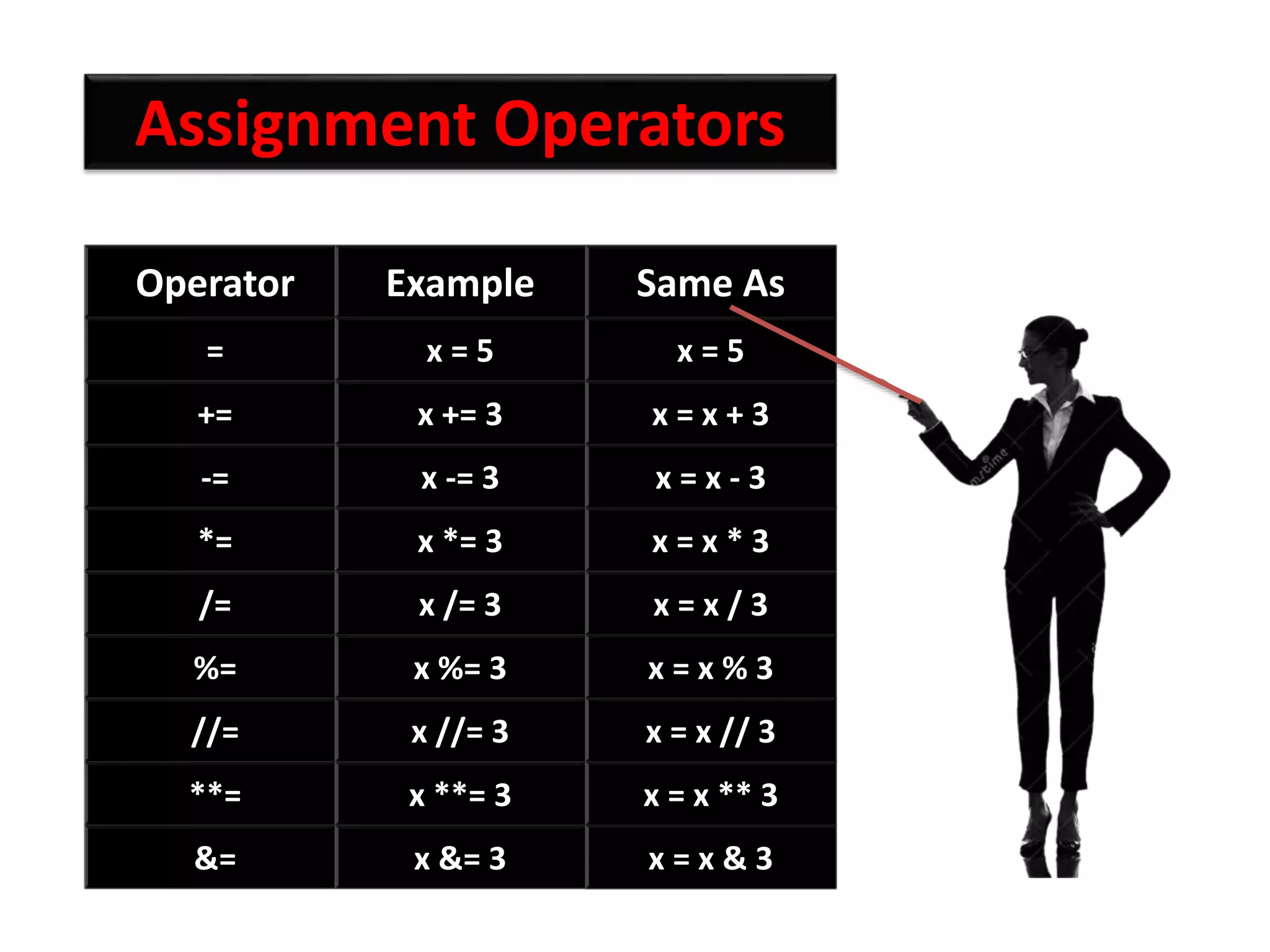
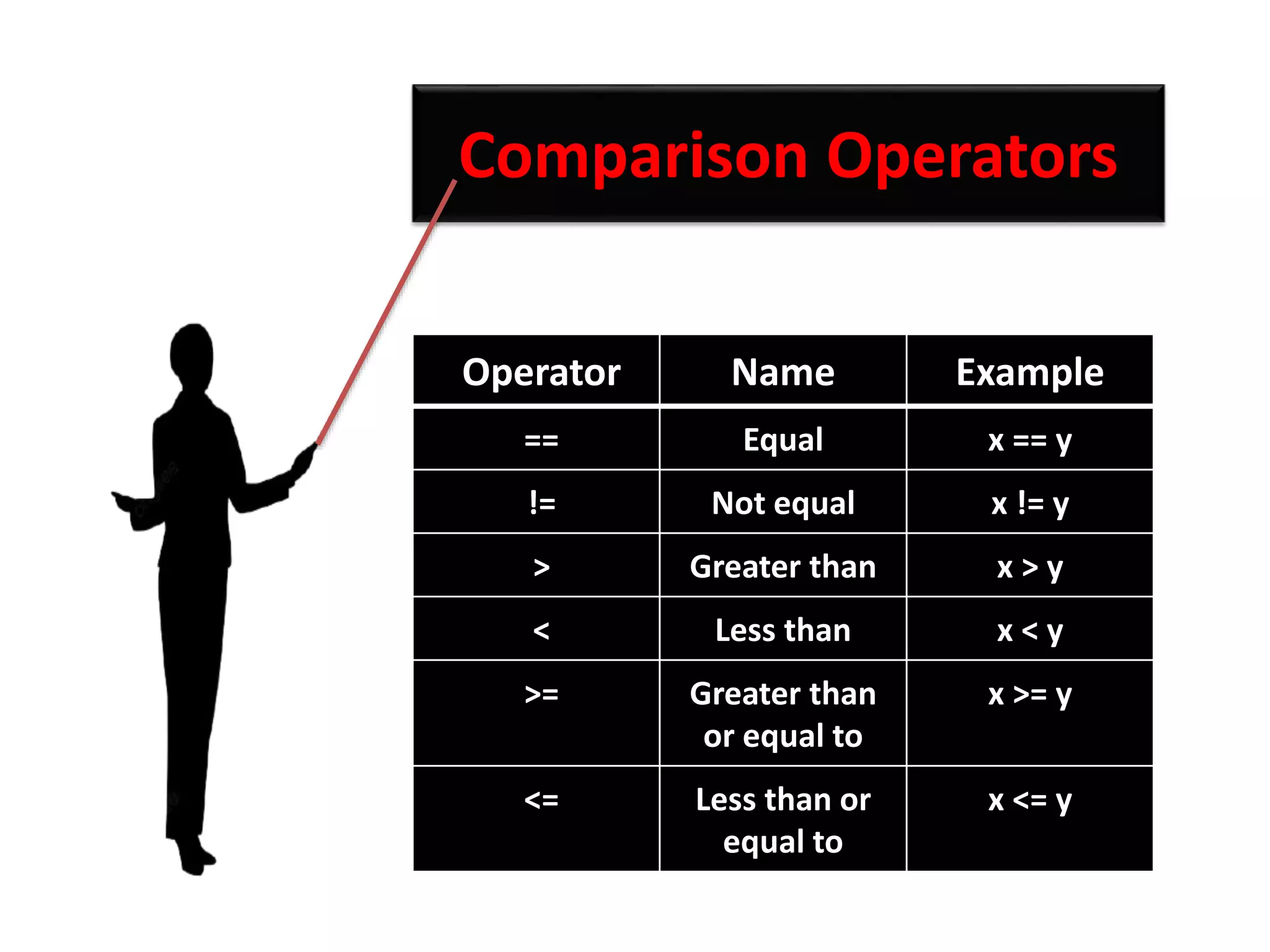
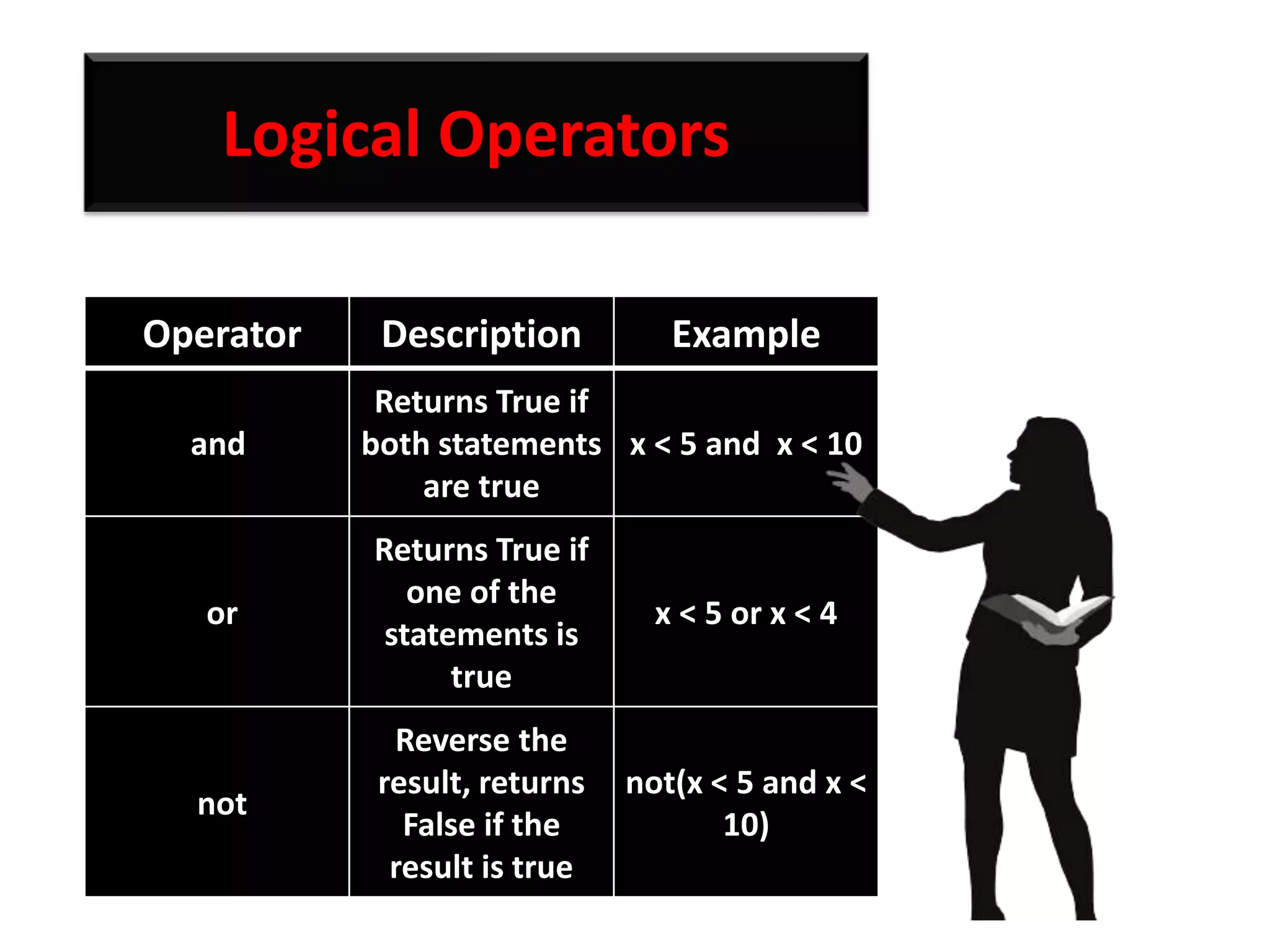
