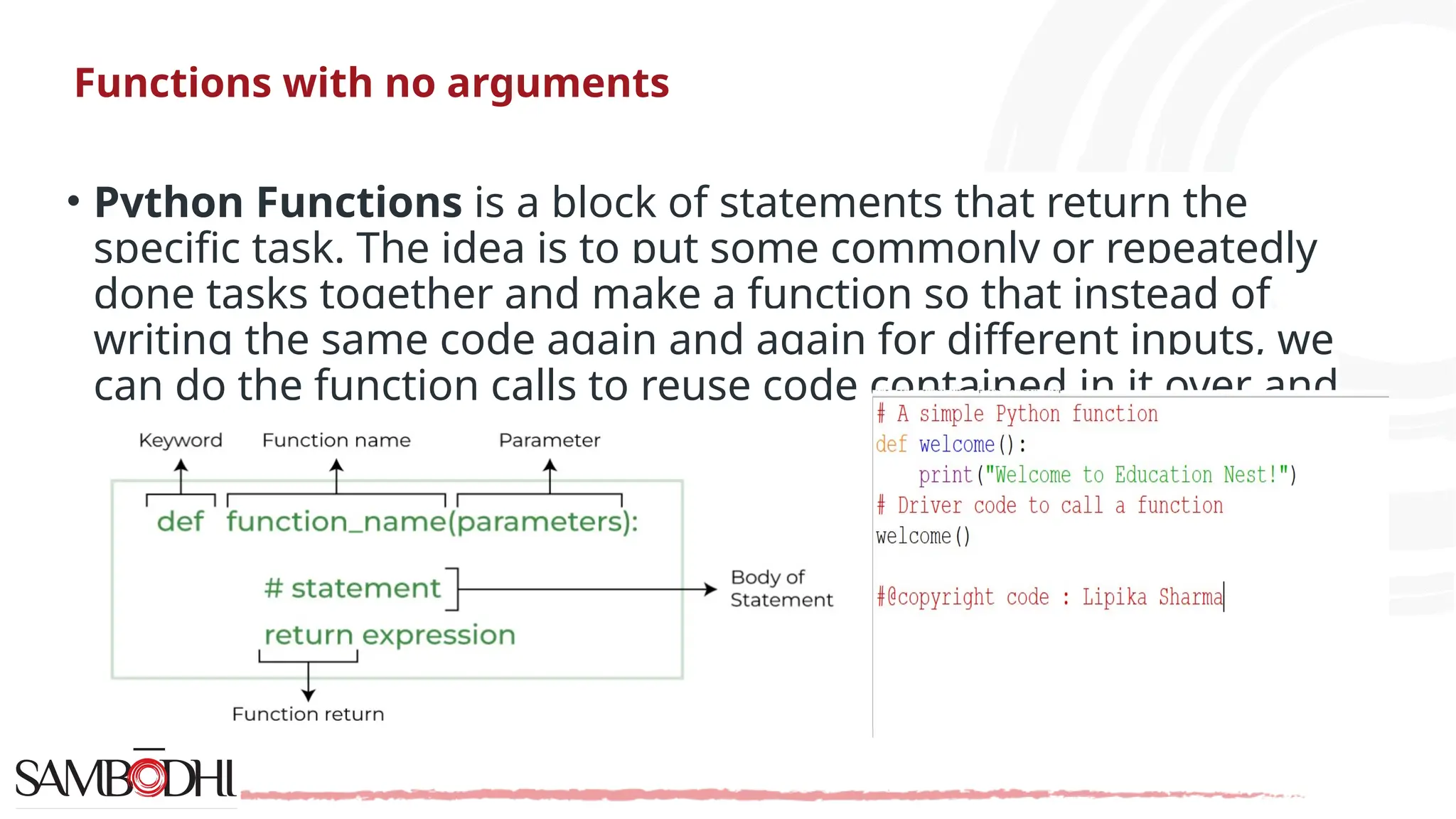
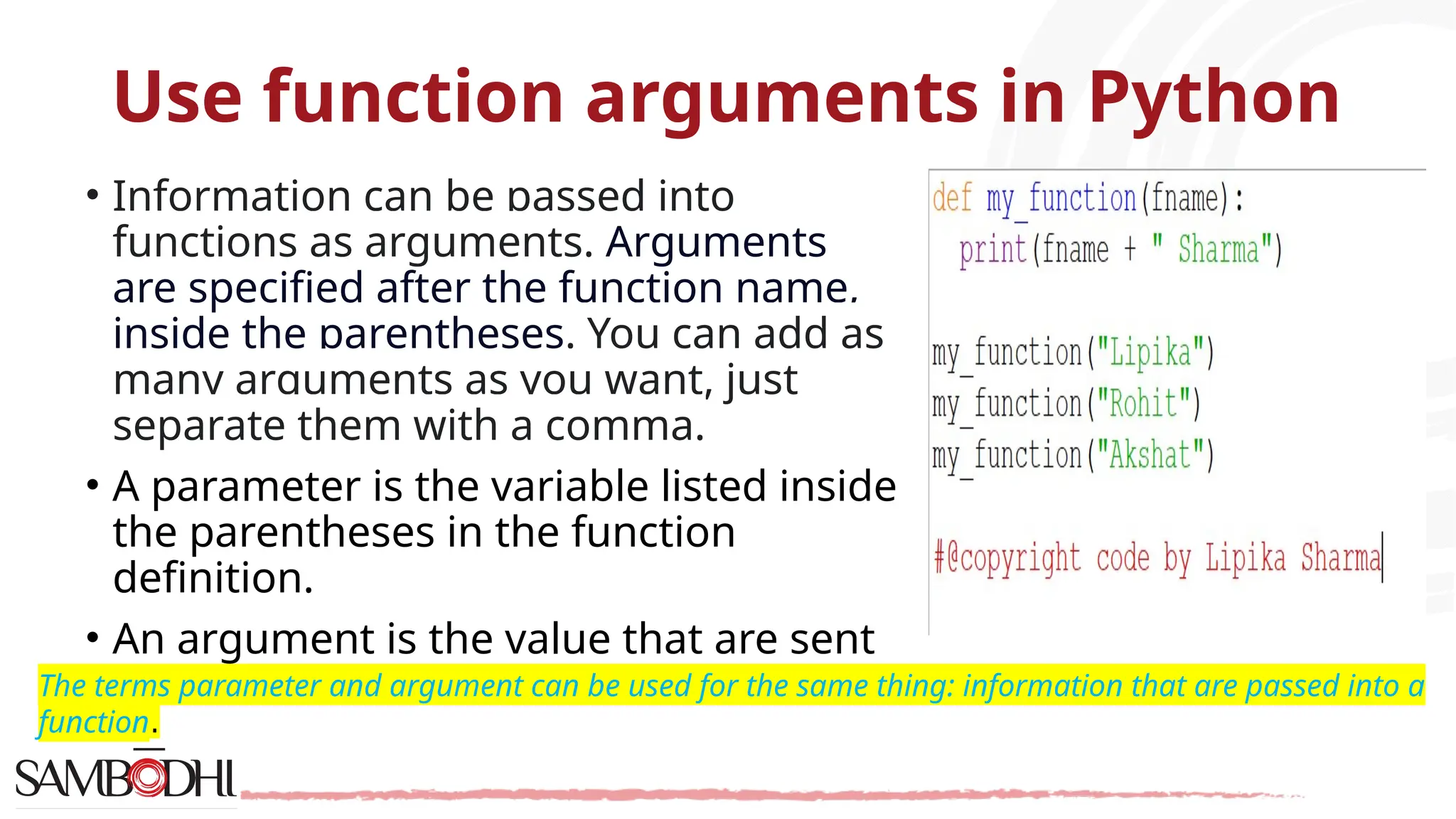
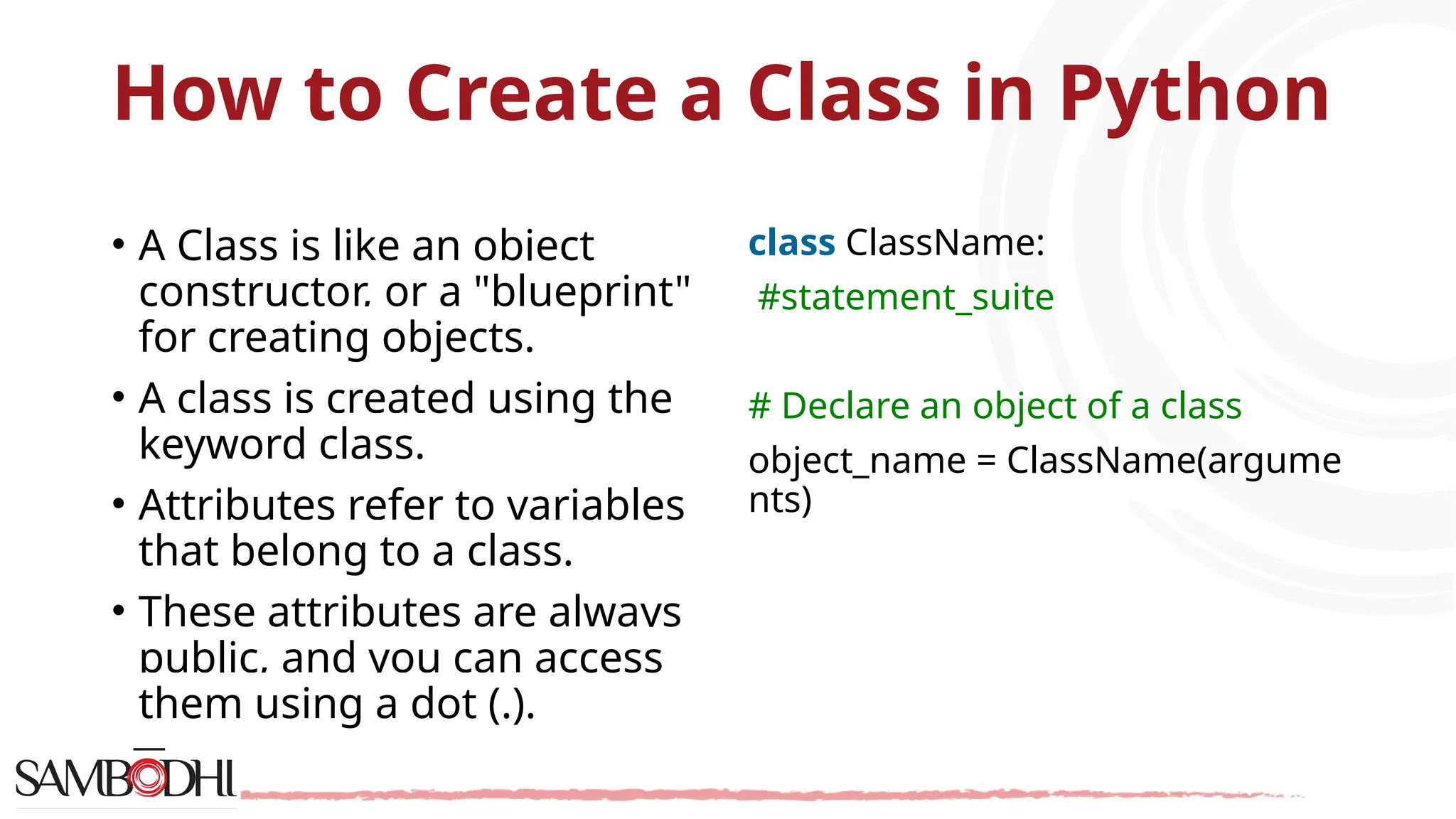
