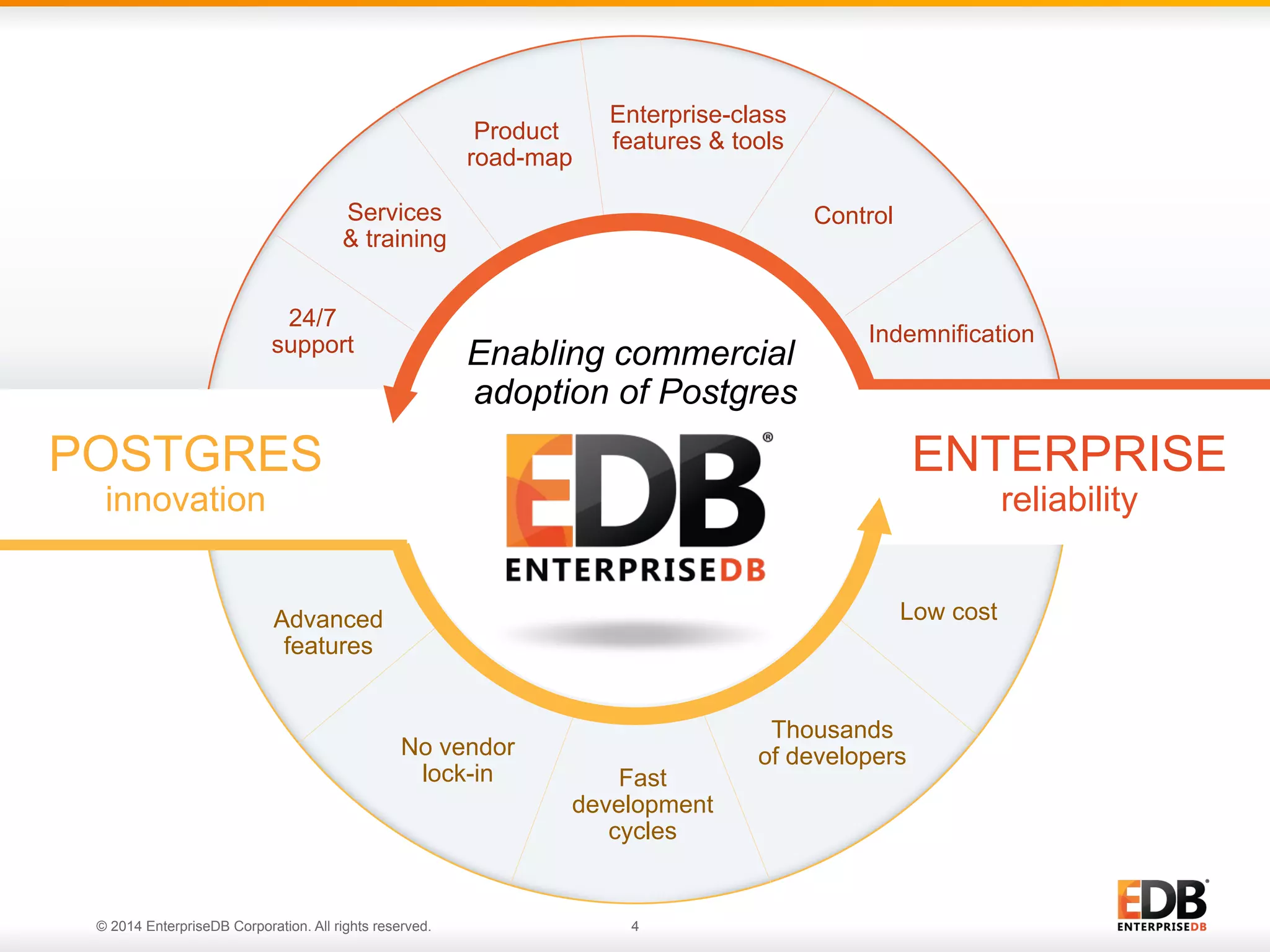
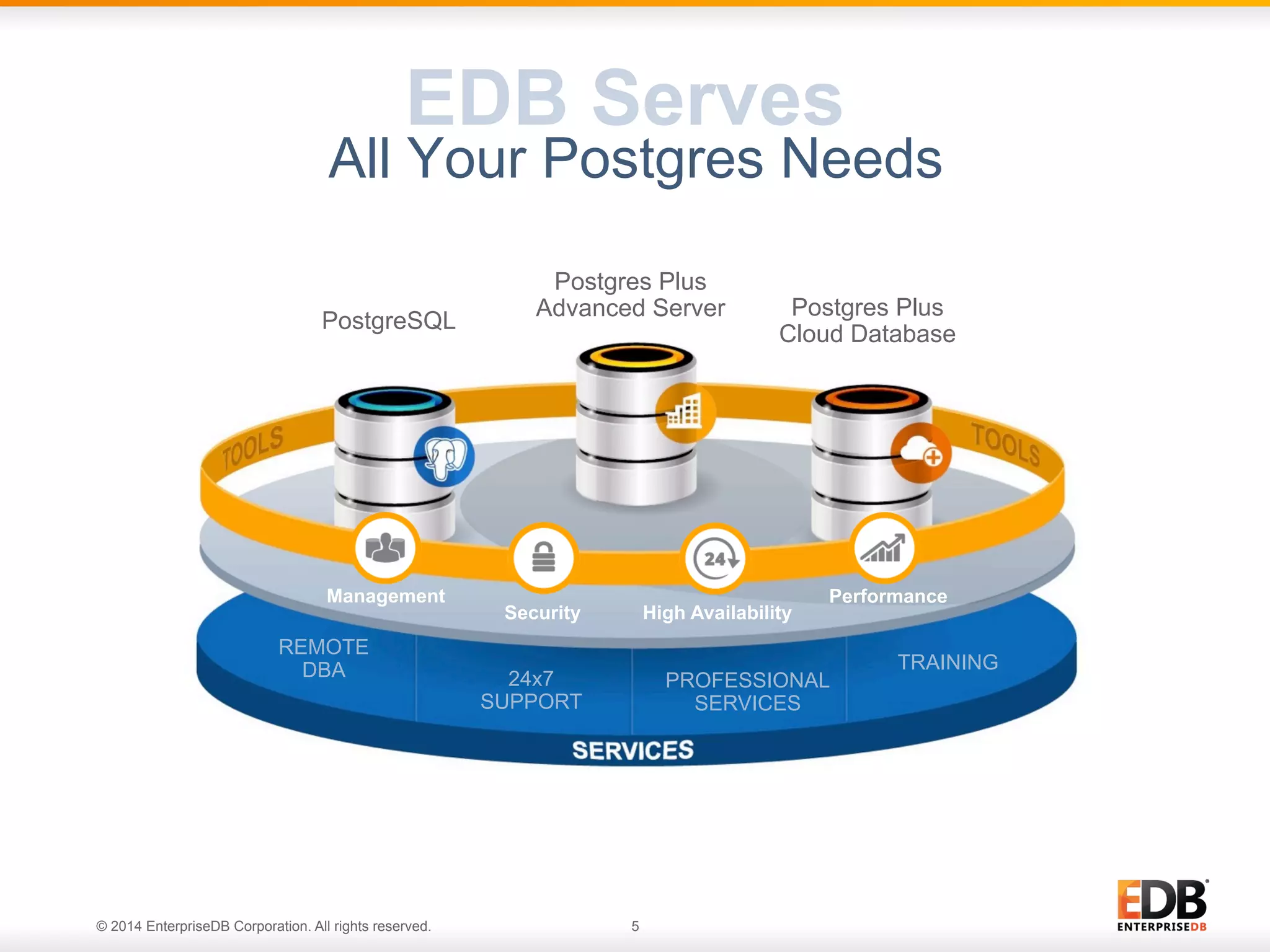
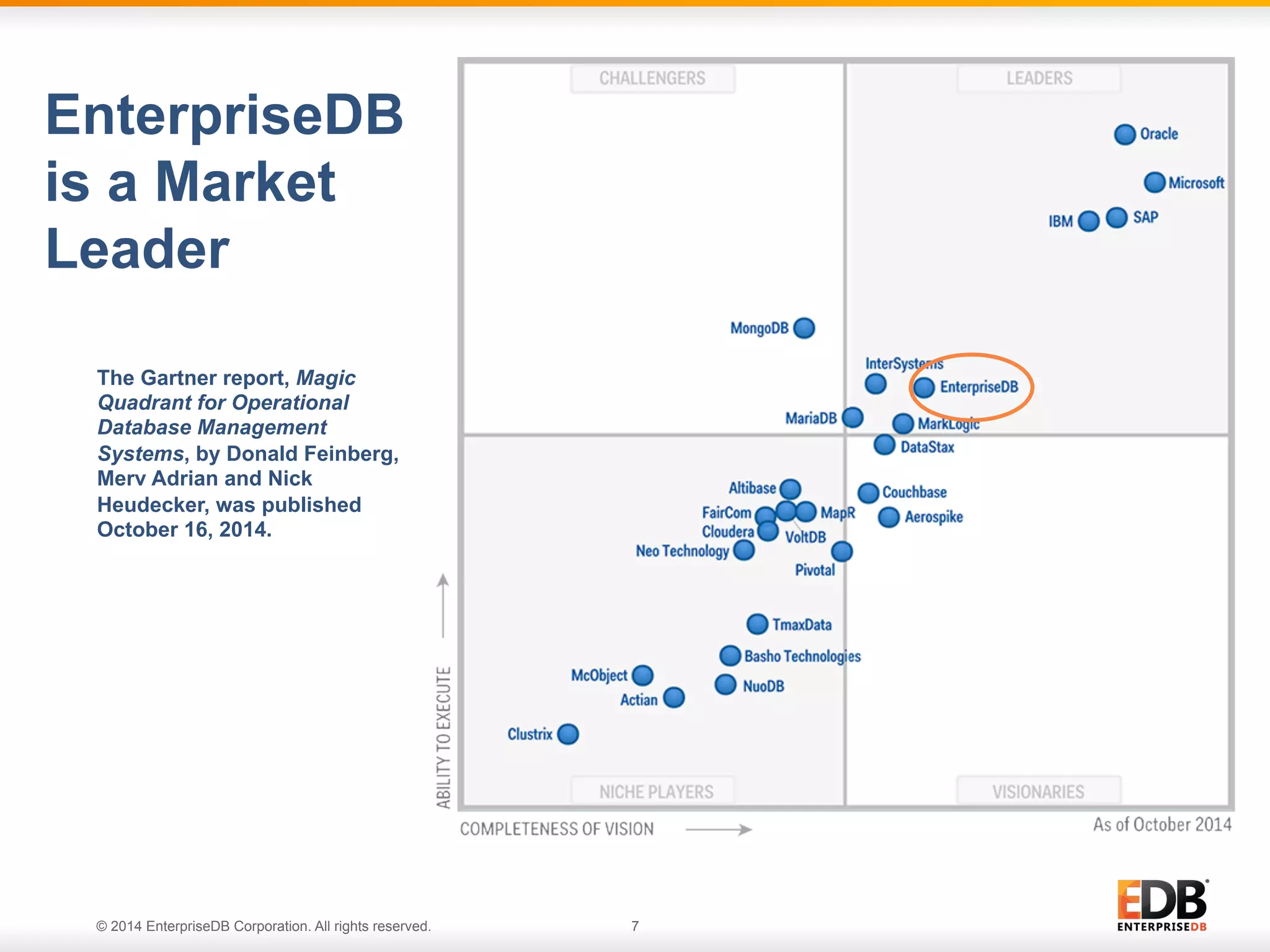
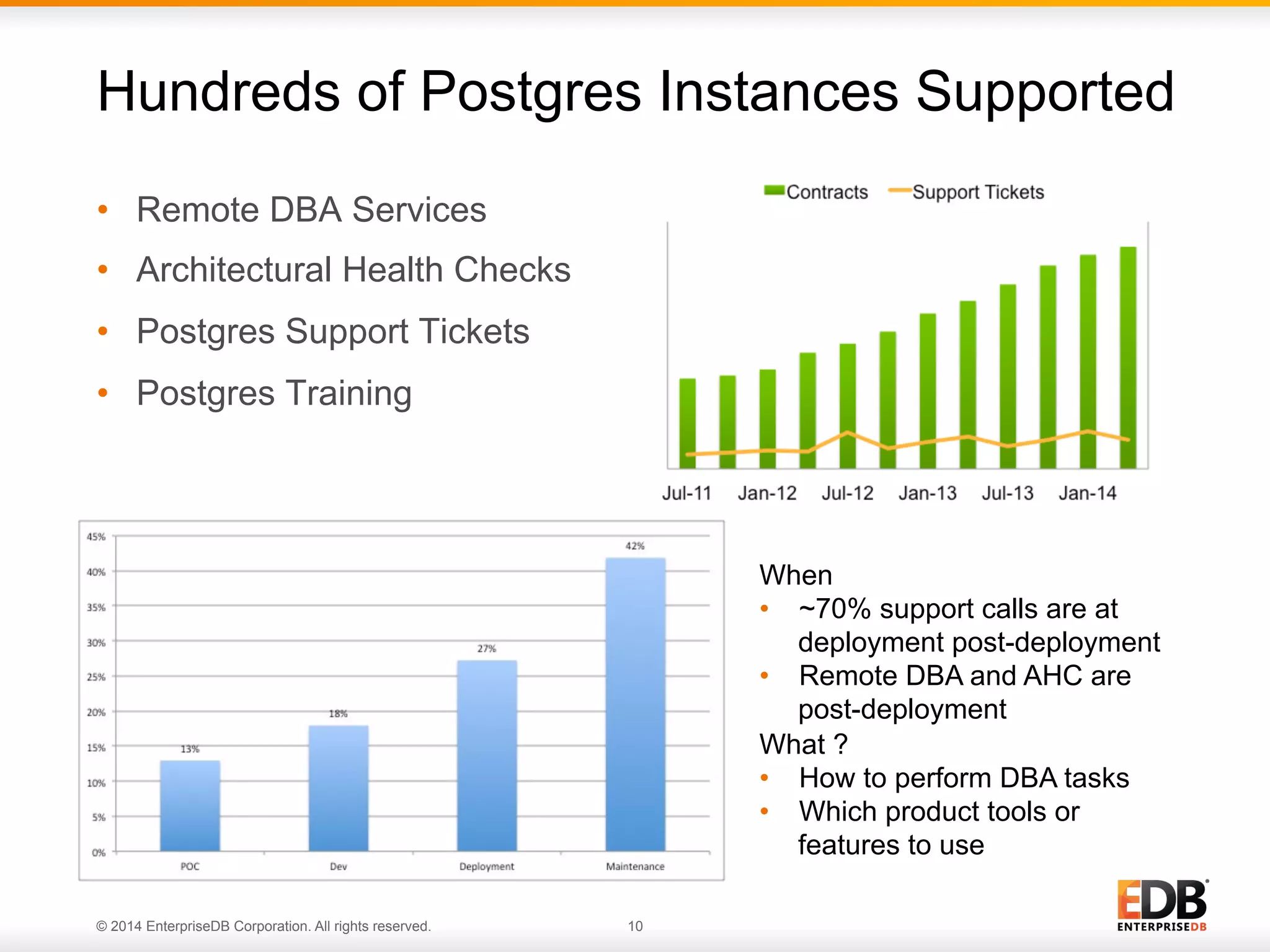
