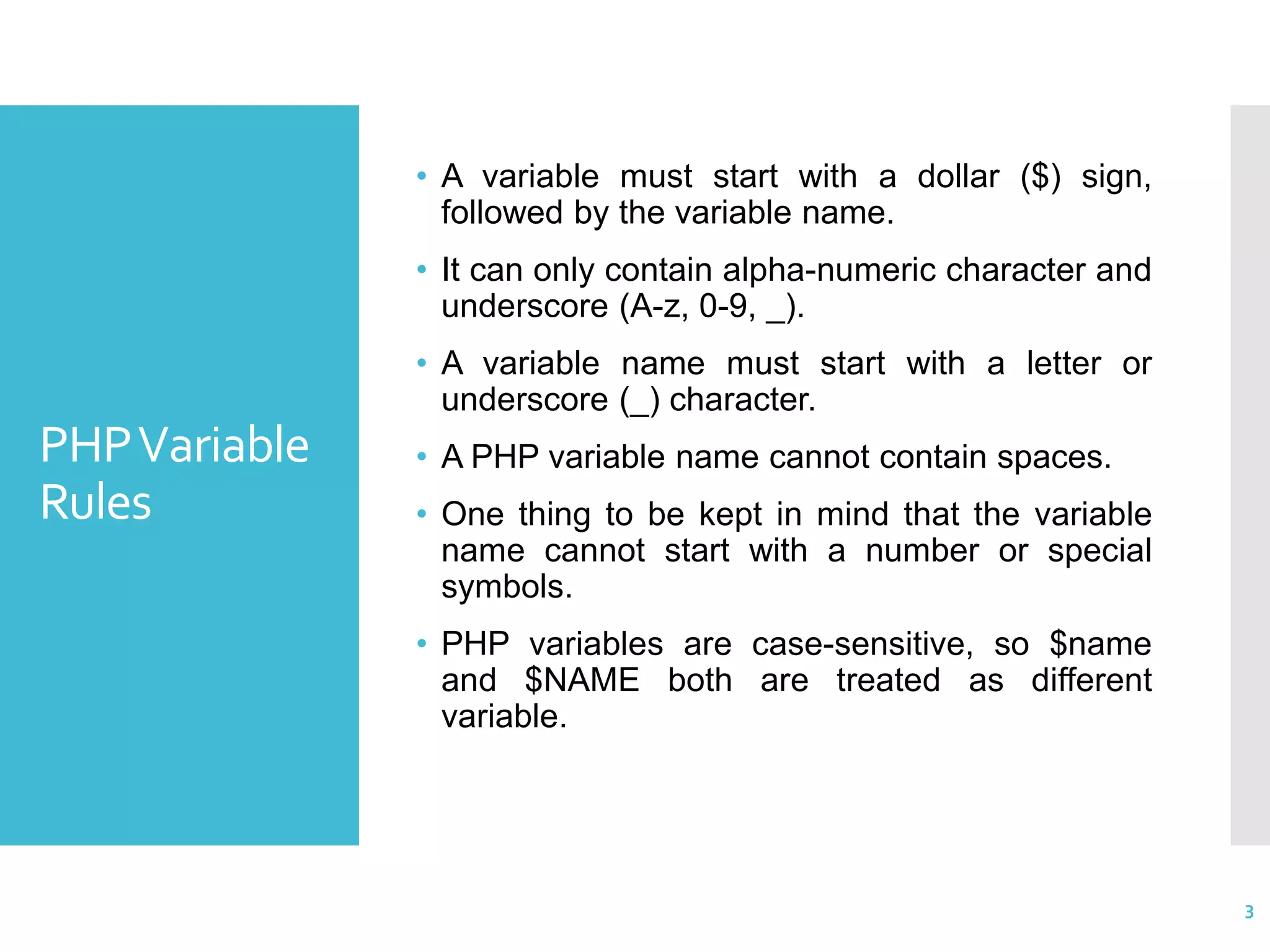
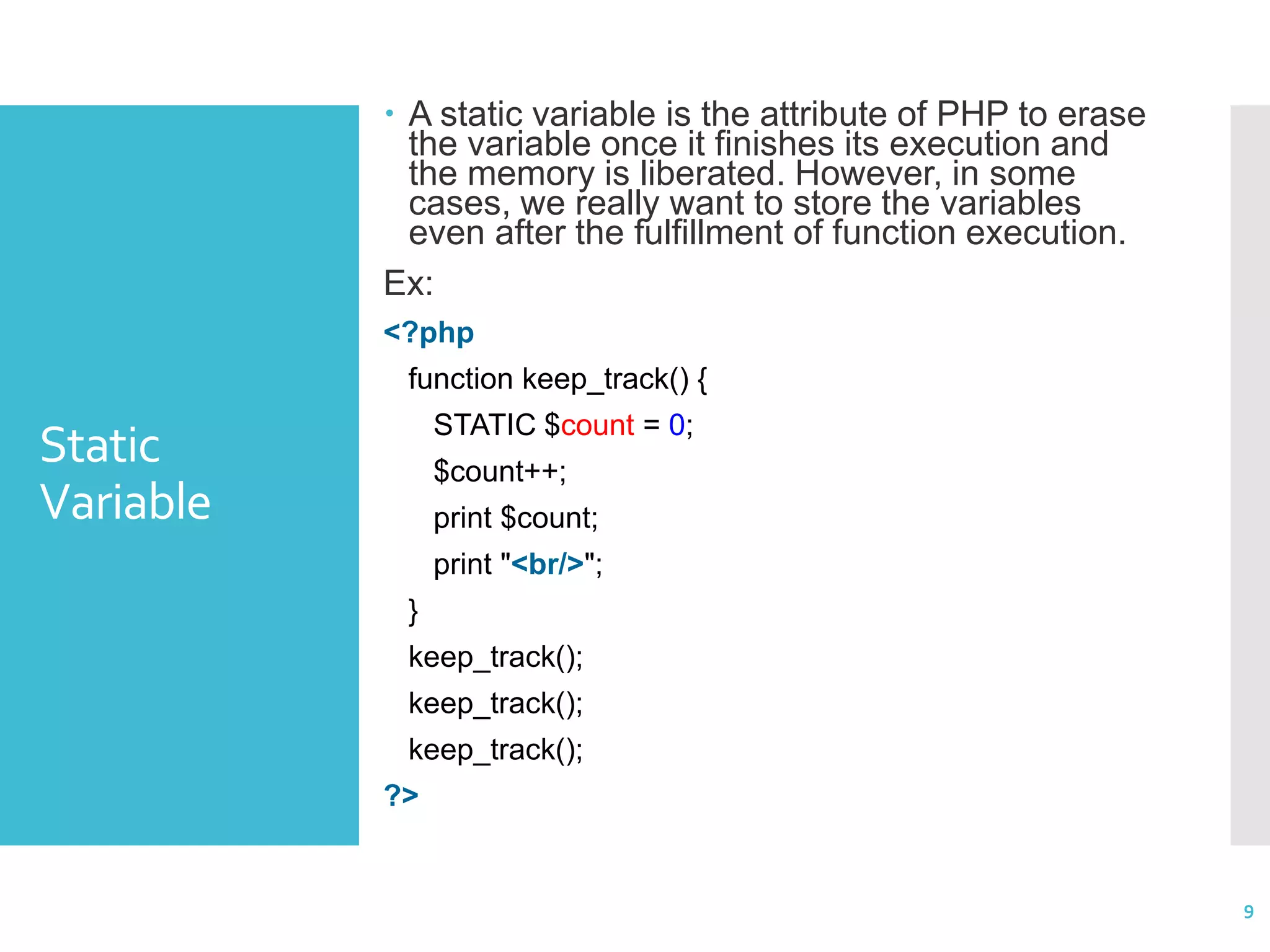
The document discusses PHP variables. It defines a variable as a name that holds the location of data in memory. Variables must start with $, can only contain alphanumeric characters and underscores, and are case-sensitive. There are different variable types like integers, strings, arrays. Variables can be assigned values and have different scopes - local variables only exist within a function, global variables can be accessed anywhere, and static variables retain their value between function calls. The document provides examples of declaring and using different variable types and scopes in PHP code.