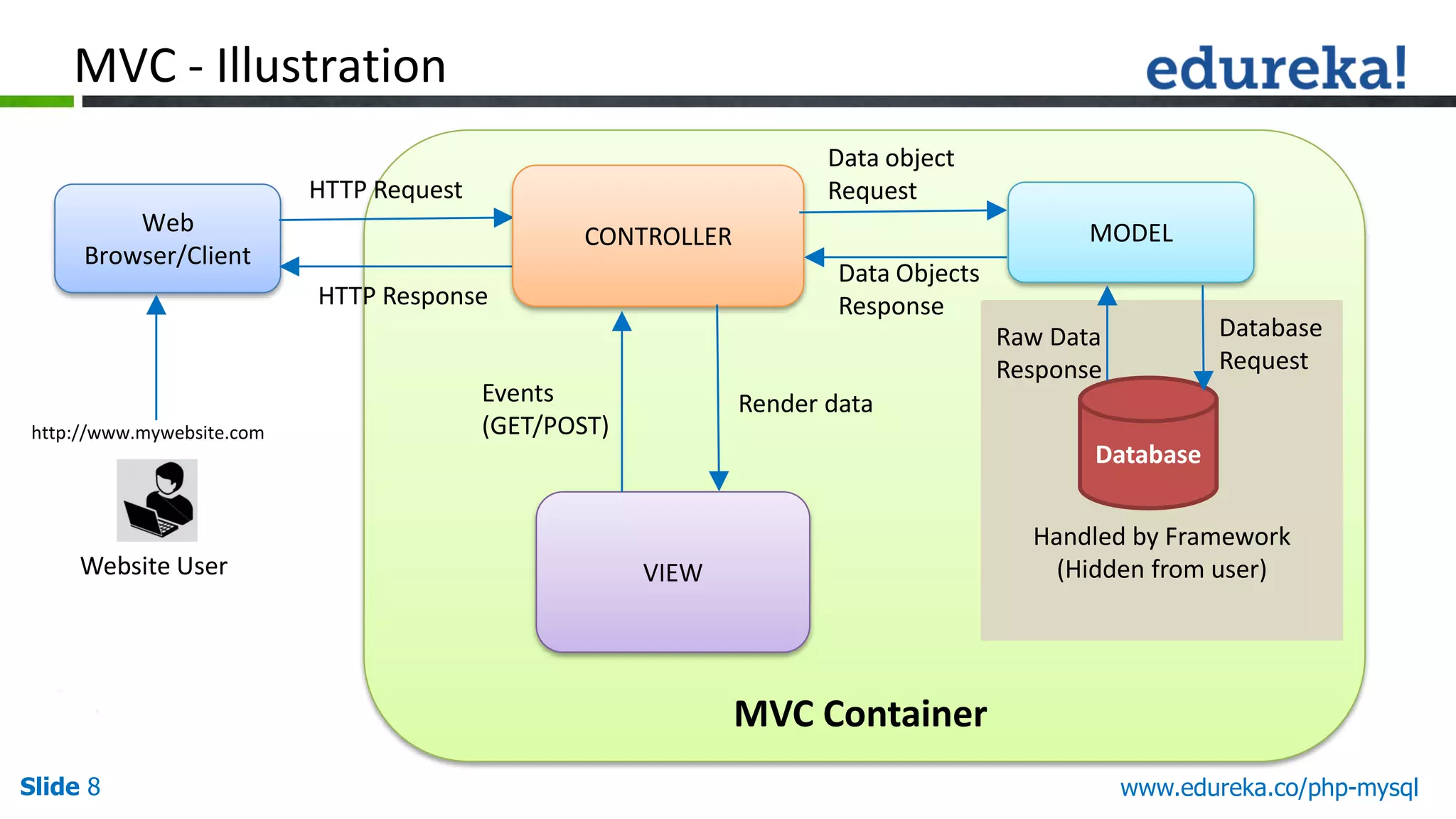
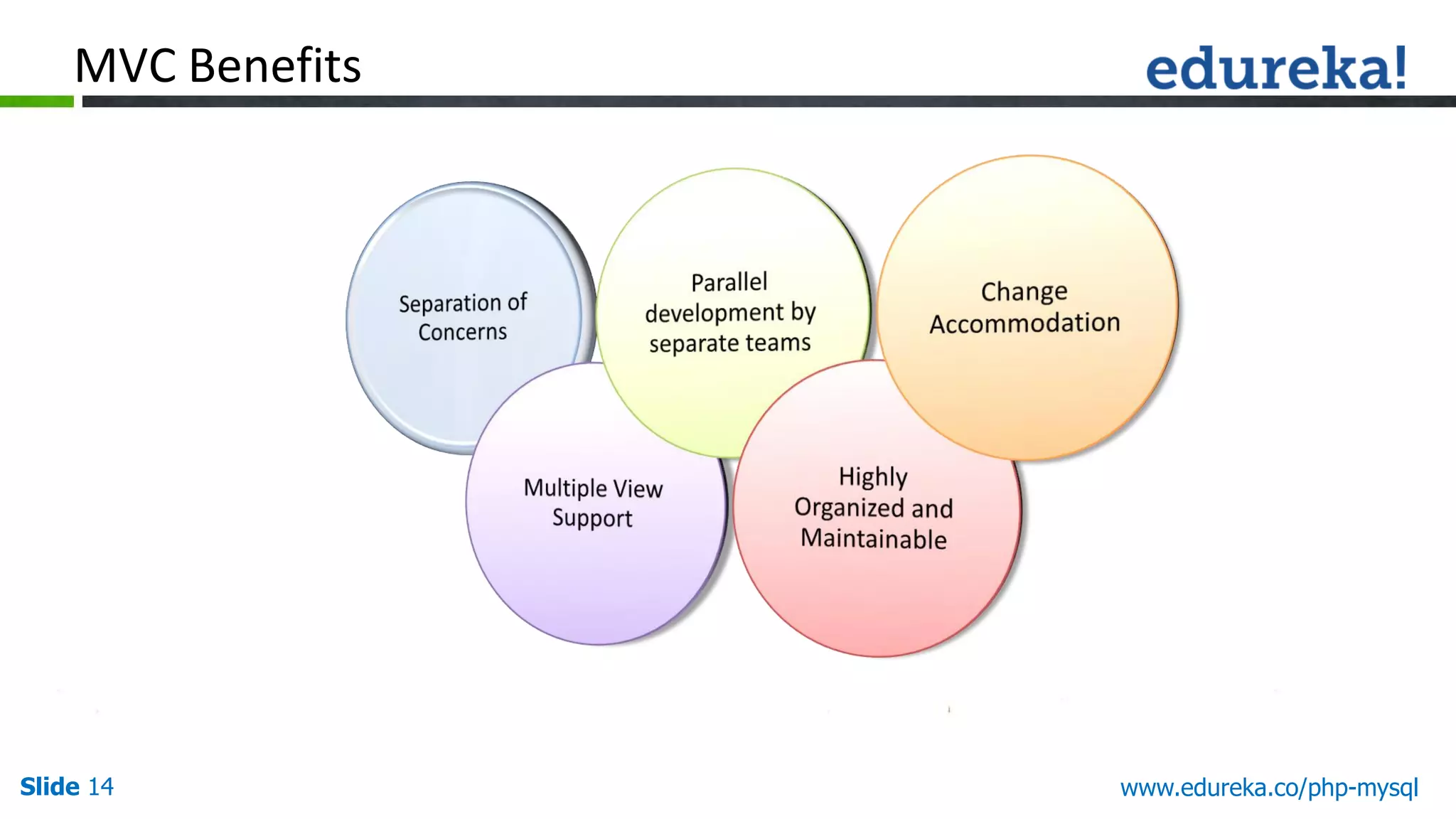
This document outlines the MVC (Model-View-Controller) design pattern, highlighting its importance for PHP developers in organizing application logic and improving code maintainability and reusability. It discusses the challenges faced when developing applications without a framework and explains the roles of each component of MVC: the model, view, and controller. Additionally, it emphasizes principles like 'Don't Repeat Yourself' (DRY) and 'Convention Over Configuration' to promote efficient coding practices.