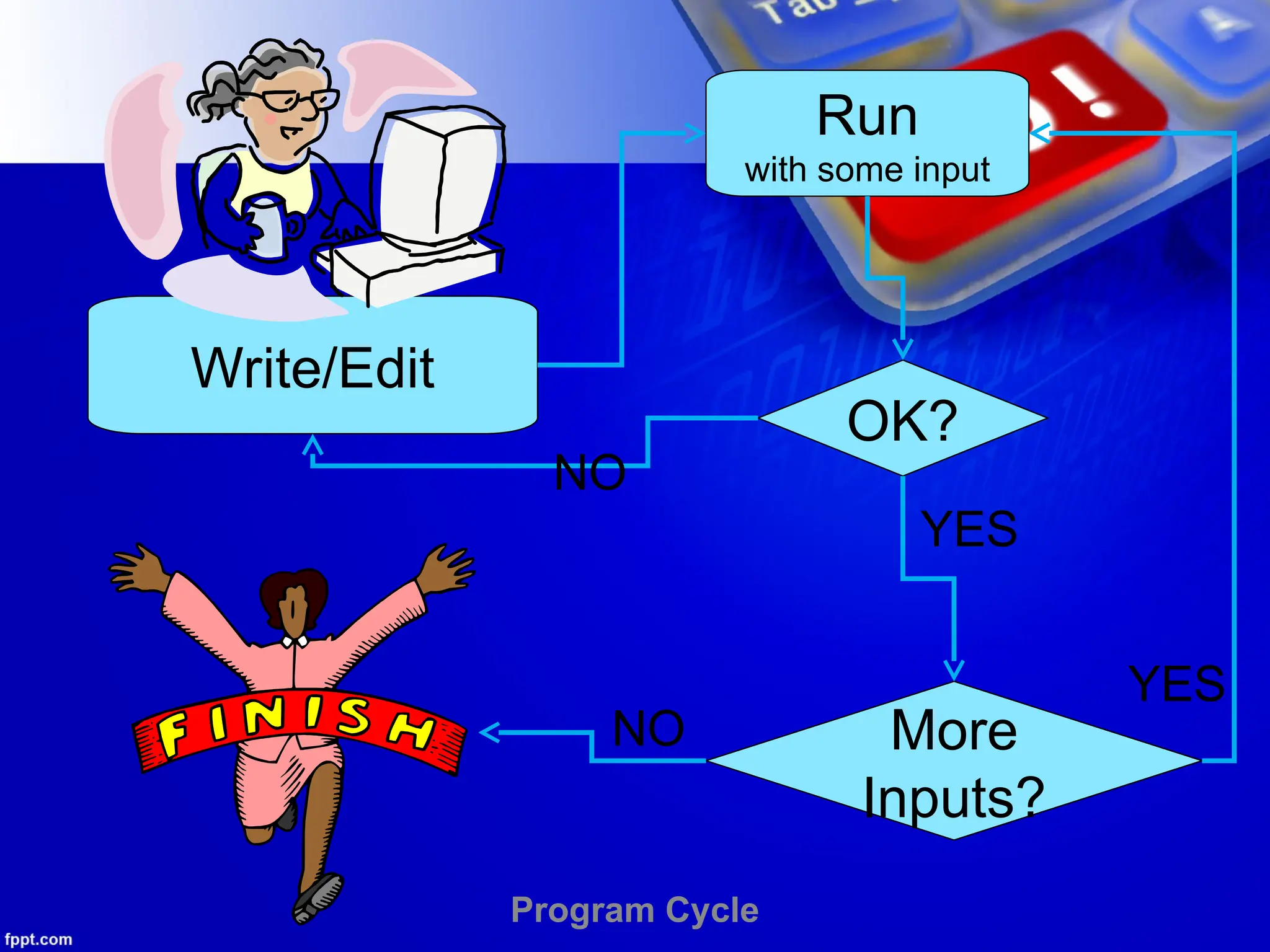
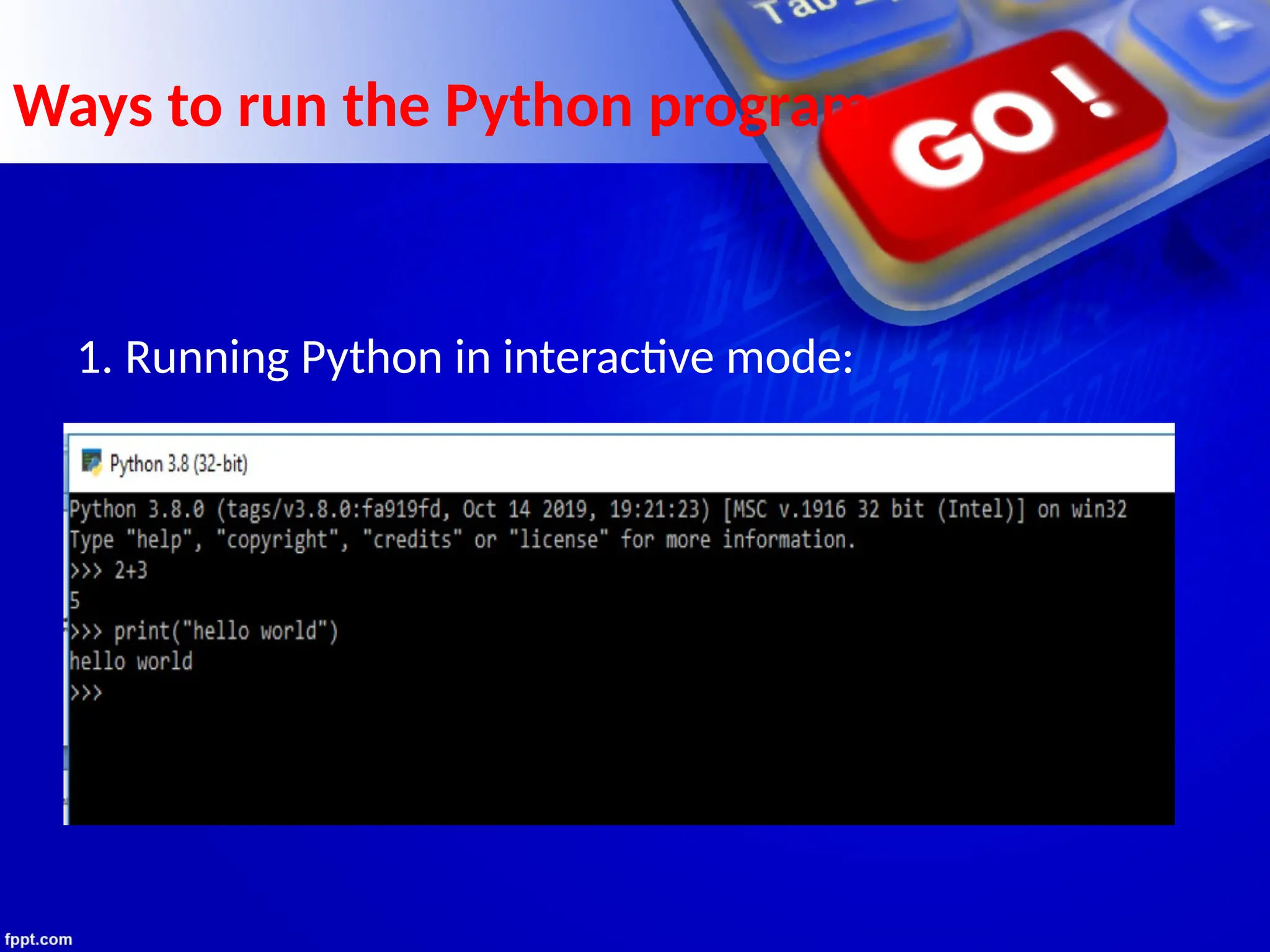
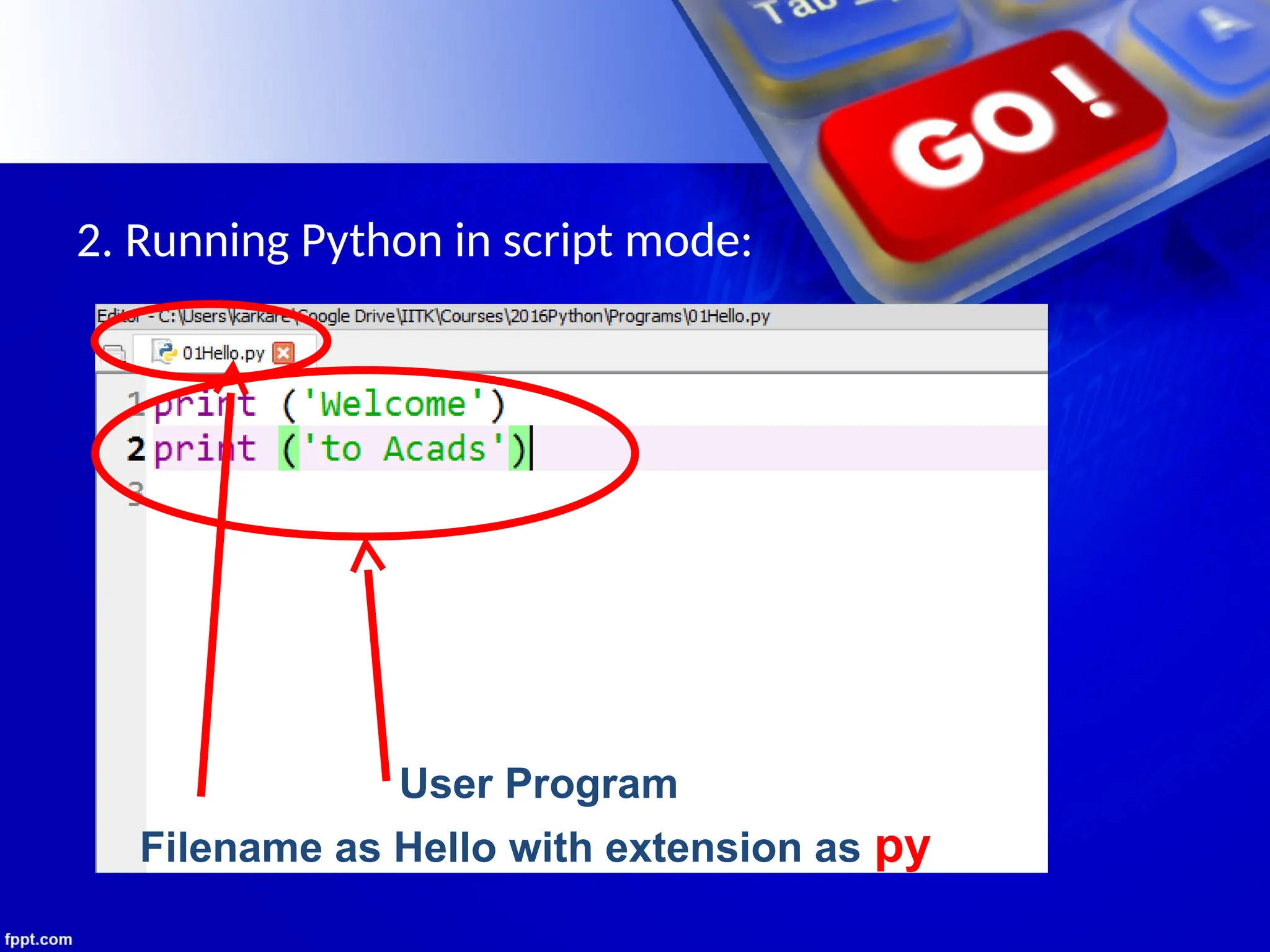