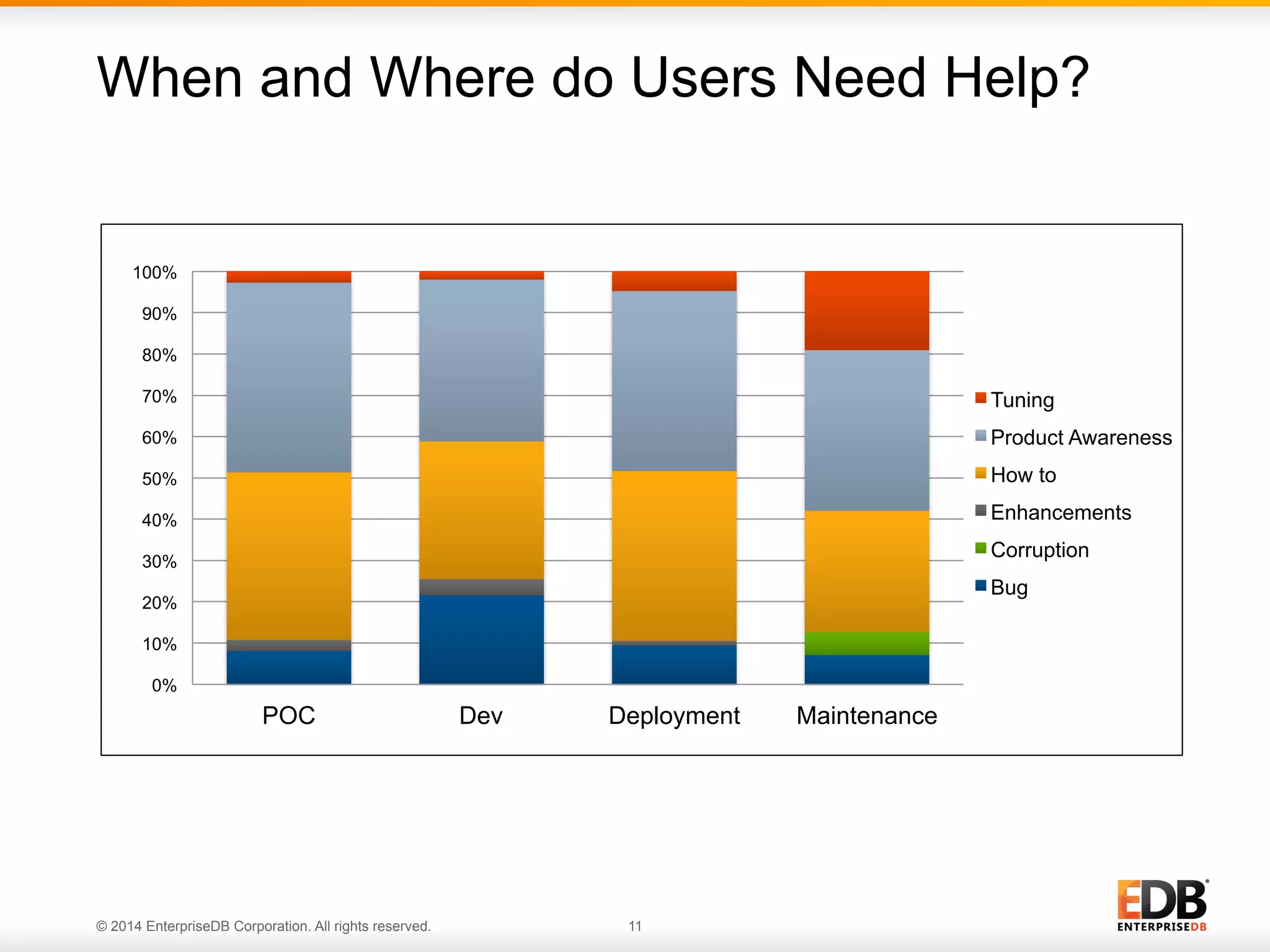
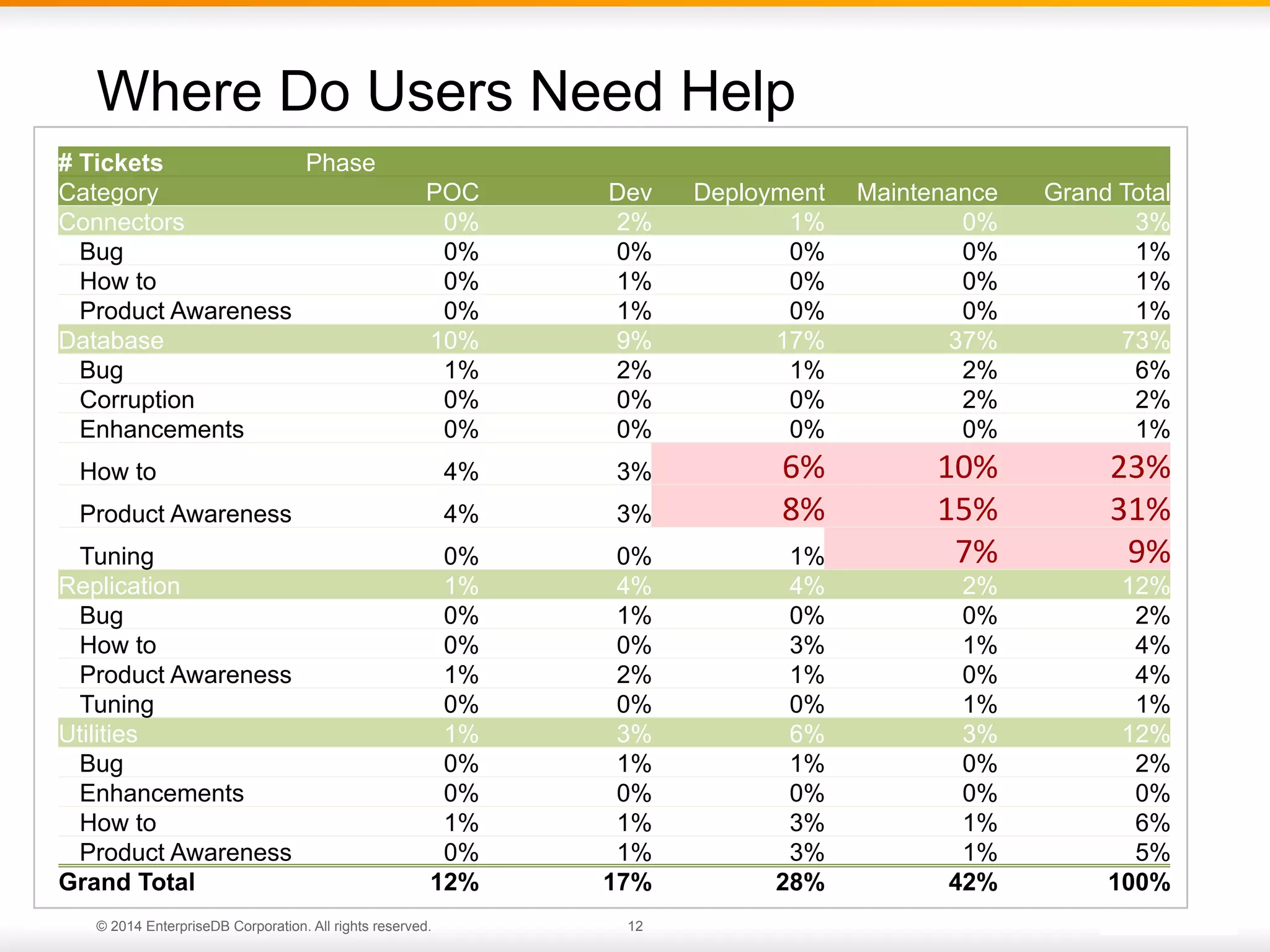
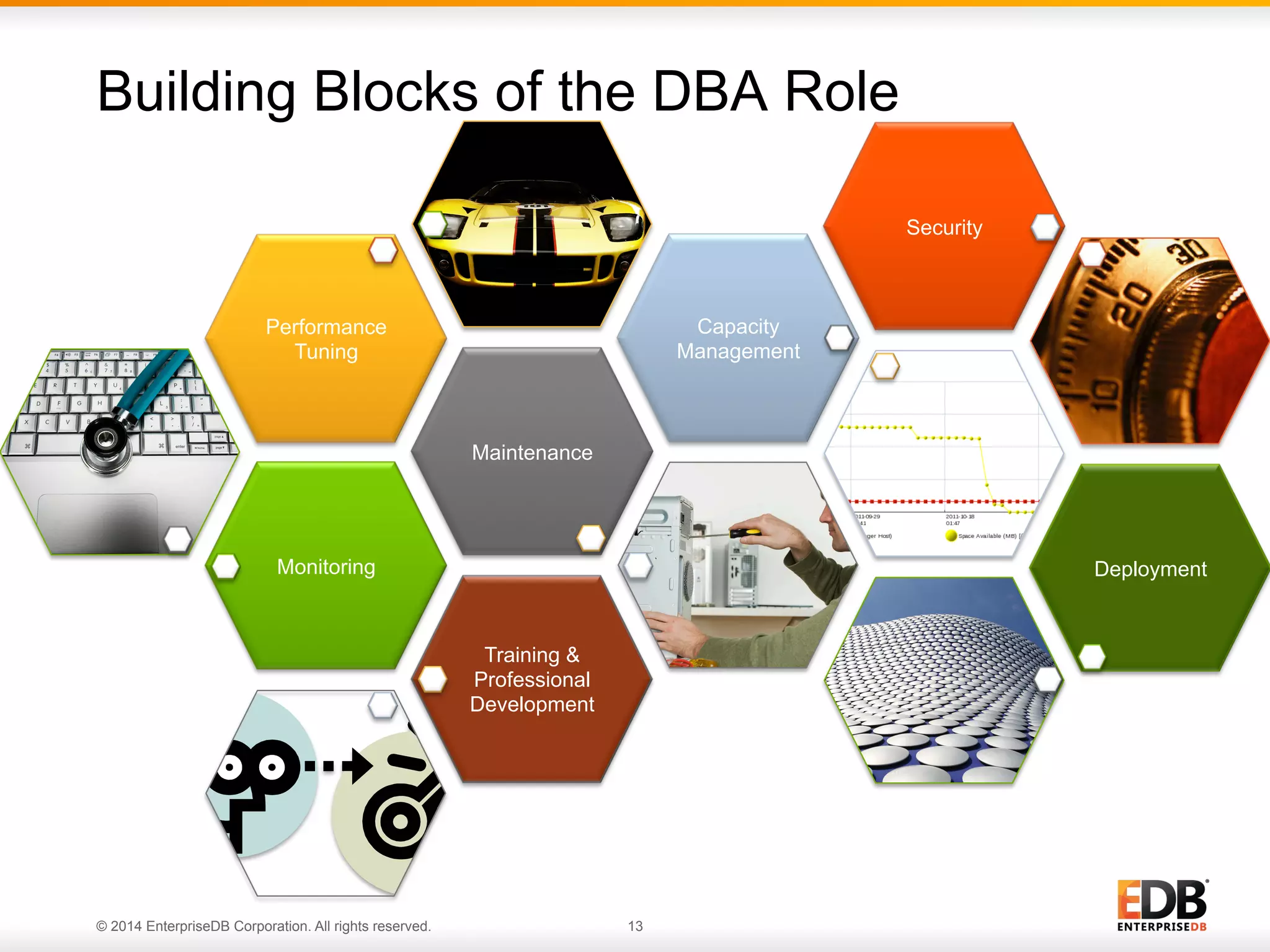
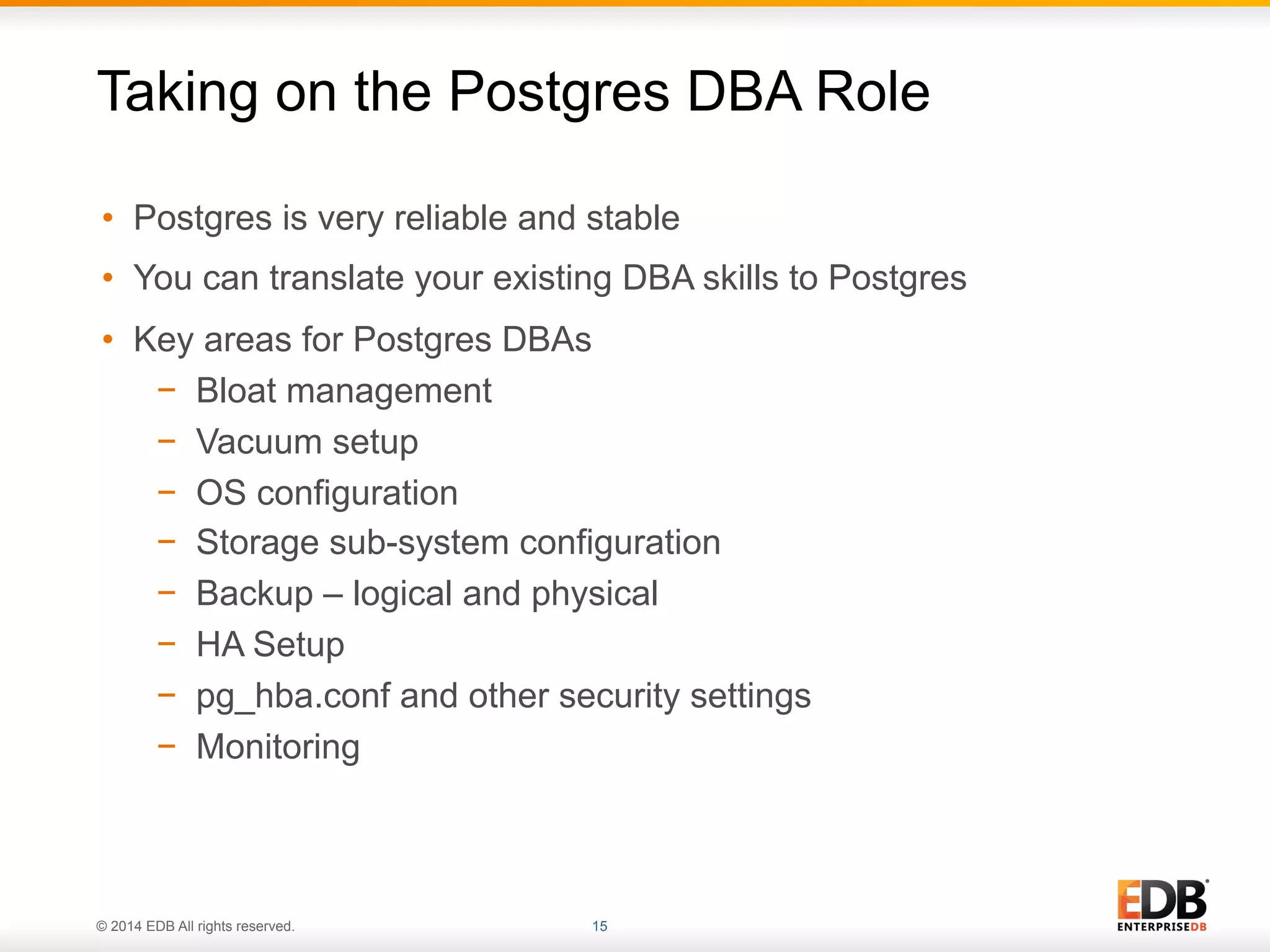
