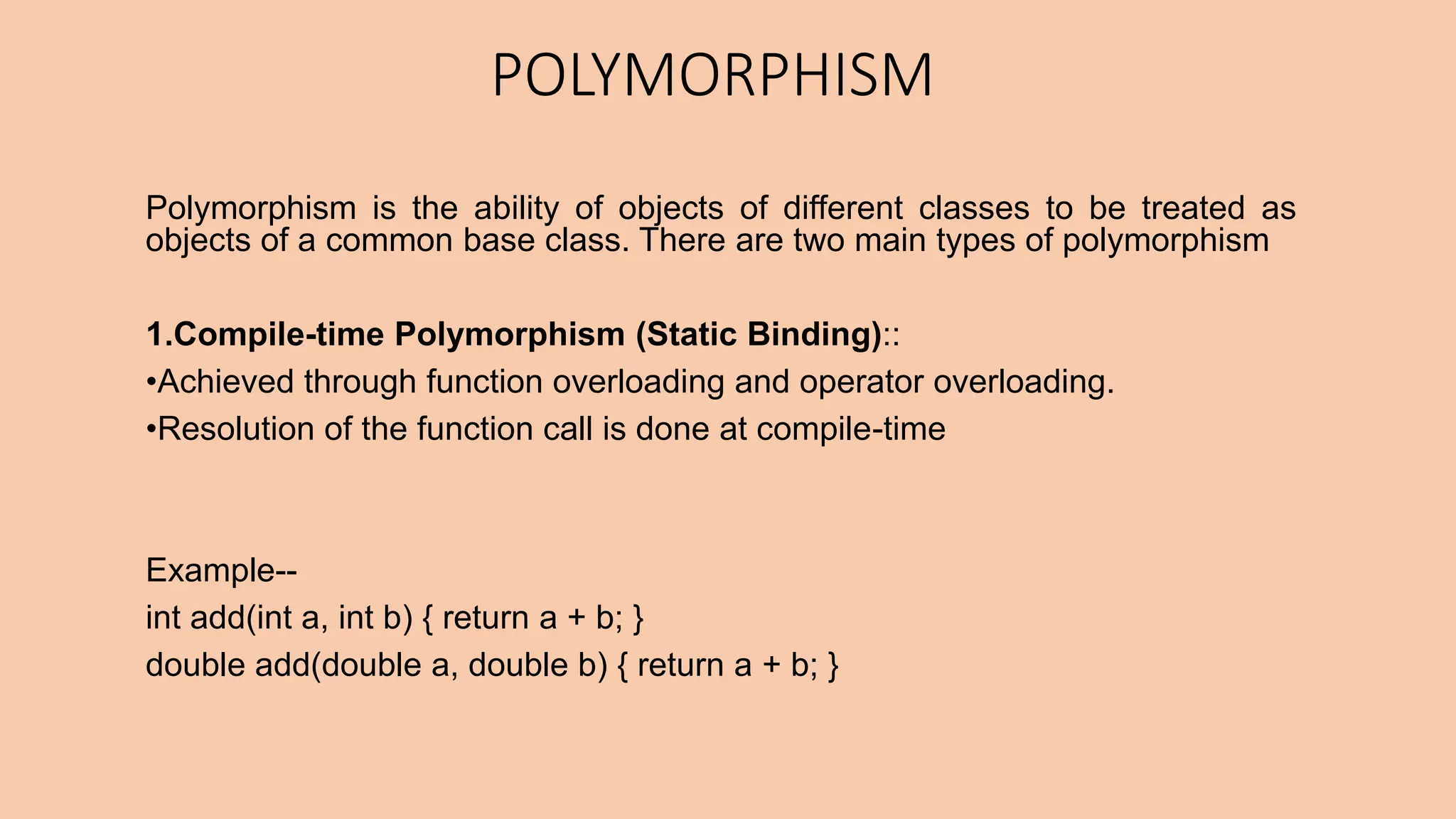
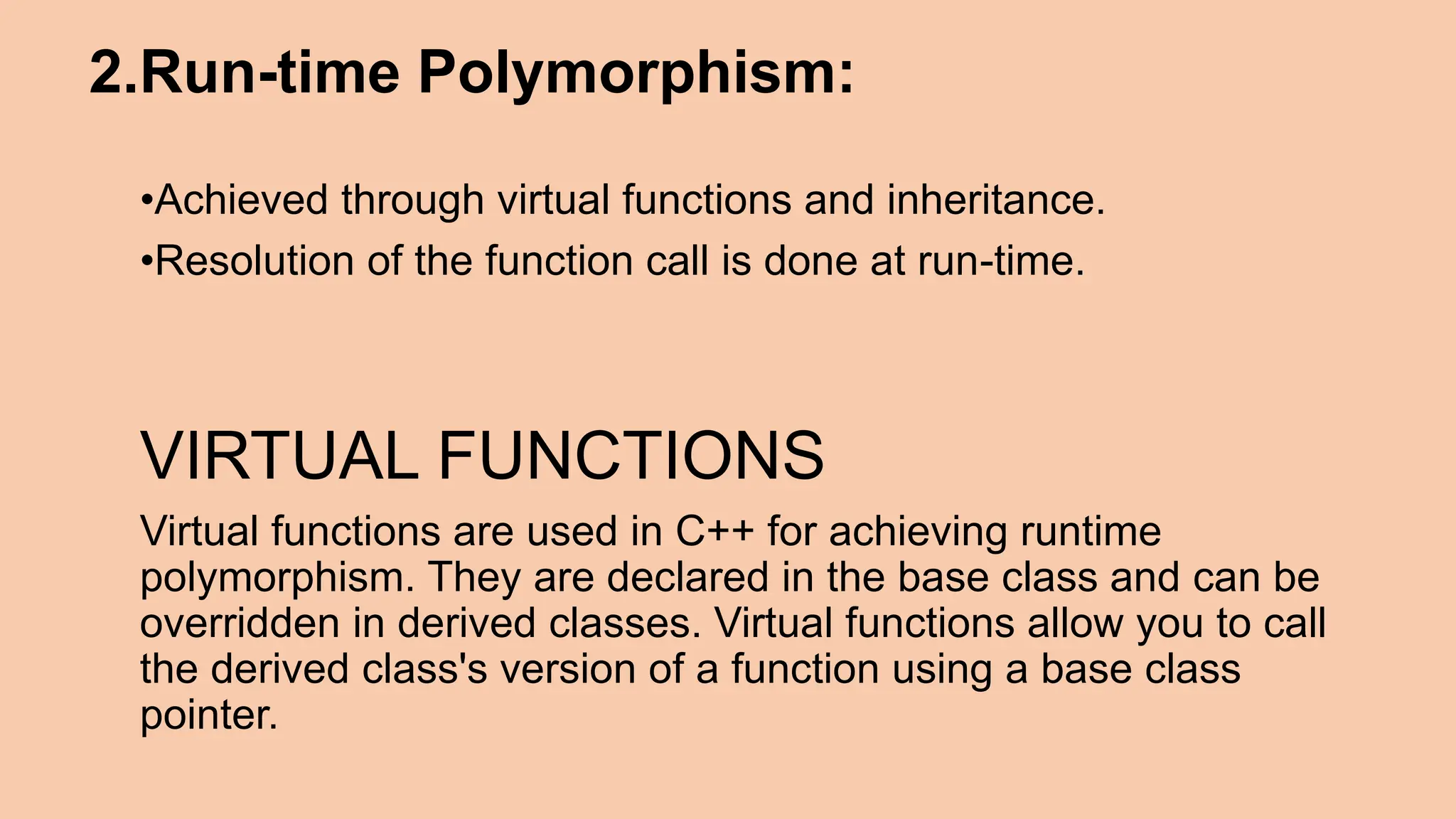
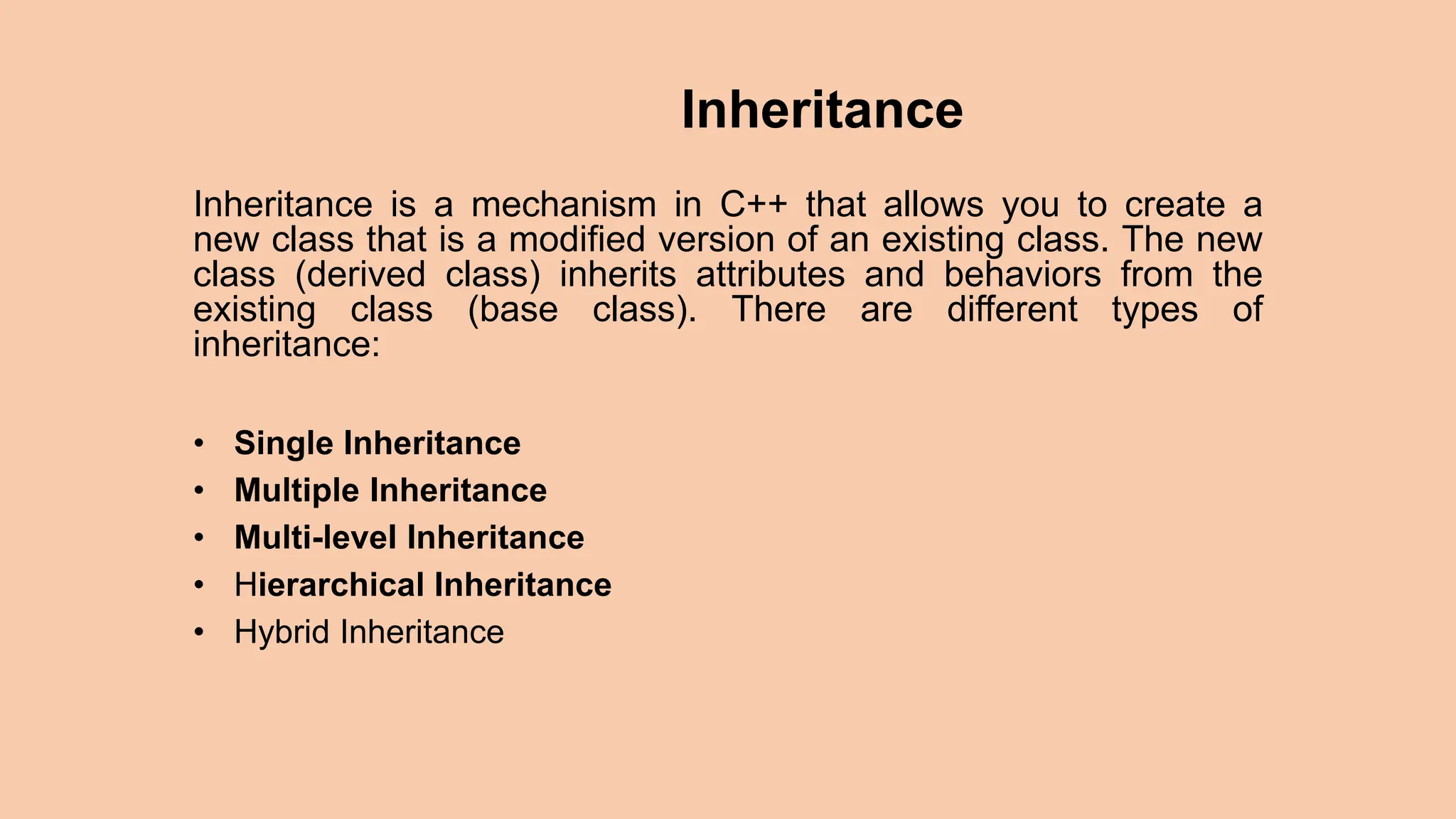
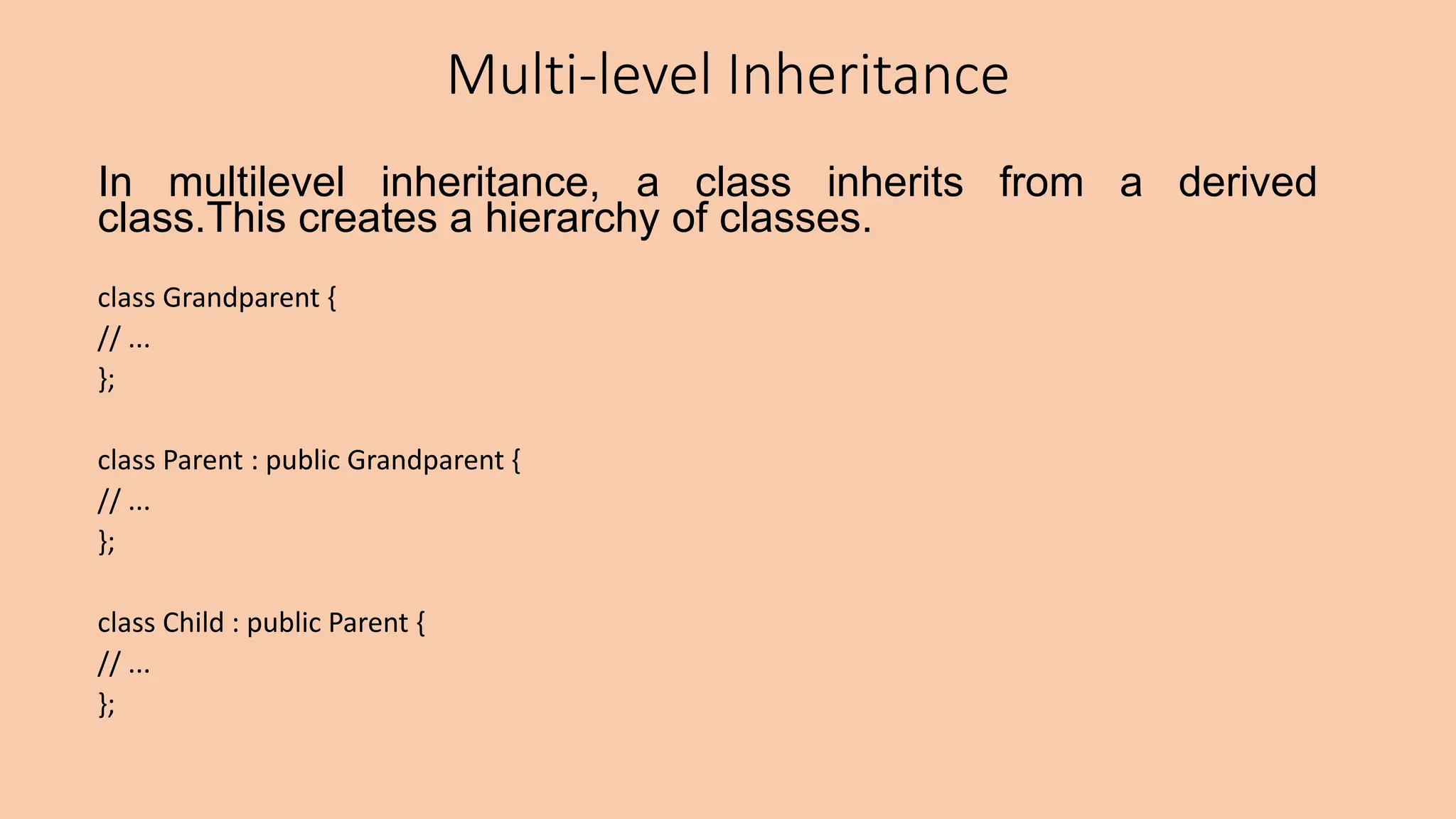
