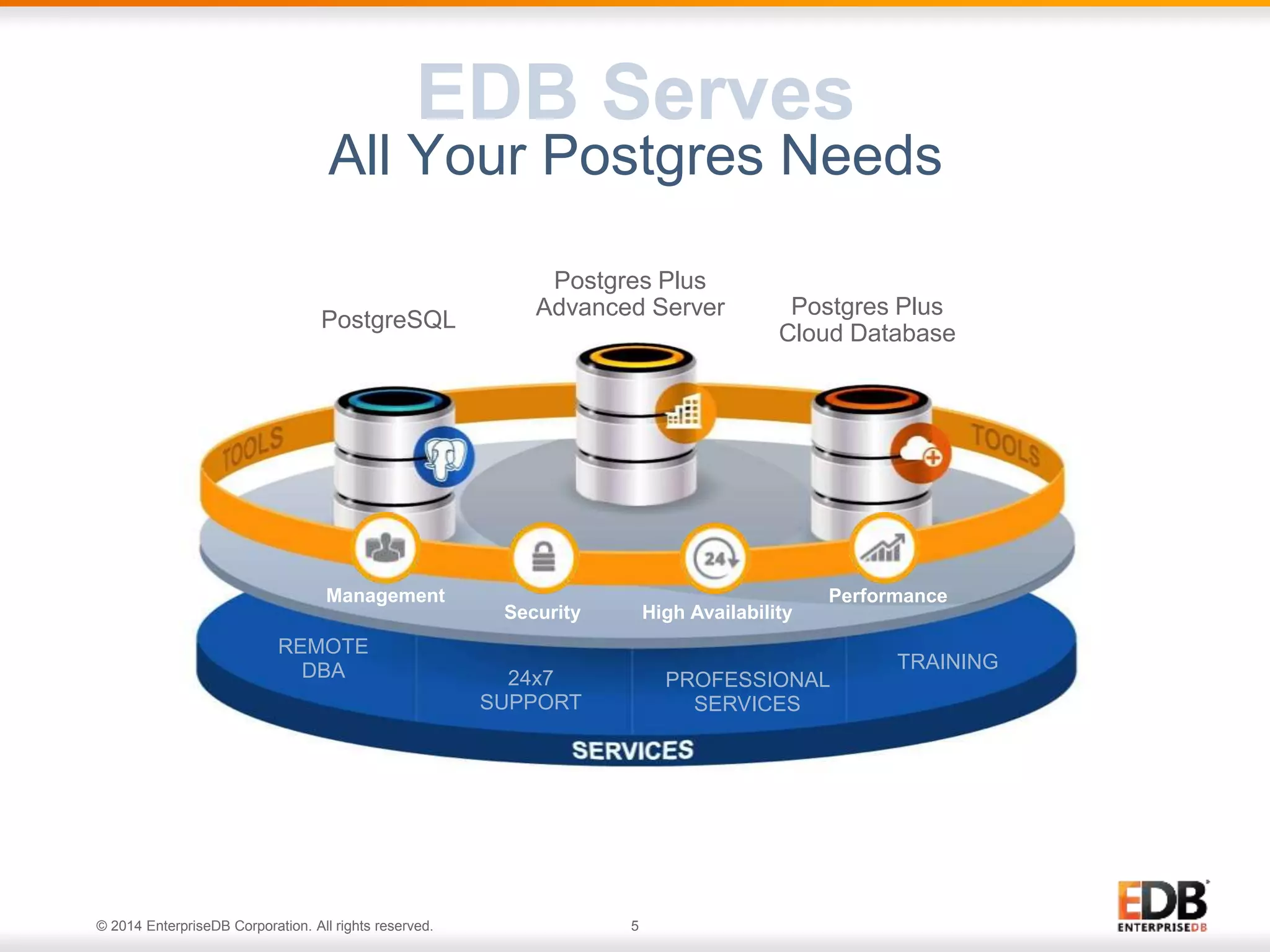
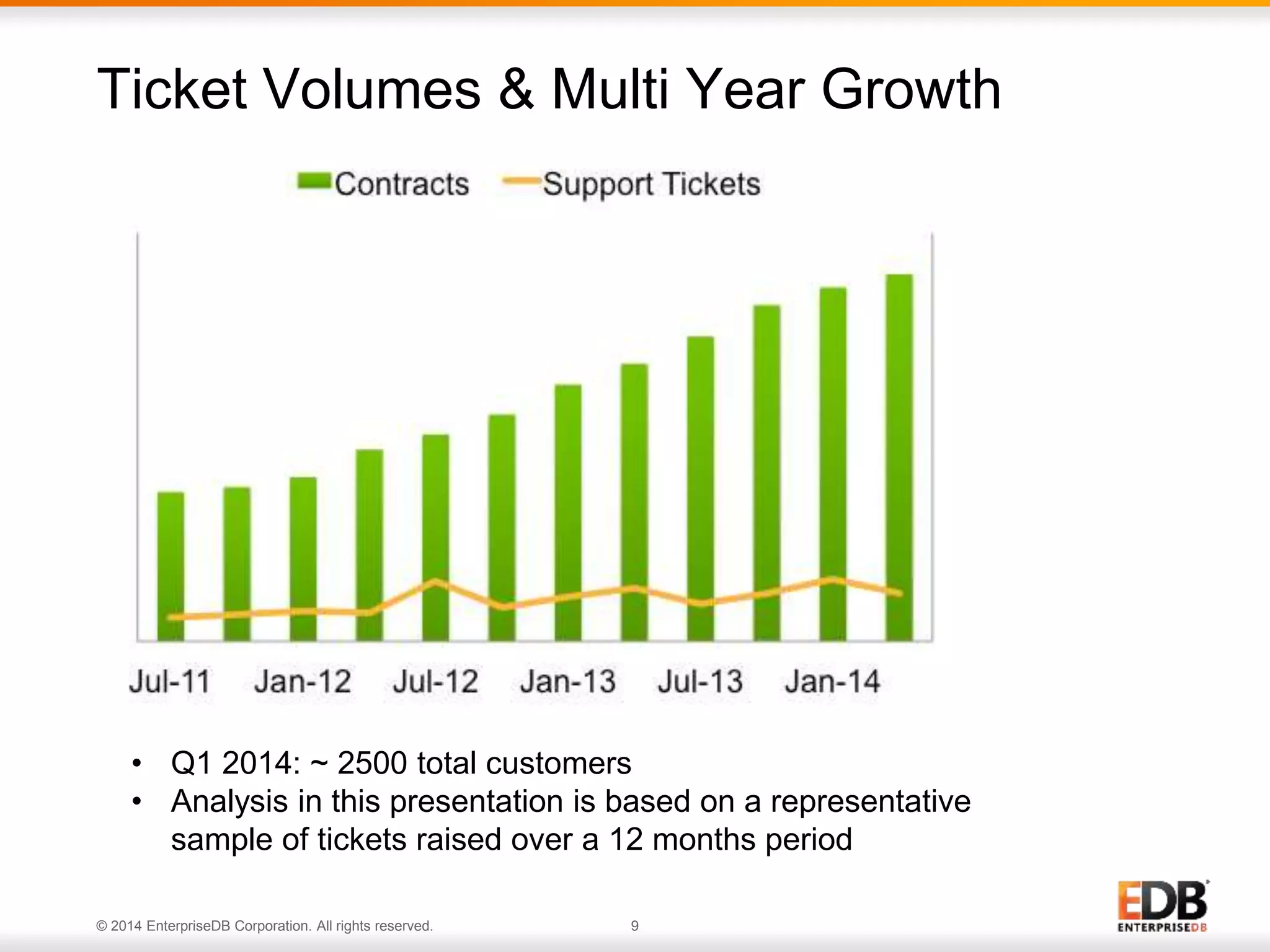
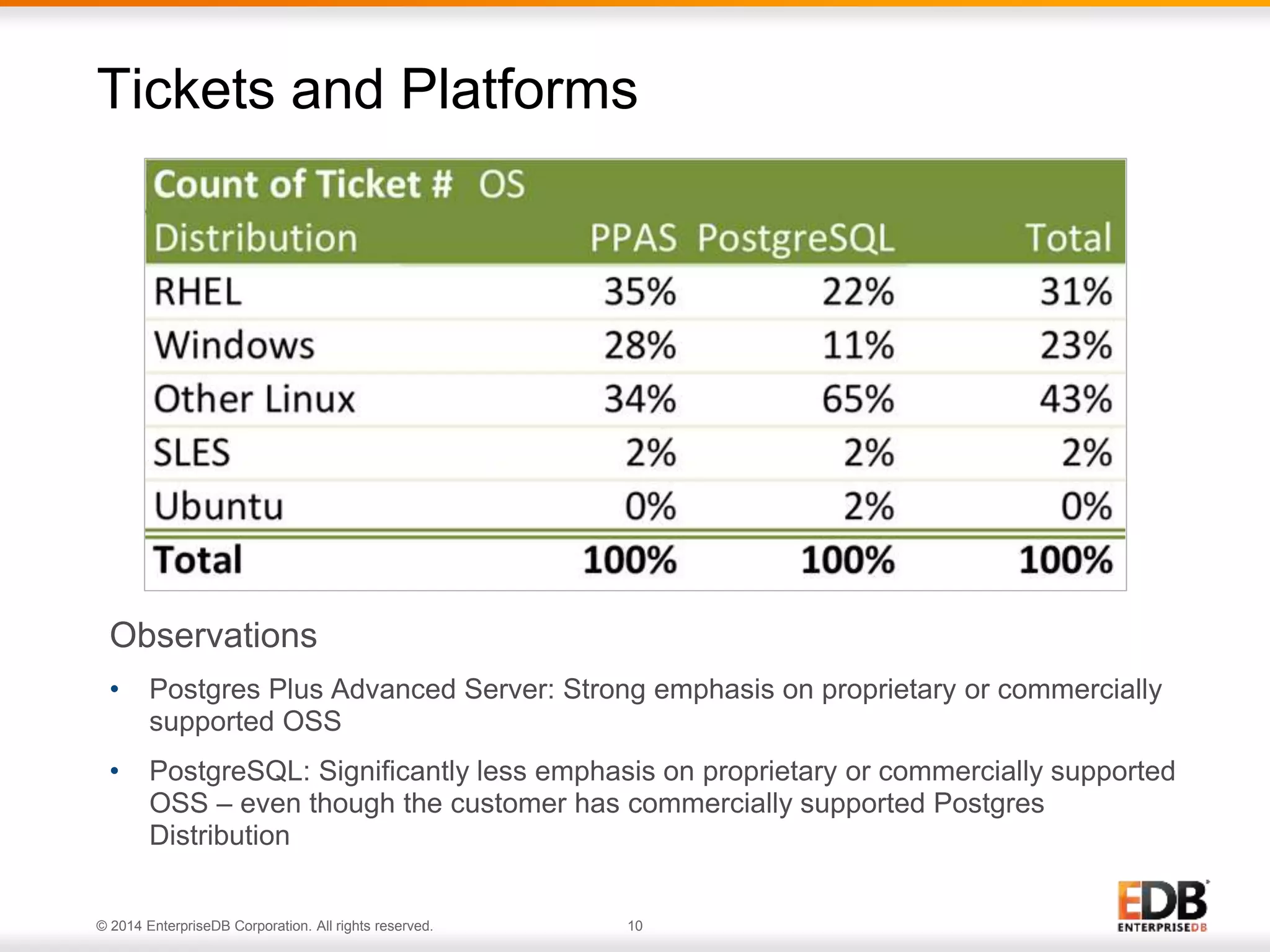
