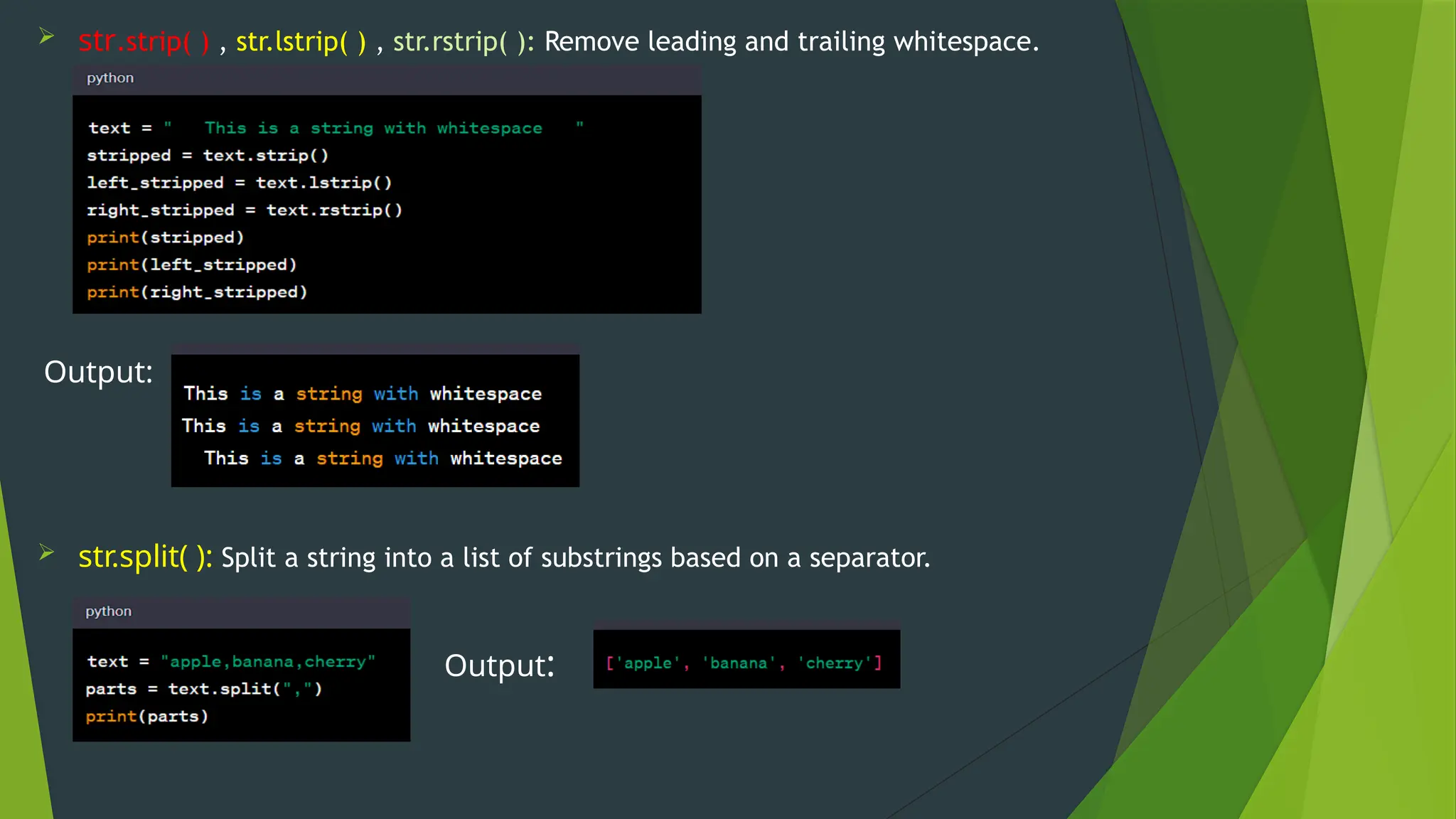
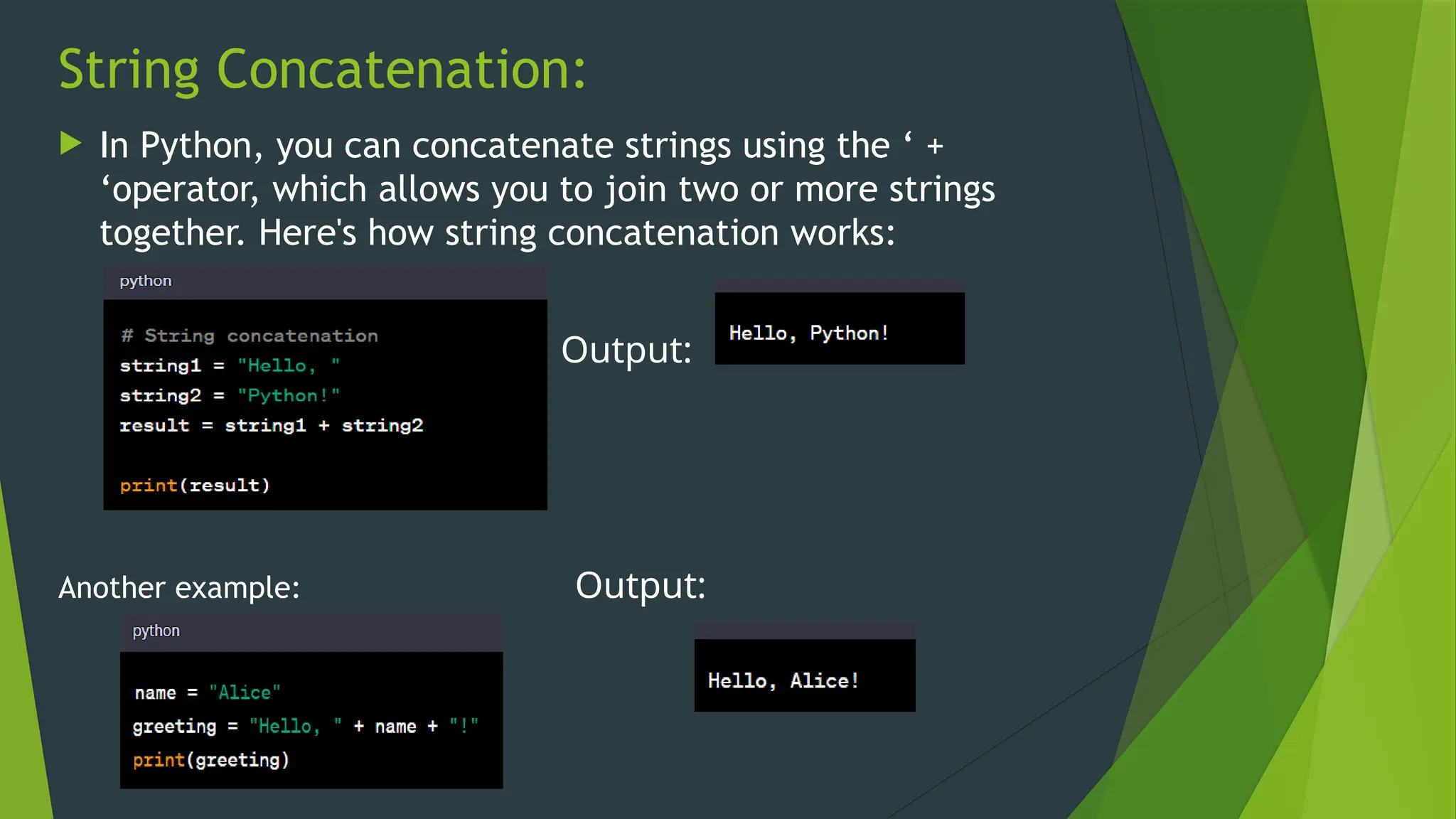
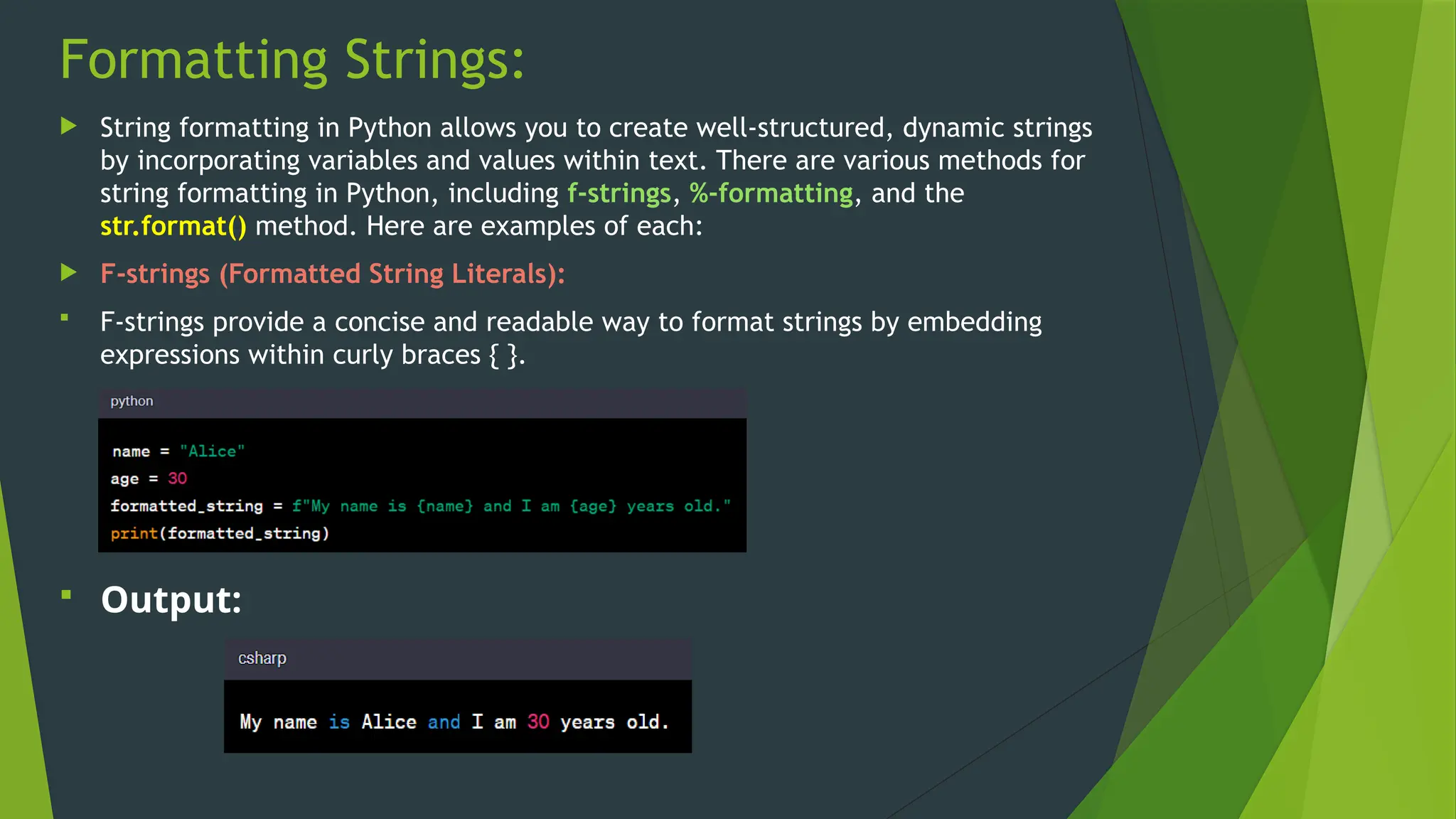
