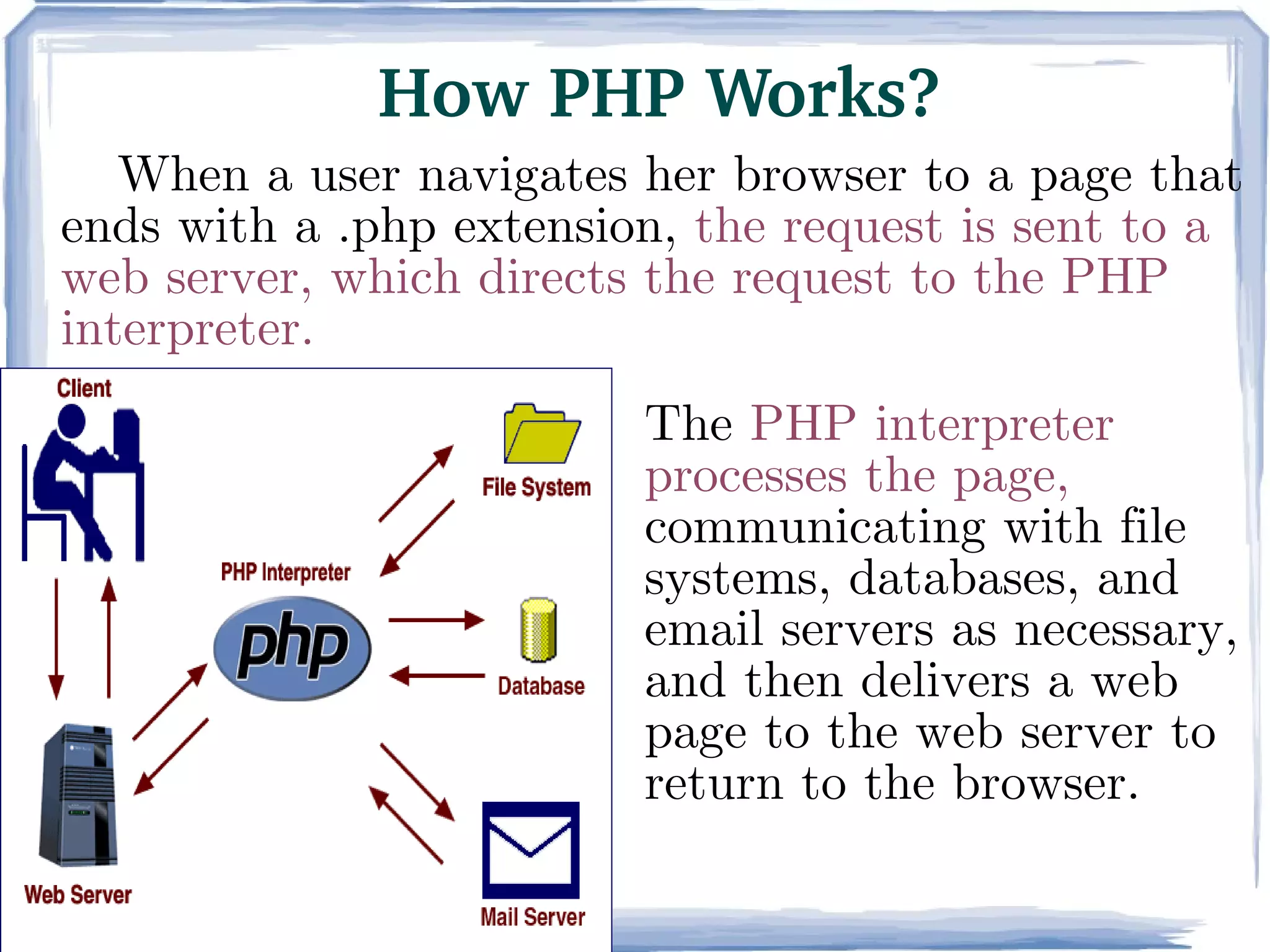
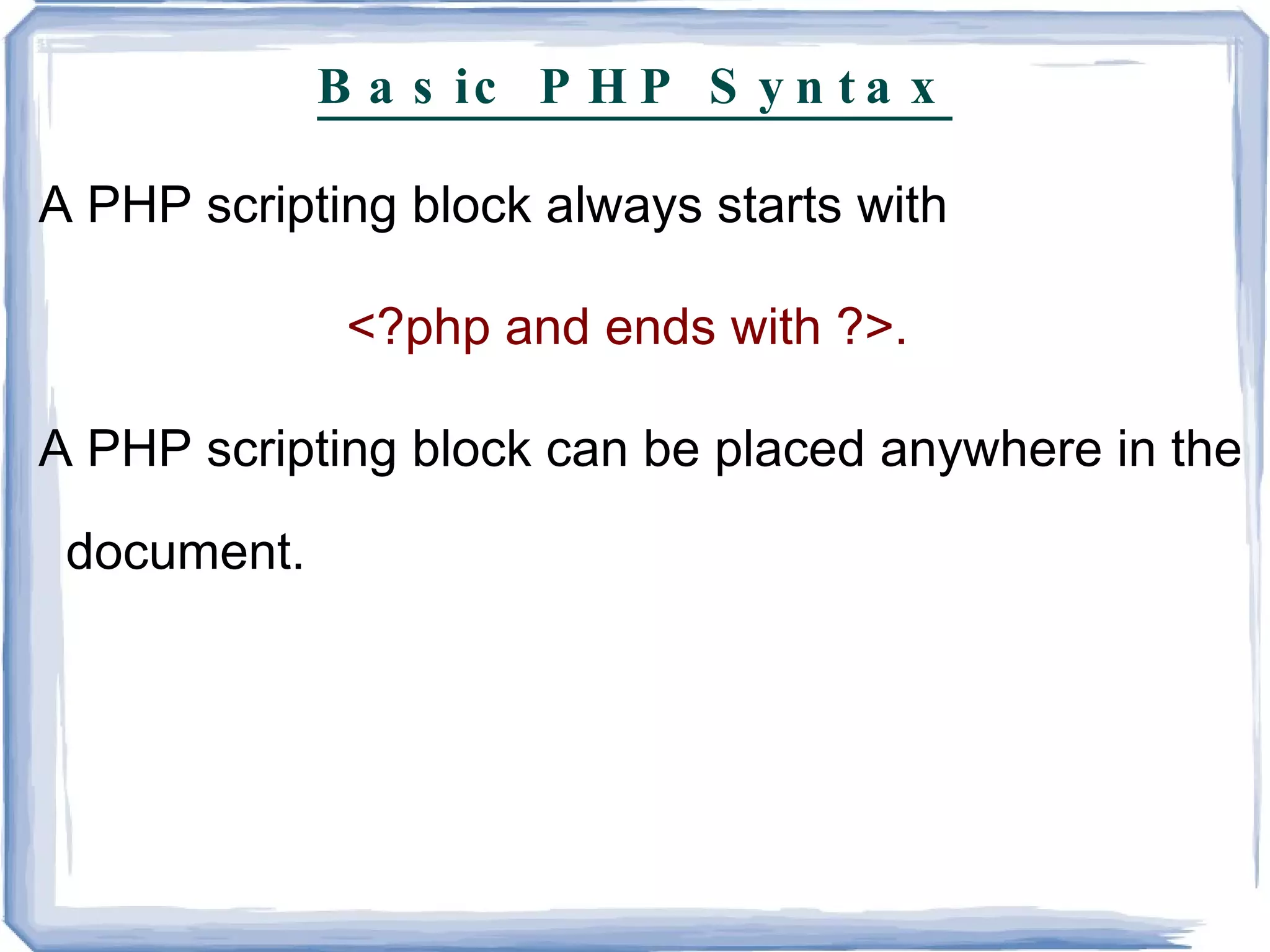
