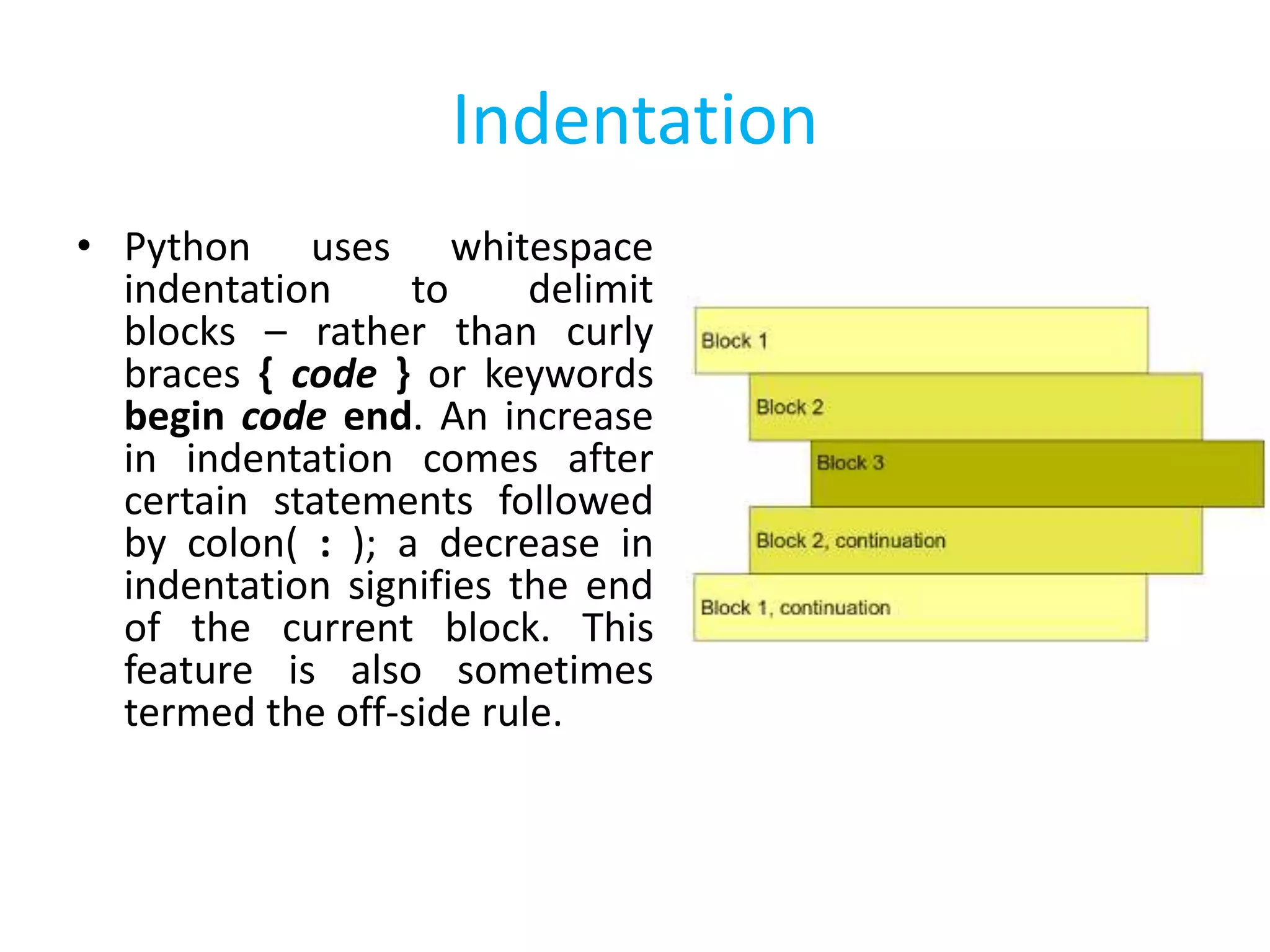
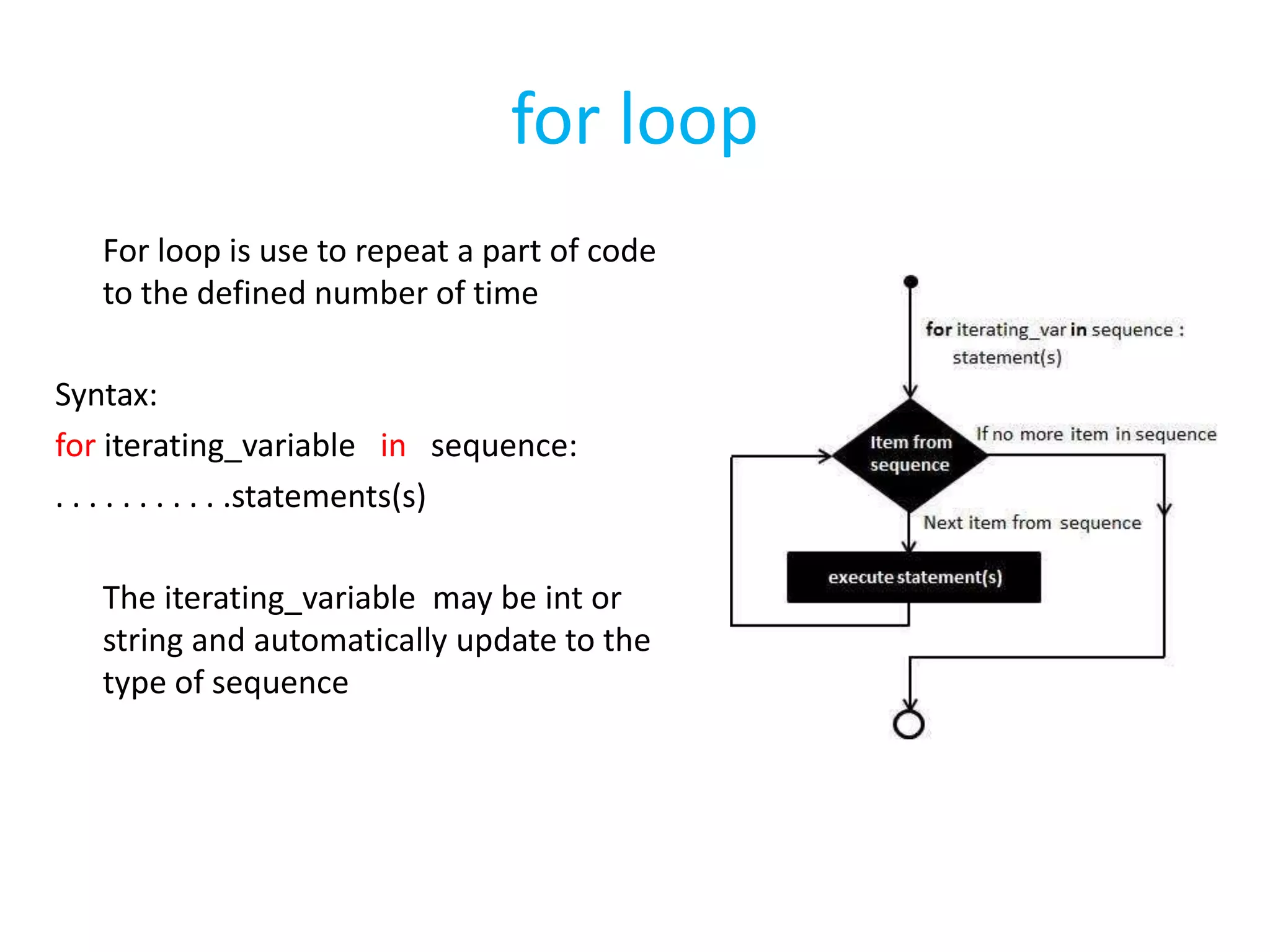
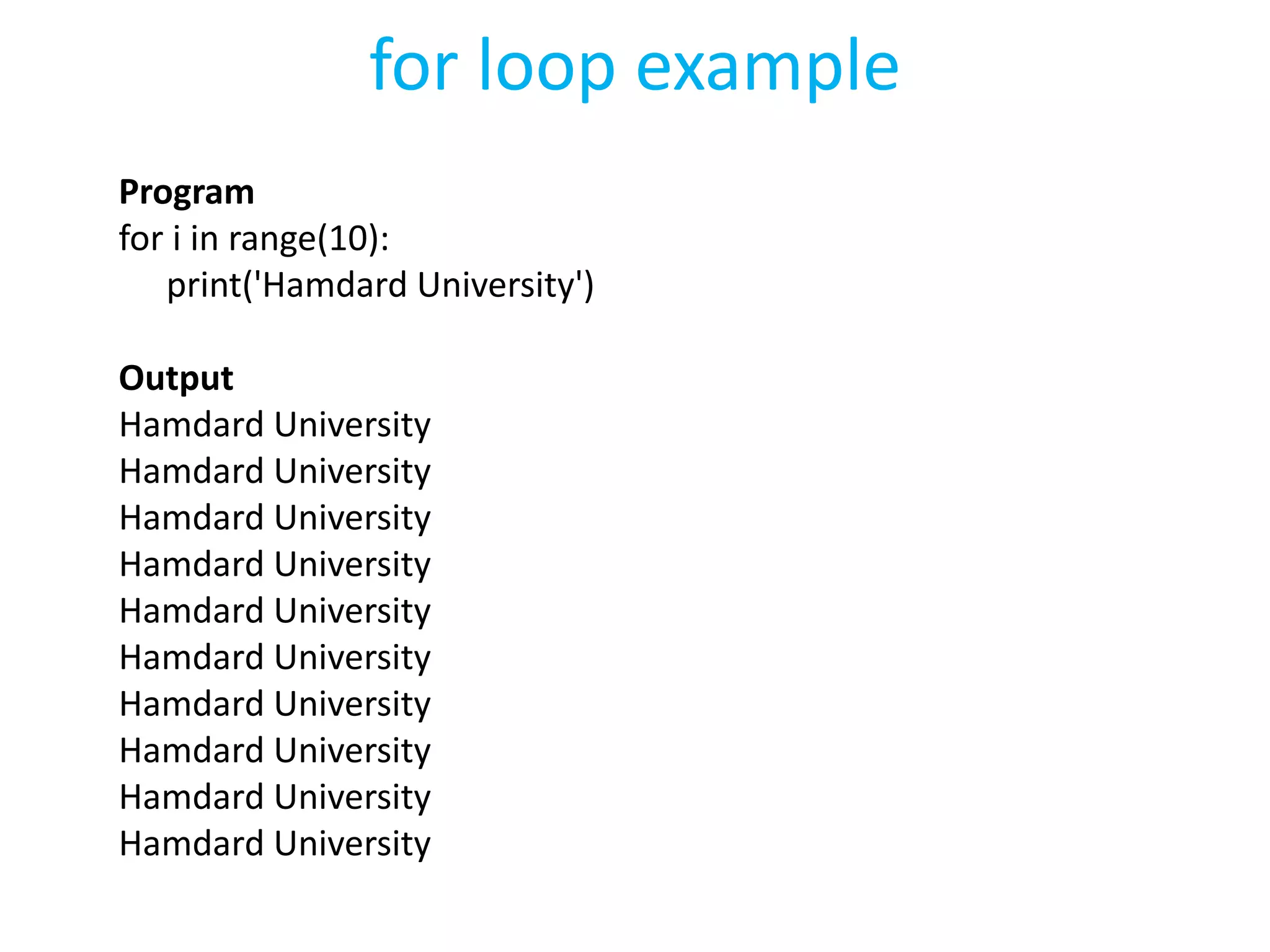