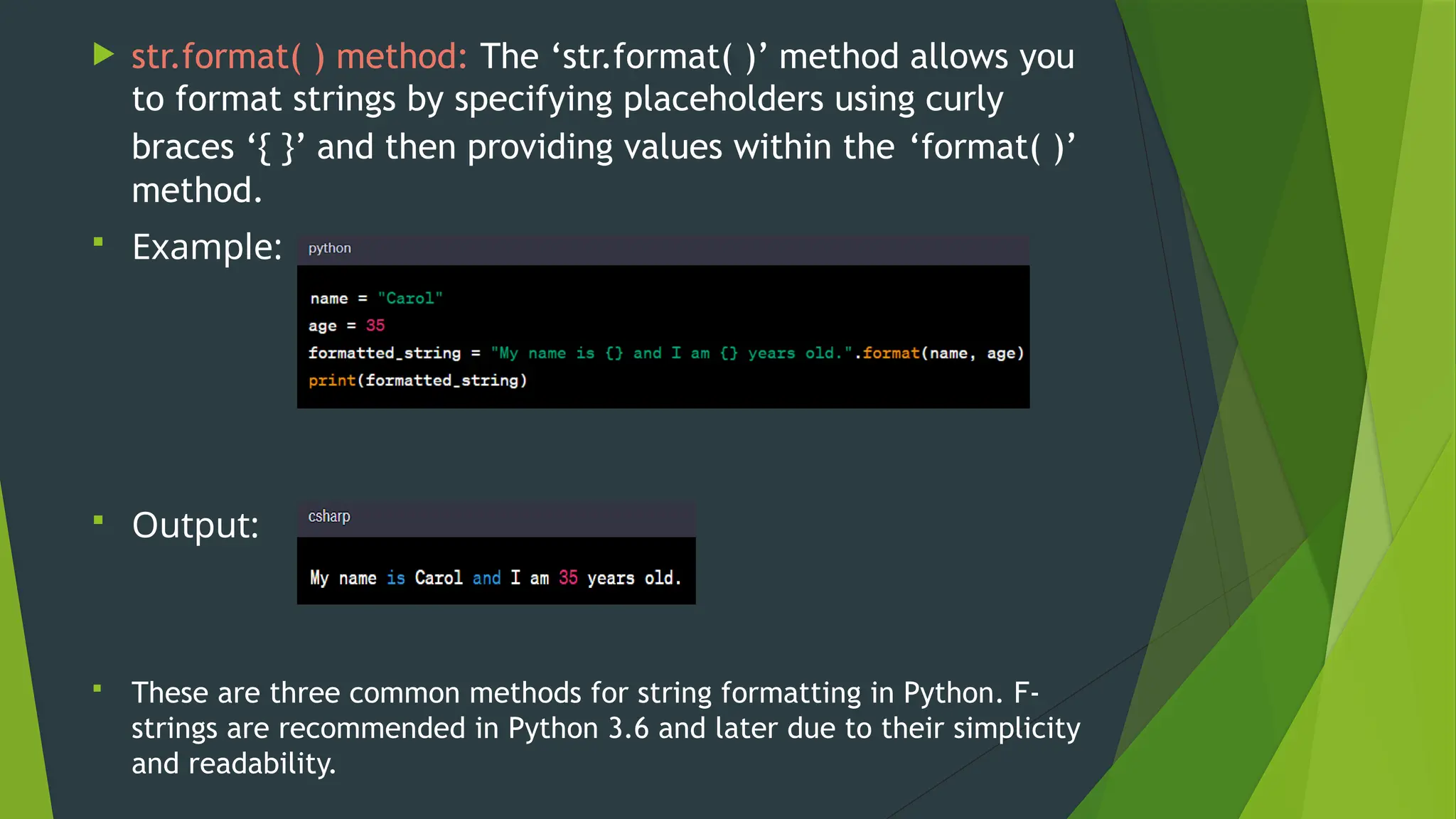
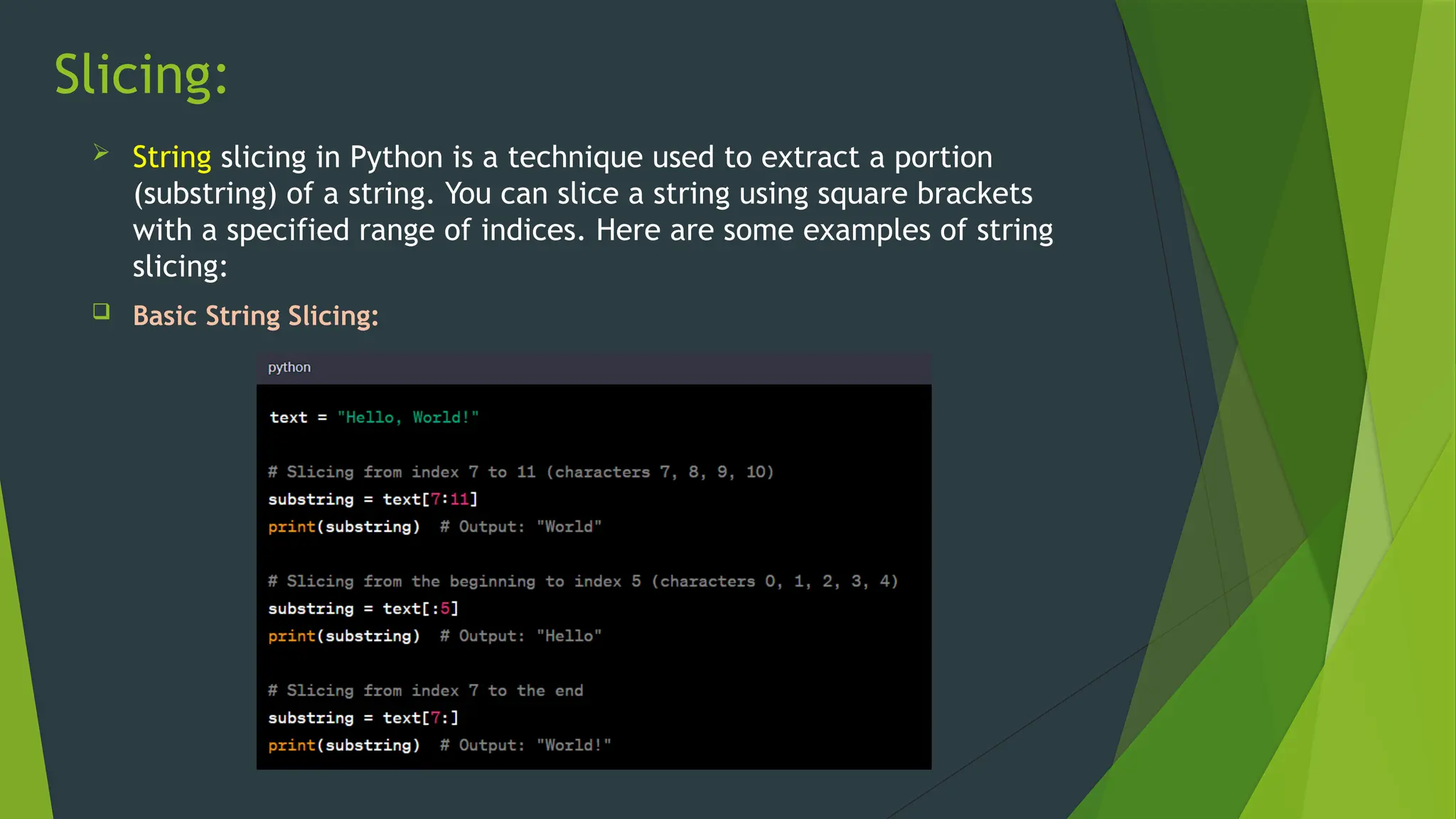
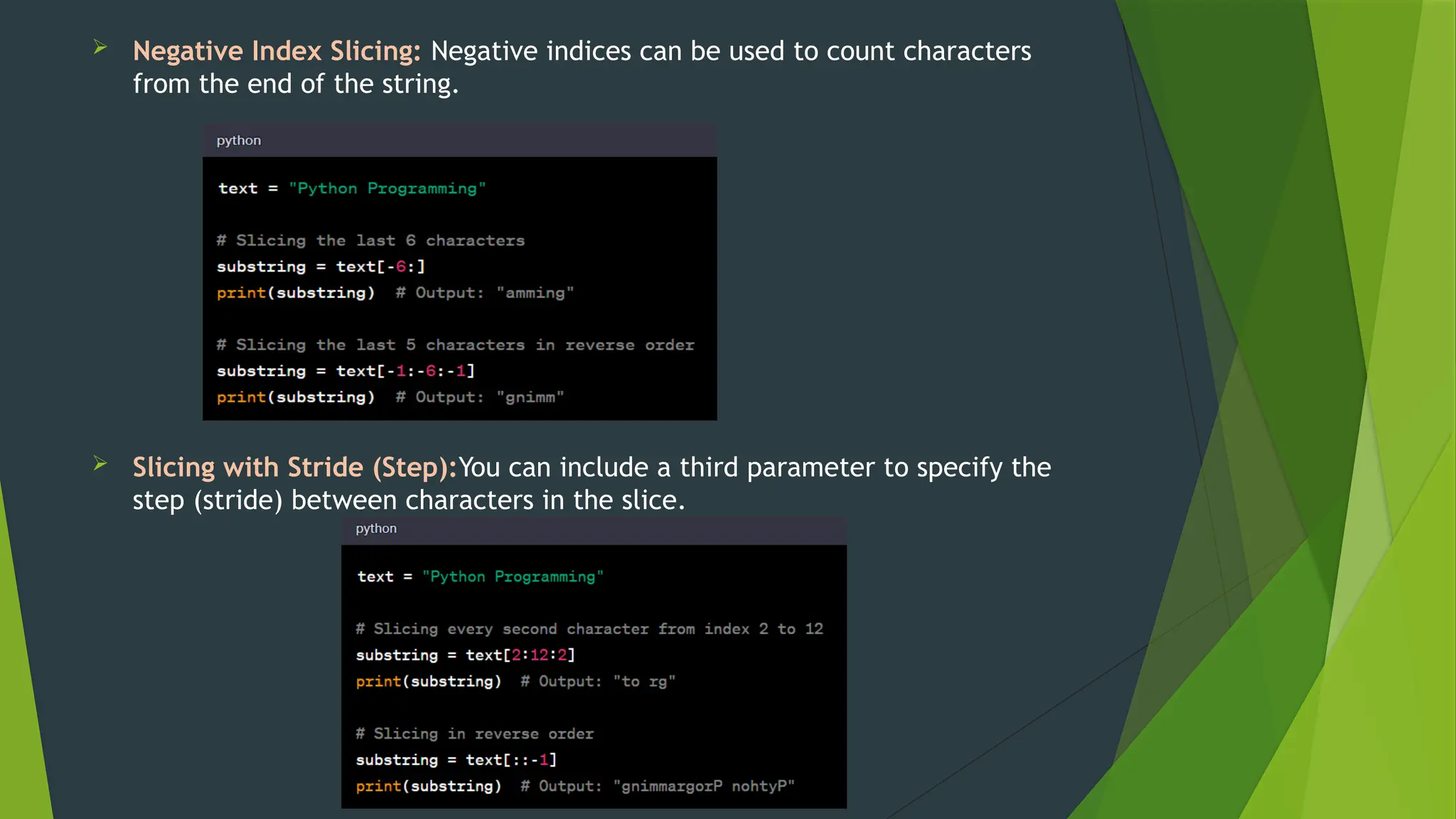