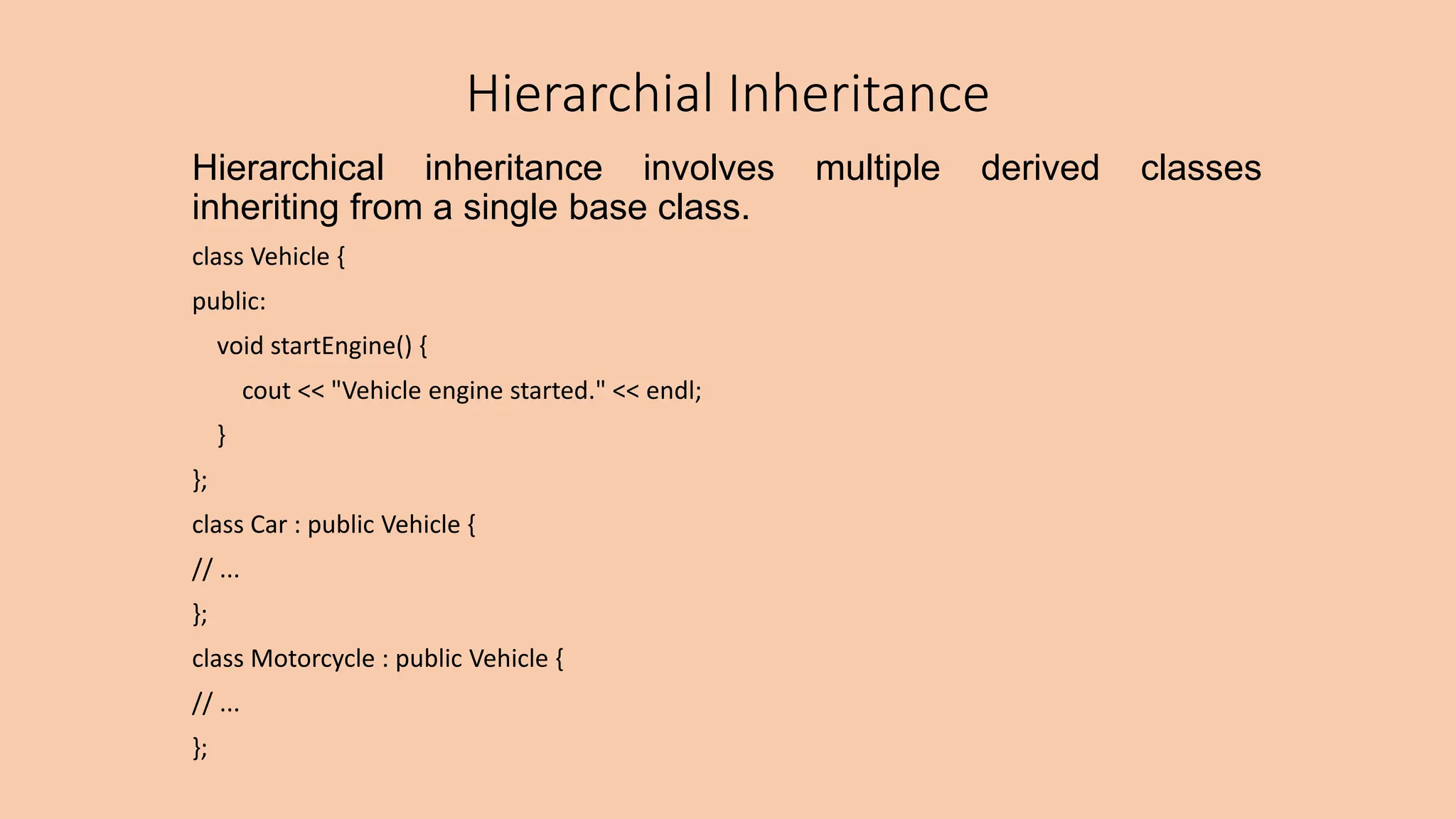
This document discusses key concepts in object-oriented programming including inheritance, polymorphism, and virtual functions. It defines inheritance as a mechanism that allows a new class to inherit attributes and behaviors from an existing class. The document outlines different types of inheritance like single, multiple, multi-level, and hierarchical inheritance. It also explains pointers, polymorphism through function overloading and virtual functions, and provides examples to illustrate these concepts.