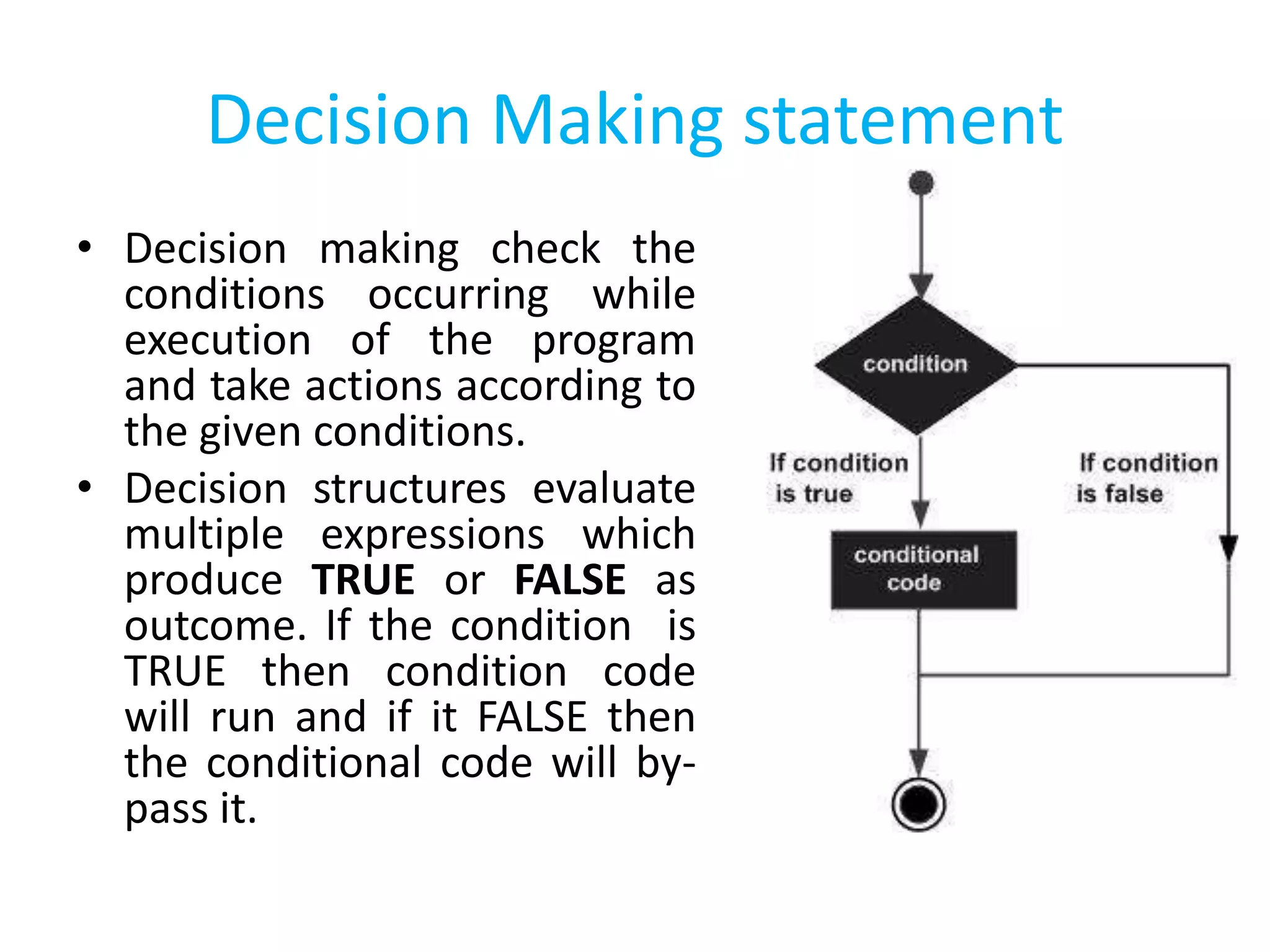
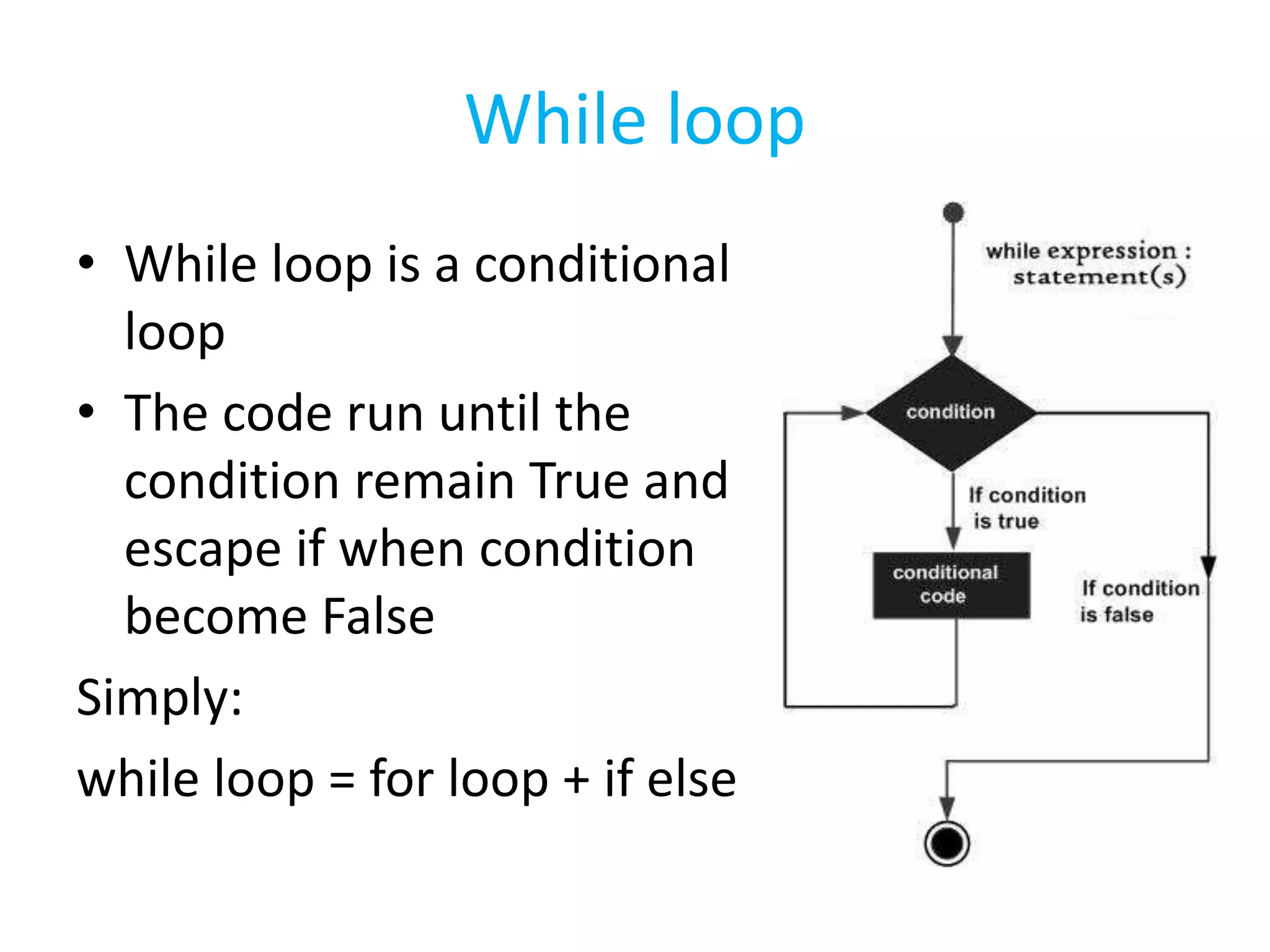
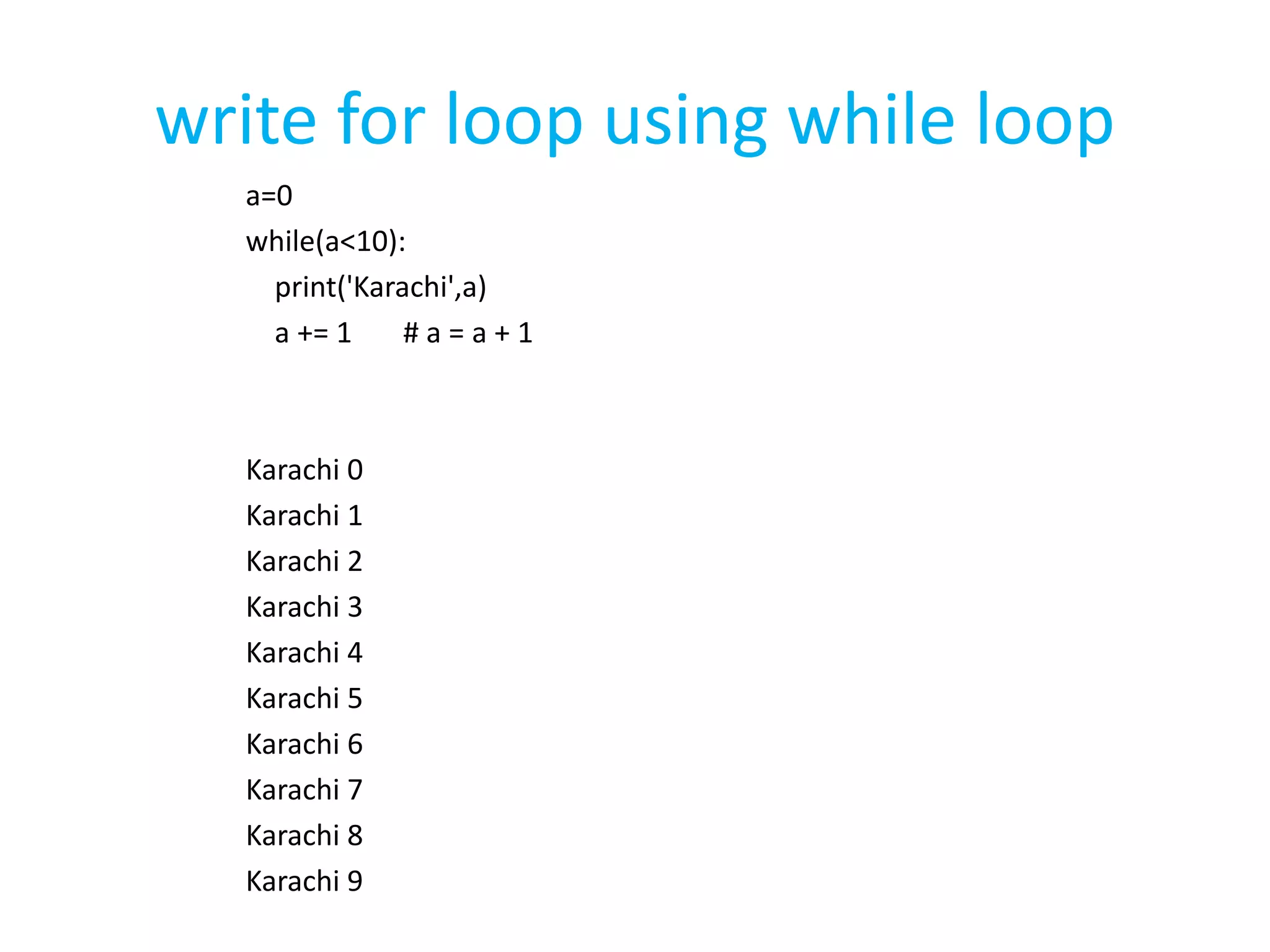