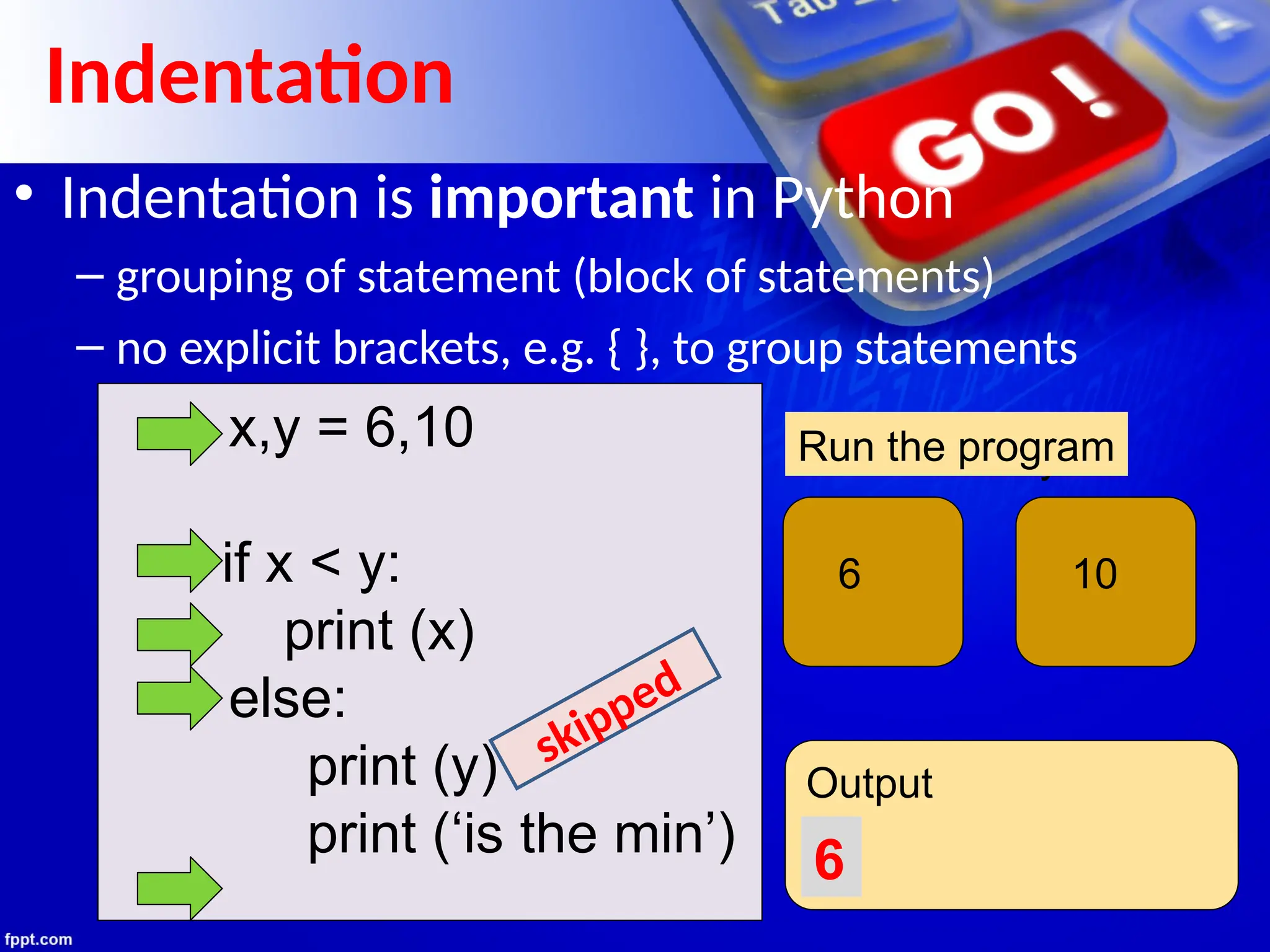
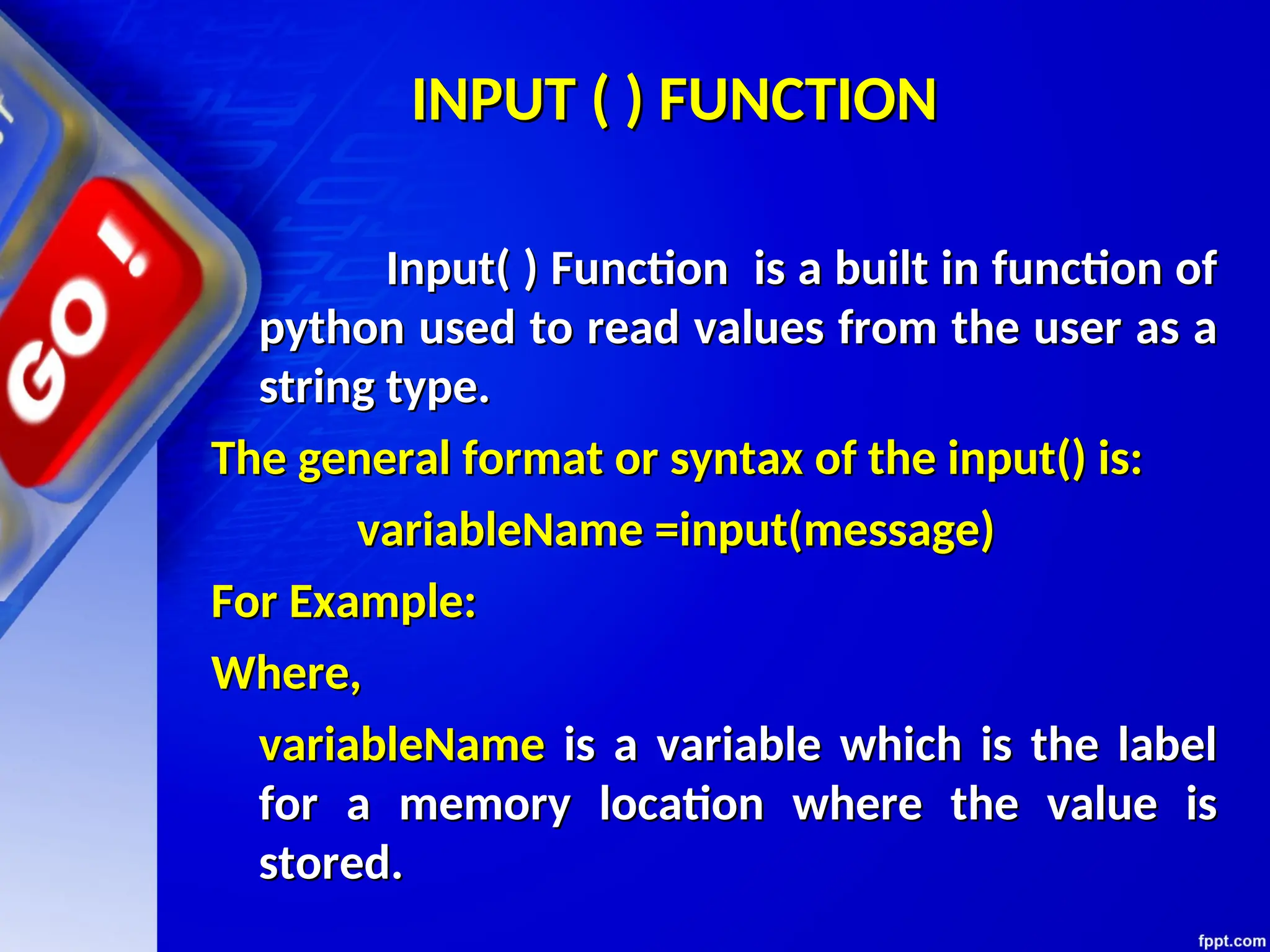