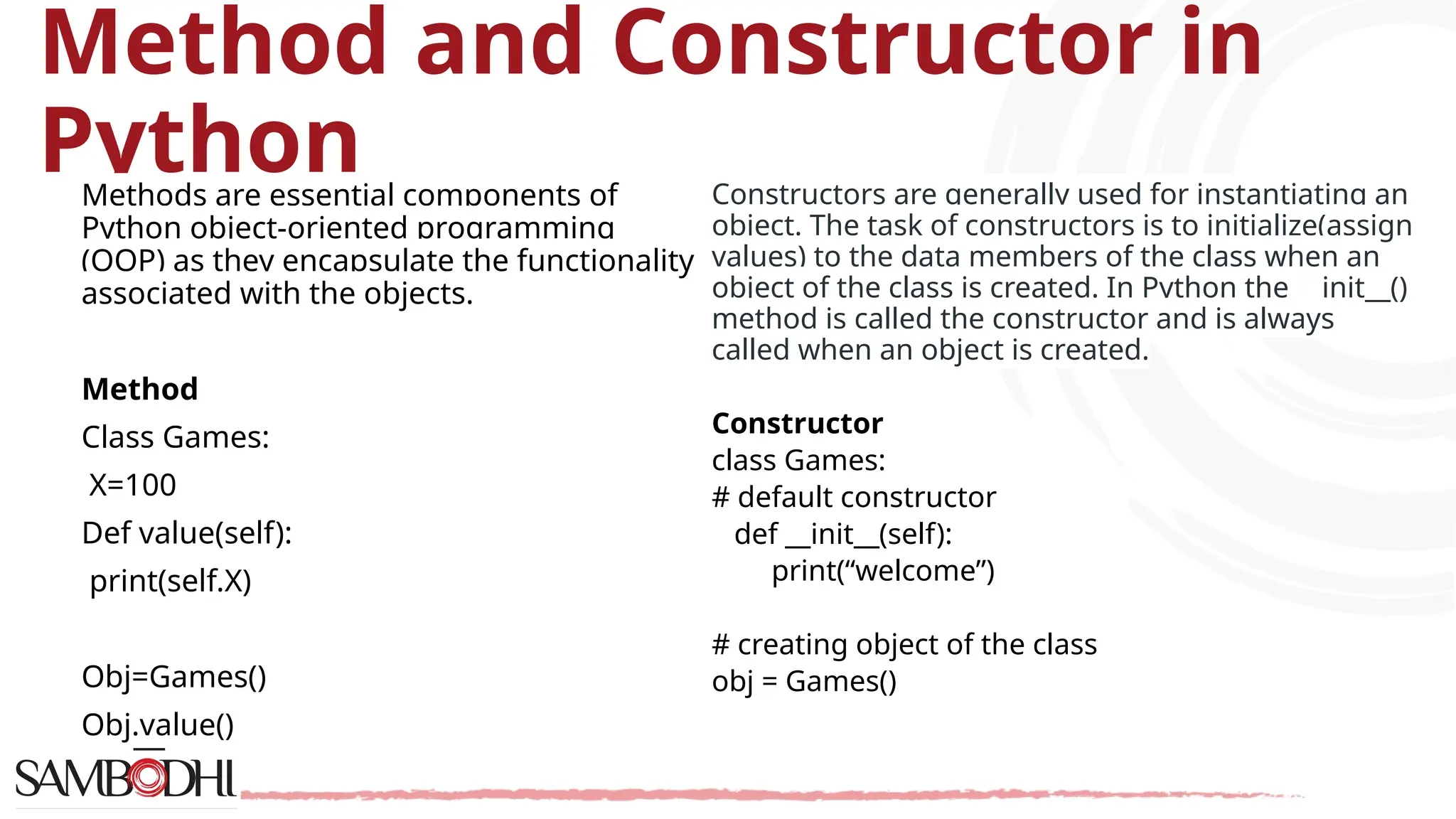
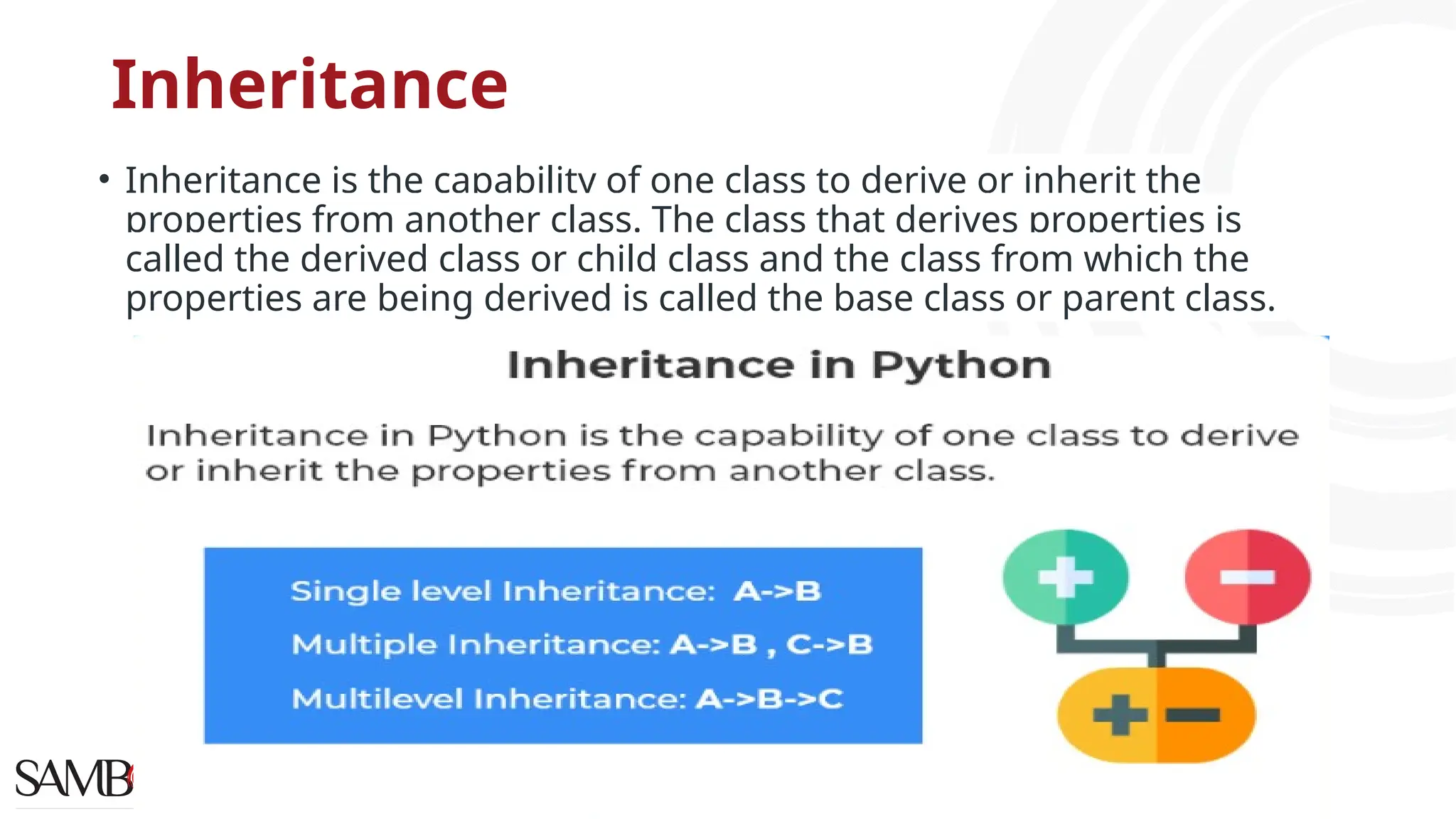
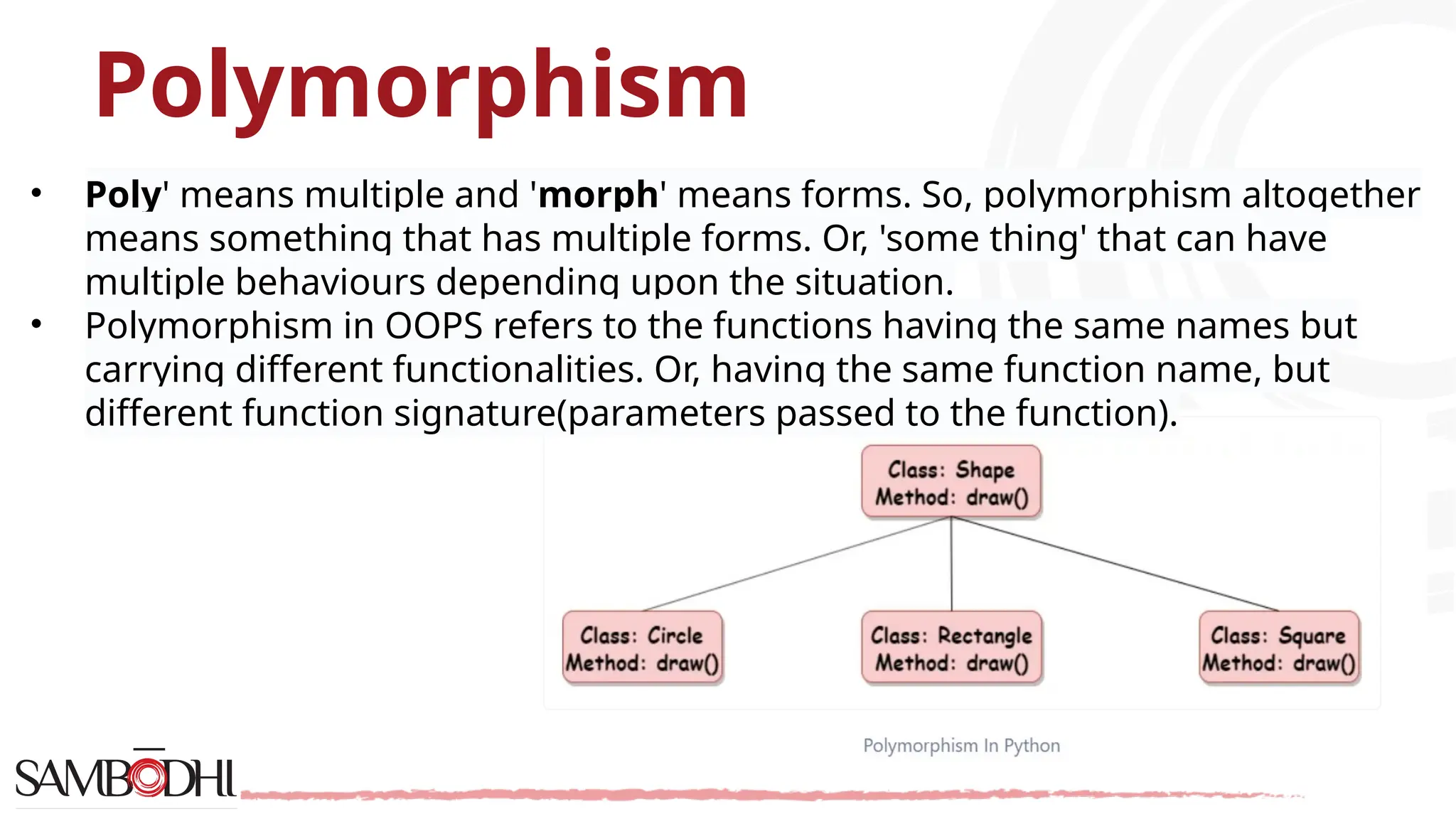
The document provides an overview of Python programming concepts relevant to data science, including functions, object-oriented programming (OOP) principles like inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, and abstraction. It explains how to create classes and methods in Python, the importance of constructors, and the usage of arguments in functions. Additionally, it includes a Q&A section addressing access specifiers and the differences between abstract classes and interfaces.