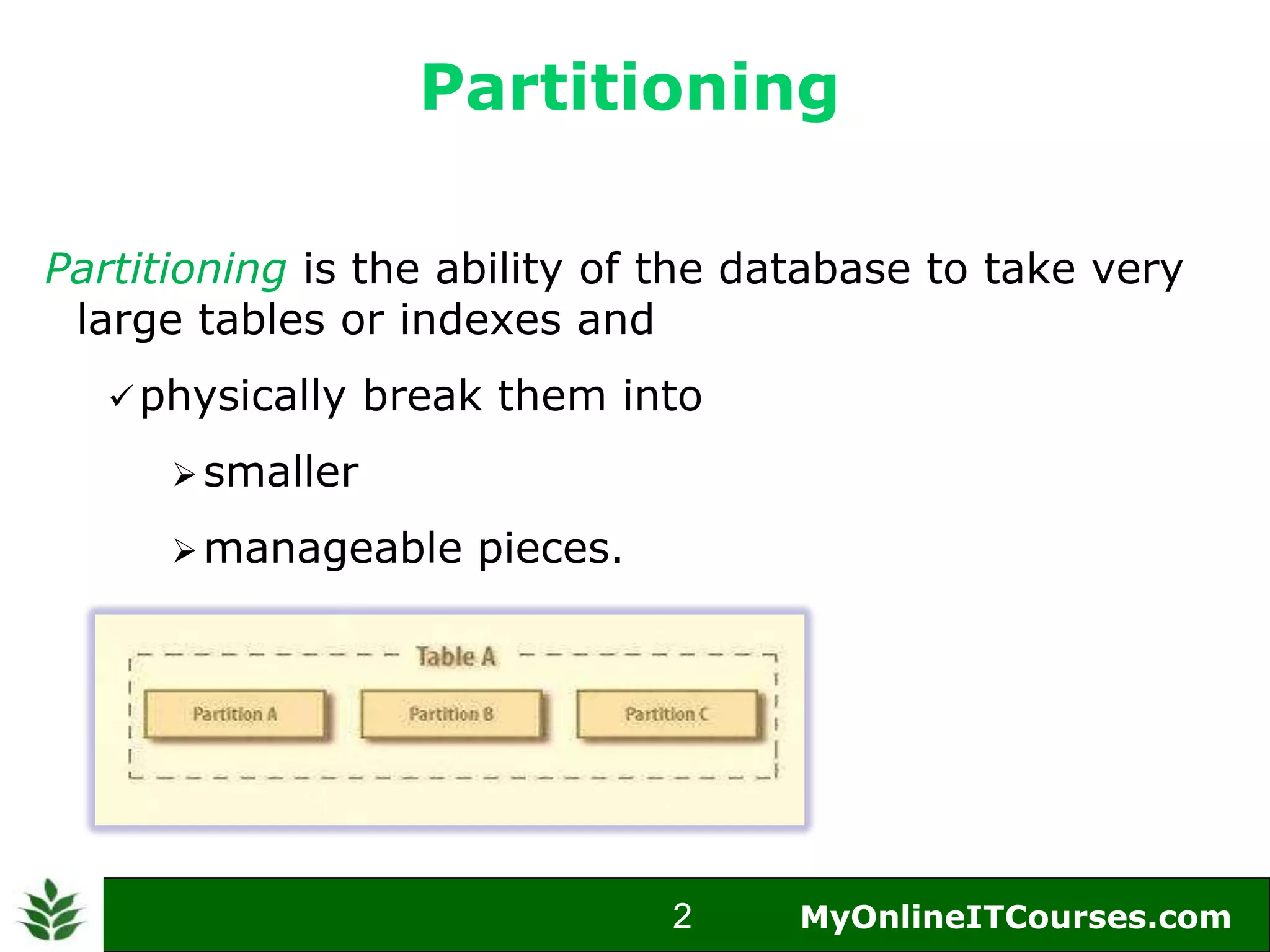
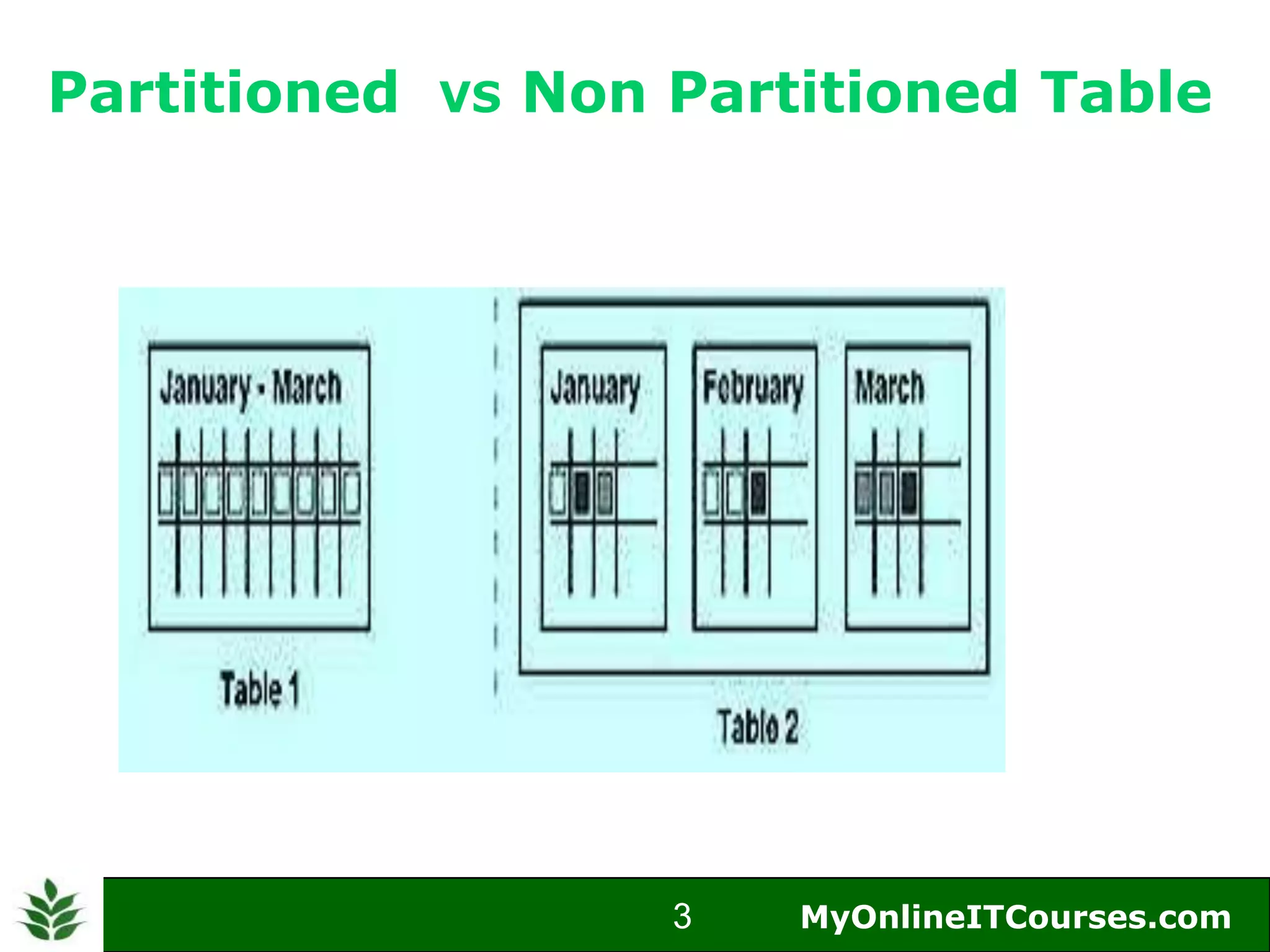
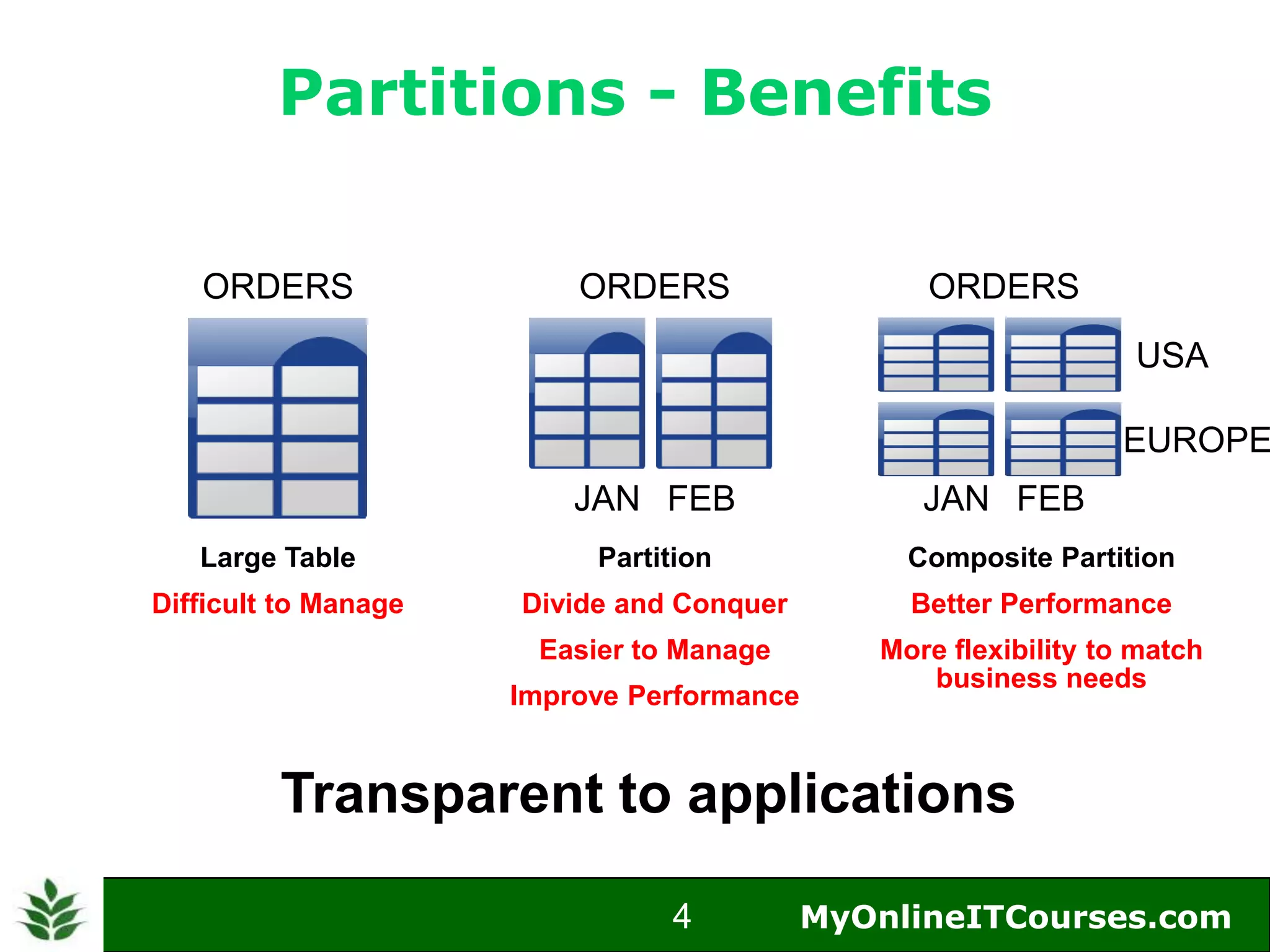
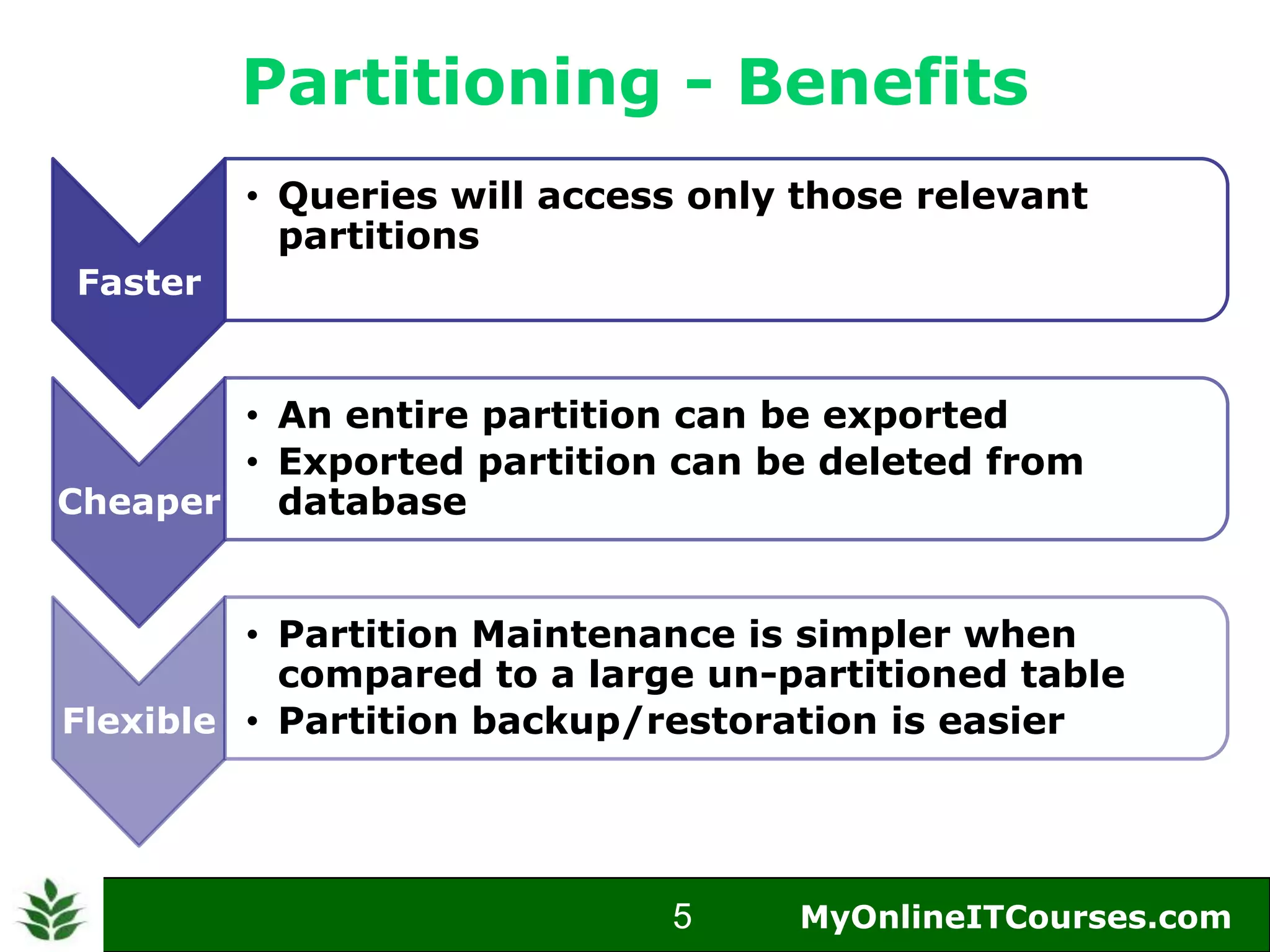