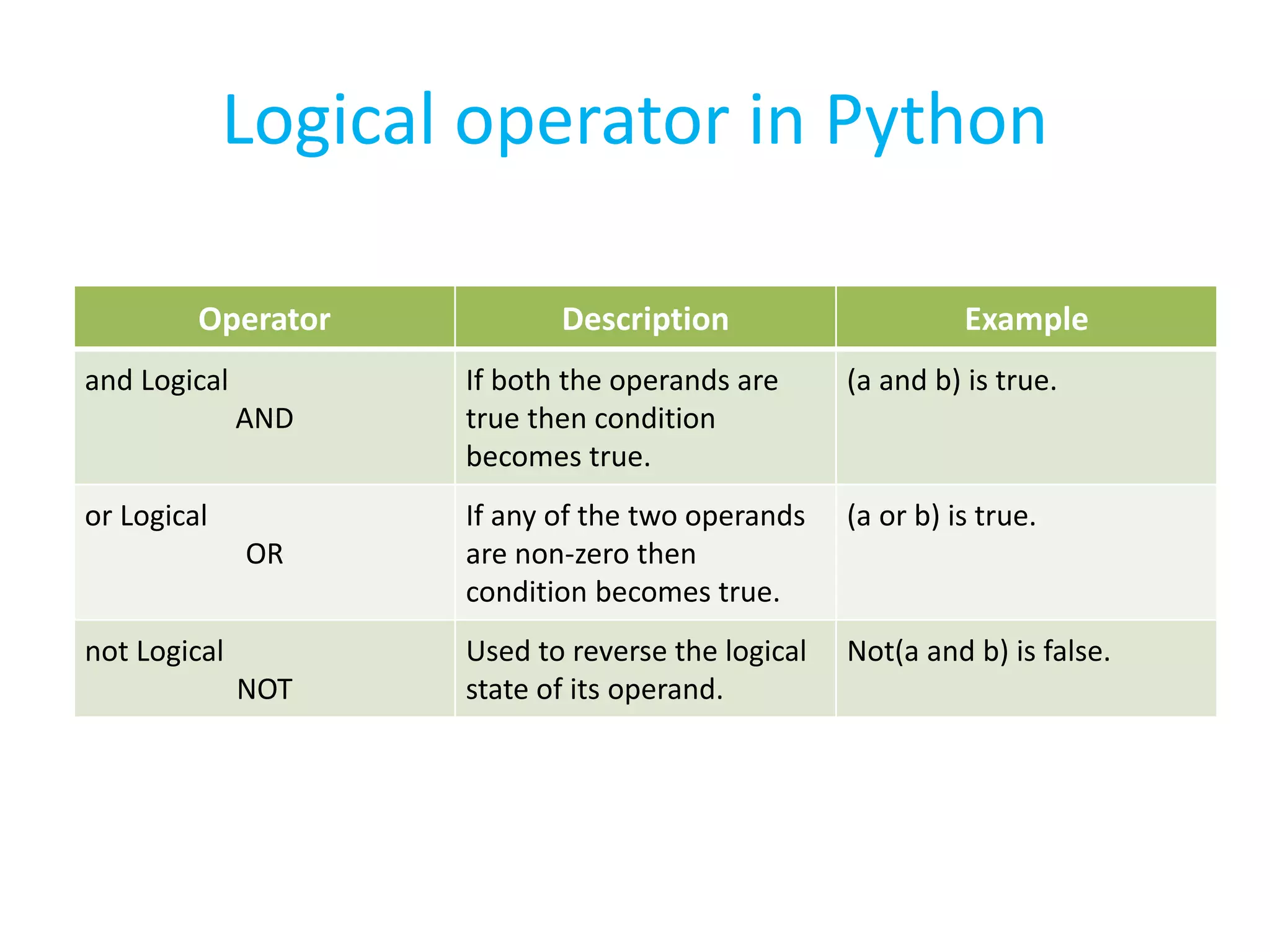
This document summarizes the contents of the second day of a hands-on workshop on the Python programming language. It discusses indentation, the range function, for and while loops, conditional statements like if/elif, and modules for math, time, and random variables. Example code is provided to demonstrate various Python concepts like loops, logical operators, and comparisons between Python and C/C++ programming.


