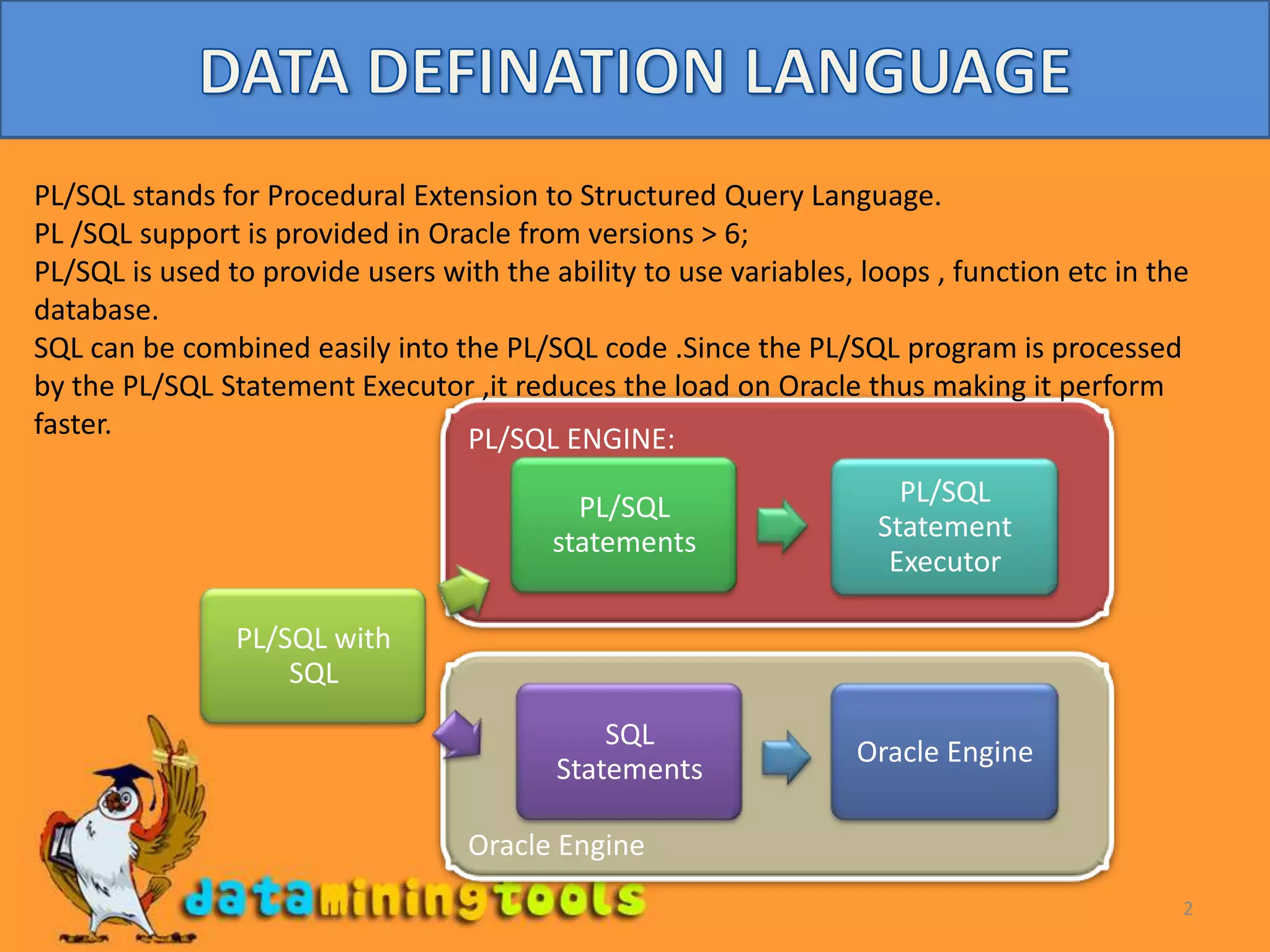
This document provides an introduction to PL/SQL, including: - PL/SQL allows for variables, loops, functions, and easier integration of SQL code for improved performance. - Code is organized into anonymous blocks with a declare, begin, and exception section. - It describes data types, variables, bind variables, substitution variables, and how to declare variables based on table columns or rows. - The goal is to explain the basic structure and capabilities of PL/SQL to allow for more complex programming within Oracle databases.

