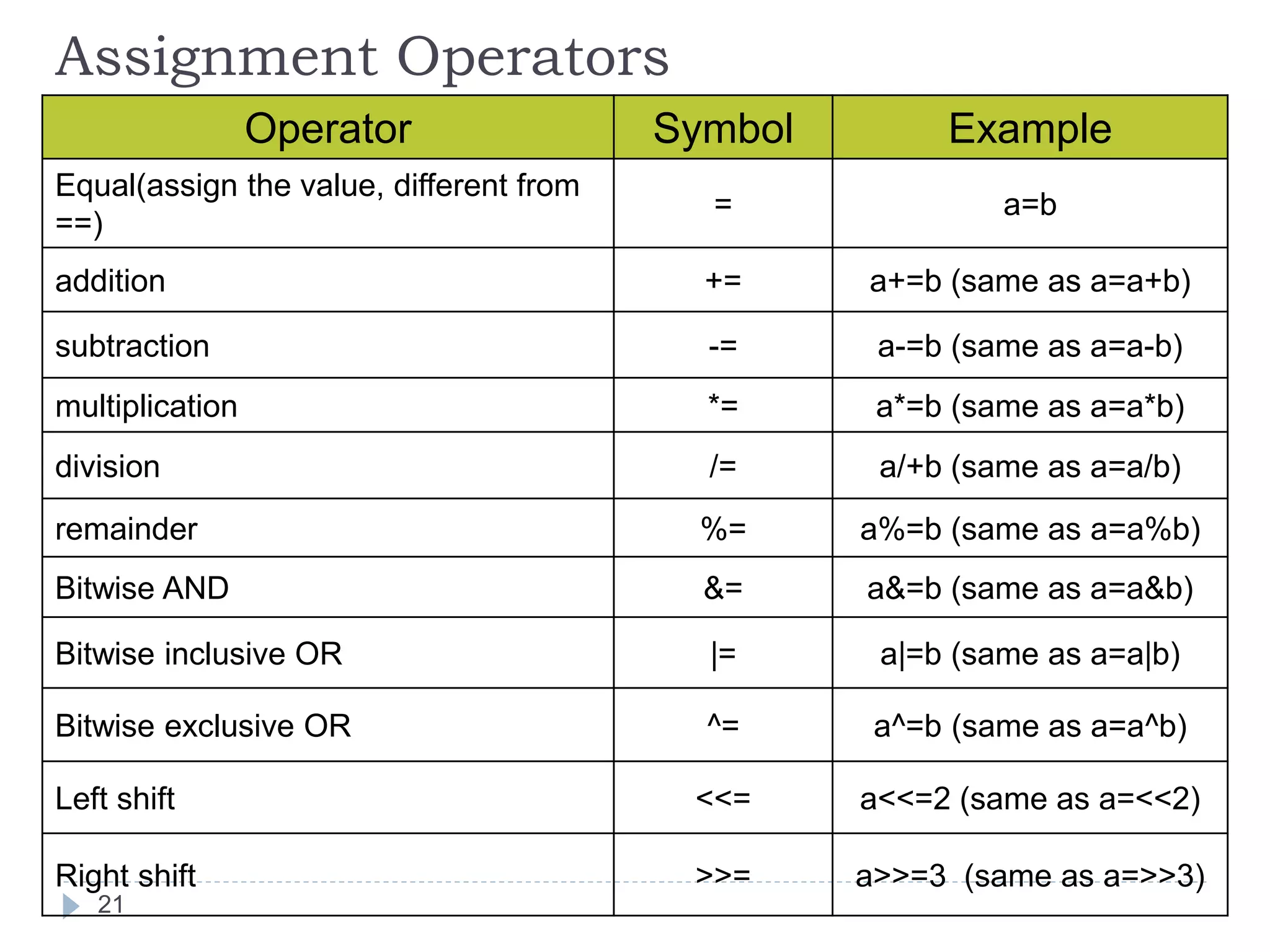
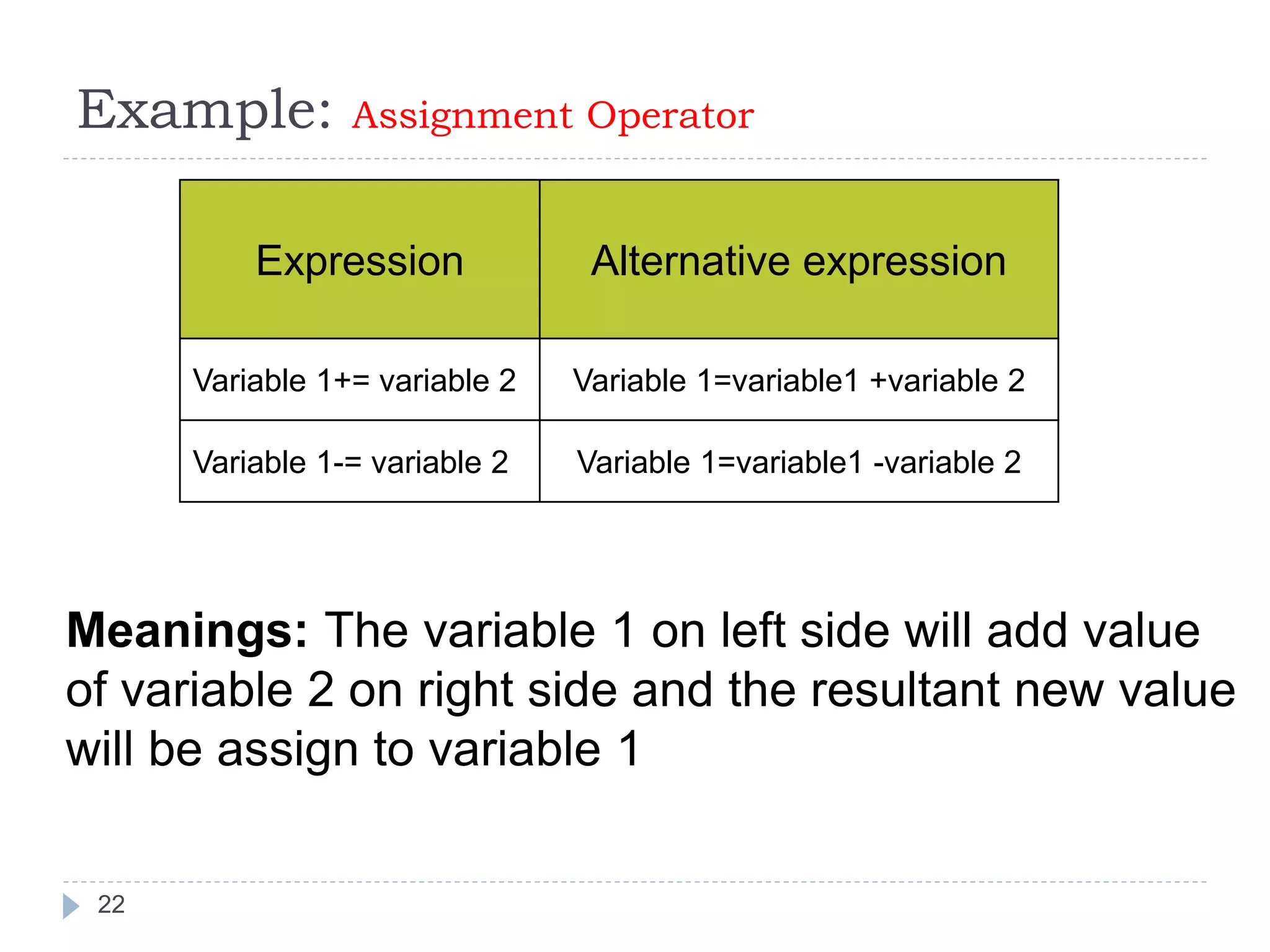
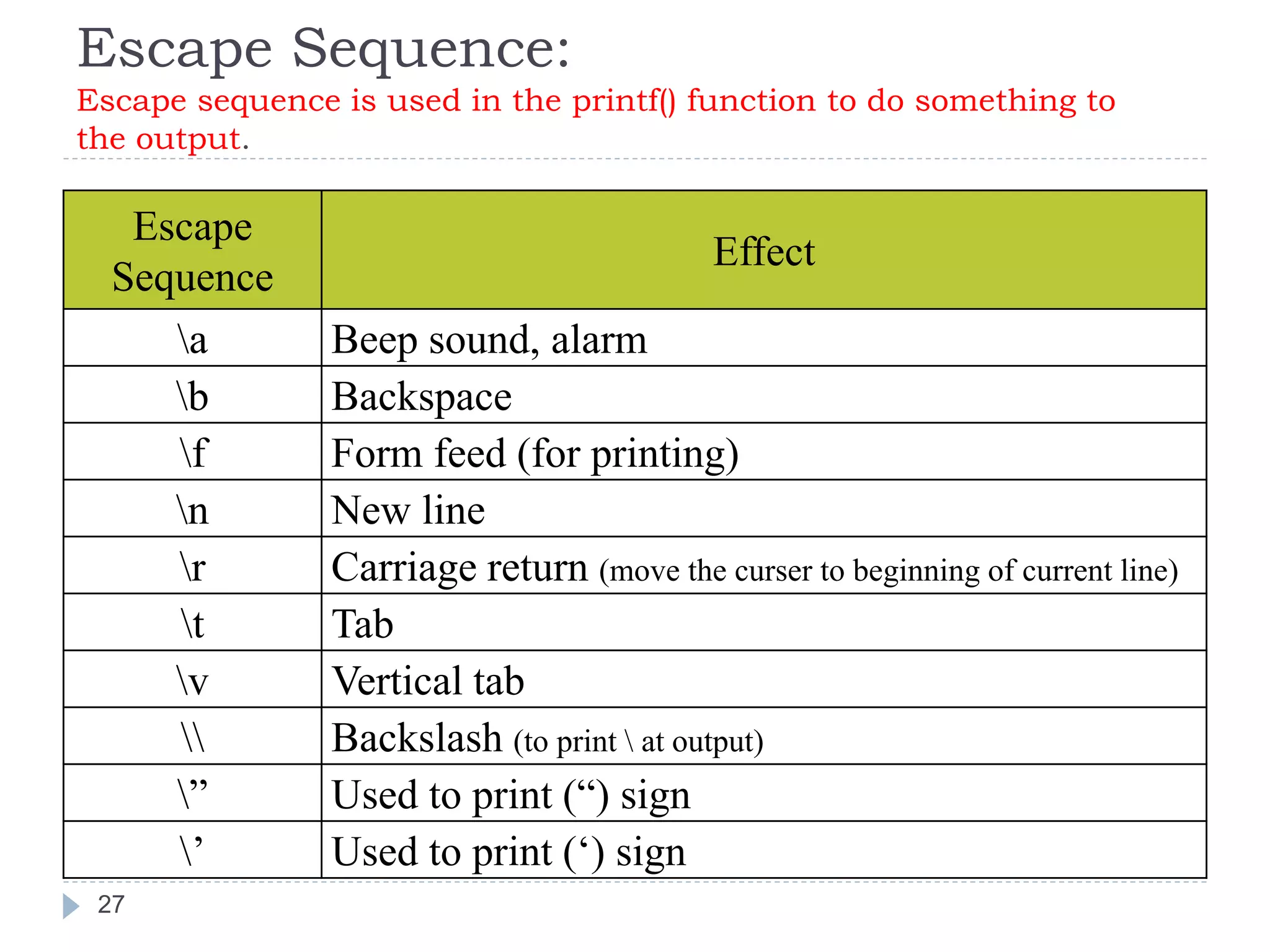
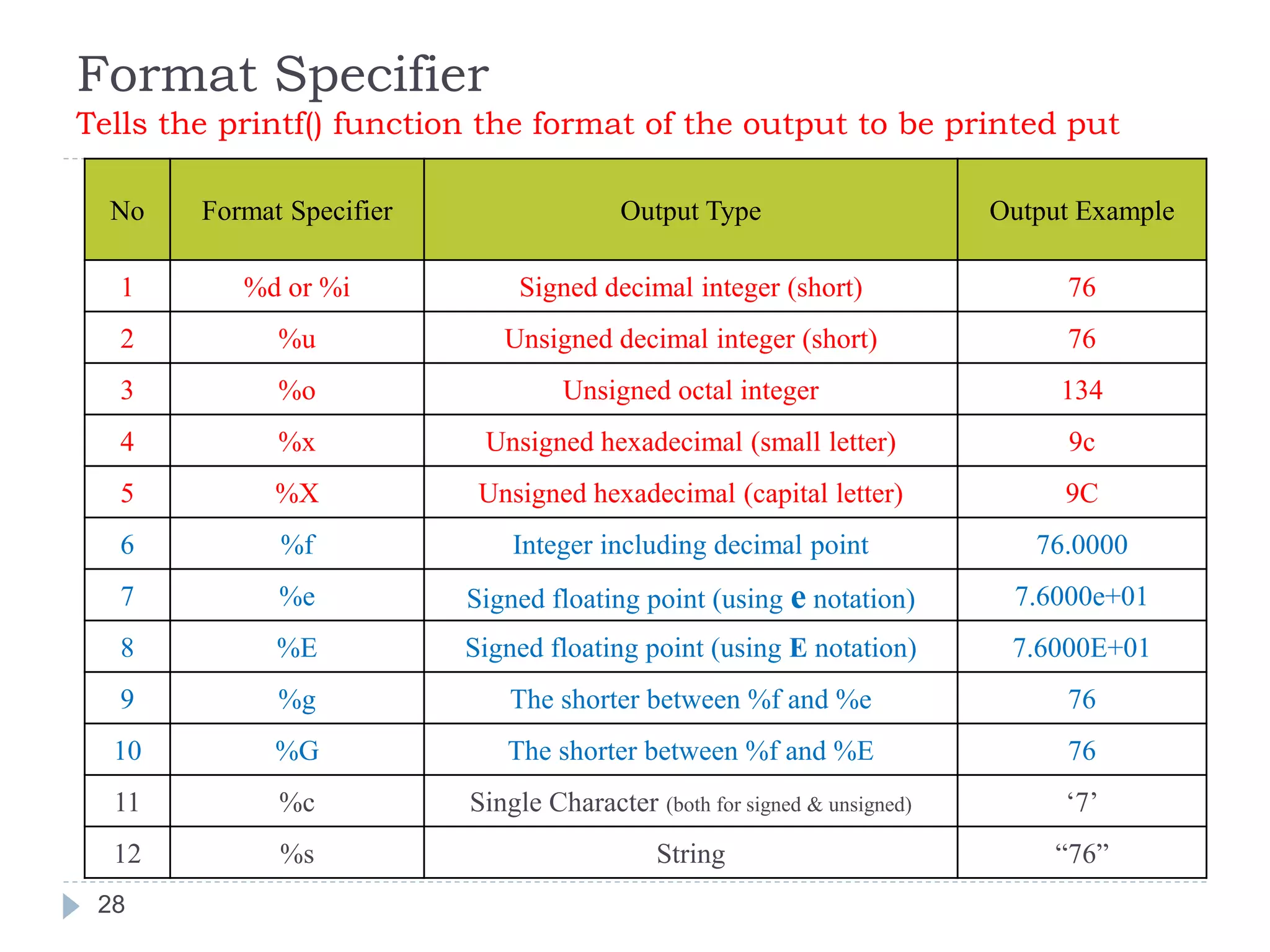
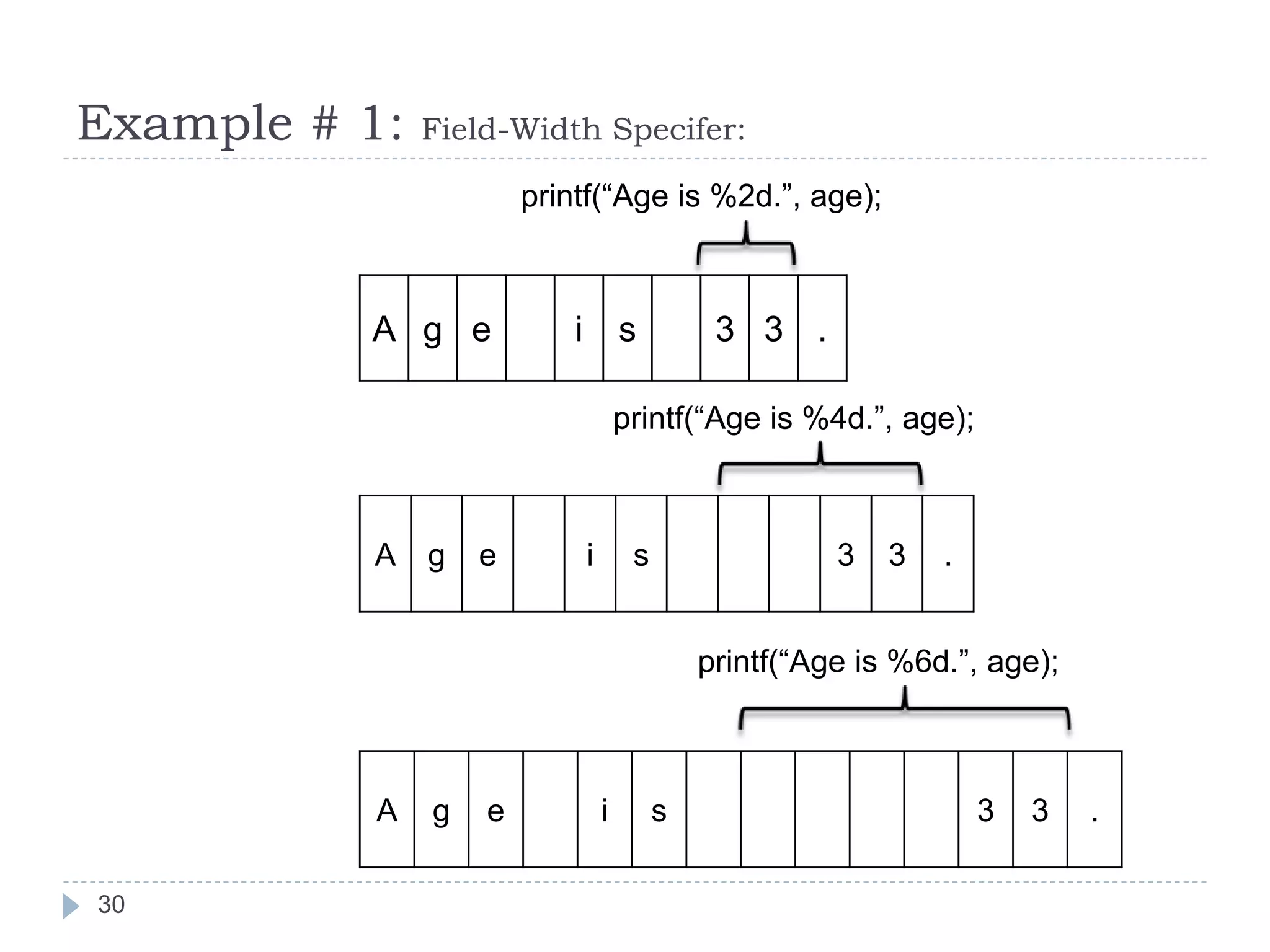
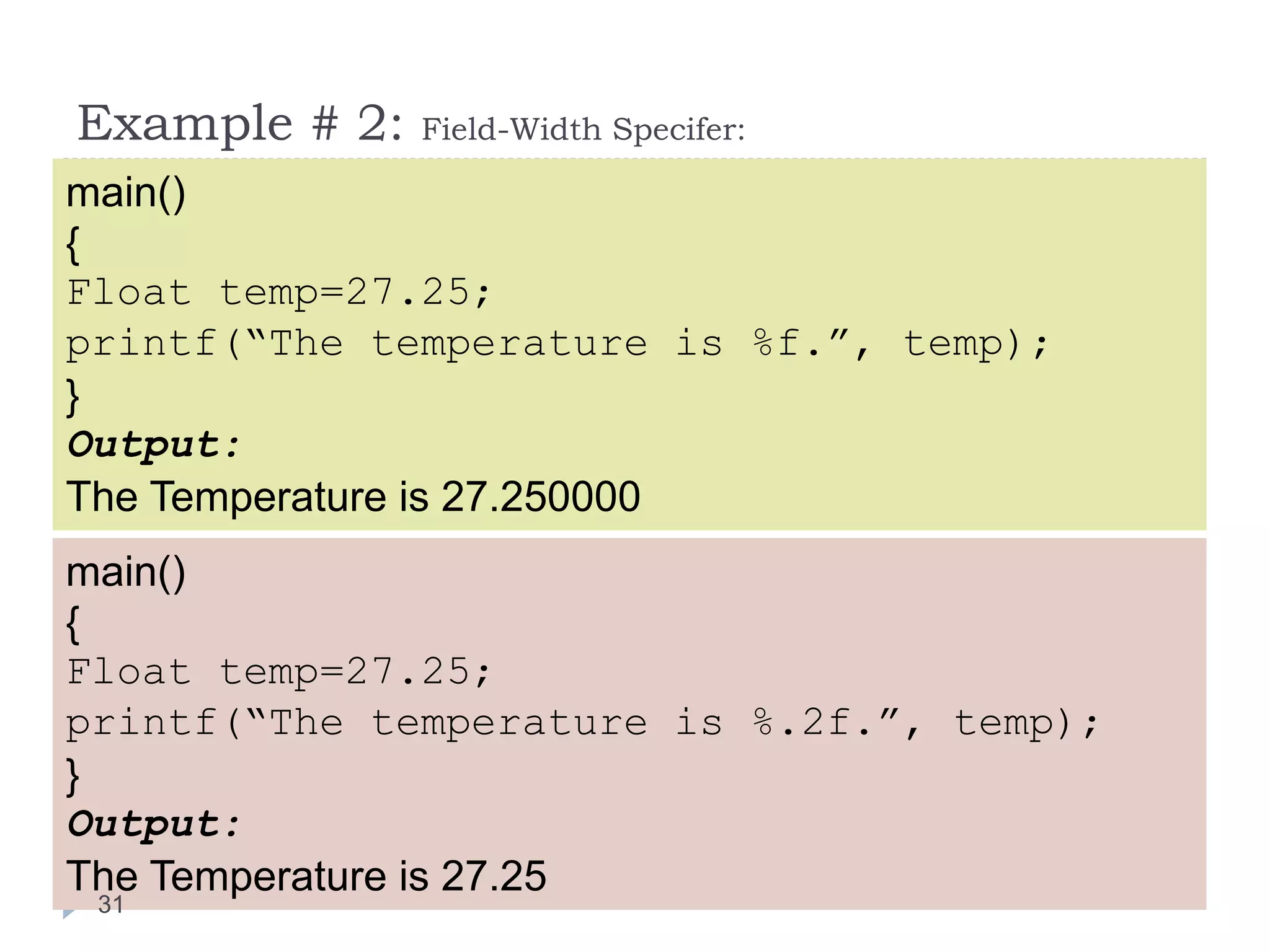