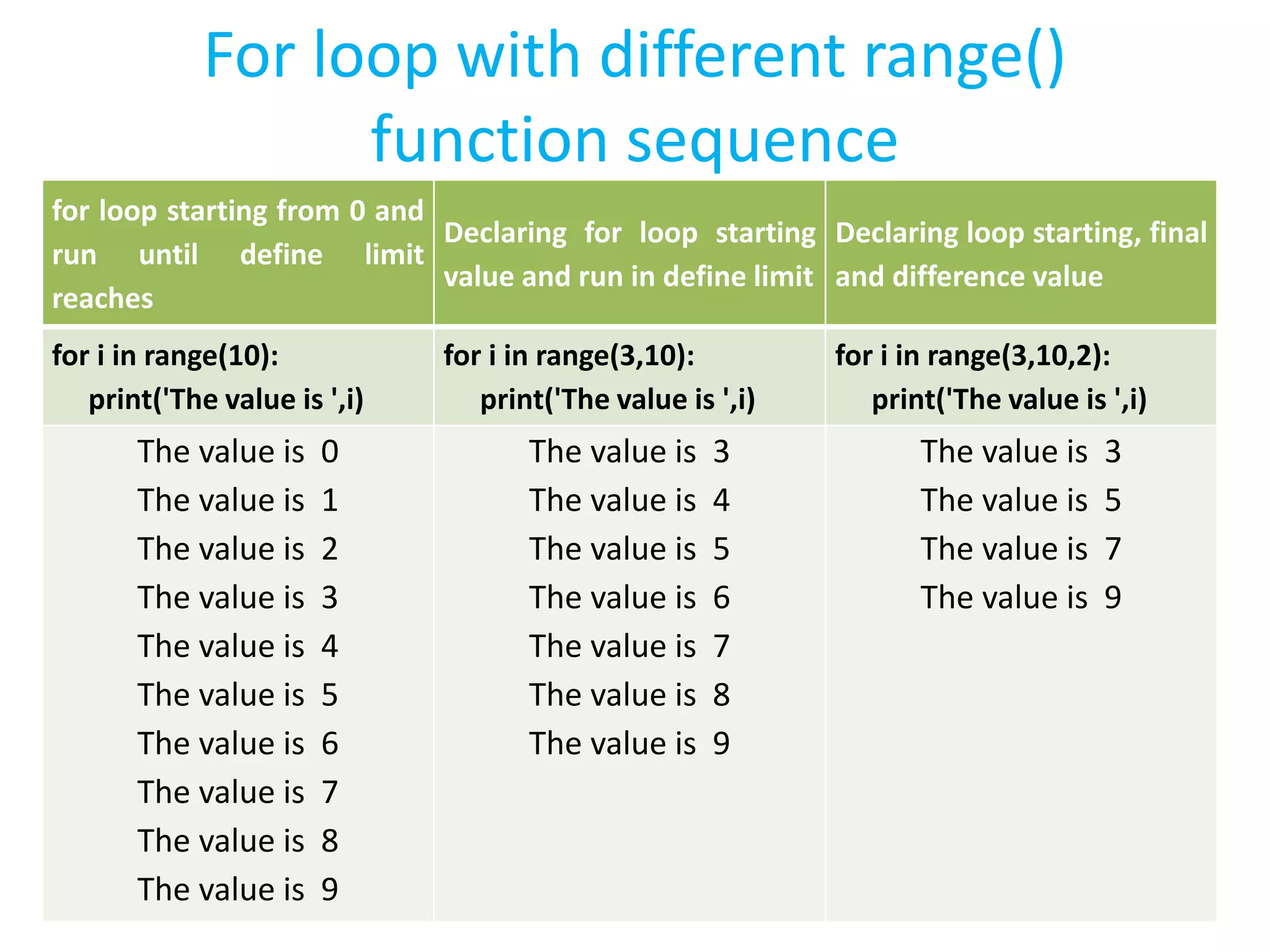
![• range(stop) -> list of integers >>> list(range(10)) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] • range(start, stop) -> list of integers >>> list(range(2,10)) [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] • range(start, stop, step) -> list of integers >>> list(range(2,10,3)) [2, 5, 8] The range() function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingworkshopsession2-180918150731/75/Python-programming-workshop-session-2-5-2048.jpg)










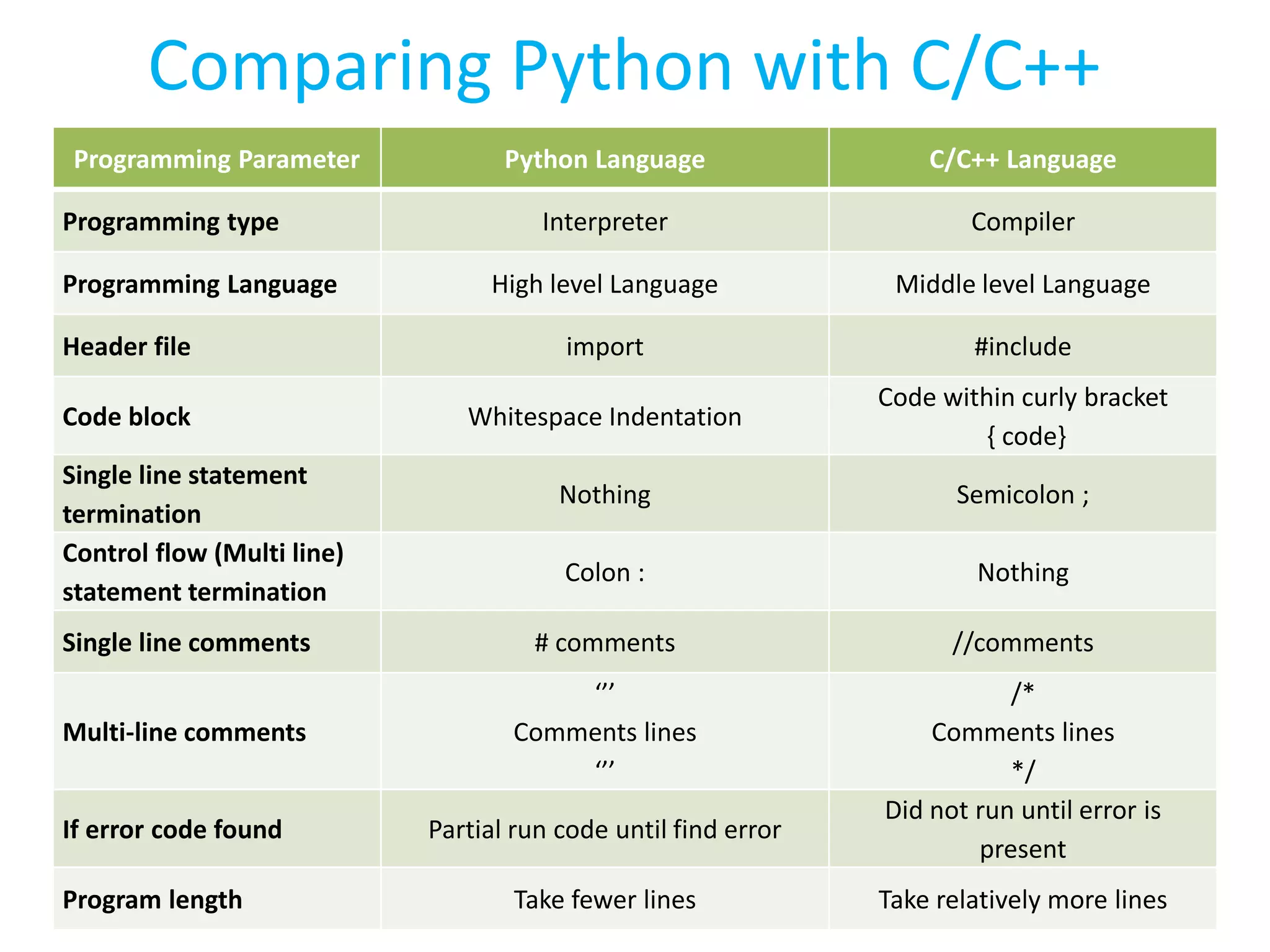
![Python Programming code comparison with C programming code Python program C/C++ program Multi-line comments Including library Declaring variable Multi-line statement Code Block Single-line statement Single line comments ‘’’ The Python Language Example code ’’’ Import time a=10 #integer value name = 'karachi' #String for i in range (a): print("Hamdard") print('University') print(name) #program end /* The C/C++ language Example code */ #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int a = 10; char name[10] = "Karachi"; for(int i =0 ; i <a ; i ++ ) { cout<<"Hamdard "; cout<<"University"<<endl; } cout<<name; return 0; } //program end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingworkshopsession2-180918150731/75/Python-programming-workshop-session-2-27-2048.jpg)