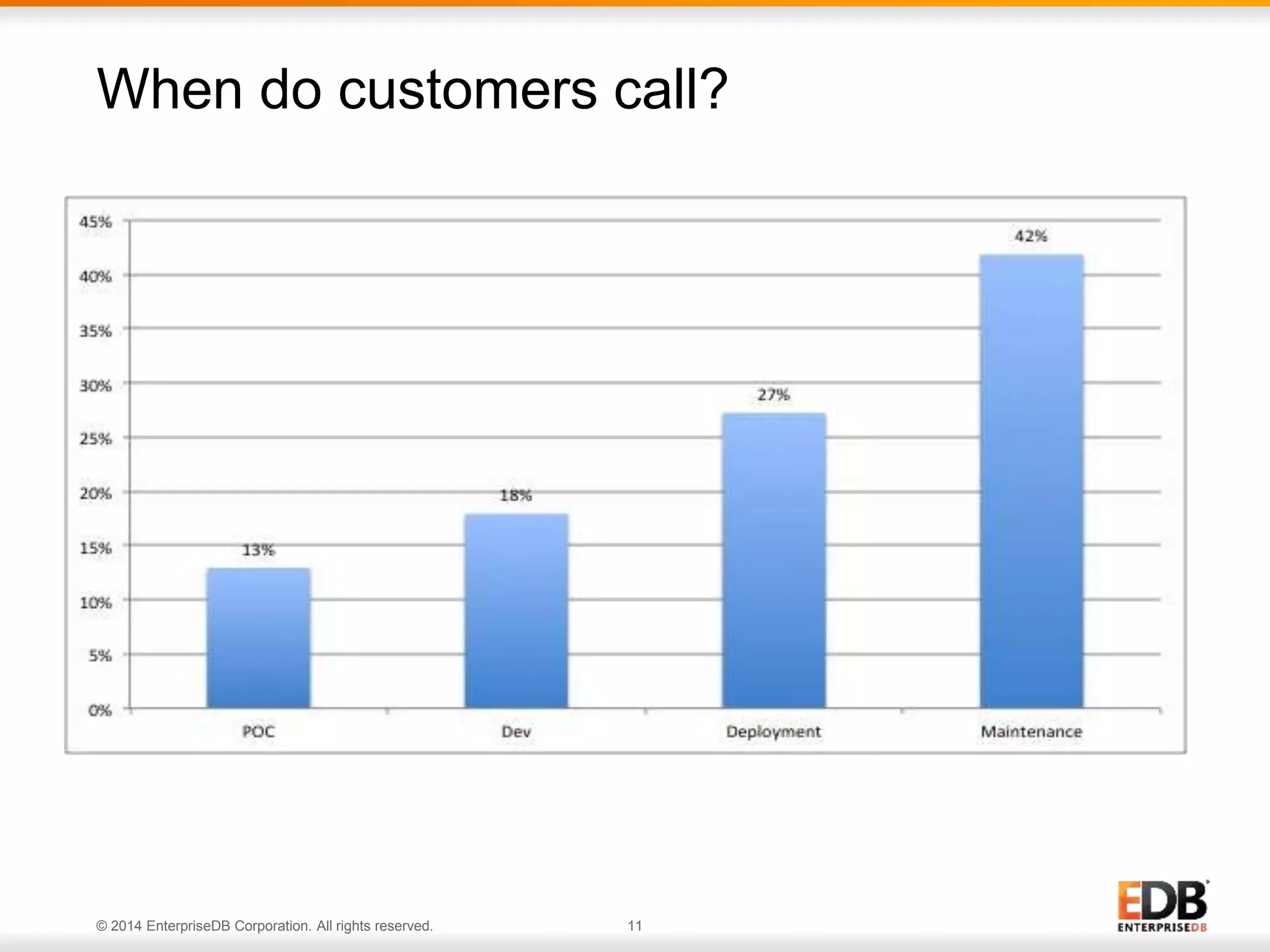
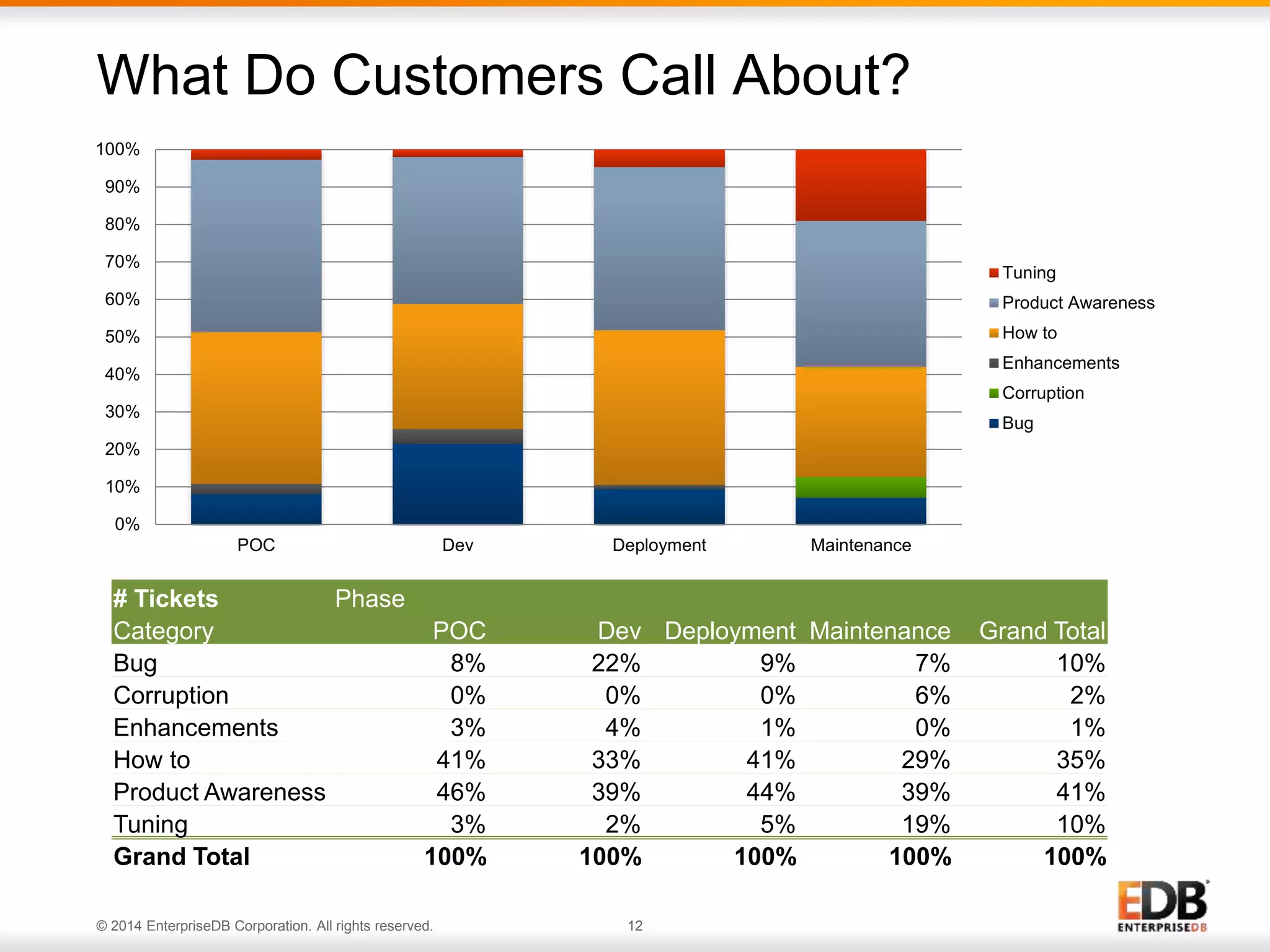
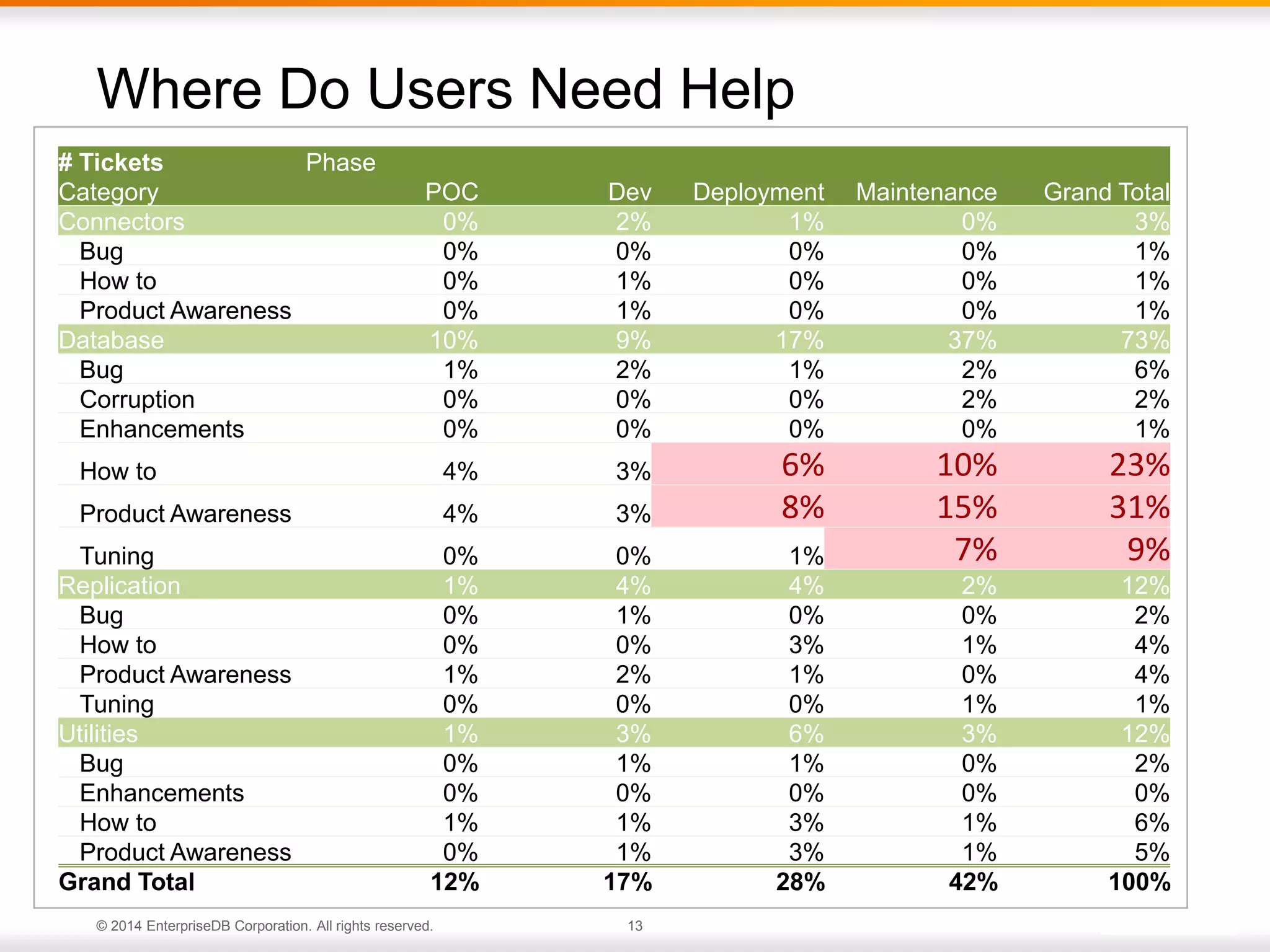