![3Anonymous BlockPL/SQL uses a block structure hence making it easier to write and maintain code.PL/SQL provides us with the following:Variables and constants.Loops and conditional constructs.Functions and Procedure that enable code reusability.Exception handling .The Anonymous Block ,the basic PL/SQL code is as follows: <<label>> [ DECLARE ] TYPE / item / FUNCTION / PROCEDURE declarations or variables. BEGIN Statements (both SQL and PL/SQL) [ EXCEPTION ] EXCEPTION handlers to handle the exception END label;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt6plsqlintrodone-100408081200-phpapp01/75/Oracle-PLSQL-Introduction-3-2048.jpg)
![4Anonymous BlockLet us write an example Anonymous block.DECLAREname varchar2[20];BEGINname := ‘Larry’;DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(‘The name is : ‘ || name);ENDThe above anonymous block print the name ‘Larry'. Key points to be highlighted here are:The variable name must follow rules similar to that of declaring Tables in SQL and the data type with size be mentioned.The := operator is the assignment operator in PL/SQL.The DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE prints text enclosed in ( ) .Here we use a ‘||’ concatenation operator to join the string and variable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt6plsqlintrodone-100408081200-phpapp01/75/Oracle-PLSQL-Introduction-4-2048.jpg)
![5VariablesThe various data types in PL/SQL are :LOB refers to large object. It could be of the type BINARY LARGE OBJECT (BLOB) or CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT (CLOB) to store image or audio in binary format (BLOB) or a text file (CLOB) up to the size of 4 GIGABYTES.BFILE refers to an external file to be stored in a database. A variable must be declared in the “DECLARE” block as: VARIABLE_NAME DATATYPE[SIZE]; A variable may be initialized when declared (otherwise set to NULL) VARIABLE_NAME DATATYPE[SIZE]:= VALUE; We may also define a variable to not hold null values. VARIABLE_NAME DATATYPE[SIZE] NOT NULL := VALUE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt6plsqlintrodone-100408081200-phpapp01/75/Oracle-PLSQL-Introduction-5-2048.jpg)
![6%TYPE and %ROWTYPE We can declare a variable to have a data type of any column or another variable using the %TYPE attribute which is prefixed with the table and column or variable name.SYNTAX: VARIABLE _NAME TABLE_NAME.COLUMN_NAME[VARIABLE_NAME]%TYPE ;EXAMPLE: name InfoTable.name%TYPE;The %ROWTYPE attribute is used to declare a variable to hold an entire row which is a collection of multiple columns of a table.SYNTAX: VARIABLE _NAME TABLE_NAME %ROWTYPEEXAMPLE: name InfoTable%ROWTYPE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt6plsqlintrodone-100408081200-phpapp01/75/Oracle-PLSQL-Introduction-6-2048.jpg)
![7BIND/HOST VARIABLESBind variables are the variables that are created in the host environment hence also called as host variable. The features of a bind variable are:Unlike normal variables the memory used by a bind variable is not cleared when the PL/SQL block execution is complete.Can be accessed outside the block by other PL/SQL and SQL code.Declared using a VARIABLE keyword and above the “DECLARE” block.While usage they are referred wit a prefixed : symbolSYNTAX:VARIABLE variable_name DATATYPE[SIZE];EXAMPLE:VARIABLE eage NUMBER; BEGIN SELECT age INTO :eage FROM InfoTable WHERE name = ‘bill’; END Only character array variables need to be given a size.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt6plsqlintrodone-100408081200-phpapp01/75/Oracle-PLSQL-Introduction-7-2048.jpg)
![8Substitution VariablesWe can either hard code the values of variable or accept the values from the user. To accept a value from the user , it has to be declared as a SUBSTITUTION VARIABLE. Substitution variables when used accept value from user.SYNTAX:VARIABLE variable_name DATATYPE[SIZE] := &variable_name;EXAMPLE :VARIABLE age NUMBER; DECLAREename VARCHAR(20) := &ename; BEGIN SELECT age INTO eage FRM InfoTable WHERE name = ename; END;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt6plsqlintrodone-100408081200-phpapp01/75/Oracle-PLSQL-Introduction-8-2048.jpg)