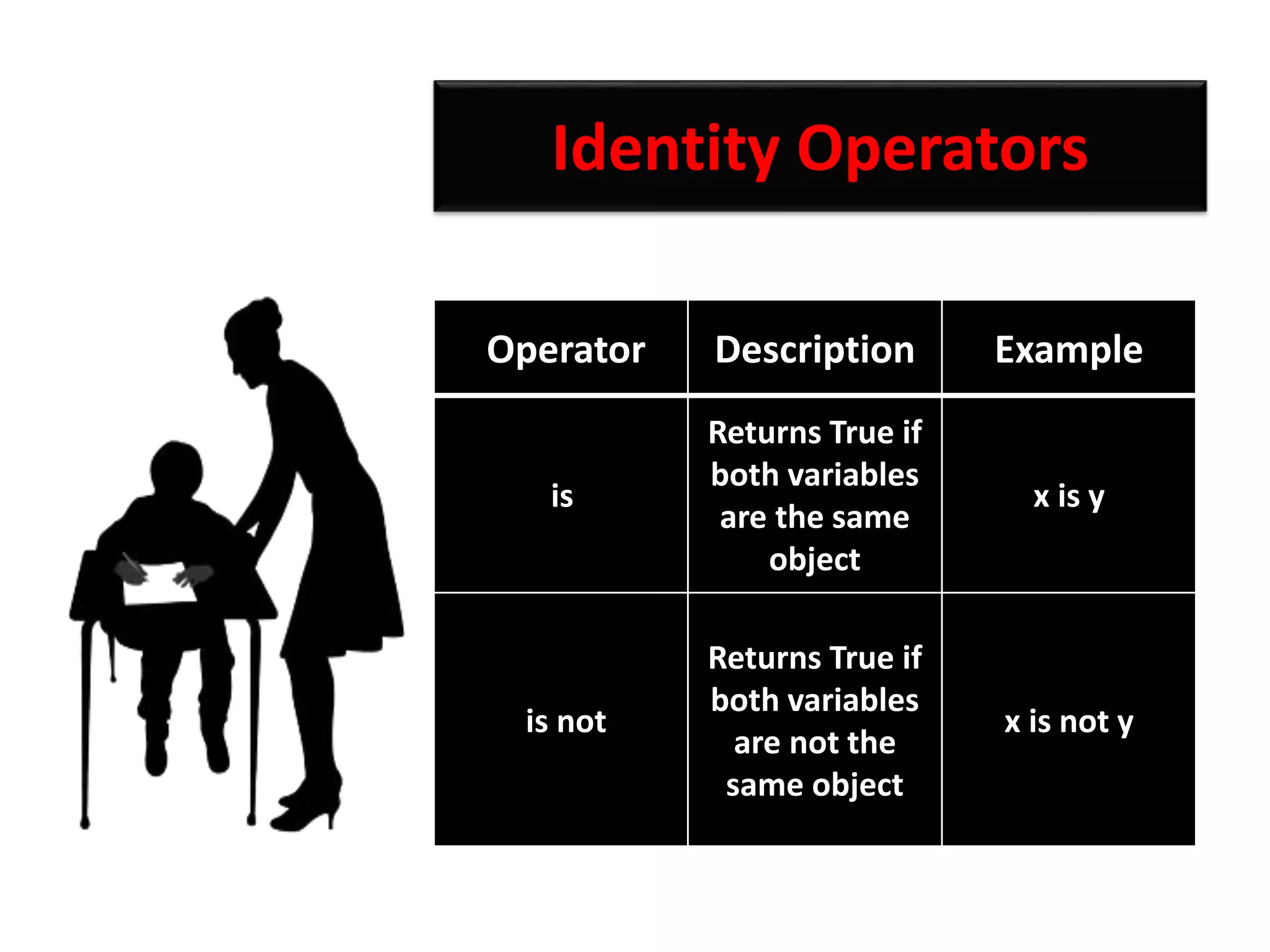
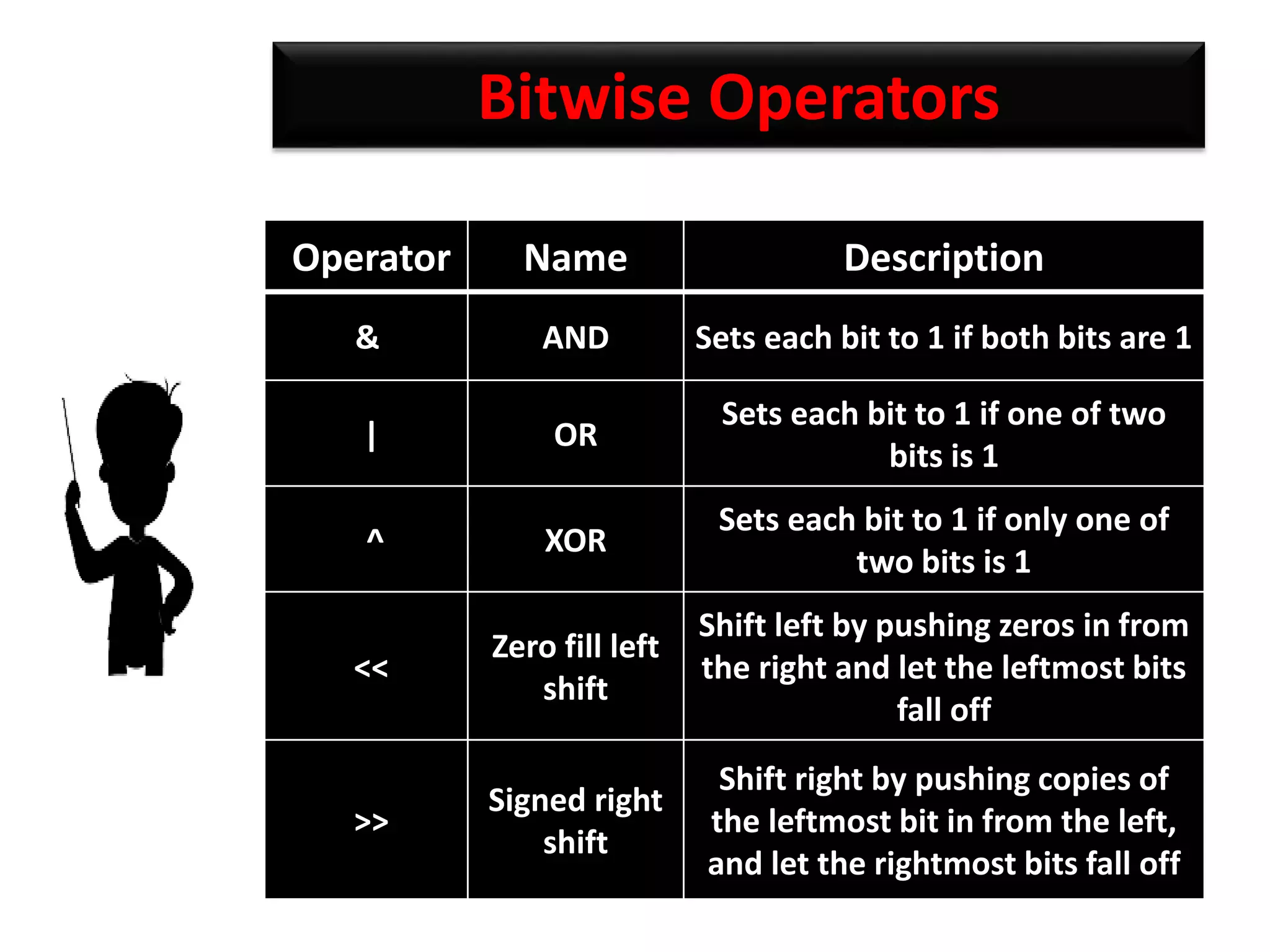