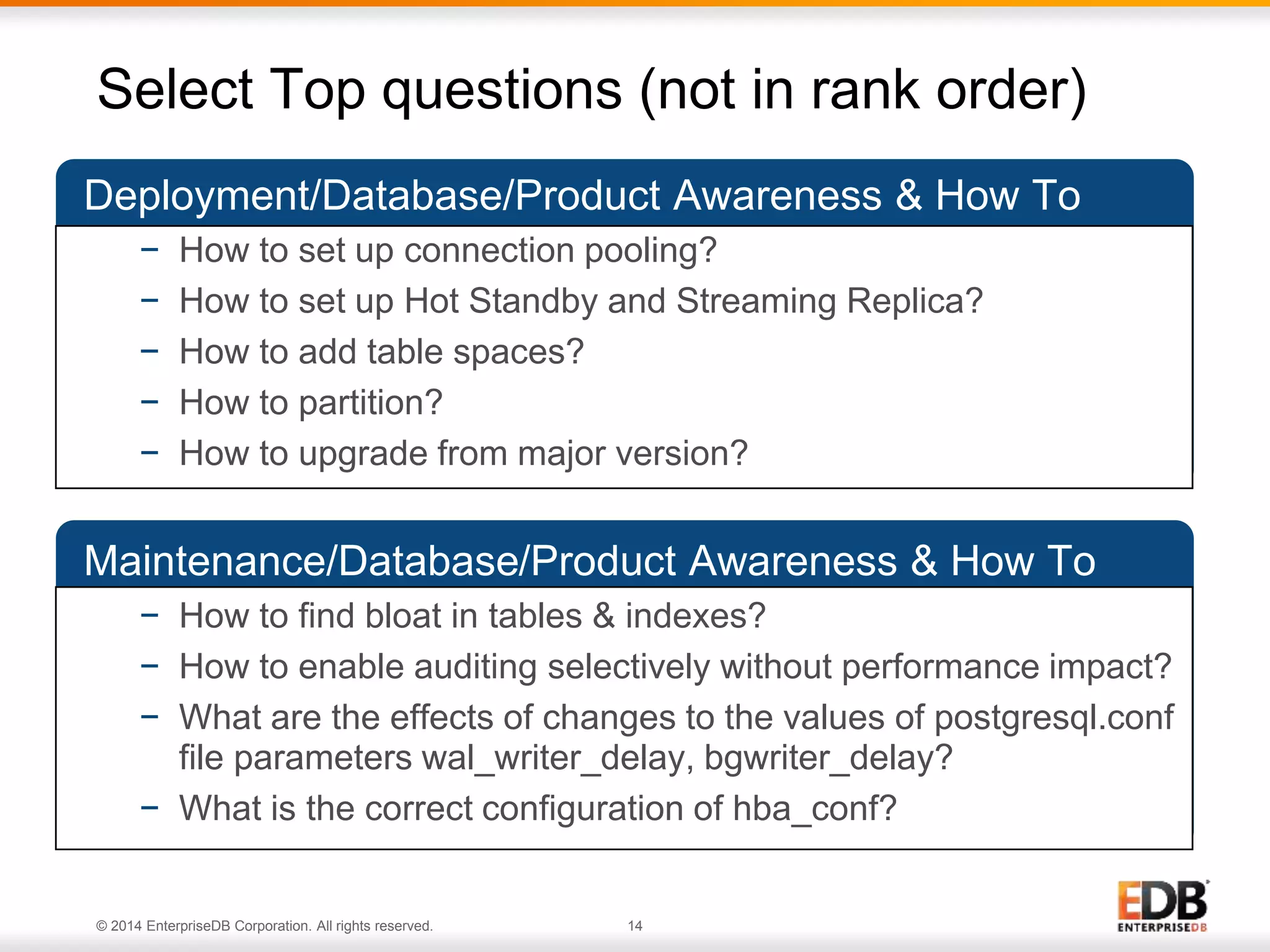
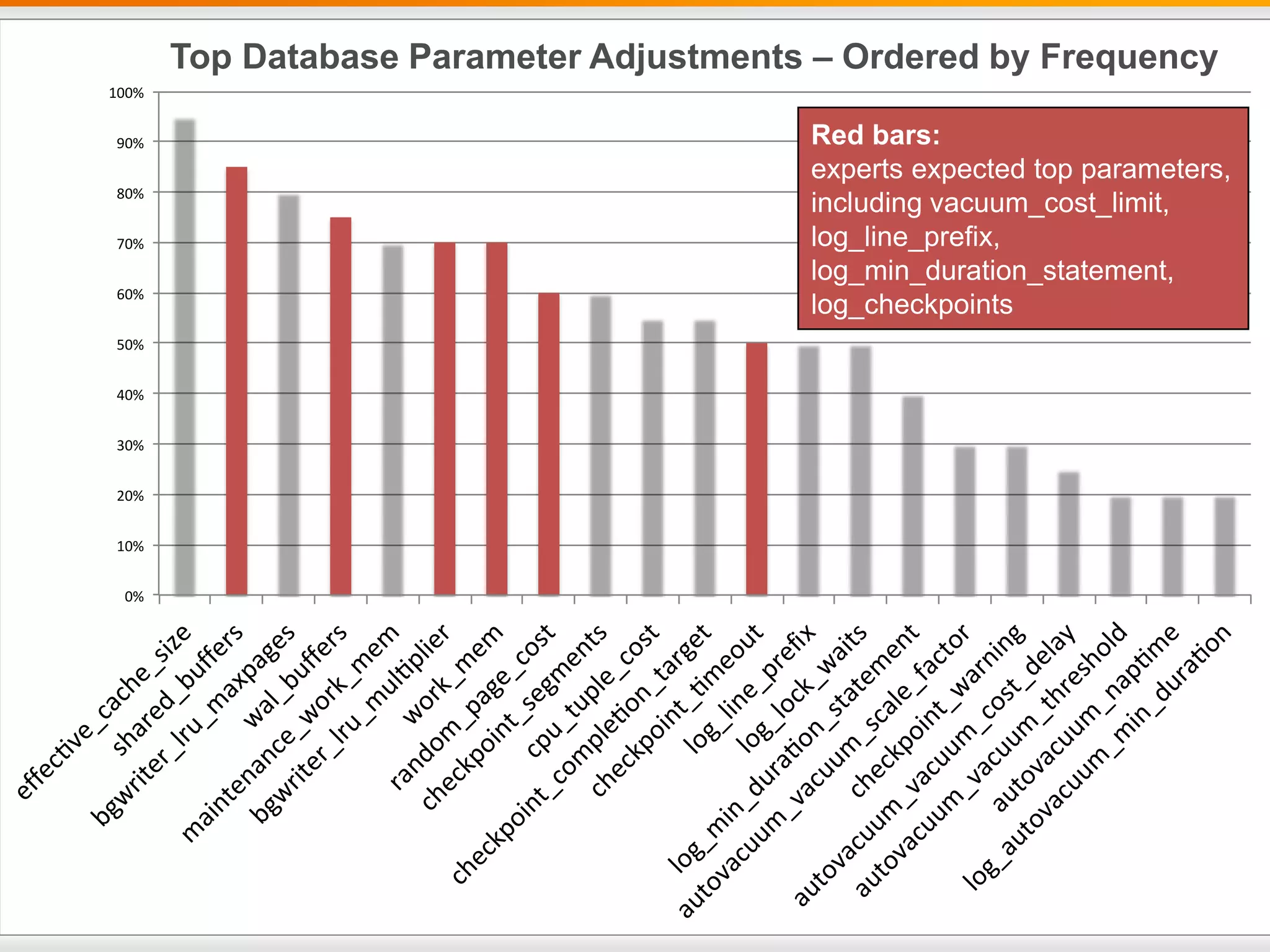
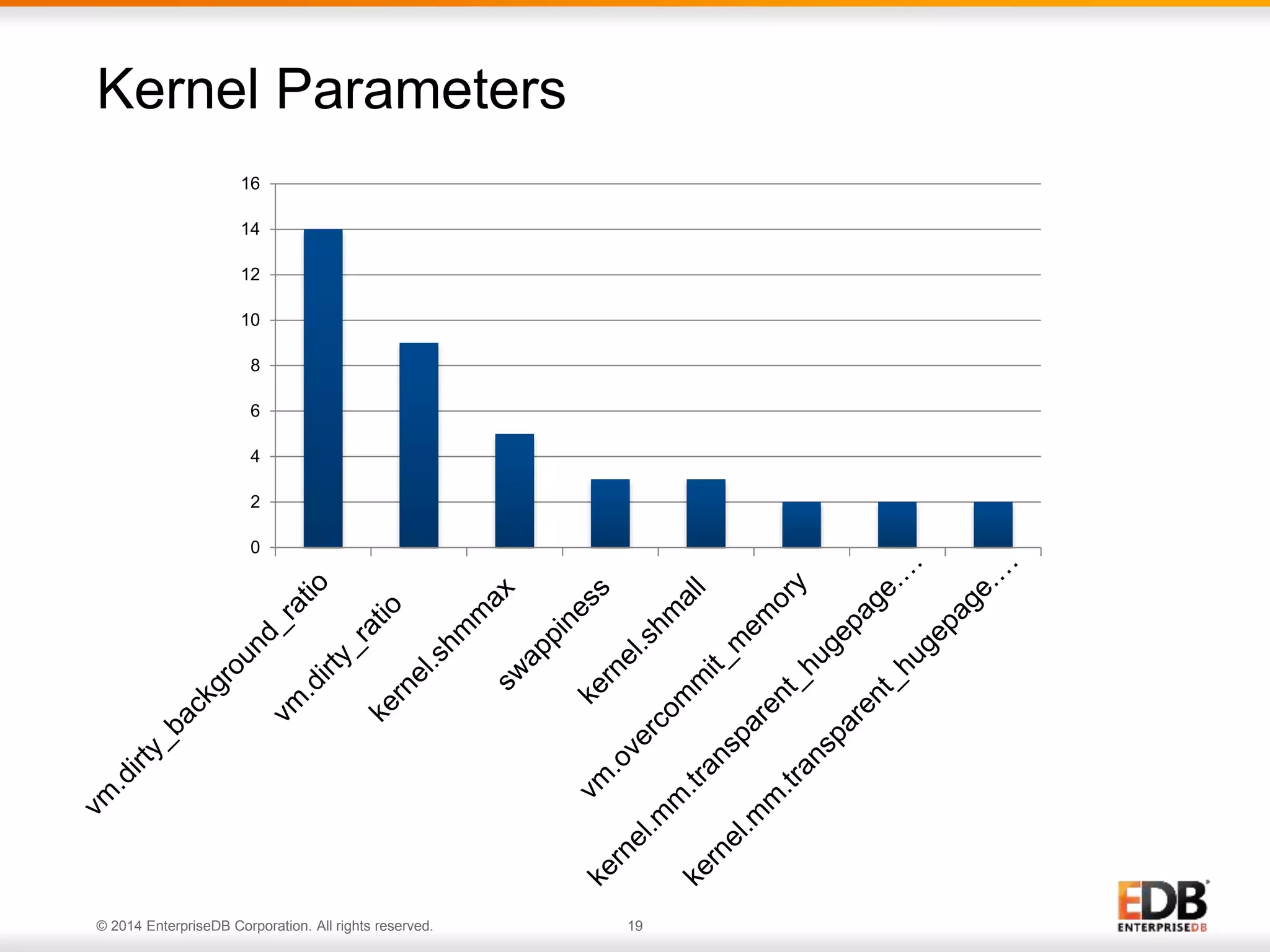