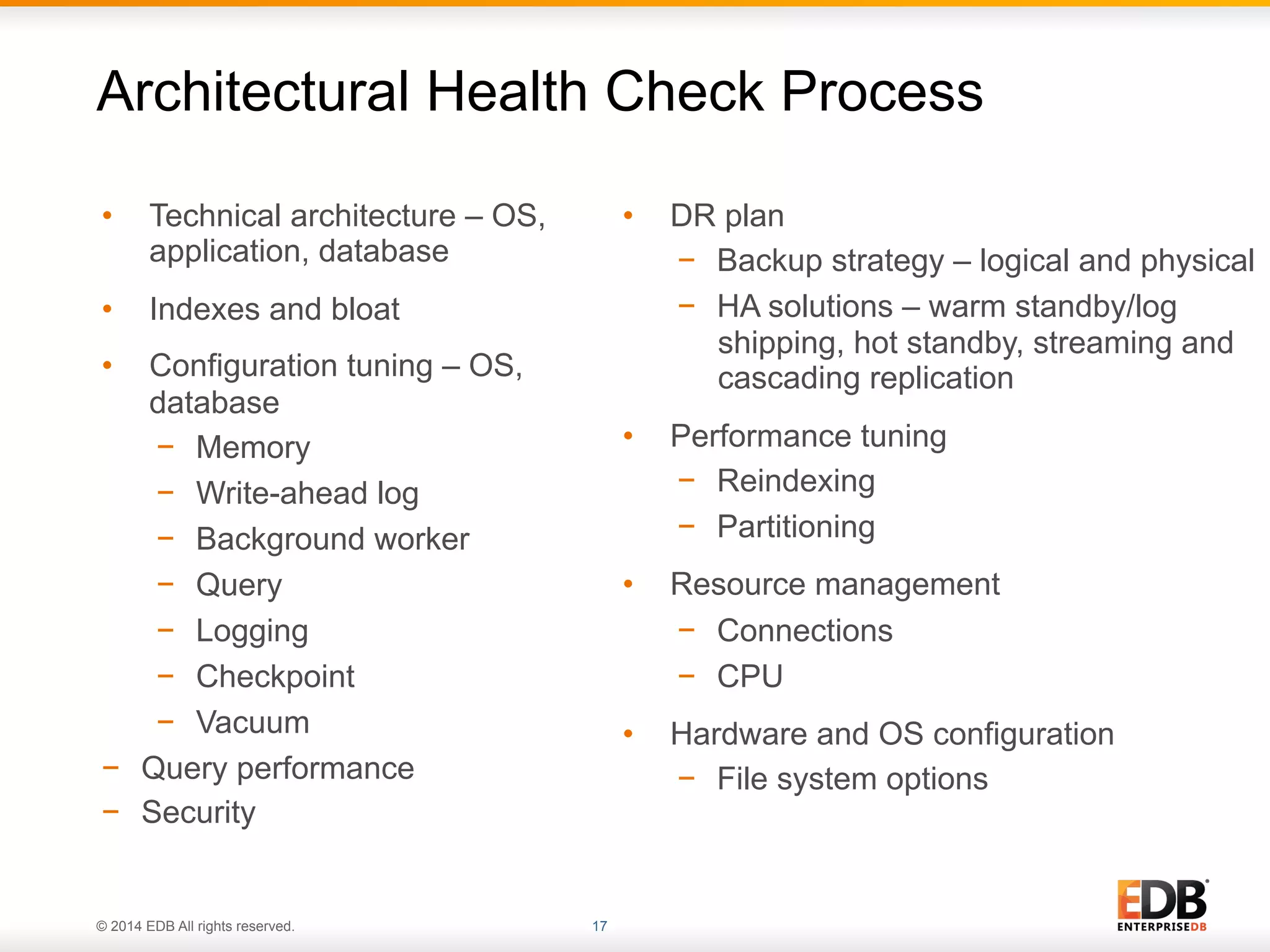
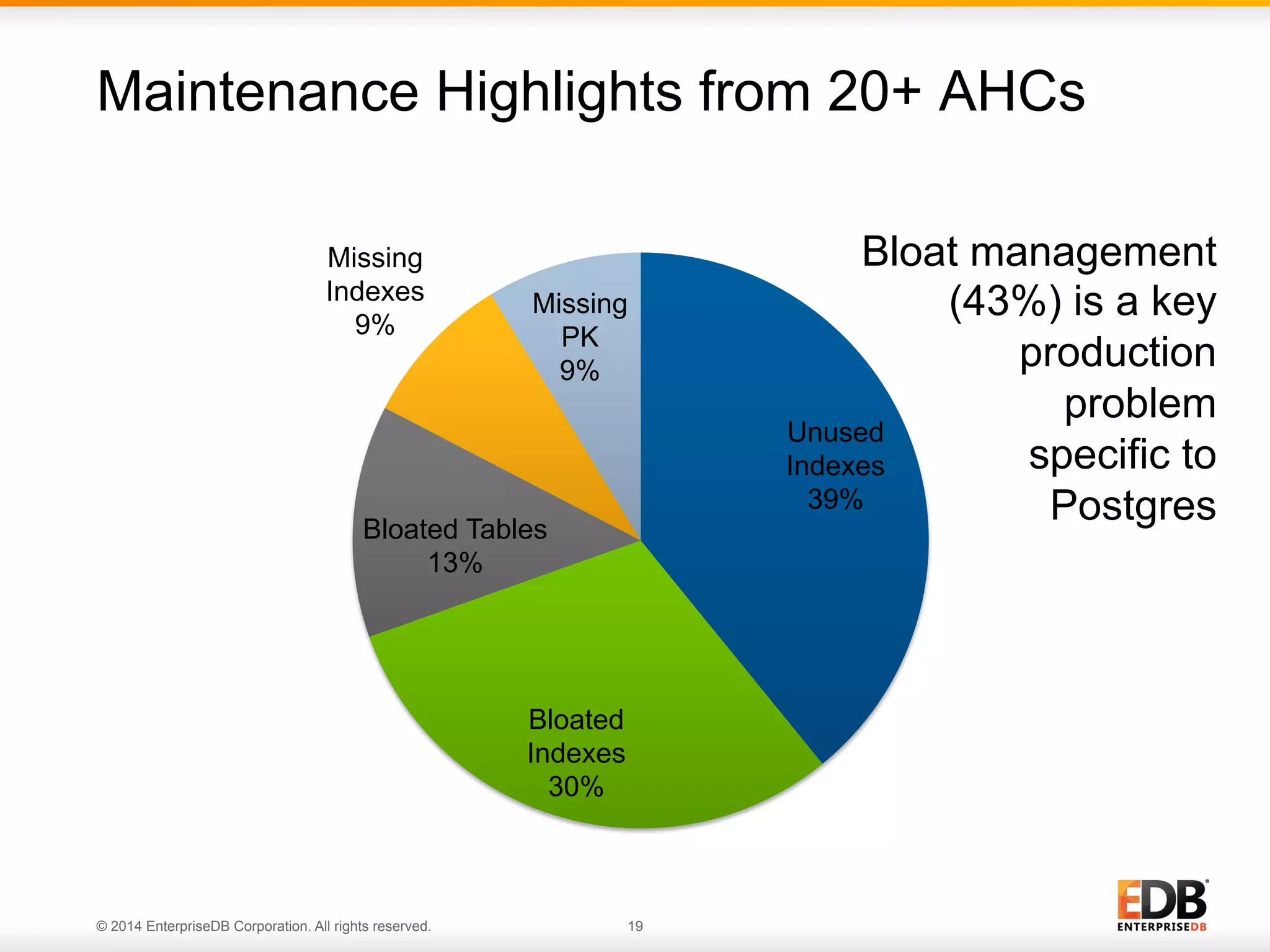
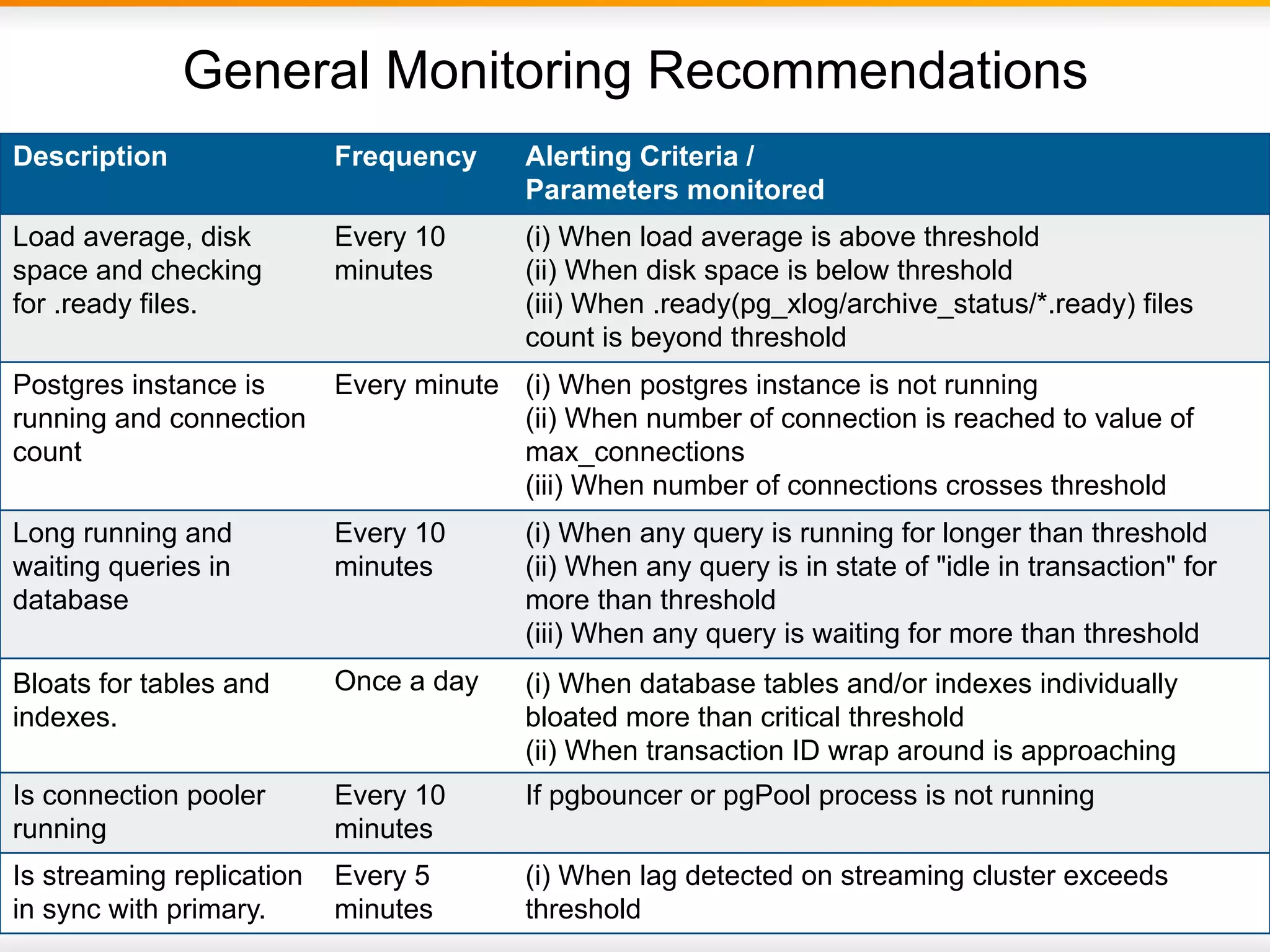
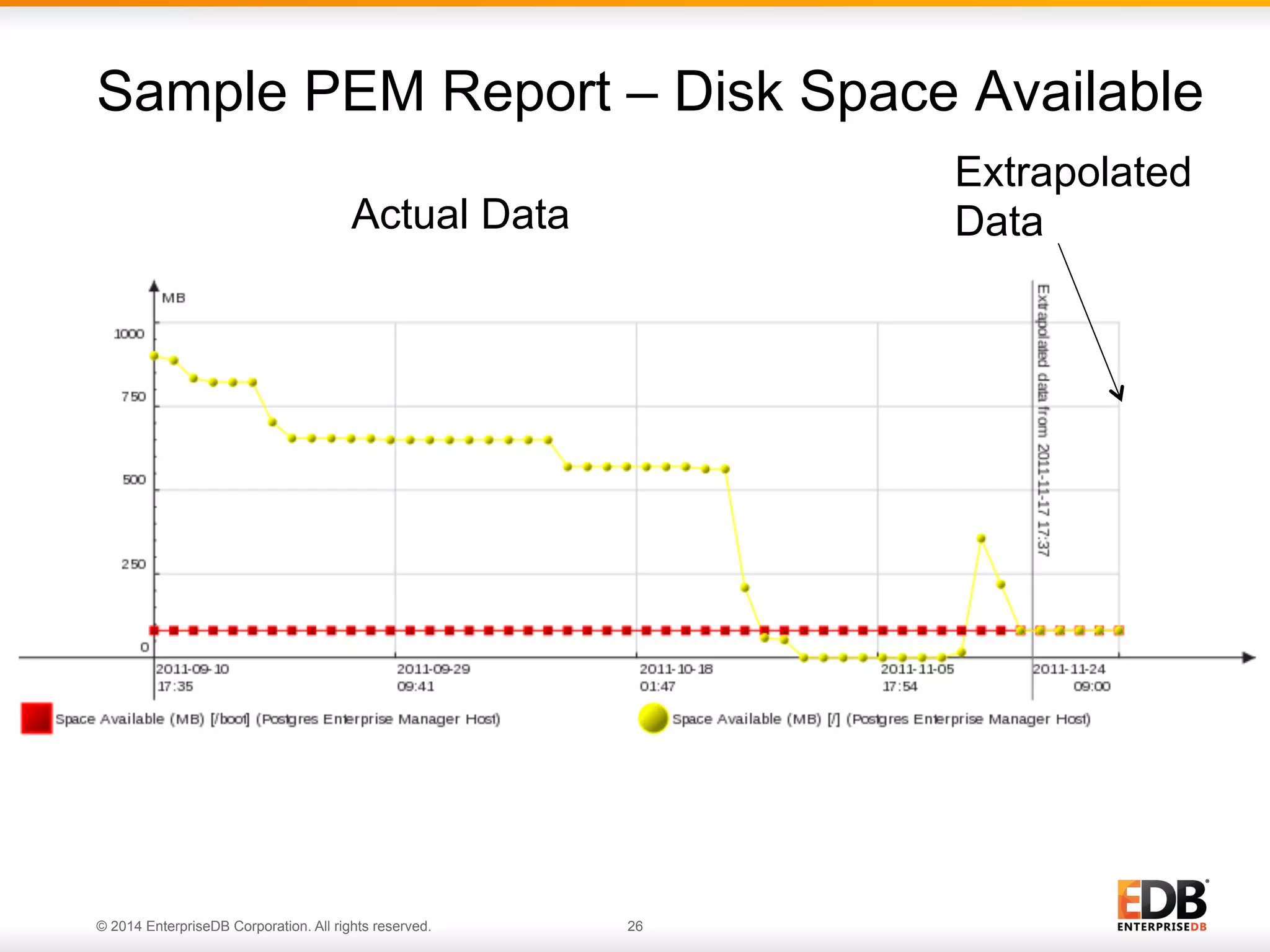