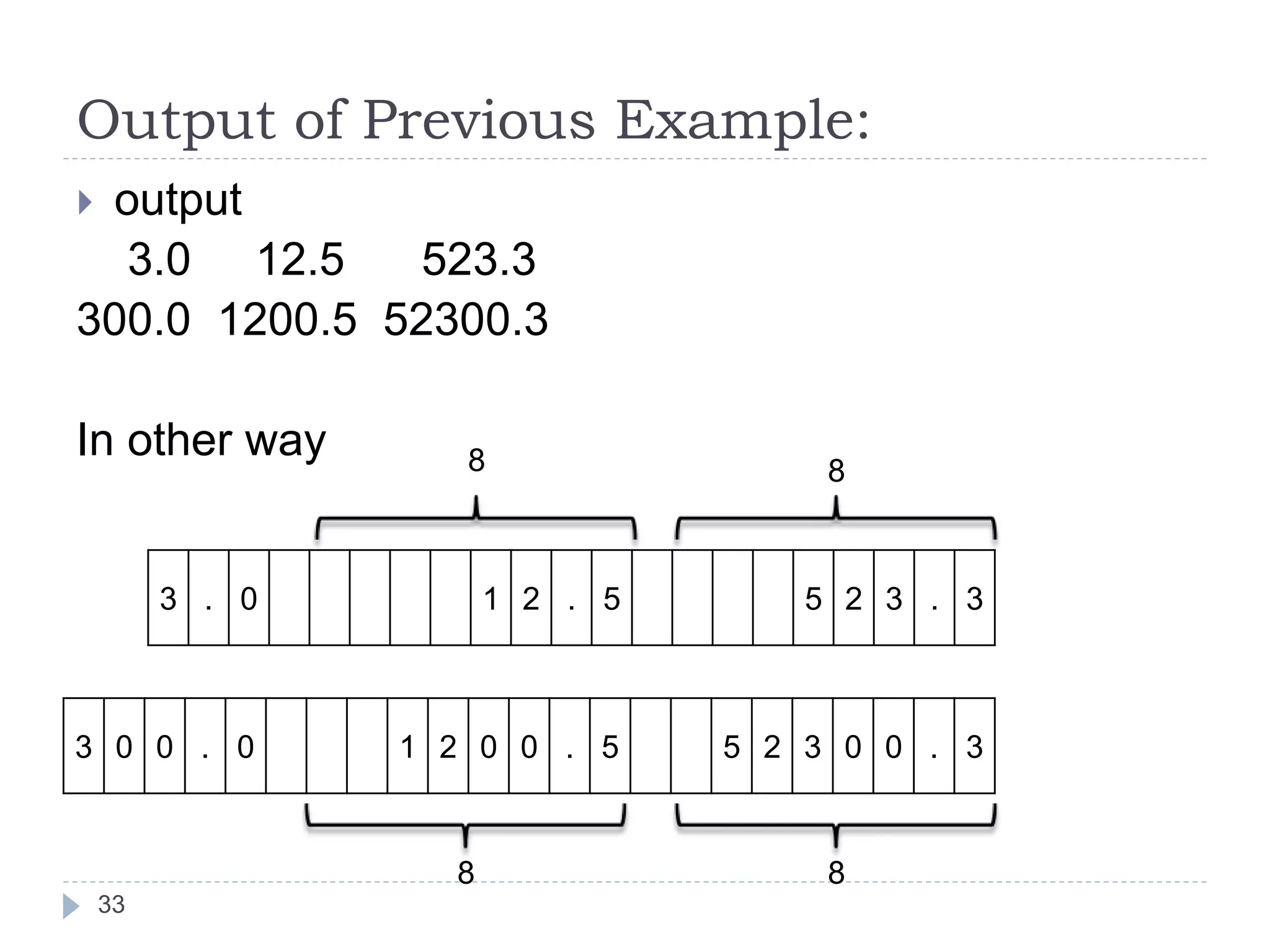
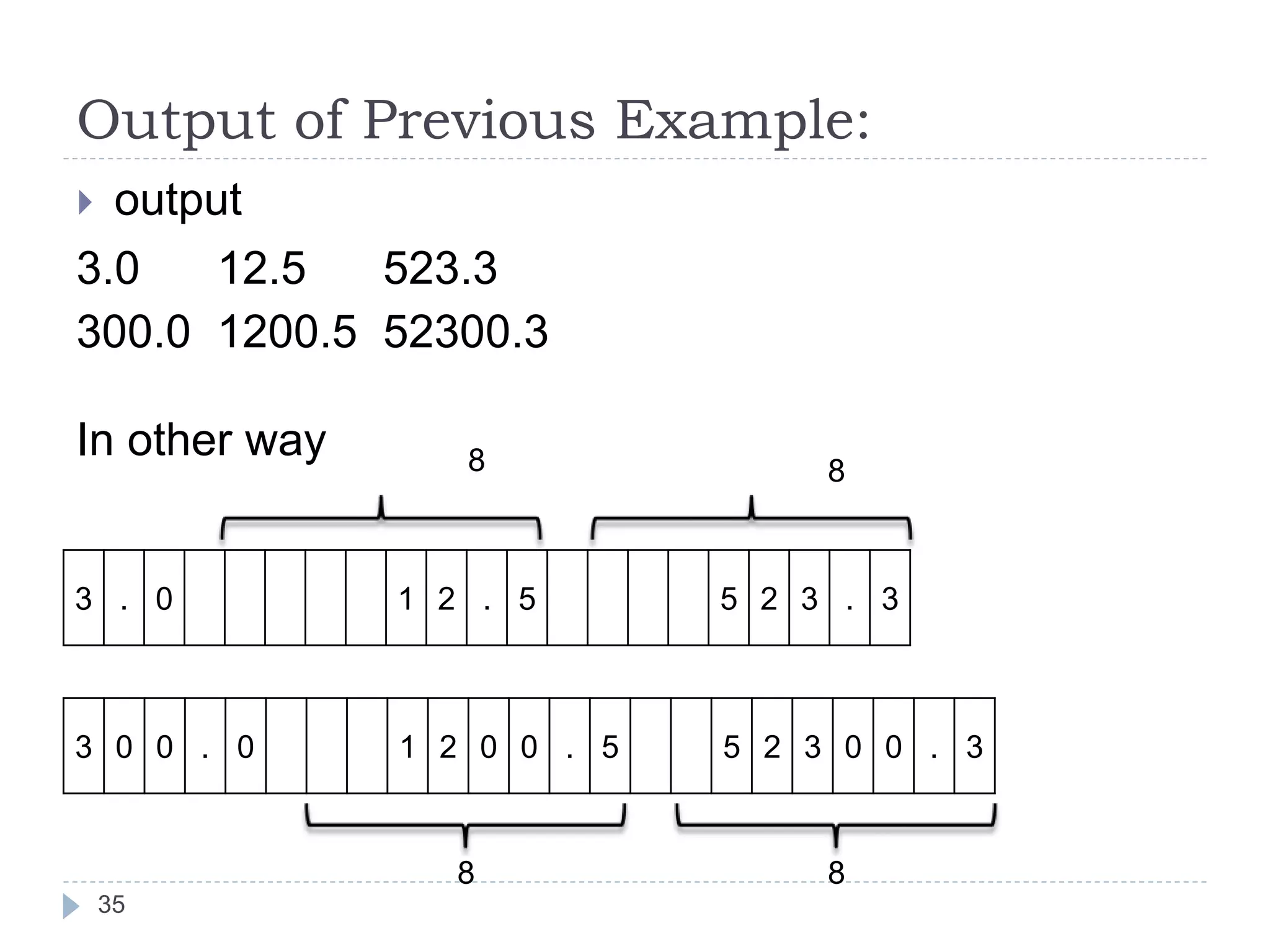
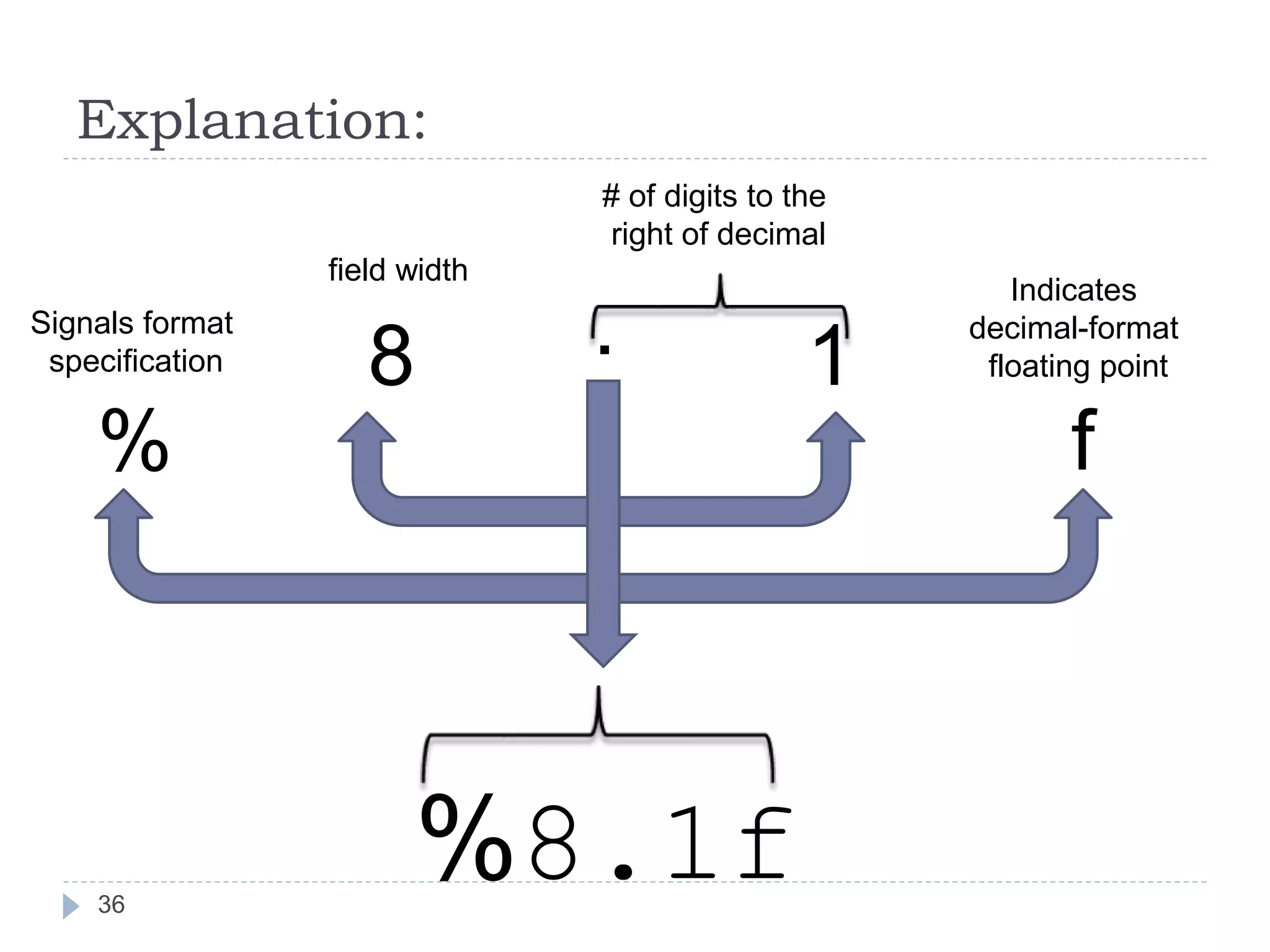
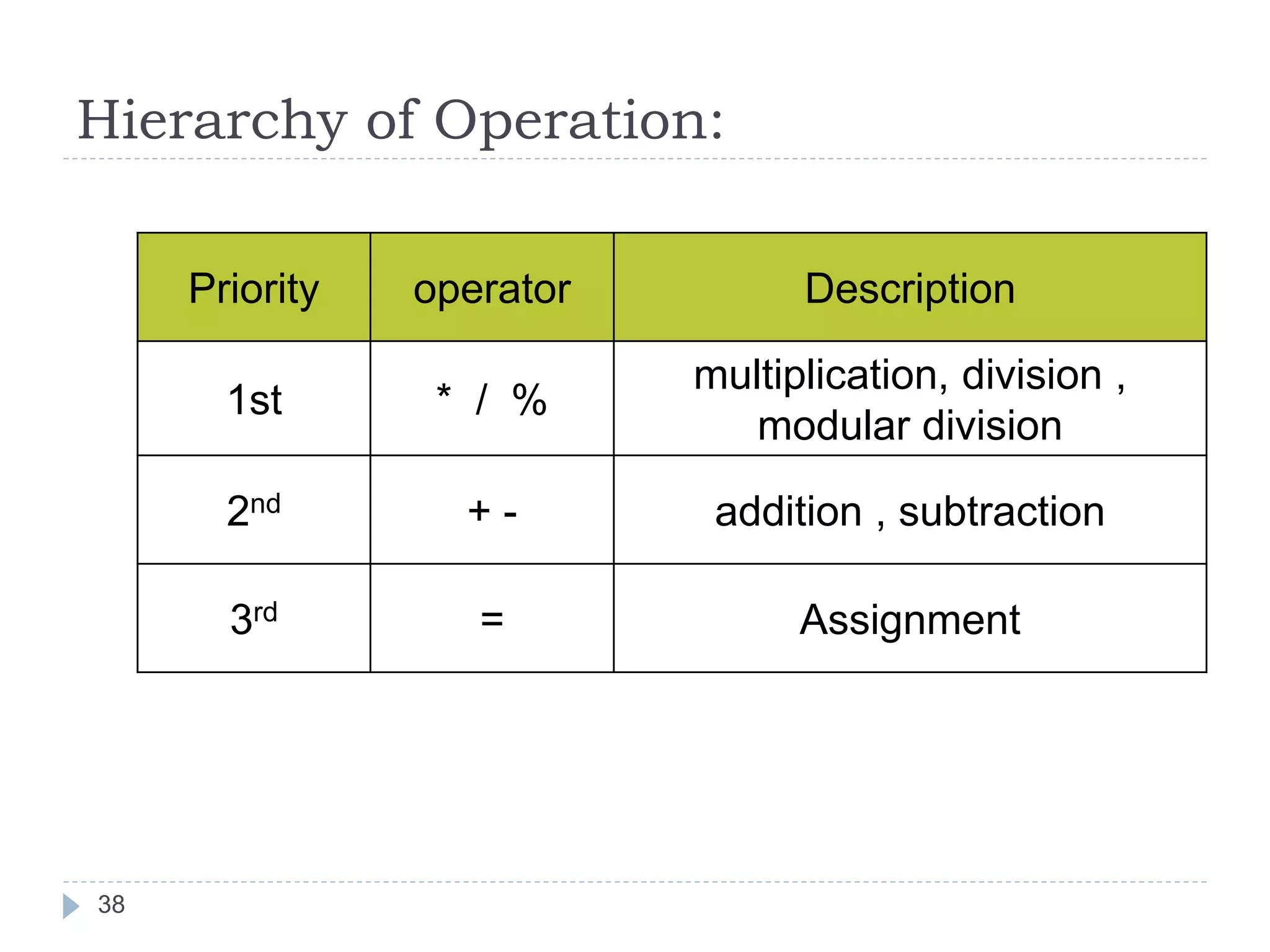
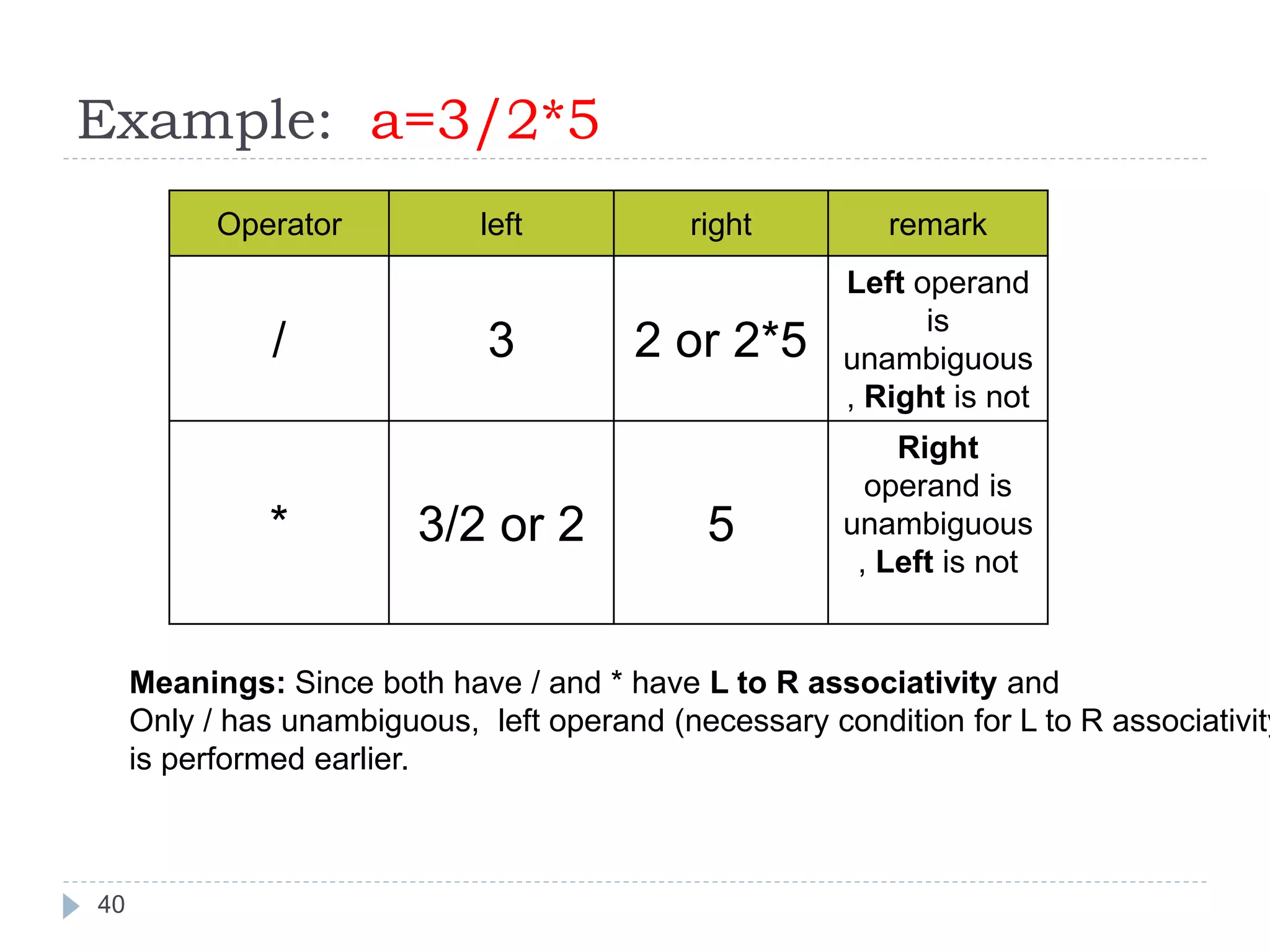
