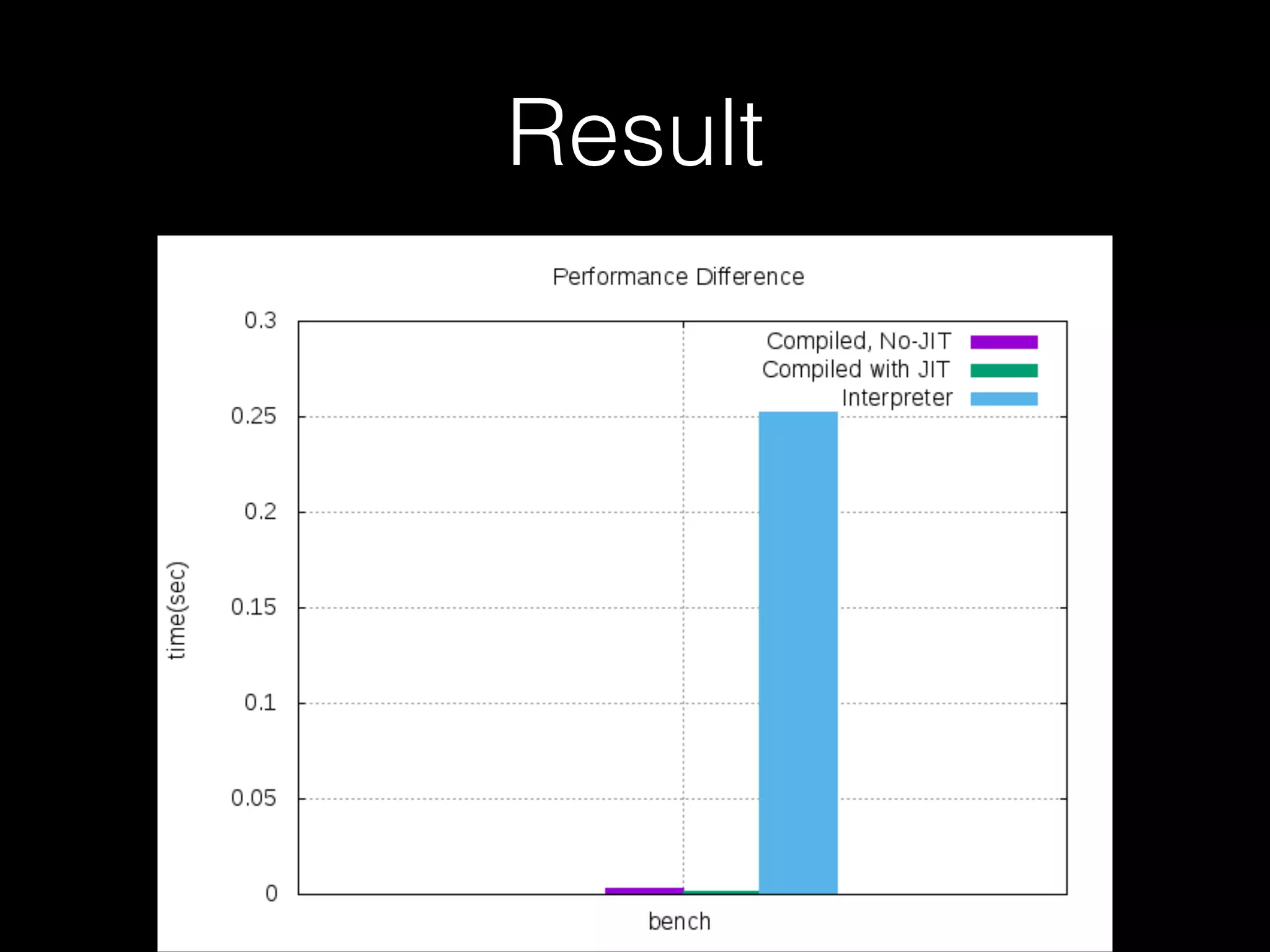
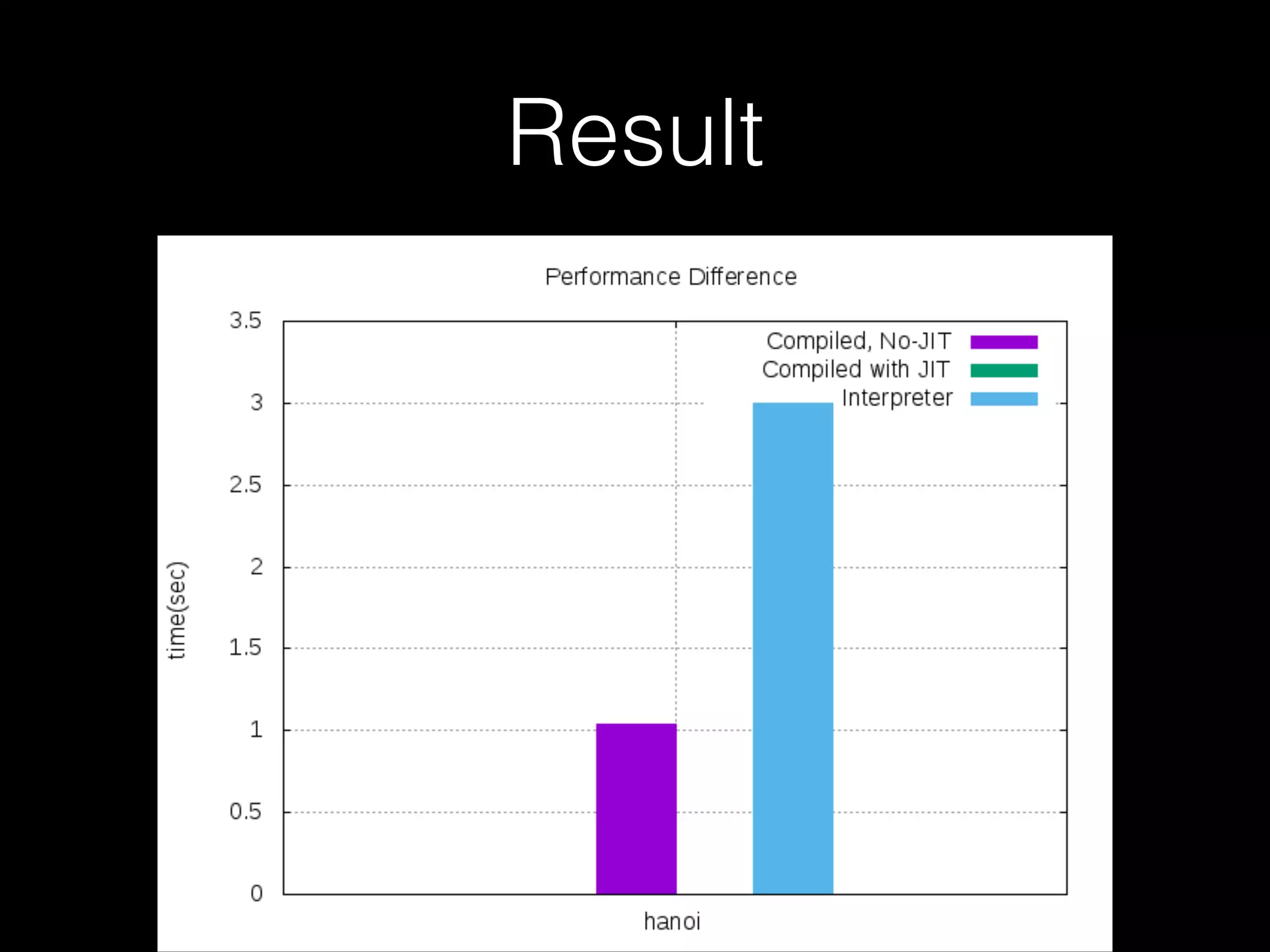
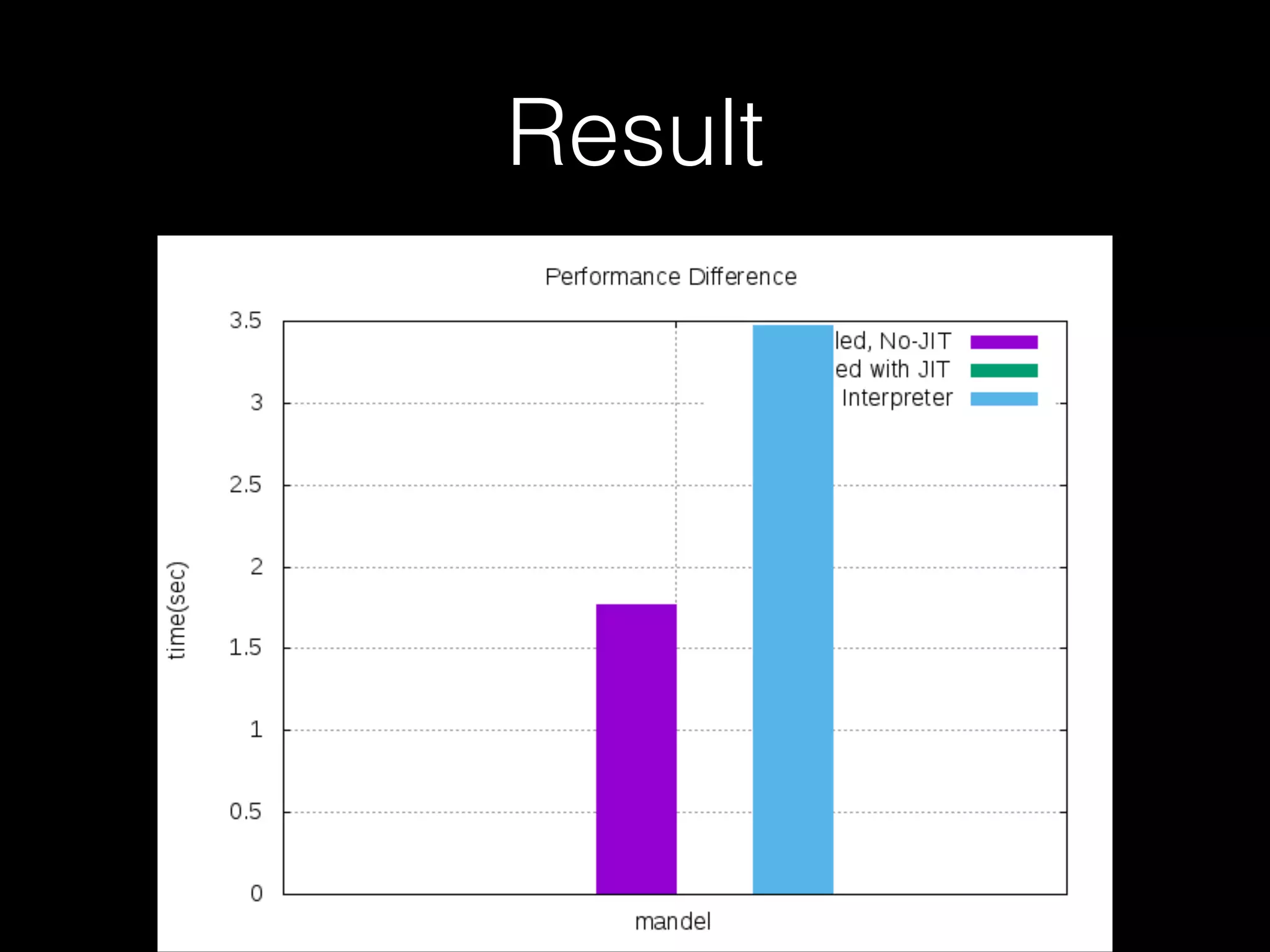
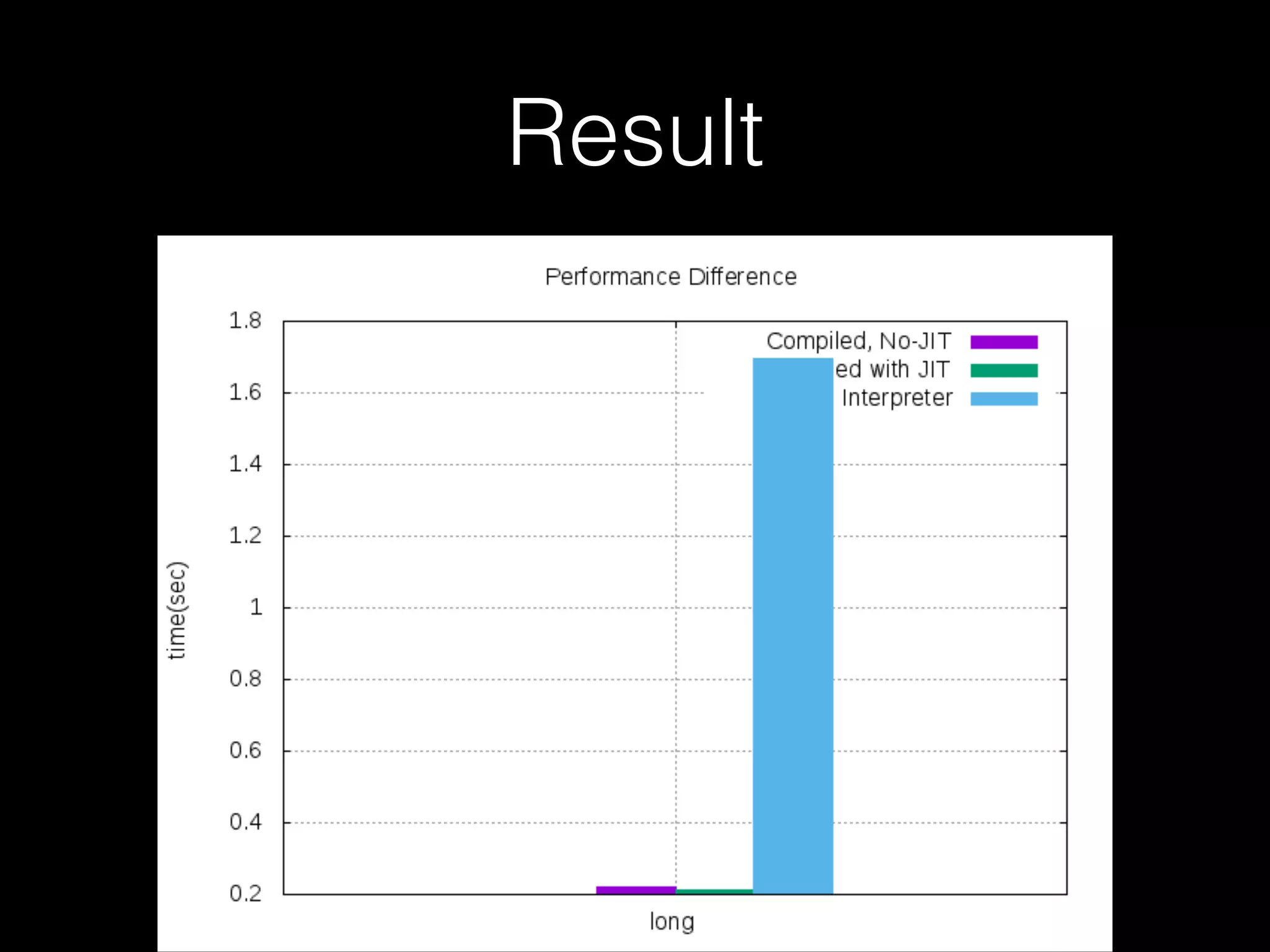
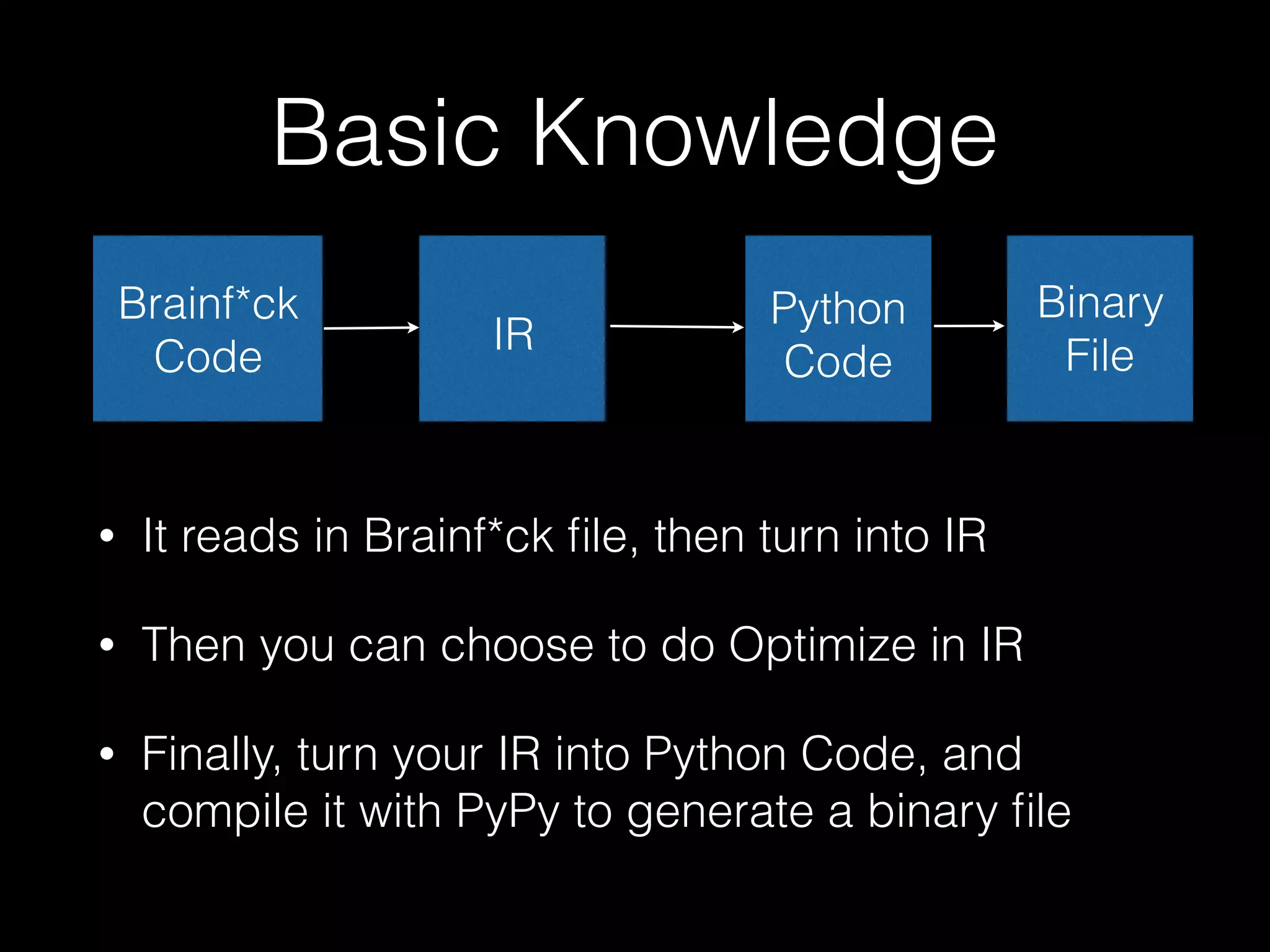
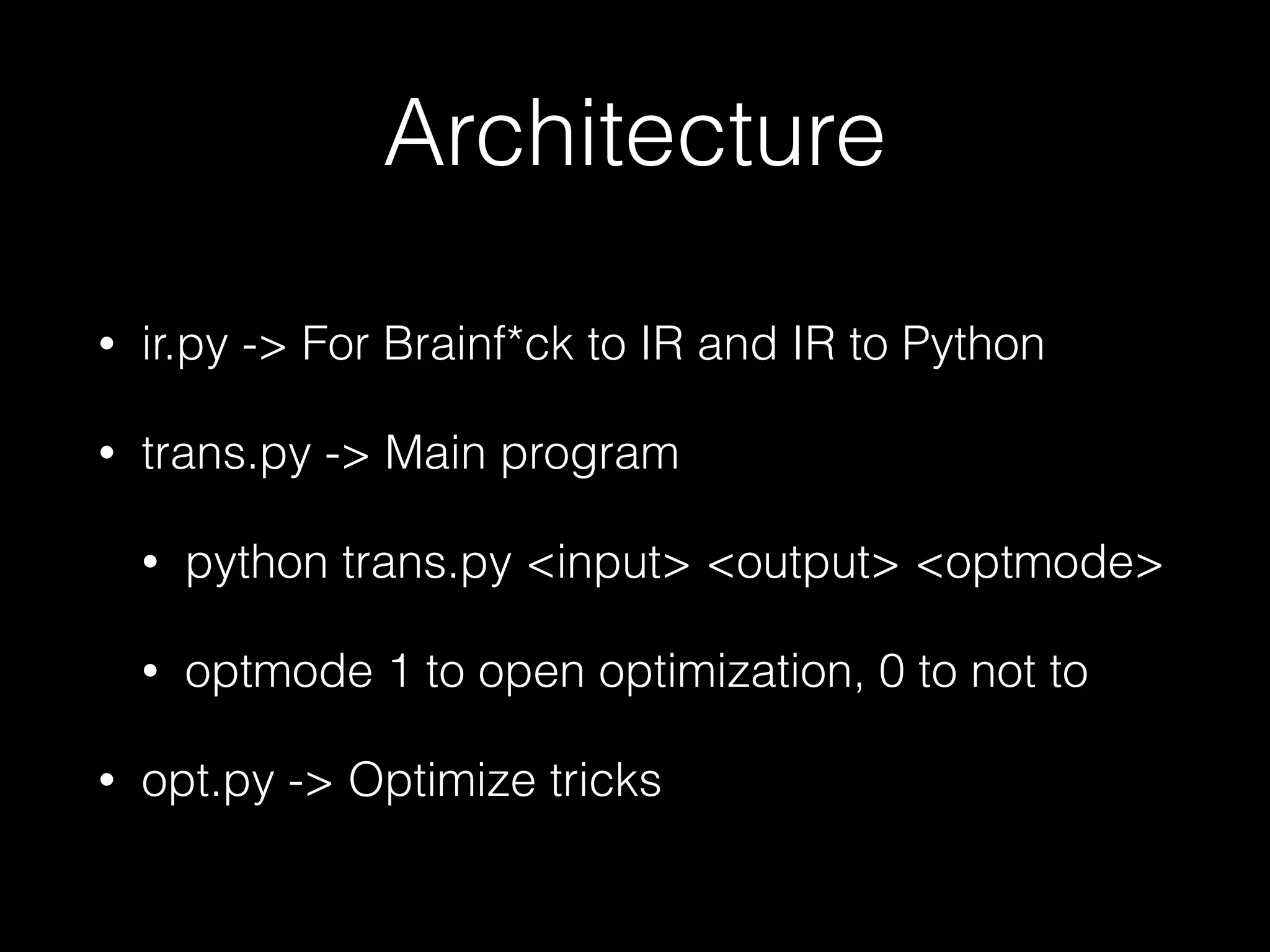
The document discusses a testing environment setup for benchmarking Python interpreters, focusing on CPython and PyPy, along with the nuances of installation and optimization techniques. It explores the challenges and advantages of using PyPy, including Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation and specific optimizations applicable to a Brainfuck interpreter construction project. The text emphasizes that while JIT can enhance performance, it is not universally beneficial and requires analysis of individual project needs.