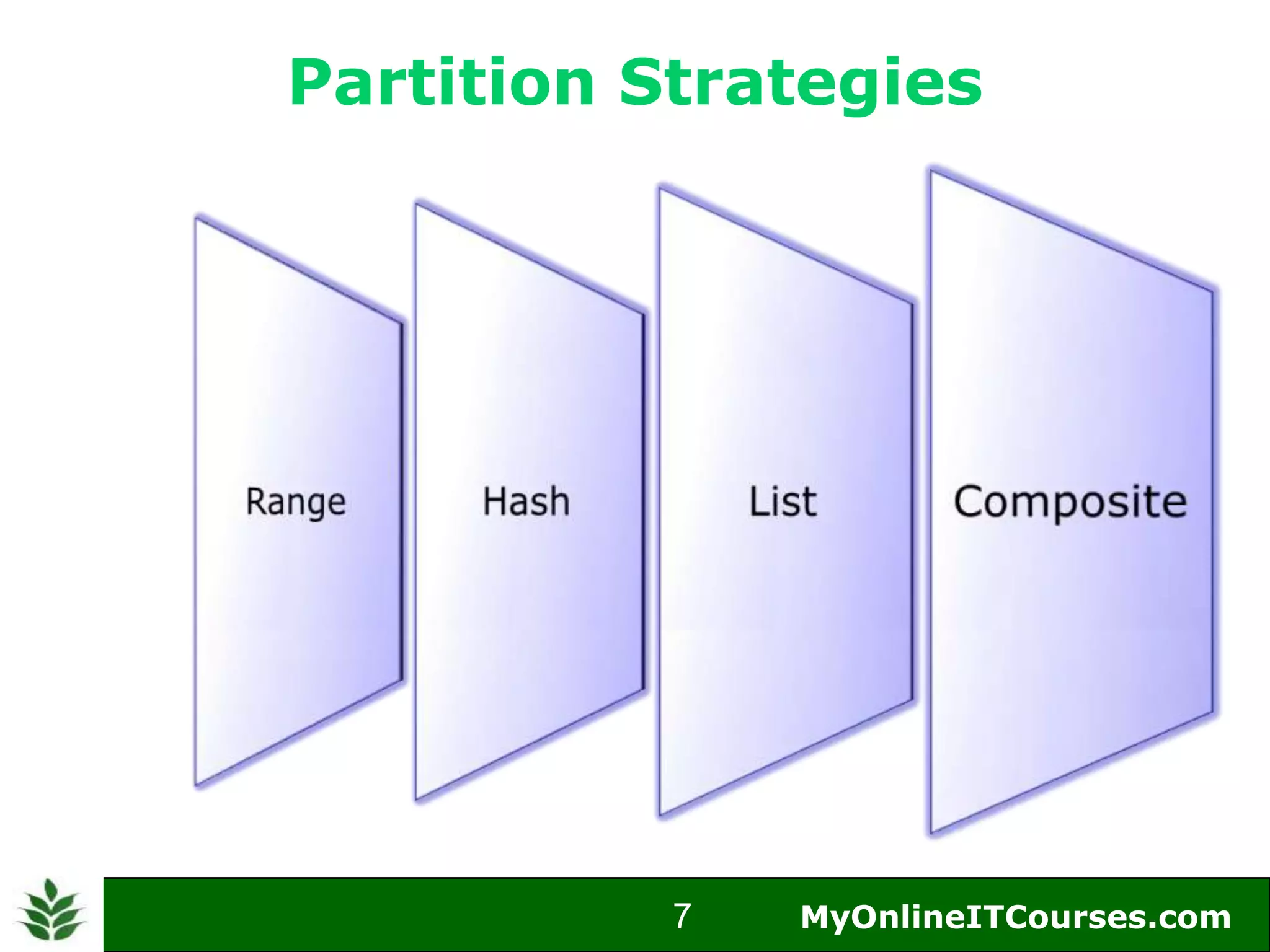
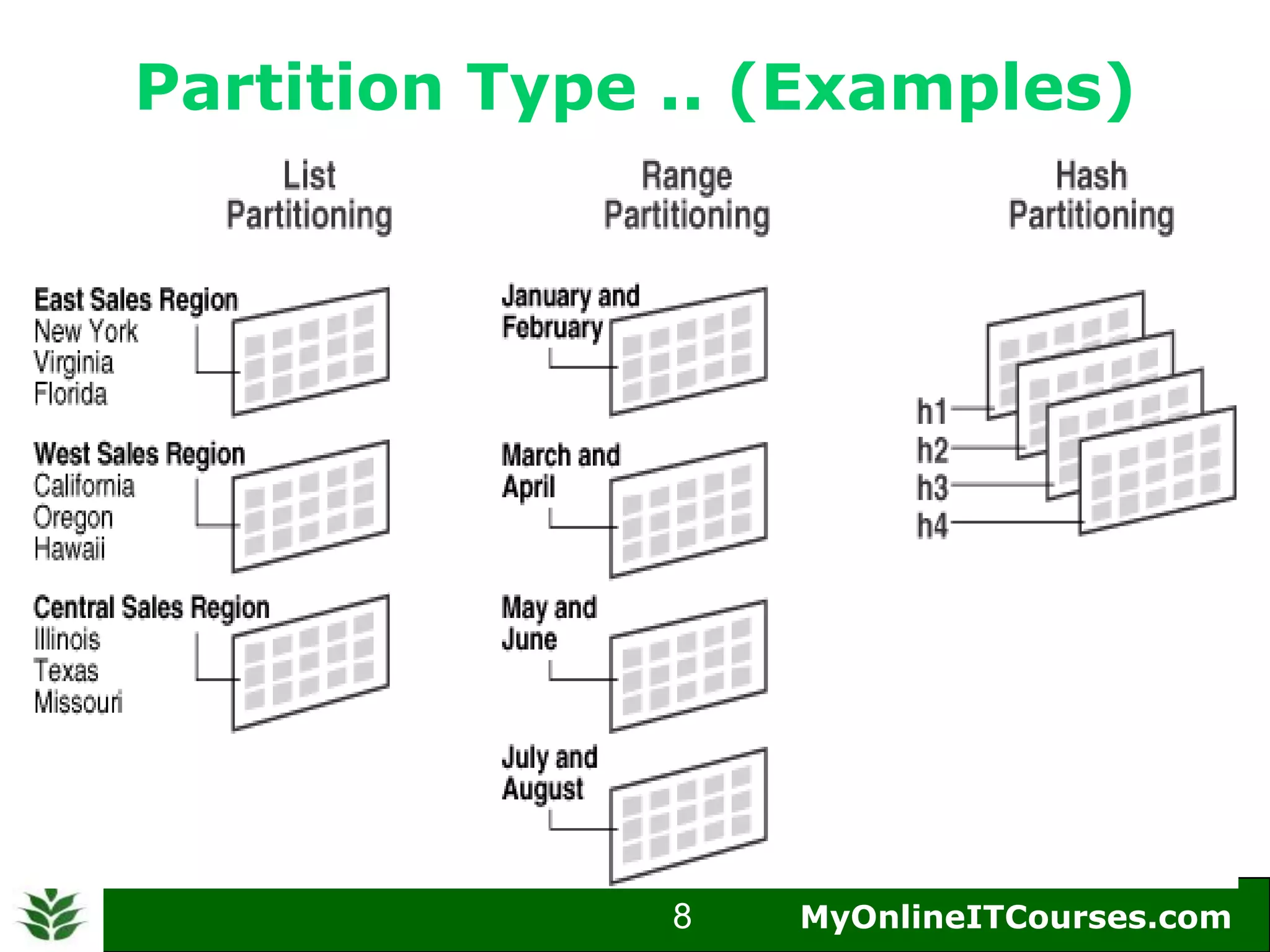
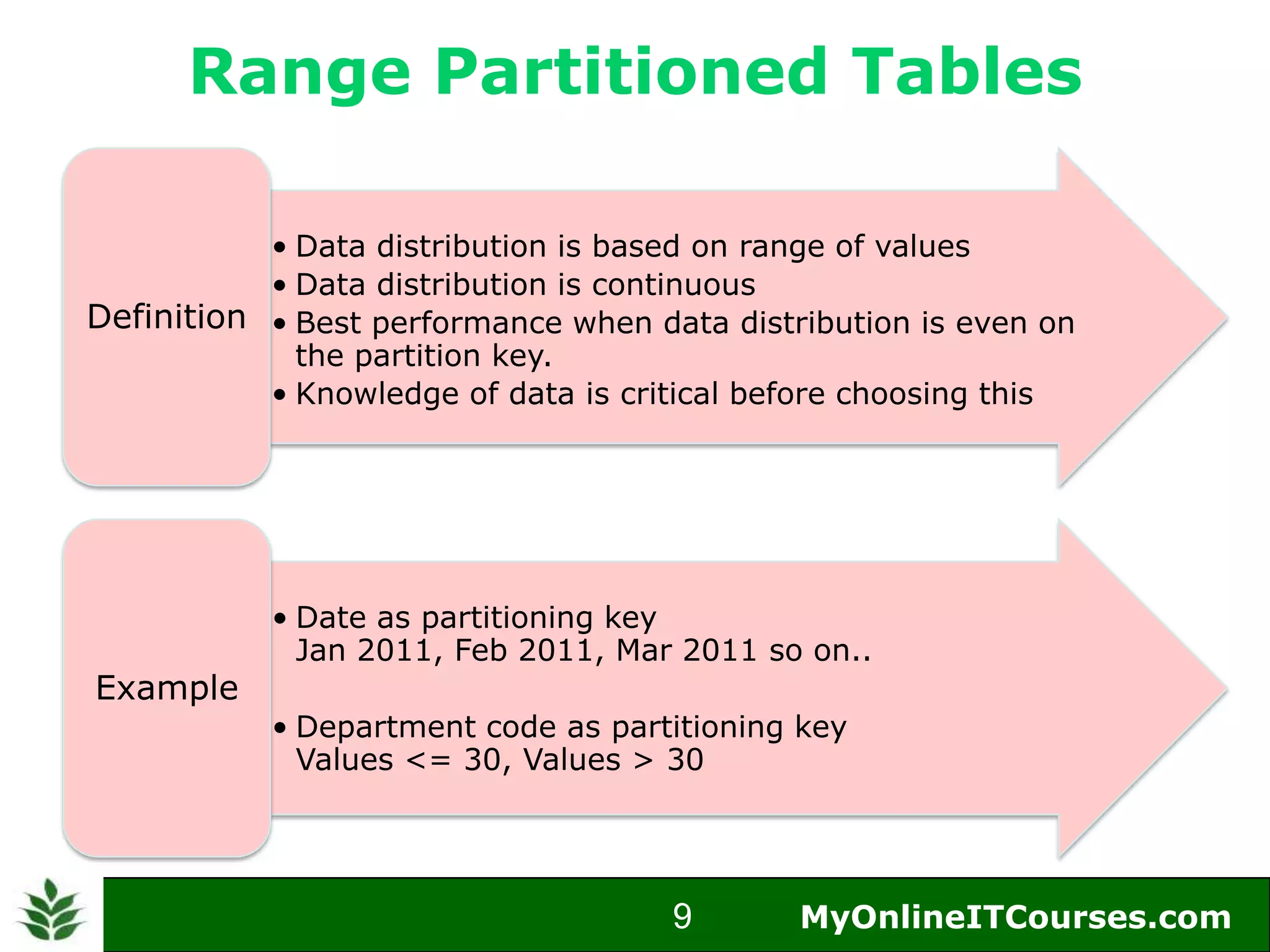
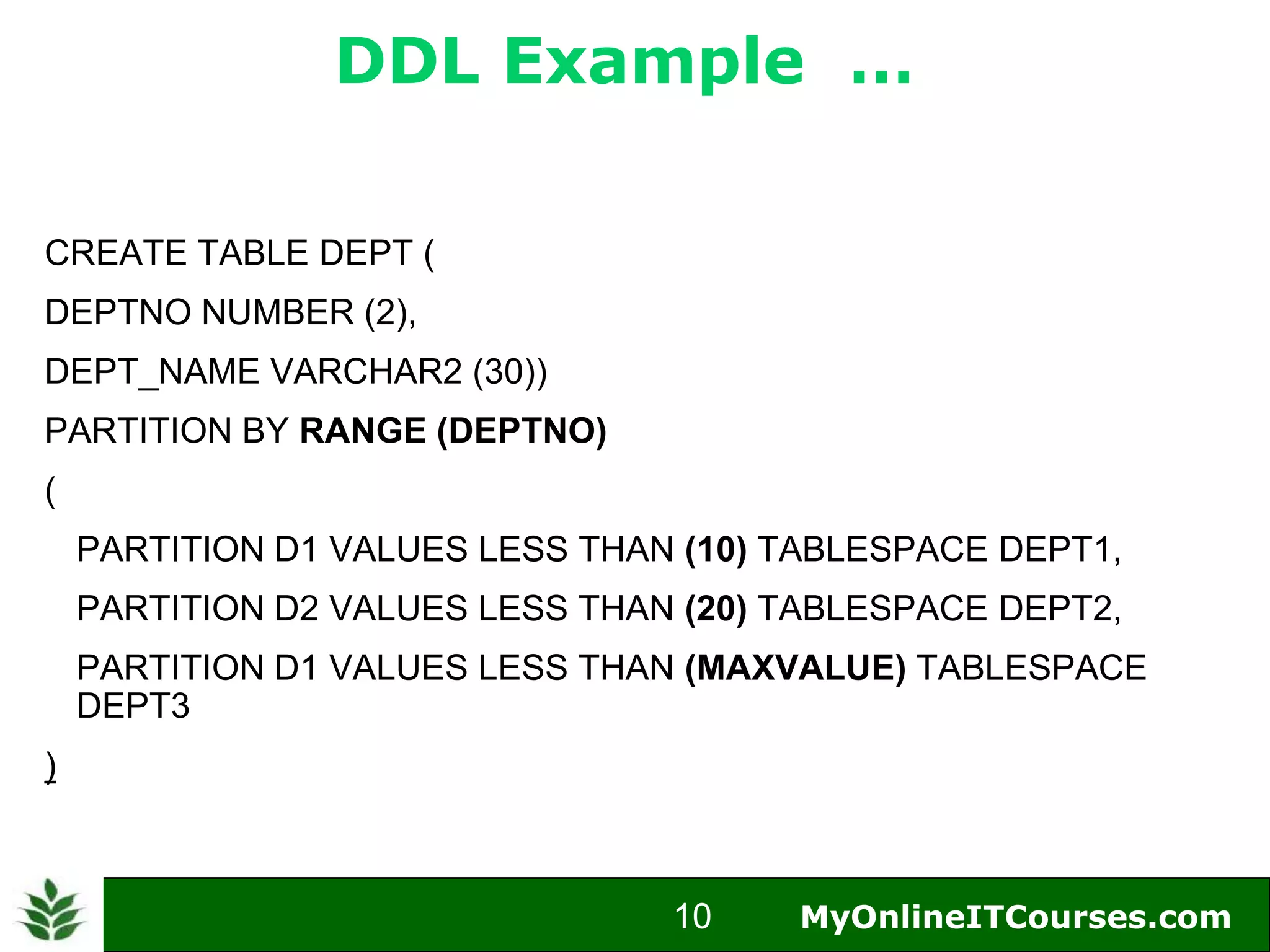