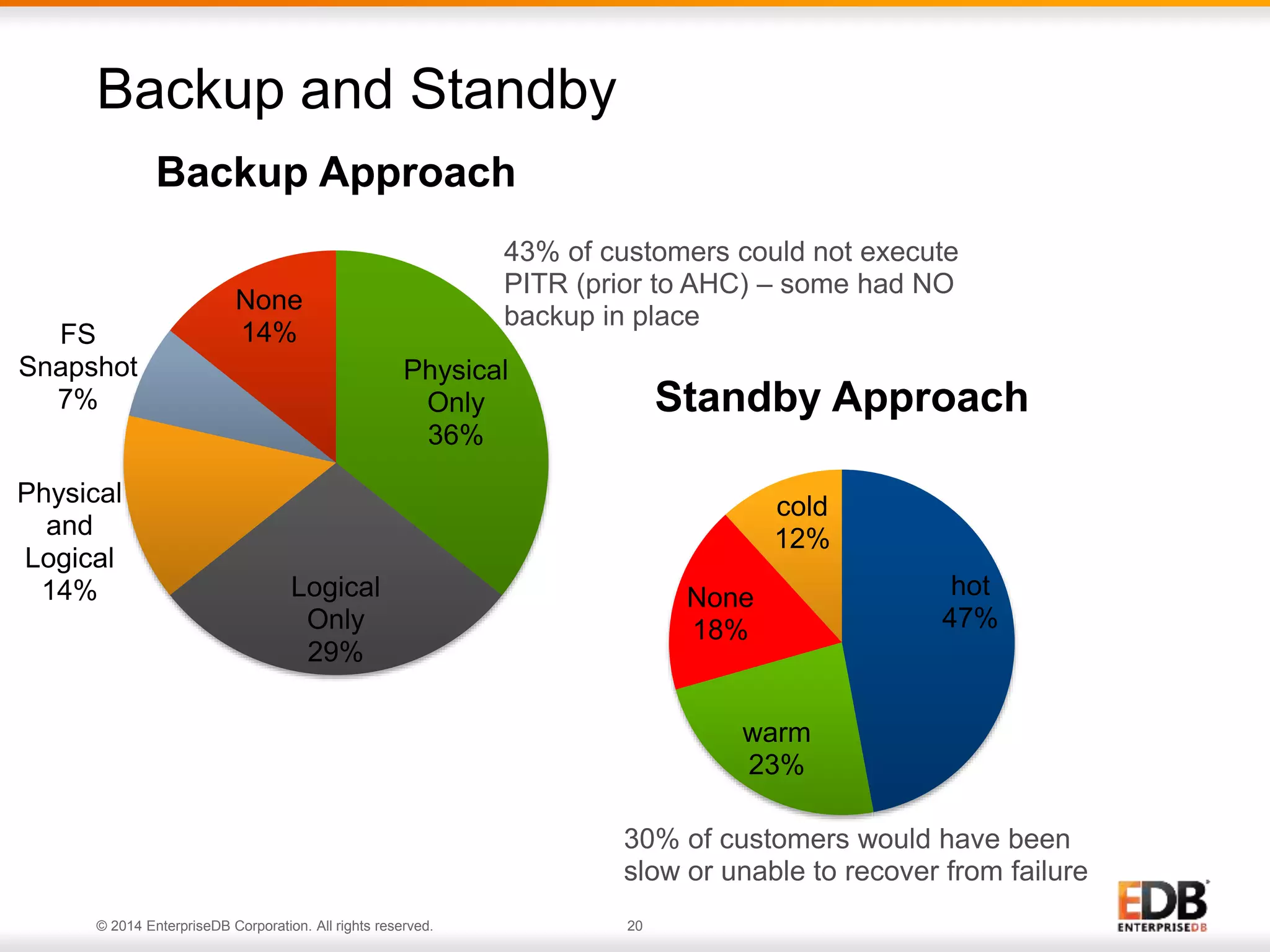
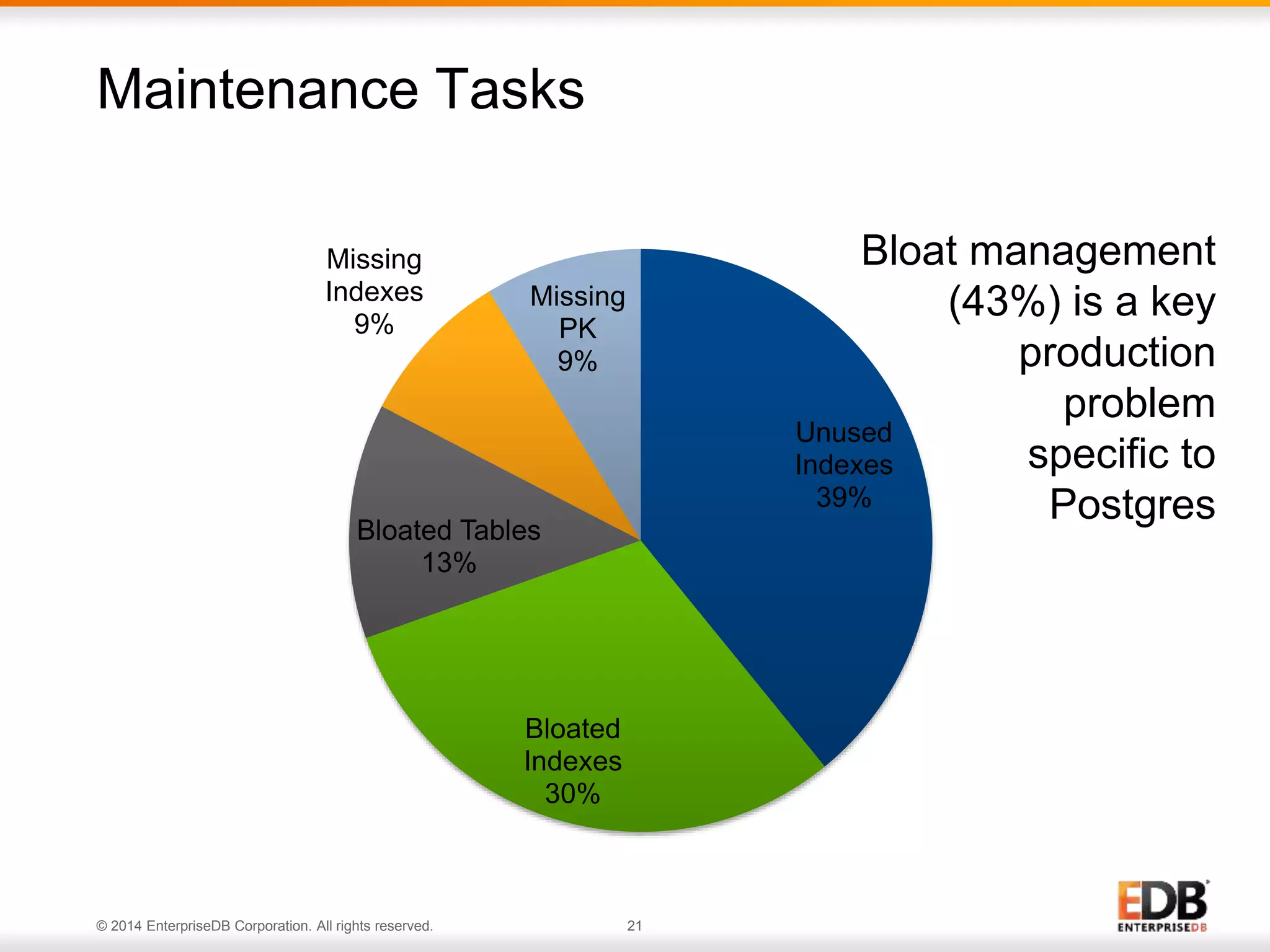
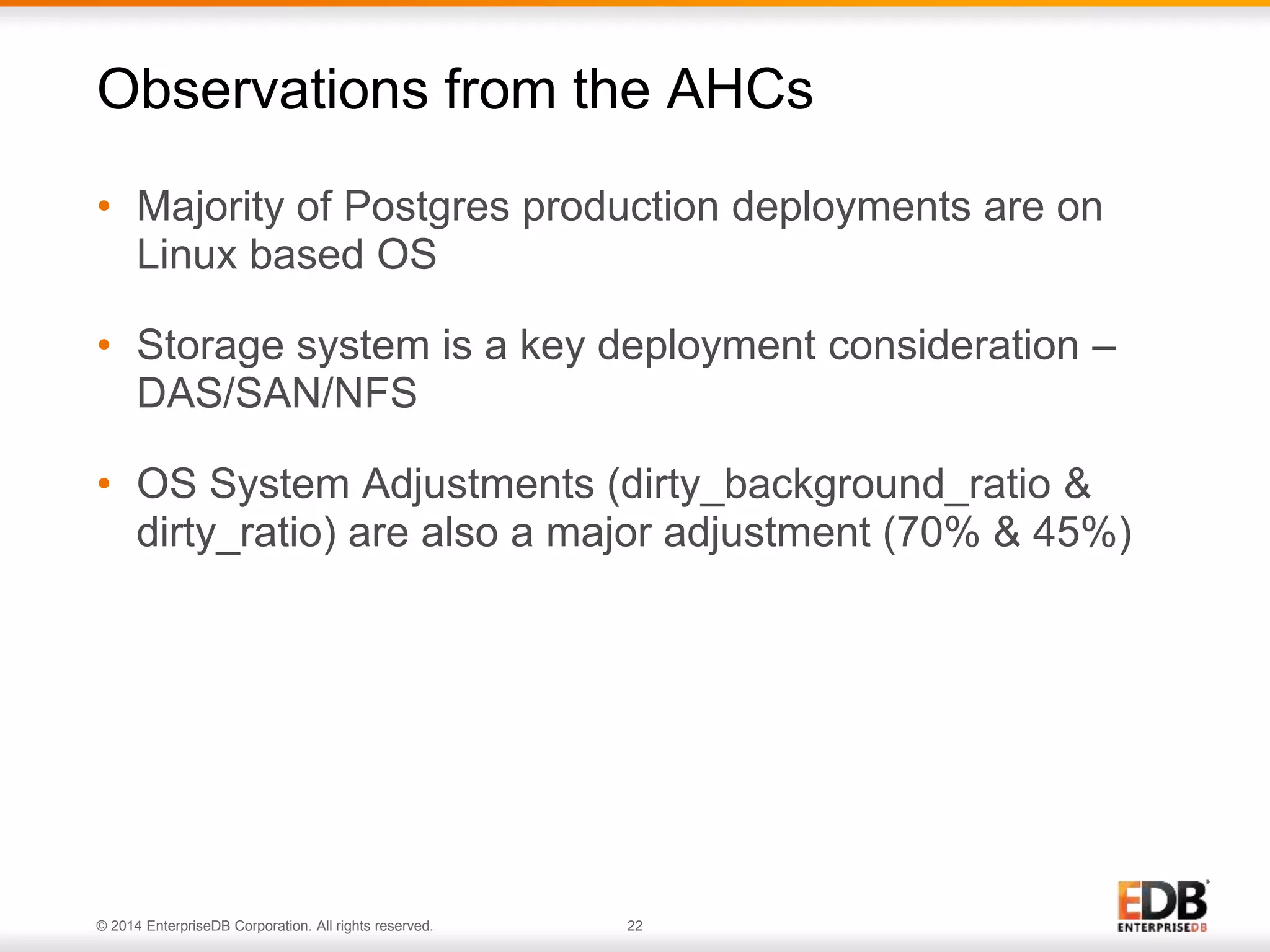