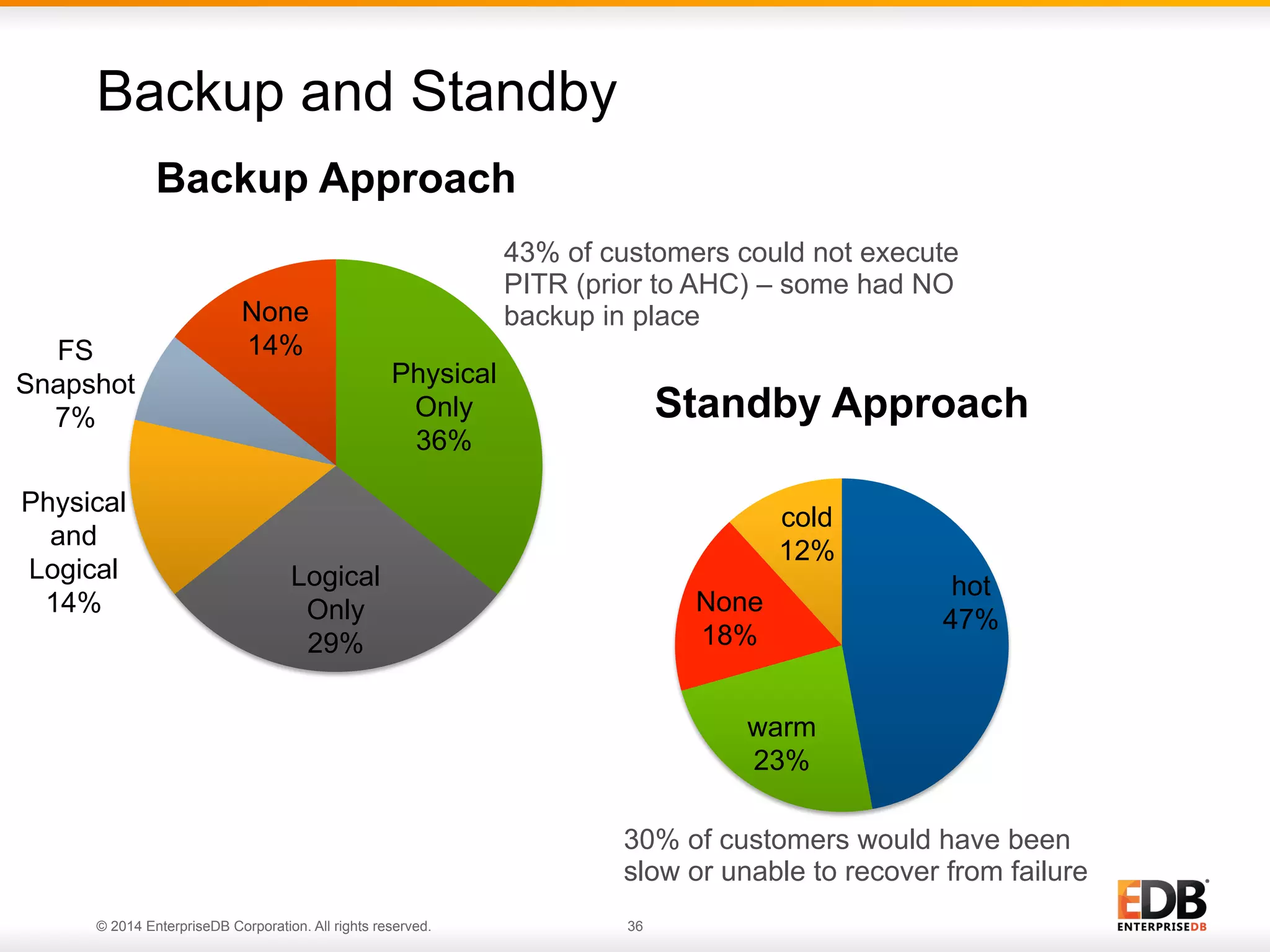
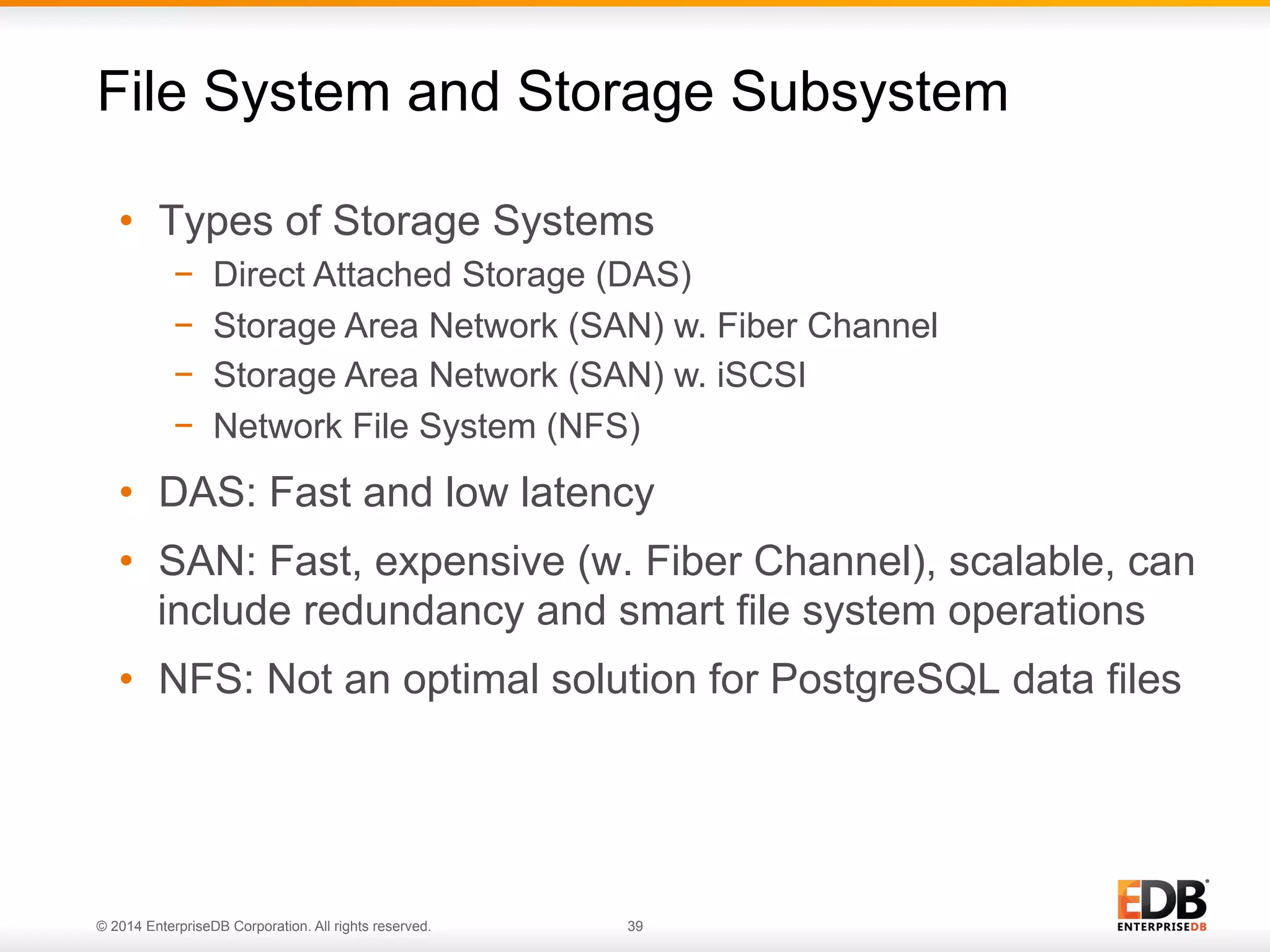
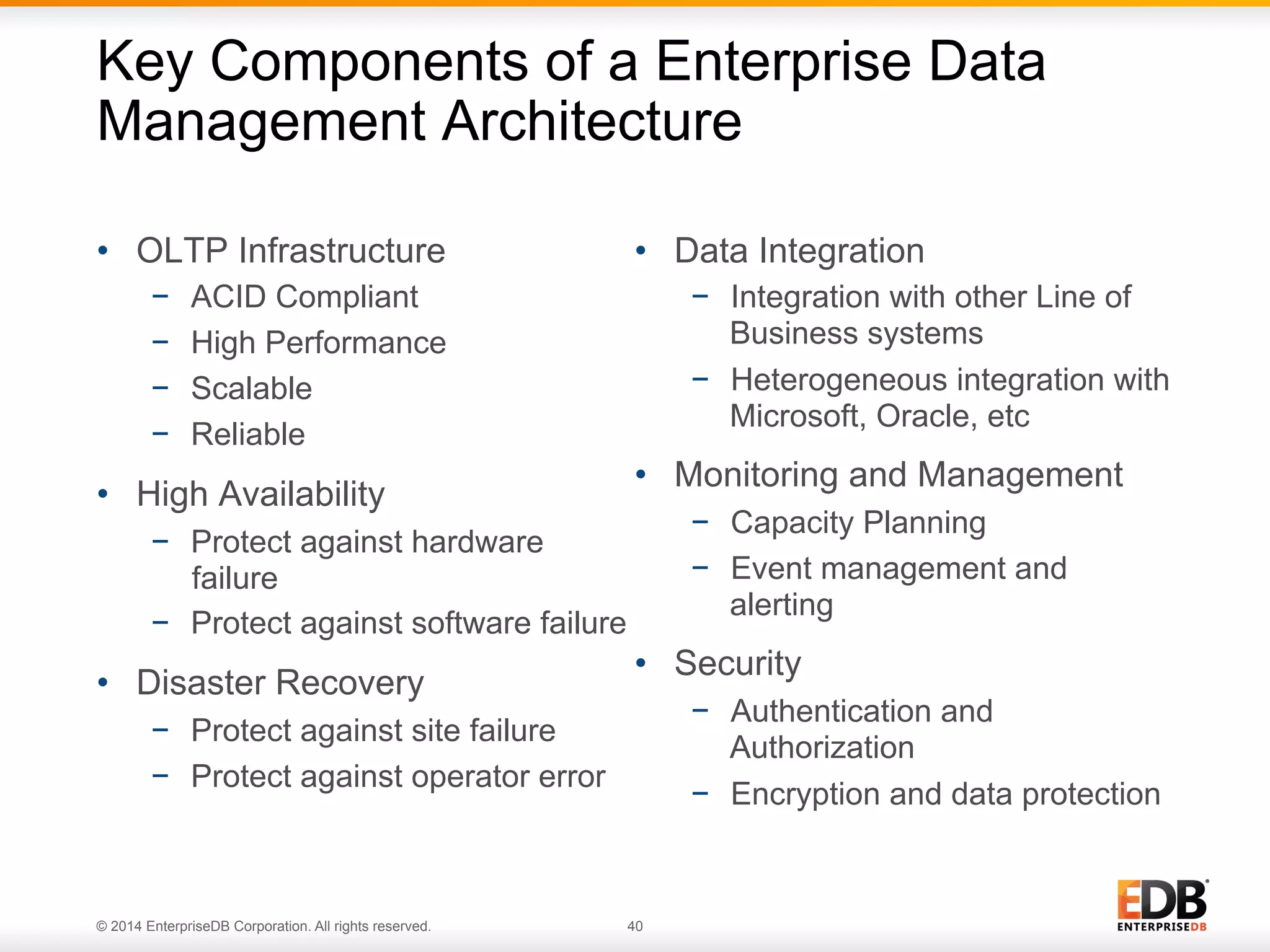
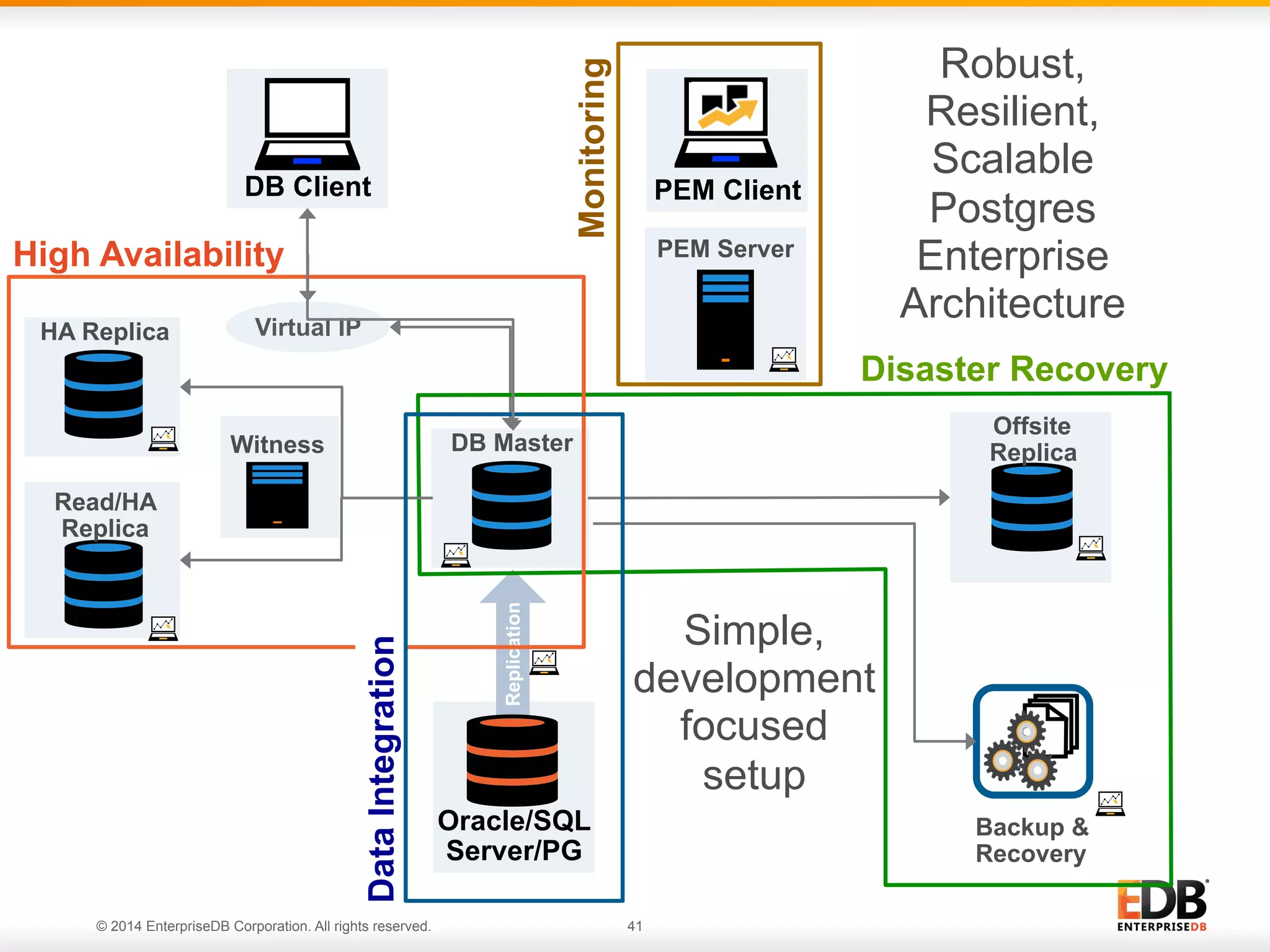
This document provides an agenda and overview for a presentation on best practices for PostgreSQL database administrators (DBAs). The presentation covers EnterpriseDB's expertise in PostgreSQL, the key responsibilities of a PostgreSQL DBA including monitoring, maintenance, capacity planning and configuration tuning. It also discusses deployment planning, professional development resources, and takes questions. Examples from architectural health checks and remote DBA services illustrate common issues found like index bloat and lack of backups. The document recommends performance monitoring and security tools and techniques for PostgreSQL.