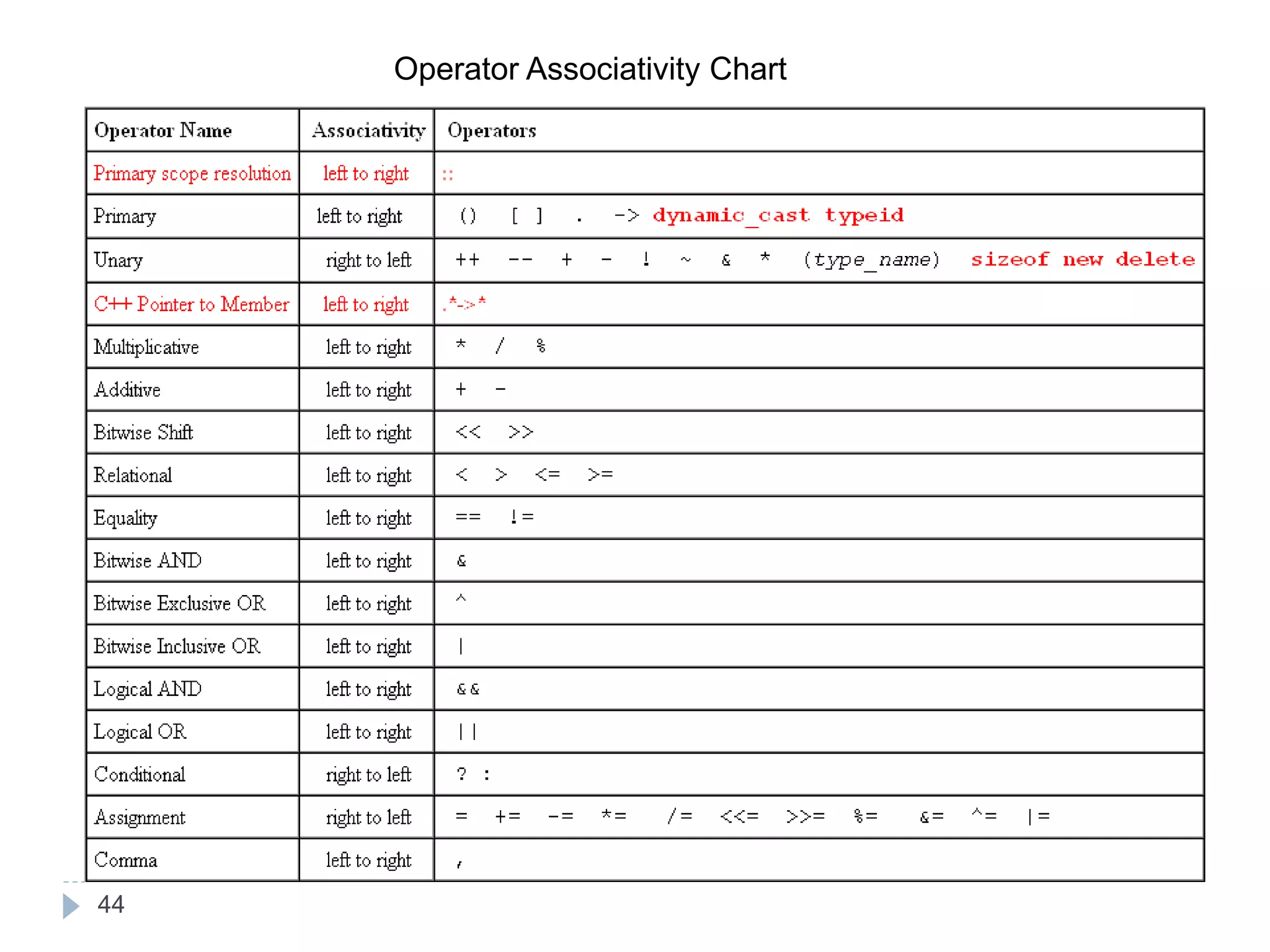
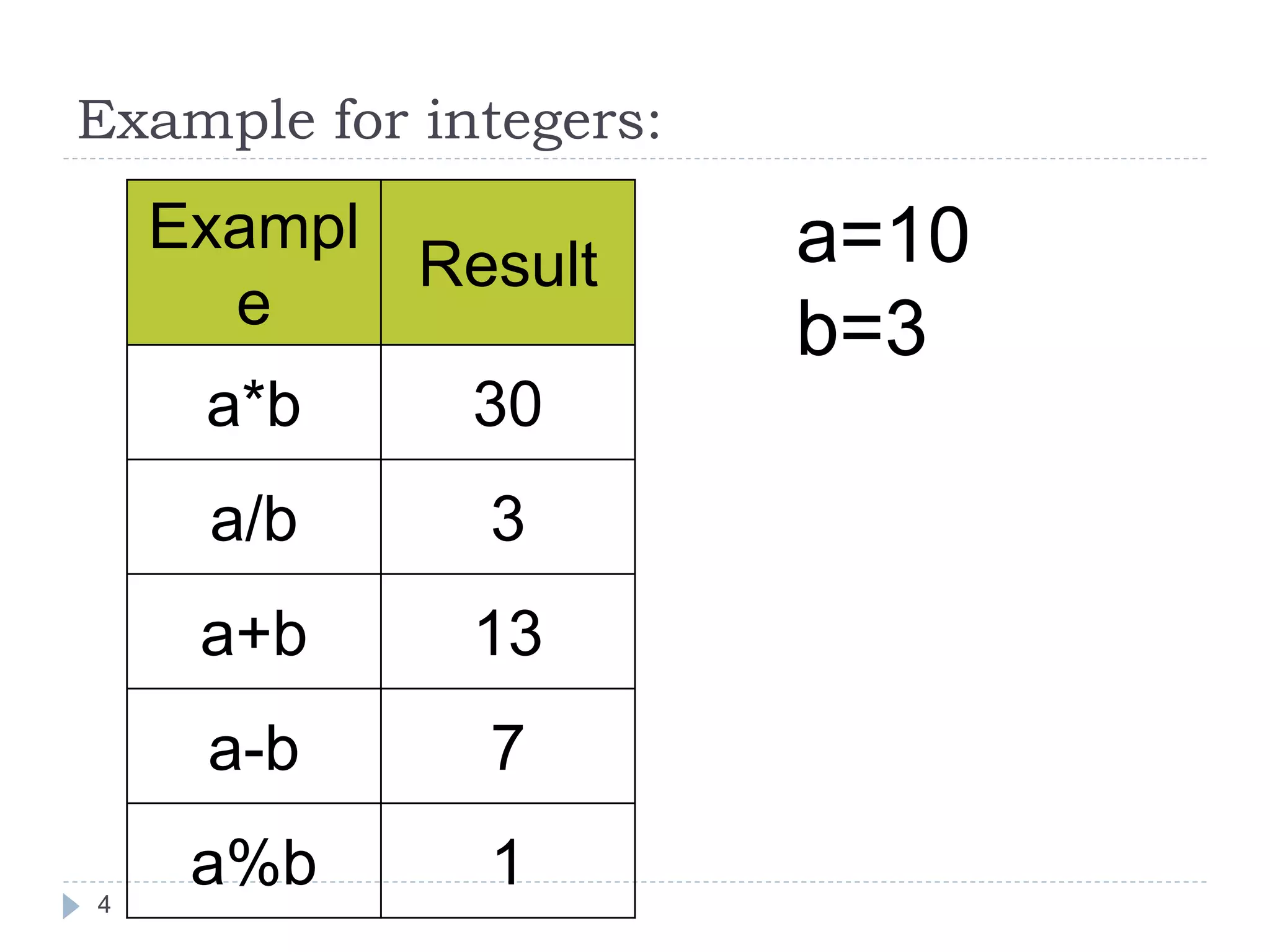
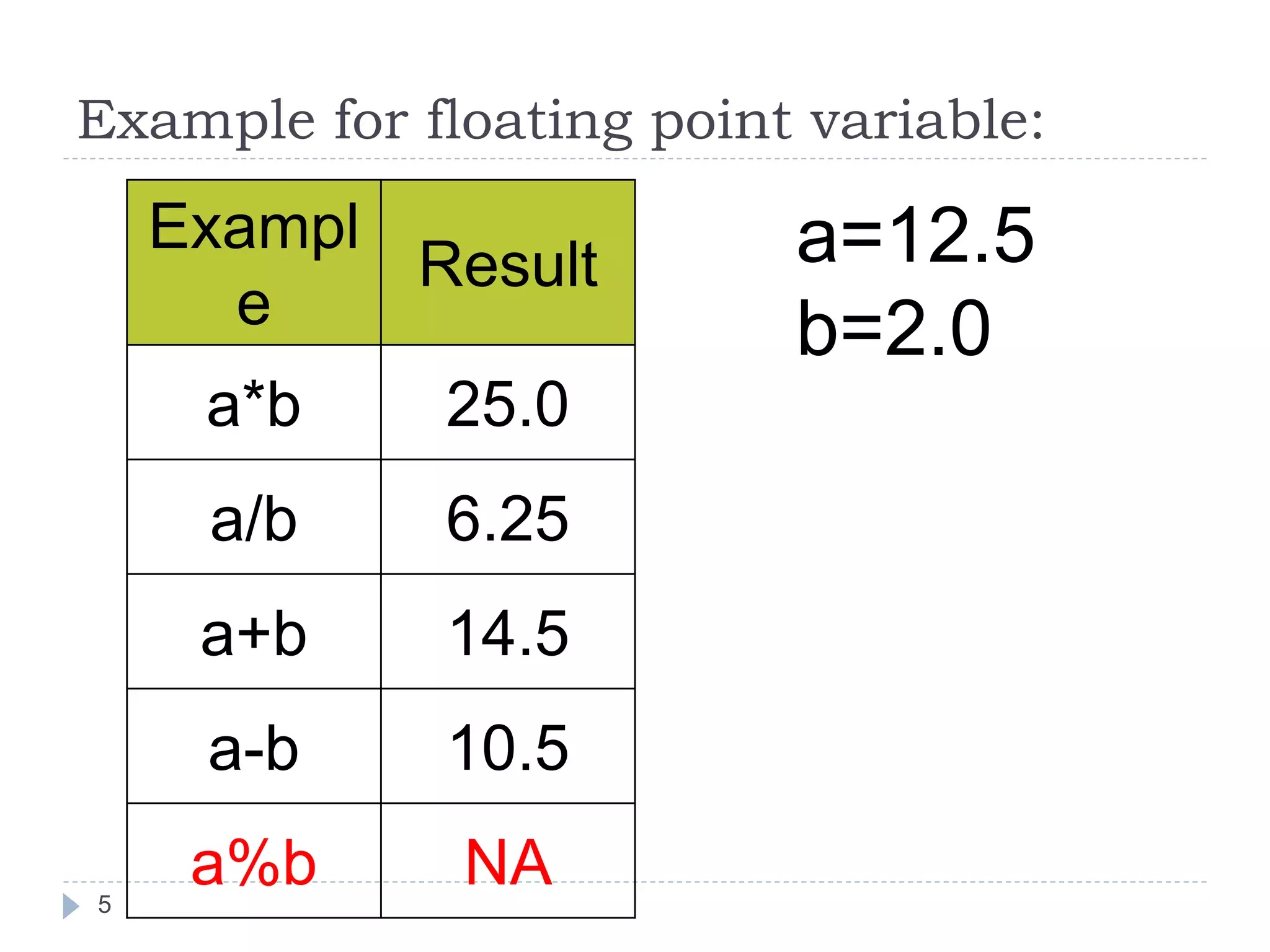
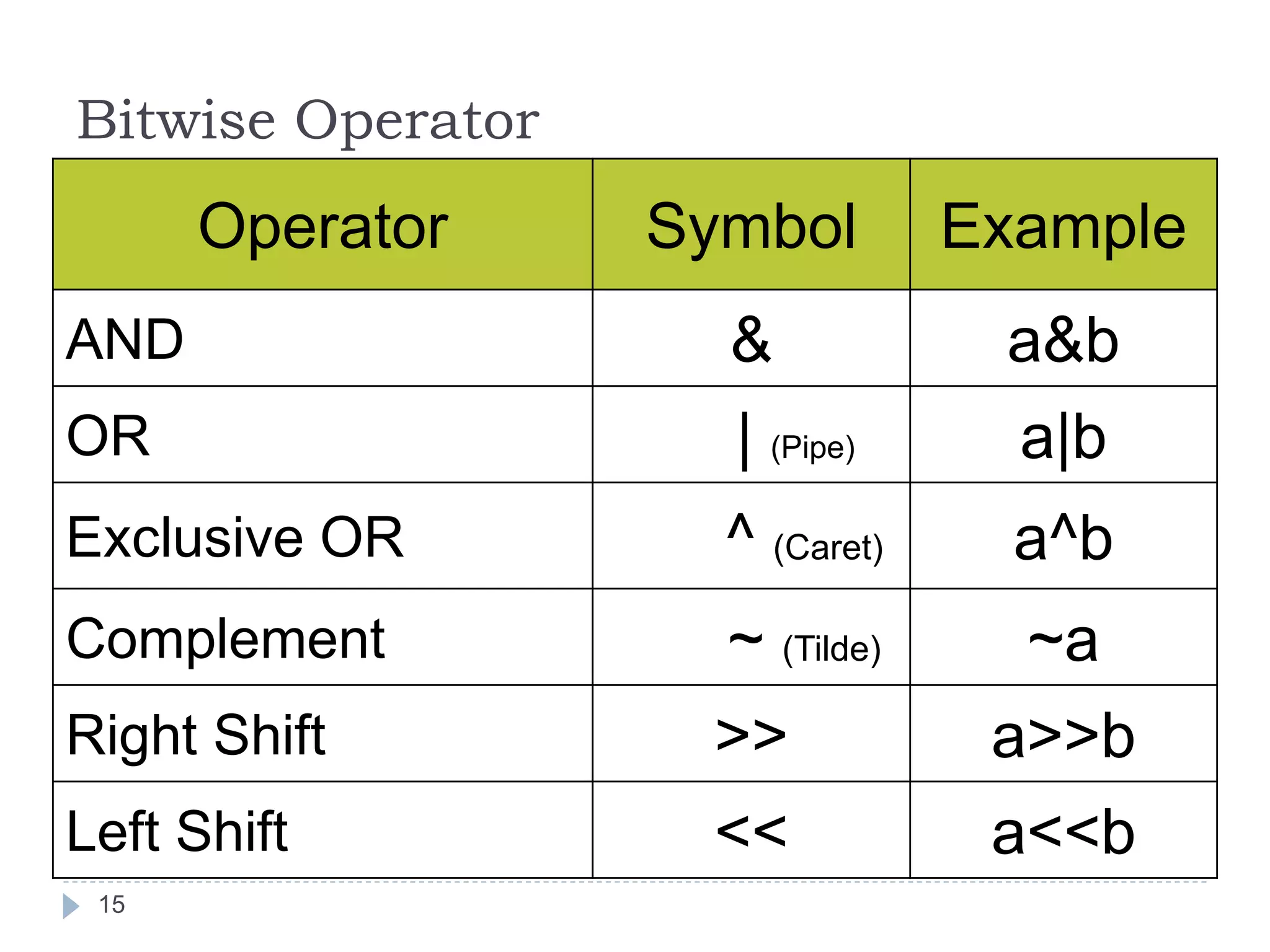
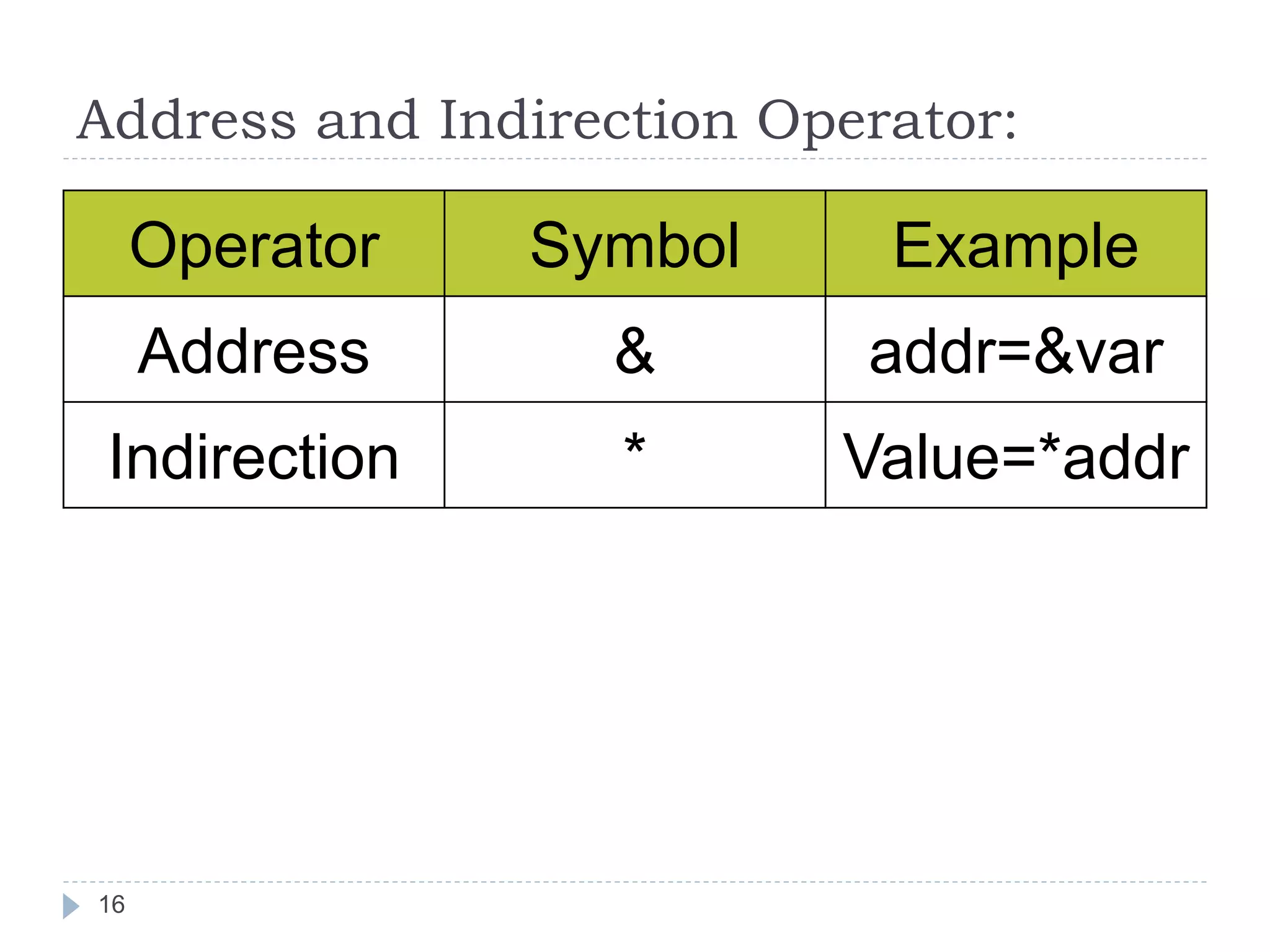
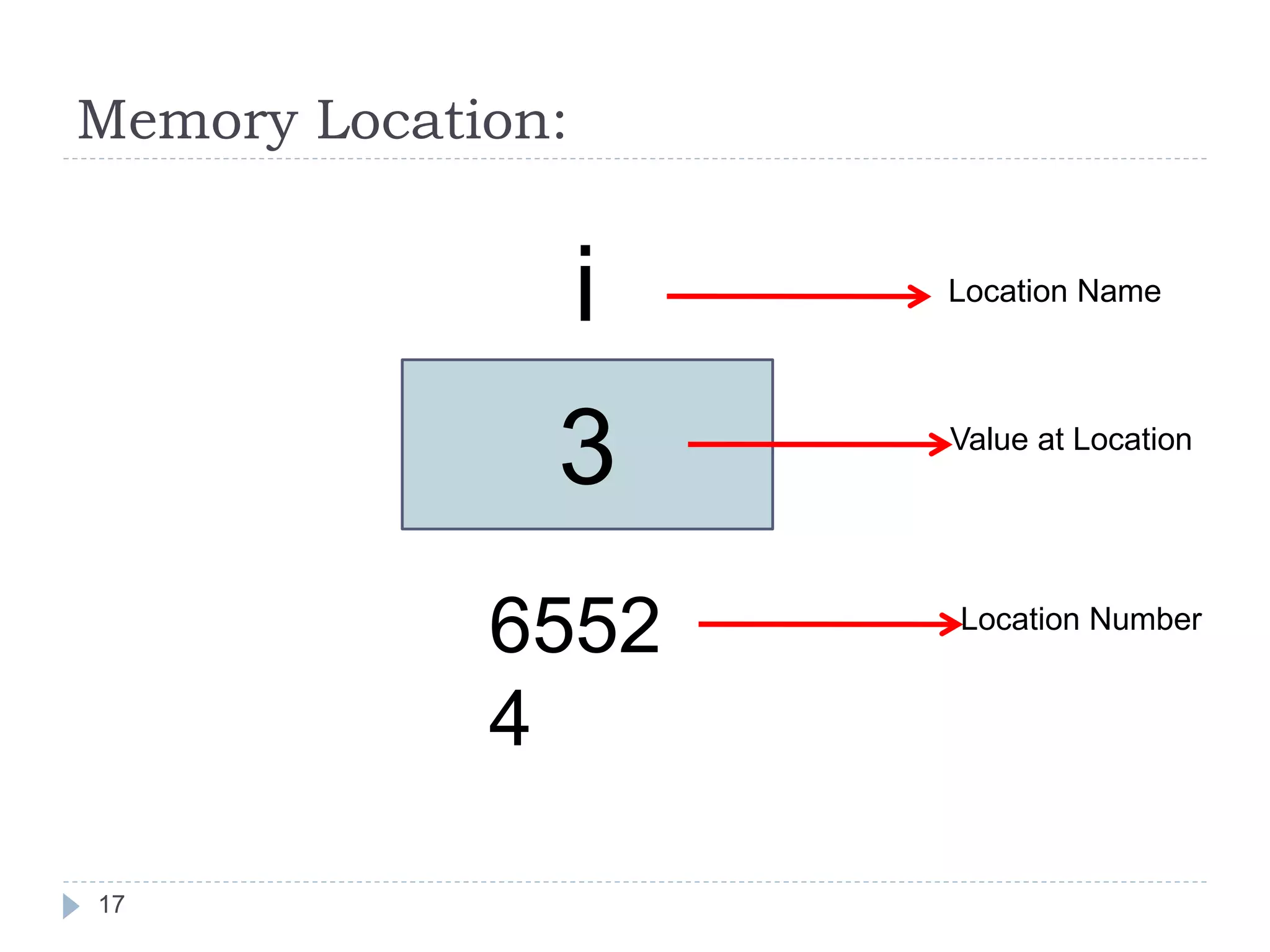