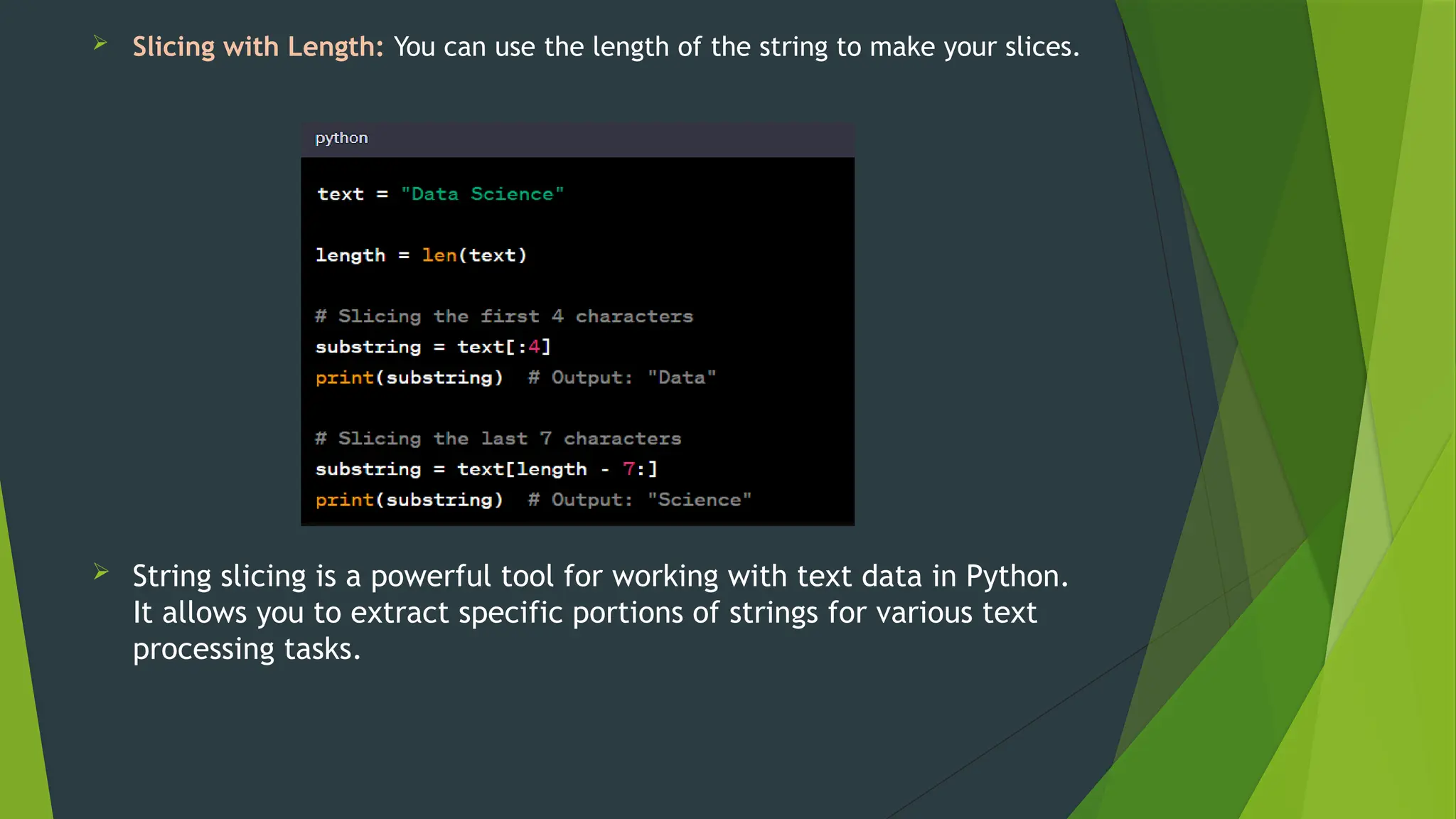
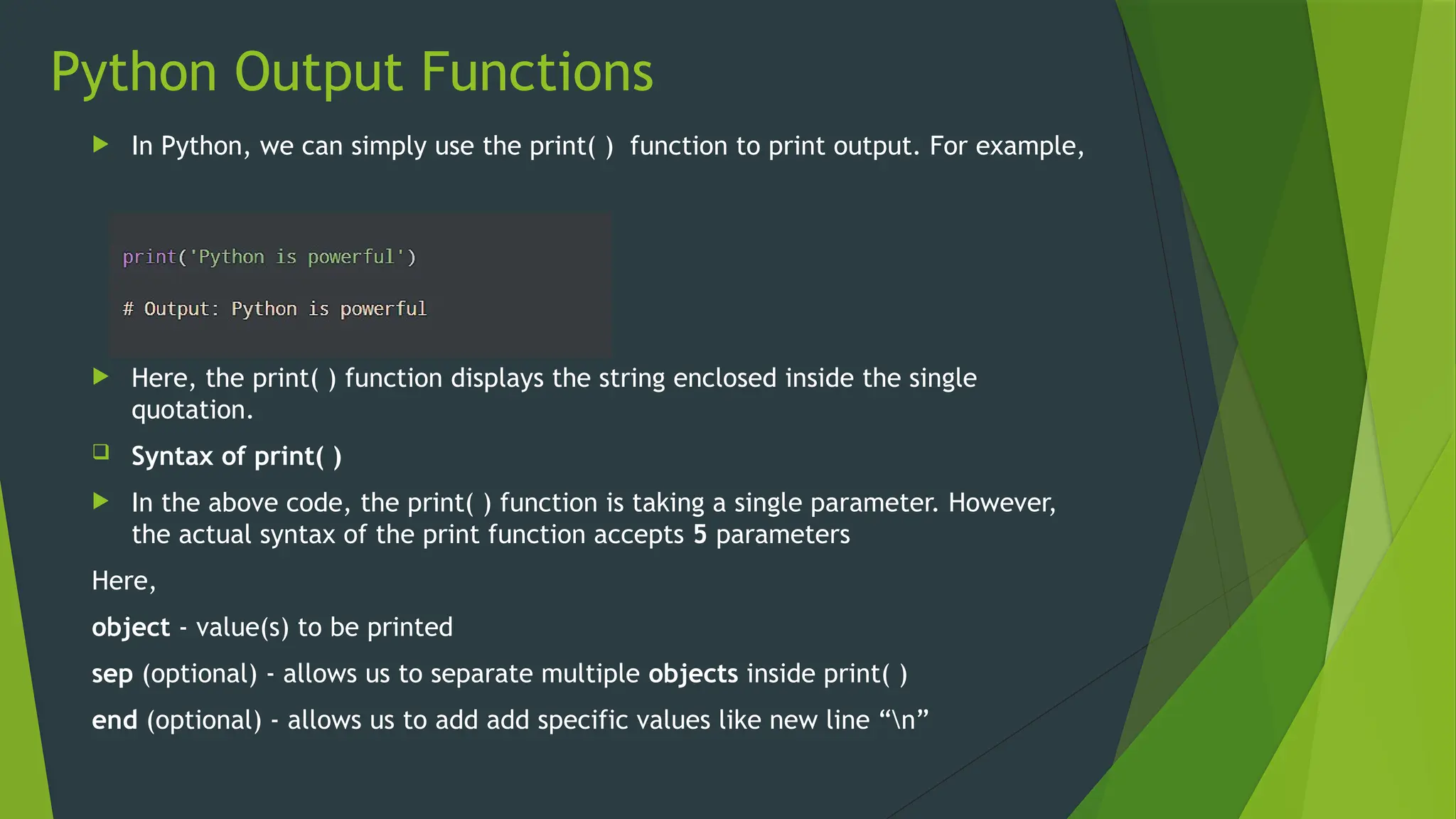
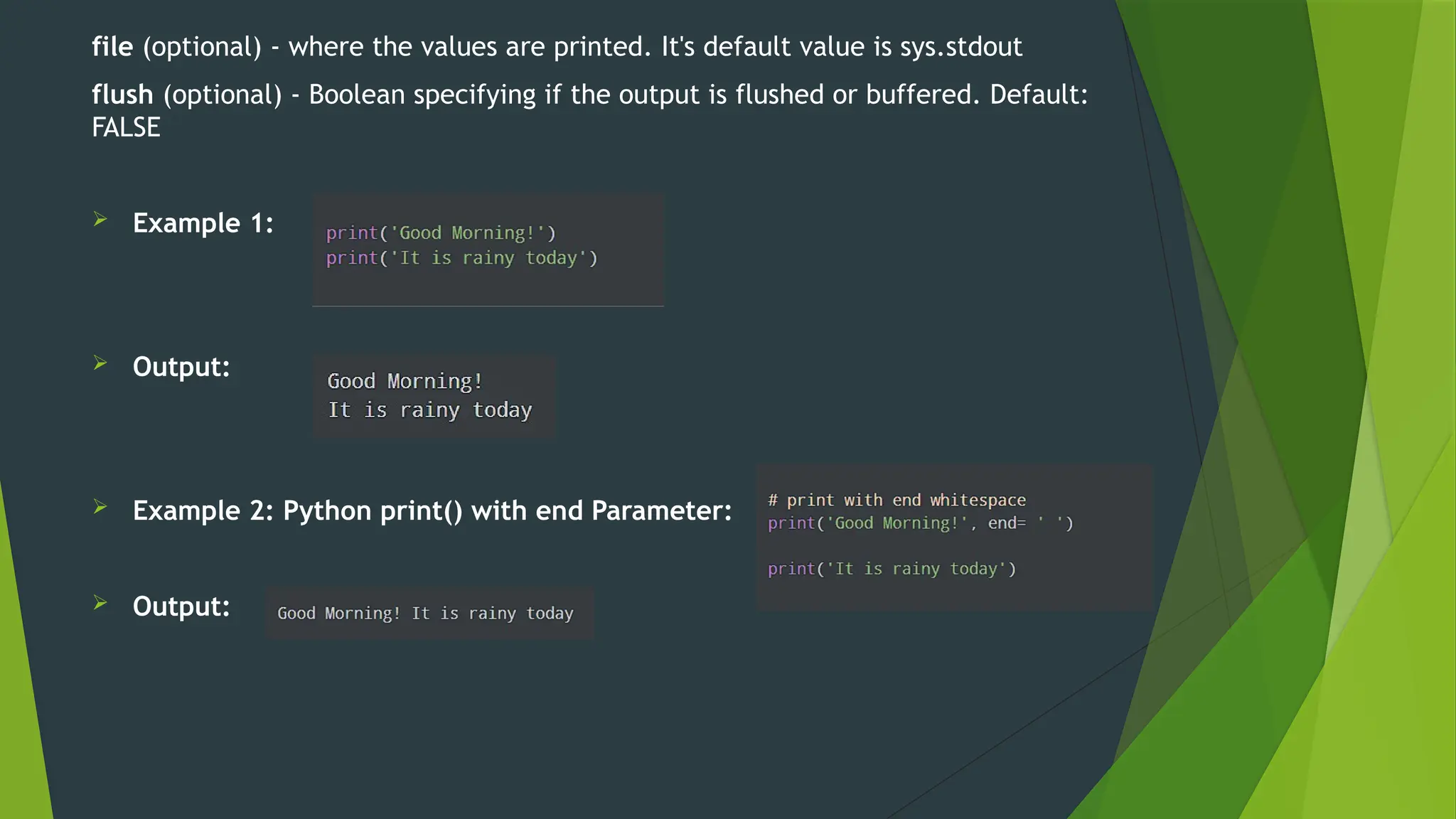