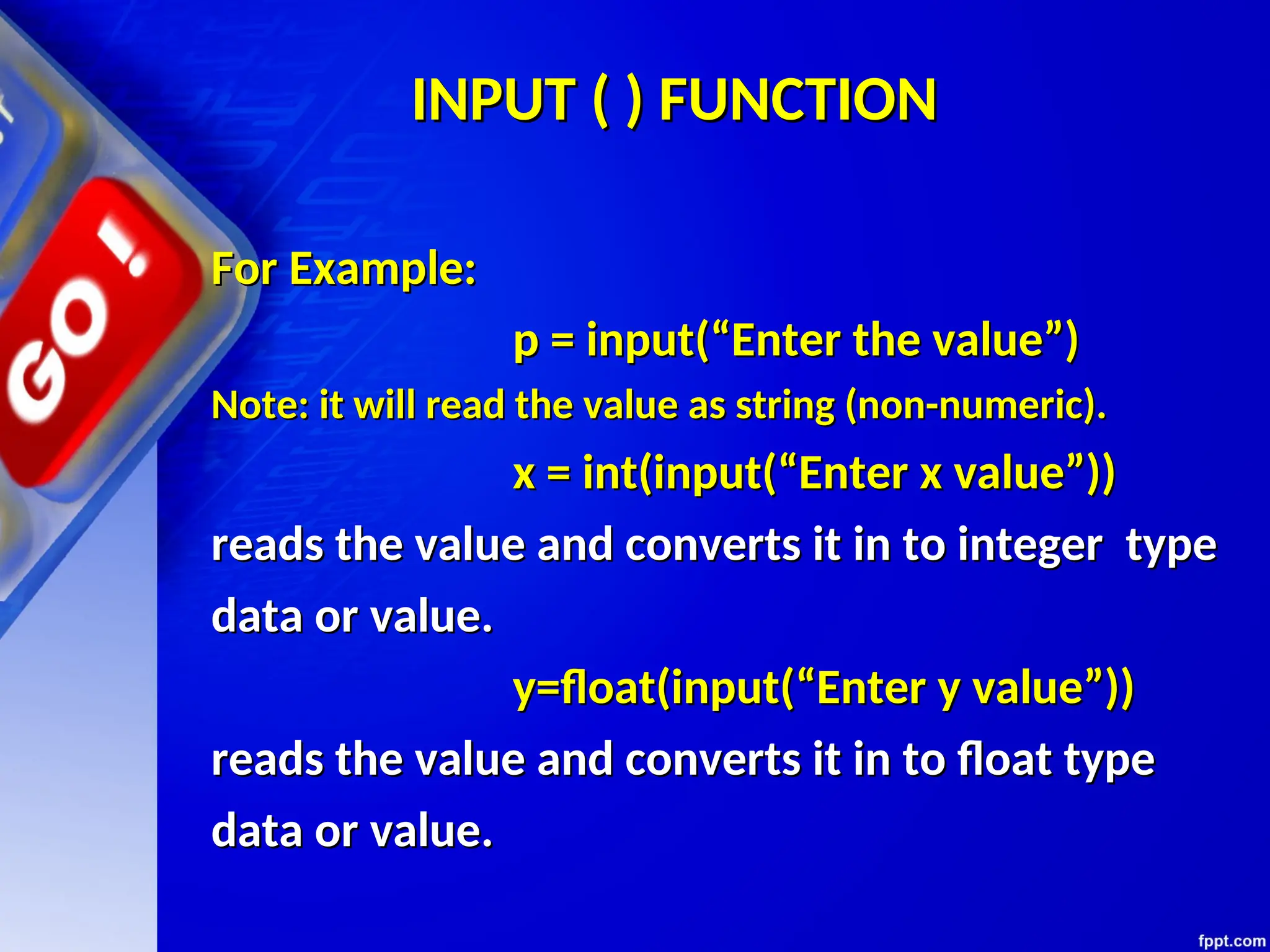
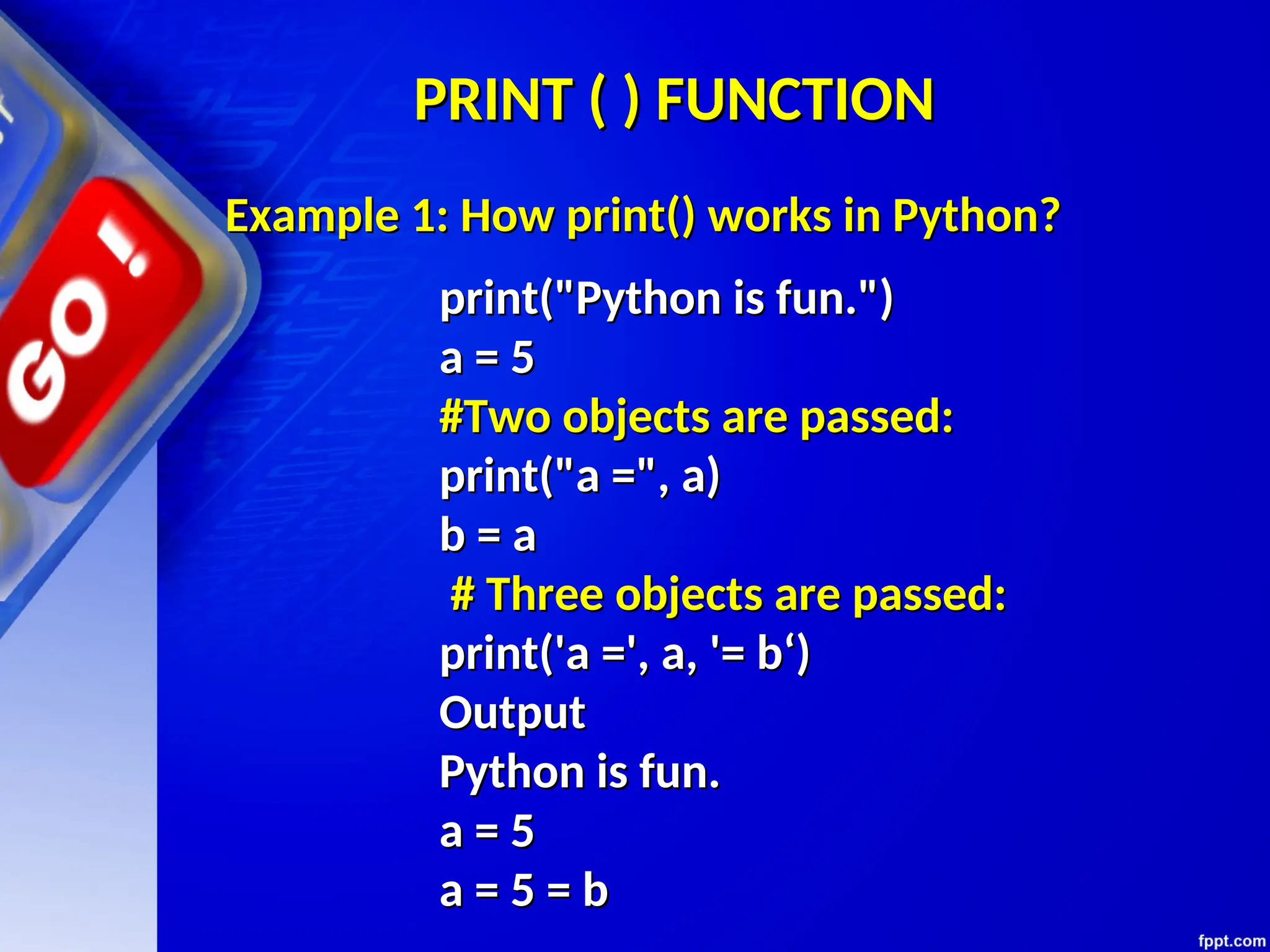
The document provides an introduction to programming languages, focusing on Python as a high-level, machine-independent language that requires compilation for different platforms. It explains the execution process of programs, error types, and how to use Python with examples of coding in both interactive and script modes. Additionally, it details the use of the input() and print() functions for user interaction and output display.