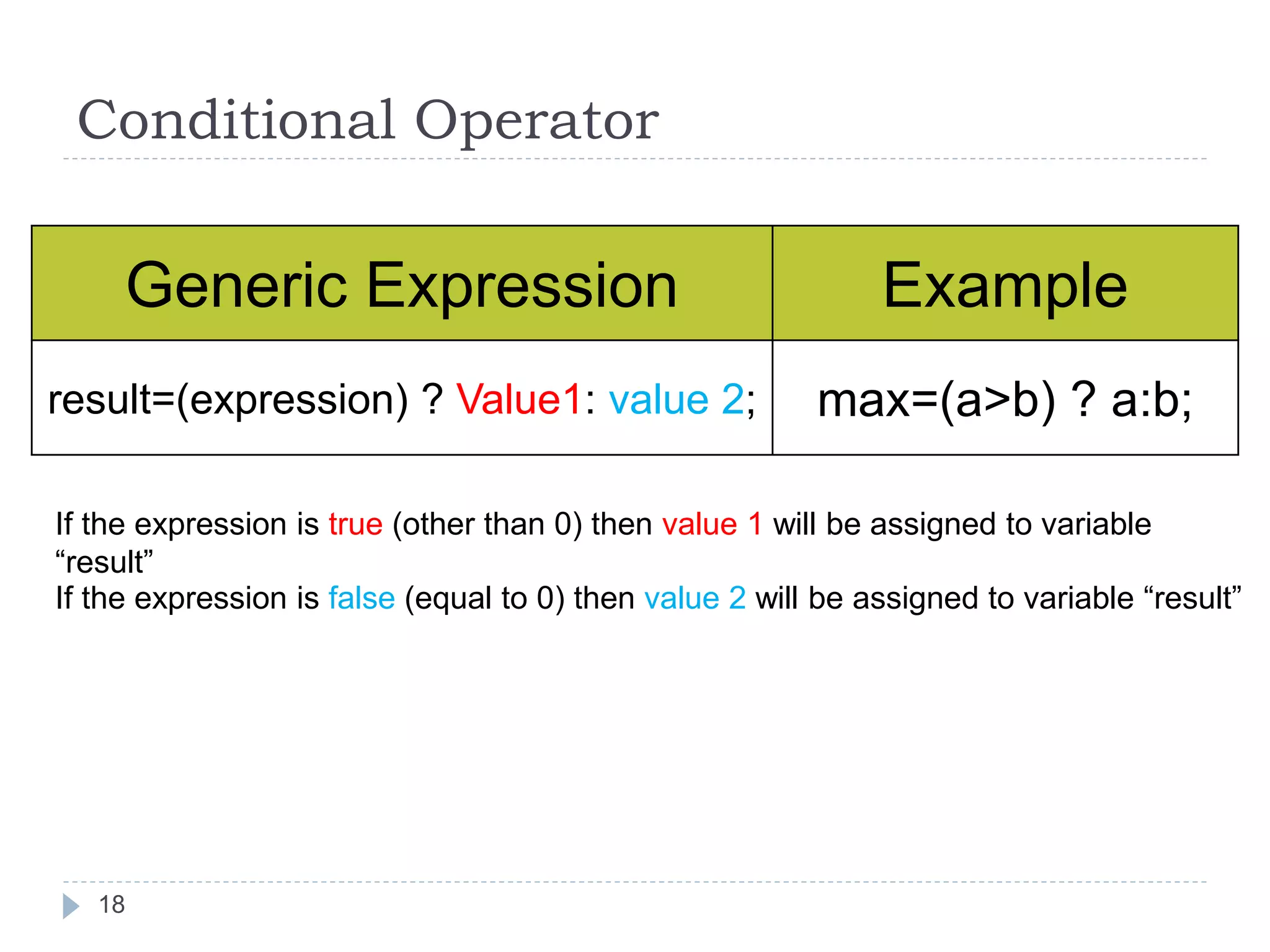
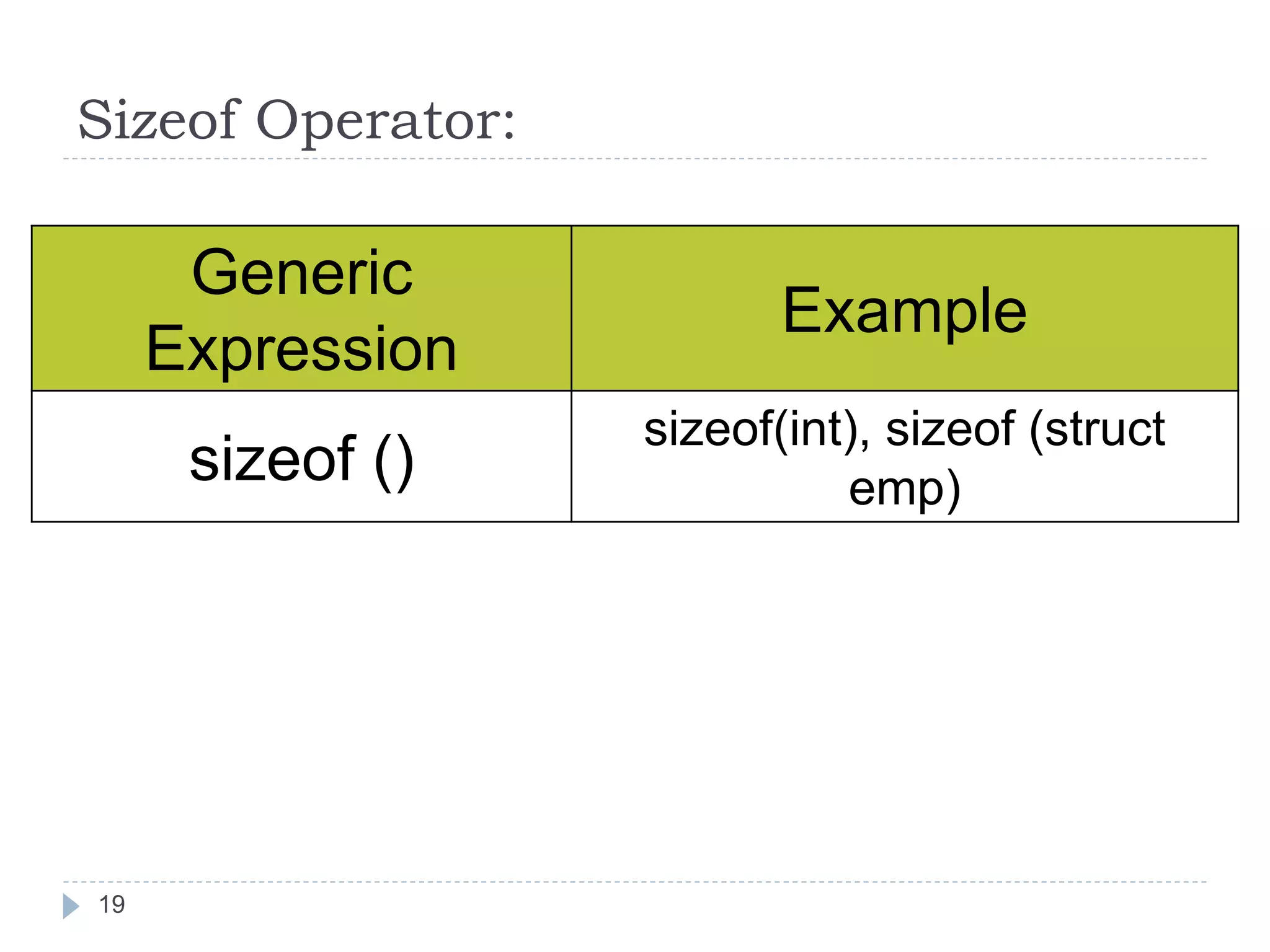
The document discusses various operators in C language including arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment and conditional