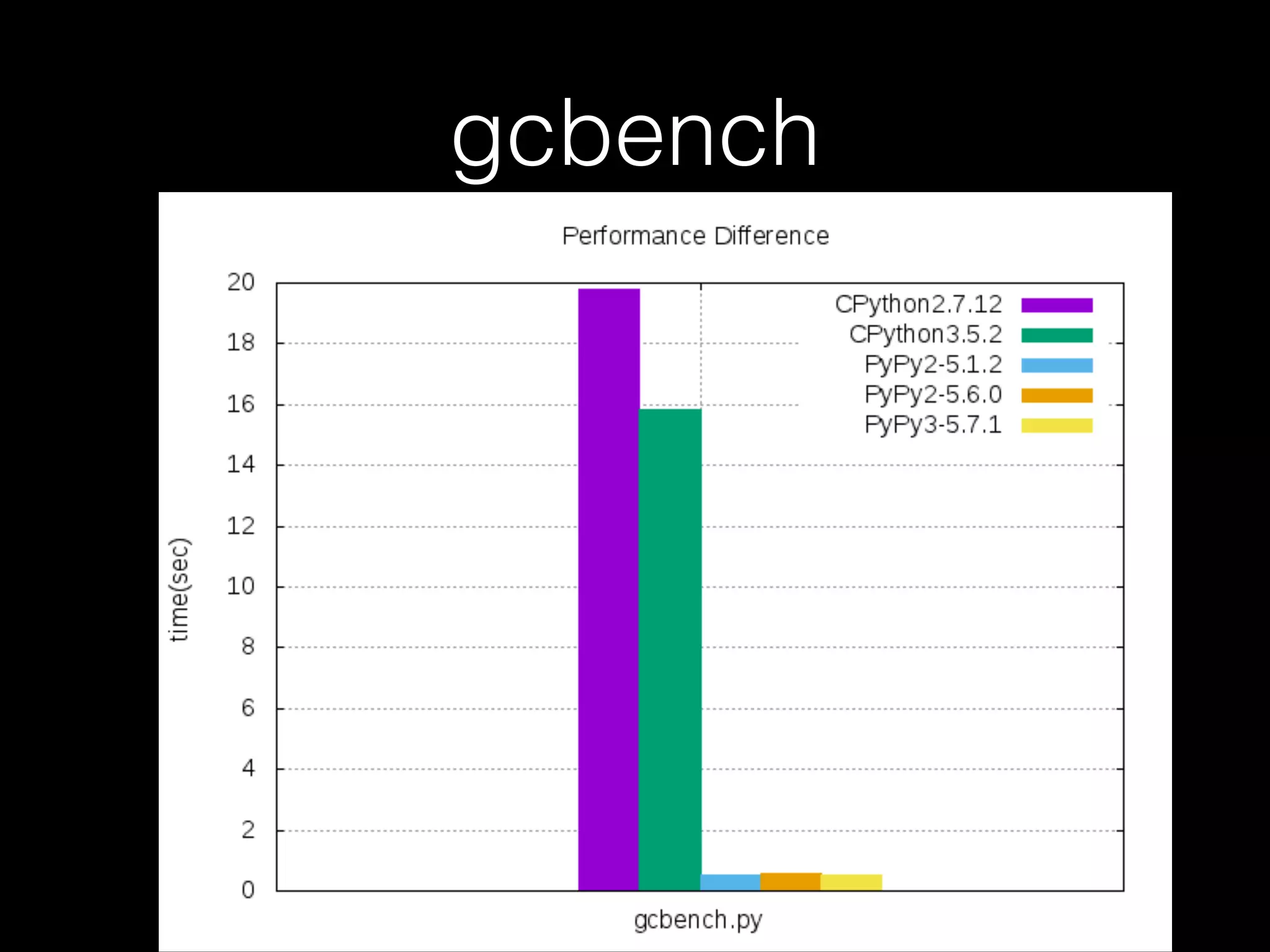
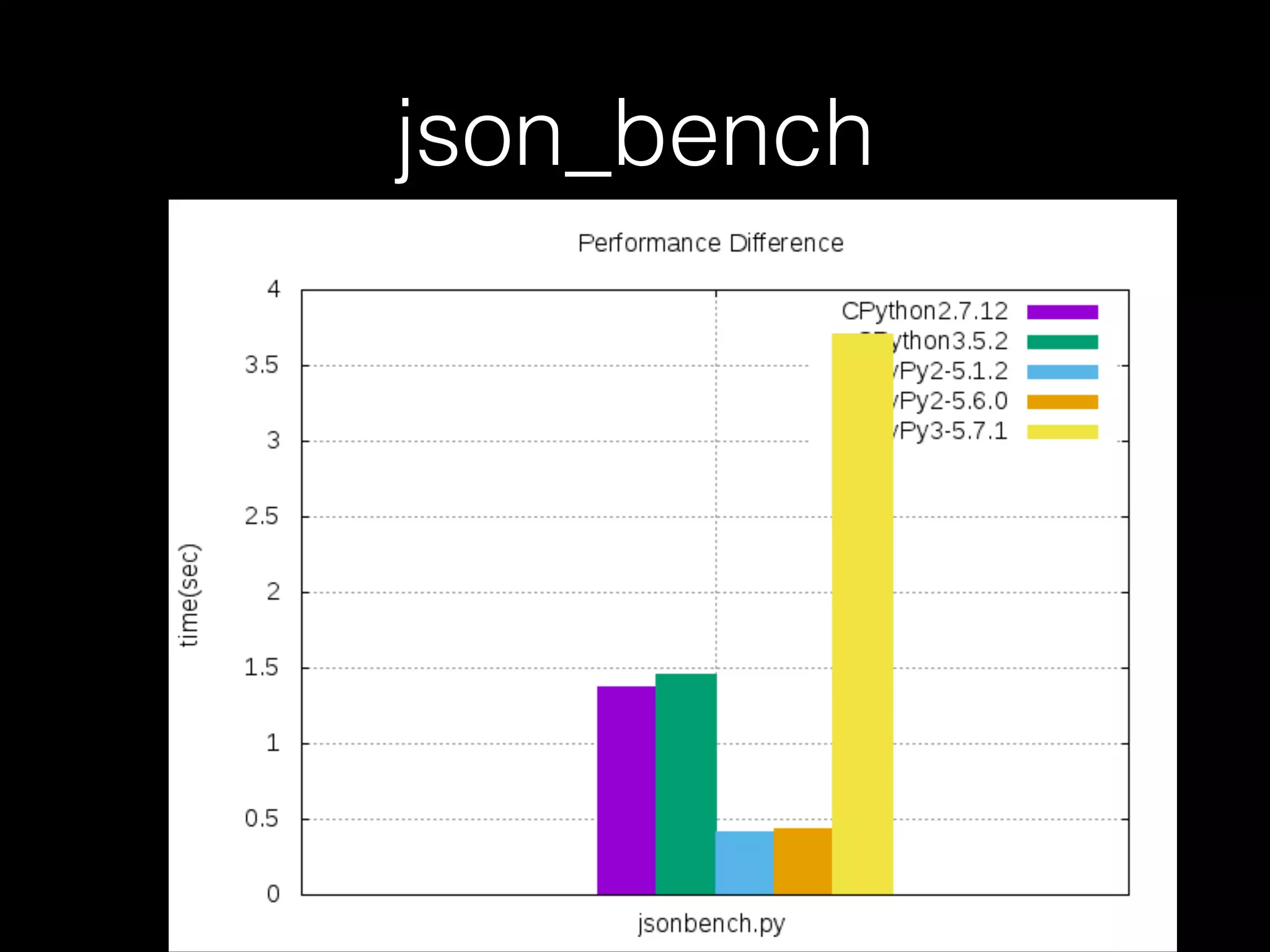
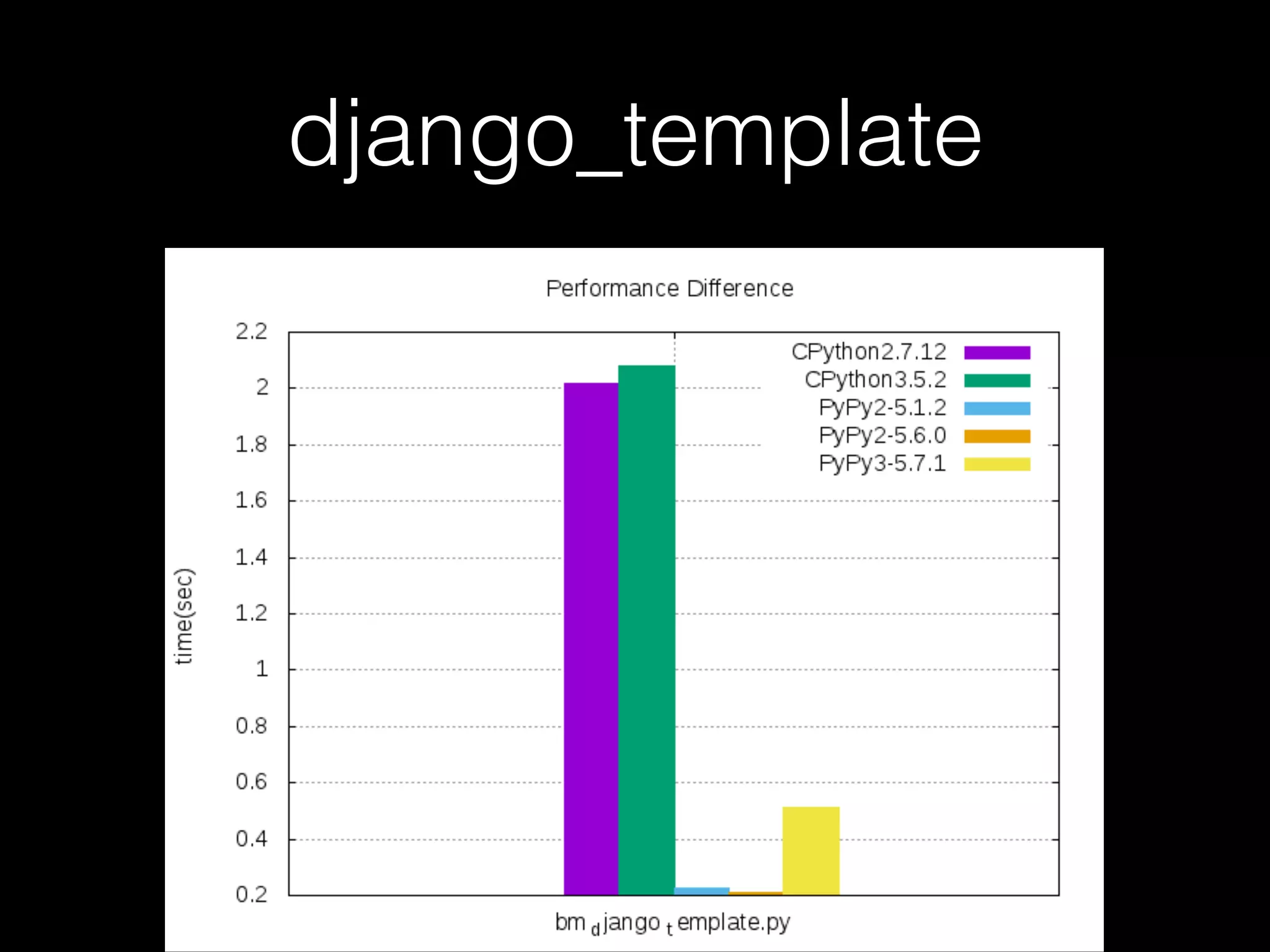
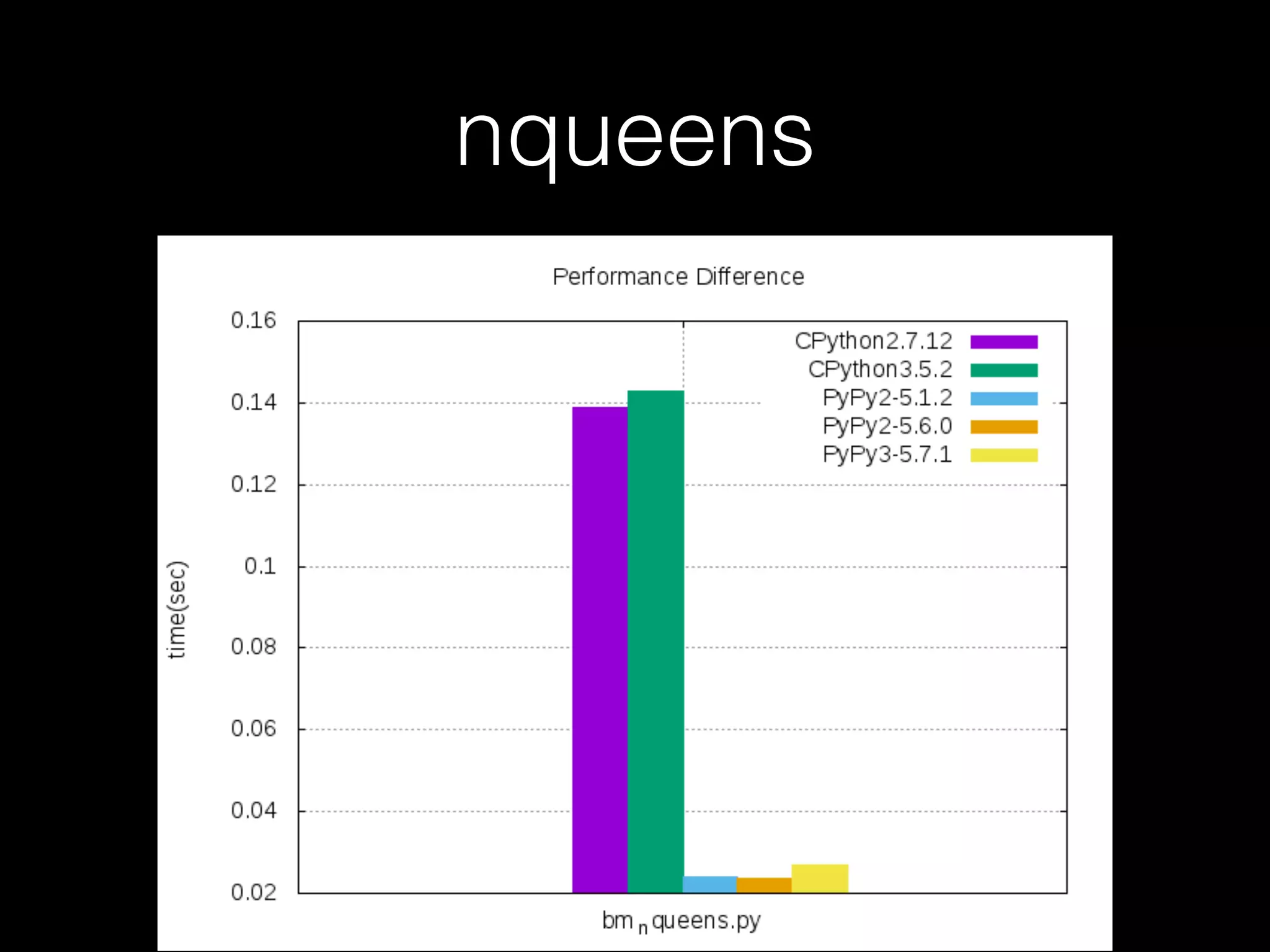
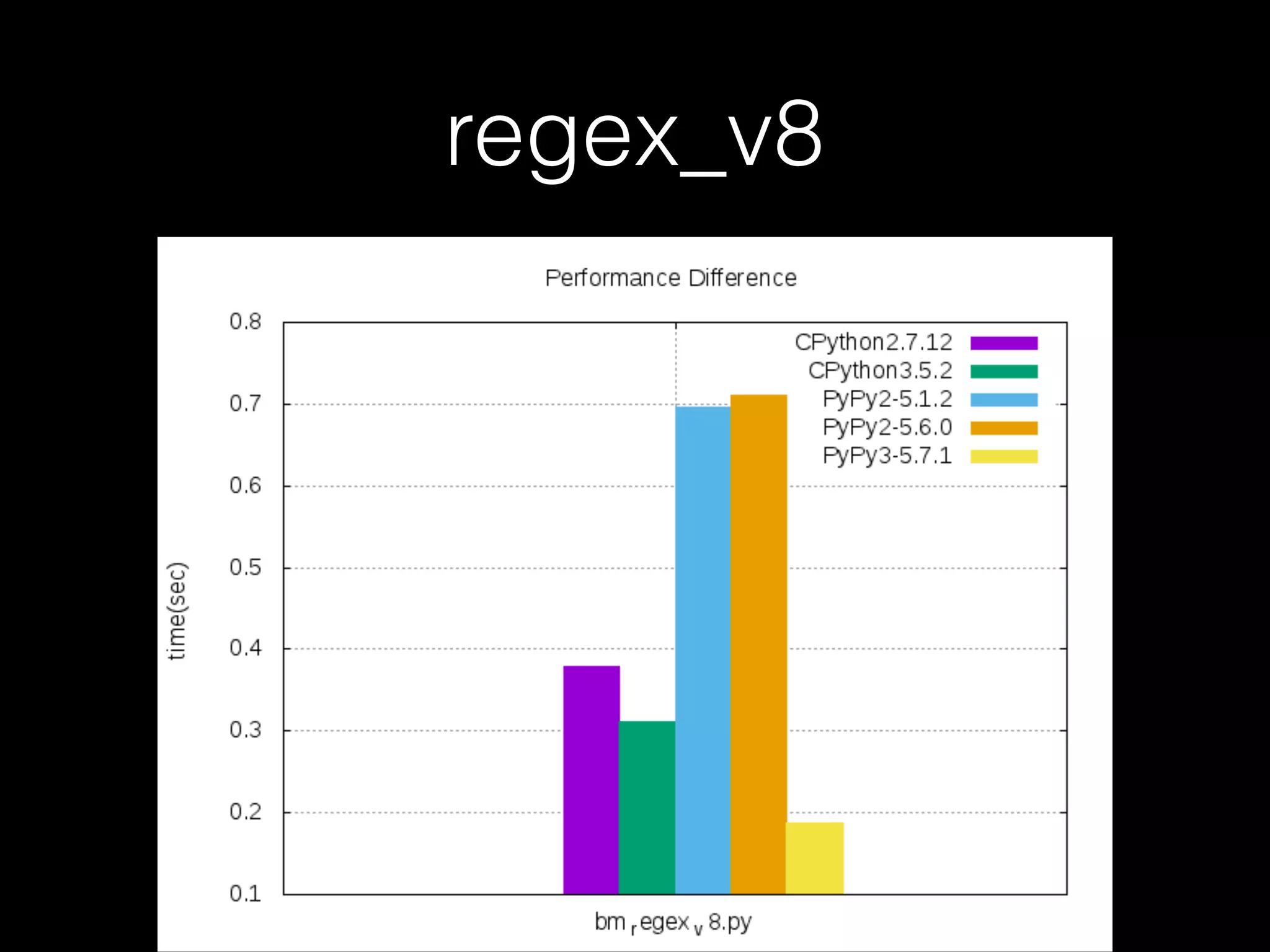
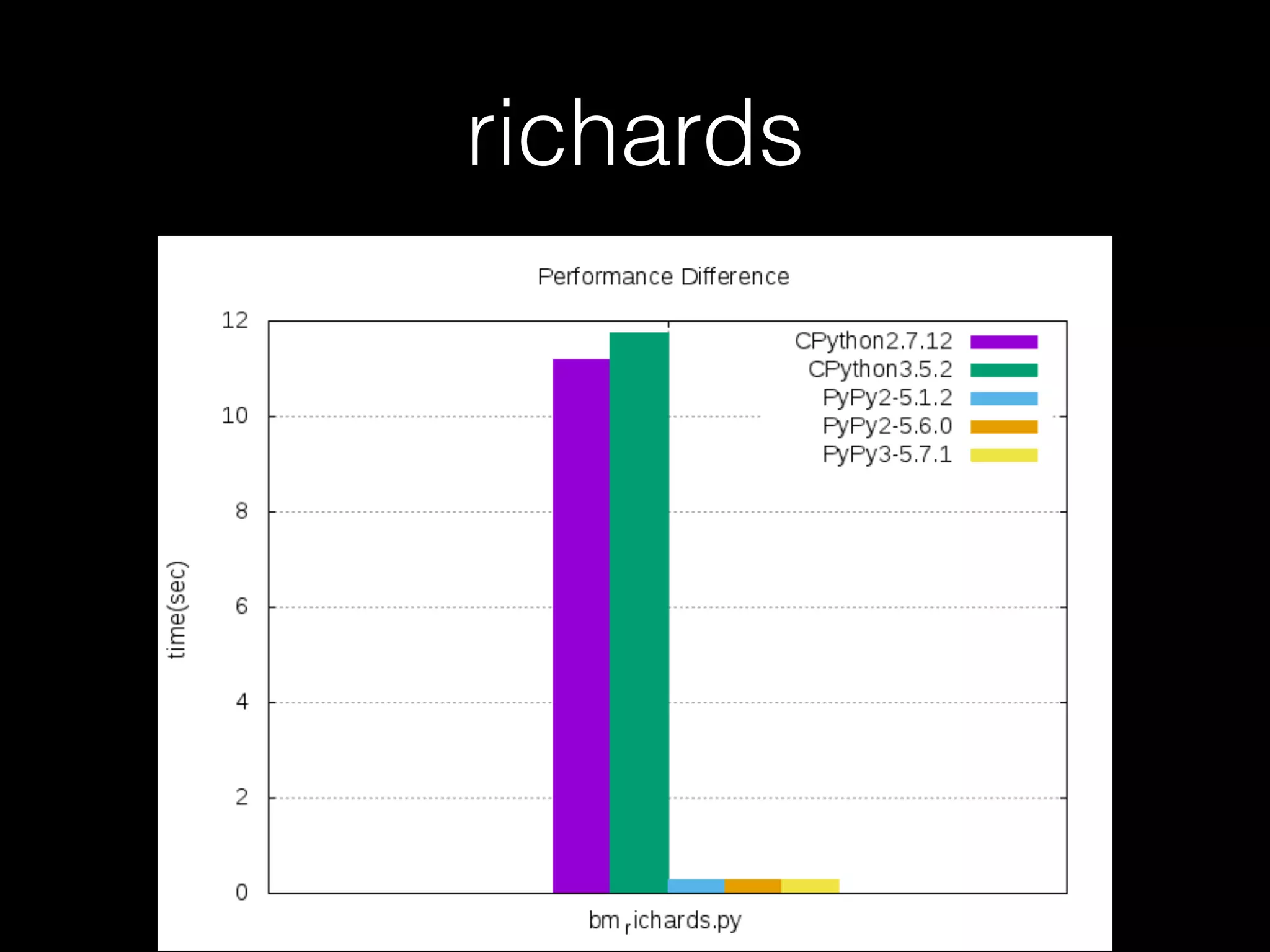
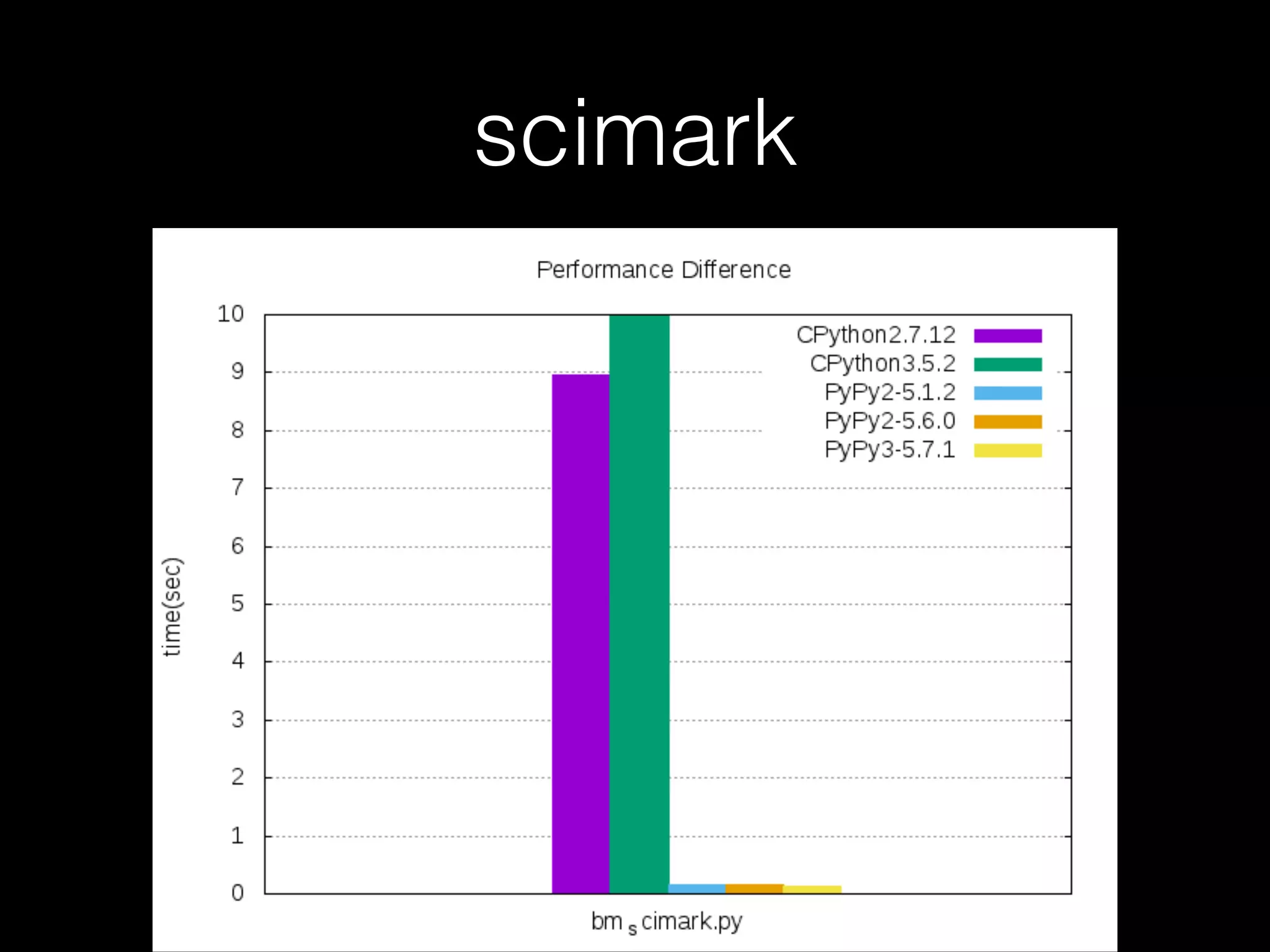
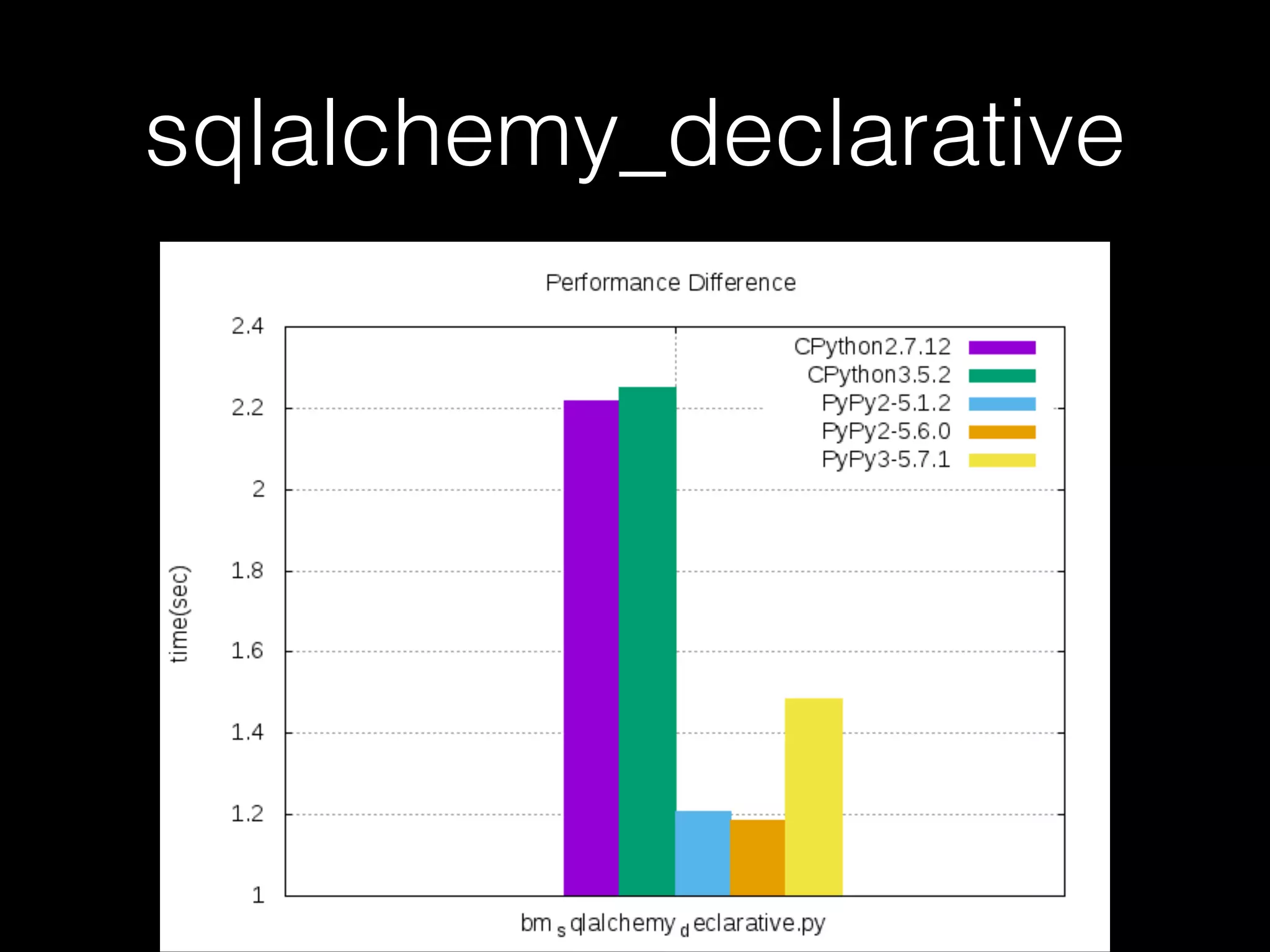
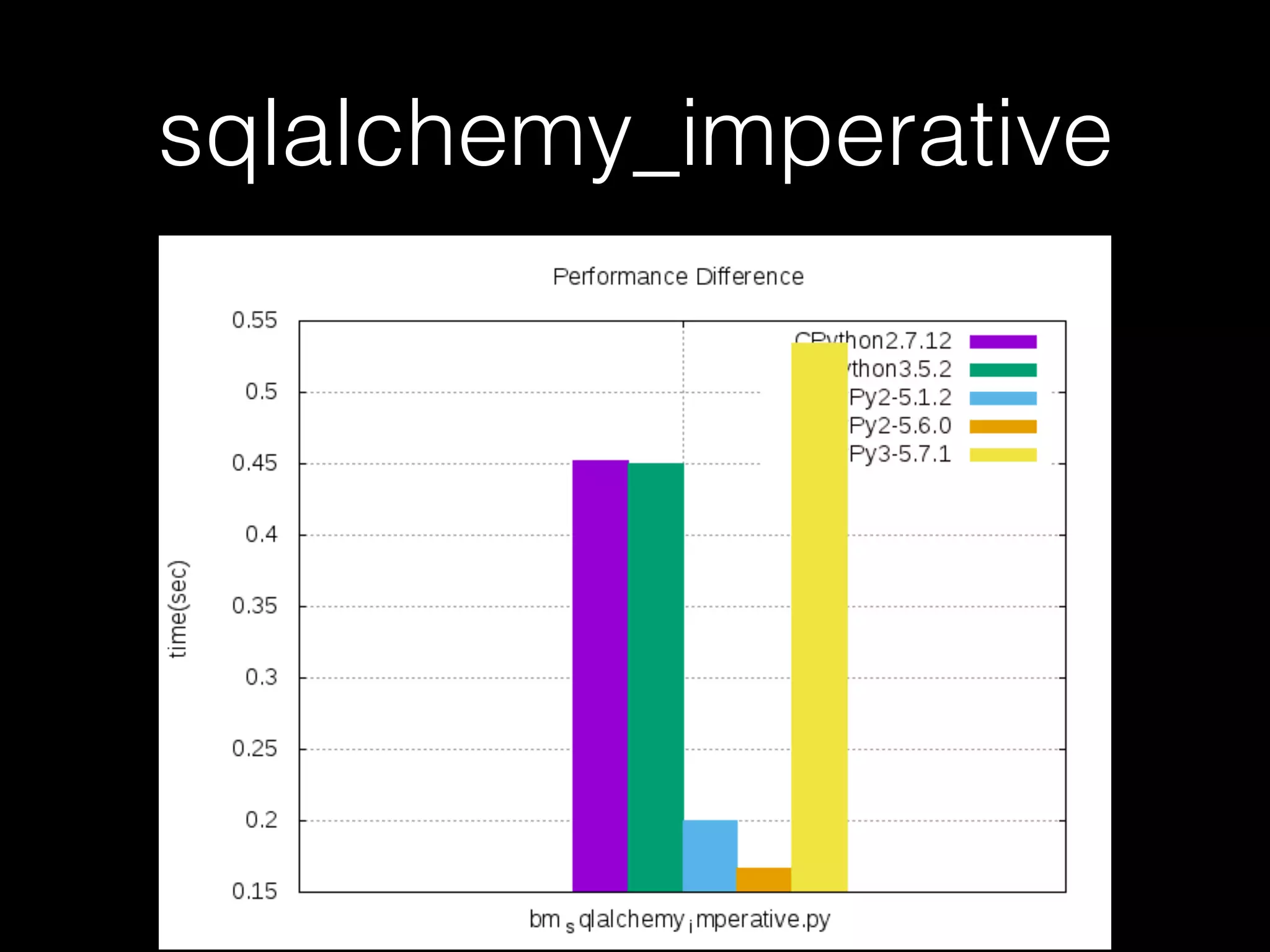

![Not every case should use PyPy • For example, when it comes to the code below, CPython is faster than PyPy
myStr = “”
for x in xrange(1, 10**6):