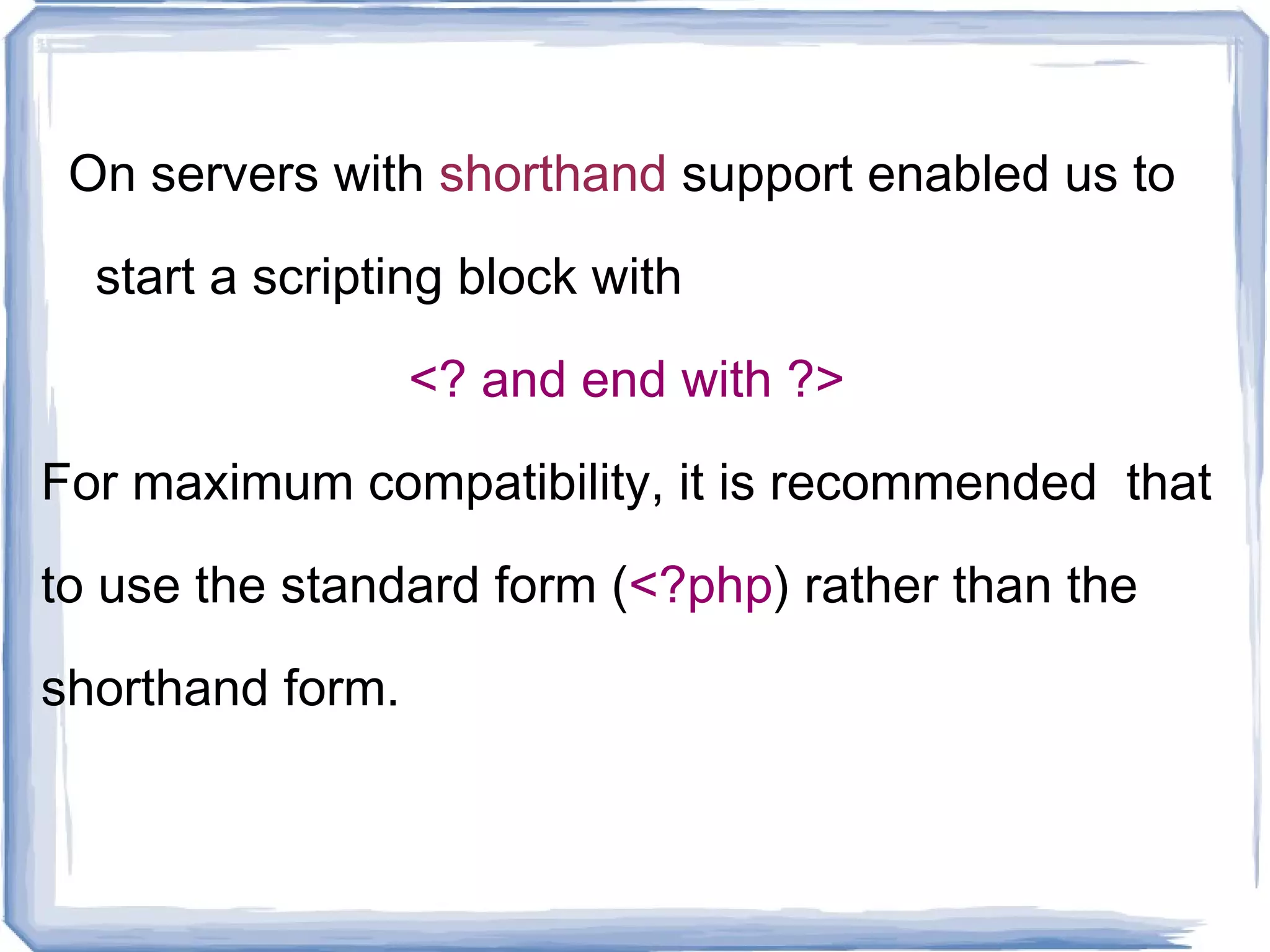
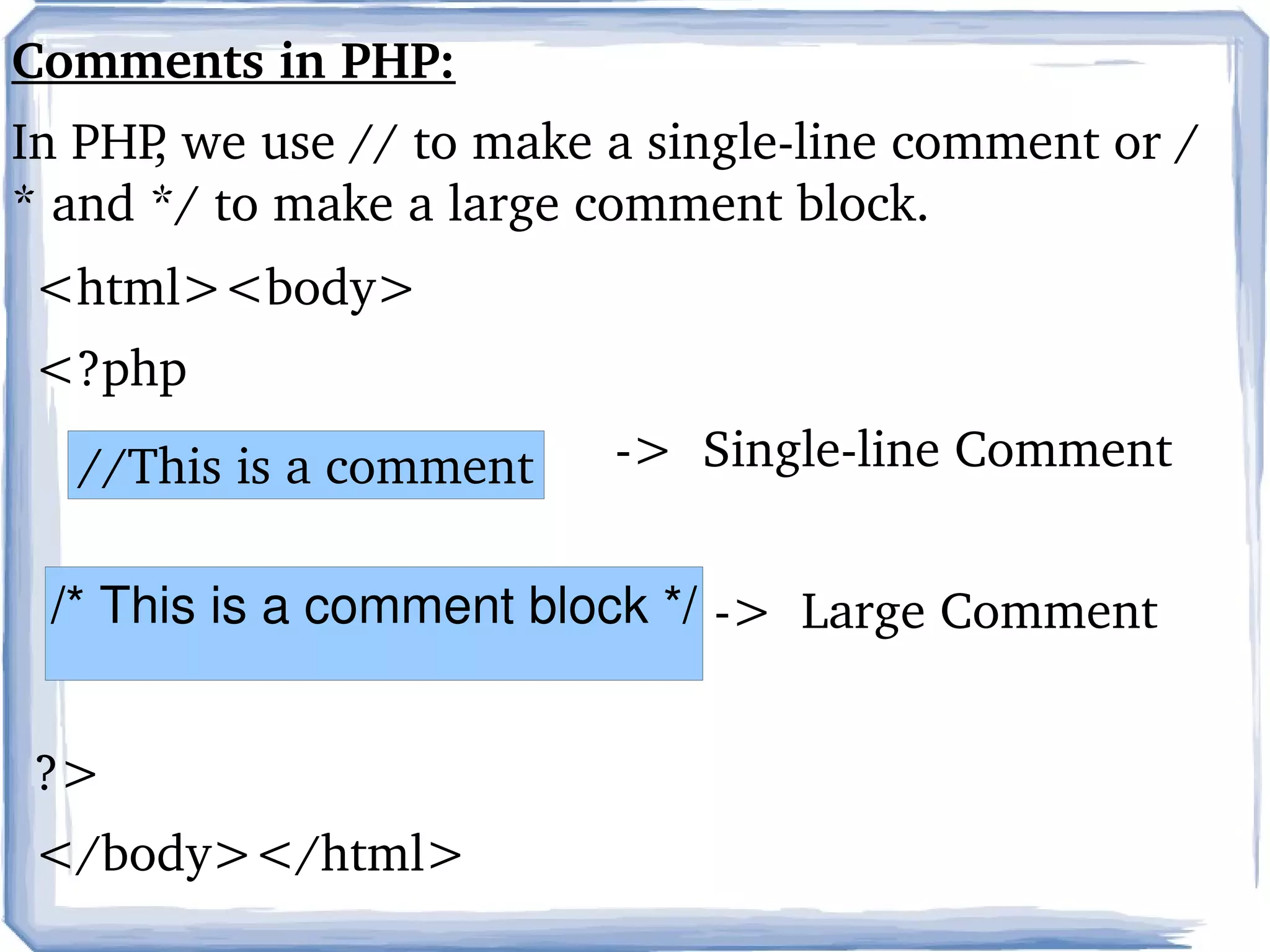
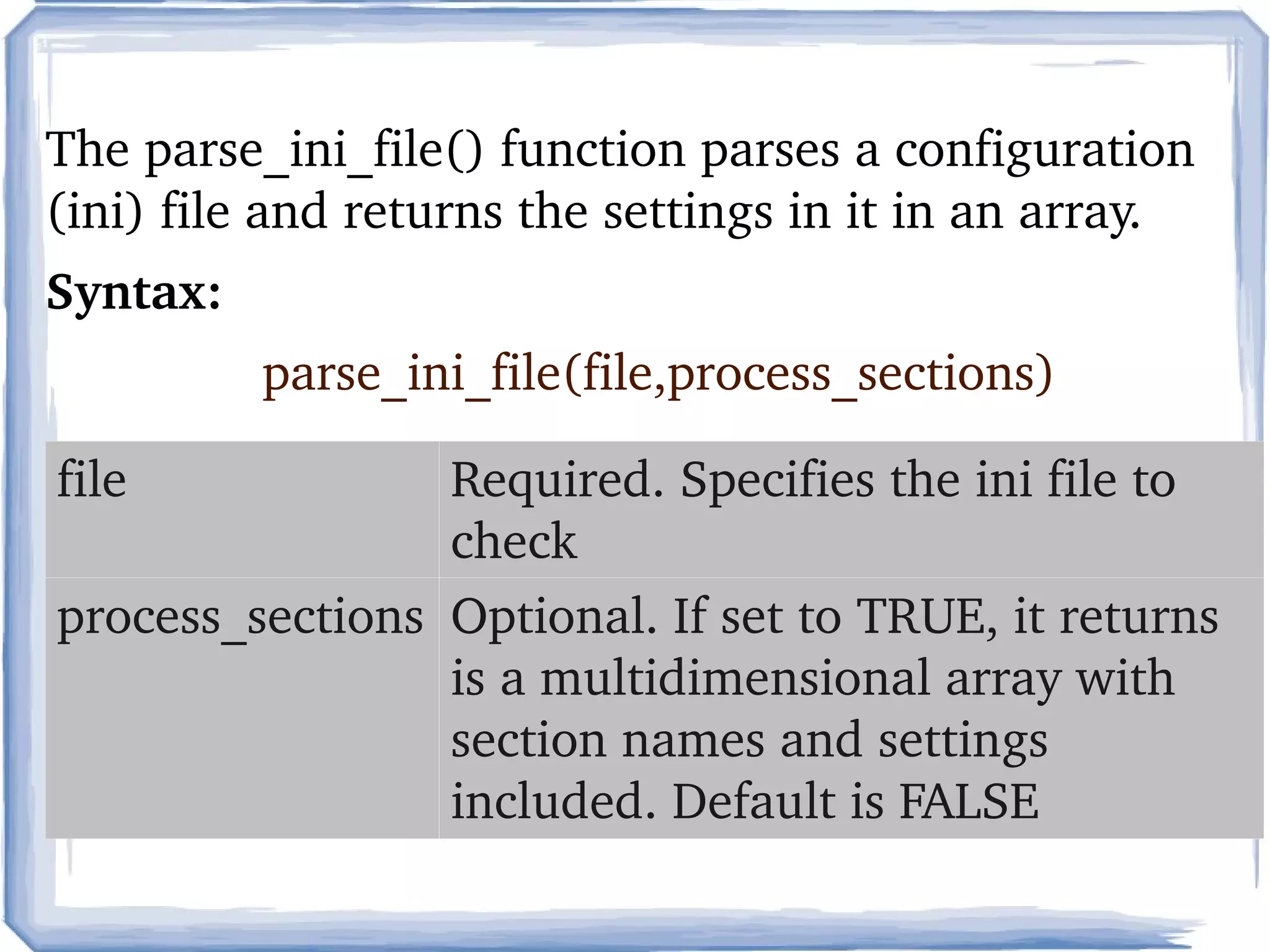
PHP is a server-side scripting language commonly used for web development. It is free, open source, and can interface with many databases. PHP code is executed on the server and generates HTML that is sent to the browser. Key elements of PHP include variables, comments, and the php.ini configuration file.