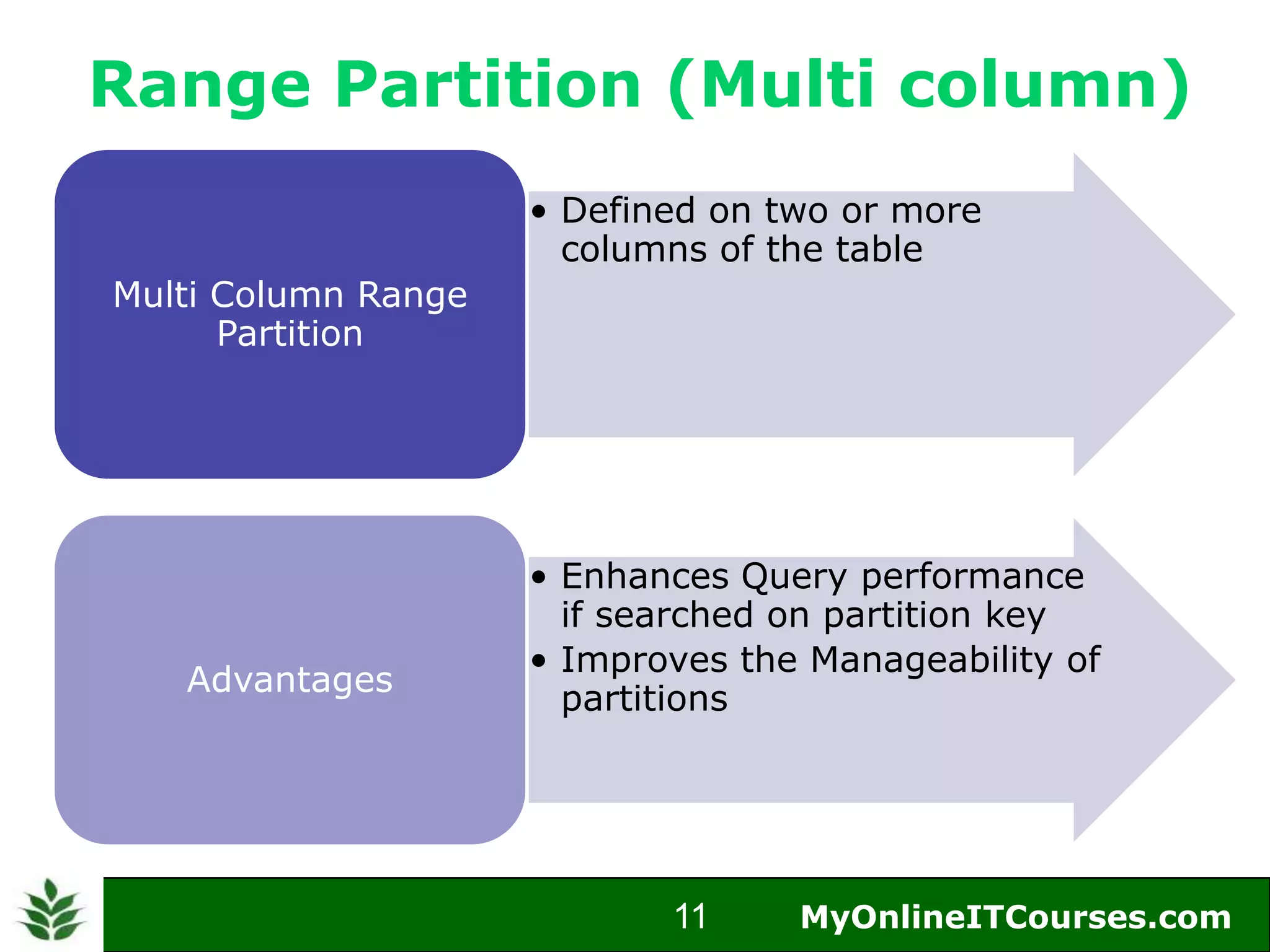
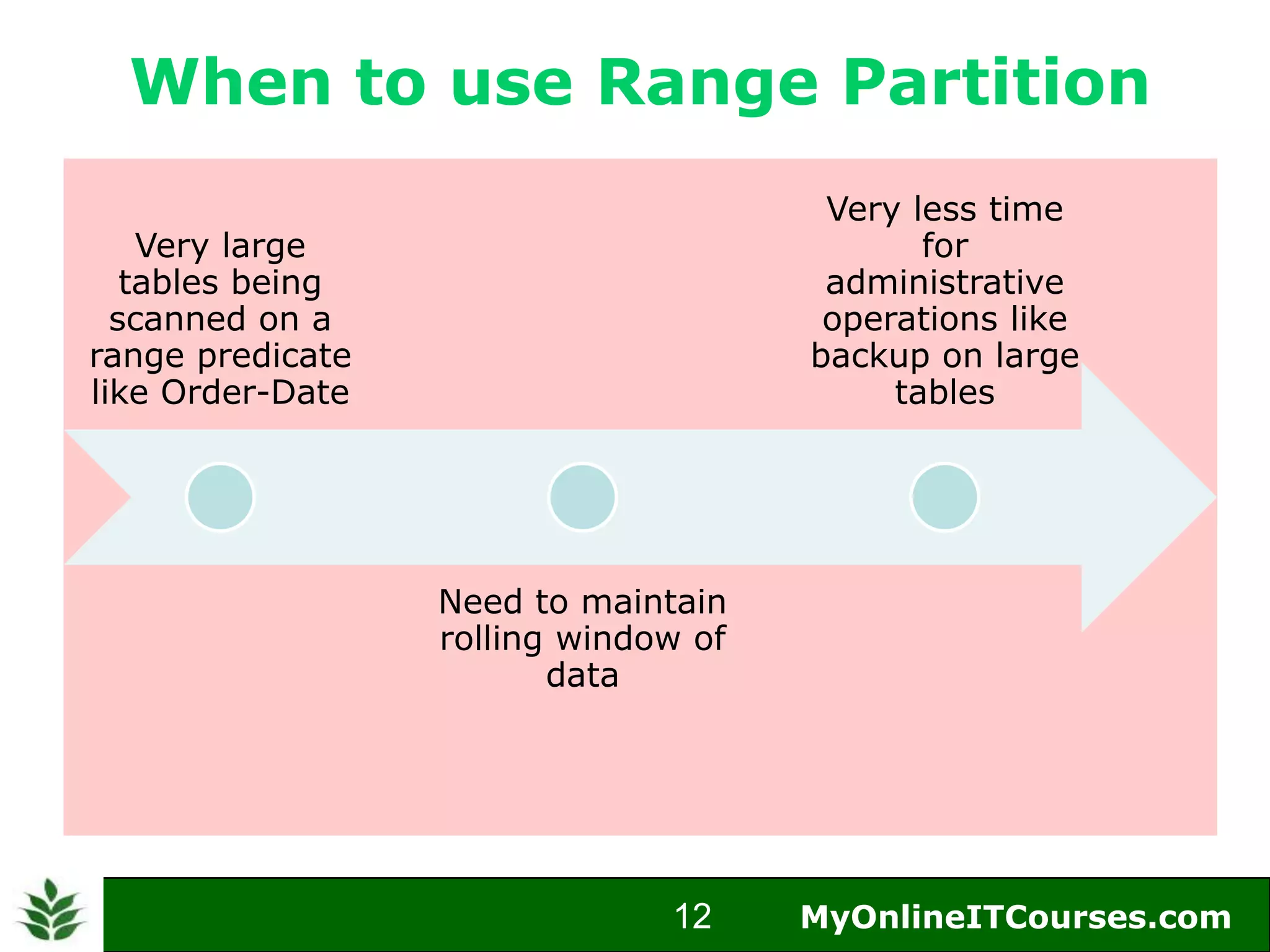
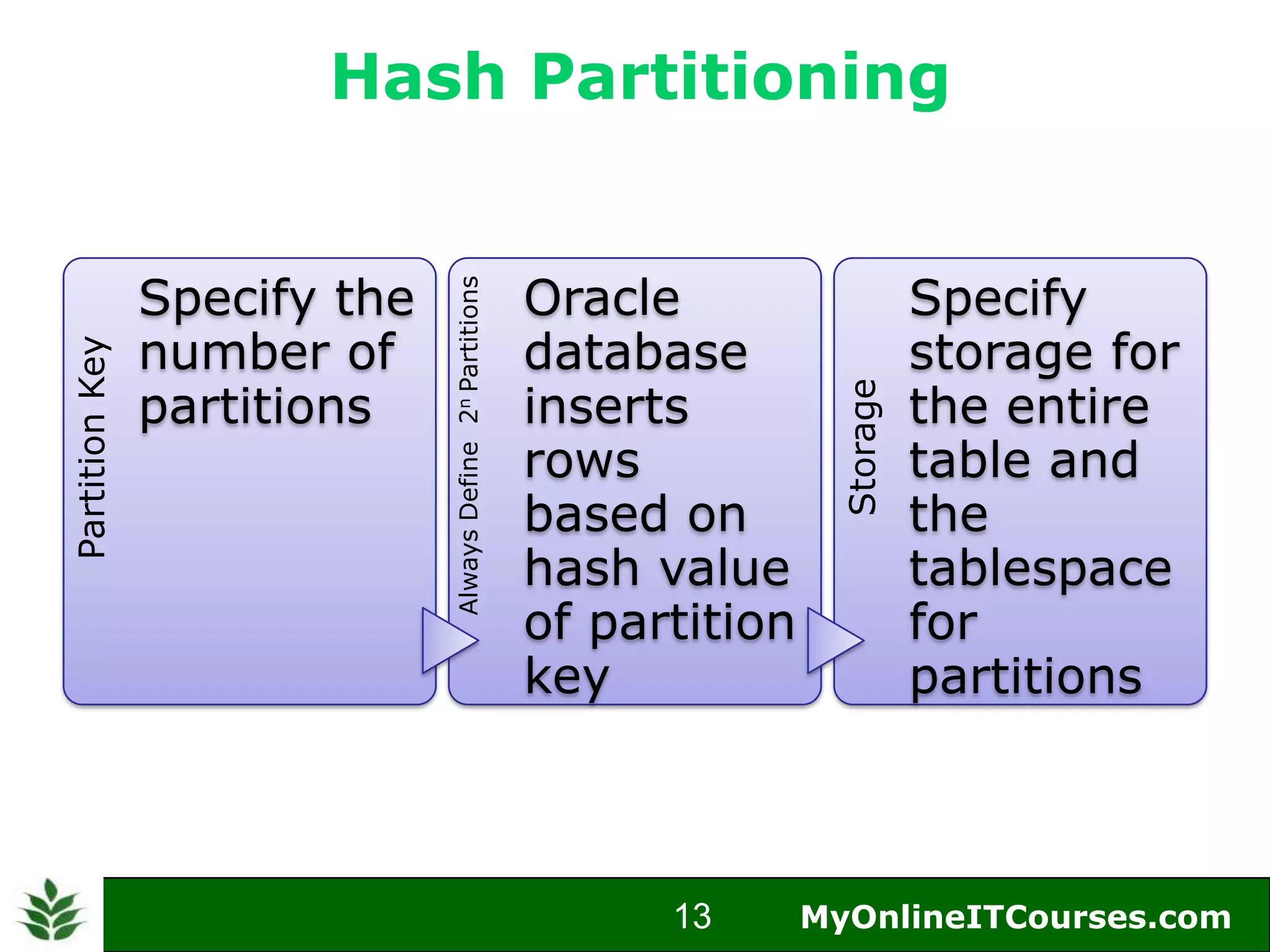
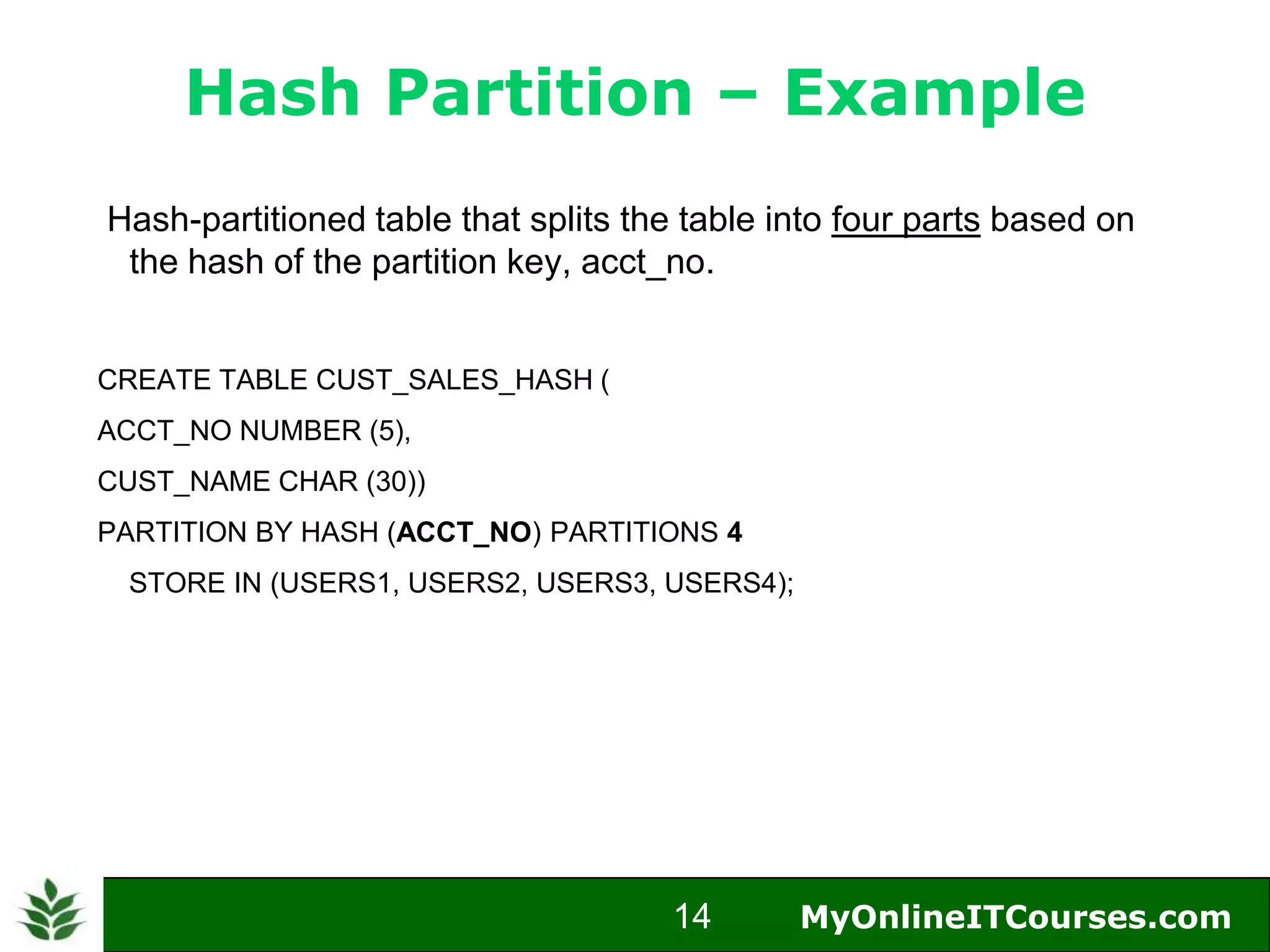