myStr += str(myStr[x])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pycontw-pypyusecaseexpr-170611020801/75/PyCon-TW-2017-PyPy-s-approach-to-construct-domain-specific-language-runtime-Part-2-24-2048.jpg)


![Example • Language: Brainf*ck • 8 commands • + mem[ptr] += 1 - mem[ptr] -= 1
< ptr -= 1 > ptr += 1
, input() . print()
[ while(mem[ptr]){ ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pycontw-pypyusecaseexpr-170611020801/75/PyCon-TW-2017-PyPy-s-approach-to-construct-domain-specific-language-runtime-Part-2-27-2048.jpg)




![What to do to add JIT • from rpython.rlib.jit import JitDriver • jitdriver = JitDriver(greens=[], reds=[]) • and add jit_merge_point to your main loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pycontw-pypyusecaseexpr-170611020801/75/PyCon-TW-2017-PyPy-s-approach-to-construct-domain-specific-language-runtime-Part-2-32-2048.jpg)


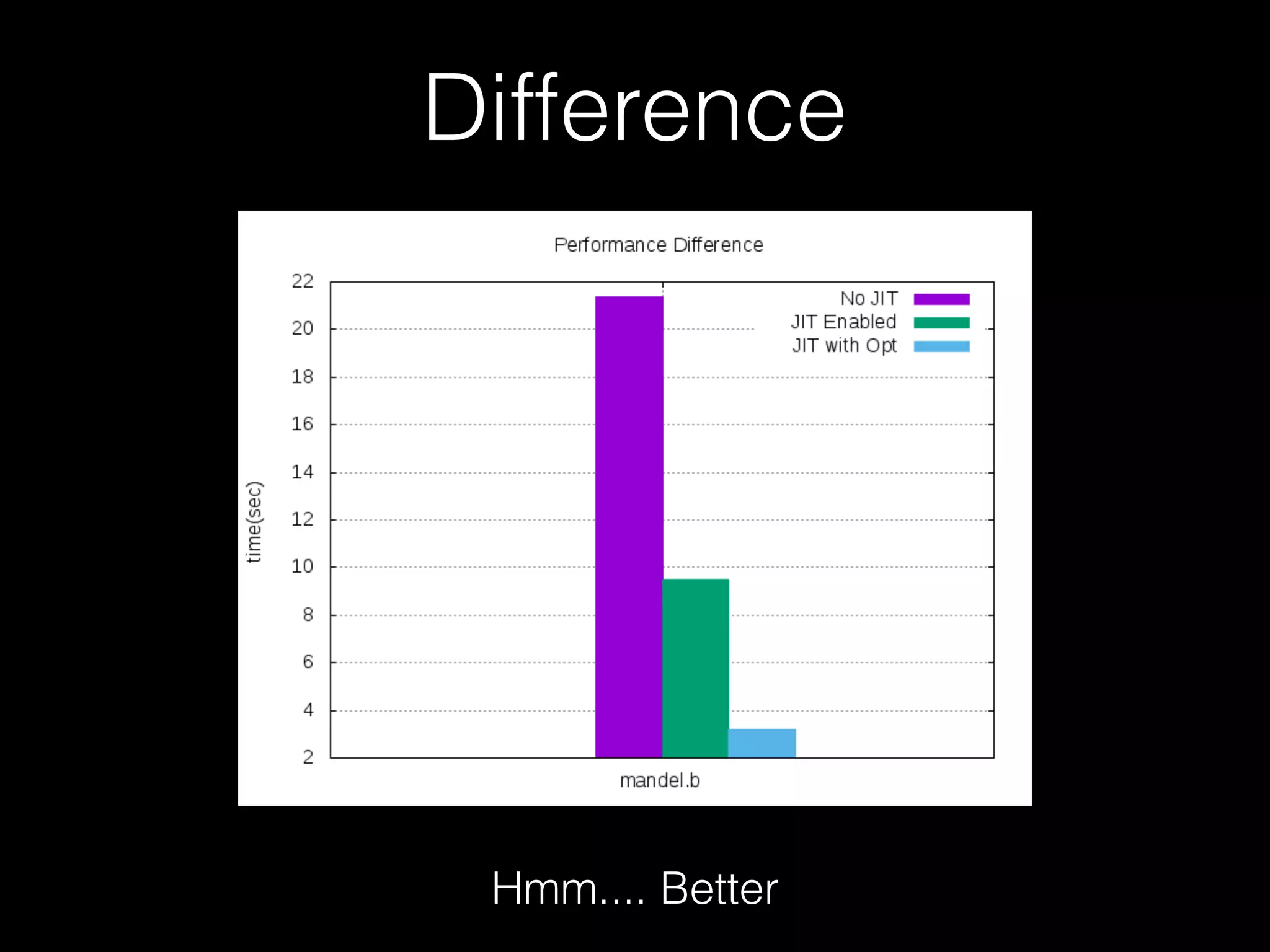
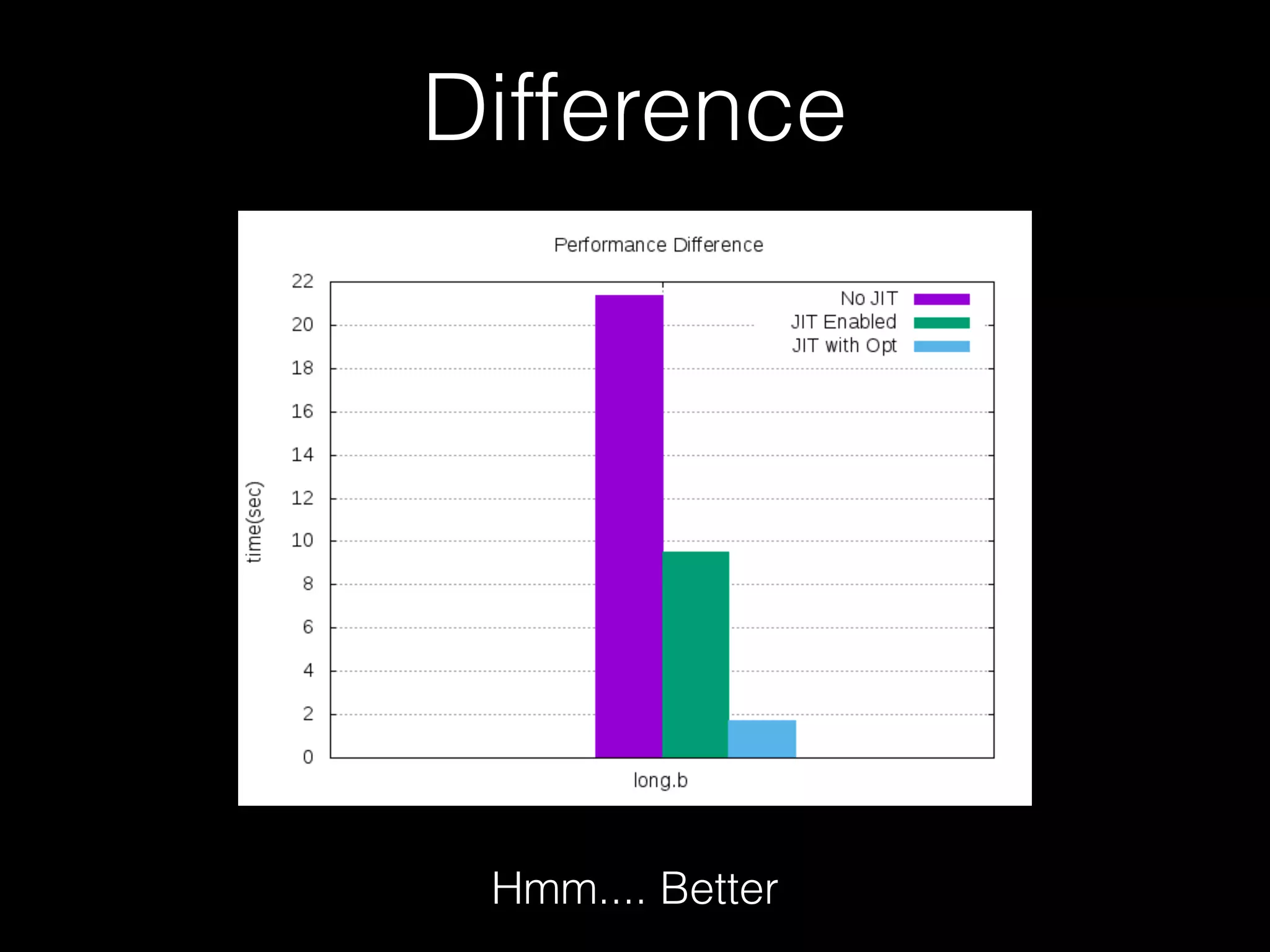

![Optimizations • opt_contract ( Contract) • Operation like " +++++ ", means that we have to do "mem[p] += 1" five times • But because we have IR, so we can change the instruction to "mem[p] += 5" • When it comes to “+ - > <“, this trick can apply](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pycontw-pypyusecaseexpr-170611020801/75/PyCon-TW-2017-PyPy-s-approach-to-construct-domain-specific-language-runtime-Part-2-43-2048.jpg)
![Optimizations • opt_clearloop (Clear Loop) • Command like [-], it means when(mem[p]), do mem[p] -= 1 • We know what the result is, so we can set mem[p] to zero directly
mem[p] = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pycontw-pypyusecaseexpr-170611020801/75/PyCon-TW-2017-PyPy-s-approach-to-construct-domain-specific-language-runtime-Part-2-44-2048.jpg)
![Optimizations • opt_multiloop & opt_copyloop (Multiplication and Copy) • Command like [->+>+<<] is copy mem[p]'s value to mem[p+1] and mem[p+2], and set mem[p] to zero • If we know what this is doing, we can make it short](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pycontw-pypyusecaseexpr-170611020801/75/PyCon-TW-2017-PyPy-s-approach-to-construct-domain-specific-language-runtime-Part-2-45-2048.jpg)
![Optimizations • opt_multiloop & opt_copyloop (Multiplication and Copy) • Same trick can apply to [->++<], make
mem[p+1] = 2 * mem[p] and set mem[p] = 0 • Which is multiplication](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pycontw-pypyusecaseexpr-170611020801/75/PyCon-TW-2017-PyPy-s-approach-to-construct-domain-specific-language-runtime-Part-2-46-2048.jpg)