operators. It provides examples of using each operator and the expected output. The order of operations and associativity rules are also covered. Various format specifiers used in printf and scanf functions are explained along with examples.



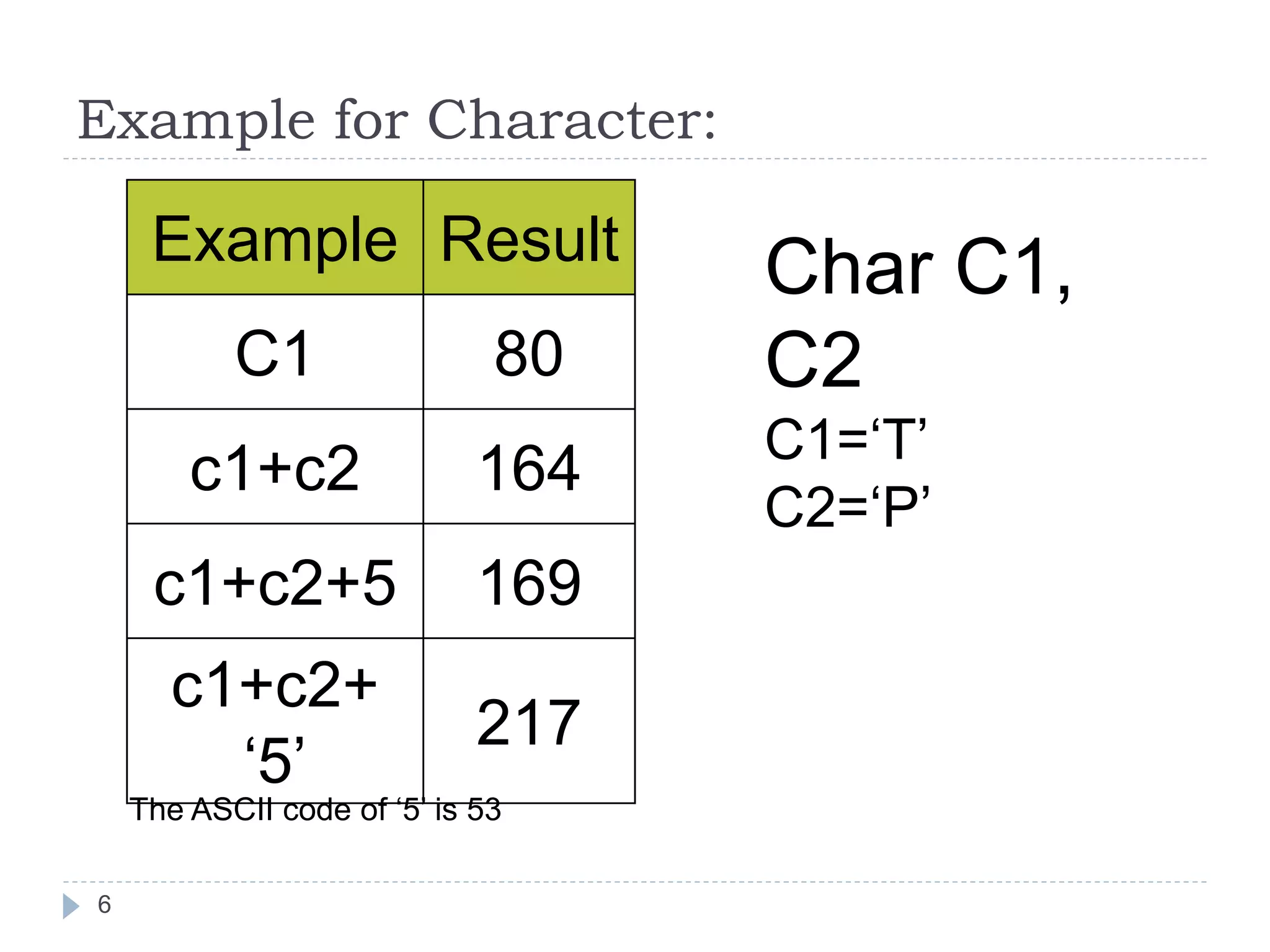
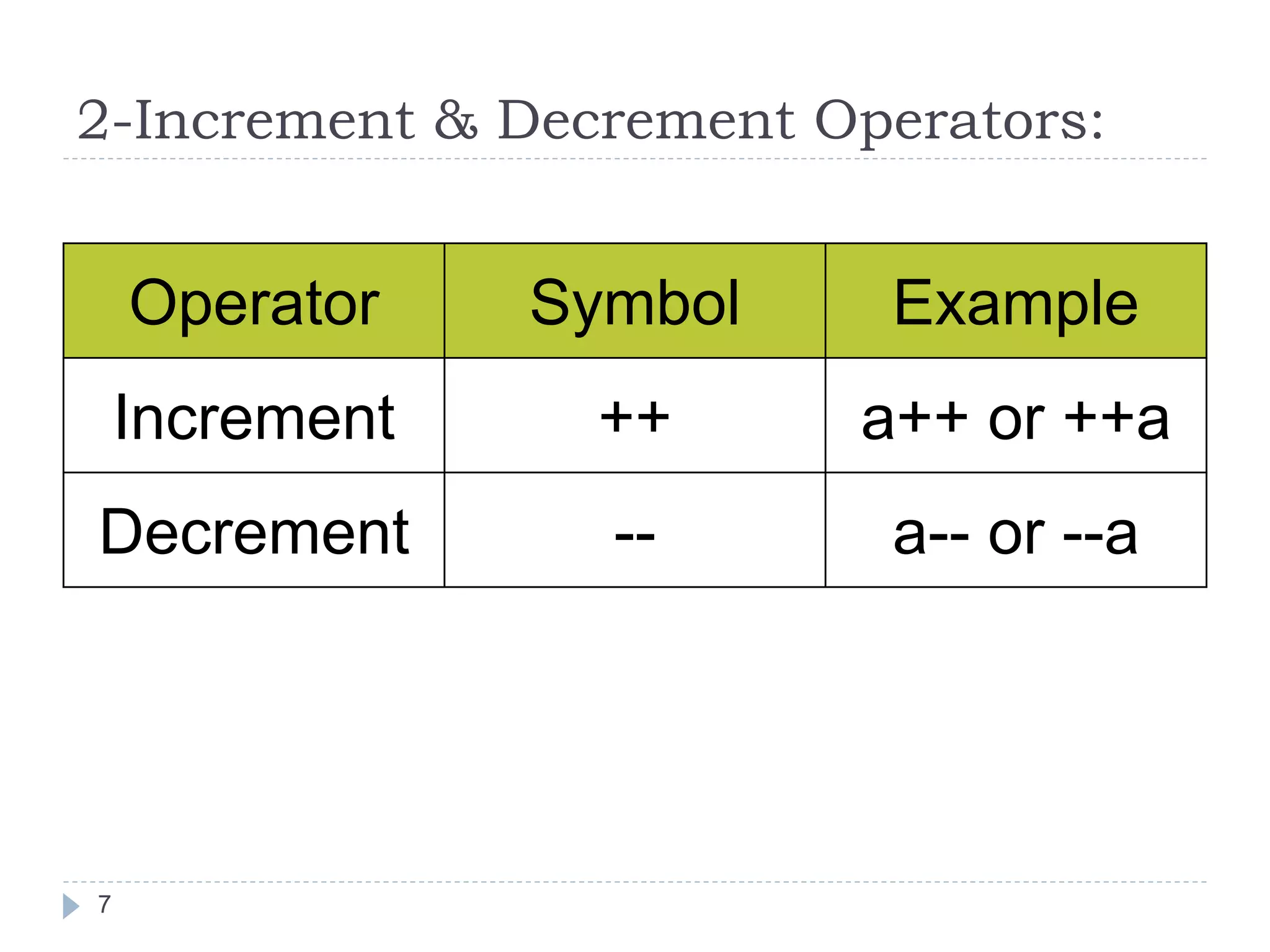
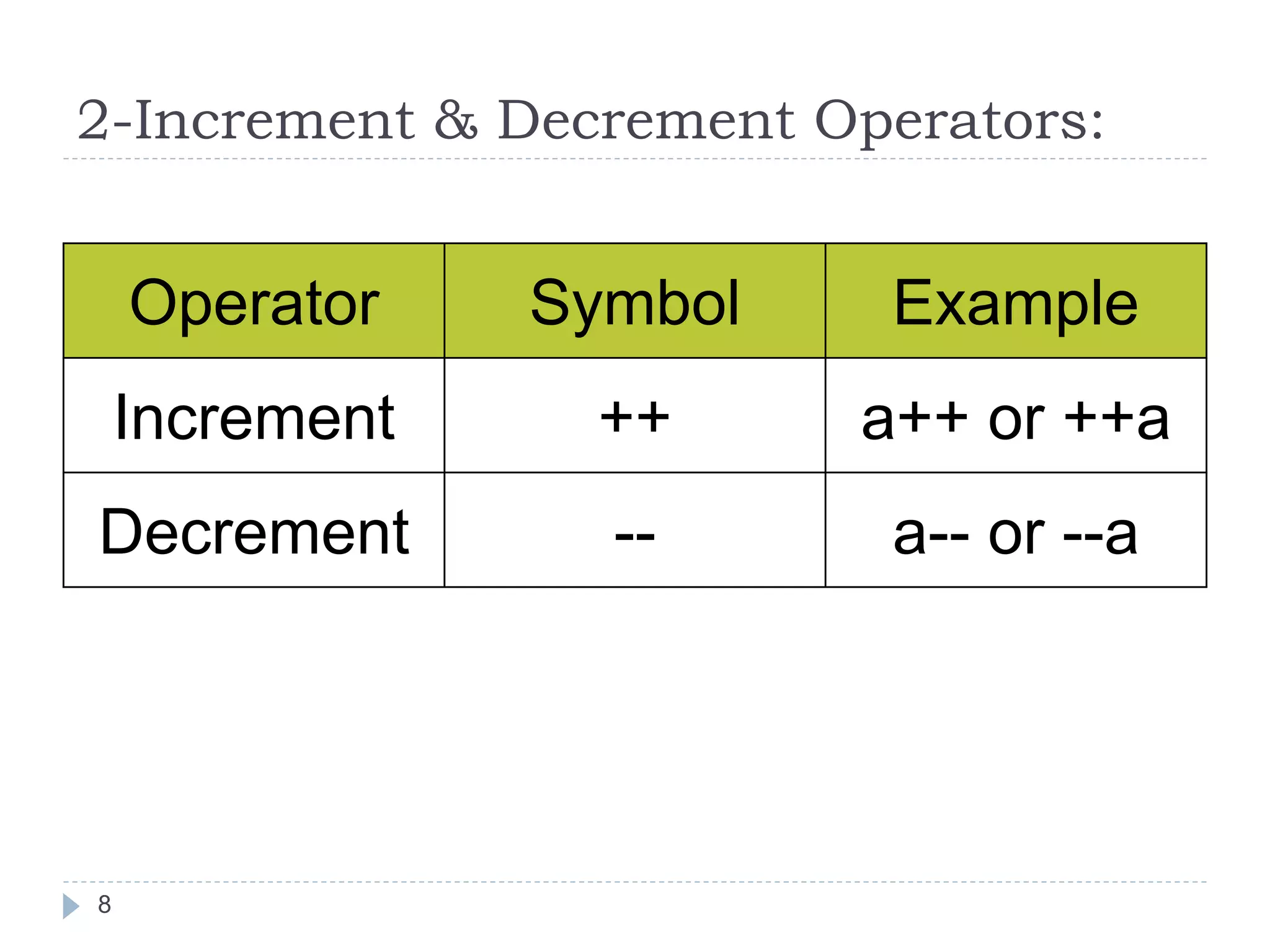
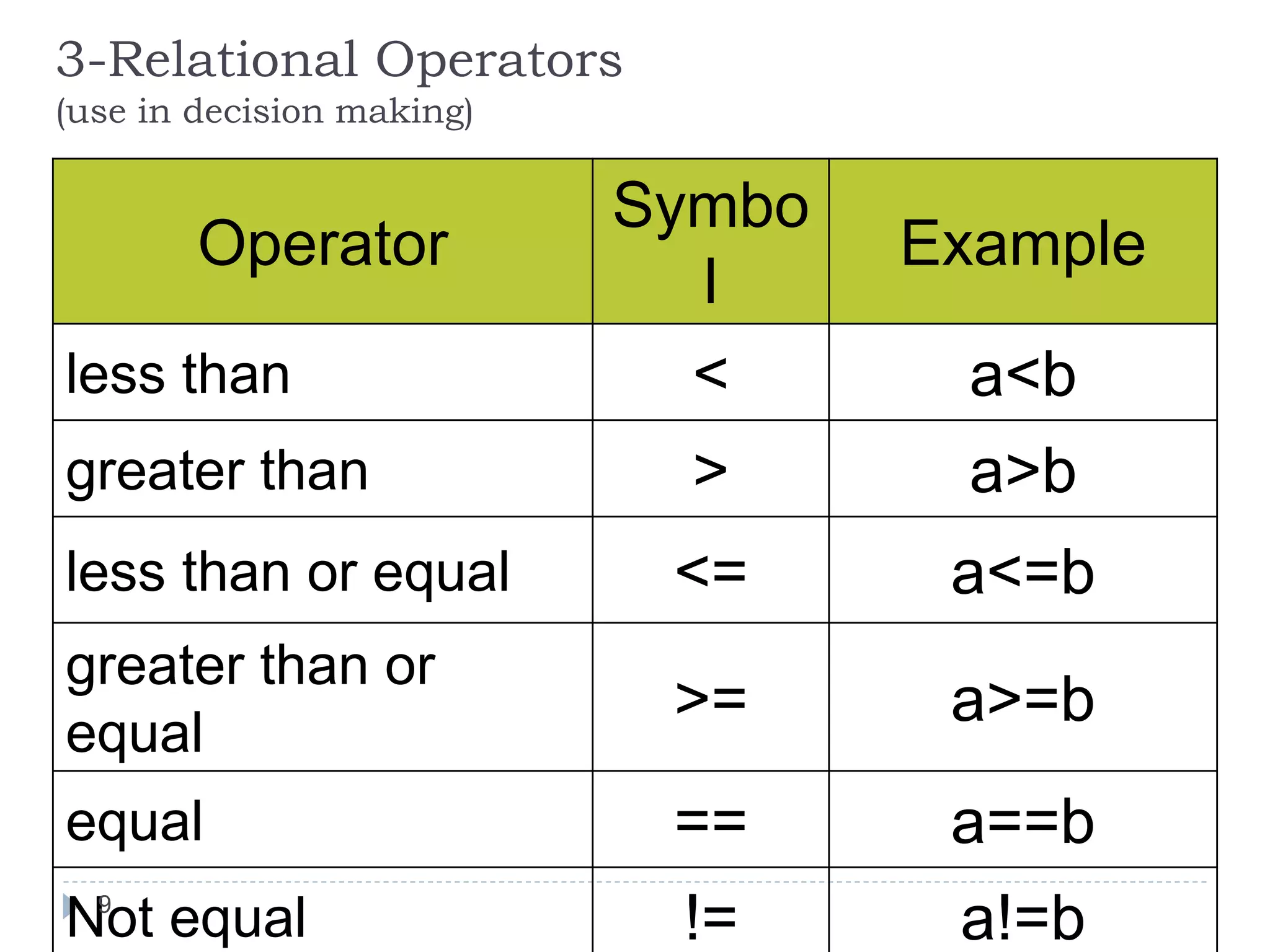
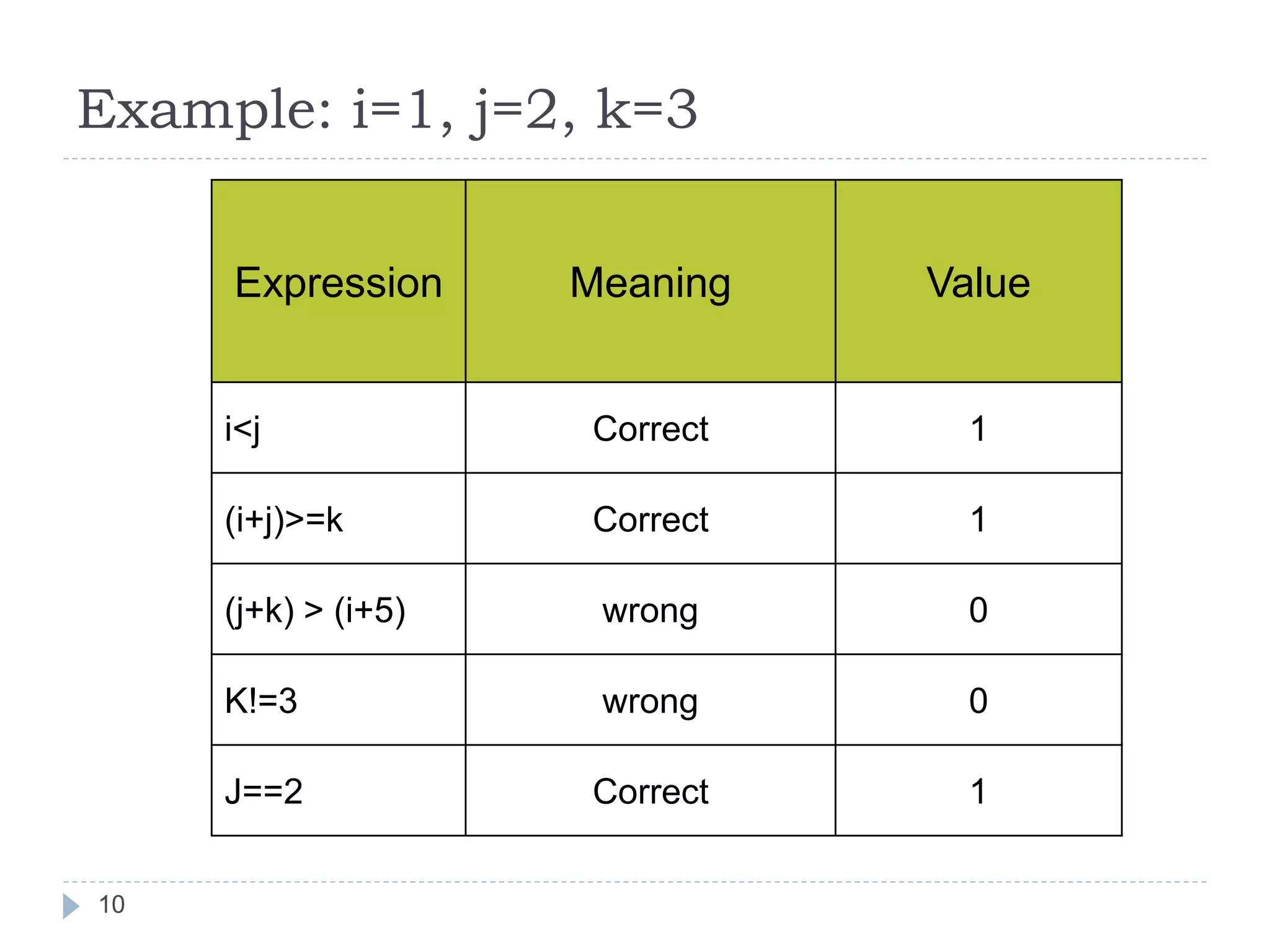