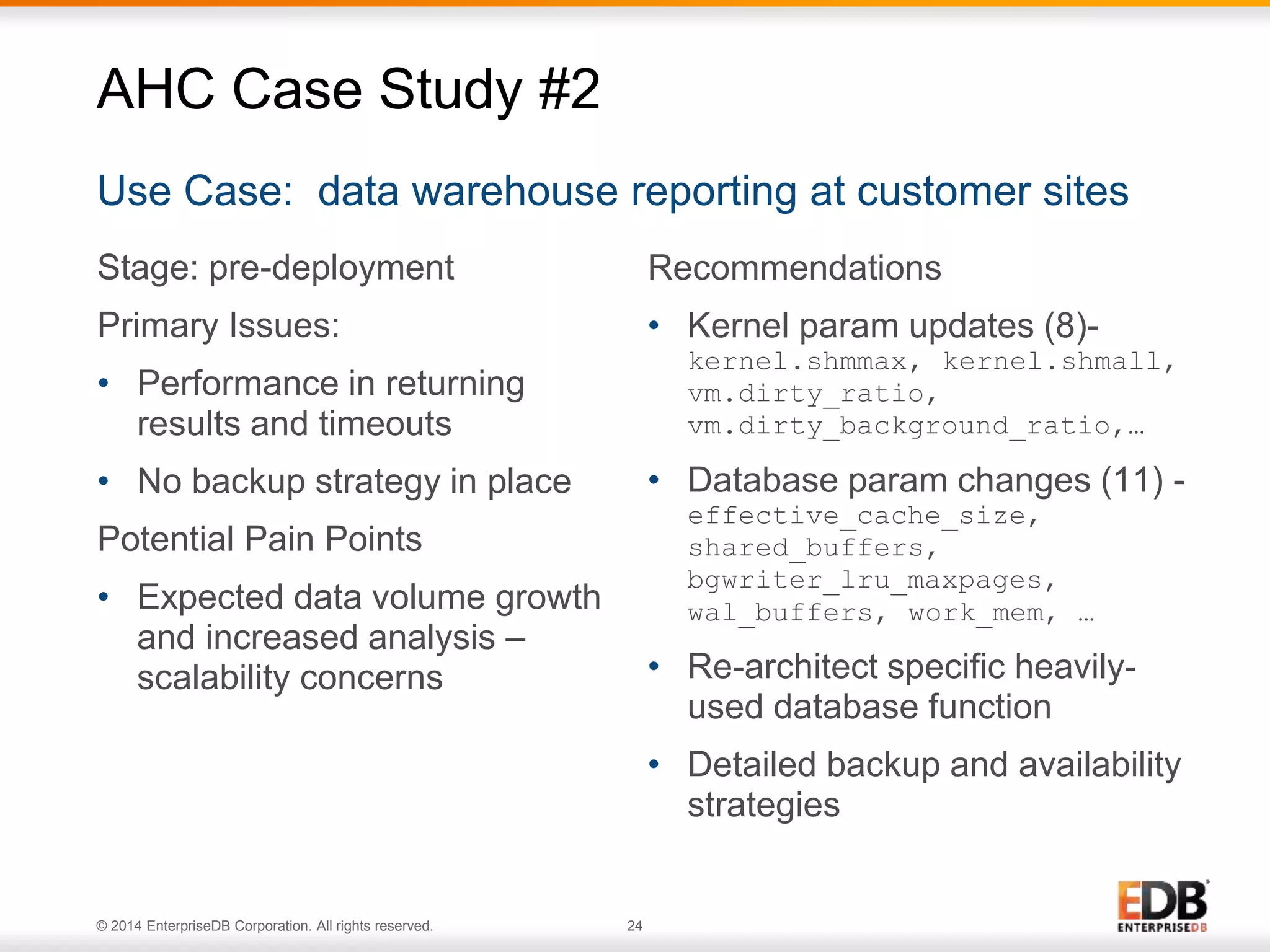
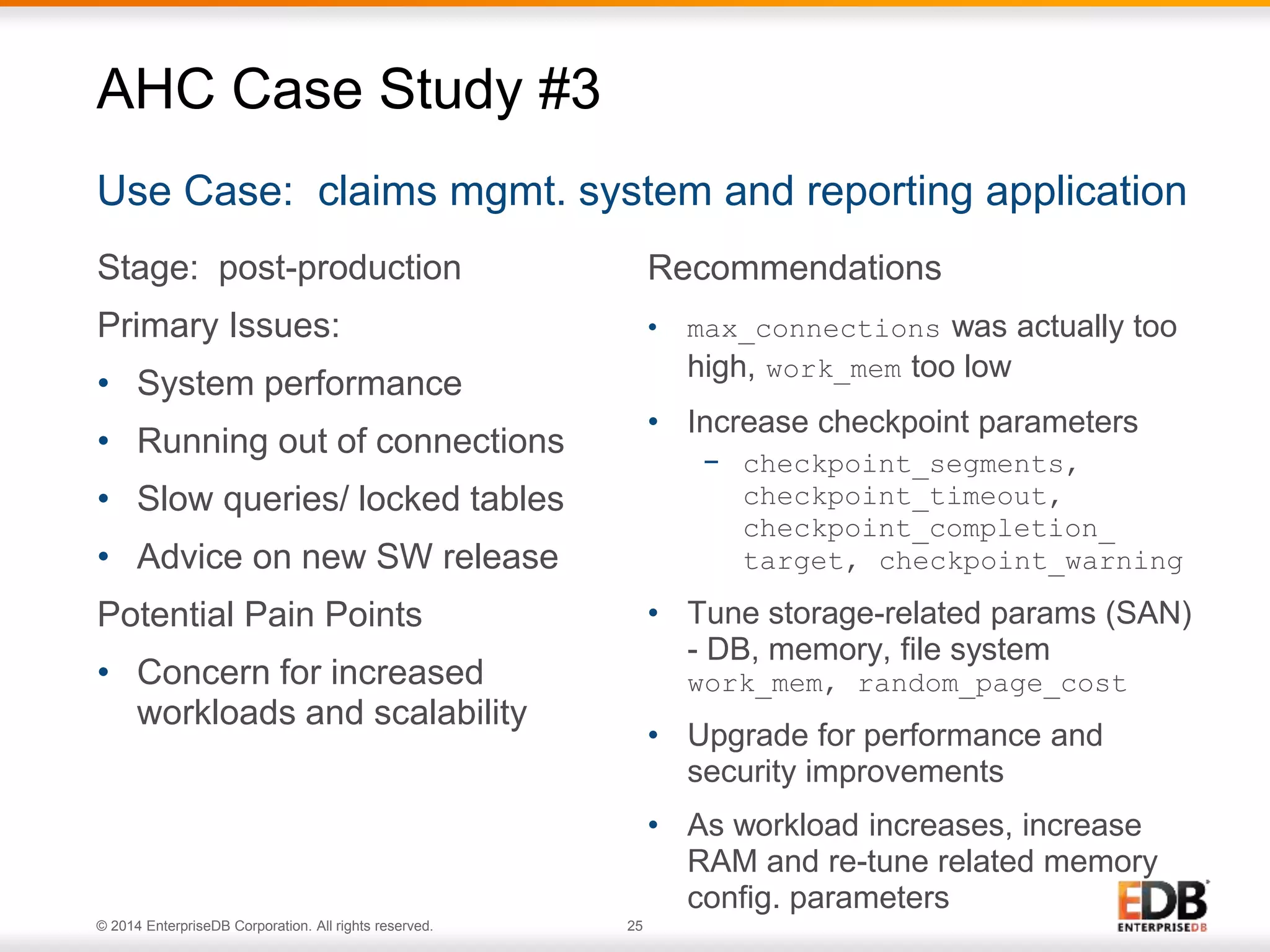
The document outlines best practices for deploying and maintaining PostgreSQL in enterprise environments, highlighting key challenges, tuning parameters, and maintenance strategies. It emphasizes the importance of backup and recovery plans, as well as the need for PostgreSQL users to enhance their understanding of the database lifecycle. The document also provides insights from support ticket analyses to improve user success with PostgreSQL.