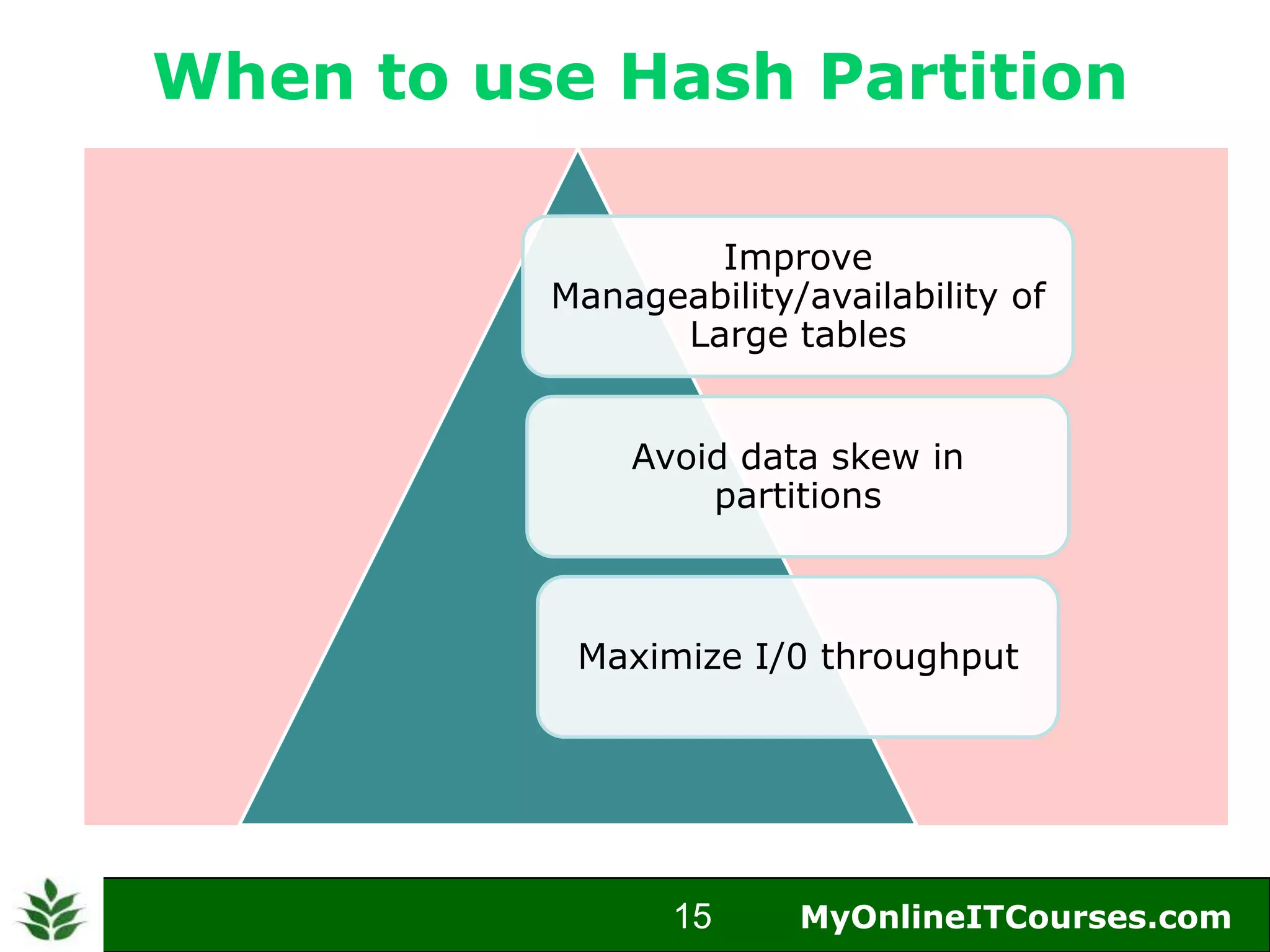
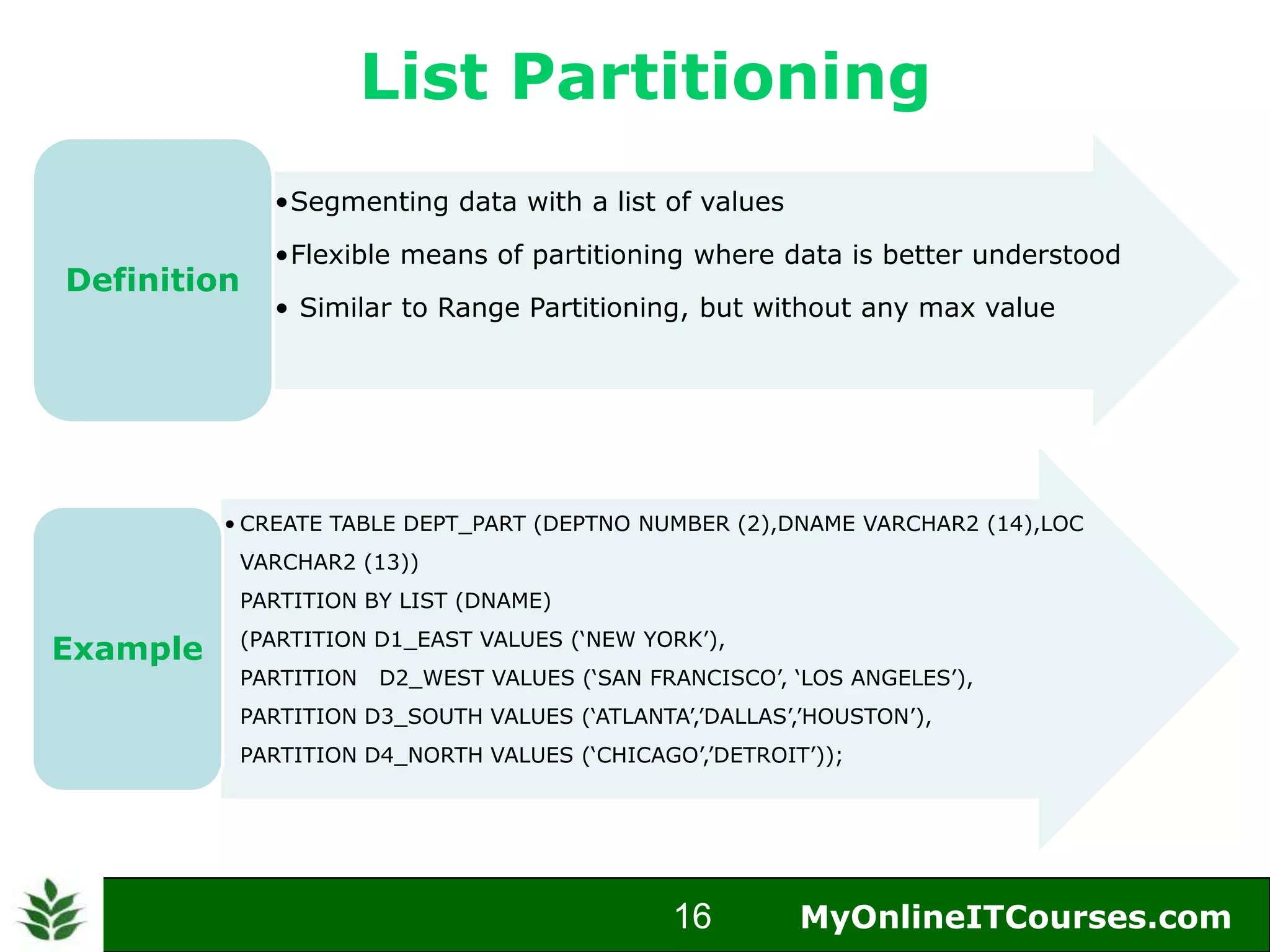
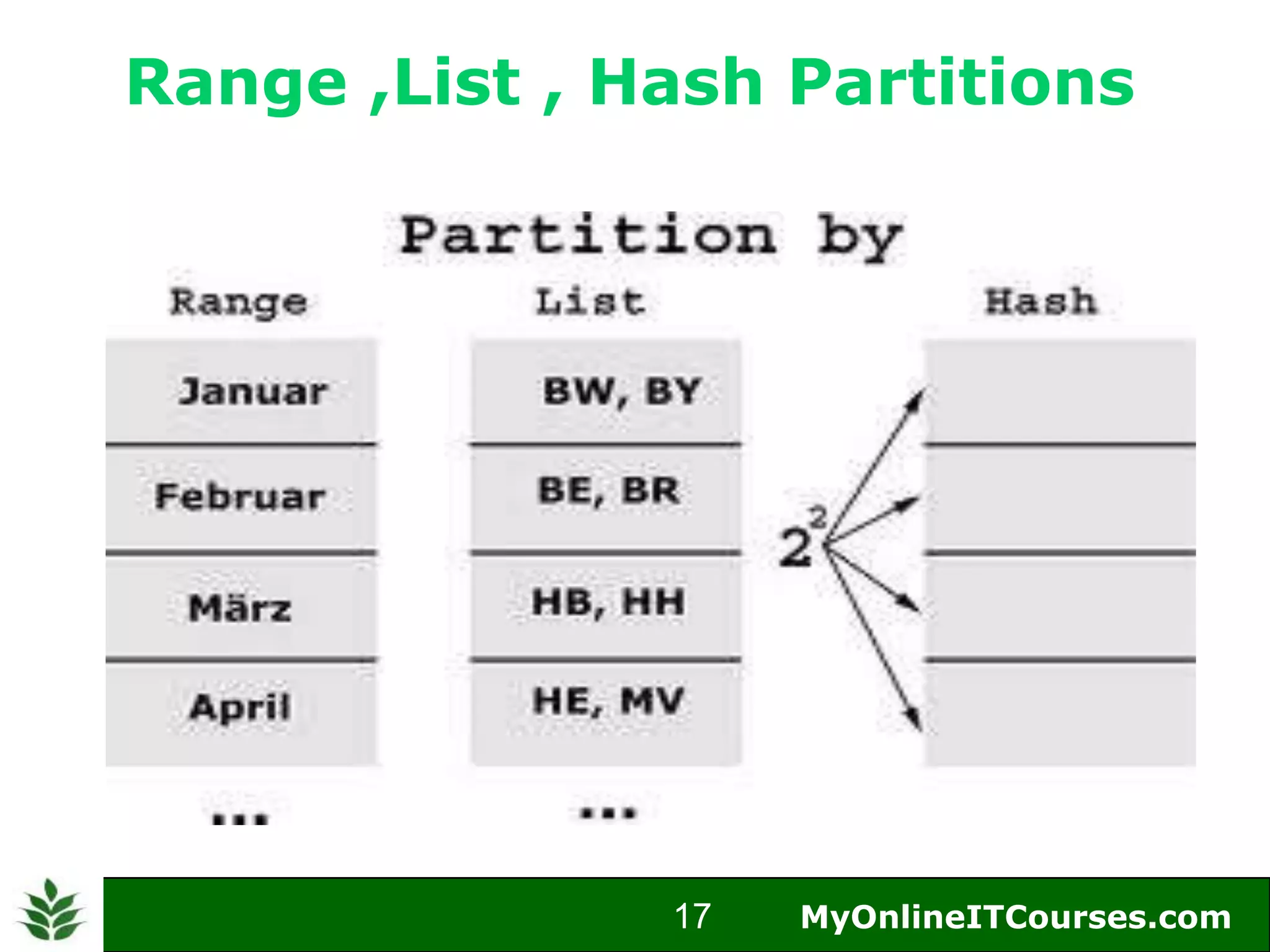
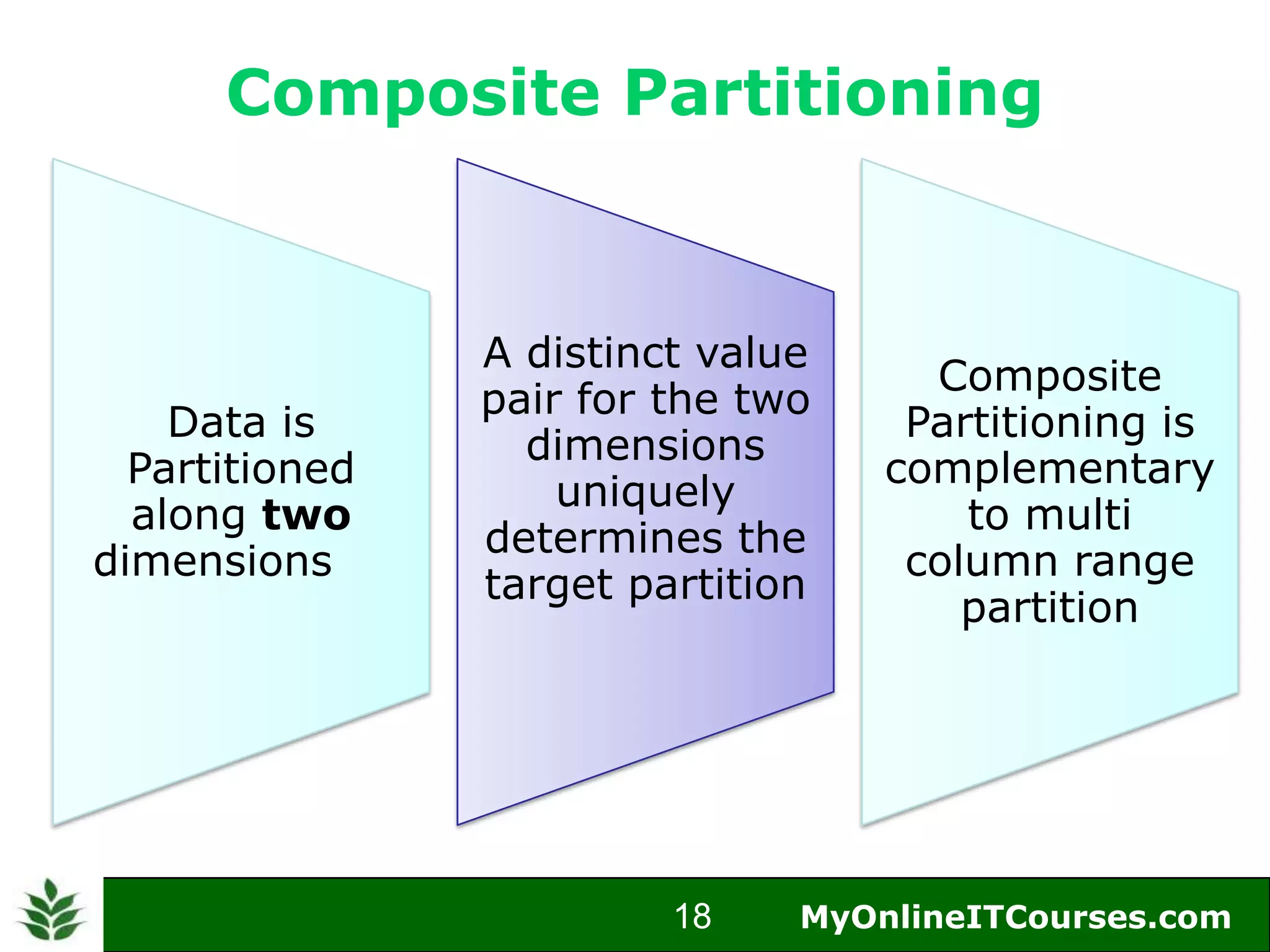