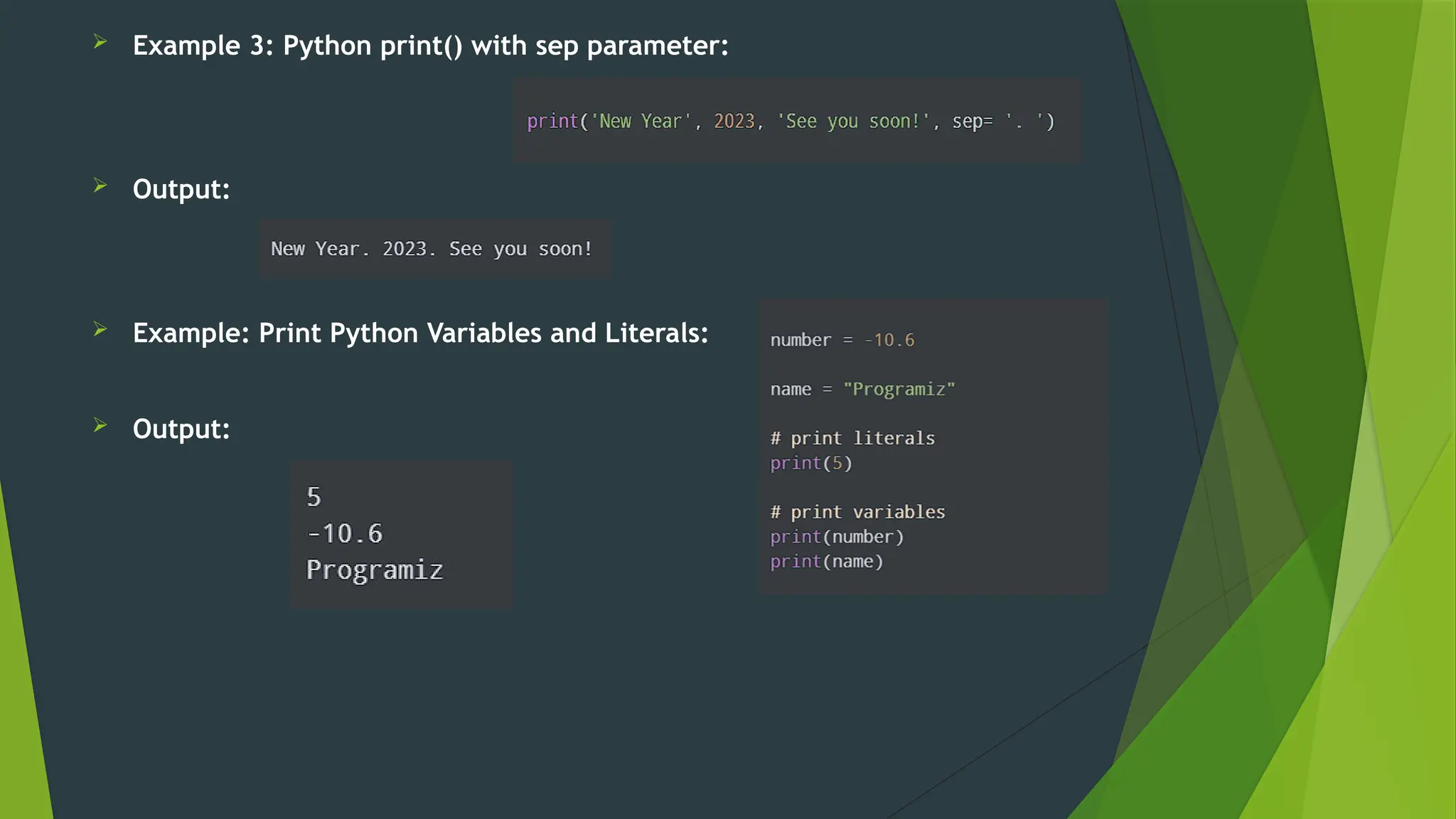
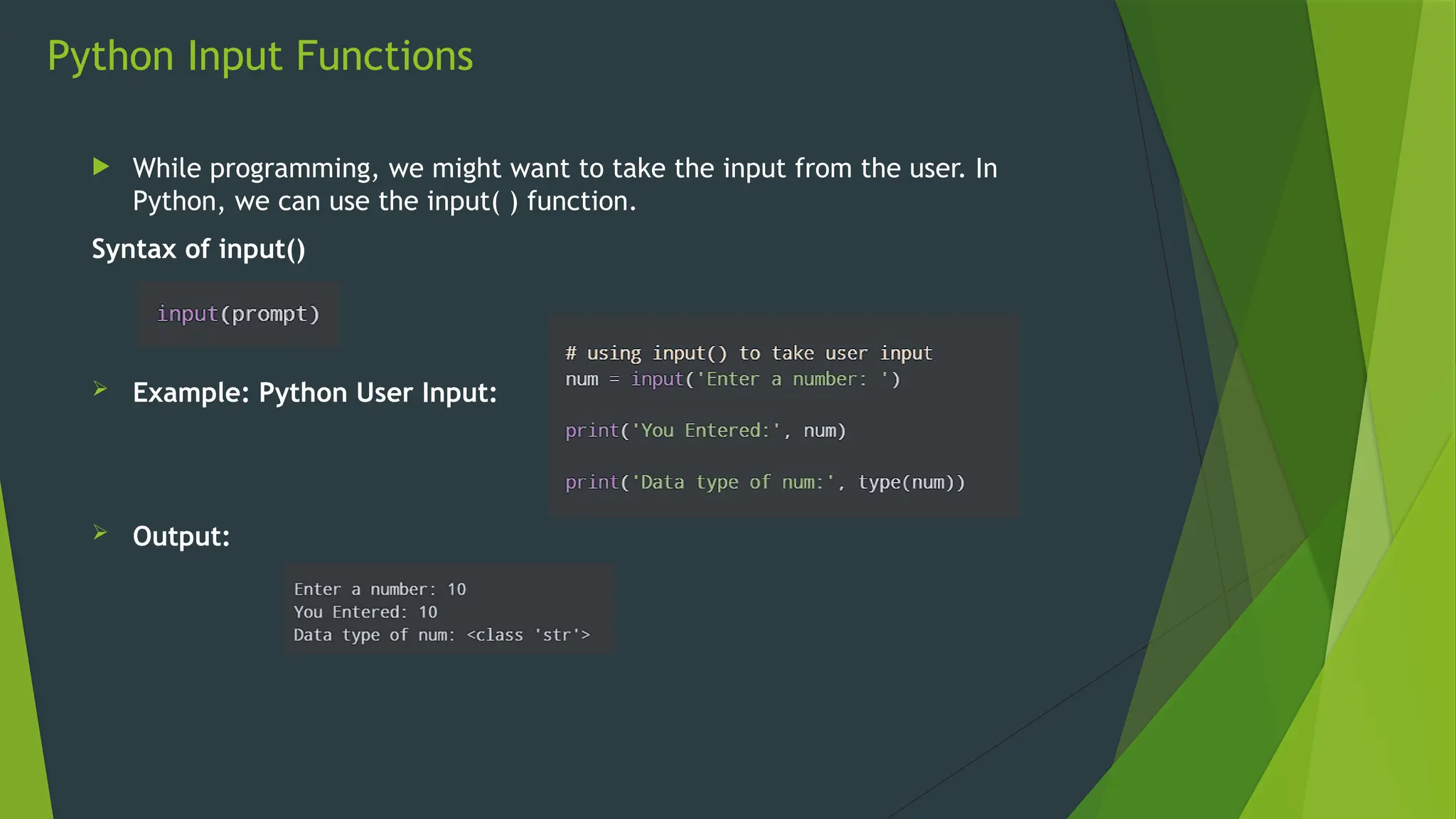
The document covers the basics of Python string functions, including string creation, characteristics, common string methods, string concatenation, formatting, escape characters, and slicing techniques. It also discusses the importance of input and output functions in Python programming, highlighting user interaction, data handling, and automation while explaining the usage of the 'print()' and 'input()' functions. The seminar aims to equip participants with essential skills for effective text manipulation and user interaction in Python.