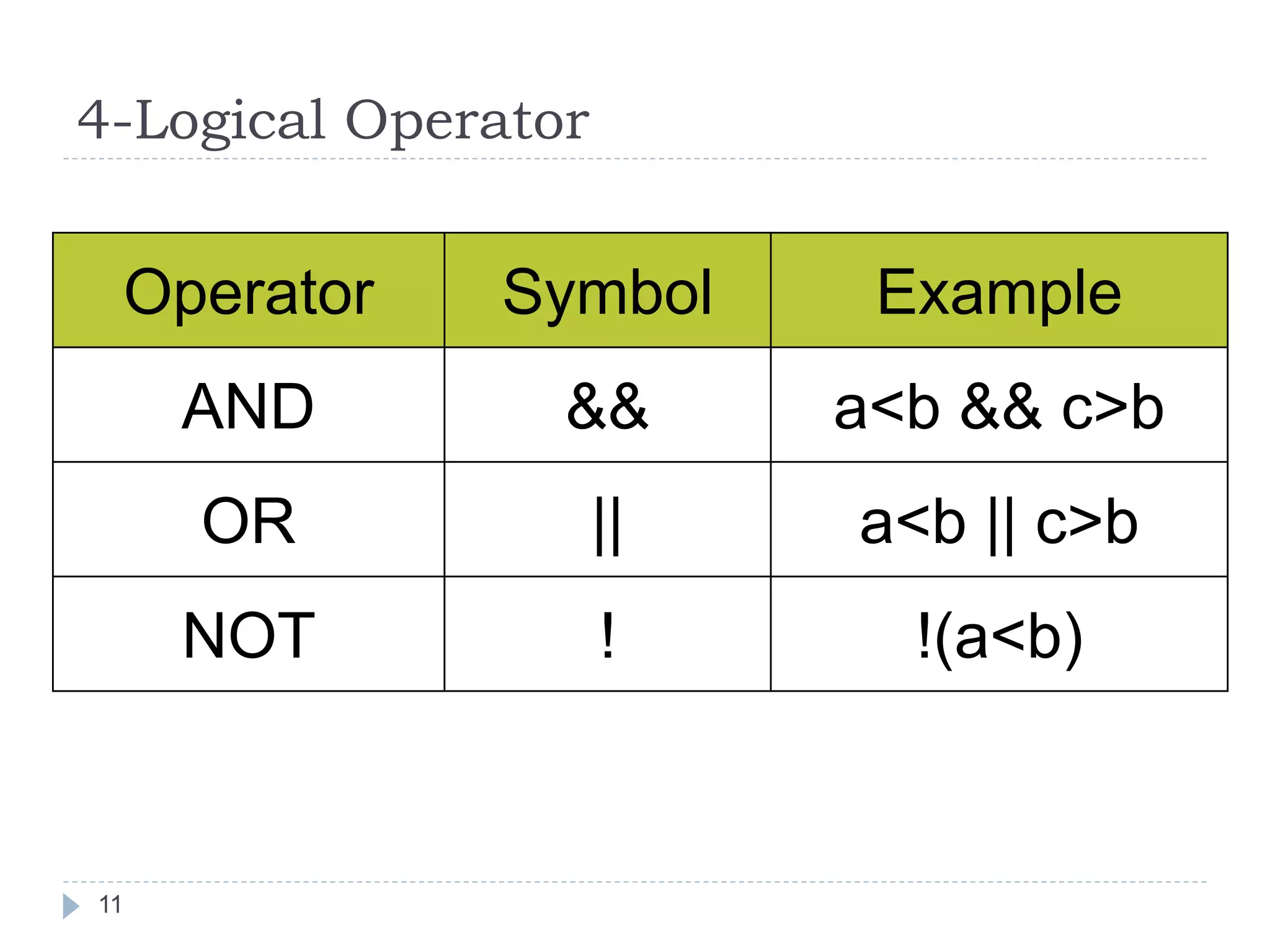
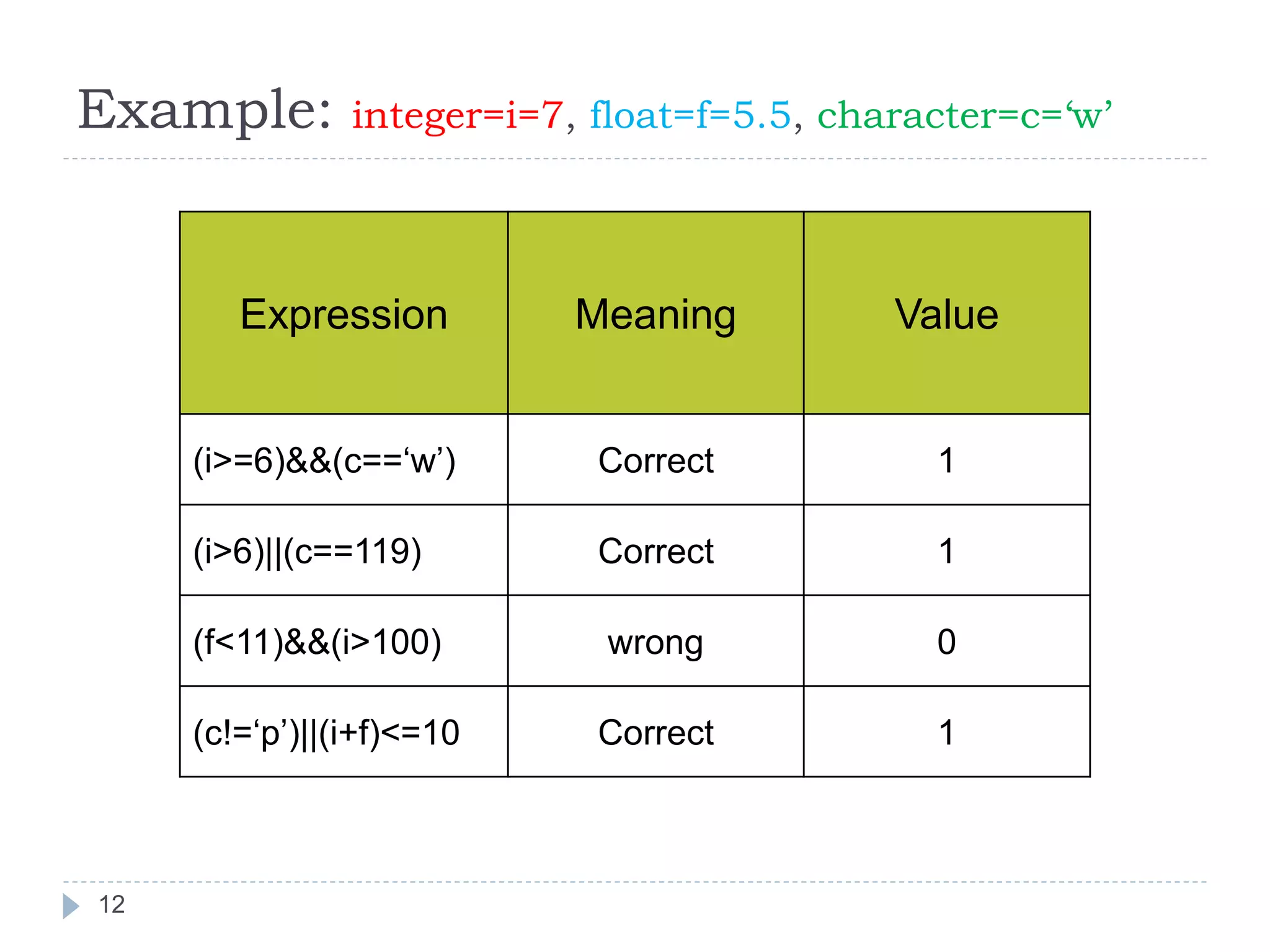
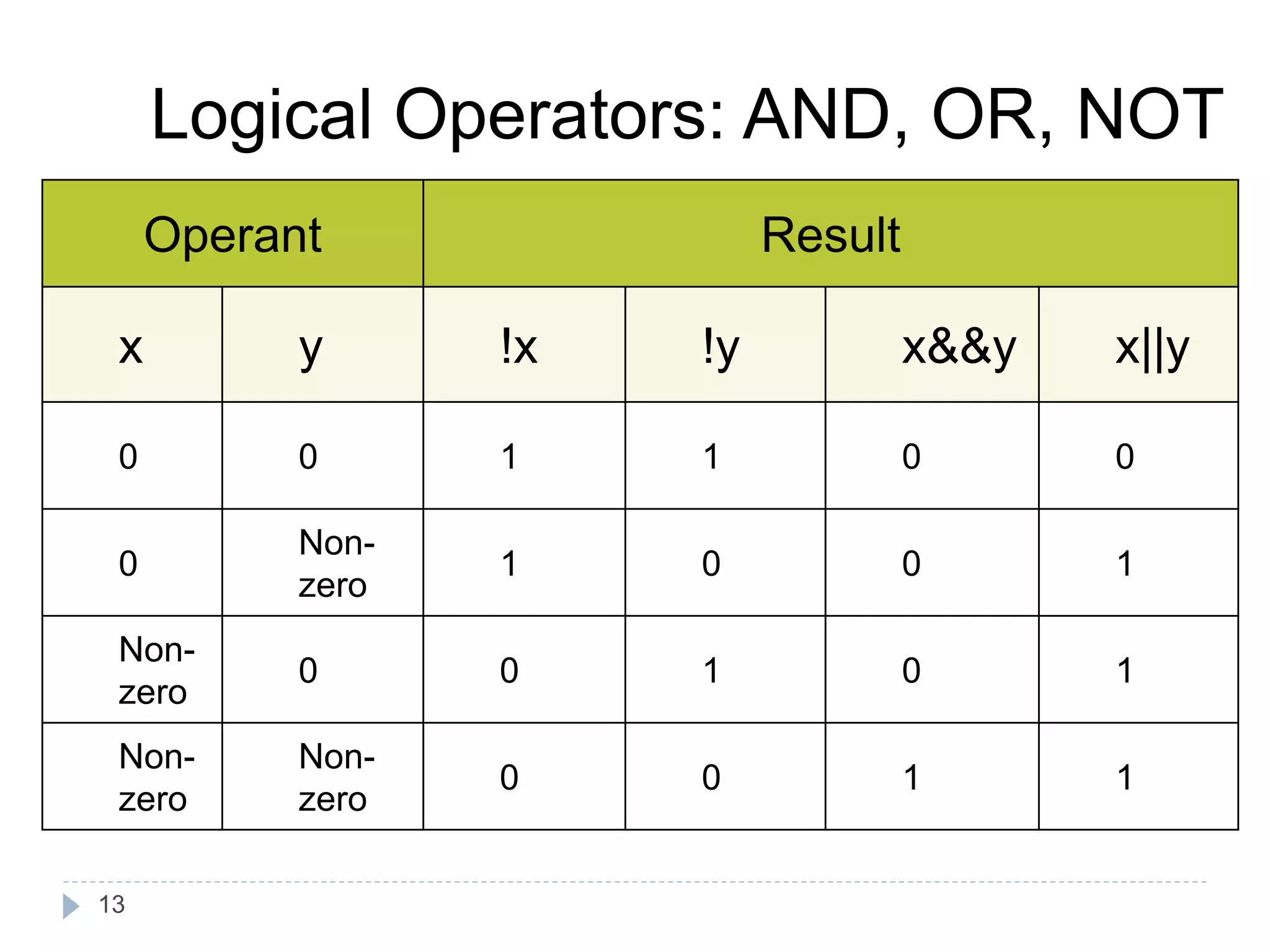
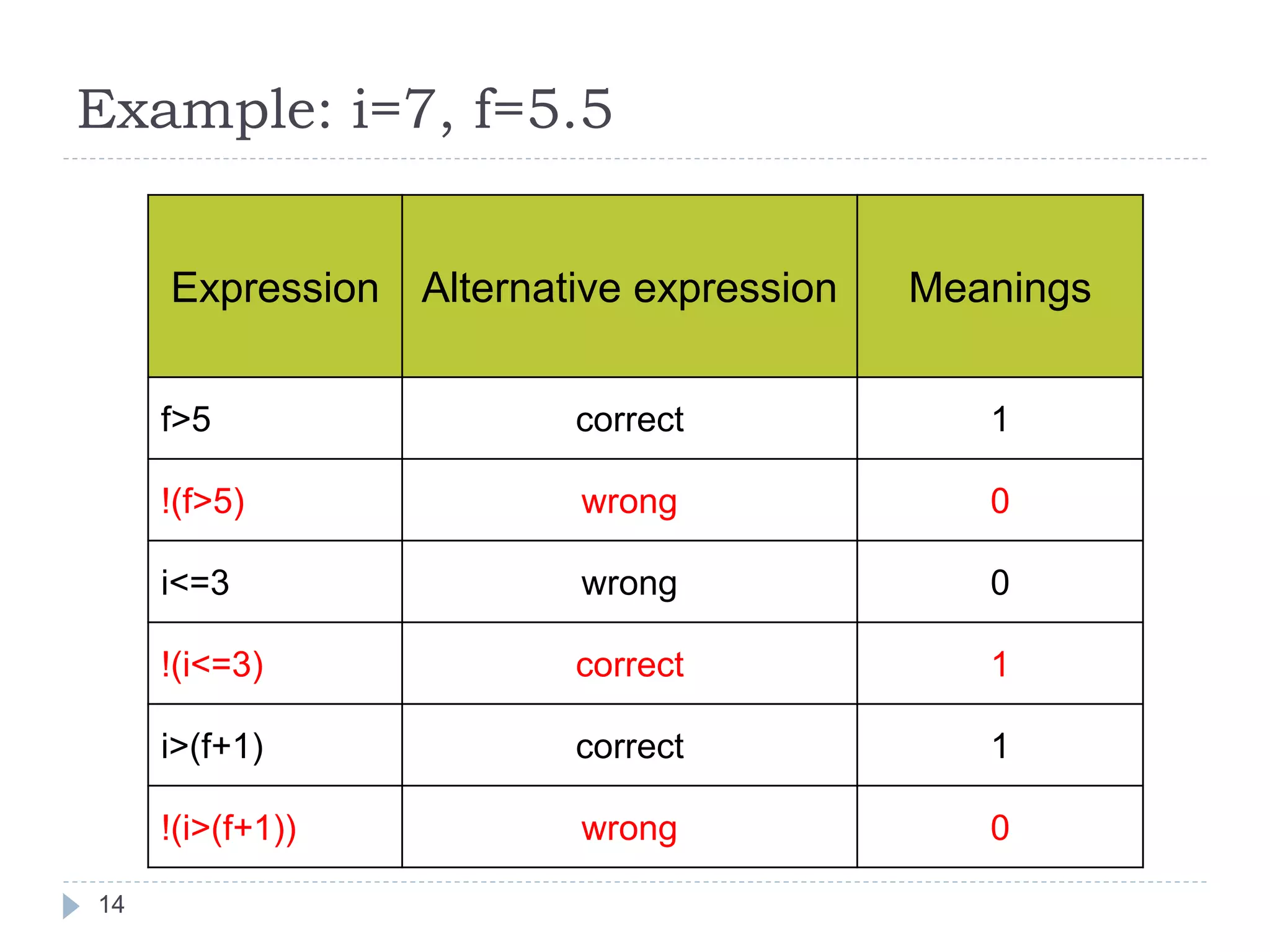
![Algebraic Expression: Algebraic Expression C Expression a x b- c x d A *b-c*d (m+n)(a+b) (m+n)*(a+b) 3x2+2x+5 3*x*x+2*x+5 a+b+c/d+e (a+b+c)/(d+e) [2by/d+1-x/3(z+y)] 2*b*y/(d+1)-x/3*(z+y) 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opertaorsinc-171008094736/75/Operators-in-C-Programming-20-2048.jpg)