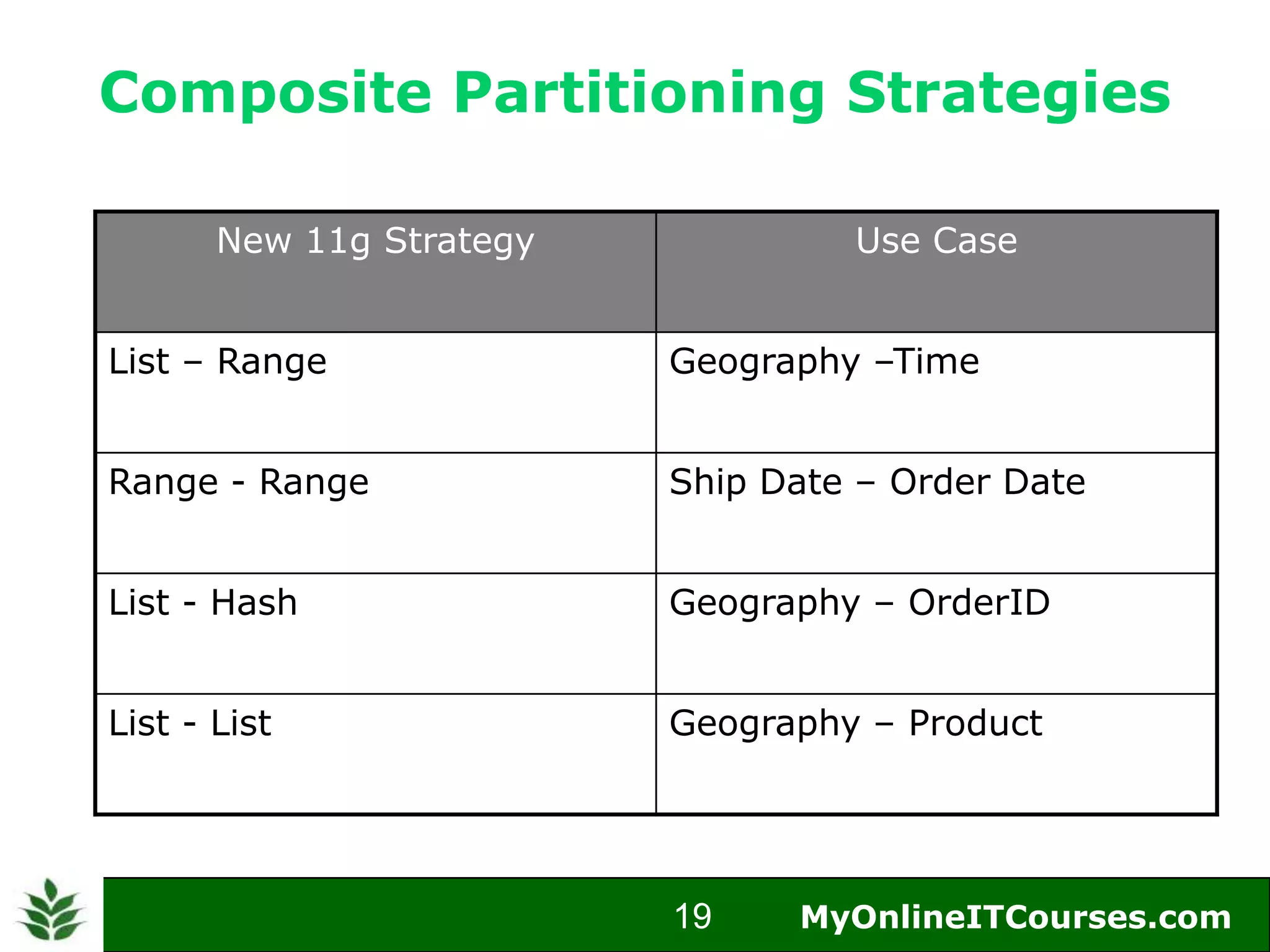
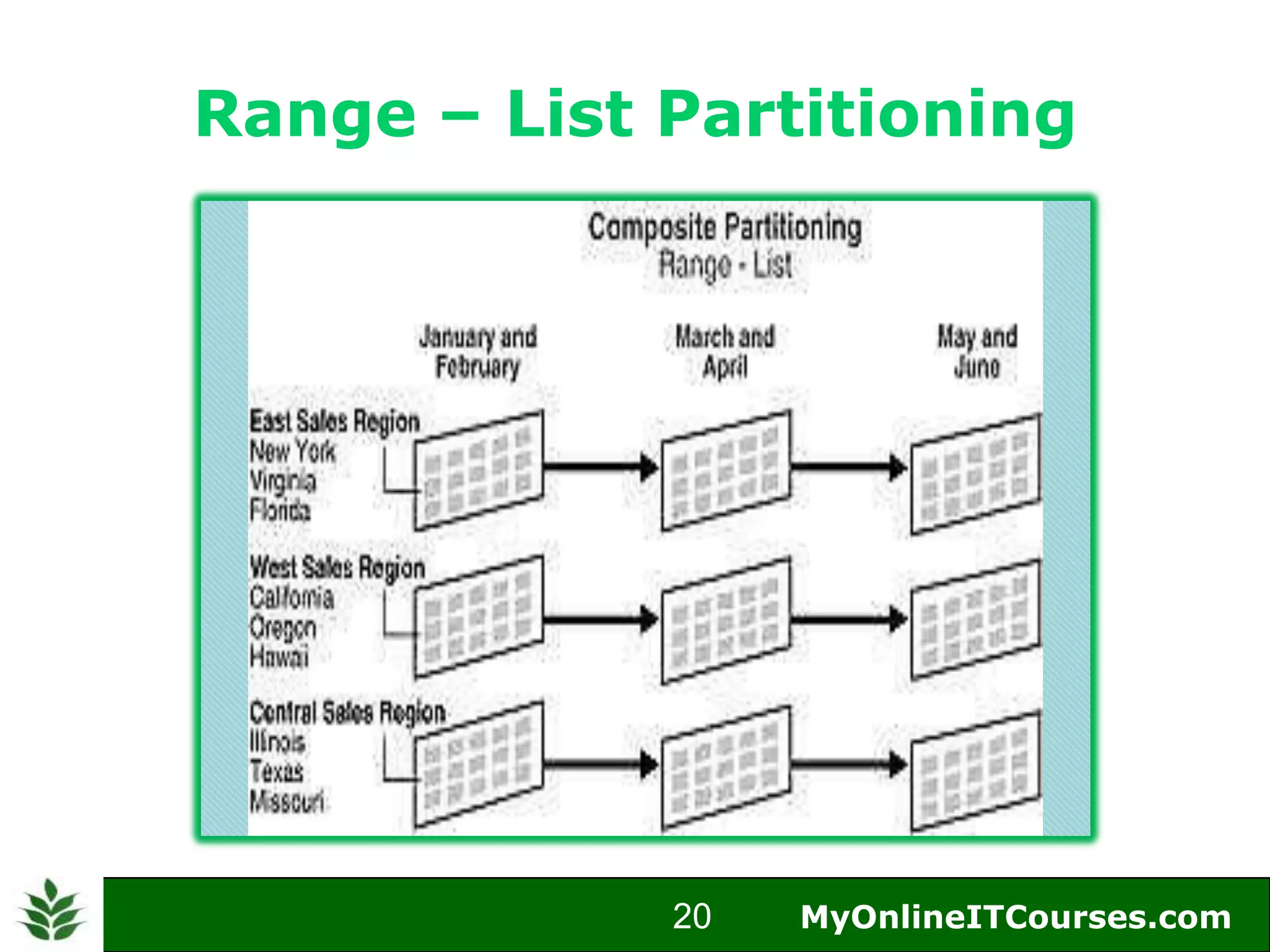
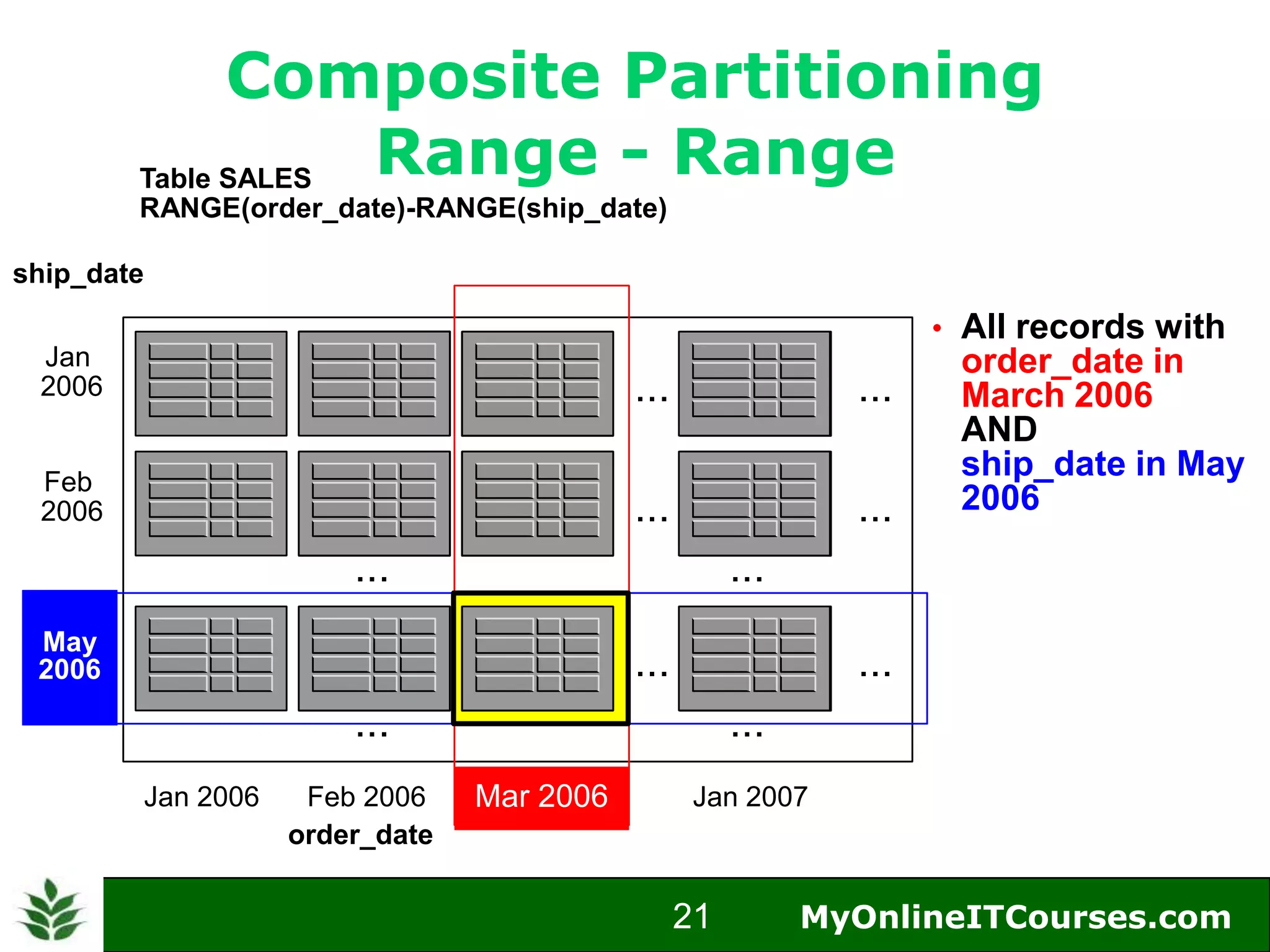
The document provides an overview of Oracle partitioning, explaining how it enables large tables or indexes to be divided into smaller and more manageable pieces for improved performance and flexibility. It discusses the benefits of partitioning, including faster query access, simplified maintenance, and easier data management strategies such as range, hash, and list partitioning. Additionally, it outlines when to partition tables, the methods for implementing different partitioning strategies, and the implications for data management.