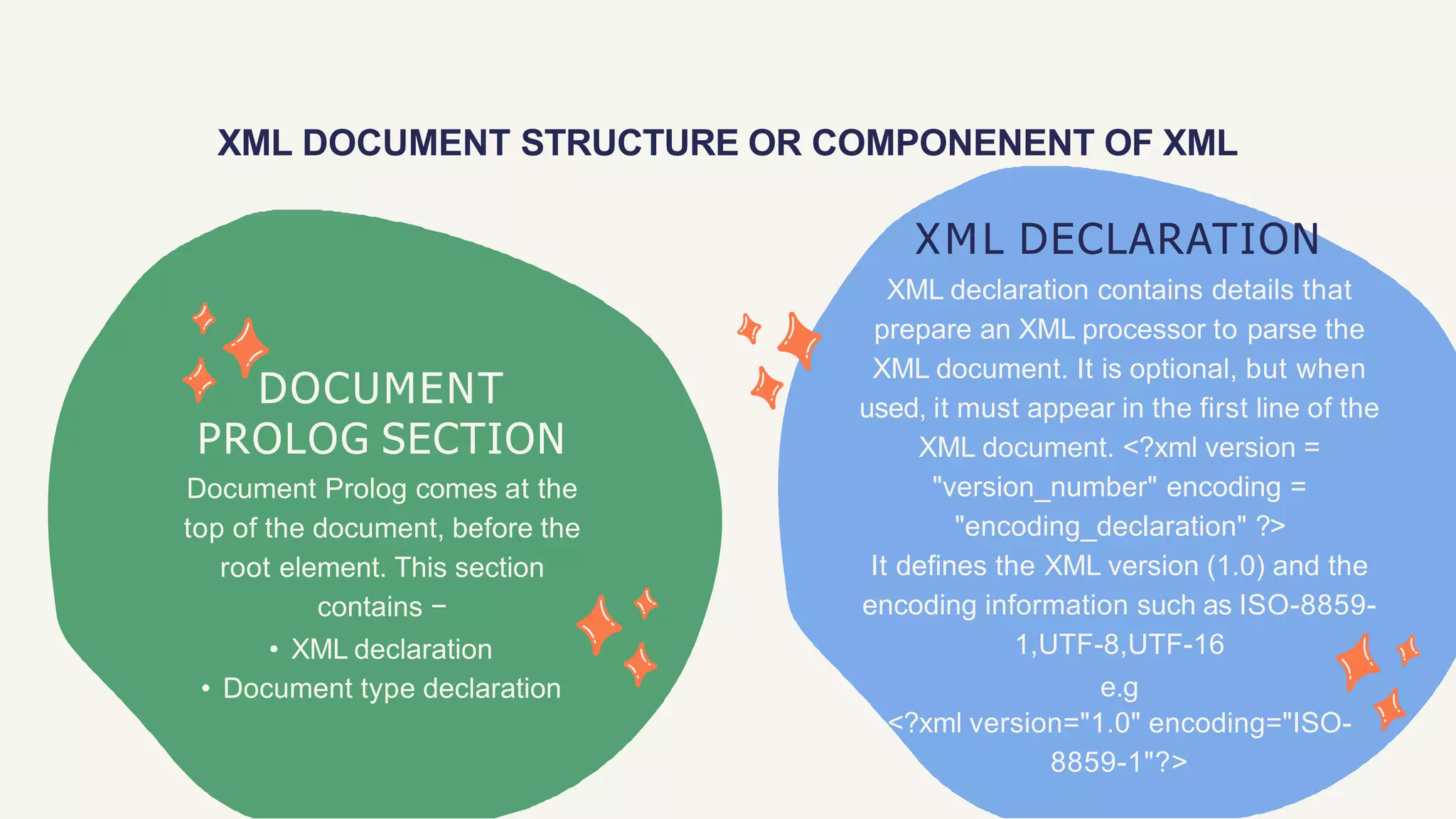
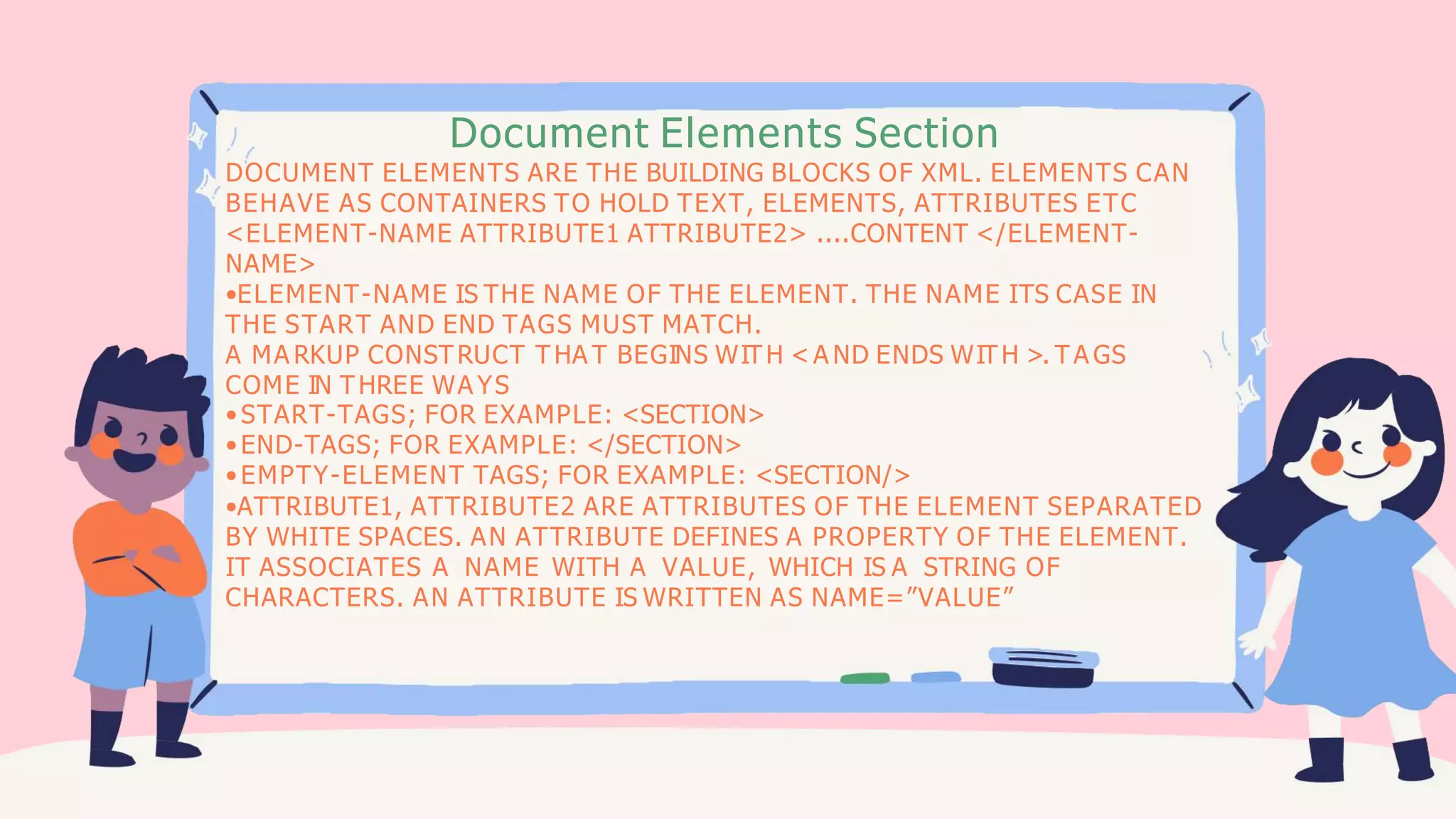
This document provides an overview of XML (Extensible Markup Language). It defines XML as a text-based markup language that stores data in a structured format using user-defined tags. The document outlines key features of XML including separating data from presentation, simplifying data sharing, and its use in web publishing, web searching, and data transfer. It also describes XML syntax rules, components like elements and attributes, and applications of XML.