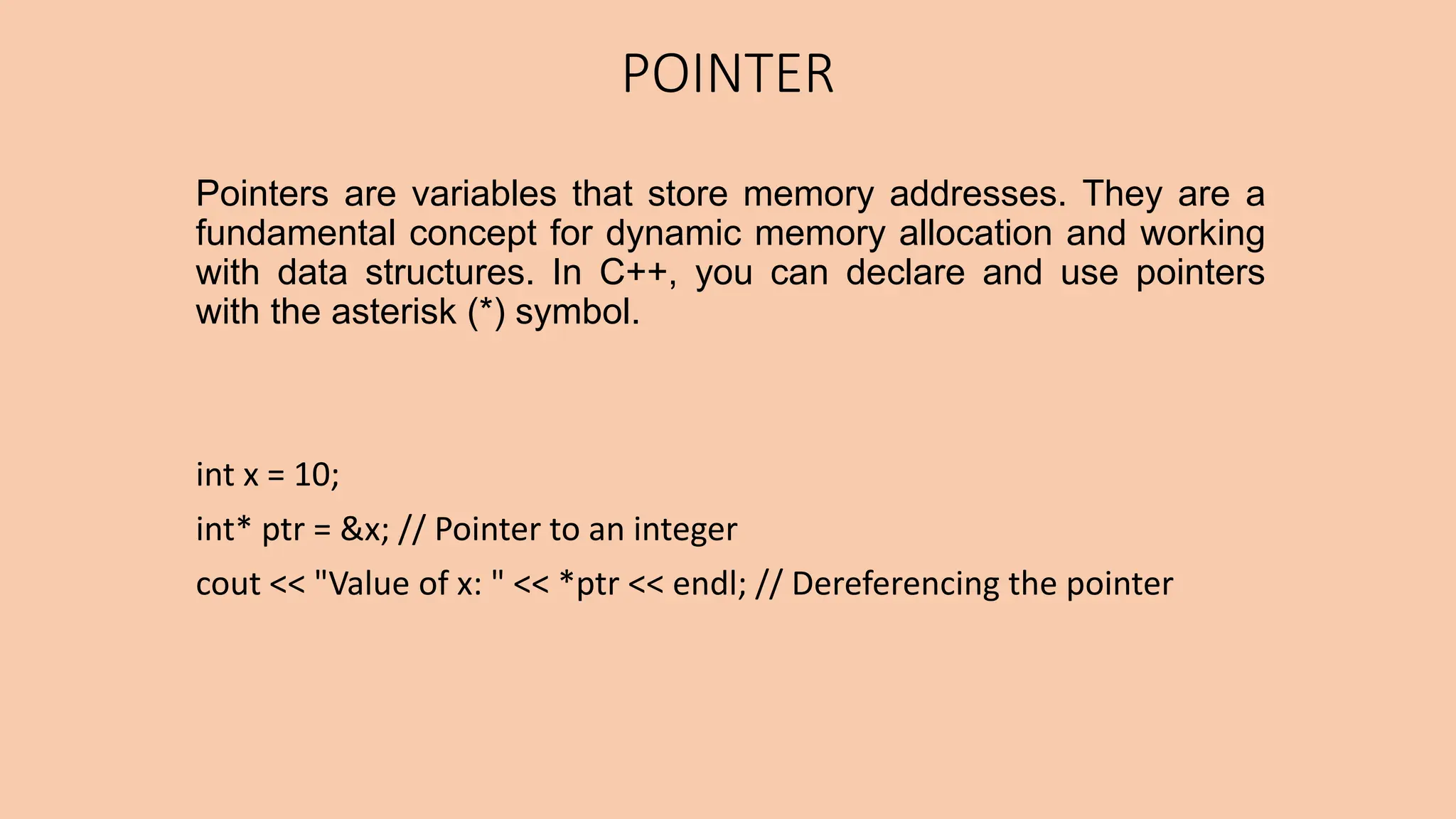
![Pointer Types: Null Pointer: A null pointer doesn't point to any memory location. It's often used to represent an invalid or uninitialized pointer. int* ptr = nullptr; Pointer to an Array: Pointers can be used to traverse arrays or access their elements. int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; int* ptr = arr; // Points to the first element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerscience-240404183221-5dea0e8c/75/Polymorphism-and-Virtual-Functions-ppt-bioinformatics-9-2048.jpg)