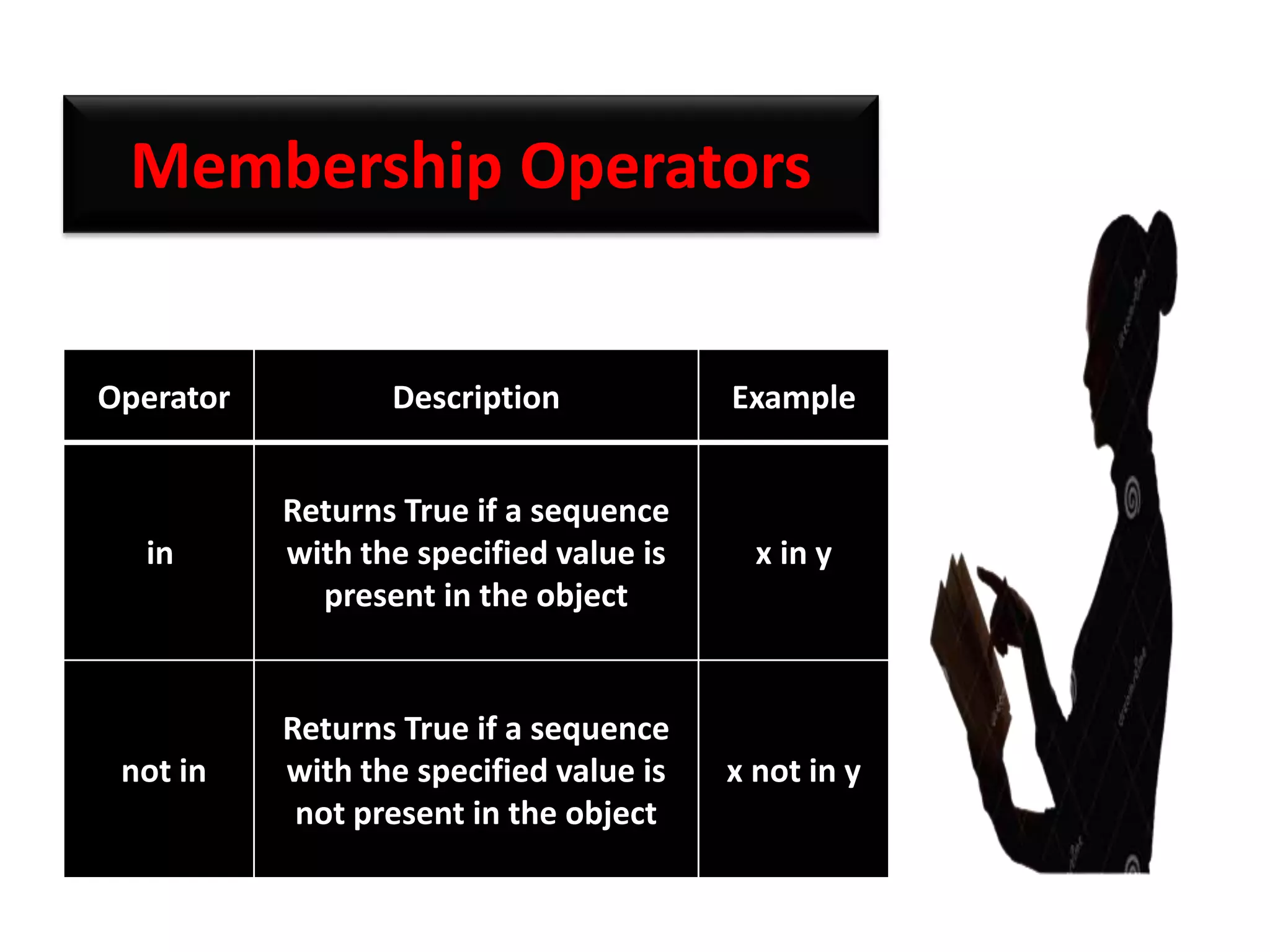
The document provides an overview of Python variables, identifiers, keywords, and various types of operators including arithmetic, comparison, assignment, logical, bitwise, and membership operators. It explains the rules for defining identifiers and the significance of comments in code. Additionally, it touches on the purpose of comments in enhancing code readability for both the original author and other programmers.